Nutrient cycling processes, fluxes and effects in the Jiulong river-estuary system under global change
-
摘要:
河流-河口系统是陆地与海洋物质循环的重要通道。人类活动和气候变化已显著改变营养盐循环并产生一系列生态环境效应(富营养化、有害藻华、缺氧、酸化等)。本文基于现场观测、实验模拟和模型分析结果,总结亚热带中小型河流——九龙江河流-河口系统的营养盐(氮、磷、硅)含量和通量的长期变化及主控因素、水体反硝化作用、梯级电站水库对营养盐的滞留、气候变化(暴雨事件、升温)影响营养盐输送与循环等方面的研究进展,讨论营养盐变化的潜在生态环境效应。与大型河流相比,中小型河流对人类活动与气候变化的干扰更为敏感。最后提出全球变化下流域-近海生物地球化学过程研究的若干重点方向:(1)在不同时空尺度上捕捉营养盐变化信号,基于多学科交叉与综合研究,揭示复杂的营养盐循环过程与驱动机制。(2)评估中小型河流的独特性及其对全球或区域尺度气候与环境变化的影响。(3)深入研究河流水坝滞留、滨海湿地净化对近海生态系统的影响。
Abstract:River-estuary is an important component of earth system linking land and ocean cycling of materials. Human activities and climatic change have substantially altered nutrient cycling accompanied by series of negative ecological effects (e.g., eutrophication, harmful algal bloom, hypoxia, acidification). Based on the recent studies using in-situ observation, experimental and modeling approaches as tools, this paper summarized current understanding of the subtropical Jiulong River-Estuary system in Southeast China, including long-term change in nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, silica) in terms of concentration and flux and controlling factors, aquatic denitrification, nutrient retention by cascade dam reservoirs, and impacts of climate change (storm events and warming) on nutrient delivery and cycling. Potential effects of nutrient variation on aquatic ecosystems are also discussed. Current results suggest that small and medium-sized rivers are more sensitive than large rivers to human and climate perturbation in terms of nutrient biogeochemistry and ecology. Research priorities on nutrient biogeochemistry of the watershed-estuary-coast continuum under global change were proposed: (1) Capture nutrient changes at various temporal and spatial scales through intensive field observation and reveal key processes and drivers of nutrient cycling using multidisciplinary integrated study approach. (2) Evaluate the uniqueness of small and medium-sized rivers and their role in regulating global or regional climate and environment. (3) Further study the nutrient retention by river dams and coastal wetlands and associated effects on the aquatic ecosystems.
-
Key words:
- nutrient /
- eutrophication /
- human activity /
- climate change /
- the Jiulong River
-

-
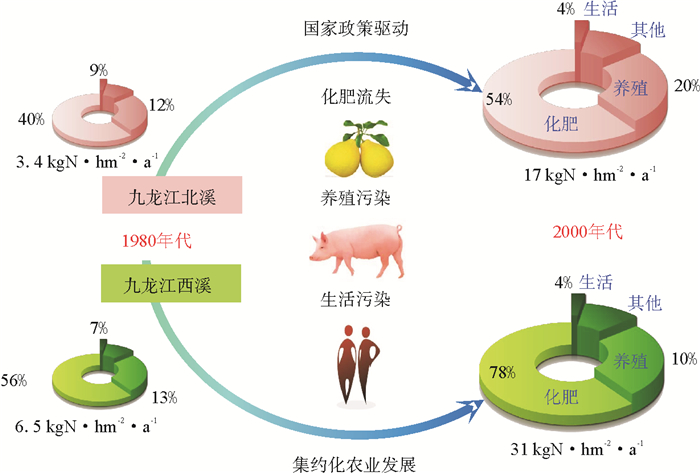
图 1 九龙江流域氮源结构及其对河流入海通量的贡献变化(1980s—2000s)[18]
Figure 1.
-
[1] Nixon S W. Coastal marine eutrophication: a definition, social causes, and future concerns[J]. Ophelia, 1995, 41(1): 199-219. doi: 10.1080/00785236.1995.10422044
[2] Gruber N, Galloway J N. An earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7176): 293-296. doi: 10.1038/nature06592
[3] Vitousek P M, Mooney H A, Lubchenco J, et al. Human domination of earth's ecosystems[J]. Science, 1997, 277(5325): 494-499. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5325.494
[4] Diaz R J, Rosenberg R. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems[J]. Science, 2008, 321(5891): 926-929. doi: 10.1126/science.1156401
[5] Wallace R B, Baumann H, Grear J S, et al. Coastal ocean acidification: The other eutrophication problem[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2014, 148: 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2014.05.027
[6] Smith V H, Joye S B, Howarth R W. Eutrophication of freshwater and marine ecosystems[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2006, 51(1): 351-355. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S0269-7491(99)00091-3/
[7] Strokal M, Yang H, Zhang Y C, et al. Increasing eutrophication in the coastal seas of China from 1970 to 2050[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 85(1): 123-140. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.06.011
[8] 陈能汪, 章颖瑶, 李延风.我国淡水藻华长期变动特征综合分析[J].生态环境学报, 2010, 19(8): 1994-1998. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.08.041
CHEN Nengwang, ZHANG Yingyao, LI Yanfeng. An integrated analysis of dynamic characteristics of harmful algal bloom in fresh water in China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2010, 19(8): 1994-1998. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.08.041
[9] Mackenzie F T, Ver L M, Lerman A. Century-scale nitrogen and phosphorus controls of the carbon cycle[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 190(1-4): 13-32. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00108-0
[10] 黄秀琴.九龙江流域水文特性[J].水利科技, 2008(1): 16-17, 20. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=shuilkj200801007
HUANG Xiuqin. Hydrologic characteristics of the Jiulong River watershed[J]. Water Conservancy Science and Technology, 2008(1): 16-17, 20 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=shuilkj200801007
[11] Yan X L, Zhai W D, Hong H S, et al. Distribution, fluxes and decadal changes of nutrients in the Jiulong River Estuary, Southwest Taiwan Strait[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(18): 2307-2318. doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5084-4
[12] Cao W Z, Hong H S, Yue S P. Modelling agricultural nitrogen contributions to the Jiulong River estuary and coastal water[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2005, 47(2-4): 111-121. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2004.10.006
[13] Chen N W, Hong H S, Zhang L P, et al. Nitrogen sources and exports in an agricultural watershed in Southeast China[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2008, 87(2): 169-179. doi: 10.1007/s10533-007-9175-2
[14] Huang J J, Lin J, Zhang Y Z, et al. Analysis of phosphorus concentration in a subtropical river basin in southeast China: Implications for management[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2013, 81: 29-37. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0964569112002712
[15] Li Y, Cao W Z, Su C X, et al. Nutrient sources and composition of recent algal blooms and eutrophication in the northern Jiulong River, Southeast China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2011, 63(5-12): 249-254. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.02.021
[16] Chen N W, Peng B R, Hong H S, et al. Nutrient enrichment and N: P ratio decline in a coastal bay-river system in southeast China: The need for a dual nutrient (N and P) management strategy[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2013, 81: 7-13. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0964569112001731
[17] 陈能汪, 王龙剑, 林晖, 等.九龙江流域经济发展与河流水质时空关联分析[J].生态与农村环境学报, 2012, 28(1): 19-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2012.01.003
CHEN Nengwang, WANG Longjian, LIN Hui, et al. A spatio-temporal correlation analysis of water quality and economic growth in the Jiulong River Basin[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2012, 28(1): 19-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2012.01.003
[18] Yu D, Yan W J, Chen N W, et al. Modeling increased riverine nitrogen export: Source tracking and integrated watershed-coast management[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 101(2): 642-652. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.10.035
[19] Chen N W, Wu Y Q, Wu J Z, et al. Natural and human influences on dissolved silica export from watershed to coast in Southeast China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2014, 119(1): 95-109. doi: 10.1002/2013JG002429
[20] Dürr H H, Meybeck M, Hartmann J, et al. Global spatial distribution of natural riverine silica inputs to the coastal zone[J]. Biogeosciences, 2011, 8(3): 597-620. doi: 10.5194/bg-8-597-2011
[21] 陈能汪, 吴杰忠, 段恒轶, 等. N2:Ar法直接测定水体反硝化产物溶解N2[J].环境科学学报, 2010, 30(12): 2479-2483. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cuihuaxb201608005
CHEN Nengwang, WU Jiezhong, DUAN Hengyi, et al. N2:Ar method for direct measurement of denitrification product (dissolved N2)using membrane inlet mass spectrometry(MIMS)[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2010, 30(12): 2479-2483. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cuihuaxb201608005
[22] Chen N W, Wu JZ, Chen Z H, et al. Spatial-temporal variation of dissolved N2 and denitrification in an agricultural river network, southeast China[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2014, 189: 1-10. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=479e5b81df468894d20aec9a1f8d7017
[23] Chen N W, Wu JZ, Zhou X P, et al. Riverine N2O production, emissions and export from a region dominated by agriculture in Southeast Asia (Jiulong River)[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2015, 208: 37-47. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=399c66078f058194ed354f88bd97d3a2
[24] Wang J N, Chen N W, Yan W J, et al. Effect of dissolved oxygen and nitrogen on emission of N2O from rivers in China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2015, 103: 347-356. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.12.054
[25] 陈朱虹, 陈能汪, 吴殷琪, 等.河流库区沉积物-水界面营养盐及气态氮的释放过程和通量[J].环境科学, 2014, 35(9): 3325-3335. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201409013
CHEN Zhuhong, CHEN Nengwang, WU Yinqi, et al. Sediment-water flux and processes of nutrients and gaseous nitrogen release in a China river reservoir[J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(9): 3325-3335. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201409013
[26] Chen N W, Chen Z H, Wu Y Q, et al. Understanding gaseous nitrogen removal through direct measurement of dissolved N2 and N2O in a subtropical river-reservoir system[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2014, 70: 56-67. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.04.017
[27] Wu J Z, Chen N W, Hong H S, et al. Direct measurement of dissolved N2 and denitrification along a subtropical river-estuary gradient, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2013, 66(1-2): 125-134. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.10.020
[28] 陈能汪, 吴杰忠, 洪华生.九龙江河口区夏季反硝化作用初探[J].环境科学, 2011, 32(11): 3229-3234. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201111015
CHEN Nengwang, WU Jiezhong, HONG Huasheng. Preliminary results concerning summer-time denitrification in the Jiulong River Estuary[J]. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(11): 3229-3234. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201111015
[29] Lu T, Chen N W, Duan S W, et al. Hydrological controls on cascade reservoirs regulating phosphorus retention and downriver fluxes[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(23): 24166-24177. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7397-3
[30] 鲁婷, 陈能汪, 陈朱虹, 等.九龙江河流-库区系统沉积物磷特征及其生态学意义[J].环境科学, 2013, 34(9): 3430-3436. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201309014
LU Ting, CHEN Nengwang, CHEN Zhuhong, et al. Characteristics of sediment phosphorus in the Jiulong River-reservoir system and its ecological significance[J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(9): 3430-3436. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201309014
[31] Cao W Z, Huang Z, Zhai W D, et al. Isotopic evidence on multiple sources of nitrogen in the northern Jiulong River, Southeast China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2015, 163: 37-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2015.05.042
[32] Li M T, Xu K Q, Watanabe M, et al. Long-term variations in dissolved silicate, nitrogen, and phosphorus flux from the Yangtze River into the East China Sea and impacts on estuarine ecosystem[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2007, 71(1-2): 3-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2006.08.013
[33] Humborg C, Ittekkot V, Cociasu A, et al. Effect of Danube River dam on Black Sea biogeochemistry and ecosystem structure[J]. Nature, 1997, 386(6623): 385-388. doi: 10.1038/386385a0
[34] Humborg C, Pastuszak M, Aigars J, et al. Decreased silica land-sea fluxes through damming in the baltic sea catchment-significance of particle trapping and hydrological alterations[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2006, 77(2): 265-281. doi: 10.1007/s10533-005-1533-3
[35] Chen N W, Wu J Z, Hong H S. Effect of storm events on riverine nitrogen dynamics in a subtropical watershed, southeastern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 431: 357-365. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.05.072
[36] Chen N W, Wu Y Q, Chen Z H, et al. Phosphorus export during storm events from a human perturbed watershed, southeast China: Implications for coastal ecology[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2015, 166: 178-188. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2015.03.023
[37] Cao W Z, Hong H S, Zhang Y Z, et al. Anthropogenic nitrogen sources and exports in a village-scale catchment in Southeast China[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2006, 28(1-2): 45-51. doi: 10.1007/s10653-005-9010-4
[38] Chen N W, Hong H S. Nitrogen export by surface runoff from a small agricultural watershed in southeast China: seasonal pattern and primary mechanism[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2011, 106(3): 311-321. doi: 10.1007/s10533-010-9514-6
[39] Chen N W, Krom M D, Wu Y Q, et al. Storm induced estuarine turbidity maxima and controls on nutrient fluxes across river-estuary-coast continuum[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018 (Accepted). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=3d31248b711ec0c84caa682157a76781
[40] Zhou X P, Chen N W, Yan Z H, et al. Warming increases nutrient mobilization and gaseous nitrogen removal from sediments across cascade reservoirs[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 219: 490-500. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.05.060
[41] Chen N W, Hong H S. Integrated management of nutrients from the watershed to coast in the subtropical region[J]. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 2012, 4(2): 233-242. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2012.03.007
[42] Vitousek P M, Aber J D, Howarth R W, et al. Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: sources and consequences[J]. Ecological Applications, 1997, 7(3): 737-750. https://www.jstor.org/stable/2269431
[43] Chen B H, Xu Z H, Zhou Q L, et al. Long-term changes of phytoplankton community in Xiagu waters of Xiamen, China[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2010, 29(6): 104-114. doi: 10.1007/s13131-010-0081-4
[44] Wu G J, Cao W Z, Huang Z, et al. Decadal changes in nutrient fluxes and environmental effects in the Jiulong River Estuary[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 124(2): 871-877. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.01.071
[45] Xu L, Hong H S, Wang H L, et al. The biogeochemistry of photosynthetic pigments in the Jiulong River Estuary and Western Xiamen Bay[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2001, 19(2): 164-171. doi: 10.1007/BF02863042
[46] Mo Q L, Chen N W, Zhou X P, et al. Ammonium and phosphate enrichment across the dry-wet transition and their ecological relevance in a subtropical reservoir, China[J]. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 2016, 18(7): 882-894. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=52232c603cd076417844a1cb372168a3
[47] Chen N, Mo Q, Kuo YM, et al. Hydrochemical controls on reservoir nutrient and phytoplankton dynamics under storms[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 619-620: 301-310. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c5c228cc158b712d6725bc3a799bfa9a
[48] Liu L M, Yang J, Zhang Y Y. Genetic diversity patterns of microbial communities in a subtropical riverine ecosystem (Jiulong River, southeast China)[J]. Hydrobiologia, 2011, 678(1): 113-125. doi: 10.1007/s10750-011-0834-x
[49] Hu A Y, Wang H J, Li J W, et al. Archaeal community in a human-disturbed watershed in southeast China: diversity, distribution, and responses to environmental changes[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 100(10): 4685-4698. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7318-x
[50] Hu A Y, Yang X Y, Chen N W, et al. Response of bacterial communities to environmental changes in a mesoscale subtropical watershed, Southeast China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 472: 746-756. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.11.097
[51] 沈焕庭.我国河口最大浑浊带研究的新认识[J].地球科学进展, 1995, 10(2): 210-212. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1995.02.001
SHEN Huanting. New understanding of estuarine turbidity maximum in China[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 1995, 10(2): 210-212. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1995.02.001
[52] Statham P J. Nutrients in estuaries-An overview and the potential impacts of climate change[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 434: 213-227. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.09.088
[53] Chen N W, Hong H S, Huang Q J, et al. Atmospheric nitrogen deposition and its long-term dynamics in a southeast China coastal area[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2011, 92(6): 1663-1667. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.01.026
[54] Hong Q Q, Cai P H, Shi X M, et al. Solute transport into the Jiulong River estuary via pore water exchange and submarine groundwater discharge: New insights from 224 Ra/228 Th disequilibrium[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2017, 198: 338-359. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2016.11.002
[55] Cao W Z, Yang J X, Li Y, et al. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium conserves nitrogen in anthropogenically affected subtropical mangrove sediments in Southeast China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2016, 110(1): 155-161. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.06.068
[56] Moss B, Kosten S, Meerhof M, et al. Allied attack: climate change and eutrophication[J]. Inland Waters, 2011, 1(2): 101-105. doi: 10.5268/IW-1.2.359
[57] Zhang Z Y, Huang Y L, Huang J L. Hydrologic alteration associated with dam construction in a medium-sized coastal watershed of southeast China[J]. Water, 2016, 8(8): 317. doi: 10.3390/w8080317
[58] Friedl G, Wüest A. Disrupting biogeochemical cycles-Consequences of damming[J]. Aquatic Sciences, 2002, 64(1): 55-65. doi: 10.1007/s00027-002-8054-0
[59] 刘丛强, 汪福顺, 王雨春, 等.河流筑坝拦截的水环境响应——来自地球化学的视角[J].长江流域资源与环境, 2009, 18(4):384-396. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8227.2009.04.015
LIU Congqiang, WANG Fushun, WANG Yuchen, et al. Responses of aquatic environment to river damming-from the geochemical view[J]. Resources and Environment in The Yangtze Basin, 2009, 18(4):384-396. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8227.2009.04.015
[60] Sebilo M, Mayer B, Nicolardot B, et al. Long-term fate of nitrate fertilizer in agricultural soils[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciencesof the United States of America, 2013, 110(45): 18185-18189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1305372110
[61] Haygarth P M, Jarvie H P, Powers S M, et al. Sustainable phosphorus management and the need for a long-term perspective: The legacy hypothesis[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(15): 8417-8419. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail/PeriodicalPaper_PM25001016
-



 下载:
下载: