Provenance and controlling factors of major elements in graded components of sediments from the Yalu River
-
摘要:
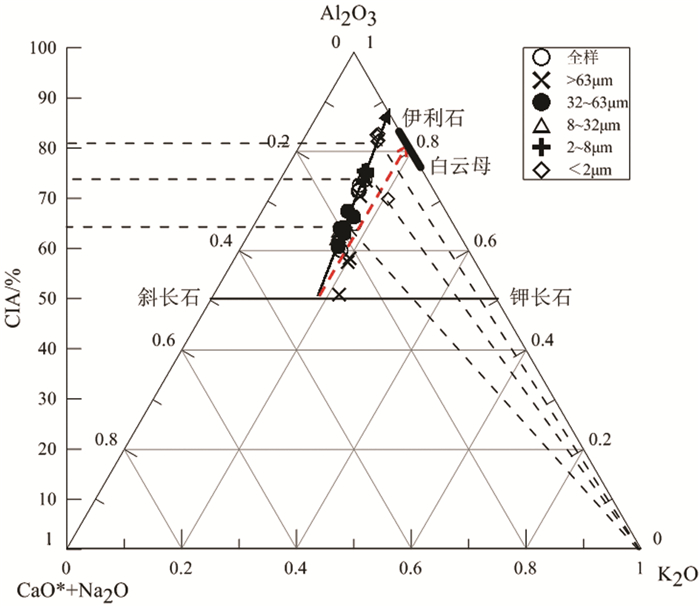
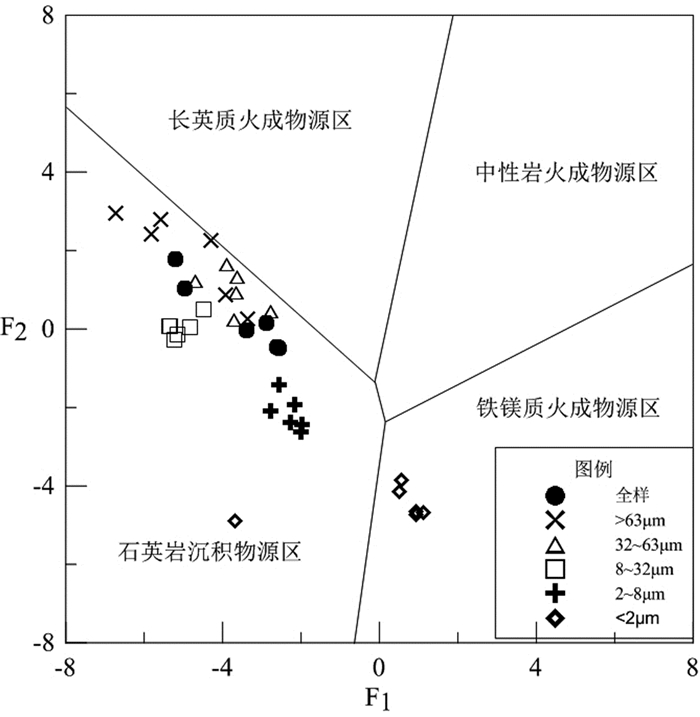
对鸭绿江河口表层沉积物陆源组分进行了水动力敏感粒度分级,以消弱“粒度效应”对沉积物地球化学组成的影响。通过多元统计方法,对不同粒级样品内常量元素含量特征、控制因素、源区特征等内容进行了探讨,并与全样测试结果进行对比分析。结果表明:源区化学风化程度是控制常量元素分布的主要因素,“粒度效应”和表生环境下的自生作用对常量元素的分布也有一定的控制作用,但“粒度效应”主要控制8μm以下样品内元素分布;源区目前处于以斜长石风化为主的中等化学风化程度阶段,风化产物未遭受钾交代影响;Al2O3、Fe2O3、MgO、MnO、TiO2、P2O5六种元素在>63μm、32~63μm和8~32μm 3个粒级内含量相近,8μm以下样品随粒级减小元素含量显著增加,CaO、Na2O两种元素在各粒级内含量分布特征与上述6种元素相反,高K2O含量且未受“粒度效应”控制,可作为鸭绿江端元的指示性元素。根据流域岩性特征分析,>2μm粒级样品可能主要来自鸭绿江中下游地区变质基底和花岗质侵入体的风化产物;而 < 2μm粒级样品则可能主要来自鸭绿江上游地区基性侵入体的风化产物。此外,对比分析还表明,全样测试结果仅相当于分粒级样品的均值水平,极大地掩盖了不同粒级内元素地球化学特征的差异性和规律性。因此,在利用全样地球化学特征进行物源示踪时需综合考虑。
Abstract:Terrigenous surface sediments taken from the Yalu River estuary were separated into grades in order to reduce the control of grain size on sediment geochemistry. With the statistical method for multivariate, major elements content, controlling factors and provenance characteristics of samples were discussed grade by grade in this paper, compared with the original testing data for bulk samples. The results show that the chemical weathering intensity in the provenance is the major factor controlling the distribution patterns of major elements. Grain size and authigenesis also play certain roles in control over the distribution patterns of elements in the samples smaller than 8μm. The provenance is now suffering from moderate chemical weathering characterized by the weathering of plagioclase and never affected by potassium replacement. The differences in Al2O3、Fe2O3、MgO、MnO、TiO2、P2O5 contents in the fractions >63μm、32~63μm and 8~32μm are rather small, but increased significantly in the fraction smaller than 8μm. The contents of CaO and Na2O in each fraction are opposite to those of the above six elements, suggesting the consistency of lithology of provenance rocks. The K2O, which can be used as an indicative element, remains high in each grain fraction. According to the lithologic characteristics of provenance, the components >2μm are mainly coming from metamorphic basement and granitic intrusive rocks at the middle and lower reaches, while the components < 2μm are mainly from the weathering products of basic intrusive rocks from the upper reach. Comparative analysis also suggests that the original bulk sample test results are close to the average of graded samples. As the result, the differences and change trend of geochemical characteristics between grades are hard to be observed. Therefore, integrated consideration is required in case the original geochemical data of bulk samples are used to trace the provenance.
-
Key words:
- surface sediments /
- grain size classification /
- major elements /
- provenance identity /
- Yalu River
-

-
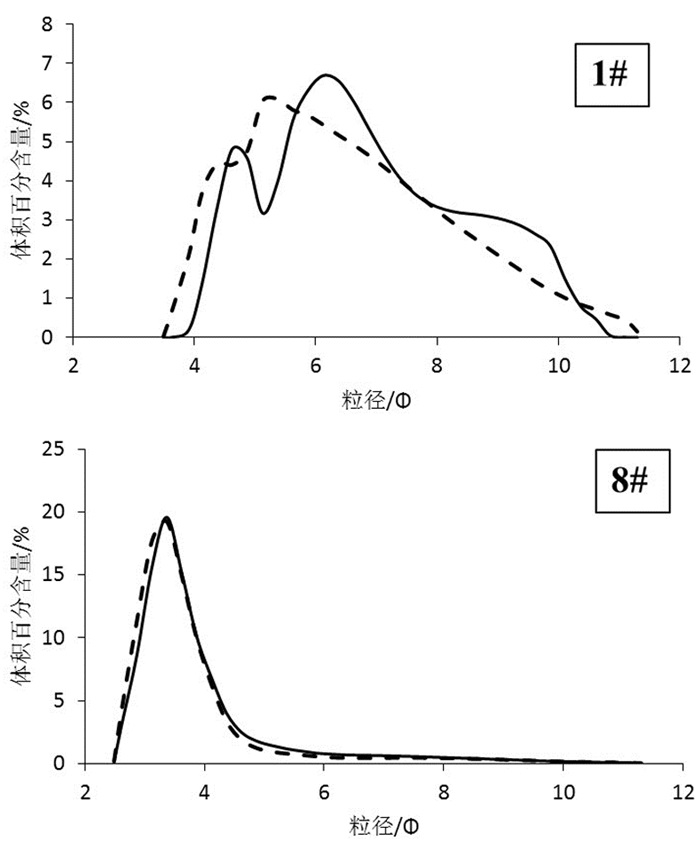
表 1 鸭绿江河口表层沉积物粒度参数
Table 1. Grain size parameters of surface sediments in the Yalu River estuary
编号 中值粒径/Φ 平均粒径/Φ 分选系数 偏态系数 峰态系数 砂组分/% 粉砂组分/% 黏土组分/% YL-01 6.6 6.9 1.6 1.1 2.0 0.2 73.5 26.3 YL-02 5.4 5.8 1.7 1.7 2.3 6.4 80.0 13.5 YL-03 5.9 6.1 1.9 1.5 2.4 17.3 64.2 18.5 YL-04 6.3 6.6 1.8 1.3 2.1 2.2 74.3 23.6 YL-05 2.4 2.9 1.5 2.0 2.6 85.2 12.7 2.1 YL-06 6.3 6.6 1.7 1.3 2.1 0.4 76.3 23.3 YL-07 6.8 7.0 1.6 1.0 1.9 0.3 72.6 27.1 YL-08 3.5 4.0 1.3 1.8 2.4 72.4 24.5 3.1 YL-09 6.7 6.9 1.6 1.0 2.0 1.0 71.3 27.7 最大值 6.8 7.0 1.9 2.0 2.6 85.2 80.0 27.7 最小值 2.4 2.9 1.3 1.0 1.9 0.2 12.7 2.1 平均值 5.6 5.9 1.6 1.4 2.2 20.6 61.0 18.4 YL01 6.3 6.5 1.7 1.4 2.2 2.7 76.6 20.6 YL02 5.1 5.5 1.9 1.7 2.5 24.1 63.1 12.9 YL03 5.7 5.9 2.1 1.5 2.6 24.8 57.1 18.1 YL04 6.2 6.4 1.9 1.4 2.3 8.9 69.1 22.0 YL05 2.5 2.9 1.4 2.0 2.6 87.4 10.5 2.1 Yl06 6.5 6.6 1.8 1.3 2.2 3.1 74.1 22.8 YL07 6.9 7.1 1.6 1.0 1.9 0.1 68.5 31.4 YL08 3.5 3.8 1.3 1.8 2.4 77.8 19.3 2.9 YL09 6.7 6.8 1.8 1.2 2.2 2.6 71.1 26.3 最大值 6.9 7.1 2.1 2.0 2.6 87.4 76.6 31.4 最小值 2.5 2.9 1.3 1.0 1.9 0.1 10.5 2.1 平均值 5.5 5.7 1.7 1.5 2.3 25.7 56.6 17.7 注:YL-01—YL-09为处理后样品测试,YL01—YL09为全样测试。 表 2 鸭绿江河口表层沉积物常量元素含量特征
Table 2. The major elements contents of surface sediments in the Yalu River estuary
% 编号 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO K2O Na2O MnO TiO2 P2O5 YL01 14.84 3.13 0.74 1.20 3.06 1.91 0.03 0.88 0.03 YL02 12.15 2.35 0.90 1.00 3.23 2.31 0.03 0.74 0.03 YL04 10.44 1.83 1.23 0.73 3.09 2.66 0.03 0.61 0.03 YL06 15.41 3.43 0.81 1.29 3.16 2.03 0.03 0.84 0.03 YL07 15.86 3.99 0.80 1.55 3.13 1.92 0.04 0.85 0.05 YL09 16.09 3.93 0.64 1.37 3.18 1.73 0.03 0.87 0.05 站位均值 14.13 3.11 0.85 1.19 3.14 2.09 0.03 0.80 0.04 标准偏差 2.30 0.87 0.20 0.29 0.06 0.34 0.00 0.11 0.01 变异系数 0.16 0.28 0.24 0.24 0.02 0.16 0.11 0.13 0.27 >63μm 11.64 1.35 0.83 0.63 3.28 2.54 0.01 0.45 0.02 32~63μm 12.69 3.12 1.10 1.27 3.14 2.66 0.03 0.55 0.05 8~32μm 11.01 3.04 1.15 1.39 2.73 2.49 0.04 0.85 0.04 2~8μm 17.12 5.96 0.69 2.47 3.26 1.63 0.05 0.95 0.08 < 2μm 18.35 8.43 0.36 2.41 3.00 0.71 0.06 0.95 0.15 粒级均值 14.16 4.38 0.83 1.64 3.08 2.01 0.04 0.75 0.07 表 3 鸭绿江河口表层沉积物样品化学蚀变指数
Table 3. The chemical index of alteration of surface sediments in the Yalu River estuary
编号 CIA 粒级/μm CIA 全样 处理后样品 YL01 72 72 >63 64 YL02 65 71 32~63 65 YL04 60 69 8~32 63 YL06 72 67 2~8 75 YL07 73 70 < 2 82 YL09 74 73 注:CIA= Al2O3/[Al2O3+ CaO*+ K2O+ Na2O]*100。当CaO的摩尔数大于Na2O时,mCaO*=mNa2O,而小于Na2O时,则mCaO*=m CaO[25]。本文中CaO*依据此方法计算获得。 表 4 鸭绿江河口表层沉积物全样常量元素相关性
Table 4. The correlation coefficient of major elements for bulk samples in the Yalu River estuary
Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO K2O Na2O MnO TiO2 P2O5 CIA 砂/% 粉砂/% 黏土/% Al2O3 1.00 Fe2O3 0.98 1.00 CaO -0.91 -0.85 1.00 MgO 0.96 0.98 -0.84 1.00 K2O 0.01 0.04 -0.18 0.08 1.00 Na2O -0.96 -0.93 0.97 -0.90 -0.03 1.00 MnO 0.39 0.51 -0.06 0.59 -0.17 -0.21 1.00 TiO2 0.95 0.89 -0.97 0.89 -0.01 -0.98 0.21 1.00 P2O5 0.71 0.82 -0.67 0.76 0.20 -0.74 0.39 0.59 1.00 CIA 0.99 0.96 -0.95 0.94 0.01 -0.99 0.31 0.98 0.69 1.00 砂/% -0.68 -0.69 0.39 -0.61 0.61 0.57 -0.50 -0.53 -0.46 -0.62 1.00 粉砂/% 0.49 0.36 -0.36 0.27 -0.67 -0.45 -0.05 0.50 -0.03 0.49 -0.75 1.00 黏土/% 0.60 0.71 -0.28 0.66 -0.36 -0.48 0.76 0.38 0.68 0.52 -0.86 0.31 1.00 注:相关系数|r|≥0.85时,在0.01水平上显著相关;|r| < 0.85时,在0.05水平上显著相关。 表 5 鸭绿江河口表层沉积物分级样品常量元素相关性
Table 5. The correlation coefficient of major elements for graded samples in the Yalu River estuary
Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO K2O Na2O MnO TiO2 P2O5 CIA 砂/% 粉砂/% 黏土/% Al2O3 1.00 Fe2O3 0.57 1.00 CaO -0.41 -0.38 1.00 MgO 0.91 0.70 -0.15 1.00 K2O 0.97 0.51 -0.53 0.81 1.00 Na2O -0.67 -0.81 0.82 -0.58 -0.69 1.00 MnO 0.18 0.67 0.37 0.55 -0.01 -0.18 1.00 TiO2 0.83 0.58 -0.61 0.69 0.80 -0.82 0.09 1.00 P2O5 0.62 0.85 -0.02 0.81 0.48 -0.58 0.81 0.63 1.00 CIA 0.99 0.63 -0.54 0.89 0.97 -0.78 0.17 0.88 0.63 1.00 砂/% 0.14 0.18 0.32 0.14 0.16 0.12 0.16 0.10 0.34 0.07 1.00 粉砂/% -0.36 0.02 0.50 -0.24 -0.38 0.32 0.26 -0.16 0.23 -0.39 0.80 1.00 黏土/% 0.15 -0.10 -0.45 0.08 0.15 -0.24 -0.23 0.05 -0.29 0.20 -0.93 -0.96 1.00 注:相关系数|r|≥0.85时,在0.01水平上显著相关;|r| < 0.85时,在0.05水平上显著相关。 表 6 鸭绿江河口表层沉积物分级样品常量元素旋转矩阵
Table 6. The rotation matrix of major elements for graded samples in the Yalu River estuary
分析要素 成份 1 2 3 Al2O3 0.90 -0.04 0.27 Fe2O3 0.57 0.06 0.69 CaO -0.71 0.38 0.31 MgO 0.70 -0.03 0.62 K2O 0.95 -0.03 0.07 Na2O -0.83 0.21 -0.24 MnO -0.07 0.12 0.99 TiO2 0.91 0.04 0.15 P2O5 0.49 0.27 0.82 CIA 0.94 -0.09 0.25 砂/% 0.14 0.97 0.06 粉砂/% -0.31 0.91 0.12 黏土/% 0.12 -0.98 -0.10 贡献方差/% 44.80 23.23 21.96 累积方差/% 44.80 68.03 89.98 表 7 分级样品与全样元素含量差异百分比
Table 7. Percentage difference in content of elements between grading samples and bulk samples
% 粒级/μm Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO K2O Na2O MnO TiO2 P2O5 >63 17.65 56.54 2.15 46.97 4.31 21.44 50.44 43.42 41.72 32~63 10.23 0.23 28.87 7.02 0.05 27.07 14.18 30.83 20.93 8~32 22.08 2.31 34.98 17.12 13.16 18.88 34.55 6.98 1.89 2~8 21.16 91.47 18.82 107.45 3.64 21.88 70.92 18.83 98.24 < 2 29.87 170.91 57.56 102.68 4.36 66.28 89.52 18.66 284.29 -
[1] 严杰, 高建华, 李军, 等.鸭绿江河口及近岸地区稀土元素的物源指示意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(4):95-103. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=a77b17f7-6932-4d73-9f87-f34ad8a4cda4
YAN Jie, GAO Jianhua, LI Jun, et al.Implications of ree for provenance in the Yalu estuary and its adjacent sea area[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(4):95-103. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=a77b17f7-6932-4d73-9f87-f34ad8a4cda4
[2] 白凤龙, 高建华, 汪亚平, 等.鸭绿江口的潮汐特征[J].海洋通报, 2008, 27(3):7-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2008.03.002
BAI Fenglong, GAO Jianhua, WANG Yaping, et al.Tidal characteristics at Yalu river estuary[J].Marine Science Bulletin, 2008, 27(3):7-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2008.03.002
[3] 高建华, 高抒, 董礼先, 等.鸭绿江河口地区沉积物特征及悬沙输送[J].海洋通报, 2003, 22(5):26-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2003.05.005
GAO Jianhua, GAO Shu, DONG Lixian, et al.Sediment distribution and suspended sediment transport in Yalu river estuary[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2003, 22(5):26-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2003.05.005
[4] 高建华, 李军, 王珍岩, 等.鸭绿江河口及近岸地区沉积物中重金属分布的影响因素分析[J].地球化学, 2008, 37(5):430-438. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2008.05.002
GAO Jianhua, LI Jun, WANG Zhenyan, et al.Heavy metal distribution and their influence factors in sediments of Yalu river estuary and its adjacent sea area[J].Geochimica, 2008, 37(5):430-438. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2008.05.002
[5] 齐君, 李凤业, 宋金明, 等.北黄海沉积速率及其沉积通量[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(2):9-14. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=9b2a3e95-2a10-4b1c-83ec-02faa116531b
QI Jun, LI Fengye, SONG Jinming, et al.Sedimentation rate and flux of the North Yellow Sea[J].Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2004, 24(2):9-14. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=9b2a3e95-2a10-4b1c-83ec-02faa116531b
[6] 冉隆江, 石勇, 高建华, 等.鸭绿江河口地区沉积物的粒度变化及其影响因素[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(2):31-42. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=136c7e48-d840-43ef-af39-7917eabb4223
RAN Longjiang, SHI Yong, GAO Jianhua, et al.Gain size variation and its influencing factors in the sediment cores of Yalu river estuary[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(2):31-42. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=136c7e48-d840-43ef-af39-7917eabb4223
[7] 李家胜, 高建华, 李军, 等.鸭绿江河口沉积物元素地球化学及其控制因素[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(1):25-31. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=8ed847e6-387b-4daa-8577-83e5ef839b07
LI Jiasheng, GAO Jianhua, LI Jun, et al.Distribution and controlling factors of major elements in sediments of the Yalu river estuary[J].Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(1):25-31. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=8ed847e6-387b-4daa-8577-83e5ef839b07
[8] 程岩, 刘月, 李富祥, 等.鸭绿江口及邻近浅海碎屑矿物特征与物源辨识[J].地理研究, 2010, 29(11):1950-1960. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlyj201011004
CHENG Yan, LIU Yue, LI FUxiang, et al.Detrital mineral characteristics and material source identification in surface sediments of Yalu river estuary and adjacent waters[J].Geographical Research, 2010, 29(11):1950-1960. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlyj201011004
[9] 高建华, 李军, 汪亚平, 等.鸭绿江河口及近岸海域沉积物中重矿物组成、分布及其沉积动力学意义[J].海洋学报, 2009, 31(3):84-94. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2009.03.010
GAO Jianhua, LI Jun, Wang Yaping, et al.Heavy mineral distribution and their implications for sediment dynamics in the Yalu estuary and its adjacent sea area[J].Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2009, 31(3):84-94. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2009.03.010
[10] 王应飞, 高建华, 石勇, 等.鸭绿江河口西岸潮间带柱状沉积物中重金属的分布特征及其对流域变化的响应[J].地球化学, 2014, 43(1):64-76. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx201401007
WANG Yingfei, GAO Jianhua, SHI Yong, et al.Distribution characteristics of intertidal sediment heavy metal of the western bank of the Yalu river, and its responses to catchment changes[J].Geochimica, 2014, 43(1):64-76. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx201401007
[11] 李红军, 程岩, 刘月, 等.鸭绿江口重金属沉积记录的环境意义[J].环境科学学报, 2017, 37(6):2296-2306. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkxxb201706035
LI Hongjun, CHENG Yan, LIU Yue, et al.Environmental significance of heavy metals in the core sediments of the Yalu river estuary[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2017, 37(6):2296-2306. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkxxb201706035
[12] 程岩, 毕连信.鸭绿江河口浅滩的基本特征和动态变化[J].泥沙研究, 2002, 3:59-63. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2002.03.010
CHENG Yan, BI Lianxin.Primary character and motive change of shallow beach in Yalu river mouth[J].Journal of Sediment Research, 2002, (3):59-63. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2002.03.010
[13] 高峰, 孙连成, 麦苗.鸭绿江河口潮流泥沙数值模拟[J].水道港口, 2009, 30(2):89-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2009.02.003
GAO Feng, SUN Liancheng, MAI Miao.Numerical simulation of tidal current and sediment in Yalu river estuary[J].Journal of Waterway and Harbor, 2009, 30(2):89-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2009.02.003
[14] 孙永根, 吴桑云.鸭绿江西水道口悬沙动力特征[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(2):33-38. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=ca871455-cec4-422d-8a56-ae607ac082fb
SUN Yonggen, WU Sangyun.Dynamic characteristics of suspended sediments in the west channel of the Yalu river[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(2):33-38. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=ca871455-cec4-422d-8a56-ae607ac082fb
[15] 程岩.鸭绿江河口地貌的形成、演变与港口建设[J].海港工程, 1988, 7(1): 28-35. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1988-HAGC198801005.htm
CHENG Yan.Formation and evolution on geomorphology of Yalu river mouth and harbor construction[J].Coastal Engineering, 1988, 7(1):28-35. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1988-HAGC198801005.htm
[16] M.Revel, M.Cremer, F.E.Grousset, et al.Grain-size and Sr-Nd isotopes as tracer of paleob-ottom current strength, Northeast Atlantic Ocean[J].Marine Geology, 1996, 131: 233-249.
[17] 赵一阳, 鄢明才.中国浅海沉积物地球化学[M].北京:科学出版社, 1994.
ZHAO Yiyang, YAN Mingcai.Sedimentary Geochemistry in China Sea[M].Beijing:Science Press, 1994.
[18] 赵一阳, 喻德科.黄海沉积物的地球化学分析[J].海洋与湖沼, 1983, 14(5):432-446. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb200703012
ZHAO Yiyang, YU Deke.Geochemical analysis of the Yellow Sea sediments[J].Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1983, 14(5) : 432-446. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb200703012
[19] Rollinson H R.Using geochemical data:evaluation, presentation, interpretation[M].New York:Longman Scientific Technical.1993.
[20] McManus J.Grain sie determination and interpretation.In:Tucker M ed[J].Techniques in Sedimentology, Backwell, Oxford.1988: 63-85.
[21] 臧家业, 汤毓祥, 邹娥梅, 等.黄海环流的分析[J].科学通报, 2001, 46:7-15. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyxb200902001
CANG Jiaye, TANG Yuxiang, ZOU Emei, et al.The analysis of the Yellow Sea circulation[J].Science Bulletin, 2001, 46:7-15. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyxb200902001
[22] 杨守业, Jung Hoi-Soo, 李从先, 等.黄河、长江与韩国Keum、Yeongsan江沉积物常量元素地球化学特征[J].地球化学, 2004, 33(1):99-105. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2004.01.013
YANG Shouye, JUNG Hoi-Soo, LI Congxian.et al.Major element geochemistry of sediments from Chinese and Korean rivers[J].Geochimica, 2004, 33(1):99-105. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2004.01.013
[23] Nesbitt H W, Young G M. Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J]:Nature, 1984, 299, 715-717. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1038-299715a0/
[24] 吴丰昌, 王立英, 黎文, 等.天然有机质及其在地表环境中的重要性[J].湖泊科学, 2008, 20(1): 1-12. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2008.01.001
WU Fengchang, WANG Liying, LI Wen, et al.Natural organic matter and its significance in terrestrial surface environment[J].Lake Sci, 2008, 20(1):1-12. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2008.01.001
[25] McLennan S W.Weathering and global denudation[J].Journal of Geology, 1993, 101:295-303. doi: 10.1086/648222
[26] Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations[J].Geochimicaet Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48:1523-1534. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90408-3
[27] Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Petrogenesis of sediments in the absence of chemical weathering effects of abrasion and sorting on bulk composition mineralogy[J].Sedimentology, 1996, 43(2):243-358. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1046-j.1365-3091.1996.d01-12.x/
[28] Nesbitt H W, Markovics G, Price R C.Chemical processes affecting alkalis and alkaline earths during continental weathering[J].Geochem Cosmochim Acta, 1980, 44(11):1659-1666. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(80)90218-5
[29] 刘若新, 樊祺诚, 郑详身, 等.长白山天池火山的岩浆演化[J].中国科学D辑, 1998, 3(20):226-231. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200403021
LIU Ruoxin, FAN Qicheng, ZHENG Xiangshen, et al.The magma evolution of tianchi volcano in changbai mountain[J].Science in China(Serics D), 1998, 3(20):226-231. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200403021
[30] 赵一阳, 喻德科.黄海沉积物地球化学分析[J].海洋与湖沼, 1983, 14(5):432-446. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb200703012
ZHAO Yiyang, YU Deke.Geochemical analusis of the sediments of the HuangHai sea[J].Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1983, 14(5):432-446. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb200703012
[31] 赵一阳, 何丽娟, 陈毓蔚.论黄海沉积物元素区域分布格局[J].海洋科学, 1989, 1:1-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYKX198901000.htm
ZHAO Yiyang, HE Lijuan, CHEN Yuwei.On regional distribution patterns of elements in sediments of the Yellow Sea[J].Marine Sciences, 1989, 1:1-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYKX198901000.htm
[32] Murray R W, Knowlton C, Leinen K W, et al.Export production and terrigenous matter in the central equatorial Pacific Ocean during interglacial oxygen isotope stage 11[J].Global and Planetary Change, 2000, 24(1):59-78. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8181(99)00066-1
[33] 米兰诺夫斯基EE.地球历史上的裂谷作用[M].北京:地质出版社, 1985.
Milanovsky EE.The Rift in Earth's History[M]. Beijing:Geological Press.1985.
[34] 于成广.辽宁鸭绿江成矿带水系沉积物地球化学特征及成矿远景预测[D].2016.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1016067854.htm YU Chengguang.Geochemical characteristics and prospective prognosis of the Yalu river metallogenic belt based on stream sediment survey[D].2016.
[35] 王成文, 刘永江, 李东涛.辽河岩群南北区域对比的新证据[J].长春地质学院学报, 1997, 27(1):17-24. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700196062
WANG Chengwen, LIU Yongjiang, LI Dongtao.New evidences on the correlation of Liaohe lithogroup between the southern and the northern regions in eastern Liaoning province[J].Journal of ChangChun University of Earth Sciences, 1997, 27(1):17-24. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700196062
[36] LI S Z, ZHAO G C, SUN M, et al.Deformation history of the paleoproterozoic Liaohe assemblage in the eastern block of the North China Craton[J].Journal of the Asian Earth Sciences, 2005, 24:659-674. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2003.11.008
[37] LI S Z, ZHAO G C.SHRIM PU-Pb zircon geochronology of the Liaoji granitoids:Constraints on the evolution of the Plaleoprot erozoic Jiao-Liao-Ji belt In the Eastern Block of the North China Craton[J].Precambrian Res., 2007, 158:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2007.04.001
[38] Roser B P, Korsch R J.Provenance Signatures of Sandstone-Mudstone Suites Determined Using Discriminant Function Analysis of Major-Element Data[J].Chem. Geol., 1988, 67:119-139. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(88)90010-1
-



 下载:
下载: