Millennial-scale paleoenvironment and paleoclimate changes recorded in the Bohai Sea sediments during the last glacial period
-
摘要:
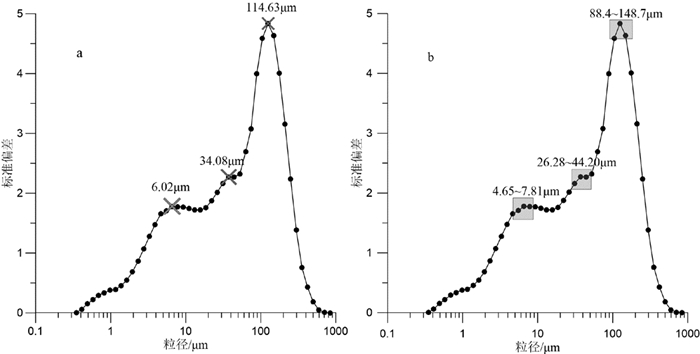
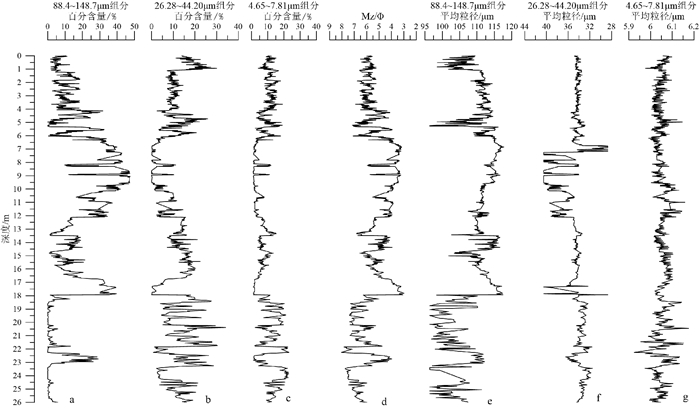
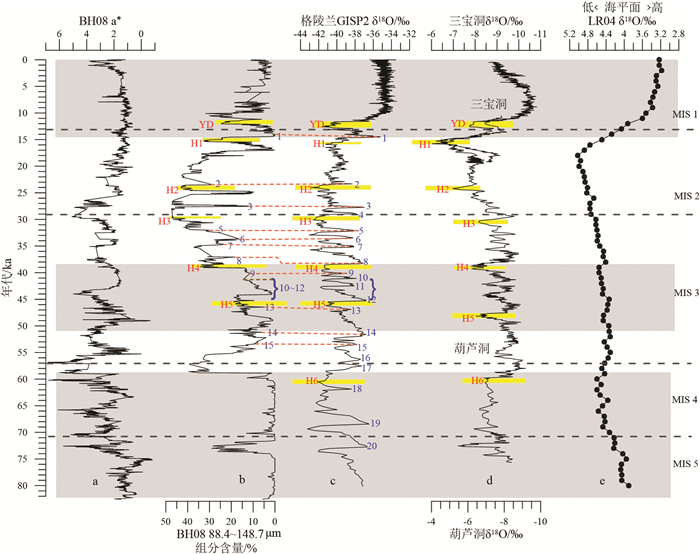
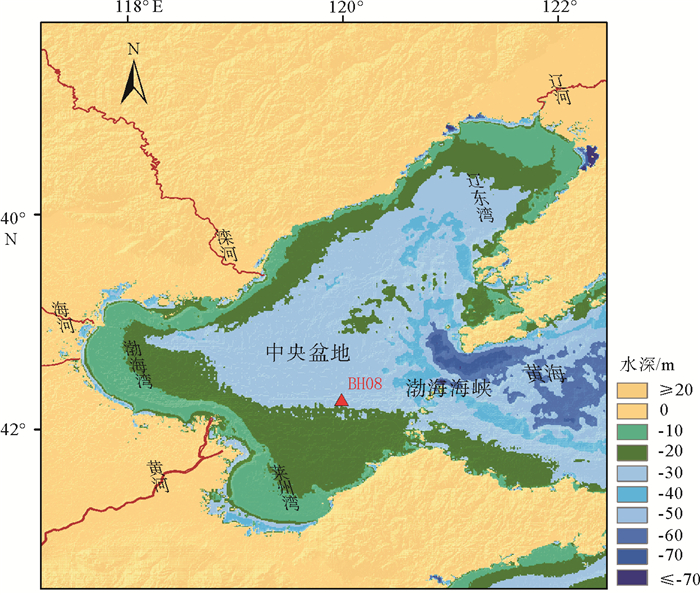
末次冰期千年尺度古气候变化事件在全球大部分载体中均有不同程度的记录,但在海岸带—陆架区的沉积记录中该事件还未见有报道。对取自渤海的BH08孔上部26m的岩芯进行了高分辨率粒度测试与分析,结合AMS 14C测年结果和微体古生物特征,探讨了研究区末次冰期以来古环境和古气候变化。运用粒级-标准偏差法对粒度数据进行研究,发现BH08孔敏感组分(88.4~148.7μm)的变化记录了末次冰期D-O(Dansgarrd-Oeschger)旋回冷暖事件:在暖期时敏感粒级粗组分(88.4~148.7μm)的含量低,而在冷期时含量高,且可以与反映东亚夏季风的指标对应。在暖期时,强盛的夏季风带来丰富的降水,增加的径流可以将粗粒沉积物搬运至更远的下游区,且暖湿气候有利于植被的发育,使得流域内粗粒沉积物减少;而在冷期呈现相反的变化趋势。我们推测,在末次冰期低海面的背景下,格陵兰和北大西洋等高纬地区气候变化导致大气环流和/或洋流系统发生改变,从而对东亚夏季风降水的调控造成河流输入物质的变化可能是造成BH08岩芯敏感组分变化的主要原因。
Abstract:The millennial-scale paleoclimatic change during the last glacial stage has been recorded in various achieves worldwide, but nothing has been heard from the sedimentary records in a coastal zone. In order to dig out the sedimentary records from the coastal region, we carried out high-resolution grain-size analysis for the upper 26m of the core BH08 collected from the Bohai Sea, together with AMS 14C dating and microfossils studies. Based upon them, the paleoenvironment and paleoclimate changes of the study area since the last glacial stage are discussed. Grain-size data is treated with the grain size and standard deviation method. It is found that the sensitive component (88.4~148.7μm) of the core BH08 sediments well recorded the D-O (Dansgarrd-Oeschger) cycle of the last glacial stage: the content of the sensitive component (88.4~148.7μm) was low in warm periods, but high in cold periods. The cyclicities of sensitive component are also corresponding to the index reflecting the East Asian summer monsoon. During the warm periods, strong summer monsoon would bring in abundant precipitation, and the increased runoff might transport the coarse-grained sediments to the distant downstream areas. In addition, warm and humid climate is conducive to the development of vegetation, resulting in the reduction of coarse-grained sediments in the drainage basin, and vise versa. It is speculated that in the last glacial stage, climate in the high latitudes such as Greenland and the North Atlantic might cause changes in atmospheric circulation and/or ocean current systems by the precipitation of the East Asian summer monsoon, and thus control the changes of the input sediments from rivers. It may be the main reason for the change of grain-size in the core BH08.
-
Key words:
- the last glacial stage /
- Grain size /
- East Asian Summer Monsoon /
- D-O Cycle /
- Bohai Sea
-

-
表 1 BH08孔年代控制点
Table 1. Age control points of core BH08
深度/m 样品类型 14C年龄/aBP 距今日历年龄/cal.aBP 沉积速率/(cm·ka-1) 1 0.18* 贝壳 600±20 498~300 45.11 2 0.66 混合底栖有孔虫 2190±30 2145~1846 30.07 3 0.96 混合底栖有孔虫 2740±30 2818~2495 45.39 4 1.37 混合底栖有孔虫 5520±30 6252~5957 11.89 5 2.25 混合底栖有孔虫 7290±30 8054~7790 48.42 6 3.47* 贝壳 8490±40 9470~8153 137.16 7 4.09* 混合底栖有孔虫 9010±35 10165~9762 53.82 8 5.46 混合底栖有孔虫 7930±30 8756~8415 - 9 8.17* 贝壳 9020±40 10175~9769 - 10 15.79# OSL - 52500 27.51 11 45.49** 控制点 - 140000 33.94 注:*引自文献[33, 34],**引自文献[33],#引自姚政权等未发表数据。 -
[1] Linsley B K. Oxygen-isotope record of sea level and climate variations in the Sulu Sea over past 150, 000 yars[J]. Nature, 1996, 380: 234-237. doi: 10.1038/380234a0
[2] Wang L J, Sarnthein M, Erlenkeuser H, et al. East Asian monsoon climate during the Late Pleistocene: High resolution sediment records from the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 1999, 156: 245-284. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(98)00182-0
[3] 牛东风, 李保生, 温小浩, 等.萨拉乌苏河流域MGS1层段微量元素记录的全新世千年尺度的气候变化[J].地质学报, 2011, 85(2): 300-308. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201102015
NIU Dongfeng, LI Baosheng, WEN Xiaohao, et al. The Holocene ka-scale climate variation indicated by trace elements of the MGS1 segment in the Salawusu River Valley, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85(2): 300-308. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201102015
[4] Lorius C, Jouzel J, Ritz C, et al. A 150, 000 year climatic record from Antarctic ice[J]. Nature, 1985, 316: 591-596. doi: 10.1038/316591a0
[5] 孙广友, 罗新正, Turner R E, 等.青藏东北部若尔盖高原全新世泥炭沉积年代学研究[J].沉积学报, 2001, 19(2): 177-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2001.02.003
SUN Guangyou, LUO Xinzheng, Turner R E, et al.. A study on peat deposition chronology of Holocene of Zorge Plateau in the Northeast Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2001, 19(2): 177-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2001.02.003
[6] Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al. A high-resolution absolute-dated late Pleistocene monsoon record from Hulu Cave, China[J]. Science, 2001, 294: 2345-2348. doi: 10.1126/science.1064618
[7] Genty. France Speleothem Stable Isotope Data[M]. National Climatic Data Center, 2003.
[8] Heinrich H. Origin and consequences of cyclic ice rafting in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean during the past 130000 years[J]. Quaternary Research, 1988, 29(2): 142-152. doi: 10.1016/0033-5894(88)90057-9
[9] Broecker W, Bond G, Klas M, et al. Origin of the northern Atlantic's Heinrich events[J]. Climate Dynamics, 1992, 6(3-4): 265-273. doi: 10.1007/BF00193540
[10] Bond G, Heinrich H, Broecker W, et al. Evidence for massive discharges of icebergs into the North Atlantic ocean during the last glacial period[J]. Nature, 1992, 360(6401): 245-249. doi: 10.1038/360245a0
[11] Andrews J T, Tedesco K. Detrital carbonate rich sediments, northwestern Labrador Sea: Implications for ice-sheet dynamics and iceberg rafting (Heinrich) events in the North Atlantic[J]. Geology, 1992, 12(20): 1087-1090.
[12] Berger W H, Burke S, Vincent E. Glacial-Holocene transition: climate pulsations and sporadic shutdown of Nadw Production[M]. Springer Netherlands, 1987.
[13] Dansgaard W, Johnsen S, Clausen, et al. Evidence for general instability of past climate from a 250 kyr ice-core record[J]. Nature, 1993, 364(6343): 218-220. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1038-364218a0/
[14] Grootes P M, Stuiver M, White J W C, et al. Comparison of oxygen isotope records from the GISP2 and GRIP Greenlandice cores[J]. Nature, 1993, 366(6455): 552-554. doi: 10.1038/366552a0
[15] Sun Y, Clemens S C, Morrill C, et al. Influence of Atlantic meridional overturning circulation on the East Asian winter monsoon[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2011, 5(1): 46-49. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz-e201809009
[16] Thompson L G, Yao T D, Davies M E, et al. Tropical climate instability: the last glacial cycle from a Qinghai Tibetan ice core[J]. Science, 1997, 276(5320): 1821-1825. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5320.1821
[17] Bender M, Sowers T, Dickson M L, et al. Climate correlations between Greenland and Antarctica during the past 100, 000 years[J]. Nature, 1994, 372(6507): 663-666. doi: 10.1038/372663a0
[18] Kennett J P, Cannariato K G, Hendy I L, et al. Methane hydrates in quaternary climate change: the clarhrate gun hypothesis[J]. Eos Transactions American Geophysical Union, 2002, 83(45): 513-516. https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2002EO000359
[19] Sakia K, Peltier W R. A multibasin reduced model of the global thermohaline circulation: paleoceangraphic analyses of the origins of ice age climate instability[J]. Journal Geophysical Research Ocean, 1996, 101: 22535-22562. doi: 10.1029/96JC00539
[20] Broecker, Wallace S. Massive iceberg discharges as triggers for global climate change[J]. Nature, 1994, 372: 421-424. doi: 10.1038/372421a0
[21] Bond G C, Lotti R, et al. Iceberg discharges into the North Atlantic on millennial time scales during the last deglaciation[J]. Science, 1995, 273: 1257-1265. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f2bcbe7e5e92dabff15cacc48d6828fc&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[22] Lang C, Leuenberger M, Schwander J, et al. Rapid temperature variation in central Greenland 70000 years ago[J]. Science, 1999, 286: 934-937. doi: 10.1126/science.286.5441.934
[23] Shi X F, Yao Z Q, Liu Q S, et al. Sedimentary architecture of the Bohai Sea China over the last 1 Ma and implications for sea-level changes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 451: 10-21. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2016.07.002
[24] Yao Z Q, Guo Z T, Xiao G Q, et al. Sedimentary history of the Western Bohai coastal plain since the late Pliocene: implications on tectonic, climatic and sea-level changes[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 2012, 54(4): 192-202.
[25] Yan Y Z, Wang H, Li F L, et al. Different depositional processes of boreholes BQ1 and BQ2 in the late Pleistocene on the west coast of Bohai Bay[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2006, 26: 321-326. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dsjyj200603002
[26] 庄振业, 许卫东, 刘东生, 等.渤海南部S3孔晚第四纪海相地层的划分及环境演变[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1999, 19(2): 27-35. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz199902004
ZHUANG Zhenye, XU Weidong, LIU Dongsheng, et al. Division and environmental evolution of late Quaternary marine beds of S3 hole in the Bohai Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1999, 19(2): 27-35. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz199902004
[27] 秦蕴珊.渤海地质[M].北京:科学出版社, 1985.
QIN Yunshan. Geology of Bohai Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985.
[28] 秦蕴珊, 李凡.黄河入海泥沙对渤海和黄海沉积作用的影响[J].海洋科学集刊, 1986, 27: 125-135. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-80180-1016904163.htm
QIN Yunshan, LI Fan. The influence of Yellow River Sediment into the sea on sedimentation in Bohai and Huanghai seas[J]. Studia Marina Sinca, 1986, 27: 125-135. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-80180-1016904163.htm
[29] 蓝先洪, 李日辉, 陈晓辉, 等.渤海西部晚更新世以来沉积地球化学研究[J].海洋科学进展, 2018, 36(1): 67-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2018.01.006
LAN Xianhong, LI Rihui, CHEN Xiaohui, et al. Study of sedimentary geochemistry in the Western Bohai sea since late Pleistocene[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2018, 36(1): 67-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2018.01.006
[30] Konert M, Vandenberghe J E F. Comparison of laser grain size analysis with pipette and sieve analysis: a solution for the underestimation of the clay fraction[J]. Sedimentology, 1997, 44(3): 523-535. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.1997.d01-38.x
[31] Bard E. Geochemical and geophysical implications of the radiocarbon calibration[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1998, 62(12): 2025-2038. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00130-6
[32] Southon J, Kashgarian M, Fontugne M, et al. Marine reservoir corrections for the Indian Ocean and Southeast Asia[J]. Radiocarbon, 2002, 44(1): 167-180. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200064778
[33] Yao Z Q, Shi X F, Liu Q S, et al. Paleomagnetic and astronomical dating of sediment core BH08 from the Bohai Sea, China: Implications for glacial-interglacial sedimentation[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 2014, 393(393): 90-101.
[34] Yao Z Q, Shi X F, Qiao S Q, et al. Persistent effects of the Yellow River on the Chinese marginal seas began at least ~880ka ago[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 2827. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03140-x
[35] 李小艳, 赵泉鸿, 姚政权, 等.渤海百万年以来的海侵记录: BH08孔有孔虫和介形类证据[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(6): 93-108. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYDZ201506016.htm
LI Xiaoyan, ZHAO Quanhong, YAO Zhengquan, et al. Transgressive records of last million years in the Bohai Sea, China: evidence from foraminifera and ostracoda of core BH08[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(6): 93-108. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYDZ201506016.htm
[36] Lisiecki E, Raymo E. A Pliocence-Pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ18O records[J]. Paleoceanography, 2005, 20: 1-17. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0e5531afb09190f1f4a35cb6f3ac7385&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[37] 王中波, 李日辉, 张志珣, 等.渤海及邻近海区表层沉积物粒度组成及沉积分区[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(6): 101-109. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201606013
WANG Zhongbo, LI Rihui, ZHANG Zhixun, et al. Grain size composition and distribution pattern of seafloor sediments in Bohai Bay and adjacent areas[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(6): 101-109. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201606013
[38] 刘升发, 石学法, 刘焱光, 等.中全新世以来东亚冬季风的东海内陆架泥质沉积记录[J].科学通报, 2010, 55: 1387-1396. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201014014
LIU Shengfa, SHI Xuefa, LIU Yanguang, et al. Records of the East Asian winter monsoon from the mud area on the inner shelf of the East China Sea since the mid-Holocene[J]. Science Bulletin, 2010, 55: 1387-1396. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201014014
[39] Boulay S, Colin C, Trentesaux A, et al. Mineralogy and sedimentology of Pleistocene sediment on the South China Sea (ODP Site 1144)[M]. In: Prell W L, Wang P, Blum P, et al, eds. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 2003, 184: 1-21.
[40] 向荣, 杨作升, Y. Saito, 等.济州岛西南泥质区近2300a来环境敏感粒度组分记录的东亚冬季风变化[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2006, 36(7): 654-662. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200607005.htm
XIANG Rong, YANG Zuosheng, Satio Y, et al.Variation of East Asia winter monsoon according grain-size component records in the mud area southwest off Cheju island for 2300 year recently[J].Science in China: Earth Sciences, 2006, 36(7): 654-662. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200607005.htm
[41] 涂路遥, 周鑫, 刘毅, 等.近海泥质沉积物敏感粒径作为冬季风强度指标的再研究:与器测数据的对比[J].第四纪研究, 2015, 35: 1393-1401. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.06.08
TU Luyao, ZHOU Xin, LIU Yi, et al. Re-analysis of sensitive grain size of coastal muddy sediments as proxy of winter monsoon strength: Comparison with instrumental data[J]. Quaternary Science, 2015, 35: 1393-1401. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.06.08
[42] 徐方建, 李安春, 万世明, 等.东海内陆架泥质区中全新世环境敏感粒度组分的地质意义[J].海洋学报, 2009, 31(3): 95-102. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2009.03.011
XU Fangjian, LI Anchun, WANG Shiming, et al. The geological significance of environmental sensitive grain-size populations in the mud wedge of the East China Sea during the mid-Holocene[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2009, 31(3): 95-102. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2009.03.011
[43] Wang Y, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al. Millennial and orbital scale changes in the East Asian monsoon over the past 224000 years[J]. Nature, 2008, 451: 1090-1093. doi: 10.1038/nature06692
[44] Zhang Z L, Liu E F, Zhang Y, et al. Environmental evolution in the saltwater intrusion area south of Laizhou Bay since late Pleistocene[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2008, 18: 37-56. doi: 10.1007/s11442-008-0037-1
[45] Boulay S, Colin C, Trentesaux A, et al. Sedimentary responses to the Pleistocene climatic variations recorded in the South China Sea[J]. Quaternary Research, 2007, 68: 162-172. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2007.03.004
[46] Liu Z, Christophe C, Alain T, et al. Late Quaternary climatic control on erosion and weathering in the eastern Tibetan Plateau and the Mekong Basin[J]. Quaternary Research, 2005, 63(3): 316-328. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2005.02.005
[47] Porter S C, An Z S. Correlation between climate events in the North Atlantic and China during the last glaciation[J]. Nature, 1995, 375(6529): 305-308. doi: 10.1038/375305a0
[48] Tada R, Irino T, Koizumi I, et al. Land-ocean linkages over orbital and millennial timescales recorded in late Quaternary sediments of the Japan Sea[J]. Paleoceanography, 1999, 14(2): 236-247. doi: 10.1029/1998PA900016
[49] Li T G, Liu Z X, Michael A H, et al. Heinrich event imprints in the Okinawa Trough: evidence from oxygen isotope and planktonic foraminifera[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 2001, 176(1): 133-146. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S0031-0182(01)00332-7/
[50] 刘长征, 王会军, 姜大膀等.东亚季风区夏季风强度和降水的配置关系[J].大气科学, 2004, 28(5): 700-712. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/daqikx200405005
LIU Changzheng, WANG Huijun, JIANG Dabang, et al. The configurable relationships between summer monsoon and precipitation over East Asia[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2004, 28(5): 700-712. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/daqikx200405005
[51] 姚菁.渤海南岸LZ908孔海陆交互相地层气候代用指标及沉积环境研究[D].中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2014.
YAO Jing. Climatic indicators and sedimentary environment studies inferred from transgressive and regressive sediment of core LZ908, south Bohai Sea[D]. Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences (institute of oceanography), 2014.
[52] Yi L, Yu H J, Ortiz J D, et al. Late quaternary linkage of sedimentary records to three astronomical rhythms and the Asian monsoon, inferred from a coastal borehole in the south Bohai Sea, China[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 2012, 329-330(3): 101-117. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e49fa43a9d0ffd03f5f16a195b120c3e
[53] 孙红雨, 王长耀, 牛铮, 等.中国地表植被覆盖变化及其与气候因子关系──基于NOAA时间序列数据分析[J].遥感学报, 1998, 2(3):204-210. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YGXB803.008.htm
SUN Hongyu, WANG Changyao, NIU Zheng, et al. Analysis of the vegetation cover change and relationship between NDVI and environment factors by using NOAA time series data[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 1998, 2(3):204-210. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YGXB803.008.htm
[54] Anklin M, Barnola J M, Beer J, et al. Climate instability during the last interglacial period recorded in the GRIP ice core[J]. Nature, 1993, 364(6434): 203-207. doi: 10.1038/364203a0
[55] Dansgaard W, Oeschger H. In the Environmental Record in Glaciers and Ice Sheets[M]. Chichester: Wiley, 1989: 287-318.
[56] Bond G C, Showers W, Elliot M, et al. The North Atlantic's 1-2 kyr climate rhythm: relation to Heinrich events, Dansgaard Oeschger cycles and the Little Ice Age[J]. Geophysical Monograph, 1999, 112: 35-58. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d7d56a5d6a0126fb986e93559c1cbde8&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[57] Schulz H, Rad U V, Erlenkeuser H, et al. Correlation between Arabian Sea and Greenland climate oscillations of the past 110000 years[J]. Nature, 1998, 393: 54-57. doi: 10.1038/31750
[58] Behl R, Kennett J. Brief interstadial events in the Santa Barbara basin, NE Pacific, during the past 60 kyr[J]. Nature, 1996, 379: 243-246. doi: 10.1038/379243a0
-



 下载:
下载: