Using uranium-series radionuclides as tools for tracing marine sedimentary processes: Source identification, sedimentation rate, and sediment resuspension
-
摘要:
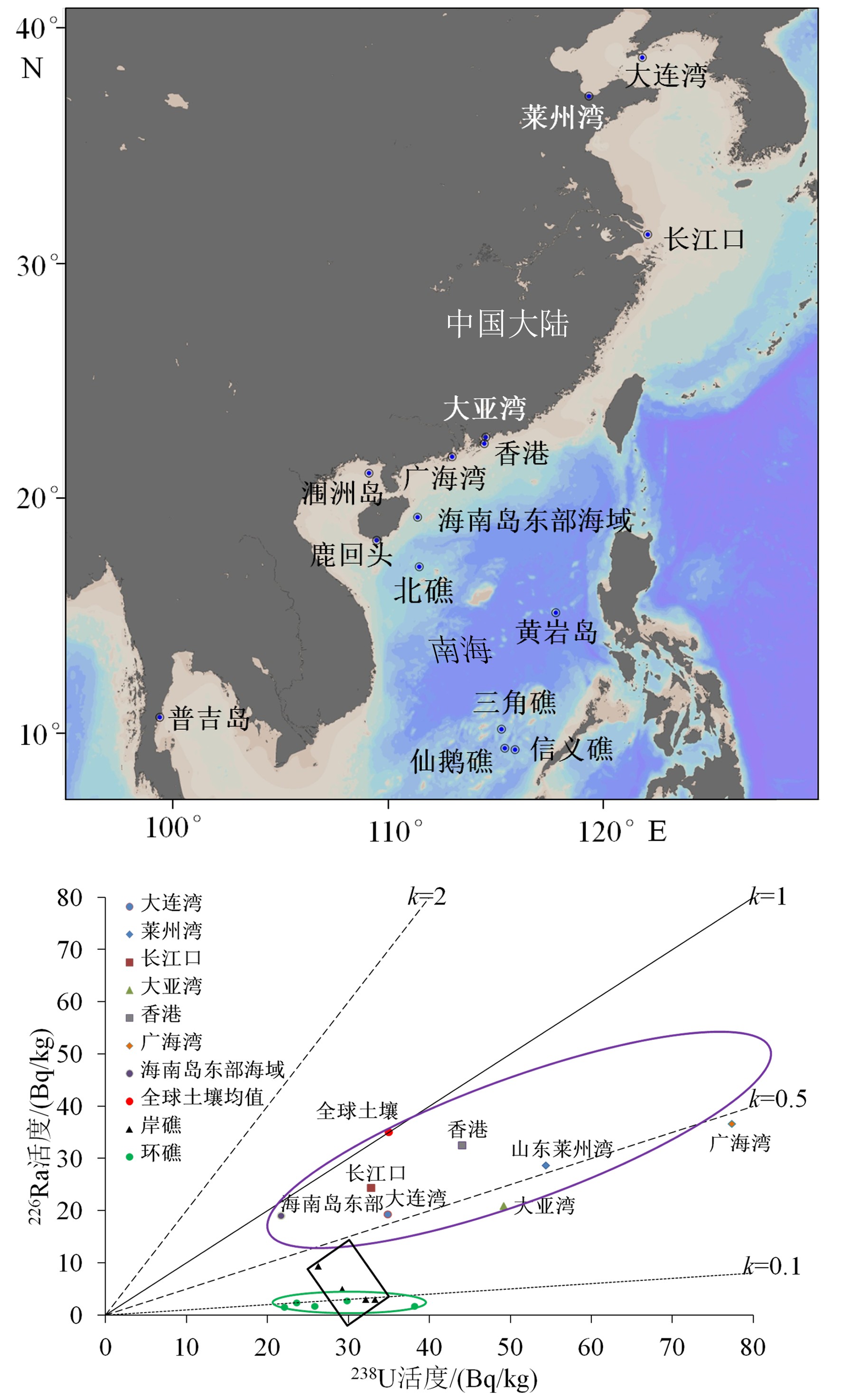
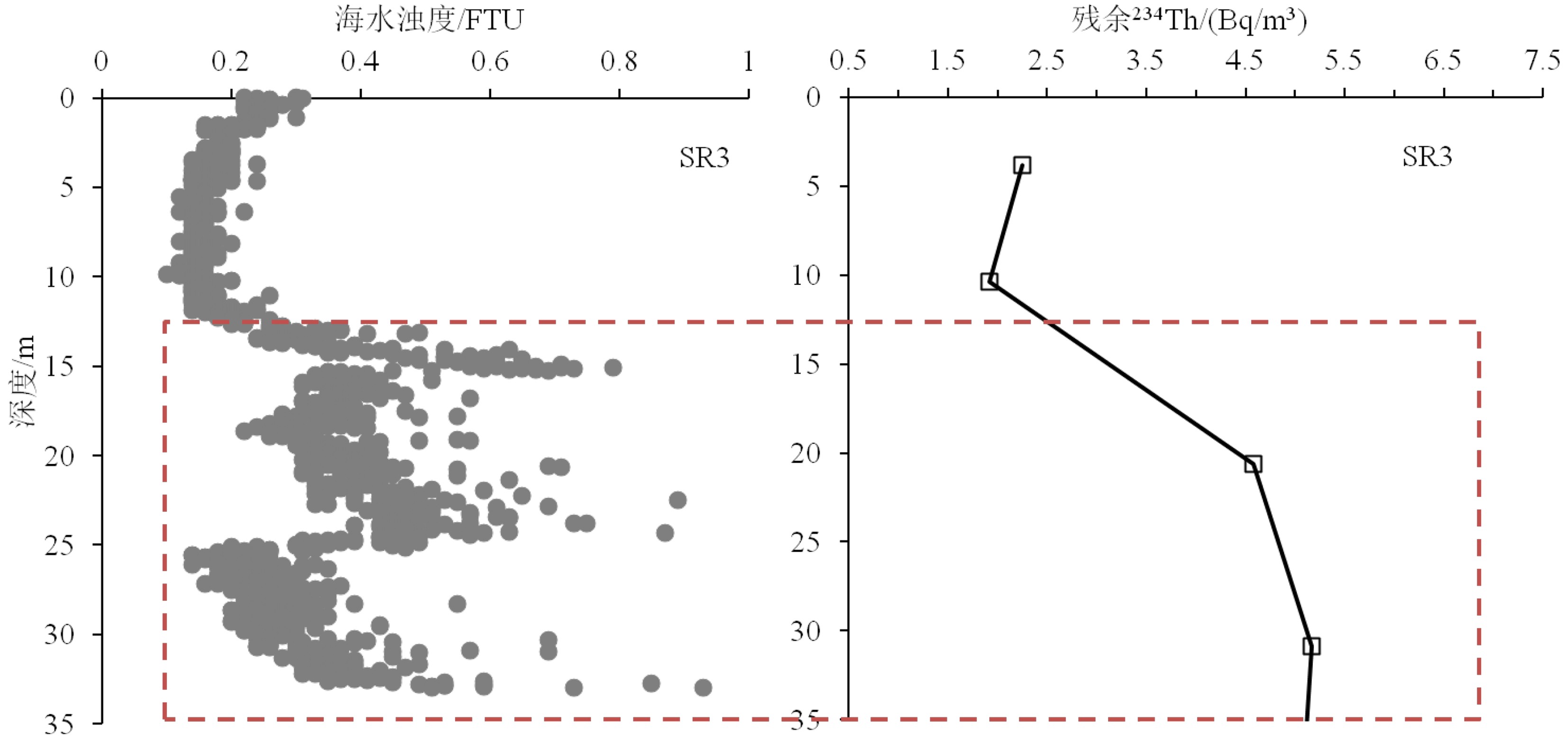
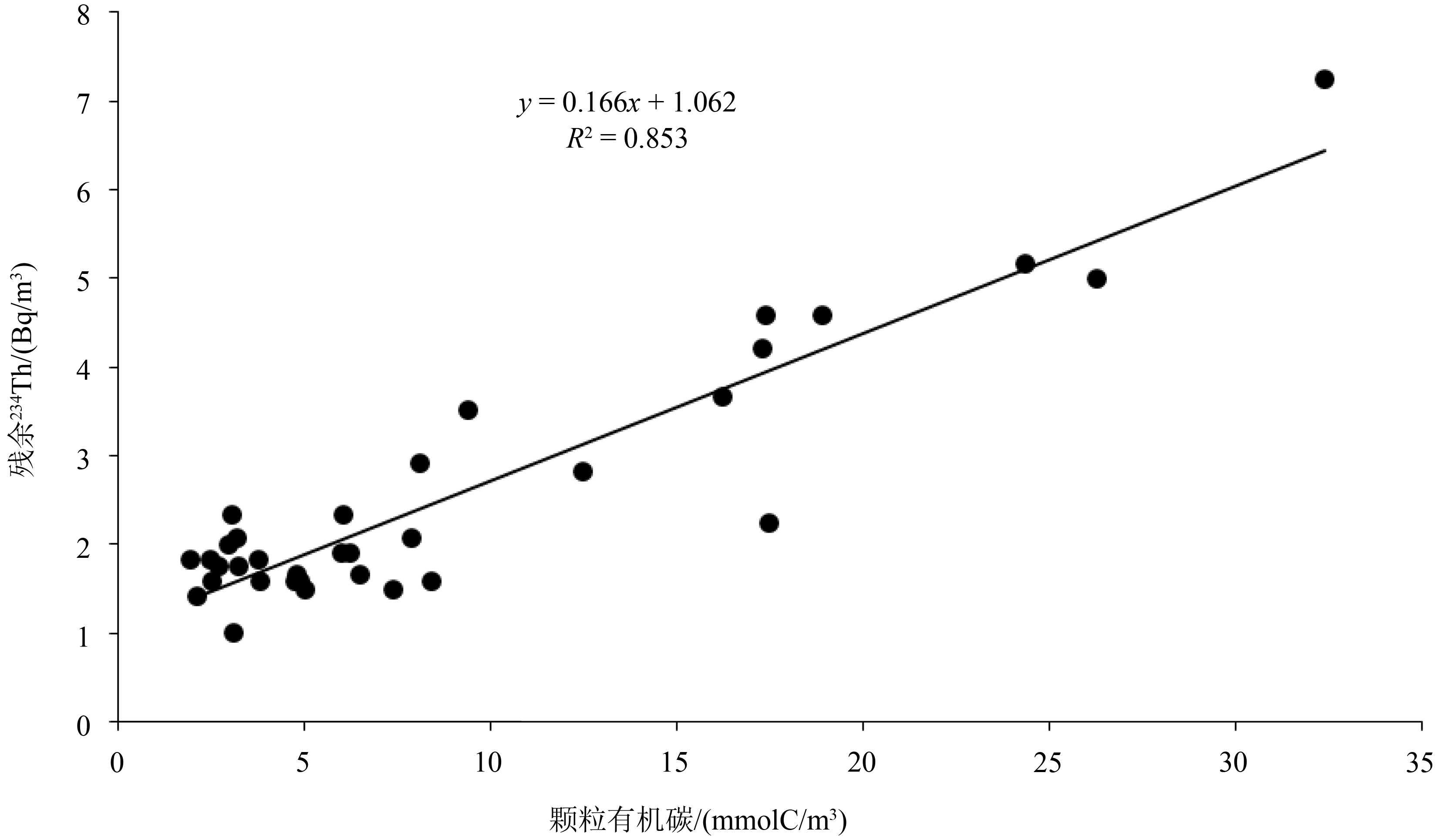
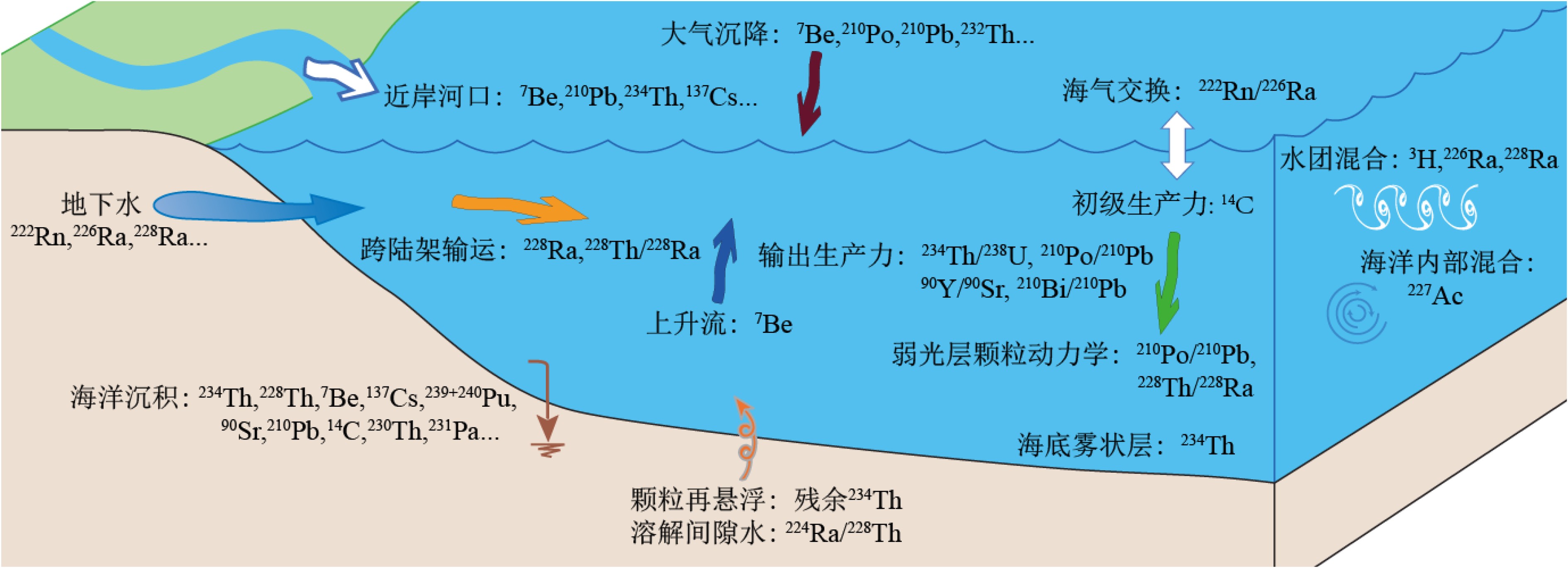
放射性核素示踪技术被广泛应用于海洋学研究。海洋沉积物是许多物质的归宿,海洋沉积过程的研究常关注3个关联问题:物质来源、沉积速率、再悬浮过程。针对这3个问题,在南海9个珊瑚礁区、北部湾涠洲岛海域、珠江口、北冰洋、南大洋等多个海区利用典型的铀系放射性核素(210Pb、226Ra、234Th、238U)示踪技术开展海洋沉积过程研究。物源识别方面,研究发现珊瑚礁区沉积物具有极低的226Ra/238U活度比值(<0.1),显著低于其他海区的226Ra/238U活度比值(0.5~1.0),该独特性质可以应用于珊瑚礁区的沉积物/悬浮物来源示踪,是其他传统元素地球化学方法(Al、Ti、稀土元素)的补充。沉积速率方面,基于210Pb的恒定通量恒定沉积速率(Constant Flux Constant Sedimentation Model, CFCS)模式,定量计算了广西涠洲岛珊瑚礁区沉积柱样的沉积速率(3.7±0.6 mm/a),该结果低于中国多个近岸海域的沉积速率(5~96 mm/a)。沉积物再悬浮方面,提出利用“残余234Th”(不同于过剩234Th)示踪海洋沉积物再悬浮过程,并成功应用于北冰洋、南海、南大洋。
Abstract:Radionuclides are widely used as tracers in oceanography. As the final fate of many substances, marine sediment is mainly concerned from three perspectives: source identification, sedimentation rate, and sediment resuspension. In the present study, uranium-series radionuclides (210Pb, 226Ra, 234Th, and 238U) are applied in several sea regions such as the nine typical coral reefs in the South China Sea, the Weizhou Island, the Pearl River Estuary, the Arctic Ocean, and the Southern Ocean, to study the sediment source, sedimentation rate, and sediment resuspension. Firstly, activity ratio of 226Ra to 238U was found extremely low (<0.1) in the marine sediment of coral reef regions comparing to the activity ratios (0.5~1.0) in other marine sediments and therefore, it could be used as the tool to identify the sources of marine sediments from coral reef regions in addition to other geochemical tools (Al, Ti, and REE). Secondly, the sedimentation rate (3.7±0.6 mm/a) was calculated for a sediment core taking from the coral reefs near the Weizhou Island via excess 210Pb (Constant Flux Constant Sedimentation Model, CFCS model in brief) which was lower than most figures (5 mm/a~96 mm/a) in other coastal areas of China. Finally, residual β activity of particulate 234Th (RAP234) was proposed for tracking marine sediment resuspension. The RAP234 was successfully applied in the Arctic Ocean, South China Sea, and Southern Ocean. In conclusion, the successful applications of these radioactive tracers have provided potential tools used for tracing marine sedimentary processes in addition to the ongoing toolbox.
-
Key words:
- radionuclides /
- sediment /
- tracer /
- coral reefs /
- residual β activity of particulate 234Th
-

-
[1] 林武辉. 高纬度边缘海海洋生物泵的多同位素示踪研究[D]. 清华大学博士学位论文, 2015: 126.
LIN Wuhui. Marine biological carbon pumps and their tracing using multi-isotope in the high latitude marginal seas[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Tsinghua University, 2015: 126.
[2] 林武辉, 陈立奇, 余雯, 等. 白令海和楚科奇海陆架区的生源物质埋藏通量研究[J]. 极地研究, 2016, 28(2):194-202
LIN Wuhui, CHEN Liqi, YU Wen, et al. Burial fluxes of biogenic materials in the Bering Sea and Chukchi Sea [J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2016, 28(2): 194-202.
[3] Lin W H, Chen L Q, Zeng S, et al. Residual β activity of particulate 234Th as a novel proxy for tracking sediment resuspension in the ocean [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 27069. doi: 10.1038/srep27069
[4] 黄奕普, 陈敏. 海洋同位素示踪技术研究进展[J]. 厦门大学学报: 自然科学版, 2001, 40(2):512-523
HUANG Yipu, CHEN Min. Progress in the isotope tracer technique for marine science [J]. Journal of Xiamen University: Natural Science, 2001, 40(2): 512-523.
[5] 毕倩倩, 杜金洲. 海洋环境中放射性分析及其应用[J]. 核化学与放射化学, 2015, 37(4):193-206 doi: 10.7538/hhx.2015.37.04.0193
BI Qianqian, DU Jinzhou. Radio-analysis and its application in the marine environment [J]. Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemistry, 2015, 37(4): 193-206. doi: 10.7538/hhx.2015.37.04.0193
[6] Hong G H, Hamilton T F, Baskaran M, et al. Applications of anthropogenic radionuclides as tracers to investigate marine environmental processes[M]//Baskaran M. Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2012: 367-394.
[7] Rutgers Van Der Loeff M M. Uranium-Thorium decay series in the oceans overview[M]//Steele J H. Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences. San Diego: Academic Press, 2001: 3135-3145.
[8] 刘广山. 同位素海洋学[M]. 郑州: 郑州大学出版社, 2010.
LIU Guangshan. Isotopic Oceanography[M]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University Press, 2010.
[9] Loose B, Kelly R P, Bigdeli A, et al. How well does wind speed predict air‐sea gas transfer in the sea ice zone? A synthesis of radon deficit profiles in the upper water column of the Arctic Ocean [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2017, 122(5): 3696-3714. doi: 10.1002/2016JC012460
[10] Hayes C T, Anderson R F, Fleisher M Q, et al. Quantifying lithogenic inputs to the North Pacific Ocean using the long-lived thorium isotopes [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2013, 383: 16-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2013.09.025
[11] Kadko D, Landing W M, Shelley R U. A novel tracer technique to quantify the atmospheric flux of trace elements to remote ocean regions [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2015, 120(2): 848-858. doi: 10.1002/2014JC010314
[12] Baskaran M. Po-210 and Pb-210 as atmospheric tracers and global atmospheric Pb-210 fallout: a review [J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2011, 102(5): 500-513. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2010.10.007
[13] Du J, Du J Z, Baskaran M, et al. Temporal variations of atmospheric depositional fluxes of 7Be and 210Pb over 8?years (2006-2013) at Shanghai, China, and synthesis of global fallout data [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2015, 120(9): 4323-4339. doi: 10.1002/2014JD022807
[14] Regaudie-de-Gioux A, Lasternas S, Agustí S, et al. Comparing marine primary production estimates through different methods and development of conversion equations [J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2014, 1: 19.
[15] Yu W, He J, Li Y, et al. Particulate organic carbon export fluxes and validation of steady state model of 234Th export in the Chukchi Sea [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2012, 81-84: 63-71. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2012.03.003
[16] He J H, Yu W, Lin W H, et al. Particulate organic carbon export fluxes on Chukchi Shelf, western Arctic Ocean, derived from 210Po/210Pb disequilibrium [J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2015, 33(3): 741-747. doi: 10.1007/s00343-015-3357-x
[17] Lin W H, Ma H, Chen L Q, et al. Decay/ingrowth uncertainty correction of 210Po/210Pb in seawater [J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2014, 137: 22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2014.06.005
[18] Cai P H, Zhao D C, Wang L, et al. Role of particle stock and phytoplankton community structure in regulating particulate organic carbon export in a large marginal sea [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2015, 120(3): 2063-2095. doi: 10.1002/2014JC010432
[19] Kadko D, Johns W. Inferring upwelling rates in the equatorial Atlantic using 7Be measurements in the upper ocean [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2011, 58(6): 647-657. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2011.03.004
[20] Geibert W, Rutgers Van Der Loeff M M, Hanfland C, et al. Actinium-227 as a deep-sea tracer: sources, distribution and applications [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 198(1-2): 147-165. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00512-5
[21] Ma H Y, Yang W F, Zhang L H, et al. Utilizing 210Po deficit to constrain particle dynamics in mesopelagic water, western South China Sea [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2017, 18(4): 1594-1607. doi: 10.1002/2017GC006899
[22] Rutgers Van Der Loeff M, Meyer R, Rudels B, et al. Resuspension and particle transport in the benthic nepheloid layer in and near Fram Strait in relation to faunal abundances and 234Th depletion [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2002, 49(11): 1941-1958. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0637(02)00113-9
[23] Cai P H, Shi X M, Moore W S, et al. 224Ra: 228Th disequilibrium in coastal sediments: Implications for solute transfer across the sediment–water interface [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 125: 68-84. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2013.09.029
[24] Du J Z, Zhang J, Baskaran M. Applications of short-lived radionuclides (7Be, 210Pb, 210Po, 137Cs and 234Th) to trace the sources, transport pathways and deposition of particles/sediments in rivers, estuaries and coasts[M]//Baskaran M. Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2012: 305-329.
[25] Huang D K, Du J Z, Moore W S, et al. Particle dynamics of the Changjiang Estuary and adjacent coastal region determined by natural particle-reactive radionuclides (7Be, 210Pb, and 234Th) [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2013, 118(4): 1736-1748. doi: 10.1002/jgrc.20148
[26] Wang J L, Du J Z, Baskaran M, et al. Mobile mud dynamics in the East China Sea elucidated using 210Pb, 137Cs, 7Be, and 234Th as tracers [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2016, 121(1): 224-239. doi: 10.1002/2015JC011300
[27] Moore W S. The effect of submarine groundwater discharge on the ocean [J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2010, 2: 59-88. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-120308-081019
[28] Wang G Z, Wang Z Y, Zhai W D, et al. Net subterranean estuarine export fluxes of dissolved inorganic C, N, P, Si, and total alkalinity into the Jiulong River estuary, China [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 149: 103-114. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.11.001
[29] Rutgers Van Der Loeff M, Cai P, Stimac I, et al. Shelf-basin exchange times of Arctic surface waters estimated from 228Th/228Ra disequilibrium [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2012, 117(C3): C03024.
[30] Charette M A, Breier C F, Henderson P B, et al. Radium-based estimates of cesium isotope transport and total direct ocean discharges from the Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant accident [J]. Biogeosciences, 2013, 10(3): 2159-2167. doi: 10.5194/bg-10-2159-2013
[31] Charette M A, Morris P J, Henderson P B, et al. Radium isotope distributions during the US GEOTRACES North Atlantic cruises [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2015, 177: 184-195. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2015.01.001
[32] 杨守业. 一沙一世界——藏于海底的地球环境变迁史[J]. 自然杂志, 2017, 39(5):313-319 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2017.05.001
YANG Shouye. To see a world in a grain of sand: Environment changes recorded in global seafloor [J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2017, 39(5): 313-319. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2017.05.001
[33] Burdige D J. Geochemistry of Marine Sediments[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2006.
[34] Liu Z F, Zhao Y L, Colin C, et al. Source-to-Sink transport processes of fluvial sediments in the South China Sea [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2016, 153: 238-273. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.08.005
[35] Qiao S Q, Shi X F, Wang G Q, et al. Sediment accumulation and budget in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2017, 390: 270-281. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2017.06.004
[36] 林武辉, 余克服, 王英辉, 等. 罕见的地表低辐射水平区域: 珊瑚礁区[J]. 辐射防护, 2018, 38(4):287-292
LIN Wuhui, YU Kefu, WANG Yinghui, et al. Unusual low radiation area on the surface of the earth: coral reefs [J]. Radiation Protection, 2018, 38(4): 287-292.
[37] 林武辉, 余克服, 王英辉, 等. 珊瑚礁区沉积物的极低放射性水平特征与成因[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(21):2173-2183
LIN Wuhui, YU Kefu, WANG Yinghui, et al. Extremely low radioactivity in marine sediment of coral reefs and its mechanism [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(21): 2173-2183.
[38] Liu X M, Lin W H. Natural radioactivity in the beach sand and soil along the coastline of Guangxi Province, China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 135: 446-450. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.07.057
[39] 毛远意, 林静, 黄德坤, 等. 北部湾白龙半岛邻近海域沉积物中放射性核素含量水平[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2018, 37(2):194-202 doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2018.02.006
MAO Yuanyi, LIN Jing, HUANG Dekun, et al. Radionuclides in the surface sediments along the coast of Bailong Peninsula in Beibu Gulf [J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2018, 37(2): 194-202. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2018.02.006
[40] 杜金秋, 关道明, 姚子伟, 等. 大连近海沉积物中放射性核素分布及环境指示[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(5):1889-1895 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.05.036
DU Jinqiu, GUAN Daoming, YAO Ziwei, et al. Distribution and environmental significances of radionuclides in sediments of Dalian coastal area [J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(5): 1889-1895. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.05.036
[41] Sanchez-Cabeza J A, Ruiz-Fernández A C. 210Pb sediment radiochronology: An integrated formulation and classification of dating models [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2012, 82: 183-200. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2010.12.024
[42] Aller R C, Cochran J K. 234Th/238U disequilibrium in near-shore sediment: particle reworking and diagenetic time scales [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1976, 29(1): 37-50. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(76)90024-8
[43] Corbett D R, Mckee B, Duncan D. An evaluation of mobile mud dynamics in the Mississippi River deltaic region [J]. Marine Geology, 2004, 209(1-4): 91-112. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2004.05.028
[44] Moberg F, Folke C. Ecological goods and services of coral reef ecosystems [J]. Ecological Economics, 1999, 29(2): 215-233. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8009(99)00009-9
[45] Hughes T P, Barnes M L, Bellwood D R, et al. Coral reefs in the Anthropocene [J]. Nature, 2017, 546(7656): 82-90. doi: 10.1038/nature22901
[46] McCulloch M, Fallon S, Wyndham T, et al. Coral record of increased sediment flux to the inner Great Barrier Reef since European settlement [J]. Nature, 2003, 421(6924): 727-730. doi: 10.1038/nature01361
[47] Jones R, Bessell-Browne P, Fisher R, et al. Assessing the impacts of sediments from dredging on corals [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2016, 102(1): 9-29. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.10.049
[48] Wang J L, Du J Z, Bi Q Q. Natural radioactivity assessment of surface sediments in the Yangtze Estuary [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 114(1): 602-608. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.09.040
[49] Huang D K, Du J Z, Deng B, et al. Distribution patterns of particle-reactive radionuclides in sediments off eastern Hainan Island, China: implications for source and transport pathways [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2013, 57: 10-17. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2012.04.019
[50] Wang Q D, Song J M, Li X G, et al. Environmental radionuclides in a coastal wetland of the Southern Laizhou Bay, China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 97(1-2): 506-511. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.05.035
[51] Zhou P, Li D M, Li H T, et al. Distribution of radionuclides in a marine sediment core off the waterspout of the nuclear power plants in Daya Bay, northeastern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2015, 145: 102-112. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2015.03.018
[52] Yu K N, Guan Z J, Stokes M J, et al. Natural and artificial radionuclides in seabed sediments of Hong Kong [J]. The International Journal of Radiation Applications and Instrumentation. Part E: Nuclear Geophysics, 1994, 8(1): 45-48.
[53] 赵峰, 吴梅桂, 周鹏, 等. 黄茅海—广海湾及其邻近海域表层沉积物中γ放射性核素含量水平[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(4):77-82 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.04.011
ZHAO Feng, WU Meigui, ZHOU Peng, et al. Radionuclides in surface sediments from the Huangmaohai Estuary-Guanghai Bay and its adjacent sea area of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(4): 77-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.04.011
[54] 林武辉, 陈立奇, 马豪, 等. 日本福岛核事故后的海洋放射性监测进展[J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(1):269-276
LIN Wuhui, CHEN Liqi, MA Hao, et al. Review on monitoring marine radioactivity since the Fukushima Nuclear Accident [J]. China Environmental Science, 2015, 35(1): 269-276.
[55] Baskaran M. Dating of biogenic and inorganic carbonates using 210Pb-226Ra disequilibrium method: a review[M]//Baskaran M. Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2012: 789-809.
[56] Saha N, Webb G E, Zhao J X. Coral skeletal geochemistry as a monitor of inshore water quality [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 566-567: 652-684. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.05.066
[57] Hart D E, Kench P S. Carbonate production of an emergent reef platform, Warraber Island, Torres Strait, Australia [J]. Coral Reefs, 2007, 26(1): 53-68. doi: 10.1007/s00338-006-0168-8
[58] Łącka M, Pawłowska J, Zajączkowski M. New methods in the reconstruction of Arctic marine palaeoenvironments[M]//Zielinski T, Weslawski M, Kuliński K. Impact of Climate Changes on Marine Environments. Cham: Springer, 2015: 127-148.
[59] Oguri K, Harada N, Tadai O. Excess 210Pb and 137Cs concentrations, mass accumulation rates, and sedimentary processes on the Bering Sea continental shelf [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2012, 61-64: 193-204. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2011.03.007
[60] Kuzyk Z Z A, Gobeil C, Macdonald R W. 210Pb and 137Cs in margin sediments of the Arctic Ocean: controls on boundary scavenging [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2013, 27(2): 422-439. doi: 10.1002/gbc.20041
[61] 曾文义, 程汉良, 曾宪章, 等. 厦门港的淤积现状及防淤建议[J]. 海洋通报, 1991, 10(1):45-49
ZENG Wenyi, CHENG Hanliang, ZENG Xianzhang, et al. Situation of modern sedimentation and propositions of preventing siltation in Xiamen Harbour [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1991, 10(1): 45-49.
[62] 刘广山. 210Pb过剩法与中国海的现代沉积物测年[M]//刘广山. 海洋放射年代学. 厦门: 厦门大学出版社, 2016: 106-136.
LIU Guangshan. 210Pb excess method and modern sediment dating in the China Sea[M]//LIU Guangshan. Marine Radiological Chronology. Xiamen: Xiamen University Press, 2016: 106-136.]
[63] 潘少明, 王雪瑜, SMITH J N. 海南岛洋浦港现代沉积速率[J]. 沉积学报, 1994, 12(2):86-93
PAN Shaoming, WANG Xueyu, SMITH J N. Recent sedimentation rates in Yangpu Harbour on Hainan Island [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1994, 12(2): 86-93.
[64] 潘少明, 施晓东, SMITH J N. 海南岛三亚港现代沉积速率的研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1995, 26(2):132-137 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1995.02.003
PAN Shaoming, SHI Xiaodong, SMITH J N. Determination of recent sedimentation rates in Sanya Harbour, Hainan Island [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1995, 26(2): 132-137. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1995.02.003
[65] 刘志勇, 潘少明, 程功弼, 等. 珠江口沉积物210Pb分布特征及环境意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2010, 28(1):166-175
LIU Zhiyong, PAN Shaoming, CHENG Gongbi, et al. 210Pb characteristic in the sediment cores from the Pearl River Mouth and its environmental implication [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2010, 28(1): 166-175.
[66] Li P Y, Wang Y H, Huang W Y, et al. Sixty-Year sedimentary record of DDTs, HCHs, CHLs and Endosulfan from emerging development gulfs: a case study in the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea [J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2014, 92(1): 23-29. doi: 10.1007/s00128-013-1130-4
[67] McCave I N. Local and global aspects of the bottom nepheloid layers in the world ocean [J]. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 1986, 20(2-3): 167-181. doi: 10.1016/0077-7579(86)90040-2
[68] Boudreau B P. A one-dimensional model for bed-boundary layer particle exchange [J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 1997, 11(3-4): 279-303. doi: 10.1016/S0924-7963(96)00127-3
[69] Middag R, Van Hulten M M P, Van Aken H M, et al. Dissolved aluminium in the ocean conveyor of the West Atlantic Ocean: effects of the biological cycle, scavenging, sediment resuspension and hydrography [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2015, 177: 69-86. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2015.02.015
[70] Hall I R, Schmidt S, McCave I N, et al. Particulate matter distribution and 234Th/238U disequilibrium along the Northern Iberian Margin: implications for particulate organic carbon export [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2000, 47(4): 557-582. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0637(99)00065-5
[71] Rutgers Van Der Loeff M M, Boudreau B P. The effect of resuspension on chemical exchanges at the sediment-water interface in the deep sea — A modelling and natural radiotracer approach [J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 1997, 11(3-4): 305-342. doi: 10.1016/S0924-7963(96)00128-5
[72] Turley C. Bacteria in the cold deep-sea benthic boundary layer and sediment-water interface of the NE Atlantic [J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2000, 33(2): 89-99.
[73] 汪卫国, 方建勇, 陈莉莉, 等. 楚科奇海悬浮体含量分布及其颗粒组分特征[J]. 极地研究, 2014, 26(1):79-88
WANG Weiguo, FANG Jianyong, CHEN Lili, et al. The distribution and composition of suspended particles in the Chukchi Sea [J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2014, 26(1): 79-88.
[74] Woodgate R A, Aagaard K, Weingartner T J. A year in the physical oceanography of the Chukchi Sea: Moored measurements from autumn 1990-1991 [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2005, 52(24-26): 3116-3149. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2005.10.016
[75] White W M. Geochemistry[M]. Chichester, West Sussex Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2013.
-



 下载:
下载: