A comparative study on the Late Quaternary stratigraphic architecture and formation of megadeltas in East and South Asia
-
摘要:
通过整理东亚、南亚典型河口三角洲末次冰消期以来演化历史的研究进展,对比各河口晚第四纪地层结构、沉积体系演替和三角洲开始建造的时间,分析其沉积历史的主要控制因素。结果显示,末次冰消期以来各河口具相似的地层结构和演变过程,即早全新世下切古河谷充填和河口湾发育,中—晚全新世三角洲建造,该过程主要受海平面变化的控制。但是各河口地层结构和沉积历史也存在差异,其中以三角洲开始建造的时间差别最为明显。对比发现这种差异与流域地貌、基岩以及河口沉积盆地的差别有关。流程短、流域基岩易侵蚀的河流,入海泥沙量大,其三角洲开始建造的时间显著早于其他河流,其中以恒河三角洲最为典型。另外,以珠江三角洲为典型,其半封闭、基底浅的河口沉积盆地特征,也有助于中全新世湾顶三角洲的建造。
Abstract:Based on the researches on the evolution of megadeltas in East and South Asia since last deglaciation, we carried out a comparative study on the Late Quaternary stratigraphic architecture, sedimentary systems and the initiation time of megadeltas at large river mouths of the region. Major control factors on deltaic evolution are revealed and discussed. Our data suggests that all the river mouths in the region seem having experienced similar evolutionary history, including the infilling of incised palaeo-valleys and estuaries in Early Holocene, and deltaic progradation in Middle to Late Holocene, controlled by the sea-level change. However, there are some differences in the stratigraphic architecture and sedimentary history from river to river. The most remarkable difference is the time of delta initiation, which is related to the geomorphology and geology of the drainage basin and the sedimentary basin at river mouths. Those rivers having short flow paths and erosive bedrocks in the drainage basin, such as the Ganges-Brahmaputra, usually produce a huge amount of sediment load. As a result, the time of the delta initiation was obviously earlier than other rivers. The Pearl River delta is another example. It has a semi-closed shallow sedimentary basin which is beneficial to the formation of delta in the Middle Holocene.
-
Key words:
- sedimentary system /
- delta initiation /
- sea level /
- sediment load /
- sedimentary basin
-

-
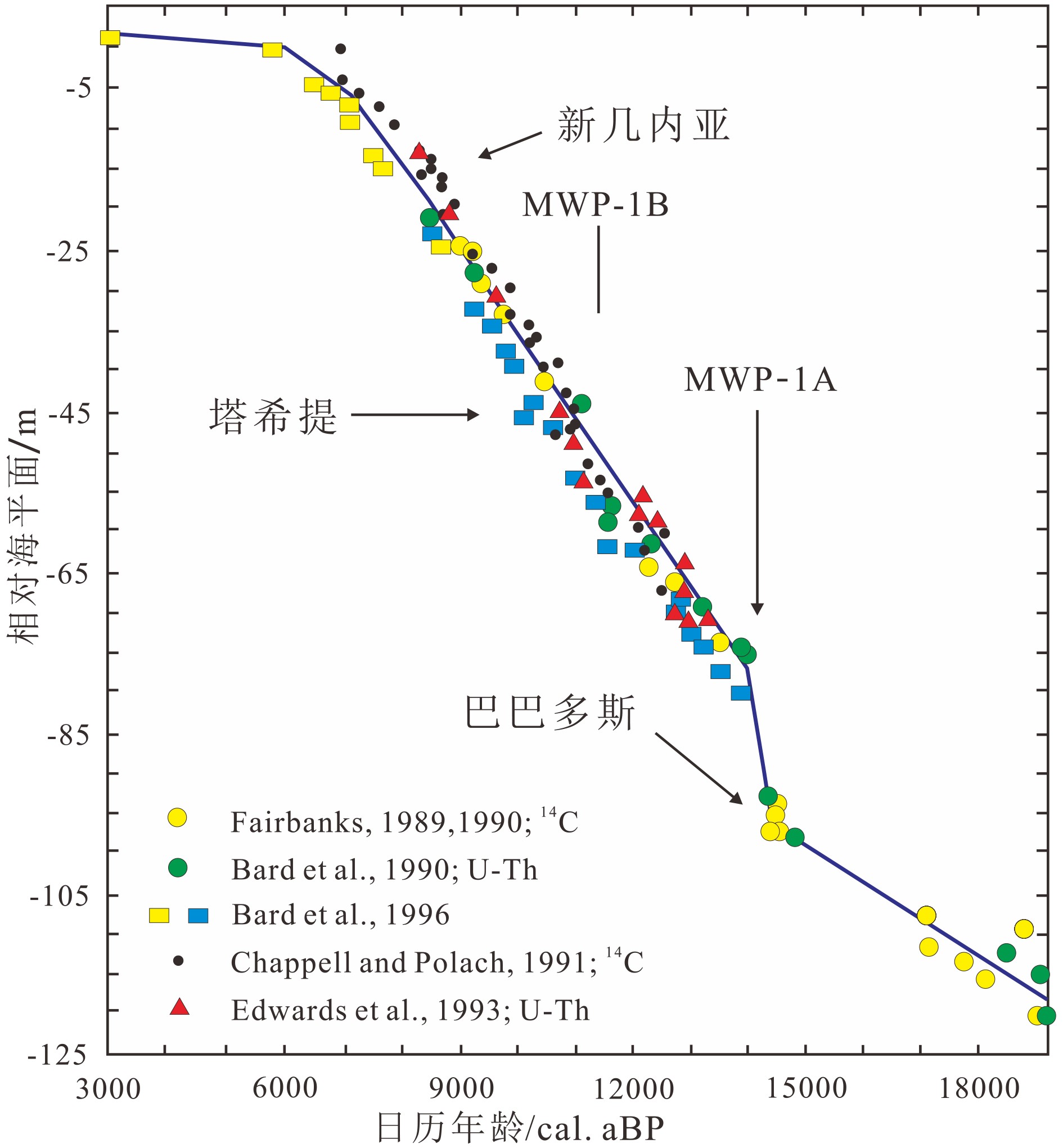
图 1 珊瑚礁记录的末次盛冰期以来全球海平面波动[15]
Figure 1.
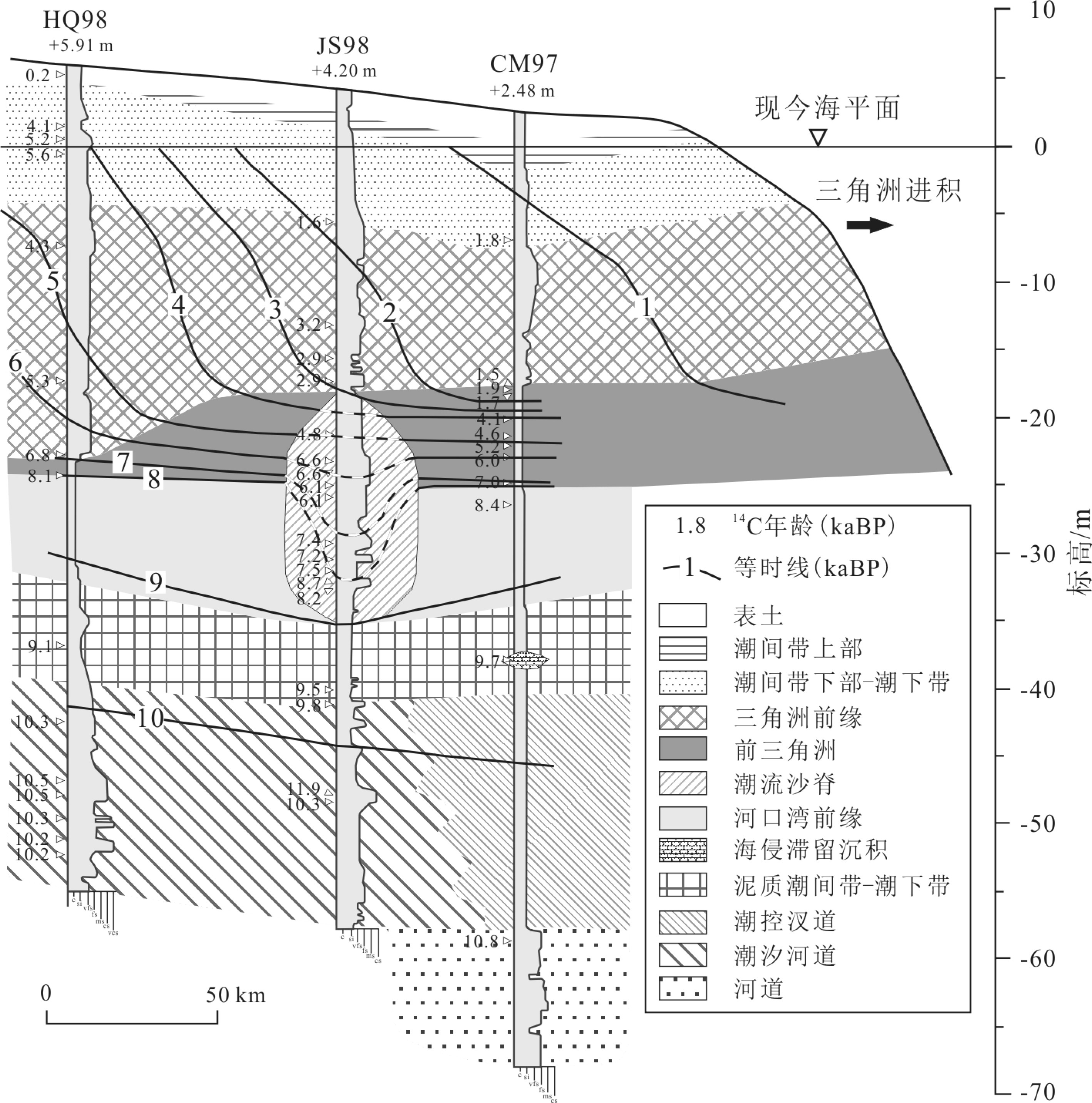
图 2 长江三角洲纵向地层剖面[32] (图中年龄未经日历校正)
Figure 2.
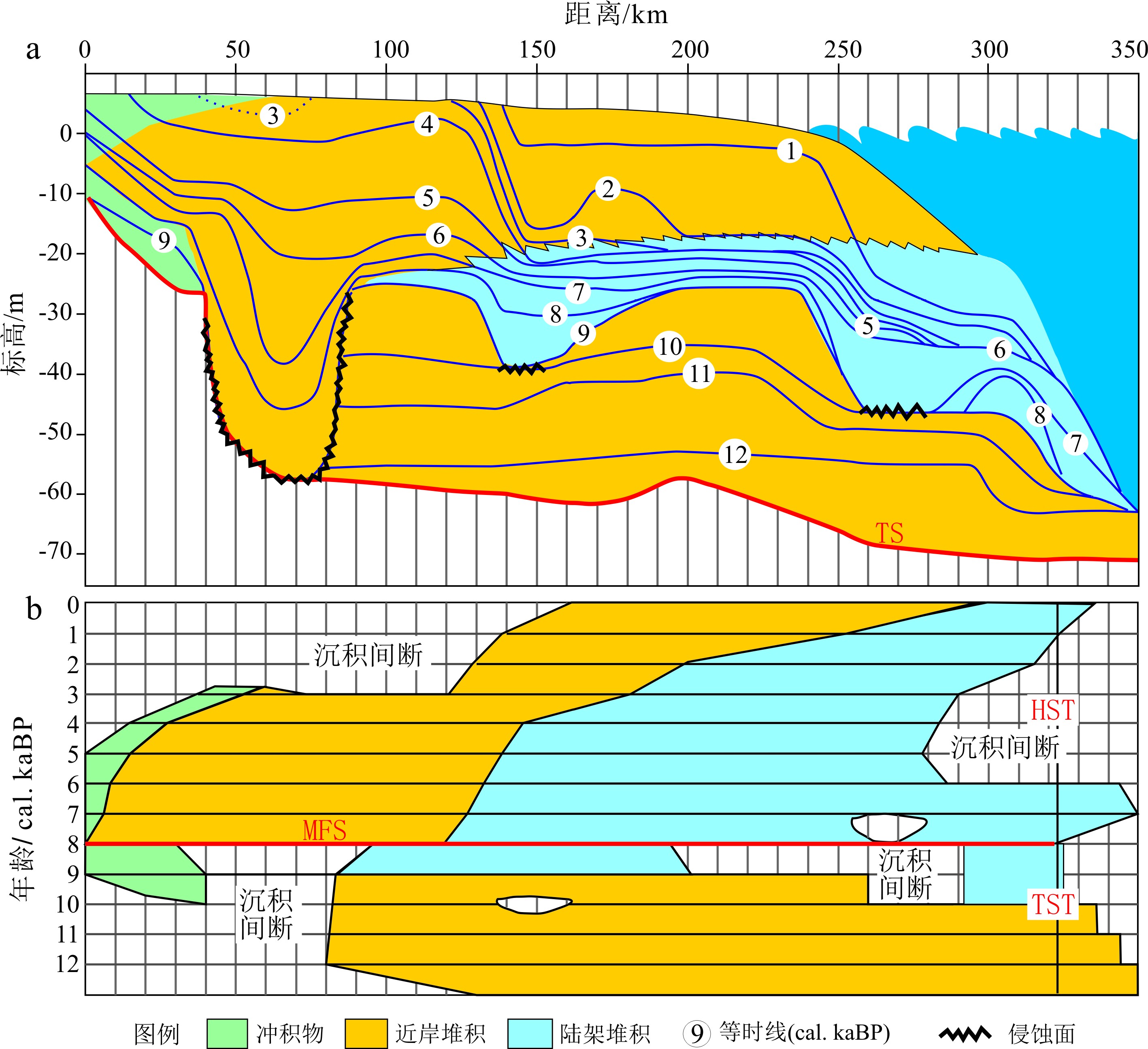
图 3 长江三角洲全新世层序地层结构[46]
Figure 3.
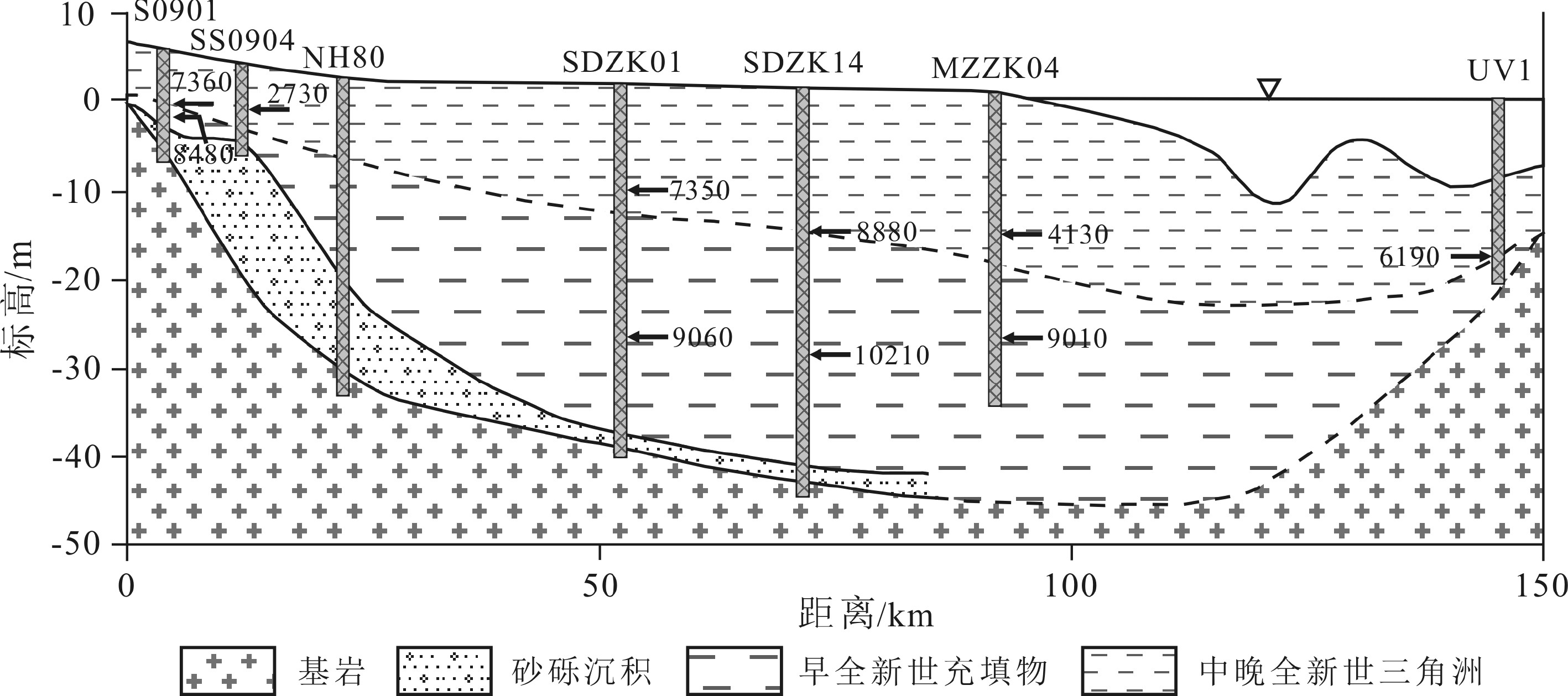
图 4 珠江三角洲典型纵向地层剖面[13]
Figure 4.
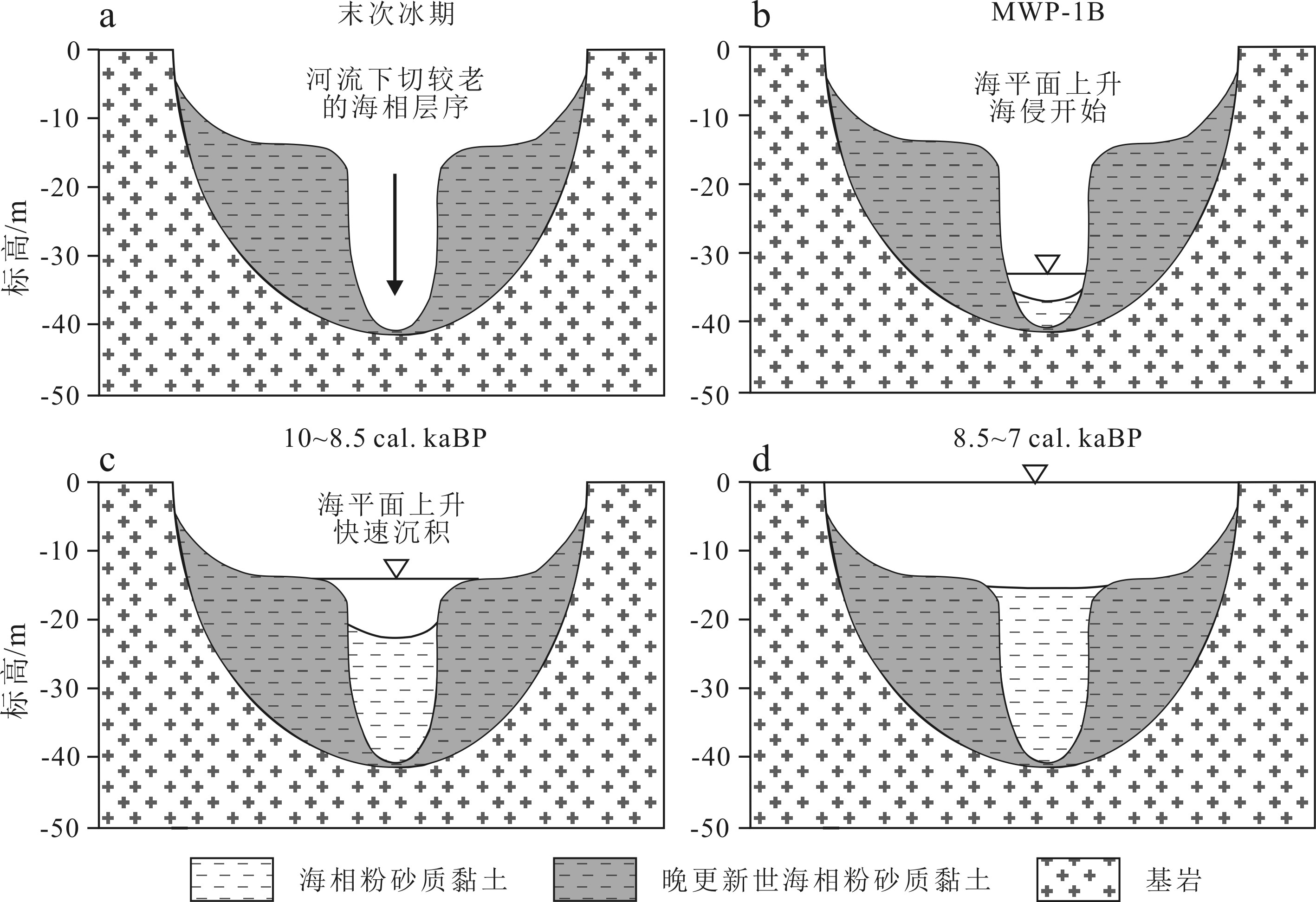
图 5 珠江河口晚第四纪—早全新世沉积环境演化的主要阶段[13]
Figure 5.
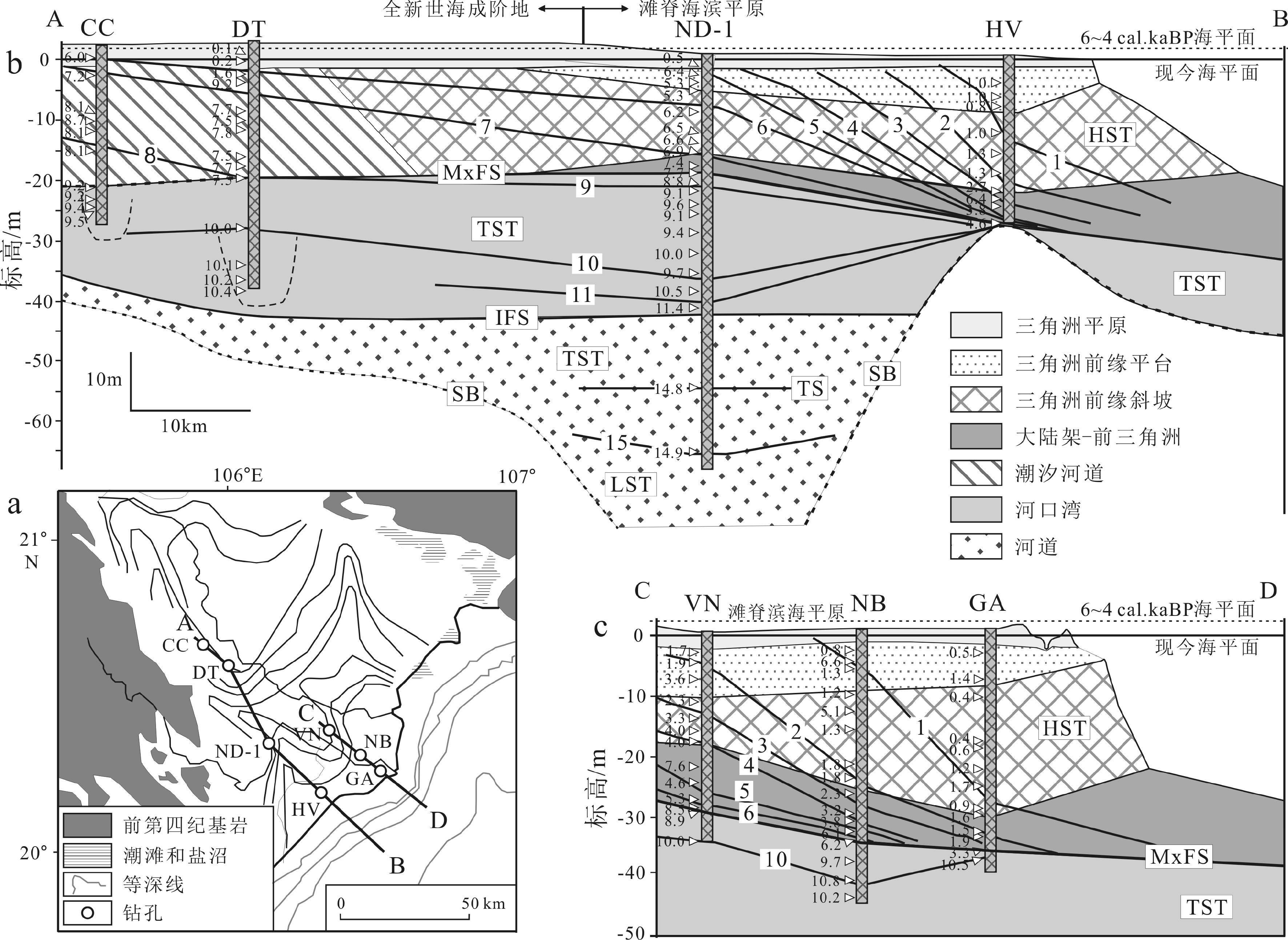
图 6 红河三角洲冰后期沉积物A-B和C-D纵剖面层序地层解释[10]
Figure 6.
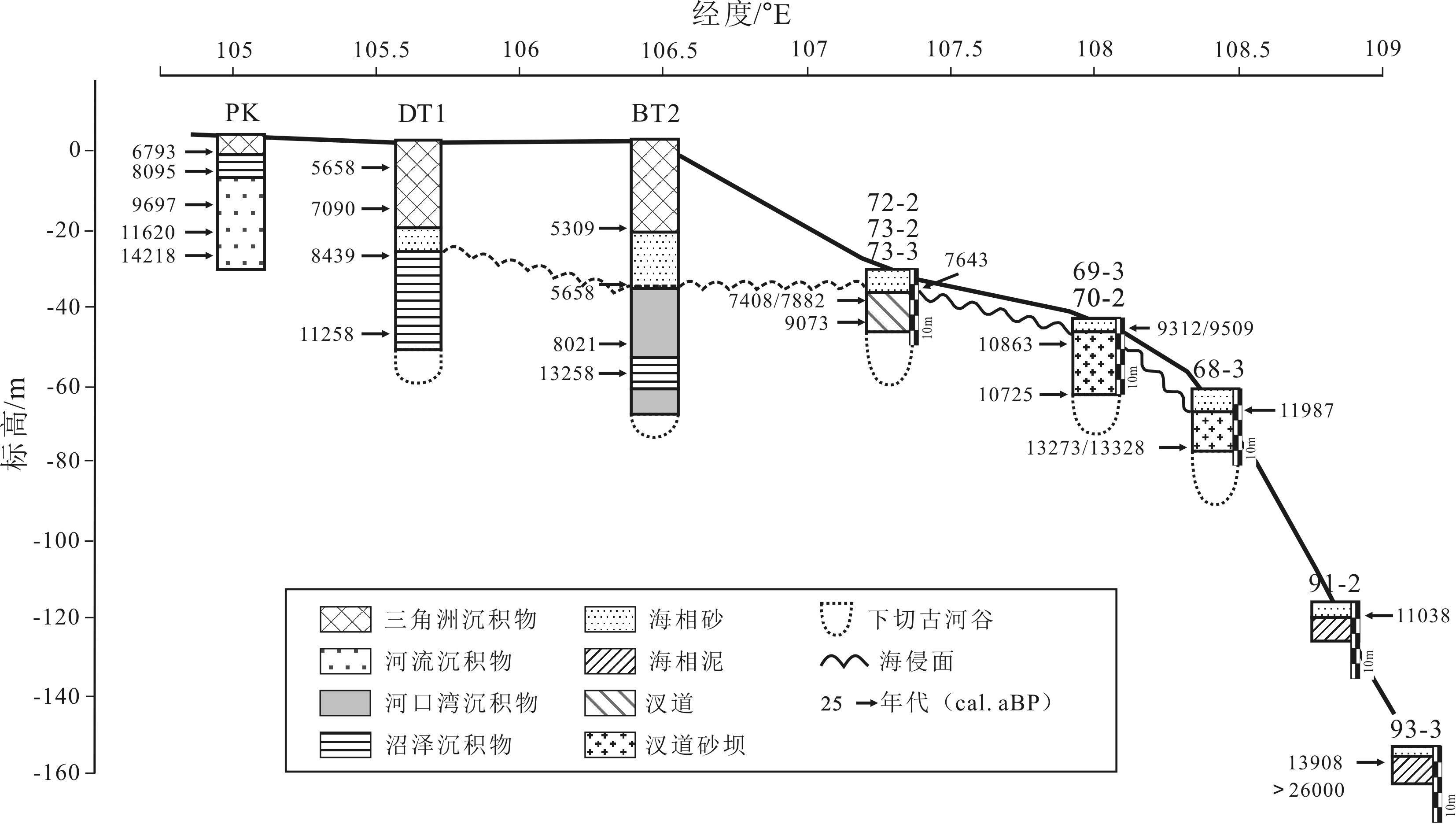
图 7 湄公河三角洲典型纵向地层剖面[39]
Figure 7.
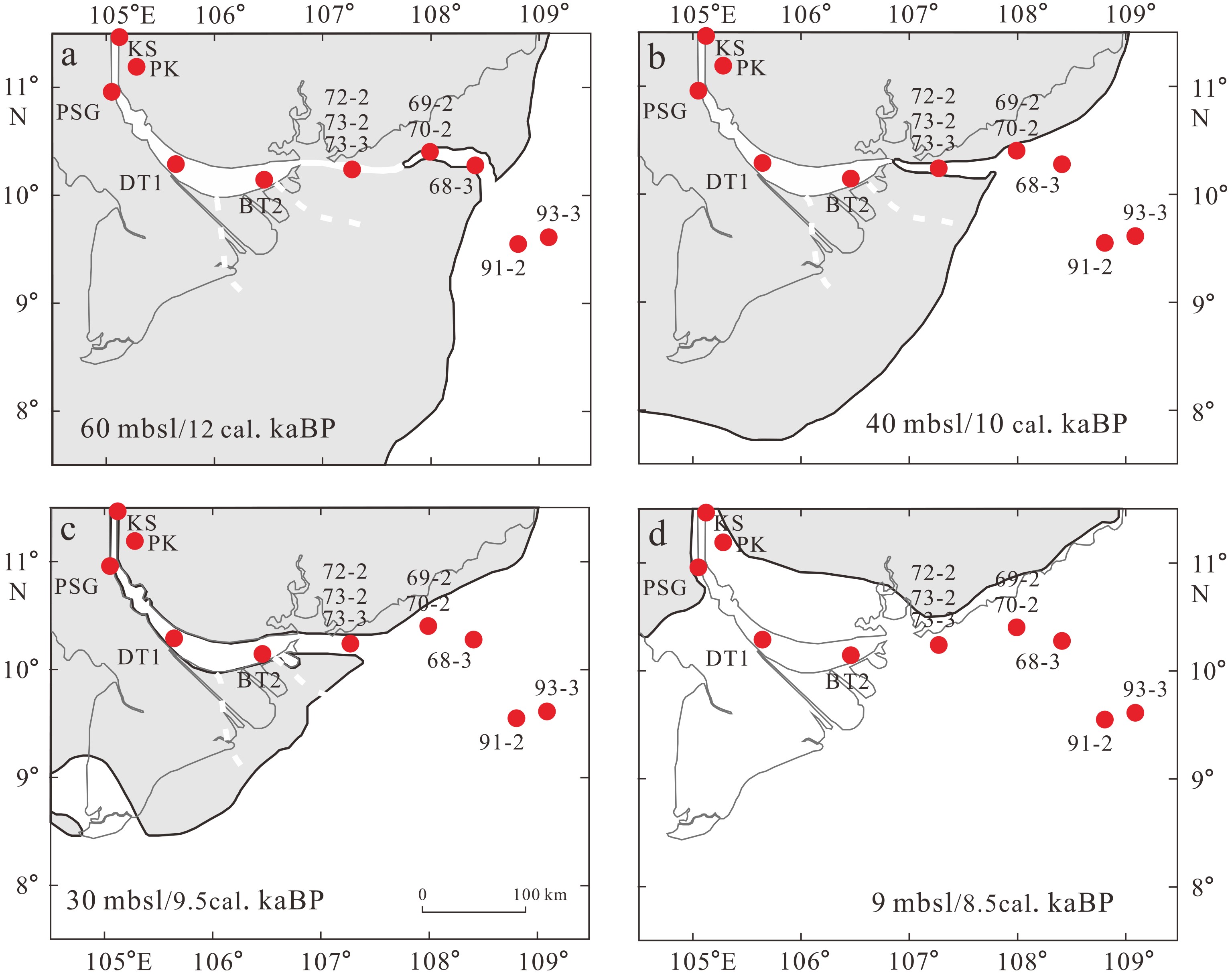
图 8 湄公河三角洲和越南东南大陆架在12,10,9.5,8.5 cal.kaBP时的古地理解释[39]
Figure 8.
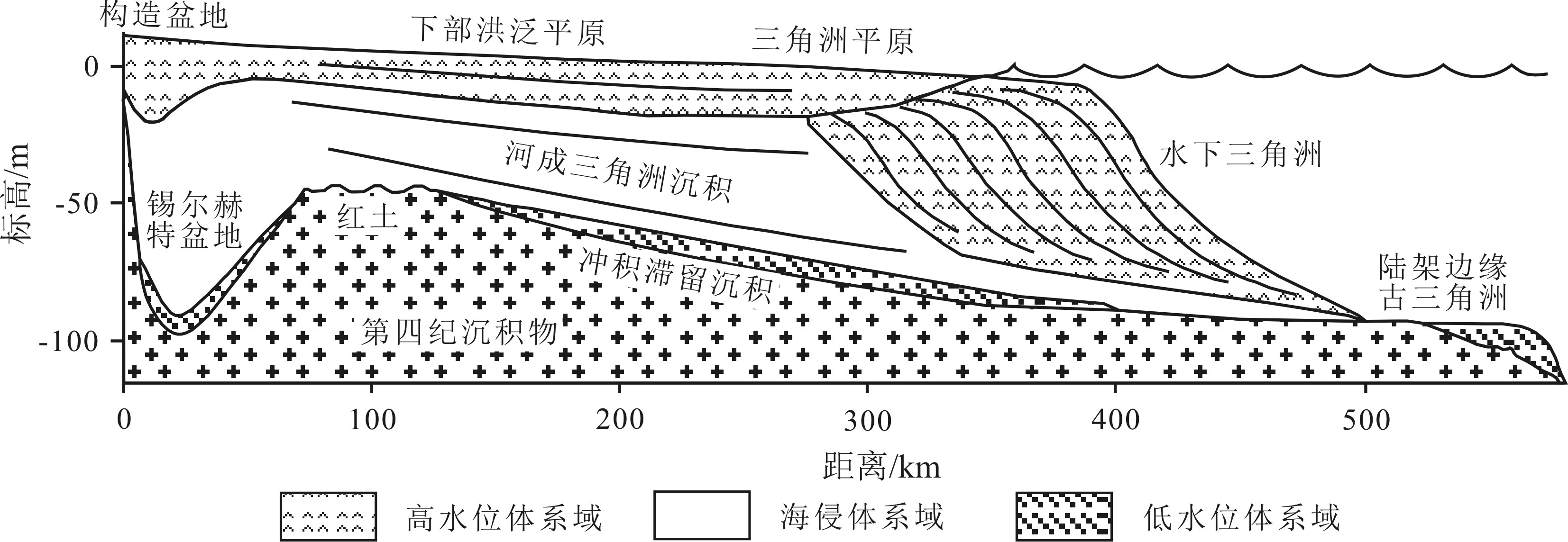
图 9 恒河-布拉马普特拉河三角洲晚第四纪层序地层[14]
Figure 9.
表 1 五大三角洲开始建造时间对比
Table 1. A comparison of delta initiation time in South and East Asian
表 2 东、南亚五大河流建坝前水文泥沙特征
Table 2. Characteristics of Hydrology and sediment load before dam construction for Eeast and South Asia rivers
-
[1] Gilbert G. The topographic features of lake shores [J]. Nature, 1886, 34(873): 269-270. doi: 10.1038/034269a0
[2] Barrell J. Criteria for the recognition of ancient delta deposits [J]. GSA Bulletin, 1912, 23(1): 377-446. doi: 10.1130/GSAB-23-377
[3] Scruton P C. Delta building and the deltaic sequence[M]//Shepard F P, Phleger F B, Van Andel T H. Recent Sediments Northwest Gulf of Mexico. Tulsa: American Association of Petroleum Geologists Symposium Volume, 1960: 82-102.
[4] Coleman J M, Wright L D. Modern river delta: vari-ability of processes and sand bodies[M]//Broussard M L. Deltas: Models for Exploration. Houston, TX: Houston Geological Society, 1975: 99-149.
[5] Galloway W E. Process framework for describing the morphologic and stratigraphic evolution of deltaic depositional systems[M]//Broussard M L. Deltas: Models for Exploration. Houston, TX: Houston Geological Society, 1975: 87-98.
[6] Stanley D J, Warne A G. Worldwide initiation of Holocene marine deltas by deceleration of sea-level rise [J]. Science, 1994, 265(5169): 228-231. doi: 10.1126/science.265.5169.228
[7] Hori K, Tanabe S, Saito Y, et al. Delta initiation and Holocene sea-level change: example from the Song Hong (Red River) delta, Vietnam [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2004, 164(3-4): 237-249. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2003.10.008
[8] Hori K, Saito Y, Zhao Q H, et al. Evolution of the coastal depositional systems of the Changjiang (Yangtze) River in response to late Pleistocene-Holocene sea-level changes [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2002, 72(6): 884-897. doi: 10.1306/052002720884
[9] Song B, Li Z, Saito Y, et al. Initiation of the Changjiang (Yangtze) delta and its response to the mid-Holocene sea level change [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2013, 388: 81-97. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.07.026
[10] Tanabe S, Saito Y, Vu Q L, et al. Holocene evolution of the Song Hong (Red River) delta system, northern Vietnam [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2006, 187(1-2): 29-61. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2005.12.004
[11] Ta T K O, Nguyen V L, Tateishi M, et al. Holocene delta evolution and depositional models of the Mekong River Delta, southern Vietnam[M]//Giosan L, Bhattacharya J P. River Deltas—Concepts, Models, and Examples. Tulsa: SEPM Society for Sedimentary Geology, 2005: 453-466.
[12] Li Y X, Törnqvist T E, Nevitt J M, et al. Synchronizing a sea-level jump, final Lake Agassiz drainage, and abrupt cooling 8200 years ago [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2012, 315-316: 41-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2011.05.034
[13] Zong Y Q, Huang K Y, Yu F L, et al. The role of sea-level rise, monsoonal discharge and the Palaeo-landscape in the early Holocene evolution of the Pearl River delta, southern China [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2012, 54: 77-88. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.01.002
[14] Goodbred Jr S L, Kuehl S A. The significance of large sediment supply, active tectonism, and eustasy on margin sequence development: late Quaternary stratigraphy and evolution of the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2000, 133(3-4): 227-248. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(00)00041-5
[15] Bard E, Hamelin B, Arnold M, et al. Deglacial sea-level record from Tahiti corals and the timing of global meltwater discharge [J]. Nature, 1996, 382(6588): 241-244. doi: 10.1038/382241a0
[16] Hanebuth T, Stattegger K, Grootes P M. Rapid flooding of the sunda shelf: a late-glacial sea-level record [J]. Science, 2000, 288(5468): 1033-1035. doi: 10.1126/science.288.5468.1033
[17] Shackleton N J. The 100, 000-year ice-age cycle identified and found to lag temperature, carbon dioxide, and orbital eccentricity [J]. Science, 2000, 289(5486): 1897-1902. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5486.1897
[18] Yokoyama Y, Lambeck K, De Deckker P, et al. Timing of the Last Glacial Maximum from observed sea-level minima [J]. Nature, 2000, 406(6797): 713-716. doi: 10.1038/35021035
[19] Siddall M, Rohling E J, Almogi-Labin A, et al. Sea-level fluctuations during the last glacial cycle [J]. Nature, 2003, 423(6942): 853-858. doi: 10.1038/nature01690
[20] Bassett S E, Milne G A, Mitrovica J X, et al. Ice sheet and solid earth influences on far-field sea-level histories [J]. Science, 2005, 309(5736): 925-928. doi: 10.1126/science.1111575
[21] Peltier W R, Fairbanks R G. Global glacial ice volume and Last Glacial Maximum duration from an extended Barbados sea level record [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2006, 25(23-24): 3322-3337. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2006.04.010
[22] Bard E, Hamelin B, Fairbanks R G. U-Th ages obtained by mass spectrometry in corals from Barbados: sea level during the past 130, 00 years [J]. Nature, 1990, 346(6283): 456-458. doi: 10.1038/346456a0
[23] Hori K, Saito Y. An early Holocene sea-level jump and delta initiation [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34(18): L18401. doi: 10.1029/2007GL031029
[24] Reed D J. Sea-level rise and coastal marsh sustainability: geological and ecological factors in the Mississippi delta plain [J]. Geomorphology, 2002, 48(1-3): 233-243. doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(02)00183-6
[25] 李高聪, 高抒, 高建华. 全新世以来亚洲七个主要河口三角洲的生长极限[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(1):11-22
LI Gaocong, GAO Shu, GAO Jianhua. Modeling the growth limit of seven major Holocene river deltas in Asia [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(1): 11-22.
[26] Coleman J M. Brahmaputra River: channel processes and sedimentation [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1969, 3(2-3): 129-239. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(69)90010-4
[27] Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al. A high-resolution absolute-dated Late Pleistocene monsoon record from Hulu Cave, China [J]. Science, 2001, 249(5550): 2345-2348.
[28] Fleitmann D, Burns S J, Mudelsee M, et al. Holocene forcing of the Indian monsoon recorded in a stalagmite from southern Oman [J]. Science, 2003, 300(5626): 1737-1739. doi: 10.1126/science.1083130
[29] Yuan D X, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al. Timing, duration, and transitions of the last interglacial Asian monsoon [J]. Science, 2004, 304(5670): 575-578. doi: 10.1126/science.1091220
[30] Li C X, Chen Q Q, Zhang J Q, et al. Stratigraphy and paleoenvironmental changes in the Yangtze delta during the Late Quaternary [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2000, 18(4): 453-469. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00078-4
[31] Li C X, Wang P, Sun H P, et al. Late Quaternary incised-valley fill of the Yangtze delta (China): its stratigraphic framework and evolution [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2002, 152(1-2): 133-158. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(02)00066-0
[32] Hori K, Saito Y, Zhao Q H, et al. Sedimentary facies of the tide-dominated paleo-Changjiang (Yangtze) estuary during the last transgression [J]. Marine Geology, 2001, 177(3-4): 331-351. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(01)00165-7
[33] Wang Z H, Zhuang C C, Saito Y, et al. Early mid-Holocene sea-level change and coastal environmental response on the southern Yangtze delta plain, China: implications for the rise of Neolithic culture [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2012, 35: 51-62. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.01.005
[34] Wang Z H, Zhan Q, Long H Y, et al. Early to mid-Holocene rapid sea-level rise and coastal response on the southern Yangtze delta plain, China [J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2013, 28(7): 659-672. doi: 10.1002/jqs.2662
[35] Zong Y, Huang G, Switzer A D, et al. An evolutionary model for the Holocene formation of the Pearl River delta, China [J]. The Holocene, 2009, 19(1): 129-142. doi: 10.1177/0959683608098957
[36] Tanabe S, Hori K, Saito Y, et al. Sedimentary facies and radiocarbon dates of the Nam Dinh-1 core from the Song Hong (Red River) delta, Vietnam [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2003, 21(5): 503-513. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(02)00082-2
[37] Nguyen V L, Ta T K O, Saito Y. Early Holocene initiation of the Mekong River delta, Vietnam, and the response to Holocene sea-level changes detected from DT1 core analyses [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2010, 230(3-4): 146-155. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2010.07.006
[38] Tamura T, Saito Y, Sieng S, et al. Initiation of the Mekong River delta at 8 ka: evidence from the sedimentary succession in the Cambodian lowland [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2009, 28(3-4): 327-344. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2008.10.010
[39] Tjallingii R, Stattegger K, Wetzel A, et al. Infilling and flooding of the Mekong River incised valley during deglacial sea-level rise [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2010, 29(11-12): 1432-1444. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.02.022
[40] 李国刚, 胡邦琦, 毕建强, 等. 黄河三角洲ZK1孔晚第四纪以来沉积层序演化及其古环境意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2013, 31(6):1050-1058
LI Guogang, HU Bangqi, BI Jianqiang, et al. Stratigraphic evolution of the Huanghe Delta (Bohai Sea) since the Late Quaternary and its Paleoenvironmental implications: evidence from core ZK1 [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(6): 1050-1058.
[41] 成国栋, 薛春汀. 黄河三角洲沉积地质学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997.
CHENG Guodong, XUE Chunting. Sedimentary Geology of the Yellow River Delta[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 1997.
[42] 庄振业, 许卫东, 刘东生, 等. 渤海南部S3孔晚第四纪海相地层的划分及环境演变[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1999, 19(2):27-35
ZHUANG Zhenye, XU Weidong, LIU Dongsheng, et al. Division and environmental evolution of Late Quaternary marine beds of S3 hole in the Bohai Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1999, 19(2): 27-35.
[43] 阎玉忠, 王宏, 李凤林, 等. 渤海湾西岸BQ1孔揭示的沉积环境与海面波动[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25(3):357-382 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.03.006
YAN Yuzhong, WANG Hong, LI Fenglin, et al. Sedimentary environment and sea-level fluctuations revealed by borehole BQ1 on the west coast of the Bohai Bay, China [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006, 25(3): 357-382. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.03.006
[44] Liu J, Saito Y, Wang H, et al. Stratigraphic development during the Late Pleistocene and Holocene offshore of the Yellow River delta, Bohai Sea [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 36(4-5): 318-331. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.06.007
[45] 庞家珍, 司书亨. 黄河河口演变 I. 近代历史变迁[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1979, 10(2):136-141
PANG Jiazhen, SI Shuheng. The estuary changes of Huanghe River I. Changes in modern time [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1979, 10(2): 136-141.
[46] Wang Z H, Saito Y, Zhan Q, et al. Three-dimensional evolution of the Yangtze River mouth, China during the Holocene: impacts of sea level, climate and human activity [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 185: 938-955. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.08.012
[47] Tamura T, Saito Y, Nguyen V L, et al. Origin and evolution of inter distributary delta plains; insights from Mekong River delta [J]. Geology, 2012, 40(4): 303-306. doi: 10.1130/G32717.1
[48] Walker M J C, Berkelhammer M, Björck S, et al. Formal subdivision of the Holocene series/epoch: a discussion paper by a working group of intimate (integration of ice-core, marine and terrestrial records) and the subcommission on quaternary stratigraphy (international commission on stratigraphy) [J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2012, 27(7): 649-659. doi: 10.1002/jqs.2565
[49] Bridge J S. Fluvial facies models: recent developments[M]//Posamentier H W, Walker R. Facies Models Revisited. Tulsa: SEPM, 2006: 85-170.
[50] 王张华, Liu J P, 赵宝成. 全新世长江泥沙堆积的时空分布及通量估算[J]. 古地理学报, 2007, 9(4):419-429 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2007.04.008
WANG Zhanghua, Liu J P, ZHAO Baocheng. Spatial and temporal distribution of Changjiang sediments and estimation of sediment budget during the Holocene [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2007, 9(4): 419-429. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2007.04.008
[51] 陈吉余, 沈焕庭, 恽才兴, 等. 长江河口动力过程和地貌演变[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1988: 205.
CHEN Jiyu, SHEN Huanting, YUN Caixing, et al. Process of Dynamics and Geomorphology of the Changjiang Estuary[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, 1988: 205.
-



 下载:
下载: