Sedimentary features and depositional model of the submarine fan of Mingyuefeng Formation in the Western Lishui Sag, East China Sea
-
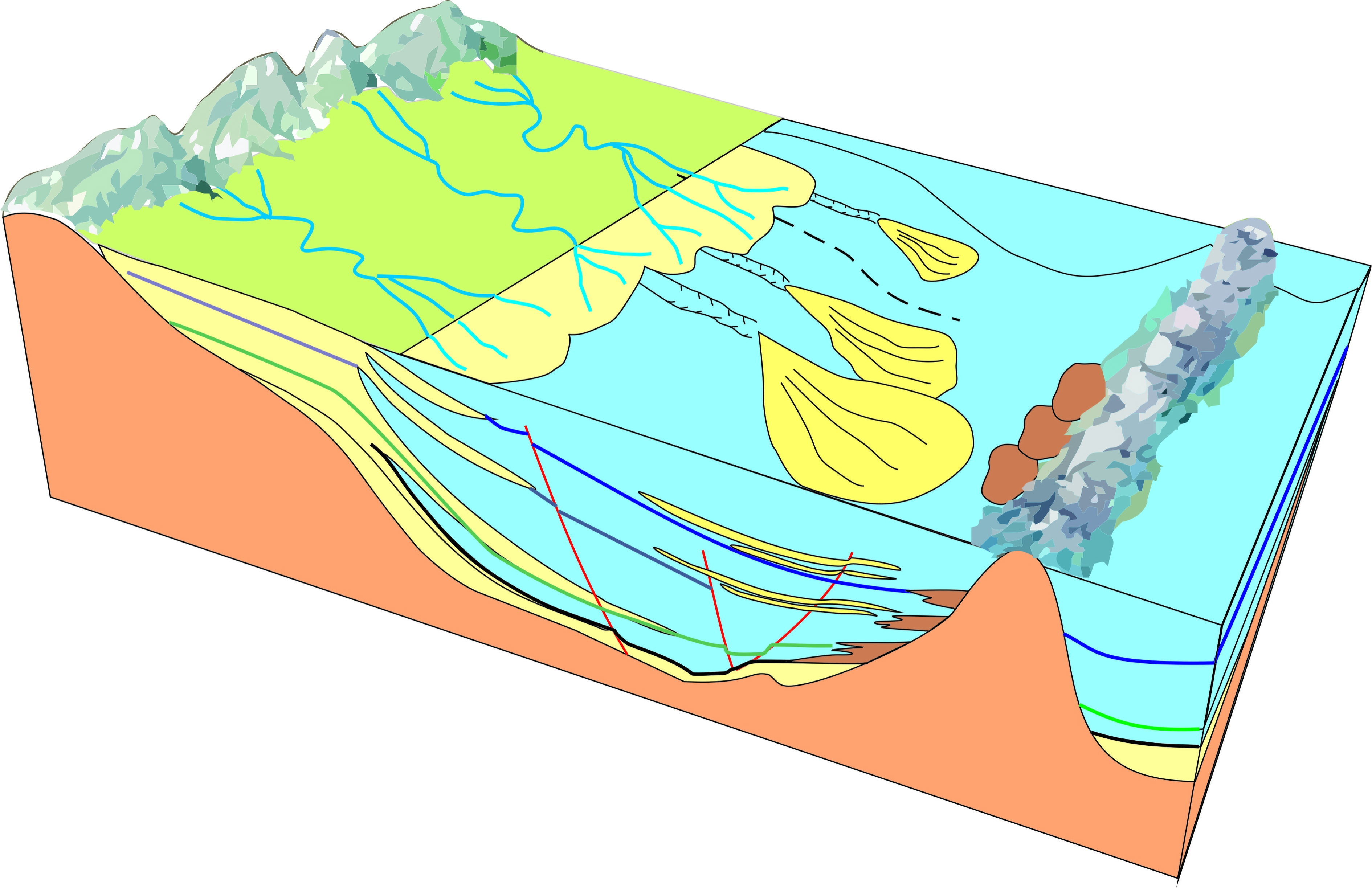
摘要:
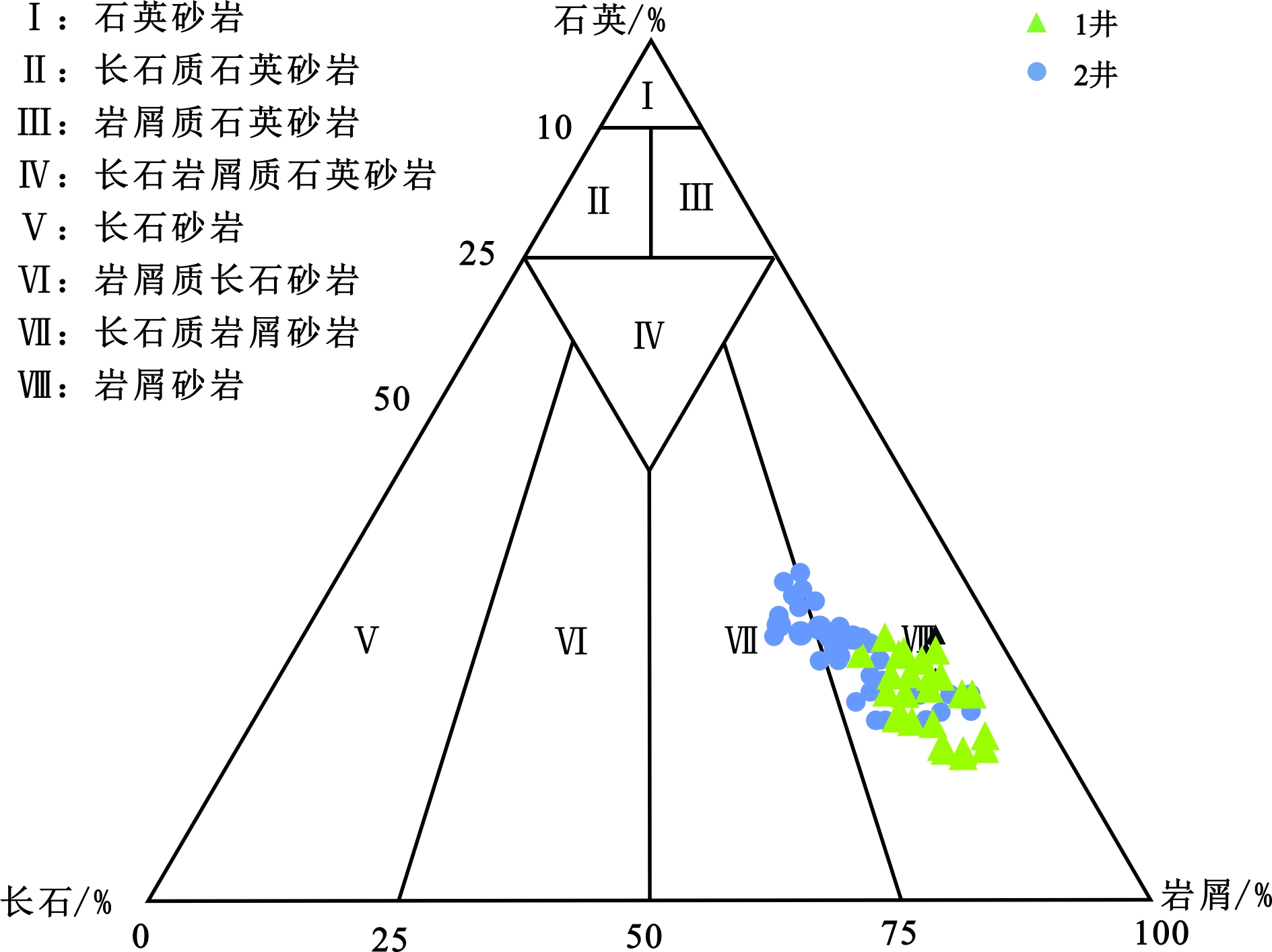
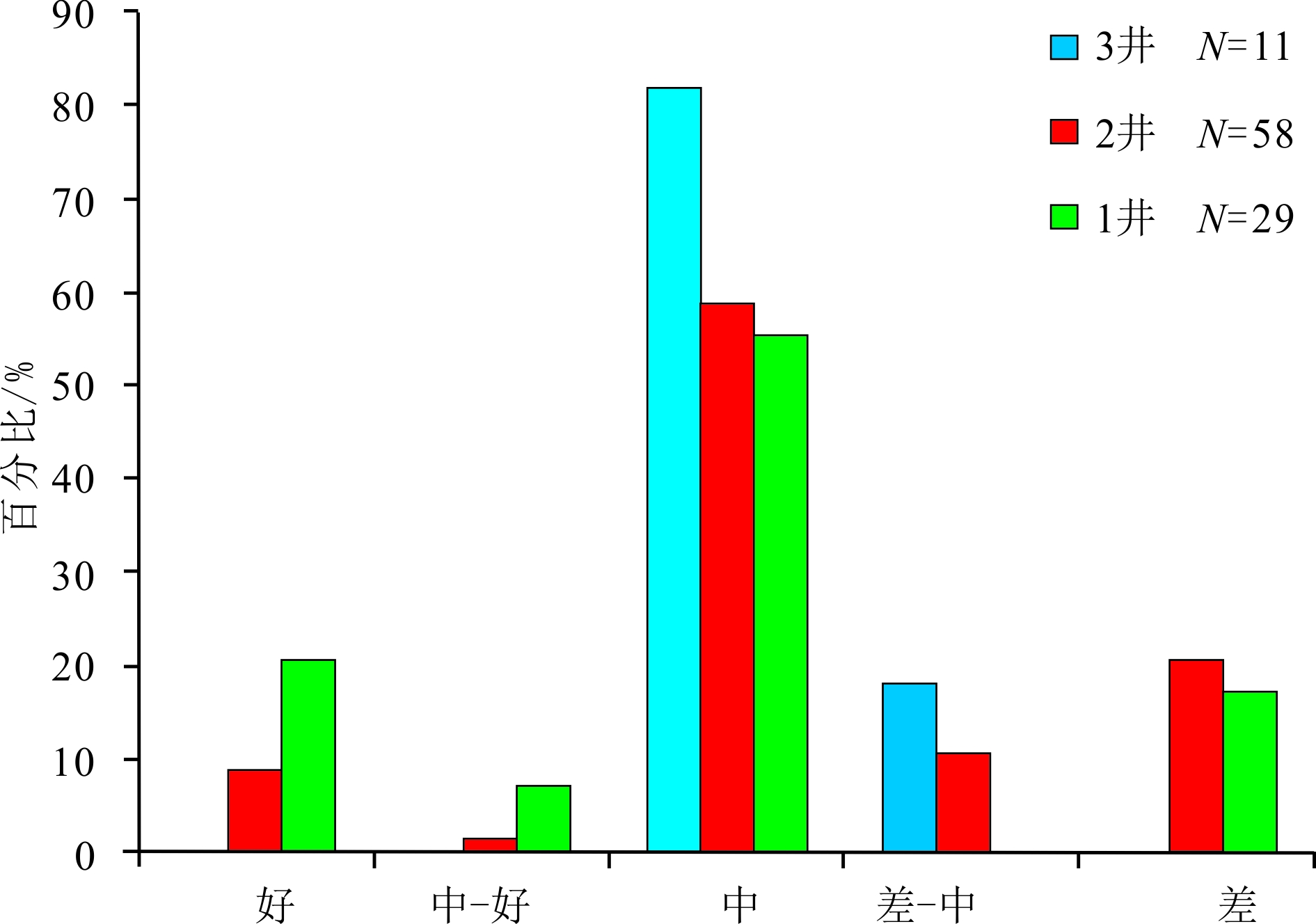
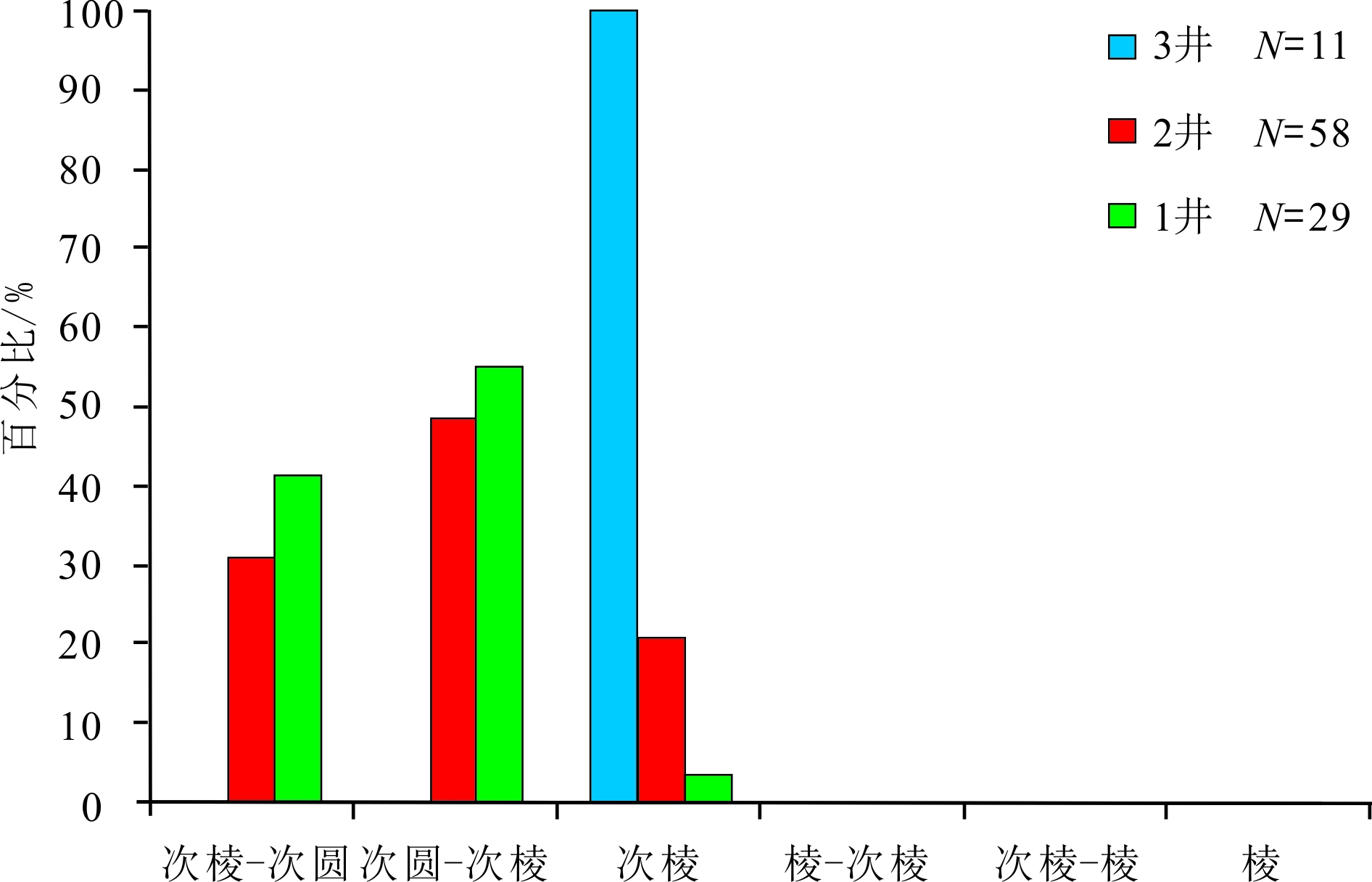
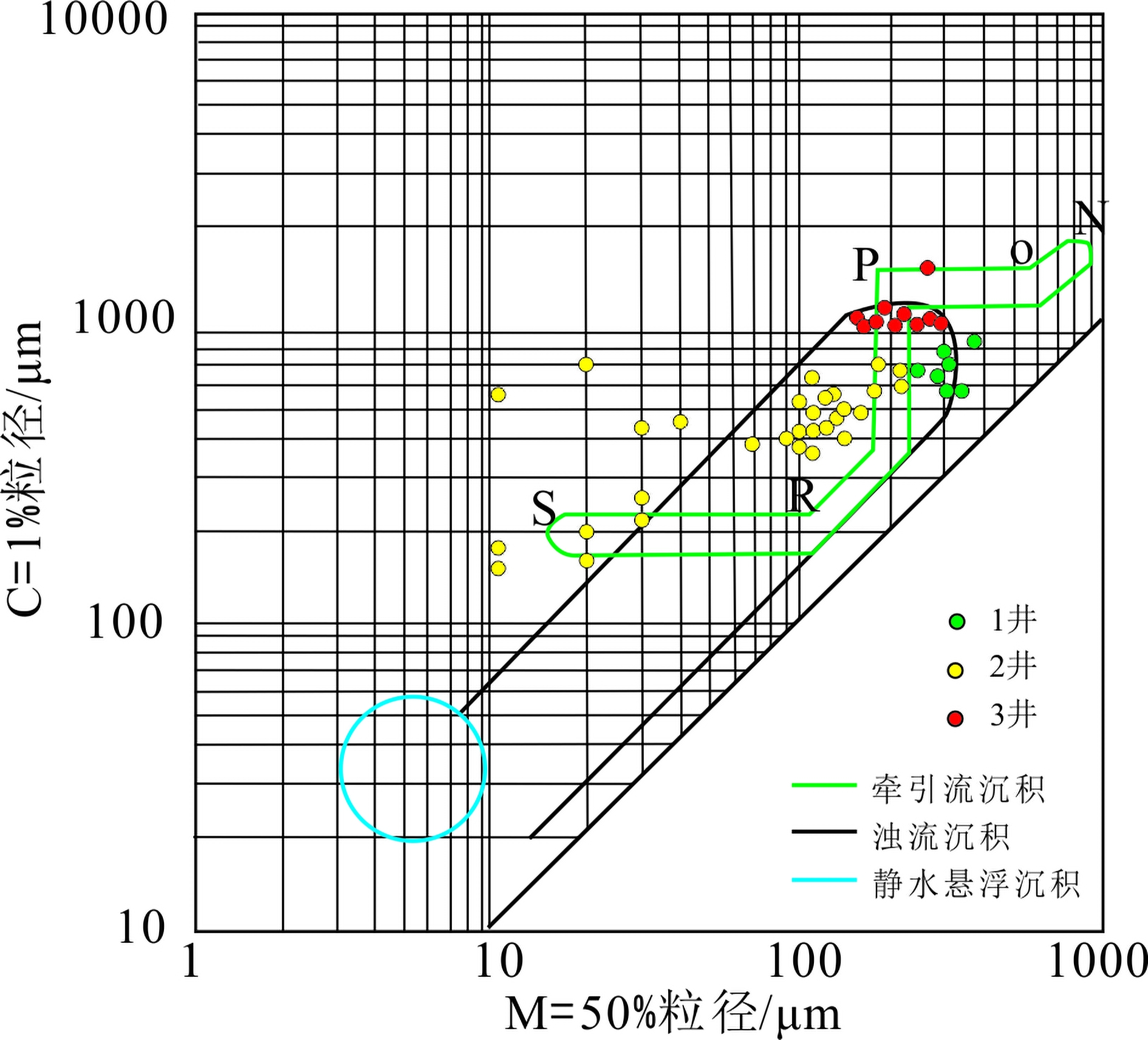
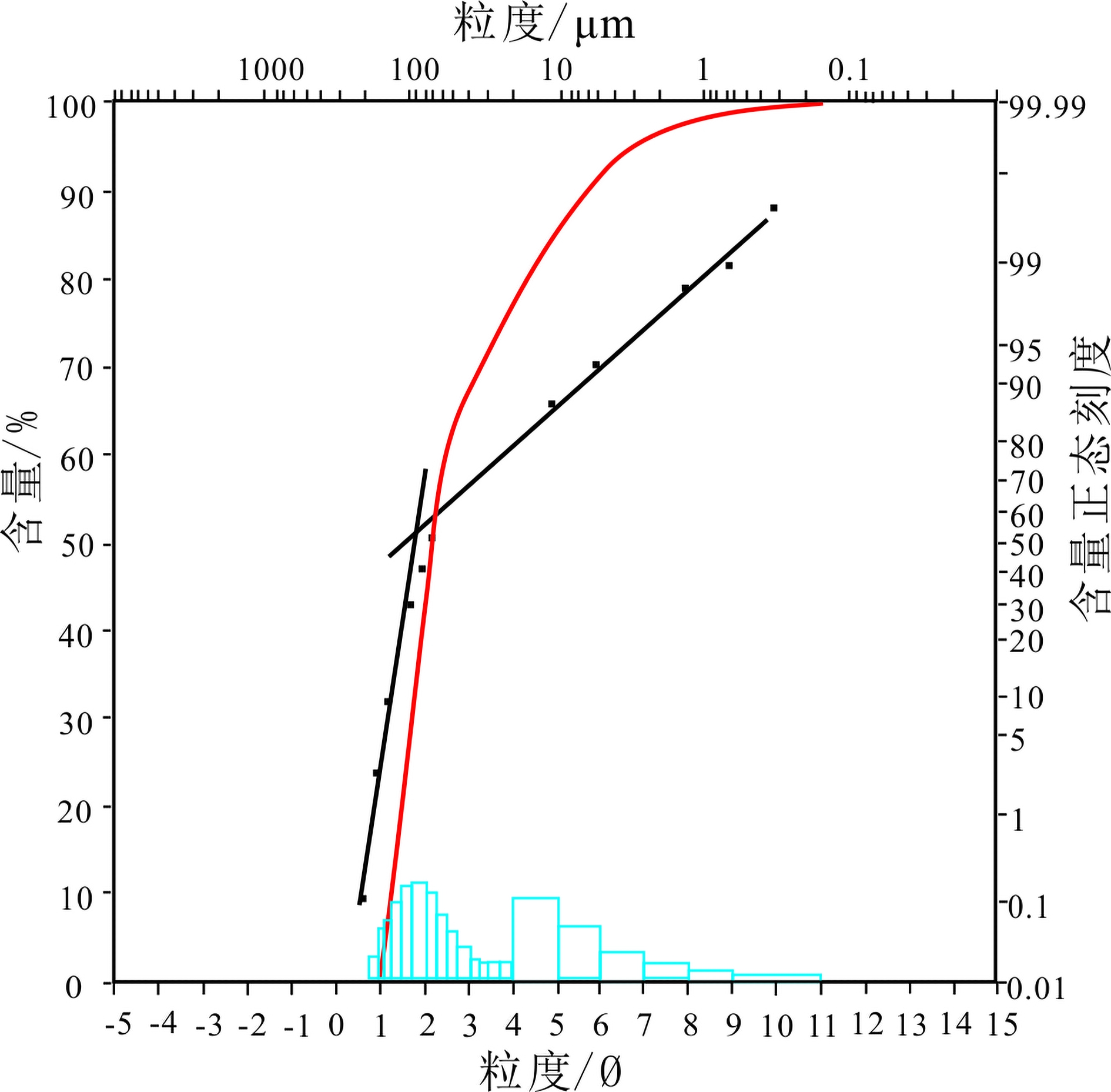
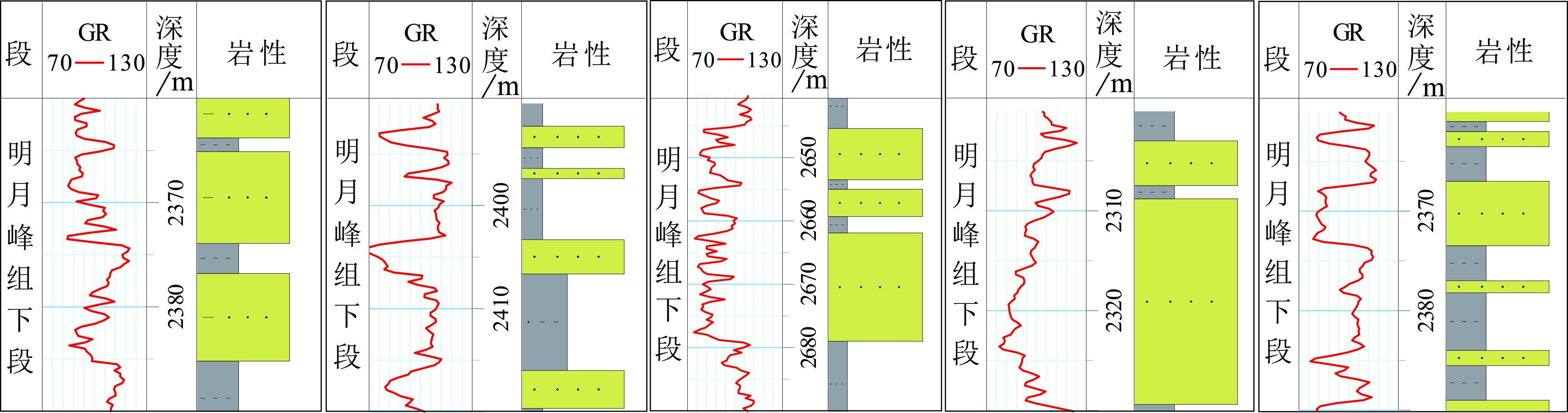
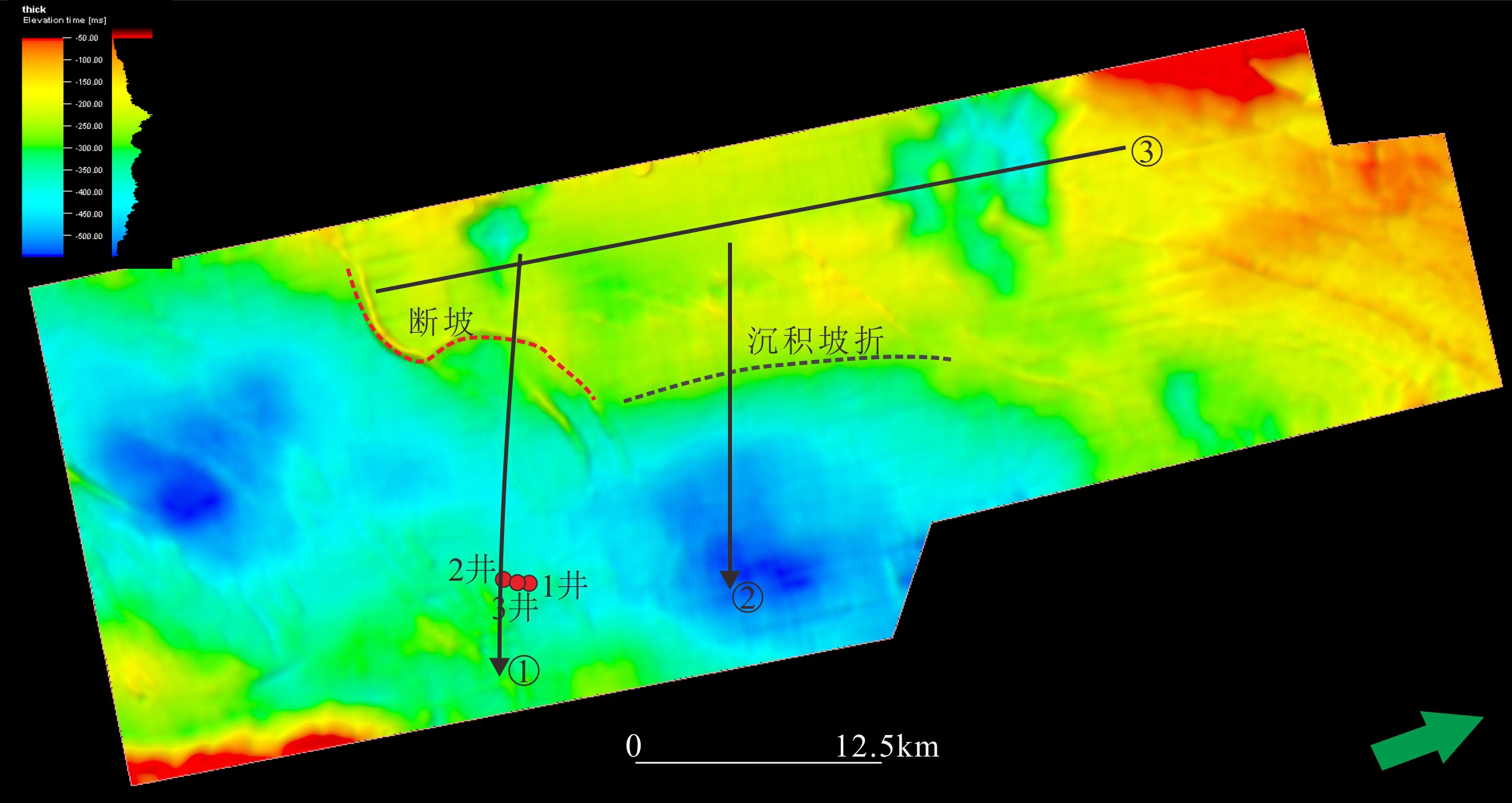
东海陆架盆地丽水凹陷古新统明月峰组发育典型的海底扇沉积,且已获得工业油气发现。该文利用现有地震地质资料,运用层序地层学理论方法,总结出丽水凹陷的海底扇沉积模式。海底扇沉积相标志包括:岩心主要表现为滑塌揉皱、包卷层理、泄水构造、块状砂岩、黑色泥岩撕裂屑、漂砾、砂注等构造;C-M图主要表现为重力流沉积特征;结构成熟度和成分成熟度中等—差。扇体地震反射结构主要为顺物源方向双向下超,垂直物源方向丘状反射特征,平面地震属性显示为典型扇形。丽水凹陷明月峰组由低位体系域、水进体系域和高位体系域组成,其中海底扇发育在低位体系域,在扇体近端发育多个下切谷,下切谷下切规模较大;坡折主要划分为断裂坡折和沉积坡折,其中断坡坡度较大,坡度7.2°左右,沉积坡折坡度较小,一般在5°左右,与下切谷相对应在谷口形成一系列的扇体,沟–坡–扇耦合关系良好。扇体规模较大,单个扇体面积最大124 km2,整个低位域由6个扇体组成,展示了丽水凹陷良好的岩性圈闭勘探前景。本次研究根据扇体的成因特点建立明月峰组低位域时期沟–坡–扇沉积模式,对指导勘探寻找出岩性圈闭和开创丽水凹陷油气勘探新局面具有一定意义。
Abstract:The Mingyuefeng Formation of Paleocene in the Lishui Sag of East China Sea Shelf Basin is characterized by typical submarine fan deposits,in which industrial hydrocarbon has been discovered. In this paper, a depositional model for the Sag is summarized based upon the existing seismic-geological data under the guidance of sequence stratigraphy. Sedimentary facies features of the submarine fan observed from cores include collapse and crumpling structures, entrapment beddings, drainage structures, massive sandstone, tear debris of black mudstone, drifting gravel structures, sand injection and other structures. The C-M diagrams show a typical pattern of gravity flow deposits with moderate to poor component and textural maturities. The seismic reflection of the fan body is characterized by two-way dipping along source direction, hill-like reflection in cross sections, and typical fan-shaped seismic attributes in plane views. The Mingyuefeng Formation in the Lishui Sag is composed of lowstand system tract, transgressive system tract and highstandl system tract of a sequence, in which submarine fans occur in the lowstand system tract. Multiple incised large valleys develop in the proximal end of the fan body. Both the fault breaks and sedimentary breaks are observed and the fault breaks are always in large scale with a slope of about 7.2 degrees, while the sedimentary slope breaks are relatively smaller with a slope around 5 degrees. Most of the depositional fans occur at the mouth of the incised valleys in a pattern including valley, slope and submarine fans. The largest fan covers an area of 124 km2, and the lowstand system tact is composed of six fans, showing good prospects for lithologic traps in the Lishui Sag. According to the genesis of the fan bodies, we established in this paper a ditch-slope-fan depositional model for the lowstand system tract of the Mingyuefeng Formation as a guide for exploration of lithologic traps in the sag.
-
Key words:
- Lishui Sag /
- lowstand system tract /
- submarine fan /
- depositional models /
- Mingyuefeng Formation
-

-
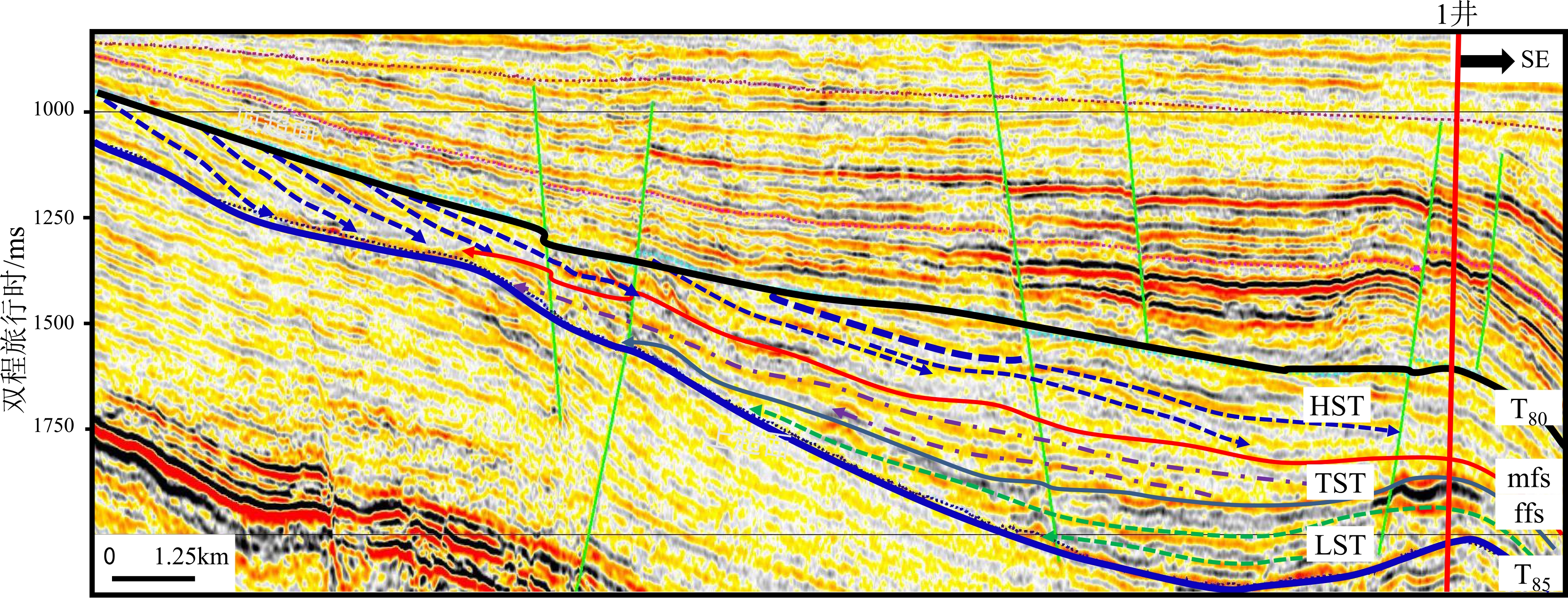
图 10 丽水凹陷明月峰组层序地层划分剖面(剖面位置见图1)
Figure 10.
图 11 单一海底扇地震反射特征(井位见图1)
Figure 11.
图 13 丽水凹陷海底扇沉积坡度剖面(剖面位置见图12)
Figure 13.
-
[1] 陈志勇. 丽水、椒江凹陷油气潜力分析和勘探突破口的选择[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 1997, 11(6):451-458
CHEN Zhiyong. Analysis of hydrocarbon potential and selection of exploration prospect of Lishui and Jiao-Jiang Sags [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 1997, 11(6): 451-458.
[2] 陈志勇, 吴培康, 吴志轩. 丽水凹陷石油地质特征及勘探前景[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2000, 14(6):384-391
CHEN Zhiyong, WU Peikang, WU Zhixuan. Petroleum geology and exploration potential of Lishui Sag [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2000, 14(6): 384-391.
[3] 周士科, 徐长贵. 轴向重力流沉积: 一种重要的深水储层—以东海盆地丽水凹陷明月峰组为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2006, 25(5):57-62 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2006.05.010
ZHOU Shike, XU Changgui. One kind of important deep-water reservoir: the longitudinal gravity currents sediments— A case study in Mingyuefeng Formation in Lishui Sag, East China Sea Basin [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2006, 25(5): 57-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2006.05.010
[4] 田兵, 李小燕, 庞国印, 等. 叠合断陷盆地沉积体系分析——以东海丽水-椒江凹陷为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(4):696-705
TIAN Bing, LI Xiaoyan, PANG Guoyin, et al. Sedimentary systems of the superimposed rift-subsidence basin: taking Lishui-Jiaojiang Sag of the East China Sea as an example [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(4): 696-705.
[5] 杨玉卿, 田洪, 刘大能, 等. 东海陆架盆地丽水凹陷丽水36-1构造上古新统物源分析[J]. 古地理学报, 2003, 5(2):171-179 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2003.02.005
YANG Yuqing, TIAN Hong, LIU Daneng, et al. Provenance analysis of the Upper Paleocene in Lishui 36-1 structure of Lishui Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2003, 5(2): 171-179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2003.02.005
[6] 侯国伟, 刘金水, 周瑞华, 等. 丽水凹陷低位扇群沉积模式[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2015, 27(5):240-244 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2015.05.039
HOU Guowei, LIU Jinshui, ZHOU Ruihua, et al. Sedimentary model of lowstand fan group in Lishui Sag [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2015, 27(5): 240-244. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2015.05.039
[7] 王红岩. 丽水凹陷远岸水下扇体识别及特征分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2019, 49(4):924-931
WANG Hongyan. Characteristic analysis and identification of far shore underwater fan in Lishui Depression [J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2019, 49(4): 924-931.
[8] 王毅, 姜亮, 杨伟利. 丽水—椒江凹陷断裂构造运动学[J]. 地质科学, 2000, 35(4):441-448 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2000.04.007
WANG Yi, JIANG Liang, YANG Weili. Kinematical analysis on faults in the Lishui-Jiaojiang Sag [J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 2000, 35(4): 441-448. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2000.04.007
[9] 杨伟利, 王毅. 丽水、椒江凹陷伸展运动分析[J]. 西南石油学院学报, 2002, 24(3):8-10
YANG Weili, WANG Yi. The anylysis of the basin’s extension in the Lishui-Jiaojiang Sag [J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum Institute, 2002, 24(3): 8-10.
[10] 刘俊海, 杨香华, 吴志轩, 等. 东海盆地丽水凹陷古新统锆石示踪作用分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(1):85-92
LIU Junhai, YANG Xianghua, WU Zhixuan, et al. Zircon tracing application of Paleocene-Eocene in Lishui Sag of the East China Sea Basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2004, 24(1): 85-92.
[11] 葛和平, 陈志勇, 方来富, 等. 丽水凹陷油气成藏期次探讨[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(1):44-50
GE Heping, CHEN Zhiyong, FANG Laifu, et al. A discussion on hydrocarbon accumulation periods in Lishui Sag, East China Sea Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2003, 17(1): 44-50.
[12] 庞雄, 柳保军, 颜承志, 等. 关于南海北部深水重力流沉积问题的讨论[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(3):114-119
PANG Xiong, LIU Baojun, YAN Chengzhi, et al. Some reviews on deep-water gravity-flow deposition in the northern South China Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2012, 34(3): 114-119.
[13] 刘景彦, 陈志勇, 林畅松, 等. 东海丽水西次凹古新统明月峰组层序-体系域分析及沉积体系展布[J]. 沉积学报, 2004, 22(3):380-386 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2004.03.002
LIU Jingyan, CHEN Zhiyong, LIN Changsong, et al. Analysis on sequence-tracts and distribution of depositional systems of Paleocene Mingyuefeng Formation in west Lishui Sag, East China Sea [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2004, 22(3): 380-386. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2004.03.002
[14] 刘丽娟, 陈建文, 张银国. 东海陆架盆地丽水凹陷古新统明月峰组层序地层学模式[J]. 世界地质, 2008, 27(2):198-203 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2008.02.013
LIU Lijuan, CHEN Jianwen, ZHANG Yinguo. Sequence stratigraphy model of Paleocene Mingyuefeng formation in Lishui Sag of the East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Global Geology, 2008, 27(2): 198-203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2008.02.013
[15] 张银国, 葛和平, 杨艳秋, 等. 东海陆架盆地丽水凹陷古新统层序地层的划分及控制因素[J]. 海相油气地质, 2012, 17(3):33-39 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2012.03.005
ZHANG Yinguo, GE Heping, YANG Yanqiu, et al. Division and controlling factors of Paleocene sequence Strata in Lishui Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2012, 17(3): 33-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2012.03.005
[16] 杨玉卿, 田洪, 姜亮, 等. 丽水凹陷晚古新世海平面变化及有利储层分布预测[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(1):69-73
YANG Yuqing, TIAN Hong, JIANG Liang, et al. Late Paleocene sea-level fluctuations and prediction of favourable reservoirs in Lishui Sag, East China Sea Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2003, 17(1): 69-73.
[17] 王丽顺, 陈琳琳. 东海瓯江凹陷下第三系层序地层学研究[J]. 上海地质, 1993(4):13-18
WANG Lishun, CHEN Linlin. Sequence stratigraphy of Eogene in Oujiang Sag [J]. Shanghai Geology, 1993(4): 13-18.
[18] 覃建雄, 田景春, 杨作升. 东海盆地第三系层序地层学初探[J]. 成都理工学院学报, 1998, 25(4):503-510
QIN Jianxiong, TIAN Jingchun, YANG Zuosheng. A study on sequence stratigraphy of tertiary in the East China Sea Basin [J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 1998, 25(4): 503-510.
[19] 武法东, 陆永潮, 李思田, 等. 东海陆架盆地第三系层序地层格架与海平面变化[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 1998, 23(1):13-20
WU Fadong, LU Yongchao, LI Sitian, et al. Tertiary sequence stratigraphic framework and sea-level changes in the East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1998, 23(1): 13-20.
[20] 林畅松, 潘元林, 肖建新, 等. “构造坡折带”——断陷盆地层序分析和油气预测的重要概念[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2000, 25(3):260-266
LIN Changsong, PAN Yuanlin, XIAO Jianxin, et al. Structural slope-break zone: key concept for stratigraphic sequence analysis and petroleum forecasting in fault subsidence basins [J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2000, 25(3): 260-266.
[21] Vail P R, Mitchum Jr R M, Thompson III S. Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level, Part 3: relative changes of sea level from coastal Onlap[M]//Payton C E. Seismic Stratigraphy-Applications to Hydrocarbon Exploration. Tulsa: AAPG, 1977: 49-212.
[22] Vail P R. Seismic stratigraphy interpretation using sequence stratigraphy, part I: seismic stratigraphy interpretation procedure[C]//Bally A W. Atlas of Seismic Stratigraphy. Tulsa: AAPG, 1987: 1-10.
[23] Catuneanu O, Abreu V, Bhattacharya J P, et al. Towards the standardization of sequence stratigraphy [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2009, 92(1-2): 1-33. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2008.10.003
-




 下载:
下载: