Thermal evolution modeling and present geothermal field of the Lishui Sag of East China Sea Basin
-
摘要:
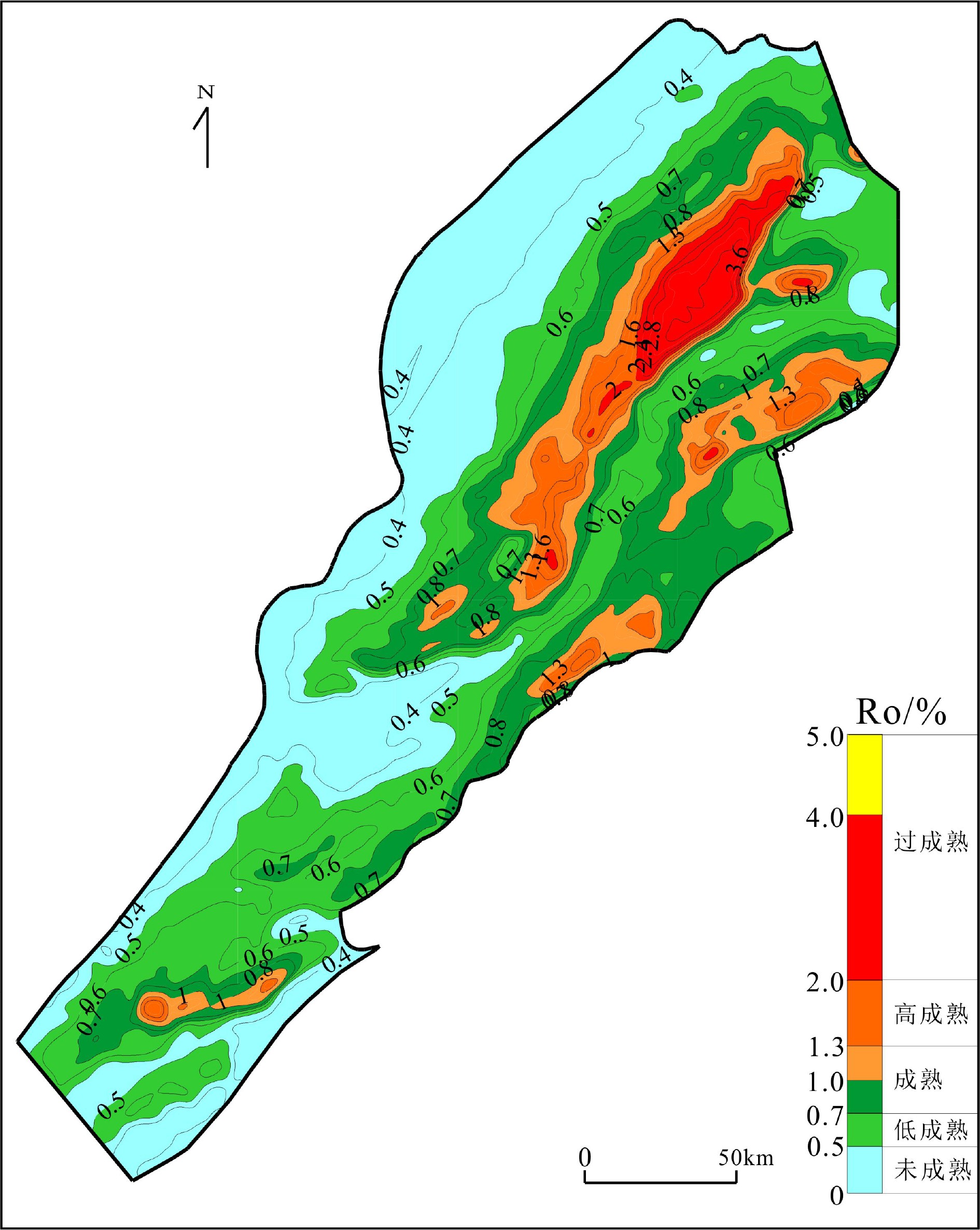
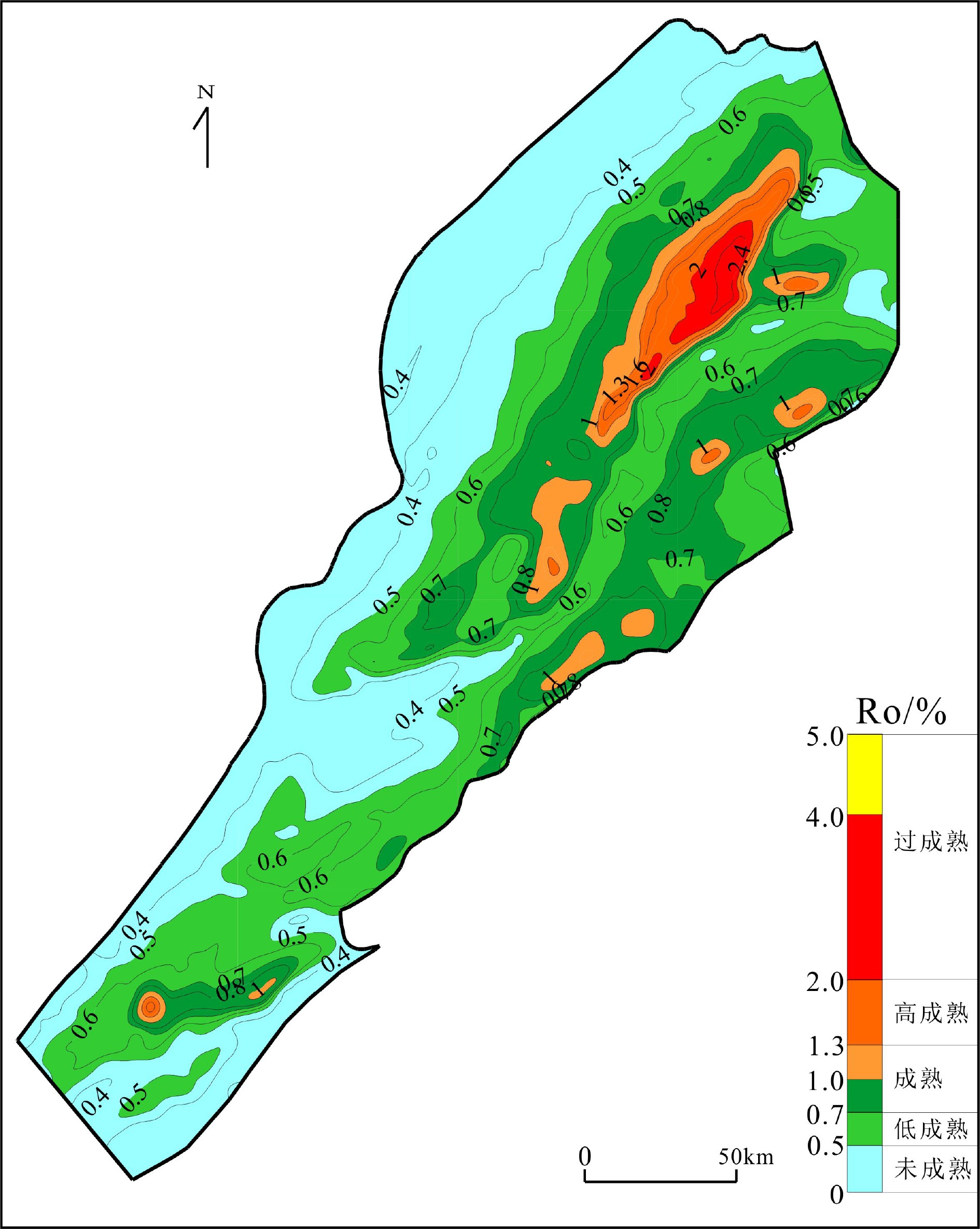
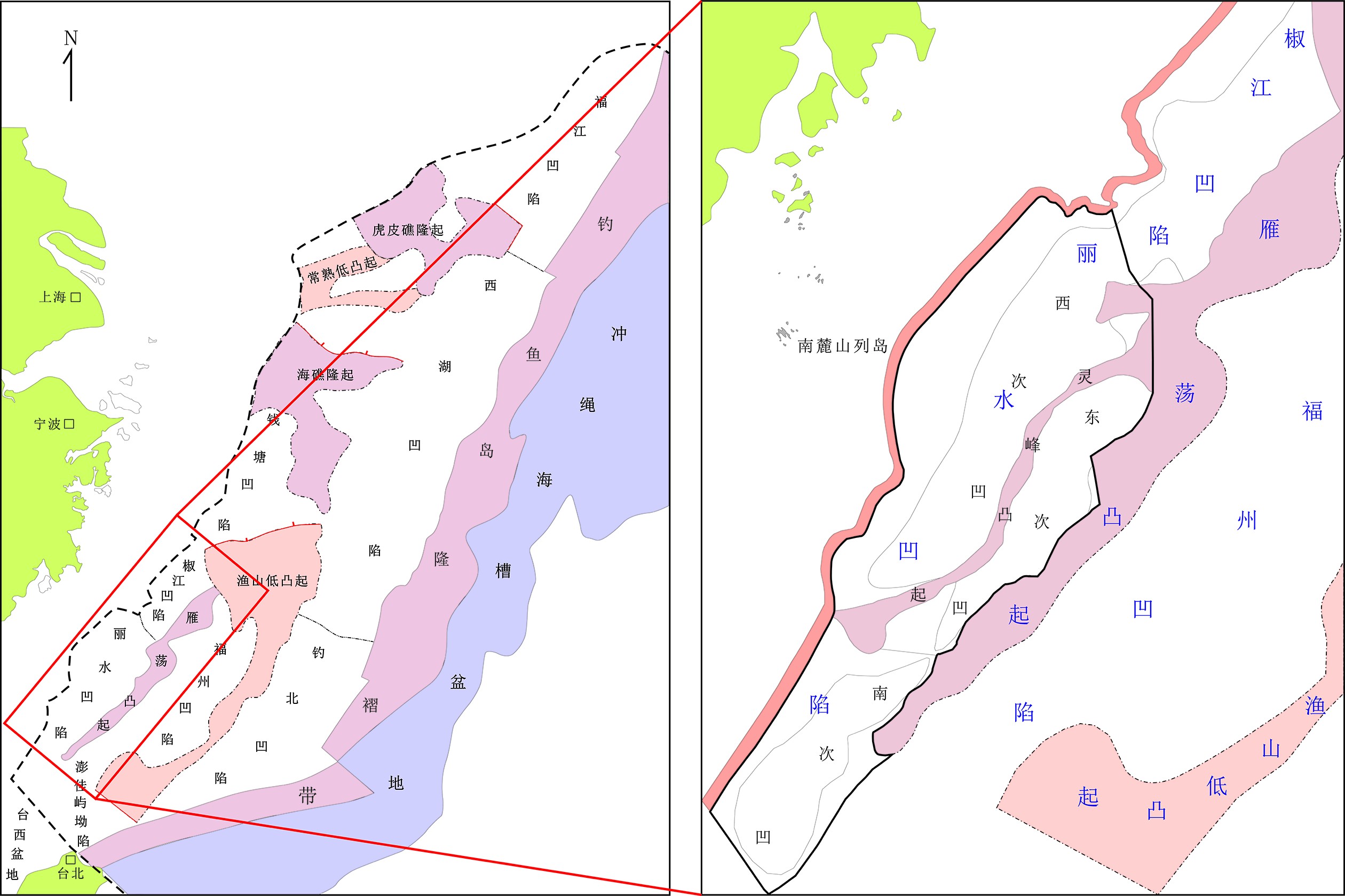
东海陆架盆地丽水凹陷烃源岩埋深大、钻井少、油气发现少,至今对其生油气能力具有较大的争议。为明确烃源岩热演化史,从少量具备实测地层温度和镜质体反射率(Ro)资料的钻井出发,利用正演模拟方法,通过地温与地层深度相关性分析,将钻井地温研究结果外推到无井区。在恢复丽水凹陷探井岩石圈结构及其演化史的基础上,首次系统建立了丽水凹陷的区域地温场并分析其对烃源岩演化的作用。研究表明,古新统下段月桂峰组底界(T100)烃源岩大部分都已成熟,次洼中心局部过成熟;月桂峰组顶界(T90)烃源岩大部分处于低熟—成熟阶段,次洼中心局部高—过成熟;灵峰组顶界(T85)烃源岩处于未熟—低熟状态,西次洼中心有成熟烃源岩。烃源岩特征及演化分析表明,古新统下段月桂峰组烃源岩是丽水凹陷的主力生油气烃源岩。
Abstract:Hydrocarbon source rocks are deeply buried in the Lishui Sag of East China Sea Basin, where drilling wells are rare and encountered only a few oil and gas discoveries. There are hot debates over the hydrocarbon generating capacity of the basin. Careful study has been made for this time to clarify the thermal evolutionary history of source rocks. Starting from drilling wells with measured formation temperature and vitrinite reflectance (Ro) data, using the forward simulation method, and through the correlation between temperature and stratum depth, we extrapolated the results of drilling temperature research to non-well areas. On the basis of restoring lithospheric structure and its evolution history, the regional geothermal field of the Lishui Sag has been systematically established for the first time. The impacts of geothermal field onto source rock evolution are analyzed. Data shows, most of the source rocks at the bottom of Yueguifeng Formation in the lower part of Paleocene are mature and the sub-depression center is partly over-matured; most of the source rocks at the top of Yueguifeng Formation are in the stage of low-maturity and maturity, the sub-depression center is partly high-mature to over-mature; the source rocks at the top of the Lingfeng Formation are immature to low-maturity, and there are mature source rocks at the center of the western sub-depression. According to the analysis of source rock characteristics and evolution, the source rocks in the lower Paleocene Yueguifeng Formation should be the main source rocks for hydrocarbon generation in the Lishui Sag.
-

-
表 2 LS5井岩石圈模型参数
Table 2. Lithospheric modeling parameters of LS5
岩石圈原始厚度ho=125 km[21] 岩石圈现今厚度ho=80 km 上地壳放射性生热率Qr0=2.8 μW/m3 原始地壳厚度hc=35 km 现今地壳厚度hc=21.5 km 上地壳热导率=3.5 W/mK 原始上地幔厚度hm=90 km 现今上地幔厚度hm=52 km 下地壳热导率=3.1 W/mK 研究区现今纬度=27° 基底深度db=6 499 m 上地幔热导率=2.5 W/mK 软流圈顶部温度Tb=1 330 ℃ 上地壳密度ρc上 =2.7 g/cm3 上地壳比热容=900 J·kg−1·K−1 拉张时间ts=27.1 Ma 下地壳密度ρc下 =2.9 g/cm3 下地壳比热容=1 050 J·kg−1·K−1 地壳拉张系数βc=1.63 上地幔密度ρm =3.4 g/cm3 上地幔比热容=1 200 J·kg−1·K−1 表 3 丽水凹陷岩石密度和热属性参数
Table 3. Density and thermal properties of rocks encountered in Lishui Sag
岩性 密度
/(g/cm3)热导率
/(W/mK)生热率
/(μW/m3)比热容
/(J·kg−1·K−1)砾岩 2.7 4.18 0.85 820 砂岩 2.65 3.85 0.7 855 粉砂岩 2.65 3.35 0.96 910 泥岩 2.72 1.62 1.5 860 煤 1.6 0.46 0.38 1 300 表 4 丽水凹陷热流值及相关参数
Table 4. Heat flow values and related parameters in Lishui Sag
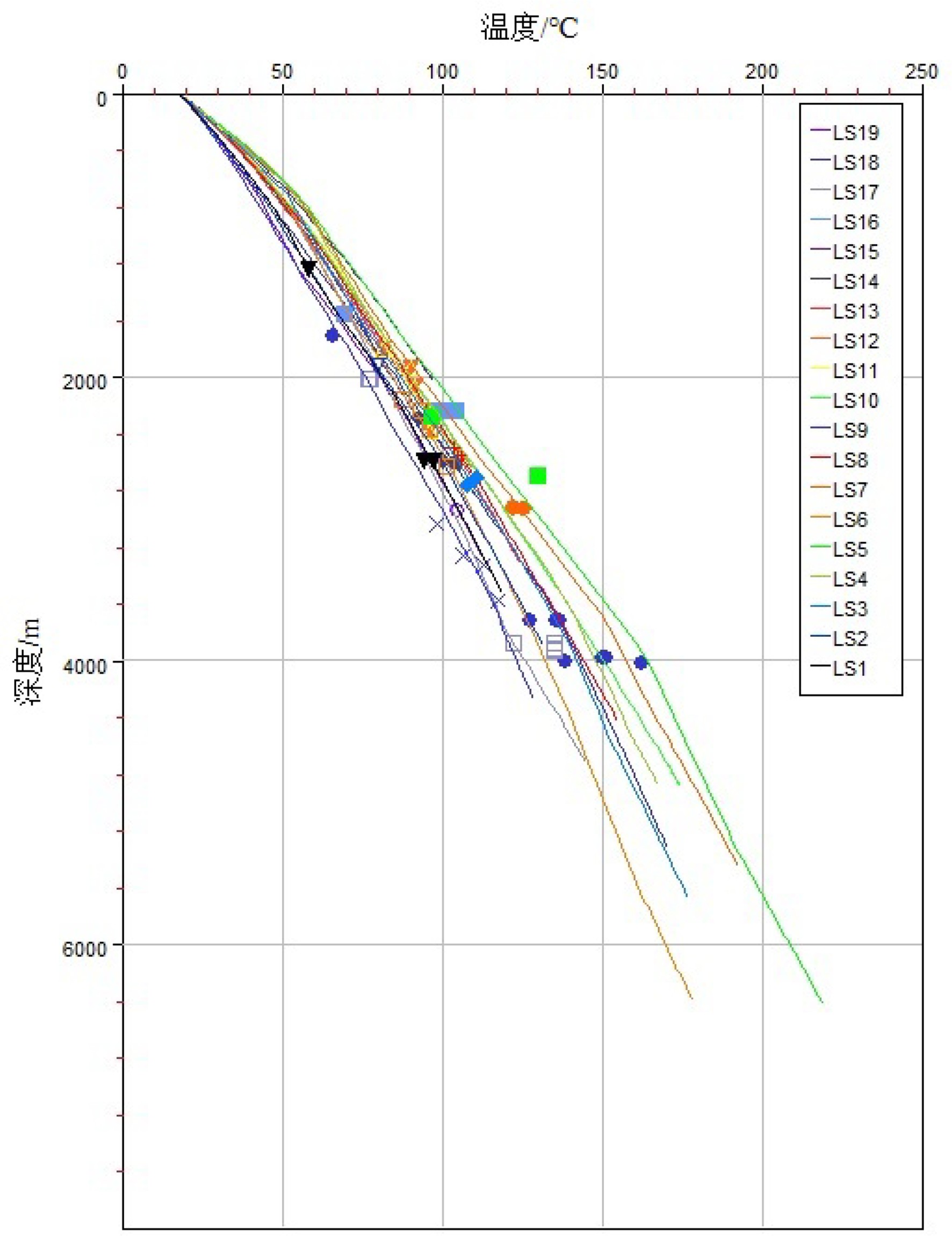
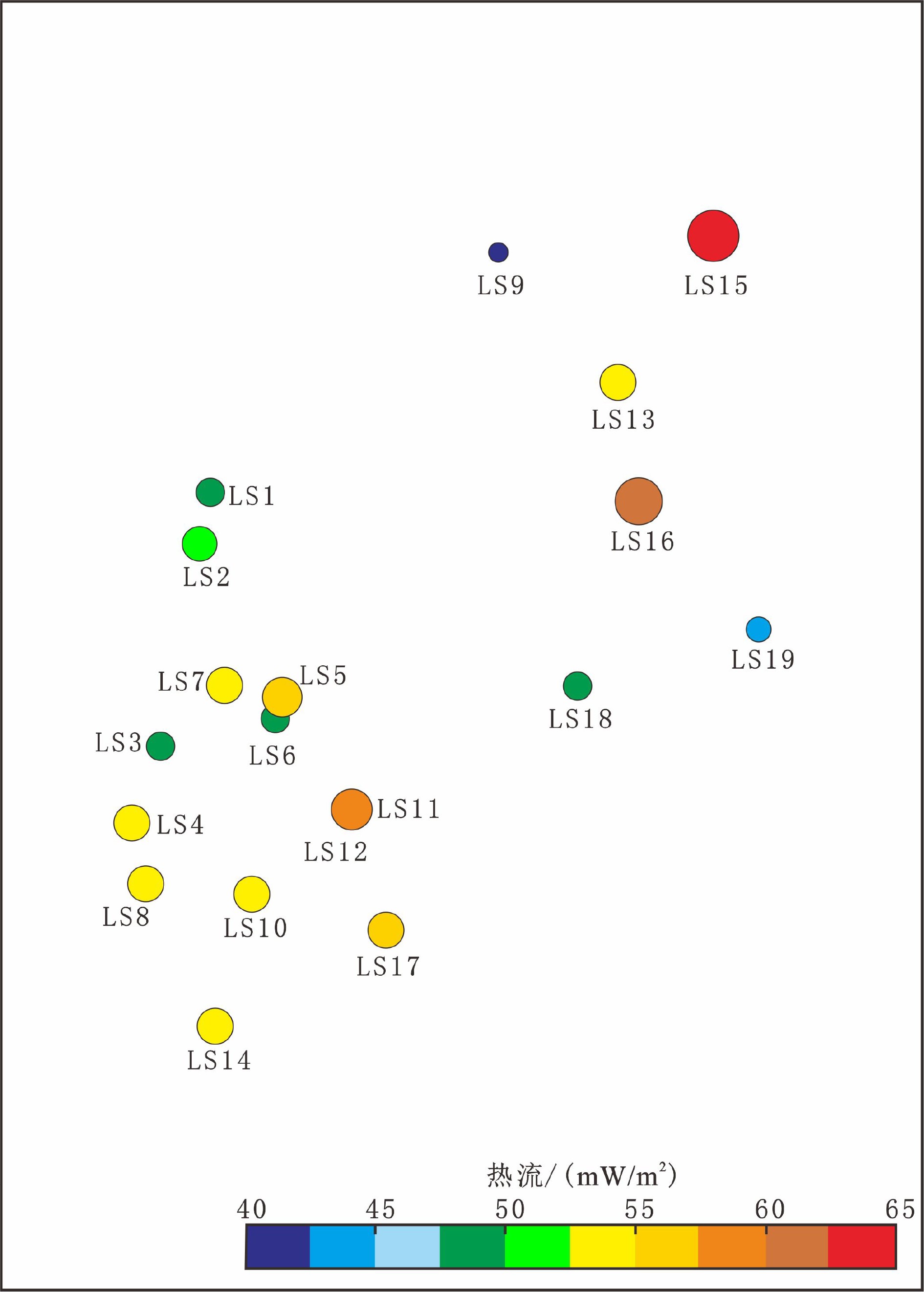
井号 测温深度/m 平均地温梯度
/(℃/100 m)基底热流
/(mW/m2)LS1井 2 665.8 2.78 48.26 LS2井 2 000.5 3.17 50.16 LS3井 2 798 2.96 49.06 LS4井 2 801 3.14 53.95 LS5井 2 791 3.21 56.08 LS6井 2 902.7 2.59 48.53 LS7井 3 022.4 3.43 54.86 LS8井 2 574~2 587.5 2.60 54.30 LS9井 3 117 2.69 41.78 LS10井 − 3.24 54.88 LS11井 2 032.67 3.26 58.53 LS12井 2 467.26 3.27 56.81 LS13井 − 3.26 53.39 LS14井 2 698.1 3.33 53.48 LS15井 1 050 3.65 62.79 LS16井 2 325 3.21 61.46 LS17井 4 015 2.72 55.56 LS18井 3 803 2.78 47.55 LS19井 3 040 2.95 44.76 -
[1] 葛和平, 陈志勇, 方来富, 等. 丽水凹陷油气成藏期次探讨[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(1):44-50
GE Heping, CHEN Zhiyong, FANG Laifu, et al. A discussion on hydrocarbon accumulation periods in Lishui Sag, East China Sea Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2003, 17(1): 44-50.
[2] 孙玉梅, 席小应. 东海盆地丽水凹陷油气源对比与成藏史[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2003, 30(6):24-28 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2003.06.007
SUN Yumei, XI Xiaoying. Petroleum reservoir filling history and oil-source correlation in the Lishui Sag, East China Sea Basin [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2003, 30(6): 24-28. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2003.06.007
[3] 陈志勇, 吴培康, 吴志轩. 丽水凹陷石油地质特征及勘探前景[J]. 中国海上油气: 地质, 2000, 14(6):384-391
CHEN Zhiyong, WU Peikang, WU Zhixuan. Petroleum geology and exploration potential of Lishui Sag [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas: Geology, 2000, 14(6): 384-391.
[4] 陈斯忠. 东海盆地主要地质特点及找气方向[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(1):6-13, 19
CHEN Sizhong. Main geological characteristics and gas exploration directions in East China Sea Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2003, 17(1): 6-13, 19.
[5] 郭永华, 于水, 葛玲. 东海盆地丽水凹陷LS36-1构造成藏机理研究[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2003, 30(6):29-31 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2003.06.008
GUO Yonghua, YU Shui, GE Ling. Formation of the LS36-1 oil and gas structure in the Lishui Sag, East China Sea Basin [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2003, 30(6): 29-31. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2003.06.008
[6] 李宁. 丽水凹陷西次凹古近系烃源岩热演化特征研究[J]. 长江大学学报: 自科版, 2013, 10(10):46-48
LI Ning. Study on the thermal evolution characteristics of hydrocarbon source rocks in Paleogene system of Lishui Sag [J]. Journal of Yangtze University: Natural Science Edition, 2013, 10(10): 46-48.
[7] 冯晓杰, 蔡东升, 王春修, 等. 东海陆架盆地中新生代构造演化特征[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(1):33-37
FENG Xiaojie, CAI Dongsheng, WANG Chunxiu, et al. The meso-cenozoic tectonic evolution in East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2003, 17(1): 33-37.
[8] 张田, 张建培, 张绍亮, 等. 平衡剖面技术在东海丽水凹陷构造演化研究中的应用[J]. 上海国土资源, 2014, 35(1):92-96 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2014.01.021
ZHANG Tian, ZHANG Jianpei, ZHANG Shaoliang, et al. An application of the balanced cross-section technique: the tectonic evolution of Lishui Sag, the East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Shanghai Land & Resources, 2014, 35(1): 92-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2014.01.021
[9] 田兵, 李小燕, 庞国印, 等. 叠合断陷盆地沉积体系分析——以东海丽水-椒江凹陷为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(4):696-705
TIAN Bing, LI Xiaoyan, PANG Guoyin, et al. Sedimentary systems of the superimposed rift-subsidence basin: Taking Lishui-Jiaojiang Sag of the East China Sea as an example [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(4): 696-705.
[10] 陈国俊, 李超, 梁建设, 等. 东海陆架盆地瓯江凹陷明月峰组沉积相及沉积特征分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2011, 22(5):760-769
CHEN Guojun, LI Chao, LIANG Jianshe, et al. Sedimentary facies of Mingyuefeng formation in Oujiang Sag, East China Sea Basin [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2011, 22(5): 760-769.
[11] Kauerauf A I, Hantschel T. Fundamentals of Basin and Petroleum Systems Modeling[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2009: 1-476.
[12] Lin C S, Zhang Y M, Li S T, et al. Quantitative modelling of multiphase lithospheric stretching and deep thermal history of some tertiary rift basins in eastern China [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2002, 76(3): 324-330.
[13] He Z Y, Crews S G, Corrigan J. Rifting and heat flow: Why the McKenzie model is only part of the story[C]//Basin Modeling Perspectives: Innovative Developments and Novel Applications. Hague, Netherlands: AAPG, 2007.
[14] 石广仁. 油气盆地数值模拟方法[M]. 3版. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004.
SHI Guangren. Approaches of Petroleum Basin Modeling[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004.
[15] 郝天珧, 徐亚, 胥颐, 等. 对黄海-东海研究区深部结构的一些新认识[J]. 地球物理学报, 2006, 49(2):458-468 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2006.02.019
HAO Tianyao, XU Ya, XU Yi, et al. Some new understandings on deep structure in Yellow Sea and East China Sea [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2006, 49(2): 458-468. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2006.02.019
[16] 蔡学林, 朱介寿, 曹家敏, 等. 中国大陆及邻区岩石圈地壳三维结构与动力学型式[J]. 中国地质, 2007, 34(4):543-557 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2007.04.001
CAI Xuelin, ZHU Jieshou, CAO Jiamin, et al. 3D structure and dynamic types of the lithospheric crust in continental China and its adjacent regions [J]. Geology in China, 2007, 34(4): 543-557. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2007.04.001
[17] 周海廷, 姜效典, 李德勇, 等. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷岩石圈热流变性质[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2017, 41(3):481-490
ZHOU Haiting, JIANG Xiaodian, LI Deyong, et al. Thermal-rheological property of lithosphere beneath Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2017, 41(3): 481-490.
[18] 高德章, 赵金海, 薄玉玲, 等. 东海及邻近地区岩石圈三维结构研究[J]. 地质科学, 2006, 41(1):10-26 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2006.01.002
GAO Dezhang, ZHAO Jinhai, BO Yuling, et al. A study on lithosphere 3D structures in the East China Sea and adjacent regions [J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2006, 41(1): 10-26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2006.01.002
[19] 江为为, 刘少华, 郝天珧, 等. 应用重力资料估算东海冲绳海槽地壳厚度[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2002, 17(1):35-41 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2002.01.004
JIANG Weiwei, LIU Shaohua, HAO Tianyao, et al. Using gravity data to compute crustal thickness of East China Sea and Okinawa Trough [J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2002, 17(1): 35-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2002.01.004
[20] 周志远, 高金耀, 吴招才, 等. 东海莫霍面起伏与地壳减薄特征初步分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 2013, 31(1):16-25 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2013.01.002
ZHOU Zhiyuan, GAO Jinyao, WU Zhaocai, et al. Preliminary analyses of the characteristics of Moho undulation and crustal thinning in East China Sea [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2013, 31(1): 16-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2013.01.002
[21] 仝志刚, 赵志刚, 杨树春, 等. 低勘探程度盆地烃源岩热演化及排烃史研究——以东海椒江凹陷为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2012, 34(3):319-324, 329 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2012.03.016
TONG Zhigang, ZHAO Zhigang, YANG Shuchun, et al. Research on thermal evolution and hydrocarbon expulsion history of source rocks in low-exploration basins: a case study on Jiaojiang Sag, East China Sea Basin [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2012, 34(3): 319-324, 329. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2012.03.016
[22] 方银霞, 刘建华. 东海的地壳结构特征[J]. 东海海洋, 2004, 22(3):9-17
FANG Yinxia, LIU Jianhua. The crustal structure character of East China Sea [J]. Donghai Marine Science, 2004, 22(3): 9-17.
[23] 栾锡武, 高德章, 喻普之, 等. 我国东海陆架地区新生代地层的热导率[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2002, 33(2):151-159 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2002.02.006
LUAN Xiwu, GAO Dezhang, YU Puzhi, et al. Thermal conductivity of the Cenozoic layer of East China Sea Shelf [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2002, 33(2): 151-159. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2002.02.006
[24] 栾锡武, 赵一阳, 秦蕴珊, 等. 我国东海陆架区新生代地层岩石生热率研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2003, 21(4):634-639 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2003.04.015
LUAN Xiwu, ZHAO Yiyang, QIN Yunshan, et al. Heat generation of the cenozoic layer of East China Sea Shelf [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2003, 21(4): 634-639. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2003.04.015
[25] 仝志刚, 杨树春, 郝建荣. 盆地模拟技术应用与发展(内部资料). 2011.
TONG Zhigang, YANG Shuchun, HAO Jianrong. Application and development of basin simulation technology(Internal data), 2011.
[26] Wygrala B P. Integrated study of an oil field in the Southern Po Basin, Northern Italy[D]. Doctor Dissertation of University of Cologne, Germany, 1989.
[27] 王斌, 赵永强, 罗宇, 等. 塔里木盆地草湖凹陷热演化与生烃史——基于IES软件盆地模拟技术[J]. 石油实验地质, 2010, 32(6):605-609 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2010.06.017
WANG Bin, ZHAO Yongqiang, LUO Yu, et al. Thermal evolution and hydrocarbon generation in the Caohu Sag of the Tarim Basin—based on IES basin simulation technology [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2010, 32(6): 605-609. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2010.06.017
[28] Waples D W, Ramly M. A statistical method for correcting log-derived temperatures [J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 2001, 7(3): 231-240. doi: 10.1144/petgeo.7.3.231
[29] Waples D W, Pacheco J, Vera A. A method for correcting log-derived temperatures in deep wells, calibrated in the Gulf of Mexico [J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 2004, 10(3): 239-245. doi: 10.1144/1354-079302-542
[30] 仝志刚, 贺清, 何仕斌, 等. 东海西湖凹陷地温场及其对烃源岩的作用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2009, 31(5):466-471, 484 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2009.05.006
TONG Zhigang, HE Qing, HE Shibin, et al. Geothermal field and its effect on source rock in the Xihu Sag, the East China Sea Basin [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2009, 31(5): 466-471, 484. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2009.05.006
-



 下载:
下载: