Spatio-temporal distribution pattern of magmatic rocks and mechanism in the South China Sea and adjacent areas
-
摘要:
南海的岩浆作用自始至终高度活跃,岩浆活动规模远远超出以前的想象。根据地壳发展阶段及其产生的岩浆作用强度和类型的差异,结合岩石同位素年龄资料,将南海及邻区划分为前吕梁期、吕梁期、晋宁期、加里东期、海西期、印支期、燕山期、喜马拉雅期等8个岩浆作用时期,主要分布于南海及周缘的广东、广西、海南岛、台湾岛、中南半岛、加里曼丹岛、菲律宾群岛,时代从前吕梁期至喜马拉雅期均有出露。南海及邻区最老的岩浆岩是在中南半岛出现的太古代黑云母花岗岩、紫苏花岗岩和辉长岩;最新的现代岩浆岩海陆均有发现,南海西南部和菲律宾等地区至今还有火山喷发岩浆活动。南海海区岩浆岩以燕山期和喜马拉雅期为主,燕山期以中酸性侵入岩为主,广泛分布于南海陆缘,尤其南海北部和西南部最甚;喜马拉雅期以强烈的基性、超基性岩浆活动为主,遍布于整个南海海区,以玄武岩为主。总体上,海区岩浆活动要比陆区晚。
Abstract:Magmatism in the South China Sea has been active for long. According to the evolutionary stage of the crust and the difference in the intensity and type of the magmatism, combined with the isotopic age data from magmatic rocks, the magmatic activities in the South China Sea and its adjacent areas can be divided into eight stages, i.e. the pre-Luliang, Luliang, Jinning, Caledonian, Hercynian, Indosinian, Yanshanian and Himalayan stages. Magmatic rocks from pre Luliang to Himalayan period are widely distributed in the South China Sea and its surrounding areas such as Guangdong, Guangxi, the Hainan Island, the Taiwan Island, the Indochina Peninsula, the Kalimantan island and the Philippine islands. The oldest magmatic rocks, the Archean biotite granite, perilla granite and gabbro, are outcropped in the Indochina Peninsula; while the latest modern magmatic rocks occur both on land and in the sea. Volcanic eruption remains active up to present. The region of the South China Sea is dominated by the Yanshanian intermediate-acid intrusive magmatic rocks, which are mainly distributed on the continental margin of the South China Sea, especially in the north and southwest. In the Himalayan period, however, the region is dominated by strong basic and ultrabasic magmatic activities, mainly consisting of basaltic rocks. In general, the magmatic activity in sea area is lagged behind that on land.
-
Key words:
- magmatic rock /
- distribution pattern /
- genesis /
- South China Sea
-

-
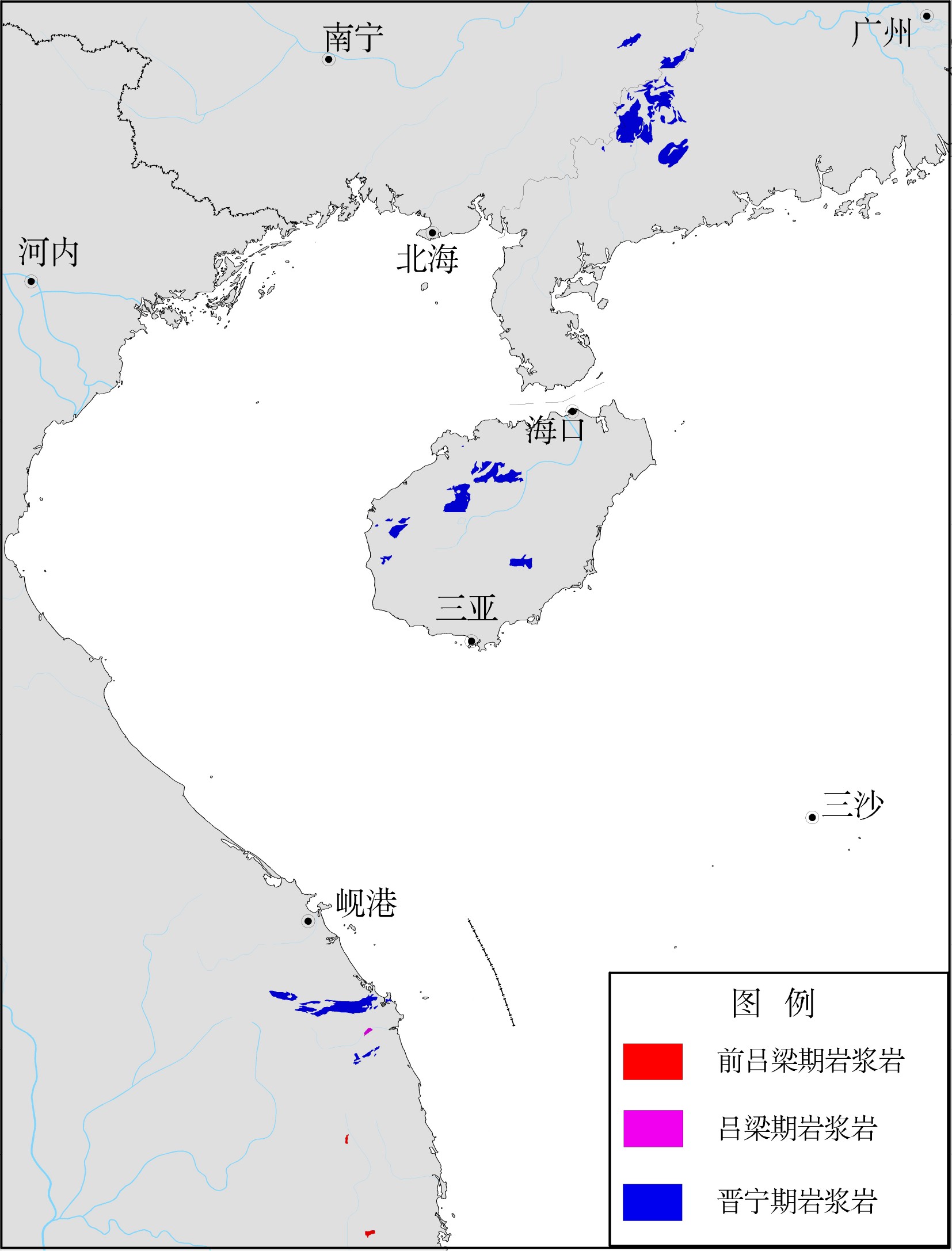
图 1 南海及邻区加里东期之前岩浆岩分布图[7]
Figure 1.
图 2 南海及邻区加里东期岩浆岩分布图[7]
Figure 2.
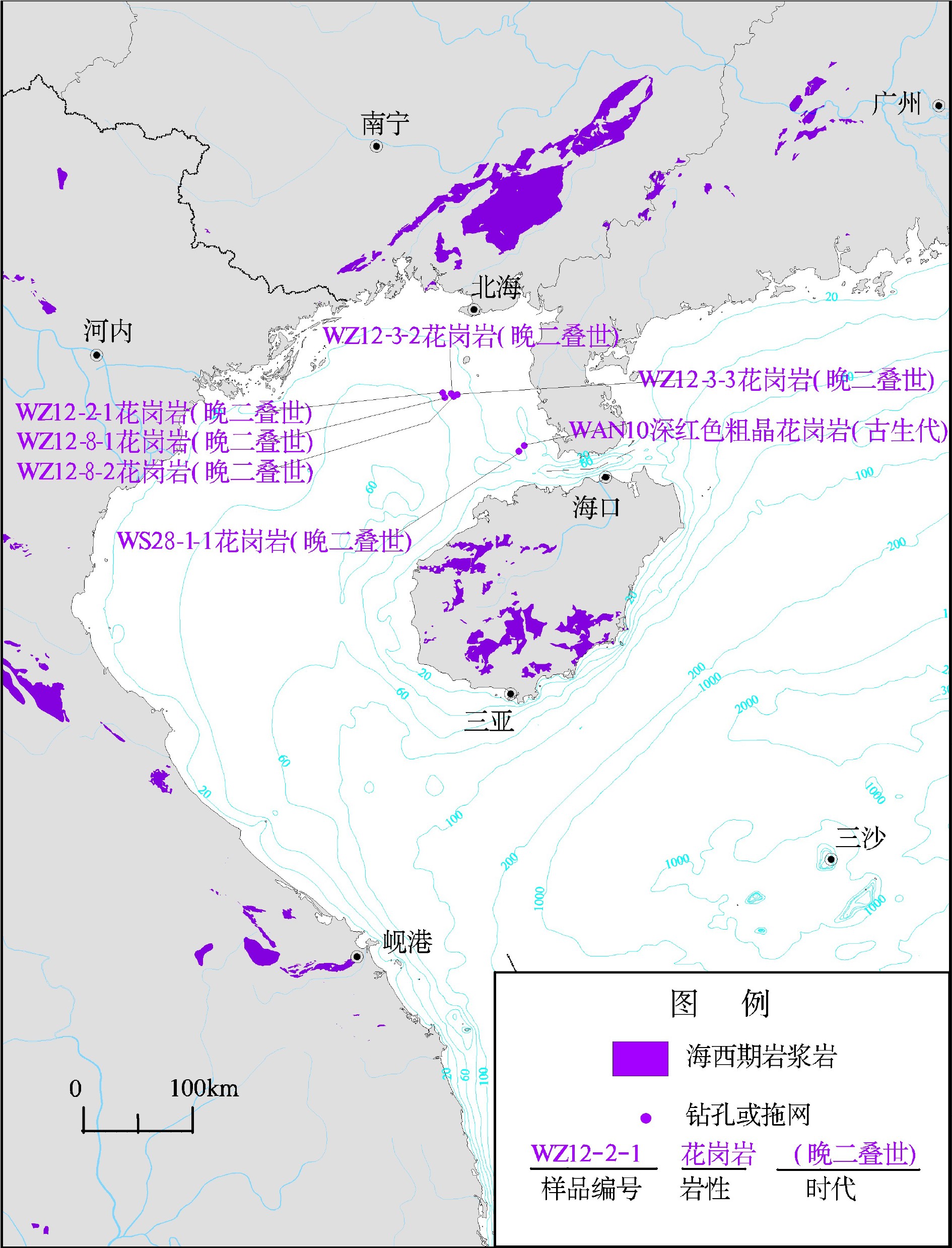
图 3 南海及邻区海西期岩浆岩分布图[7]
Figure 3.
图 4 南海及邻区印支期岩浆岩分布图[7]
Figure 4.
图 5 南海及邻区燕山期岩浆岩分布图[7]
Figure 5.
图 7 南海及邻区喜马拉雅期岩浆岩分布图[89]
Figure 7.
表 1 南海侵入岩的钻孔和拖网数据
Table 1. Intrusive rocks collected by borehole and trawling in the South China Sea
编号 位置 水深/m 钻孔深度或钻穿厚度/m 基底岩性 地质时代/Ma 测试方法 所属盆地 数据来源 WZ12-2-1 20.7707858°N 108.9019064°E 3075 花岗岩(γ) 晚二叠世? 北部湾盆地 文献[24] WZ12-3-1 20.7600861°N 108.9971083°E 1490.0 花岗岩(γ) 237.8±3.6/? 涠西南坳陷 文献[24] 1490.0 花岗岩(γ) 237.8~243.3 涠西南坳陷 文献[36] WZ12-3-2 20.7629417°N 108.9791333°E 1786.24 花岗岩(γ) 晚二叠世 北部湾盆地 文献[24] WZ12-3-3 20.755125°N 109.0311417°E 1536.4 花岗岩(γ) 晚二叠世 北部湾盆地 文献[24] WZ12-8-1 20.7317261°N 108.9209772°E 1335 花岗岩(γ) 晚二叠世? 北部湾盆地 文献[24] WZ12-8-2 20.7390947°N 108.9987897°E 1352 花岗岩(γ) 晚二叠世? 北部湾盆地 文献[24] WAN10 20.3326667°N 109.6249444°E 1741~1871.87 深红色粗晶花岗岩 古生代(Pz) 流沙凸起 文献[25] WS28-1-1 20.2828611°N 109.5755278°E 1666 花岗岩(γ) 晚白垩世 北部湾盆地 文献[24] HK17-1-1 19.6626164°N 107.7470506°E 1525 花岗片麻岩(gn) 早白垩世 莺歌海盆地 文献[24, 36-37] HK30-3-1A 19.2515728°N 107.9488453°E 1986 花岗片麻岩(gn) 早白垩世 莺歌海盆地 文献[24, 36-37] YINGQ2或Y7 18.3885222°N 108.5550556°E 683.4~689.4 黑云母花岗岩(γβ) 90.41~95.51 莺歌海盆地 文献[24, 36-37] 海2 18.4843311°N 108.6989831°E 143.09 花岗岩(γ) 白垩纪(K) 莺歌海盆地 文献[24, 36-37] 海3 18.4088889°N 108.7254167°E 312.25 花岗岩(γ) 白垩纪(K) 莺歌海盆地 文献[24, 36-37] LT35-1-1(Y8) 18.0300889°N 108.7725611°E 1715 花岗岩(γ) 224±2 莺歌海盆地 文献[24, 36-37] YC13-1-1 17.514225°N 109.0087556°E 3822.19 花岗岩(γ) 194~226 莺歌海盆地 文献[24, 36-37] YC19-1-1 17.3844944°N 109.1117444°E 5120.7 花岗闪长岩(γδ) 白垩纪? 莺歌海盆地 文献[24, 36-37] YING9 18.081625°N 110.29935°E 2850 花岗岩(γ) 156~185/106.9 琼东南盆地 文献[24] QH36-2-1 19.1214722°N 111.8535111°E 1251 花岗岩(γ) 前新生代? 神狐隆起 文献[24] WC2-1-1 19.8497694°N 112.2389°E 3594~3641.3 黑云母闪长岩(δβ) 118 珠三凹陷 文献[24] YJ23-1-1 20.4111775°N 112.8087492°E 1865~1874.5 花岗闪长岩 47~55 珠三凹陷 文献[24] EP25-1-1 20.2899428°N 113.1222039°E 3164 花岗岩(γ) 晚白垩世 珠三凹陷 文献[24] KP9-1-1 19.8209222°N 113.4849167°E 1753/ 23 石英岩(碎裂花岗岩(γ)?) 153±6 Rb-Sr 珠三凹陷 文献[24] 1662~1774 石英岩(碎裂花岗岩(γ)?) 153±6 Rb-Sr 神狐隆起 文献[38] EP18-1-1A 20.5353861°N 113.9861556°E 3448.25 A型花岗岩(γ) 100.5±1.7 K-Ar 番禺凸起 文献[39] L2-1A 2480~2483.5 二云母花岗岩 100.38±1.46 K-Ar 番禺凸起 文献[38] 2480~2483.5 二云母花岗岩 94.38±1.89 Rb-Sr 番禺凸起 文献[38] EP25-1-1 3164/ 26 花岗岩(γ) 番禺凸起 文献[7] PY3-1-1 20.9753833°N 114.4358683°E 3171/ 21.5 花岗岩(γ) 90.7±3.3 K-Ar 番禺凸起 文献[7] PY4-1-1 20.8704°N 114.6006075°E 3192~3192.5 花岗岩(γ) 130±5 K-Ar 番禺凸起 文献[24, 38] P4-1-1 20.8704°N 114.6006075°E (3160?) 花岗岩(γ) 130±5 K-Ar 番禺凸起 文献[24, 38] PY14-5-1 20.6664969°N 114.2142311°E 3164 花岗岩(γ) 晚白垩世 番禺凸起 文献[24, 38] 3788/ 29 花岗岩(γ) 晚白垩世 番禺凸起 文献[7] PY15-1-1 20.5591781°N 114.4061464°E 4401.5/ 78.5 A型花岗岩(γ) 89.8 番禺凸起 文献[7, 24] PY16-1-1 20.4256994°N 114.9925253°E 2375.5/ 13.5 苏长岩 番禺凸起 文献[3, 7] PY20-1-1 3856/ 57 黑云母花岗岩 番禺凸起 文献[3, 7] PY21-3-1 20.4634531°N 114.3774097°E 4019.5 黑云母花岗岩(γβ) 晚白垩世 番禺凸起 文献[24] 4018~4019.5 黑云母碎裂花岗岩 89.83±1.32 K-Ar 番禺凸起 文献[38] 4019.5~4068 黑云母碎裂花岗岩 89.83±1.32 K-Ar 番禺凸起 文献[7] PY24-1-1 20.4651103°N 114.9123403°E 4414.3 石英闪长岩(δo) 31.4±1.6 番禺凸起 文献[24] 4417 绿帘斜长角闪岩 45.3±2.2 番禺凸起 文献[7] 4414.9 绿帘斜长角闪岩 42.5±2.1 番禺凸起 文献[7] 4391/ 27.6 闪长岩 42.5±2.1 番禺凸起 文献[7] 3577 石英二长岩(ηo) 118.9±2.1 K-Ar 番禺凸起 文献[24] 3607~3609 石英二长岩(ηo) 118.9±2.1 K-Ar 番禺凸起 文献[8, 38] 3577.5/ 31.5 石英二长岩(碎裂花岗岩) 118.9±2.1 K-Ar 番禺凸起 文献[7] ZHU1 21.1954167°N 113.5735°E 1756.6 粗粒花岗岩(γ) 晚白垩世 珠一凹陷 文献[24] 1817.9/ 30.02 粗粒花岗岩(γ) 73~76 K-Ar 珠一凹陷 文献[7] 1846~1847 粗粒花岗岩(γ) 73~76 K-Ar 珠一凹陷 文献[38] ZHU2 21.3818°N 114.51625°E 2270.2 粗粒黑云母花岗岩(γβ) 70.6 珠一凹陷 文献[24] 2372/ 8.2 粗粒黑云母花岗岩(γβ) 70.5 K-Ar 珠一凹陷 文献[7] ZHU3 21.0088889°N 113.6030556°E 3150.3 花岗闪长斑岩(γδπ) 69~70.5 珠一凹陷 文献[24] ZHU4 21.2248556°N 114.2726°E 3203.5/ 21.9 粗粒黑云母花岗岩(γβ) 75 珠一凹陷 文献[7, 24] ZHU5 21.0178583°N 114.5018278°E 3231/ 31.3 花岗闪长斑岩(γδπ) 75 K-Ar 珠一凹陷 文献[7, 24] ZHU7 21.3546389°N 114.7583889°E 3664.5/ 18.5 花岗岩(γ) 晚白垩世 珠一凹陷 文献[7, 24] XJ17-3-1 21.5356314°N 114.6825517°E 2122.4~2124.7 碎裂花岗岩(γ) 79.2±2.8 K-Ar 珠一凹陷 文献[39] XJ24-3-1A 21.3793353°N 114.9174625°E 4318.8~4319.1 碎裂花岗岩(γ) 98 K-Ar 珠一凹陷 文献[24] XJ24-3-1A 21.3793353°N 114.9174625°E 4123/ 196.1 石英二长岩(碎裂花岗岩) 98 K-Ar 珠一凹陷 文献[7] XJ24-1-1X 21.3457967°N 114.9778269°E 3760/ 93.1 碎裂石英二长岩 84 K-Ar 珠一凹陷 文献[7, 24] XJ30-1-1X 21.2426089°N 114.9531644°E 3152/ 18.1 花岗闪长岩(γδ) 晚白垩世 珠一凹陷 文献[7, 24] XJ30-2-1X 21.2685792°N 114.9648378°E 3577/ 59.2 花岗岩(γ) 晚白垩世 珠一凹陷 文献[7, 24] XJ36-3-1X 21.1412375°N 114.8985233°E 3725/ 127.7 花岗闪长碎裂岩 晚白垩世 珠一凹陷 文献[7, 24] HZ10-1-1 21.78743°N 115.65173°E 2763/ 26 花岗岩(γ) 晚白垩世 珠一凹陷 文献[7, 24] HZ25-2-1X 21.2361169°N 115.0153417°E 3176/ 20.4 A型花岗碎裂岩(γ) 99.8±1.53 K-Ar 珠一凹陷 文献[7, 38] HZ26-1-1 21.1808186°N 115.2542047°E 2470.5 花岗岩(γ) 前新生代? 珠一凹陷 文献[24] HZ26-1-2 21.1666197°N 115.2690072°E 2591/ 29 花岗岩(γ) 前新生代? 珠一凹陷 文献[24] HZ32-3-2 21.1645289°N 115.1681739°E 2662 花岗岩(γ) 前新生代? 珠一凹陷 文献[24] HZ32-2-1 21.1613889°N 115.1699444°E 2718/ 9 花岗岩(γ) 88.5±3.6/K2 K-Ar 珠一凹陷 文献[7, 24, 39] HZ32-2-2 21.1613136°N 115.1698689°E 2783.5/ 17.5 花岗岩(γ) 前新生代? 珠一凹陷 文献[7, 24, 39] HZ32-3-1 21.1645694°N 115.2181278°E 2614/ 11 花岗岩(γ) 前新生代? 珠一凹陷 文献[7, 24, 39] HZ32-4-1 21.0886822°N 115.2174694°E 2740/ 11 花岗岩(γ)或火山碎屑岩 前新生代? 珠一凹陷 文献[7, 24, 39] HZ32-1-1 21.0798314°N 115.2805522°E 2785.5 花岗碎裂岩(γ) 前新生代? 珠一凹陷 文献[24] 2785.5/ 13.5 花岗碎裂岩(石英二长岩) 88.5±3.6 K-Ar 珠一凹陷 文献[7] LF13-1-1 21.5883236°N 116.15731°E 3193/ 32 S型花岗碎裂岩(γ) 晚白垩世 珠一凹陷 文献[24] LF22-1-1 21.4791908°N 116.6324847°E 1726/ 49 花岗岩(γ) 前新生代? 珠一凹陷 文献[24] HF28-2-1 20.2650631°N 116.61801°E 3898/ 45.6 苏长岩(花岗闪长岩?) 92.9、109.25±2.4 K-Ar 珠一凹陷 文献[7] HJ32-1-1 22.0798547°N 117.2266481°E 1719 花岗岩(γ) 前新生代? 珠一凹陷 文献[24] HF33-3-1 22.0085583°N 116.407725°E 3278.2 辉岩闪长玢岩(νδ) 晚白垩世 珠一凹陷 文献[24] 3277~3286.5 辉岩闪长玢岩(νδ) 31.9±0.67 珠一凹陷 文献[7] HZ33-1-1 21.1485683°N 115.3502656°E 2610~2683.3 花岗岩(γ) 86.2~93.2 东沙隆起 文献[7] HZ22-1-1 21.3382947°N 115.6333631°E 2798.5/ 26.5 花岗岩(γ) 前新生代? 东沙隆起 文献[7, 24, 38] HZ34-1-1 21.0542189°N 115.5494719°E 2300/ 26 花岗岩(γ) 前新生代? 东沙隆起 文献[7, 24, 38] HZ35-1-1 21.09249°N 115.6803603°E 2212.5/ 6.4 花岗岩(γ) 105 K-Ar 东沙隆起 文献[7, 24, 38] LH11-1-1A 20.8219019°N 115.6984806°E 1836.5 碎裂花岗闪长岩 90.62±1.49 K-Ar 东沙隆起 文献[38] L11-1-1A 20.8219019°N 115.6984806°E 1822~1837.5 碎裂花岗闪长岩 72.78±1.37 Rb-Sr 东沙隆起 文献[38] LH1-1-1X 2572.5/ 20.5 花岗碎裂岩 东沙隆起 文献[7] LH11-1-2 20.7844997°N 115.8489944°E 花岗岩(γ) 前新生代? 珠一凹陷 文献[24] LF15-1-1 21.46°N 116.49°E 2160 闪长岩(错误?) 40.9±1.63 珠一凹陷 文献[7] 2166.5 闪长岩(错误?) 45.1±1.8 珠一凹陷 文献[7] LH18-1-1 20.5918061°N 116.9363603°E 1838/ 36.5 花岗岩(γ) 前新生代? 东沙隆起 文献[7, 24] LH18-2-1 20.5025308°N 116.9559031°E 1864/ 20.3 花岗岩(γ) 前新生代? 东沙隆起 文献[7, 24] DS7-1-1 20.6810181°N 116.1058203°E 1333/ 40.7 花岗岩(γ) 前新生代? 东沙隆起 文献[7, 24] LH19-4-1 20.2068056°N 116.1330833°E 3068.5 闪长岩(δ) 早白垩世 白云凹陷 文献[24] LH21-1-1 20.4725725°N 115.3597025°E 2779 闪长岩(δ) 前新生代? 白云凹陷 文献[24] LF35-1-1 21.0586278°N 116.7017308°E 1423~1500 花岗岩 102 Ar/Ar 潮汕凹陷 文献[40] XY1 16.8413806°N 112.3432639°E 1384 花岗片麻岩(gnγ) 1450 西沙群岛 文献[24] 1251~1384.6 花岗片麻岩、花岗岩 1400、627、68.9 西沙群岛 文献[41] XK1-2 16.8458333°N 112.3472222°E 1260~1262 花岗岩(γ) 107.8±3.6 U-Pb 西沙群岛 文献[42] WT-67 3552.3 碎裂黑云母花岗岩 108±3 K-Ar 湄公盆地 文献[4, 43-44] WT-91 3540.8 黑云母花岗闪长岩 149±5 K-Ar 湄公盆地 文献[4, 43-44] WT-810 3411.8 角闪石黑云母花岗闪长岩 135±4 K-Ar 湄公盆地 文献[4, 43-44] WT-402 3594.1 黑云母花岗岩(微碎裂岩) 108±4 K-Ar 湄公盆地 文献[4, 43-44] Dragon-3 3548.3 黑云母微斜长石花岗岩 159±5 K-Ar 湄公盆地 文献[4, 43-44] Dragon-9 2597 黑云母花岗岩(碎裂岩) 178±5 K-Ar 湄公盆地 文献[4, 43-44] Tamdao-1 3391.5 浅色斑状石英闪长岩 97±3 K-Ar 湄公盆地 文献[4, 43-44] DaiHung2 8.4861111°N 108.69°E 3685 花岗岩 前第三纪 湄公盆地 文献[4, 43-44] BB-2 8.4861111°N 108.69°E 2805.7 花岗闪长岩和石英闪长岩 109±5 K-Ar 万安盆地 文献[45] BB-3 8.4975°N 108.635833°E 3533.1 花岗闪长岩和石英闪长岩 105±5 K-Ar 万安盆地 文献[45] DaiHung-1 8.4533333°N 108.64472°E 3352 花岗闪长岩(γδ) 前新生代? 文献[24] 15G-1x 10.424722°N 108.36278°E 2925 花岗岩(γ) 前第三纪 湄公盆地 文献[24] 15C-1x 9.966944°N 108.30389°E 3276 花岗岩(γ) 前第三纪 湄公盆地 文献[24] 28-A-1X 7.3973056°N 106.86684°E 1504 石英闪长岩(δo) 前新生代? 万安盆地 文献[24] Dua-12-B-1X 7.5002778°N 108.2675°E 3889 花岗岩(γ) 前新生代? 万安盆地 文献[24] Dua-12-C-1X 7.5213889°N 108.02222°E 花岗岩(γ) 前新生代? 万安盆地 文献[24] 3587 花岗岩(γ) 万安盆地 文献[43] Dua-1X 7.4394444°N 108.42889°E 4013 花岗岩(γ) 白垩纪 万安盆地 文献[43] Cipta-B 6.3036111°N 108.54861°E 3274 花岗闪长岩(γδ) 万安盆地 文献[43] AT-1X 5.485°N 108.66472°E 1768 黑云母花岗闪长岩 80±2.4 万安盆地 文献[43] AS-1X 6.84785°N 108.42414°E 1726 黑云母角闪石花岗闪长岩 129±7 万安盆地 文献[43] 两兄弟群岛 花岗岩(γ) 70±3 湄公盆地 文献[43] AP-1X 5.5169694°N 109.61806°E 4199 花岗闪长岩(γδ) 79.3±4.7 K-Ar 曾母盆地 文献[24] 4199 深成岩 文献[43] Non-name-1 1.95°N 109.48333°E 花岗岩(γ) 75±5 K-Ar 曾母盆地 文献[24] 花岗岩(γ) 75±5 K-Ar 婆罗洲西北 文献[43] Non-name-2 1.616667°N 109.71667°E 花岗岩(γ) 75.6±4 K-Ar 曾母盆地 文献[24] 花岗岩(γ) 75.6±4 K-Ar 婆罗洲西北 文献[43] Ga-bus-6 1301.5 云母角闪石英二长岩 110 K-Ar 纳土纳盆地 文献[22] Dumaran-1 10.326667°N 119.93944°E 2043 超基性岩(σ) 晚白垩世 西北巴拉望 文献[24] 130 2033 蛇纹石化橄榄岩 文献[46] SO23-23 9.9°N 115.86667°E 1900 橄榄辉长岩及流纹凝灰岩 T3~J1 礼乐滩 文献[24] 1700 橄榄石辉长岩与流纹岩 T3~J1 礼乐滩 文献[45] SO27-24 9.883333°N 115.83333°E 2100 闪长岩及流纹质凝灰岩 中三叠世(T2)? 礼乐滩 文献[45] SO49-16 闪长岩、
辉长岩140~150 中沙海台 文献[41] SO49-36 闪长岩、
辉长岩140~150 中沙海台 文献[41] SO23-36 12.1°N 116.58°E 2373 多孔玄武岩(角闪岩?) 146 文献[47] 1yDG 11.483333°N 114.066666°E 3000 细粒黑云母花岗岩 早白垩世晚期 西南次海盆 文献[24] 3000 二长花岗岩 109.7、114.2、120 Ar/Ar 西南次海盆 文献[48] 3000 二长花岗岩 109.7、114.2、120 K-Ar 西南次海盆 文献[48] 3000 二长花岗岩 153.6±0.3、127.2±0.2 U-Pb 西南次海盆 文献[49] 2yDG 11.7833333°N 114.943333°E 2800 花岗岩 早白垩世晚期 西南次海盆 文献[24] 2800 斜长花岗岩 159.1±1.6、157.8±1.0 U-Pb 西南次海盆 文献[49] 3yDG 13.466666°N 114.333333°E 花岗闪长岩 早白垩世晚期 西南次海盆 文献[24] 大珍珠海山 12.715842°N 115.931635°′E 花岗闪长岩 127~122 西南次海盆 文献[7] 表 2 南海喷出岩的钻孔和拖网数据
Table 2. Extrusive rocks collected by borehole and trawling in the South China Sea
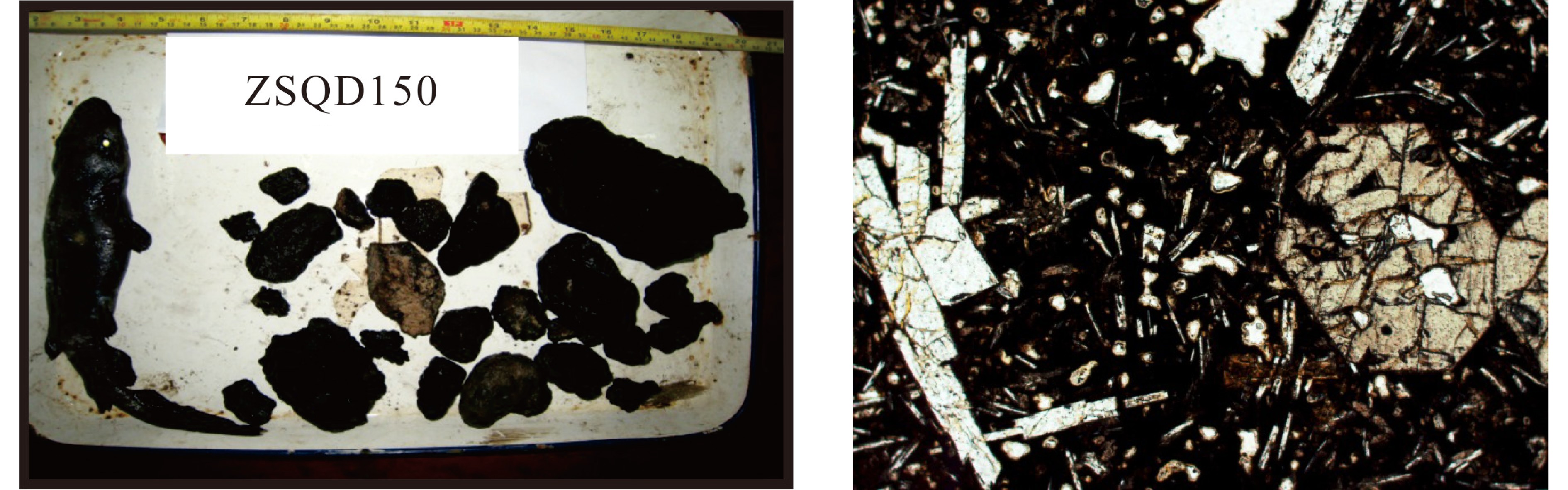
编号 位置 水深/m 钻孔深度或钻穿厚度/m 基底岩性 地质时代/Ma 测年方法 所属盆地 数据来源 YING6 (YIN6) 17.9209528°N 108.9414694°E 2222.4~2132.1 安山岩(α) 68.24/K2 莺歌海盆地 文献[24, 36] 2222.4~2132.1 凝灰质砂岩 97.21 莺歌海盆地 文献[24, 36] YX32-1-1 18.0498178°N 109.2959547°E 680 安山岩(α) 白垩纪(K)? 莺歌海盆地 文献[24, 36] YC14-1-1 17.6895472°N 109.2135361°E 3158 英安流纹岩(ξλ) 82.8±1.7 莺歌海盆地 文献[24, 36] Y5 凝灰质砂岩 97.21(K) 莺歌海盆地 文献[37] LS2-1-1 17.9196208°N 110.1194206°E 2769 安山玢岩(αμ) 93.92 琼东南盆地 文献[24] BD6-1-1 18.9361917°N 111.8582528°E 2133 火山集块岩 87 神狐隆起 文献[24] WC8-2-1 19.7298319°N 112.1648825°E 2682 流纹斑岩(λπ) 前新生代? 珠三凹陷 文献[24] YJ26-1-1 20.2053333°N 112.2934167°E 1702.8 流纹斑岩(λπ) 89.2±1.6 K-Ar 珠三凹陷 文献[24] 1700~1702 流纹斑岩(λπ) 89.2±1.58 K-Ar 珠三凹陷 文献[39] YJ21-1-1 20.5063347°N 112.4169481°E 1620~1656 流纹岩 51.6 珠三凹陷 文献[24] YJ21-1-1 20.45°N 112.3°E 1650 流纹岩 51.6±0.2 珠三凹陷 文献[7] 1648~1656 流纹质岩屑晶屑熔岩 51.6±8.3 珠三凹陷 文献[3] KP6-1-1 19.8369458°N 113.8571342°E 2728/ 28.7 凝灰角砾岩 前新生代? 珠三凹陷 文献[24] PY16-1-1 20.48°N 114.85°E 2384 含长石玄武岩(β) 41.2±2 番禺凸起 文献[69] 2384~2387 含长石玄武岩(β) 41.2±2 番禺凸起 文献[3] XJ33-2-1A 21.11°N 114.3°E 4868.5~4887 玄武岩 24.3±1.3 番禺凸起 文献[3] XJ34-3-1 21.0090358°N 114.5016478°E 3296/ 4 火山集块岩 78.5±3.2 番禺凸起 文献[24] HZ18-1-1 3410/ 1 凝灰岩 珠一凹陷 文献[7] HZ25-1-1X 3041/ 1 火山集块岩 珠一凹陷 文献[7] HZ32-4-1 21.0886822°N 115.2174694°E 2740/ 11 花岗岩(γ)或火山碎屑岩 前新生代? 珠一凹陷 文献[24] LF1-1-1 21.9°N 116.05°E 3324~3455 流纹质凝灰岩 32±1.4或33.6±0.7 珠一凹陷 文献[69] 3445.4~3455 凝灰岩 33.58±0.7或32.0±1.4 珠一凹陷 文献[3] LF13-2-1 21.6324761°N 116.0436628°E 3280 安山岩(α) 晚白垩世(K2) 珠一凹陷 文献[24] HF28-2-1 20.2650631°N 116.61801°E 3898/ 45.6 苏长岩(花岗闪长岩?) 92.9、109.25±2.4 珠一凹陷 文献[7] HJ32-1-1 22.0798547°N 117.2266481°E 1695/ 24 火山集块岩/凝灰质砂岩 前新生代? 珠一凹陷 文献[7] BY7-1-1 19.65°N 114°E 3500.7 玄武质熔岩层 35.5±2.78 K-Ar 珠二坳陷 文献[3, 69] 2752 凝灰岩 17.6±1.8 K-Ar 珠二坳陷 文献[3, 69] 2429 玄武岩 17.1±2.5 K-Ar 珠二坳陷 文献[3, 69] HZ33-1-1 21.1485683°N 115.3502656°E 2731 玄武岩 41.1±4 东沙隆起 文献[3] HZ33-2-2 21.2617428°N 115.4557706°E 2455.5/ 14.5 安山岩(α) 前新生代? 东沙隆起 文献[24] LH11-1-2 20.77°N 115.8°E 1800 英安岩 27.2±0.6 珠一凹陷 文献[3, 69] 1672~1813 玄武岩 27.17±0.55 珠一凹陷 文献[3, 69] LH4-1-1 20.85°N 115.5°E 1669~1979 英安岩、凝灰岩 43.15±0.7 珠一凹陷 文献[69] HZ21-1-1 21.32°N 115.31°E 4480~4696 英安岩 41.1 K-Ar 东沙隆起 文献[69] 4591 英安斑岩 27.7±1.8 K-Ar 东沙隆起 文献[7, 38] 4588~4604 41.1±0.67 K-Ar 东沙隆起 文献[7, 38] HZ27-1-1 21.36°N 115.4°E 3016~3066 安山岩 57.1±2.5 东沙隆起 文献[3] 井底捞块 安山岩 45.3±2.9 东沙隆起 文献[7] LF15-1-1 21.46°N 116.49°E 2166.5 玄武岩 45.1±1.63 珠一凹陷 文献[3] L15-1-1 21.46°N 116.49°E (2175?) 玄武岩 45.1±1.63 陆丰坳陷 文献[70] LF21-1-1 21.4°N 116.37°E 2223~2446 流纹质凝灰岩 49.33 珠一凹陷 文献[69] 2290 凝灰岩 47.3±1.1 珠一凹陷 文献[7] ODP1148 18.84°N 116.57°E 3249 英安质凝灰岩 <1 珠江口盆地 文献[69] LF35-1-1 21.0586278°N 116.7017308°E 1030 流纹岩 珠一凹陷 文献[7] 1369~2376 玄武岩 36~118 珠一凹陷 文献[24] LW3-1-1 19.9°N 115.4°E 2746~3458 砂泥岩夹层含火山岩 珠江组 白云凹陷 文献[71] SO9-1 18.2997222°N 115.1172222°E 粗面岩 23.29±0.22 40Ar/39Ar 双峰海山 文献[57] SO9-2 18.2997222°N 115.1172222°E 粗面岩 23.8±0.18 40Ar/39Ar 双峰海山 文献[57] SCS-1 21.1666666°N 119.2°E 碱性玄武岩 21±0.2 40Ar/39Ar 浦元海山 文献[72] SCS-2-3 21°10′N 119.2°′E 碱性玄武岩 22.1±0.2 40Ar/39Ar 浦元海山 文献[72] CM-1X 14°16′22″N 109°38′17″E 500 玄武岩 中新世 西部陆架 文献[73] 04-B-1X 8.6277778°N 108.97222°E 2442 火山岩(v) 白垩纪(K)? 万安盆地 文献[24] 2442 火山岩(v) 燕山期的前白垩纪 万安盆地 文献[4] 04-B-2X 8.6272222°N 108.89056°E 2593 火山岩(v) 白垩纪(K)? 万安盆地 文献[24] 2593 火山岩(v) 燕山期的前第三纪 万安盆地 文献[4] AY-1X 5.6188889°N 109.46889°E 2811 火山集块岩 54.6±2.7 K-Ar 曾母盆地 文献[43] Terubuk-1 2563.6 安山质变质熔岩 169±7 纳土纳盆地 文献[22] Af-1x 3048~3094.9 喷出岩 92.4 K-Ar 纳土纳盆地 文献[22] Ilog-1 10.2012333°N 122.6373333°E 57 1676 砾岩火山岩 ?中中新世 文献[46] ODP769 08.7853333°N 121.2946666°E 3644 376.9 凝灰岩和火山泥石流 早中新世晚期 文献[46] ODP767 04.7916666°N 123.5033333°E 4916 786.6 玄武岩 上层中始新世粘土岩 文献[46] SO23-23 9.9°N 115.86667°E 1900 橄榄辉长岩及流纹凝灰岩 T3~J1 礼乐滩 文献[24] 1700 橄榄石辉长岩与流纹岩 T3~J1 礼乐滩 文献[45] SO27-24 9.883333°N 115.83333°E 2100 蚀变闪长岩及流纹质凝灰岩 中三叠世(T2)? 礼乐滩 文献[45] SO23-36 12.1°N 116.58°E 2373 多孔玄武岩(角闪岩?) 146 礼乐滩 文献[47] SO23-37 12.08°N 116.62°E 3227~ 气孔状玄武岩 0.4 K-Ar 文献[45] 3043 气孔状玄武岩 0.4 K-Ar 文献[45] SO23-38 11.73°N 118.3°E 1610~ 橄榄玄武岩 0.5 K-Ar 文献[45] 1356 橄榄玄武岩 0.5 K-Ar 文献[45] SO23-40 12.35°N 118.82°E 1050~765 气孔状斑晶玄武岩 2.7 K-Ar 文献[45] SO23-15 8.17°N 119.37°E 3312 斑状安山岩 14.7±0.6 K-Ar 文献[45] SO27-70 9.310666°N 115.336166°E 1589 蚀变斑状流纹岩 文献[47] Tara-1 11.444333°N 119.066833°E 80.2 2166.8 火山凝灰岩夹层 文献[46] Batas-1 11.338333°N 118.928333°E 83.5 2432.3 火山角砾岩 文献[46] Cadlao-1 11.3205°N 118.9965°E 94.8 3191.2 凝灰岩 晚侏罗世 文献[46] Boayan 1-1A 10.669166°N 118.5595°E 93.7 3095.2 火山岩 文献[46] Cacnipa-1 10.648166°N 118.5975°E 76.2 2775.8 下中新统灰岩下为火山岩 文献[46] Albion- head1 9.518°N 117.786833°E 9.2 3776.5 火山碎块 文献[46] ODP771 8.678166°N 120.679666°′E 2859 304.1 火山碎屑 17.8 文献[46] ODP768 8.000666°N 121.219666°E 4395.5 1268.5 早中新世晚期凝灰岩 文献[46] Odp184-1143 9.36°N 113.28°E 2772 凝灰岩,火山灰 <2 文献[69] ZF-1 19.33°N 116.16°E 1500~2000 流纹英安岩 18.61±4.88 K-Ar 尖峰海山 文献[74] S8 17.616666°N 116.983333°E 3429 石英拉斑玄武岩 14.1±1.14 K-Ar 玳瑁海山 文献[75-76] S8 3429 石英拉斑玄武岩 13.8±1.03 40Ar/39Ar 玳瑁海山 文献[75-76] 9DG 15.23333°N 117.08333°E 粗面玄武岩 7.77±0.49 K-Ar 黄岩海山 文献[77] 玳瑁海山 17.22°N 117.01°E 碱性玄武岩 20~26 玳瑁海山 文献[7] 涨中海山 13.68°N 115.27°E 碱性玄武岩 7 涨中海山 文献[7] CB-2 拉斑玄武岩 38±1.2 宪北海山 文献[74] ZSQD148 16.7°N 116.8°E 碱性玄武岩(火山角砾) 22.9±0.42 K-Ar 宪北海山 文献[7] 碱性玄武岩(火山角砾) 15.26±0.26 K-Ar 宪北海山 文献[7] 二辉橄榄岩(火山角砾 87.21±2.17 K-Ar 宪北海山 文献[7] ZSQD119 16.39°N 116.29°E 气孔状伊丁玄武岩 12.4±0.21 Ar-Ar 石星海山 文献[7] ZSQD150 16.11°N 116.73°E 气孔状拉斑玄武岩 15.04±1.61 Ar-Ar 宪南海山 文献[7] 9 14.8°N 116.5°E 石英拉斑玄武岩 9.5±0.92 K-Ar 珍贝海山 文献[76] 石英拉斑玄武岩 9.9±1.4 40Ar/39Ar 珍贝海山 文献[76] V36D10 14°N 115.59°E 碱性玄武岩 3.49±0.58 K-Ar 中南海山 文献[78] NO.8 17.75°N 116.98°E 拉斑玄武岩 13.95 K-Ar 南海海盆 文献[64] NO.9 15.00°N 116.52°E 拉斑玄武岩 9.7 K-Ar 南海海盆 文献[64] DR01 15.75°N 116.18°E 碱性玄武岩 11~6 南海海盆 文献[7] DR02 15.30°N 115.96°E 碱性玄武岩 11~6 南海海盆 文献[7] DR03 14.95°N 116.21°E 粗玄岩 8~6 南海海盆 文献[7] D1 13.37°N 111.97°E 碱性玄武岩 0.4 南海海盆 文献[4] D3 9.95°N 111.17°E 碱性玄武岩 4.3 K-Ar 南海海盆 文献[4] 黄岩西海山 15.17°N 117.20°E 玄武岩 7.94±0.06 南海海盆 文献[7] U1431 15.3756333°N 116.999838°E 4240± 拉斑玄武岩 15±0.2 南海海盆 文献[7] U1433 12.918855°N 115.047473°E 4379± 拉斑玄武岩 17.5 南海海盆 文献[7] 大珍珠海山 12.7158416°N 115.9315°E 花岗闪长岩 127~122 南海海盆 文献[7] 小珍珠海山 12.903086°N 116.5495°E 火山玻璃 0.95 南海海盆 文献[7] HYD239 15.40720°N 118.54394°E 3093 碱性玄武岩 8.98±0.18 Ar-Ar 黄岩海山 文献[7] HYD180a 15.14337°N 117.37870°E 2430 碱性玄武岩 7.83±0.06 Ar-Ar 黄岩海山 文献[7] HYD224 15.26368°N 118.19459°E 2660 碱性玄武岩 7.88±0.01 Ar-Ar 黄岩海山 文献[7] HYD-104-3 15.56346°N 116.18180°E 815 碱性玄武岩 6.67±0.03 Ar-Ar 涨中海山 文献[7] HYD66-2 13.67885°N 115.27288°E 1378 碱性玄武岩 8.29±0.06 Ar-Ar 中南海山 文献[7] HYD-22QZ 15.02395°N 116.51811°E 1064? 碱性玄武岩 8.26±0.03 Ar-Ar 珍贝海山 文献[7] 碱性玄武岩 9 珍贝海山 文献[7] S04-11 16.34361°N 116.09922°E 2200 碱性玄武岩 7.91±0.19 K-Ar 宪北海山 文献[79] S04-12-10 15.57200°N 113.15934°E 1290 碱性玄武岩 4.78±0.11 K-Ar 涨中海山 文献[79] S04-12-11 15.57200°N 113.15934°E 1290 碱性玄武岩 5.74±0.13 K-Ar 涨中海山 文献[79] S04-12-18 15.57200°N 113.15934°E 1290 碱性玄武岩 5.18±0.17 K-Ar 涨中海山 文献[79] S04-12-20 15.57200°N 113.15934°E 1290 碱性玄武岩 4.76±0.12 K-Ar 涨中海山 文献[79] S04-12-21 15.57200°N 113.15934°E 1290 碱性玄武岩 4.94±0.11 K-Ar 涨中海山 文献[79] S04-14-1 14.03915°N 115.38454°E 1470 碱性玄武岩 6.33±0.20 K-Ar 中南海山 文献[79] S08-69-1 10.32166°N 112.53469°E 2280 碱性玄武岩 3.80±0.10 K-Ar 长屿海山 文献[79] -
[1] 汪品先, 翦知湣. 探索南海深部的回顾与展望[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2019, 62(10):1473-1488 doi: 10.1007/s11430-019-9484-4
WANG Pinxian, JIAN Zhimin. Exploring the deep South China Sea: Retrospects and prospects [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2019, 62(10): 1473-1488. doi: 10.1007/s11430-019-9484-4
[2] Sun Z, Lin J, Qiu N, et al. The role of magmatism in the thinning and breakup of the South China Sea continental margin: Special Topic: The South China Sea Ocean Drilling [J]. National Science Review, 2019, 6(5): 871-876. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwz116
[3] 李平鲁, 梁慧娴. 珠江口盆地新生代岩浆活动与盆地演化、油气聚集的关系[J]. 广东地质, 1994, 9(2):23-34
LI Pinglu, LIANG Huixian. Relation between Cenozoic igneous activity and basin evolution and oil-gas accumulation in Pearl River Mouth basin [J]. Guangdong Geology, 1994, 9(2): 23-34.
[4] 周蒂, 刘海玲, 陈汉宗. 南沙海区及其周缘中-新生代岩浆活动及构造意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2005, 29(3):354-363
ZHOU Di, LIU Hailing, CHEN Hanzong. Mesozoic-Cenozoic magmatism in southern South China Sea and its surrounding areas and its implications to tectonics [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2005, 29(3): 354-363.
[5] Yan P, Deng H, Liu H L, et al. The temporal and spatial distribution of volcanism in the South China Sea region [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2006, 27(5): 647-659. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.06.005
[6] 林间, 李家彪, 徐义刚, 等. 南海大洋钻探及海洋地质与地球物理前沿研究新突破[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(10):125-140
LIN Jian, LI Jiabiao, XU Yigang, et al. Ocean drilling and major advances in marine geological and geophysical research of the South China Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2019, 41(10): 125-140.
[7] 李学杰, 杨楚鹏, 姚永坚, 等. XX海域1: 100万海洋区域地质调查成果集成与应用研究成果报告[R]. 广州海洋地质调查局内部报告, 2018: 1-1439.
LI Xuejie, YANG Chupeng, YAO Yongjian, et al. Report on integration and application of 1: 1 million marine regional geological survey results in XX sea area[R]. Internal report of Guangzhou Marine Geological Survey Bureau, 2018: 1-1439.
[8] 张业明, 张仁杰, 姚华舟, 等. 海南岛前寒武纪地壳构造演化[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 1997, 22(4):395-400
ZHANG Yeming, ZHANG Renjie, YAO Huazhou, et al. The Precambrian crustal tectonic evolution in Hainan island [J]. Earth Science–Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1997, 22(4): 395-400.
[9] 广西壮族自治区地质矿产局. 广西壮族自治区区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1985: 1-853.
Bureau of Geology and Mineral of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. Regional Geology of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1985: 1-853.
[10] 许德如, 夏斌, 李鹏春, 等. 海南岛北西部前寒武纪花岗质岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2006, 30(4):510-518
XU Deru, XIA Bin, LI Pengchun, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb dating of Zircon from the Precambrian granitoids in northwest Hainan island and its geological implications [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2006, 30(4): 510-518.
[11] 吴良士. 越南社会主义共和国地质构造与区域成矿[J]. 矿床地质, 2009, 28(5):725-726
WU Liangshi. Geological tectonic and regional mineralization of Vietnam [J]. Mineral Deposits, 2009, 28(5): 725-726.
[12] 覃小锋, 周府生, 胡贵昂, 等. 云开地块北缘MORB型火山岩的首次发现及其大地构造意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2005, 24(3):20-24
QIN Xiaofeng, ZHOU Fusheng, HU Guiang, et al. First discovery of MORB volcanic rock and its tectonic significance on the north margin of the Yunkai block, southeastern Guangxi [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2005, 24(3): 20-24.
[13] 郭良田, 洪裕荣, 黄继春, 等. 粤西信宜地区坑坪细碧-角斑岩系的发现及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2005, 24(7):648-654
GUO Liangtian, HONG Yurong, HUANG Jichun, et al. Discovery of the Kengping spilite-kratophyre series in Xinyi, western Guangdong, China and its geological significance [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2005, 24(7): 648-654.
[14] 舒良树. 华南构造演化的基本特征[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(7):1035-1053
SHU Liangshu. An analysis of principal features of tectonic evolution in South China Block [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2012, 31(7): 1035-1053.
[15] 张业明, 付建明, 赵子杰, 等. 海南岛西部变基性火山岩的岩石特征及Sm-Nd同位素定年[J]. 矿物岩石, 1998, 18(1):79-84
ZHANG Yeming, FU Jianming, ZHAO Zijie, et al. Petrographic characteristics and Sm-Nd isotopic dating of the metamorphic basic volcanic rocks in western part of Hainan island [J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 1998, 18(1): 79-84.
[16] 梁新权, 范蔚茗, 许德如. 海南岛屯昌玄武质科马提岩Sm-Nd同位素年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质科学, 2000, 35(2):240-244
LIANG Xinquan, FAN Weiming, XU Deru. Sm-Nd age of Tunchang basaltic komatiites and its geological significance in Hainan island [J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 2000, 35(2): 240-244.
[17] 广东省地质矿产局. 广东省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1988: 1-941.
Bureau of Geology and Mineral of Guangdong Province. Regional Geology of Guangdong Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1988: 1-941.
[18] 周云, 梁新权, 梁细荣, 等. 莺歌海盆地志留纪花岗岩的发现及其构造意义[C]//2013年全国岩石学与地球动力学研讨会(摘要). 广州: 中国地质学会, 2013: 732-733.
ZHOU Yun, LIANG Xinquan, LIANG Xirong, et al. Discovery and tectonic significance of Silurian granites in Yinggehai Basin[C]//2013’s National Symposium on Petrology and Geodynamics (Abstract). Guangzhou: Geological Society of China, 2013: 732-733.
[19] 张业明, 徐安武, 付建明, 等. 海南岛几个重大基础地质问题的探讨[J]. 地质论评, 1998, 44(6):568-575
ZHANG Yeming, XU Anwu, FU Jianming, et al. Some important fundamental geological problems in Hainan Island [J]. Geological Review, 1998, 44(6): 568-575.
[20] 张喜松, 徐夕生. 华南早古生代火山岩分布、岩石成因及地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2015, 45(S1):75
ZHANG Xisong, XU Xisheng. Distribution, petrogenesis and geological significance of Early Paleozoic volcanic rocks in South China [J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2015, 45(S1): 75.
[21] 黄义聪, 卓伟华. 广西岑溪糯垌基性火山岩研究[J]. 广东地质, 2013(1):11-15
HUANG Yicong, ZHUO Weihua. Study on basic volcanic rocks in Nuodong, Cenxi, Guangxi [J]. Guangdong Geology, 2013(1): 11-15.
[22] 金庆焕. 南海地质与油气资源[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1989.
JIN Qinghuan. Geology and petroleum resources of the South China Sea[M]. Beijing: The Geological Publishing House, 1989.
[23] 毛建仁, 厉子龙, 叶海敏. 华南中生代构造-岩浆活动研究: 现状与前景[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2014, 57(12):2853-2877 doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-5006-1
MAO Jianren, LI Zilong, YE Haimin. Mesozoic tectono-magmatic activities in South China: Retrospect and prospect [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2014, 57(12): 2853-2877. doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-5006-1
[24] 邱燕, 王立飞, 黄文凯, 等. 中国海域中新生代沉积盆地[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016: 1-233.
QIU Yan, WANG Lifei, HUANG Wenkai, et al. Mesozoic Cenozoic sedimentary basins in China Sea area[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2016: 1-233.
[25] 赵汉卿, 梁经喜. 南海北部湾地区湾5井完井地质总结报告[R]. 茂名石油工业公司南海石油勘探指挥部, 1979.
ZHAO Hanqing, LIANG Jingxi. Summary report on completion geology of well Wan 5 in Beibu Gulf area of South China Sea[R]. South China Sea petroleum exploration headquarters, Maoming Petroleum Industry Company, 1979.
[26] 陈新跃, 王岳军, 张玉芝, 等. 海南晨星安山质火山岩地球化学、年代学特征及其构造意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2013, 37(1):99-108
CHEN Xinyue, WANG Yuejun, ZHANG Yuzhi, et al. Geochemical and geochronological characteristics and its tectonic significance of andesitic volcanic rocks in Chenxing Area, Hainan [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2013, 37(1): 99-108.
[27] 何慧莹, 王岳军, 张玉芝, 等. 海南岛晨星早石炭世高度亏损N-MORB型玄武岩及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(8):1361-1375
HE Huiying, WANG Yuejun, ZHANG Yuzhi, et al. Extremely depleted Carbonferous N-MORB metabasite at the Chenxing area (Hainan) and its geological significance [J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(8): 1361-1375.
[28] 王智琳, 许德如, 吴传军, 等. 海南岛晚古生代洋岛玄武岩(OIB型)的发现及地球动力学暗示[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(3):875-886
WANG Zhilin, XU Deru, WU Chuanjun, et al. Discovery of the Late Paleozoic ocean island basalts (OIB) in Hainan Island and their geodynamic implications [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(3): 875-886.
[29] 章金海, 洪清照, 何立士. 台湾省岩浆岩变质岩概况[J]. 中国地质, 1984(7):26-28
ZHANG Jinhai, HONG Qingzhao, HE Lishi. Overview of magmatic metamorphic rocks in Taiwan Province [J]. Chinese Geology, 1984(7): 26-28.
[30] 福建省地质矿产局. 台湾省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1992: 1-223.
Fujian Province Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. Regional geology of Fujian Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1992: 1-223.
[31] 黄长煌. 台湾玉里带变质岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(10):1722-1739
HUANG Changhuang. U-Pb isotopic ages of zircon from Yuli Belt in Taiwan and its geological significance [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2017, 36(10): 1722-1739.
[32] Tan B K. “Suture zones” in peninsular Malaysia and Thailand: Implications for Palaeotectonic reconstruction of southeast Asia [J]. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 1996, 13(3-5): 243-249. doi: 10.1016/0743-9547(96)00031-1
[33] 夏邦栋, 于津海, 方中, 等. 海南岛海西-印支期花岗岩的地球化学特征及成因[J]. 地球化学, 1990(4):365-373
XIA Bangdong, YU Jinhai, FANG Zhong, et al. Geochemical characteristics and origin of the Hercynian-Indosinian granites of Hainan Island, China [J]. Geochimica, 1990(4): 365-373.
[34] 唐立梅, 陈汉林, 董传万, 等. 中国东南部晚中生代构造伸展作用——来自海南岛基性岩墙群的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(4):1204-1216
TANG Limei, CHEN Hanlin, DONG Chuanwan, et al. Late Mesozoic tectonic extension in SE China: Evidence from the basic dike swarms in Hainan Island, China [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(4): 1204-1216.
[35] 唐立梅, 陈汉林, 董传万, 等. 海南岛三叠纪中基性岩的年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 地质科学, 2010, 45(4):1139-1155
TANG Limei, CHEN Hanlin, DONG Chuanwan, et al. Triassic neutral and basic rocks in Hainan Island, geochemistry and their geological signinficance [J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2010, 45(4): 1139-1155.
[36] 何家雄, 刘海龄, 姚永坚, 等. 南海北部边缘盆地油气地质及资源前景[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2008: 1-185.
HE Jiaxiong, LIU Hailing, YAO Yongjian, et al. Margin basins' petroleum geology and resources prospect of northern South China Sea[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2008: 1-185.
[37] 尤龙, 王璞珺, 吴景富, 等. 莺歌海盆地前新生代基底特征[J]. 世界地质, 2014, 33(3):511-523
YOU Long, WANG Pujun, WU Jingfu, et al. Basement characteristics of Yinggehai basin in pre-Cenozoic [J]. Global Geology, 2014, 33(3): 511-523.
[38] 李平鲁, 梁慧娴, 戴一丁. 珠江口盆地基岩油气藏远景探讨[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 1998, 12(6):361-369
LI Pinglu, LIANG Huixian, DAI Yiding. Exploration perspective of basement hydrocarbon accumulations in the Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 1998, 12(6): 361-369.
[39] 李平鲁, 梁慧娴, 戴一丁, 等. 珠江口盆地燕山期岩浆岩的成因及构造环境[J]. 广东地质, 1999, 14(1):1-8
LI Pinglu, LIANG Huixian, DAI Yiding, et al. Origin and tectonic setting of the Yanshanian igneous rocks in the Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Guangdong Geology, 1999, 14(1): 1-8.
[40] 邵磊, 尤洪庆, 郝沪军, 等. 南海东北部中生界岩石学特征及沉积环境[J]. 地质评论, 2007, 53(2):164-169
SHAO Lei, YOU Hongqing, HAO Hujun, et al. Petrology and depositional environments of Mesozoic strata in the northeastern South China Sea [J]. Geological Review, 2007, 53(2): 164-169.
[41] 龚再升, 李思田, 谢泰俊, 等. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地分析与油气聚集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997: 27-41.
GONG Zaisheng, LI Sitian, XIE Taijun, et al. Continental Margin Basin Analysis and Hydrocarbon Accumulation of the Northern South China Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1997: 27-41.
[42] 朱伟林, 解习农, 王振峰, 等. 南海西沙隆起基底成因新认识[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2017, 60(12):2214-2222 doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9089-9
ZHU Weilin, XIE Xinong, WANG Zhenfeng, et al. New insights on the origin of the basement of the Xisha Uplift, South China Sea [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2017, 60(12): 2214-2222. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9089-9
[43] 吴进民, 杨木壮. 南海西南部地震层序的时代分析[J]. 南海地质研究, 1994(6):16-29
WU Jinmin, YANG Muzhuang. Age analysis of seismic sequences in the southwestern south China Sea [J]. Geological Research of South China Sea, 1994(6): 16-29.
[44] 龚铭, 李唐根, 吴亚军, 等. 南沙海域构造特征与盆地演化[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2001: 1-87.
GONG Ming, LI Tanggen, WU Yajun, et al. The Structural Characteristics of the Nansha Sea Basin Evolution[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2001: 1-87.
[45] Areshev E G, Dong T L, San N T, et al. Reservoirs in fractured basement on the continental shelf of southern Vietnam [J]. Journal of Petroleum Geology, 1992, 15(4): 451-464. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-5457.1992.tb01045.x
[46] Schlüter H U, Hinz K, Block M. Tectono-stratigraphic terranes and detachment faulting of the South China Sea and Sulu Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 1996, 130(1-2): 39-78. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(95)00137-9
[47] Kudrass H R, Wiedicke M, Cepek P, et al. Mesozoic and Cainozoic rocks dredged from the South China Sea (Reed Bank area) and Sulu Sea and their significance for plate-tectonic reconstructions [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, l986, 3(1): 19-30. doi: 10.1016/0264-8172(86)90053-X
[48] 邱燕, 陈国能, 刘方兰, 等. 南海西南海盆花岗岩的发现及其构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(12):2104-2107
QIU Yan, CHEN Guoneng, LIU Fanglan, et al. Discover of granite and its tectonic significance in southwestern basin of the South China Sea [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(12): 2104-2107.
[49] 鄢全树, 石学法, 王昆山, 等. 南沙微地块花岗质岩石LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 82(8):1057-1067
YAN Quanshu, SHI Xuefa, WANG Kunshan, et al. LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb dating of granitic rocks from the Nansha micro-block, South China Sea, and its geological significance [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2008, 82(8): 1057-1067.
[50] 刘书生, 范文玉, 罗茂金, 等. 老挝南部帕莱通双峰式火山岩锆石U-Pb定年及岩石地球化学特征[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2014, 44(2):540-553
LIU Shusheng, FAN Wenyu, Luo Maojin, et al. Zircon U-Pb dating and geochemistry characteristics of the Bimodal volcanic rocks in Phlaythong area, Southern Laos [J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2014, 44(2): 540-553.
[51] 徐克勤, 孙鼐, 王德滋, 等. 华南多旋迴的花崗岩类的侵入时代、岩性特征、分布規律及其成矿专属性的探討[J]. 地质学报, 1963, 43(1):1-26
XU Keqin, SUN Nai, WANG Dezi, et al. Discussion on the intrusive age, lithologic characteristics, distribution regularity and metallogenic exclusivity of multicycle granitoids in South China [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1963, 43(1): 1-26.
[52] 梁敦杰, 许益民. 广东省区域地质基本特征[J]. 中国区域地质, 1988(1):9-15
LIANG Dunjie, XU Yimin. The basic characteristics of regional geology of Guangdong Province [J]. Regional Geology of China, 1988(1): 9-15.
[53] 许德如, 陈广浩, 夏斌, 等. 海南岛几个重大基础地质问题评述[J]. 地质科技情报, 2003, 23(4):37-44
XU Deru, CHEN Guanghao, XIA Bin, et al. Comment on several important basic geological problems in Hainan island, China [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2003, 23(4): 37-44.
[54] 黄长煌. 台湾东部未变形花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(10):1740-1749
HUANG Changhuang. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of the undeformed granite in eastern Taiwan and its geological significance [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2017, 36(10): 1740-1749.
[55] 张开毕, 徐维光, 陈淑华, 等. 台湾区域地质概论[J]. 福建地质, 2017, 36(2):79-93
ZHANG Kaibi, XU Weiguang, CHEN Shuhua, et al. Geological survey in Taiwan area [J]. Geology of Fujian, 2017, 36(2): 79-93.
[56] 张成晨, 许长海, 何敏, 等. 东海到南海晚中生代岩浆弧及陆缘汇聚体制综述[J]. 地球科学进展, 2019, 34(9):950-961
ZHANG Chengchen, XU Changhai, HE Min, et al. Late Mesozoic convergent continental margin with magmatic arc from East to South China Seas: A review [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2019, 34(9): 950-961.
[57] Li X H, Li J B, Yu X, et al. 40Ar/39Ar ages of seamount trachytes from the South China Sea and implications for the evolution of the northwestern sub-basin [J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2015, 6(4): 571-577. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2014.08.003
[58] Hutchison C S. Geological Evolution of South-East Asia[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1989: 1-368.
[59] Holloway N H. North Palawan block, Philippine-its relation to Asian mainland and role in evolution of South China Sea [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1982, 66(9): 1355-1383.
[60] 吴良士. 菲律宾地质构造及其区域成矿主要特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2012, 31(3):642-644
WU Liangshi. Geological tectonic and regional mineralization of Philippine [J]. Mineral Deposits, 2012, 31(3): 642-644.
[61] 邓江洪, 杨晓勇, 孙卫东. 菲律宾群岛中部Cebu地区早白垩火山弧型(VA)蛇绿岩年代学、地球化学研究及其构造意义[C]//中国地球科学联合学术年会. 北京: 中国地球物理学会, 2014: 1770.
DENG Jianghong, YANG Xiaoyong, SUN Weidong. Chronology, geochemistry and tectonic significance of Early Cretaceous volcanic arc (VA) ophiolite in Cebu area, central Philippines[C]//Annual Meeting of China Geoscience Federation. Beijing: Chinese Geophysical Society, 2014: 1770.
[62] 杨树春, 仝志刚, 贺清, 等. 潮汕坳陷中生界生烃历史及火成岩侵入影响分析:以LF35-1-1井为例[J]. 中国海上油气, 2008, 20(3):152-156
YANG Shuchun, TONG Zhigang, HE Qing, et al. Mesozoic hydrocarbon generation history and igneous intrusion impacts in Chaoshan depression, South China sea: a case of LF35-1-1 well [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2008, 20(3): 152-156.
[63] 修淳, 张道军, 翟世奎, 等. 西沙岛礁基底花岗质岩石的锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(3):115-126
XIU Chun, ZHANG Daojun, ZHAI Shikui, et al. Zricon U-Pb age of granitic rocks from the basement beneath the Shi Island, Xisha islands and its geological significance [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(3): 115-126.
[64] 金翔龙. 南海地球科学研究报告[J]. 东海海洋, 1989, 7(4):10-19
JIN Xianglong. The geosciences research report in South China Sea [J]. Donghai Marine Science, 1989, 7(4): 10-19.
[65] 鄢全树, 石学法, 高晶晶, 等. 南沙地块花岗质岩石矿物学特征及其成因信息[J]. 矿物学报, 2012, 32(1):131-138
YAN Quanshu, SHI Xuefa, GAO Jinjin, et al. Mineralogical characteristics of granitic rocks from the Nansha Block (South China Sea) and its implications for magmatic process [J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2012, 32(1): 131-138.
[66] 贾大成, 丘学林, 胡瑞忠, 等. 北部湾玄武岩地幔源区性质的地球化学示踪及其构造环境[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2003, 22(2):30-39
JIA Dacheng, QIU Xuelin, HU Ruizhong, et al. Geochemical nature of mantle reservoirs and tectonic setting of basalts in Beibu gulf and its adjacent region [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2003, 22(2): 30-39.
[67] 周云, 梁新权, 梁细荣, 等. 海南白垩纪六罗村组火山岩的年代学、地球化学特征及其大地构造意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2015, 39(5):903-918
ZHOU Yun, LIANG Xinquan, LIANG Xirong, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of Cretaceous volcanic rocks from Liuluo Formation in Hainan Island and their tectonic implications [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2015, 39(5): 903-918.
[68] Chen C H, Hsieh P S, Wang K L, et al. Zircon LA-ICPMS U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes of Huayu (Penghu Islands) volcanics in the Taiwan Strait and tectonic implication [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2010, 37(1): 17-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.07.003
[69] 阎贫, 刘海龄. 南海及其周缘中新生代火山活动时空特征与南海的形成模式[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2005, 24(2):33-41
YAN Pin, LIU Hailing. Temporal and spatial distributions of Meso-Cenozoic igneous rocks over South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2005, 24(2): 33-41.
[70] 邹和平, 李平鲁, 饶春涛. 珠江口盆地新生代火山岩地球化学特征及其地球动力学意义[J]. 地球化学, 1995, 24(S1):33-45
ZOU Heping, LI Pinglu, RAO Chuntao. Geochemistry of Cenozoic volcanic rocks in Zhujiangkou Basin and its geodynamic significance [J]. Geochimica, 1995, 24(S1): 33-45.
[71] 王友华, 王文海, 蒋兴迅. 南海深水钻井作业面临的挑战和对策[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2011, 39(2):50-55
WANG Youhua, WANG Wenhai, JIANG Xingxun. South China Sea deepwater drilling challenges and solutions [J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2011, 39(2): 50-55.
[72] Wang K L, Lo Y M, Chung S L, et al. Age and geochemical features of dredged basalts from offshore SW Taiwan: the coincidence of intra-plate magmatism with the spreading south China Sea [J]. Terrestrial, Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, 2012, 23(6): 657-669. doi: 10.3319/TAO.2012.07.06.01(TT)
[73] Vu A T, Fyhn M B W, Xuan C T, et al. Cenozoic tectonic and stratigraphic development of the Central Vietnamese continental margin [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 86: 386-401. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.06.001
[74] 李兆麟, 丘志力, 秦社彩, 等. 南海海山玄武岩形成条件研究[J]. 矿物学报, 1991(4):325-333
LI Zhaolin, QIU Zhili, QIN Shecai, et al. A study on the forming conditions of basalts in seamounts of the South China Sea [J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 1991(4): 325-333.
[75] 邱华宁, 魏静娴, 徐义刚, 等. 南海玳瑁火山岩40Ar/39Ar定年初步结果[C]//“南海深海过程演变”重大研究计划2013年度学术研讨会论文集. 上海: 同济大学海洋地质国家重点实验室, 2013: 16.
QIU Huaning, WEI Jingxian, XU Yigang, et al. Preliminary results of 40Ar/39Ar dating of Daimao hill volcanic rocks in the South China Sea[C]//Proceedings of 2013 Annual Symposium on "the Evolution of Deep Sea Processes in the South China Sea". Shanghai, 2013: 16.
[76] 王贤觉, 吴明清, 梁德华,等. 南海玄武岩的某些地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学, 1984(4):332-340
WANG Xianjue, WU Mingqing, LIANG Dehua, et al. Some geochemical characteristics of basalts in the South China Sea [J]. Geochimica, 1984(4): 332-340.
[77] 王叶剑, 韩喜球, 罗照华, 等. 晚中新世南海珍贝-黄岩海山岩浆活动及其演化: 岩石地球化学和年代学证据[J]. 海洋学报, 2009, 31(4):93-102
WANG Yejian, HAN Xiqiu, LUO Zhaohua, et al. Late Miocene magmatism and evolution of Zhenbei-Huangyan seamount in the South China Sea: evidence from petrochemistry and chronology [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2009, 31(4): 93-102.
[78] Taylor B, Hayes D E. Origin and history of the south China Sea basin[C]//Hayes D E. The Tectonic and Geologic Evolution of Southeast Asian Seas and Islands, Part 2. Washington, DC: American Geophysical Union, 1983, 27: 23-56.
[79] 鄢全树. 南海新生代碱性玄武岩的特征及其地球动力学意义[D]. 中国科学院研究生院博士学位论文, 2008: 1-132.
YAN Quanshu. Geochemistry of Cenozoic alkali basalts from the South China Sea and its geodynamical significance[D]. Doctor Dissertation of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2008: 1-132.
[80] 林正良, 李红敬, 张永超, 等. 北部湾盆地福山凹陷古近纪辉长岩地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2016, 40(5):1064-1074
LIN Zhengliang, LI Hongjing, ZHANG Yongchao, et al. Geochemistry and tectonic implications of the Paleogene Gabbros in Fushan Sag, Beibu Gulf Basin [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2016, 40(5): 1064-1074.
[81] 李美俊, 卢鸿, 王铁冠, 等. 北部湾盆地福山凹陷岩浆活动与CO2成藏的关系[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2006, 17(1):55-59
LI Meijun, LU Hong, WANG Tieguan, et al. Relationship between magma activity and CO2 gas accumulation in Fushan depression, Beibuwan basin [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2006, 17(1): 55-59.
[82] 钱星, 张莉, 徐立明, 等. 台湾海峡盆地九龙江凹陷火成岩发育特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(5):111-116
QIAN Xing, ZHANG Li, XU Liming, et al. Igneous rocks in Jiulongjiang sag of Taiwan strait basin and implications for petroleum geology [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(5): 111-116.
[83] 徐义刚, 魏静娴, 邱华宁, 等. 用火山岩制约南海的形成演化: 初步认识与研究设想[J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57(24):3150-3164 doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4921-1
XU Yigang, WEI Jingxian, QIU Huaning, et al. Opening and evolution of the South China Sea constrained by studies on volcanic rocks: Preliminary results and a research design [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(24): 3150-3164. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4921-1
[84] Chung S L, Cheng H, Jahn B M, et al. Major and trace element, and Sr-Nd isotope constraints on the origin of Paleogene volcanism in South China prior to the South China Sea opening [J]. Lithos, 1997, 40(2-4): 203-220. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(97)00028-5
[85] Huang X L, Niu Y L, Xu Y G, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of Cenozoic basalts from eastern Guangdong, SE China: constraints on the lithosphere evolution beneath the northern margin of the South China Sea [J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2013, 165(3): 437-455. doi: 10.1007/s00410-012-0816-7
[86] 邹和平. 南海北部-台湾海峡及邻区新生代火山活动时序与分布[J]. 华东地质学院学报, 1993, 16(1):24-31
ZOU Heping. Episodes and distribution of Cenozoic volcanism in Northern part of South China sea and Taiwan strait as well as their neighboring areas [J]. Journal of East China Geological Institute, 1993, 16(1): 24-31.
[87] 杨蜀颖. 南海玳瑁海山与相邻陆域玄武岩的地球化学特征及其构造意义[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2015: 1-112.
YANG Shuying. Geochemical characteristics of basalts from the Daimao seamount in the South China Sea (SCS) and from the SCS’s neighboring lands: Implications for the regional tectonic evolution[D]. Doctor Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2015: 1-112.
[88] 冯国荣. 华南沿海晚新生代玄武岩基本特征及其与构造环境的关系[J]. 中山大学学报论丛, 1992(1):93-103
Feng Guorong. Basic characteristics and relationship to tectonic environment of the Late Cenozoic basalts along the coast of South China Sea [J]. Supplement to the Journal of Sunyatsen University, 1992(1): 93-103.
[89] 杨胜雄, 邱燕, 朱本铎, 等. 南海地质地球物理图系(1: 200万)[M]. 天津: 中国航海图书出版社, 2015.
YANG Shengxiong, QIU Yan, ZHU Benduo, et al. The atlas of geology and geophysics of the South China Sea (1: 2000000)[M]. Tianjin: China Navigation Publications Press, 2015.
[90] Soeria-Atmadja R, Noeradi D, Priadi B. Cenozoic magmatism in Kalimantan and its related geodynamic evolution [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 1999, 17(1-2): 25-45. doi: 10.1016/S0743-9547(98)00062-2
[91] 孙嘉诗. 南海北部及广东沿海新生代火山活动[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1991, 11(3):45-67
SUN Jiashi. Cenozoic volcanic activity in the northern South China Sea and Guangdong coastal area [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1991, 11(3): 45-67.
[92] Chung S L, Yang T F, Lee C Y, et al. The igneous provinciality in Taiwan: Consequence of continental rifting superimposed by Luzon and Ryukyu subduction systems [J]. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 1995, 11(2): 73-80. doi: 10.1016/0743-9547(94)00040-L
[93] Barr S M, Cooper M A. Late Cenozoic basalt and gabbro in the subsurface in the Phetchabun Basin, Thailand: Implications for the Southeast Asian Volcanic Province [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 76: 169-184. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.01.013
[94] 曾罡, 郑丽波, 陈立辉, 等. 南海洋脊抽吸作用对其周边新生代玄武质岩浆活动的影响[J]. 高校地质学报, 2017, 23(3):373-382
ZENG Gang, ZHENG Libo, CHEN Lihui, et al. Influence of ridge suction on Cenozoic basaltic Magmatism in the surroundings of the South China Sea [J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2017, 23(3): 373-382.
[95] Zhang G L, Luo Q, Zhao J, et al. Geochemical nature of sub-ridge mantle and opening dynamics of the South China Sea [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2018, 489: 145-155. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2018.02.040
[96] Yan Q S, Castillo P, Shi X F, et al. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of volcanic rocks from Daimao Seamount (South China Sea) and their tectonic implications [J]. Lithos, 2015, 218-219: 117-126. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.12.023
[97] 杨蜀颖, 方念乔, 杨胜雄, 等. 关于南海中央次海盆海山火山岩形成背景与构造约束的再认识[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2011, 36(3):455-470
YANG Shuying, FANG Nianqiao, YANG Shengxiong, et al. A further discussion on formation background and tectonic constraints of igneous rocks in central sub-basin of the South China Sea [J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2011, 36(3): 455-470.
[98] 李诗颖, 余克服, 张瑜, 等. 西沙群岛基底火山碎屑岩中单斜辉石的矿物化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(7):65-76
LI Shiying, YU Kefu, ZHANG Yu, et al. Mineral chemistry of clinopyroxene in pyroclastic rocks of the Xisha Islands and their geological significance [J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(7): 65-76.
[99] 樊祺诚, 孙谦, 隋建立, 等. 北部湾涠洲岛及斜阳岛火山岩微量元素和同位素地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(6):1323-1332
FAN Qicheng, SUN Qian, SUI Jianli, et al. Trace-element and isotopic geochemistry of volcanic rocks and it’s techtonic implications in Weizhou Island and Xieyang Island, Northern Bay [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24(6): 1323-1332.
[100] Hoang N, Flower M. Petrogenesis of Cenozoic basalts from Vietnam: Implication for origins of a ‘Diffuse Igneous Province’ [J]. Journal of Petrology, 1998, 39(3): 369-395. doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.3.369
[101] Lee T Y, Lo C H, Chung S L, et al. 40Ar/39Ar dating result of Neogene basalts in Vietnam and its tectonic implication[C]//Mantle Dynamics and Plate Interactions in East Asia. American Geophysical Union, 1998, 27: 317-330.
[102] Yang T F, Tien J L, Chen C H, et al. Fission-track dating of volcanics in the northern part of the Taiwan-Luzon Arc: eruption ages and evidence for crustal contamination [J]. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 1995, 11(2): 81-93. doi: 10.1016/0743-9547(94)00041-C
[103] 杜劲光. 菲律宾地质矿产概况[J]. 地质与勘探, 1984(9):33-36
DU Jingguang. The geological features and ore deposits in Philippine [J]. Geology and Exploratory, 1984(9): 33-36.
[104] Tu K, Flower M F J, Carlson R W, et al. Magmatism in the South China Basin: 1. Isotopic and trace-element evidence for an endogenous Dupal mantle component [J]. Chemical Geology, 1992, 97(1-2): 47-63. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(92)90135-R
[105] 真允庆, 牛树银, 孙爱群. 南海热幔柱构造与油气分布[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2013, 28(3):401-411
ZHEN Yunqing, NIU Shuyin, SUN Aiqun. The mantle plume structure and oil-gas distribution in the South China Sea [J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2013, 28(3): 401-411.
[106] 韩宗珠, 吕迎秋, 许红, 等. 西沙群岛浮岩的岩石地球化学特征及成因[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(6):1-8
HAN Zongzhu, LV Yingqiu, XU Hong, et al. Petro-geochemistry and genesis of the pumices at Dongdao of Xisha islands [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2017, 33(6): 1-8.
[107] 业治铮, 何起祥, 张明书, 等. 西沙群岛岛屿类型划分及其特征的研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1985, 5(1):1-13
YE Zhizheng, HE Qixiang, ZHANG Mingshu, et al. Classification and characteristics of islands in the Xisha archipelago [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1985, 5(1): 1-13.
[108] 张丙坤, 李三忠, 夏真, 等. 南海北部深水区新生代岩浆岩分布规律及其与海底地质灾害的相关性[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(11):90-100
ZHANG Bingkun, LI Sanzhong, XIA Zhen, et al. Distribution of Cenozoic igneous rocks and its relation to submarine geological hazards in the deepwater area of the northern South China Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2014, 36(11): 90-100.
[109] Fan C Y, Xia S H, Zhao F, et al. New insights into the magmatism in the northern margin of the South China Sea: spatial features and volume of intraplate seamounts [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2017, 18(6): 2216-2239. doi: 10.1002/2016GC006792
[110] Zhao F, Alves T M, Wu S G, et al. Prolonged post-rift magmatism on highly extended crust of divergent continental margins (Baiyun Sag, South China Sea) [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 445: 79-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.04.001
[111] 刘安, 吴世敏. 珠江口盆地花岗岩成因探讨及其对油气资源指示意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2011, 18(1):141-148
LIU An, WU Shimin. A discussion on the formation of granite in the Pearl River Mouth Basin and its implication to hydrocarbon resource [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2011, 18(1): 141-148.
[112] Song X X, Li C F, Yao Y J, et al. Magmatism in the evolution of the South China Sea: geophysical characterization [J]. Marine Geology, 2017, 394: 4-15. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2017.07.021
[113] Larsen H C, Mohn G, Nirrengarten M, et al. Rapid transition from continental breakup to igneous oceanic crust in the South China Sea [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2018, 11(10): 782-789. doi: 10.1038/s41561-018-0198-1
-



 下载:
下载: