Geochemical characteristics and genesis of detrital apatites from the surrounding rivers into the Bohai Sea
-
摘要:
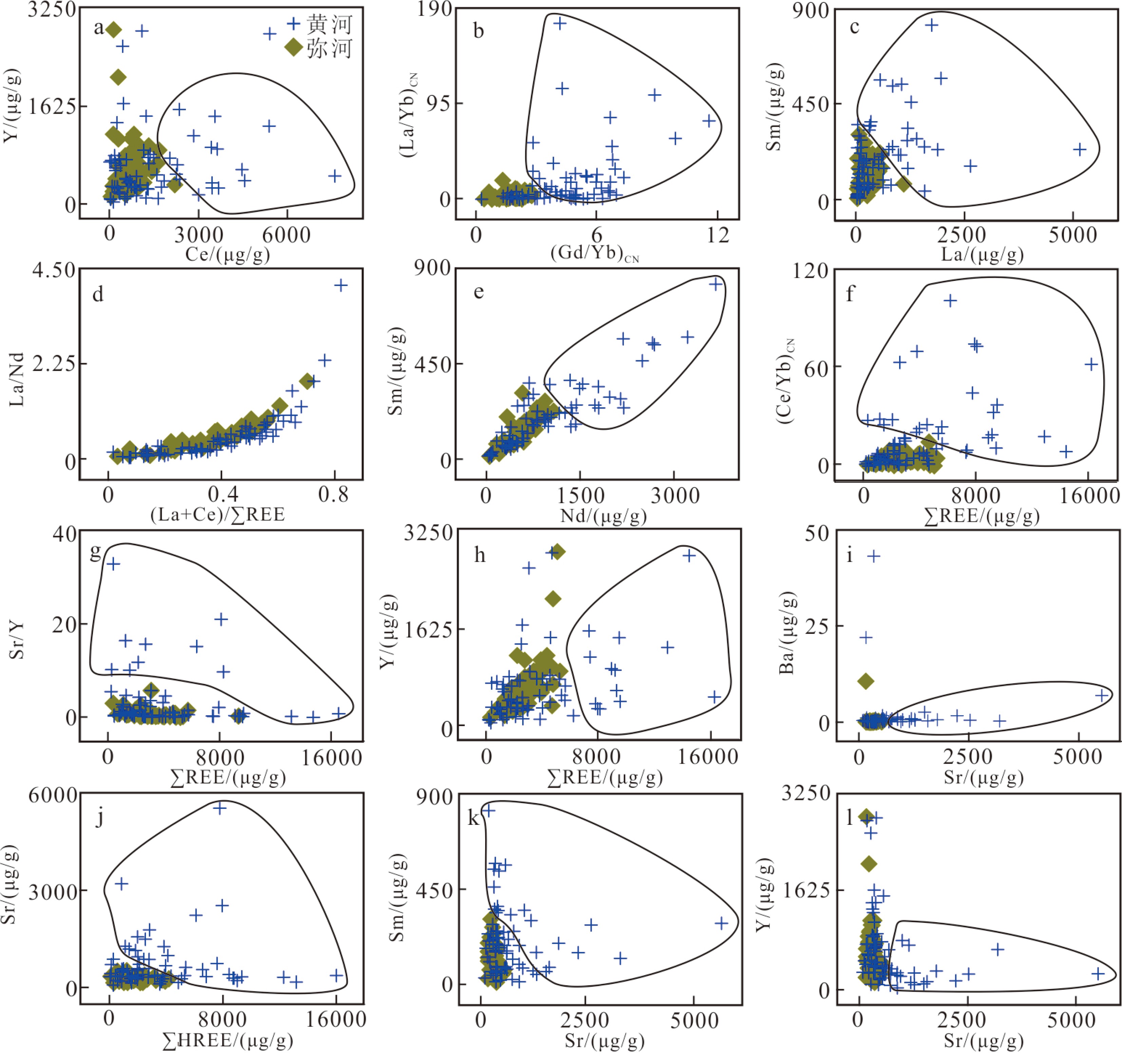
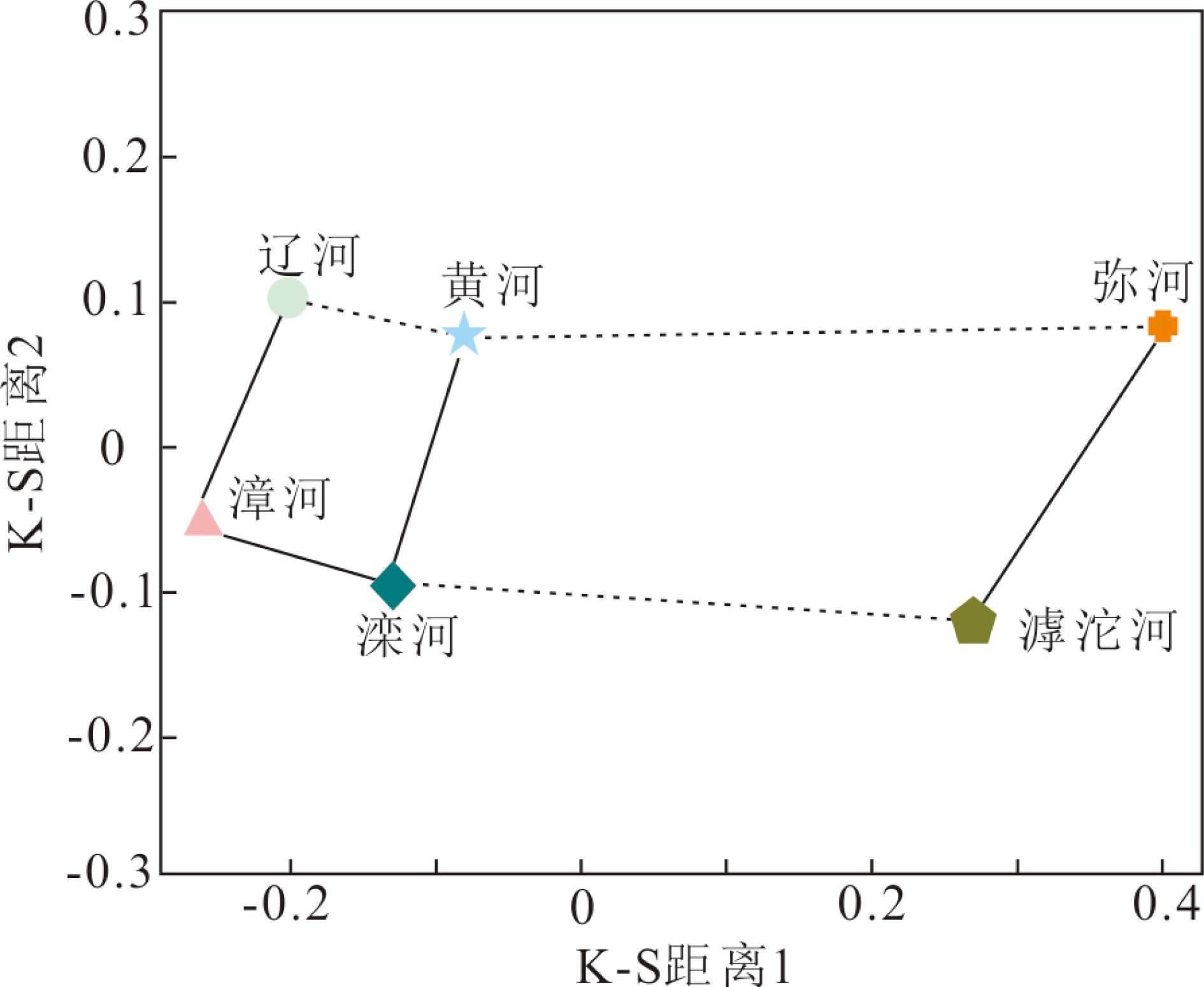
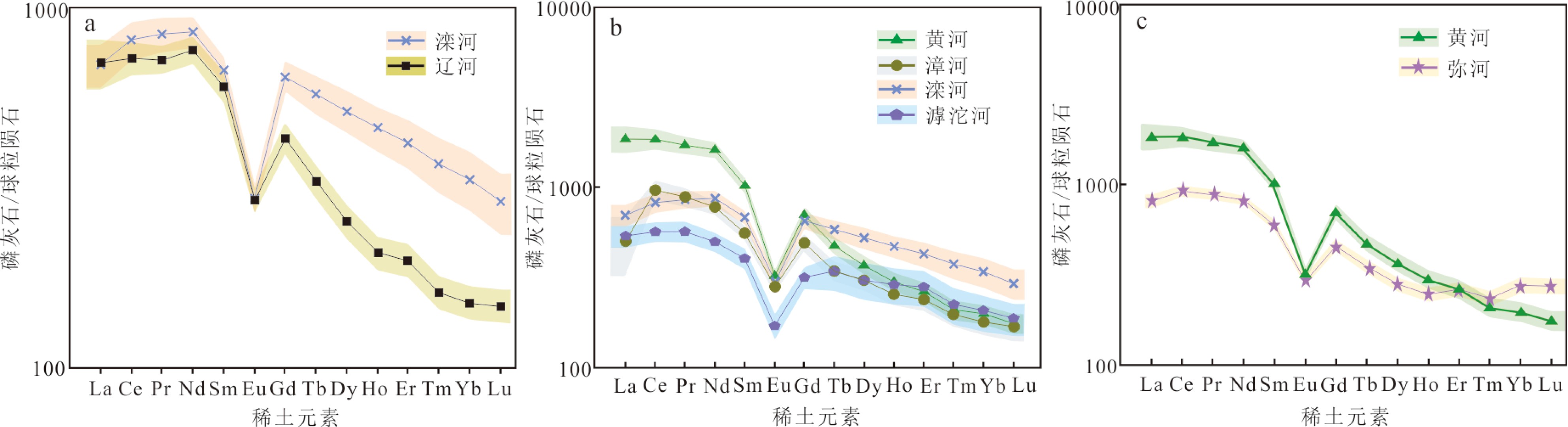
渤海的碎屑物质详细记录了源区的地质信息,对其进行物源示踪研究有助于提高我们对周围造山带及黄河的演化、中国东部陆架海碎屑物质扩散等的认识。本文利用激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子质谱分别对辽东湾、渤海湾及莱州湾周围主要汇入河流的碎屑磷灰石进行原位微量元素分析,结合Kolmogorov-Smirnov统计方法的多维判别图与反向传播神经网络等方法,分析渤海主要汇入河流碎屑磷灰石的微量元素与稀土元素。结果表明在汇入渤海的主要河流中,碎屑磷灰石的微量元素主要以Sr元素与Y元素为主,且都出现较为明显的HREE富集,但在不同河流之间的碎屑磷灰石Sr元素与REE也存在一定差异,这可能与其母岩不同相关。
Abstract:To trace where the detrital deposits of the Bohai Sea come from is important for better understanding the basin-mountain coupling and the formation of the Yellow River, in addition to the distribution of the detrital sediments around the Bohai Sea. In this paper, the laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) is applied to analyze the composition of trace elements of the detrital apatite grains from the main rivers pouring into Liaodong Bay, Bohai Bay, and Laizhou Bay, combining with Kolmogorov-Smirnov multi-dimensional discrimination diagram (MDS) and Back Propagation(BP) neural network to perform sediment provenance discrimination. Results show that they are all characterized by high Sr, Y and light rare earth elements(LREE). However, there are some differences in the sediments from different rivers, which may be related to the source rocks of apatite.
-
Key words:
- apatite /
- trace element /
- provenance tracing /
- Bohai Sea
-

-
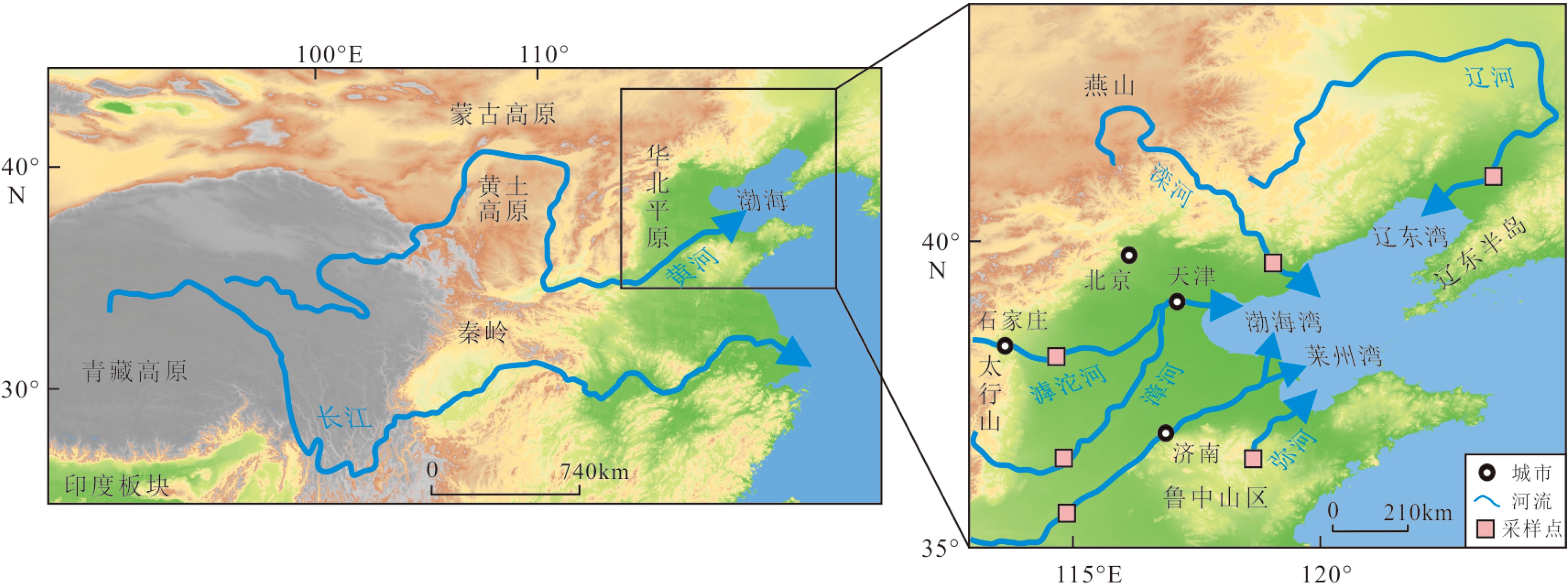
表 1 渤海主要汇入河流的水文特征
Table 1. Hydrological characteristics of the main rivers flowing into the Bohai Sea
河流 发源山区 总长度/km 流域总面积/104 km2 输沙量/104 t 径流量/108 m3 入海海湾 辽河 燕山、大兴安岭 1345 21.96 173(2009—2019年) 26.12(2009—2019年) 辽东湾* 滦河 燕山 877 4.4 1739(1950—1984年) 46.5(1950—1984年) 辽东湾[16] 黄河 青藏高原 5500 75 17200(2009—2019年) 282.3(2009—2019年) 渤海湾* 滹沱河 太行山 587 2.7 – 9.46(1956—2000年) 渤海湾[42] 漳河 太行山 412 1.8 728(1951—2015年) 8.59(1951—2015年) 渤海湾* 弥河 鲁中山区 206 0.38 84.1(多年平均) 4.27(多年平均) 莱州湾[24] 注:*数据来源于《2019中国河流泥沙公报》。 表 2 渤海主要汇入河流碎屑磷灰石微量元素游程检验
Table 2. Runs test of trace elements in main rivers of Bohai Sea
辽河 滦河 漳河 滹沱河 黄河 弥河 Li 0.76 0.514 0.625 0.97 0.739 0.328 B 0.096 0.888 0.801 0.412 0.713 0.801 Sc 0.571 0.574 0.803 0.838 0.675 0.379 V 0.982 0.576 0.092 0.246 0.637 0.317 Cr 0.466 0.33 0.468 0.502 0.071 0.201 Co 0.329 0.706 0.125 0.653 0.036 0.6 Ni 0.896 0.964 0.626 0.158 0.54 0.54 Cu 0.827 0.36 0.37 0.906 0.488 0.002 Zn 0.76 0.328 0.803 0.54 0.86 0.283 Ga 0.088 0.178 0.919 0.013 0.749 0.801 Rb 0.756 0.502 0.317 0.861 0.899 0.758 Sr 0.173 0.061 0.118 0.05 0.112 0.795 Y 0.492 0.088 0.695 0.818 0.637 0.514 Zr 0.851 0.845 0.861 0.054 0.772 0.046 Nb 0.466 0.709 0.246 0.54 0.861 0.302 Mo 0.894 0.125 0.656 0.828 0.245 0.602 Ag 0.398 0.434 0.75 0.755 0.772 0.349 Cd 0.163 0.577 0.067 0.201 0.016 0.477 Sn 0.695 0.902 0.195 0.28 0.938 0.412 Sb 0.078 0.845 0.125 0.545 0.686 0.6 Cs 0.87 0.328 0.289 0.493 0.329 0.16 Ba 0.063 0.656 0.22 0.32 0.47 0.555 Hf 0.851 0.803 0.435 0.606 0.772 0.046 Ta 0.386 0.795 0.801 0.755 0.772 0.036 W 0.517 0.204 0.353 0.468 0.049 0.876 Tl 0.576 0.709 0.434 0.071 0.179 0.732 Bi 0.334 0.205 0.076 0.576 0.464 0.992 Pb 0.236 0.97 0.577 0.033 0.153 0.193 Th 0.659 0.814 0.222 0.04 0.416 0.05 U 0.571 0.449 0.599 0.768 0.223 0.732 La 0.002 0.379 0.069 0.964 0.25 0.625 Ce 0.238 0.246 0.246 0.172 0.494 0.193 Pr 0.088 0.178 0.195 0.134 0.749 0.821 Nd 0.276 0.223 0.782 0.235 0.863 0.602 Sm 0.96 0.773 0.574 0.33 0.722 0.655 Eu 0.695 0.803 0.258 0.007 0.22 0.828 Gd 0.982 0.106 0.081 0.119 0.829 0.919 Tb 0.692 0.371 0.514 0.838 0.954 0.919 Dy 0.576 0.625 0.709 0.95 0.829 0.919 Ho 0.692 0.755 0.97 0.95 0.452 0.97 Er 0.626 0.493 0.695 0.66 0.546 0.514 Tm 0.96 0.75 0.695 0.383 0.723 0.278 Yb 0.886 0.178 0.54 0.845 0.954 0.344 Lu 0.768 0.022 0.54 0.858 0.749 0.344 表 3 辽东湾、渤海湾及莱州湾主要汇入河流微量元素数据统计
Table 3. The value of the trace elements of apatite from the main rivers around Liaodong Bay, Bohai Bay and Laizhou Bay
μg/g 辽河(n=60) 滦河(n=60) 漳河(n=60) 滹沱河(n=60) 黄河(n=67) 弥河(n=60) 最大值 最小值 平均值 最大值 最小值 平均值 最大值 最小值 平均值 最大值 最小值 平均值 最大值 最小值 平均值 最大值 最小值 平均值 Li 5.4 0 0.5 2.0 0 0.4 2.9 0 0.4 4.5 0 0.4 10.4 0 0.8 5.5 0.2 1.4 B 3.7 0 2.4 3.8 0.4 1.8 3.9 0.4 2.0 5.9 0.6 2.2 6.6 0 1.3 4.2 0 2.1 Sc 2.6 0 0.3 11.6 0 0.7 1.9 0 0.2 1.4 0 0.2 66.9 0 1.2 0.9 0 0.3 V 15.6 0.1 4.2 186.2 0 7.8 40.6 0 5.2 8.3 0 2.2 32.1 0 6.0 12.5 0.9 5.6 Cr 2.2 0 0.5 2.1 0 0.6 3.6 0 0.7 2.4 0 0.5 6.7 0 0.3 3.0 0 0.7 Co 0.5 0 0 0.2 0 0 2.2 0 0.1 0.1 0 0 7.3 0 0.2 0.6 0 0 Ni 11.9 0 0.3 0.8 0 0.2 3.6 0 0.3 0.9 0 0.2 12.7 0 0.5 1.6 0 0.2 Cu 4.5 0 0.2 2.5 0 0.3 9.5 0 0.2 1.4 0 0.1 89.9 0 2.8 1.2 0 0.2 Zn 1.8 0 0.2 1.3 0 0.2 2.5 0 0.3 1.8 0 0.2 21.3 0 0.6 7.0 0 0.2 Ga 23.9 0.8 8.3 30.1 0.3 9.7 47.9 0.5 9.7 29.5 0.7 6.5 39.0 0.3 10.5 20.3 1.3 9.6 Rb 14.0 0 0.3 0.6 0 0.1 0.3 0 0.1 0.7 0 0.1 2.3 0 0.1 19.1 0 0.4 Sr 1049.6 252.7 534.9 6083.4 87.9 990.3 8672.2 123.6 911.8 1709.9 76.3 370.7 5526.5 95.0 717.2 537.1 165.8 303.2 Y 1683.4 17.5 472.0 3136.1 74.6 919.0 2914.4 38.2 550.3 3717.5 0.7 521.9 2876.5 27.0 631.7 2897.1 119.0 609.6 Zr 3126.7 0 53.6 9.3 0 0.5 3.6 0 0.6 333.9 0 6.5 131785.6 0 2052.0 122.2 0 3.4 Nb 0.1 0 0 0.2 0 0 0.2 0 0 0.1 0 0 31.5 0 0.5 0.1 0 0 Mo 0.4 0 0 0.5 0 0 11.2 0 0.2 0.2 0 0 0.7 0 0.1 0.1 0 0 Ag 0.1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4.9 0 0.1 0 0 0 Cd 1.1 0 0.2 13.2 0 3.6 1.1 0 0.3 0.5 0 0.1 4.2 0 0.2 0.6 0 0.2 Sn 1.3 0 0.6 1.8 0 0.9 1.1 0 0.6 1.4 0 0.6 1.5 0 0.4 1.2 0.1 0.6 Sb 0.1 0 0 0.6 0 0.1 0.2 0 0 0.2 0 0 0.1 0 0 0.3 0 0 Cs 0.1 0 0 0.1 0 0 0.1 0 0 0.1 0 0 0.2 0 0 0.4 0 0 Ba 6.1 0 0.7 74.7 0 2.4 13.0 0 1.2 2.7 0 0.4 43.3 0 1.5 10.7 0 0.3 Hf 78.0 0 1.3 0.1 0 0 0.1 0 0 8.2 0 0.2 2775.4 0 43.3 3.5 0 0.1 Ta 0.1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2.5 0 0 0 0 0 W 16.6 0 0.8 6.5 0 0.8 2.0 0 0.2 2.7 0 0.6 10.8 0 1.1 2.3 0 0.2 Hg 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Tl 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0.1 0 0 Bi 0.1 0 0 0.6 0 0 0.3 0 0 0.3 0 0 5.1 0 0.4 0.2 0 0 Pb 6.6 1.1 3.2 26.4 0.6 6.6 10.9 0.6 3.0 10.4 0.9 3.3 17.8 1.0 4.3 29.9 4.5 11.5 Th 165.2 0 15.2 174.2 0.1 18.5 53.8 0 11.7 103.9 0 7.3 161.6 0 17.8 145.2 5.7 43.4 U 110.9 0.5 14.6 58.1 1.7 14.8 71.6 0.2 10.6 60.7 0 12.5 46.4 0.2 11.5 62.5 8.1 31.4 表 4 辽东湾、渤海湾及莱州湾主要汇入河流碎屑磷灰石REE含量
Table 4. The average value of the rare earth elements of apatite from the main rivers around Bohai Bay Basin
μg/g La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu 辽河(n=60) 最大值 1407.1 2132.7 252.3 1179.8 396.3 63.6 377.4 56.3 318.6 51.5 134.9 17.5 106.4 18.2 最小值 1.5 8.4 1.9 14.4 5.9 1.4 4.8 0.7 3.0 0.5 1.3 0.2 1.4 0.3 平均值 221.1 593.0 88.9 464.6 119.1 21.5 113.7 15.7 83.0 15.1 42.2 5.3 32.0 4.8 滦河(n=60) 最大值 1082.7 2664.6 327.7 1541.2 361.8 84.6 642.7 110.4 842.3 201.4 670.4 111.7 734.8 100.2 最小值 0.1 0.5 0.1 1.5 1.4 0.6 6.7 1.6 13.7 2.2 6.1 0.7 2.8 0.3 平均值 218.2 666.4 104.5 522.1 132.9 21.8 169.3 27.4 168.8 33.7 89.7 12.2 70.8 9.4 漳河(n=60) 最大值 1626.7 3794.5 575.9 1172.0 265.7 69.7 576.8 78.9 525.3 100.6 289.5 38.4 230.1 34.9 最小值 1.2 4.7 0.9 4.9 2.4 0.3 4.3 0.8 7.2 1.2 3.3 0.4 1.8 0.4 平均值 348.6 779.2 107.4 461.9 109.1 20.7 127.8 16.2 98.9 18.4 50.3 6.4 37.4 5.4 滹沱河(n=60) 最大值 887.7 1977.9 372.0 1082.4 279.0 98.2 326.8 182.6 1174.6 235.5 645.1 80.7 463.8 58.5 最小值 0.3 1.1 0.2 1.4 0.4 0.1 0.2 0.0 0.2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 平均值 166.4 458.7 69.5 298.4 78.6 12.4 81.9 16.0 99.5 20.8 58.9 7.3 42.4 6.0 黄河(n=67) 最大值 5126.7 7593.3 794.5 3656.9 822.0 87.6 776.2 101.9 561.5 100.5 277.2 38.0 246.9 31.3 最小值 3.5 13.1 3.0 21.0 10.7 2.8 10.3 1.0 5.2 0.8 2.0 0.2 1.2 0.2 平均值 578.1 1502.4 210.4 973.3 200.2 23.6 183.1 22.4 119.5 21.5 55.6 6.8 41.3 5.7 弥河(n=60) 最大值 1079.7 2199.5 242.5 1062.1 308.0 48.2 430.0 67.6 376.1 68.6 236.0 37.7 326.7 53.2 最小值 15.8 53.3 7.9 38.3 8.7 5.2 10.5 1.7 11.3 3.0 12.2 2.2 18.7 2.9 平均值 251.6 745.0 107.7 491.8 115.9 21.3 119.7 16.6 90.2 17.6 55.1 7.6 57.9 8.8 -
[1] 闫义, 林舸, 王岳军, 等. 盆地陆源碎屑沉积物对源区构造背景的指示意义[J]. 地球科学进展, 2002, 17(1):85-90 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2002.01.013
YAN Yi, LIN Ge, WANG Yuejun, et al. The indication of continental detrital sediment to tectonic setting [J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 2002, 17(1): 85-90. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2002.01.013
[2] 赵红格, 刘池洋. 物源分析方法及研究进展[J]. 沉积学报, 2003, 21(3):409-415 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2003.03.007
ZHAO Hongge, LIU Chiyang. Approaches and prospects of provenance analysis [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2003, 21(3): 409-415. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2003.03.007
[3] 林旭, 刘静, 吴中海, 等. 中国北部陆架海碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄和钾长石主微量元素物源示踪研究[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(10):3024-3035 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.10.016
LIN Xu, LIU Jing, WU Zhonghai, et al. Detrital zircon U-Pb ages and K-feldspar main and trace elements provenance studying from fluvial to marine sediments in northern China [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(10): 3024-3035. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.10.016
[4] 林旭, 刘静. 江汉和洞庭盆地与周缘造山带盆山耦合研究进展[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(2):499-520 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2019.02.015
LIN Xu, LIU Jing. A review of mountain-basin coupling of Jianghan and Dongting basins with their surrounding mountains [J]. Seismology and Geology, 2019, 41(2): 499-520. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2019.02.015
[5] Huang X T, Song J Z, Yue W, et al. Detrital Zircon U-Pb ages in the East China seas: implications for provenance analysis and sediment budgeting [J]. Minerals, 2020, 10(5): 398. doi: 10.3390/min10050398
[6] 杨守业. 亚洲主要河流的沉积地球化学示踪研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2006, 21(6):648-655 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2006.06.013
YANG Shouye. Advances in sedimentary geochemistry and tracing applications of Asian rivers [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2006, 21(6): 648-655. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2006.06.013
[7] 林旭, 刘静, 彭保发, 等. 青藏高原周围河流基岩和碎屑矿物低温热年代学研究进展[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(6):1091-1110 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.06.001
LIN Xu, LIU Jing, PENG Baofa, et al. A review of low-temperature thermochronology on bedrock and detritus from rivers around the Xizang Plateau [J]. Seismology and Geology, 2017, 39(6): 1091-1110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.06.001
[8] Liu J, Zhang J Q, Miao X D, et al. Mineralogy of the core YRD-1101 of the Yellow River Delta: implications for sediment origin and environmental evolution during the last ~1.9 Myr [J]. Quaternary International, 2020, 537: 79-87. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2019.12.025
[9] Pan B T, Pang H L, Gao H S, et al. Heavy-mineral analysis and provenance of Yellow River sediments around the China Loess Plateau [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 127: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.06.006
[10] 张伟, 金秉福, 岳伟, 等. 黄河口和长江口沉积绿帘石地球化学特征及物源意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2020, 39(3):576-586
ZHANG Wei, JIN Bingfu, YUE Wei, et al. Geochemical characteristics and provenance of epidote grains in sediments in estuaries of the Yellow River and Yangtze River [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2020, 39(3): 576-586.
[11] Dou Y G, Li J, Zhao J T, et al. Clay mineral distributions in surface sediments of the Liaodong Bay, Bohai Sea and surrounding river sediments: Sources and transport patterns [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 73: 72-82. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2013.11.023
[12] Li S Z, Suo Y H, Li X Y, et al. Mesozoic tectono-magmatic response in the East Asian ocean-continent connection zone to subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Plate [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 192: 91-137. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.03.003
[13] 张义丰, 李凤新. 黄河、滦河三角洲的物质组成及其来源[J]. 海洋科学, 1983(8):15-18
ZHANG Yifeng, LI Fengxin. The characteristics of material component and the material resource in Huanghe (Yellow) River, Luanhe River [J]. Marine Sciences, 1983(8): 15-18.
[14] Lu J, Qiao F L, Wang X H, et al. A numerical study of transport dynamics and seasonal variability of the Yellow River sediment in the Bohai and Yellow seas [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 95(1): 39-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.08.001
[15] 林晓彤, 李巍然, 时振波. 黄河物源碎屑沉积物的重矿物特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(3):17-21
LIN Xiaotong, LI Weiran, SHI Zhenbo. Characteristics of mineralogy in the clastic sediments from the Yellow River provenance, China [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2003, 23(3): 17-21.
[16] 韩宗珠, 衣伟虹, 李敏, 等. 渤海湾北部沉积物重矿物特征及物源分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2013, 43(4):73-79
HAN Zongzhu, YI Weihong, LI Min, et al. Analysis for heavy mineral characteristics and material provenance in the sediments of the northern Bohai Bay [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2013, 43(4): 73-79.
[17] 张连杰, 胡日军, 朱龙海, 等. 渤海湾碎屑矿物特征及其物源和沉积动力环境指示意义[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2019, 49(5):60-70
ZHANG Lianjie, HU Rijun, ZHU Longhai, et al. Characteristics of detrital minerals in Bohai Bay and their implications for provenance and sedimentary Dynamical Environment [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2019, 49(5): 60-70.
[18] 张剑, 李日辉, 王中波, 等. 渤海东部与黄海北部表层沉积物的粒度特征及其沉积环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(5):1-12
ZHANG Jian, LI Rihui, WANG Zhongbo, et al. Grain size characteristics of surface sediments in the east Bohai Sea and the northern Yellow Sea and their implications for environments [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(5): 1-12.
[19] 马晓红, 韩宗珠, 艾丽娜, 等. 中国渤黄海的沉积物源及输运路径研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2018, 48(6):96-101
MA Xiaohong, HAN Zongzhu, AI Li’na, et al. Research on provenance and transport pattern in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2018, 48(6): 96-101.
[20] Song S, Feng X L, Li G G, et al. Change in sediment provenance near the current estuary of Yellow River since the Holocene transgression [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2018, 17(3): 535-544. doi: 10.1007/s11802-018-3377-1
[21] 王双. 黄渤海表层沉积物磁学特征及其环境指示意义[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2014: 25-47.
WANG Shuang. The magnetic characteristics and environmental implications of the surface sediments of the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2014: 25-47.
[22] Wang Y H, Dong H L, Li G X, et al. Magnetic properties of muddy sediments on the northeastern continental shelves of China: implication for provenance and transportation[J]. Marine Geology, 274(1-4): 107-119.
[23] 廖永杰. 渤海中南部沉积地球化学特征和黄河改道事件[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2014: 10-27.
LIAO Yongjie. Geochemical characteristics of sediments in Bohai sea and relocation of Huanghe River[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2014: 10-27.
[24] 郭飞. 莱州湾晚更新世以来的沉积演化及物源分析[D]. 中国石油大学(华东)硕士学位论文, 2016: 8-11.
GUO Fei. Sedimentary evolution and source analysis in Laizhou Bay since late Pleistocene[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Petroleum (East China), 2016: 8-11.
[25] 蓝先洪, 秦亚超, 陈晓辉, 等. 渤海东部晚第四纪沉积环境变化的稀土元素地球化学记录[J]. 海洋通报, 2016, 35(6):674-682
LAN Xianhong, QIN Yachao, CHEN Xiaohui, et al. Rare earth element records of palaeoenvironmental changes during the Late Quaternary from core sediments of the eastern Bohai Sea [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2016, 35(6): 674-682.
[26] Xiao G Q, Sun Y Q, Yang J L, et al. Early Pleistocene integration of the Yellow River I: Detrital-zircon evidence from the North China Plain [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 546: 109691. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.109691
[27] 郑萍, 李大鹏, 陈岳龙, 等. 黄河口河流沙碎屑沉积物锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(1):79-90 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.01.008
ZHENG Ping, LI Dapeng, CHEN Yuelong, et al. Zircon U-Pb Ages of Clastic sediment from the outfall of the Yellow River and their geological significance [J]. Geoscience, 2013, 27(1): 79-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.01.008
[28] 岳保静, 廖晶. 黄河流域现代沉积物碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄物源探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(5):109-119
YUE Baojing, LIAO Jing. Provenance study of Yellow River sediments by U-Pb dating of the detrital zircons [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(5): 109-119.
[29] 金秉福, 岳伟, 王昆山. 黄河沉积中角闪石矿物晶体化学特征和成因分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2013, 35(1):131-143
JIN Bingfu, YUE Wei, WANG Kunshan. The crystallochemistry characteristics and genetic analysis of amphibole in the sediments of the Huanghe River [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2013, 35(1): 131-143.
[30] 金秉福, 岳伟, 王昆山. 黄河、辽河和鸭绿江沉积角闪石矿物化学特征对比及物源识别[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(4):11-21
JIN Bingfu, YUE Wei, WANG Kunshan. Chemical composition of detrital amphibole in the sediments of the Huanghe River, Liaohe River and Yalu River, and its implication for sediment provenance [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2014, 36(4): 11-21.
[31] Sha L K, Chappell B W. Apatite chemical composition, determined by electron microprobe and laser-ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, as a probe into granite petrogenesis [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(22): 3861-3881. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00210-0
[32] 赵振华. 副矿物微量元素地球化学特征在成岩成矿作用研究中的应用[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(1):267-286
ZHAO Zhenhua. Trace element geochemistry of accessory minerals and its applications in petrogenesis and metallogenesis [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(1): 267-286.
[33] O'Sullivan G J, Chew D M, Morton A C, et al. An integrated apatite geochronology and geochemistry tool for sedimentary provenance analysis [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2018, 19(4): 1309-1326. doi: 10.1002/2017GC007343
[34] Belousova E A, Griffin W L, O'Reilly S Y, et al. Apatite as an indicator mineral for mineral exploration: trace-element compositions and their relationship to host rock type [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2002, 76(1): 45-69. doi: 10.1016/S0375-6742(02)00204-2
[35] Bruand E, Fowler M, Storey C, et al. Apatite trace element and isotope applications to petrogenesis and provenance [J]. American Mineralogist, 2017, 102(1): 75-84. doi: 10.2138/am-2017-5744
[36] Morton A C, Yaxley G M. Detrital apatite geochemistry and its application in provenance studies [J]. Special Papers-Geological Society of America, 2007, 420: 319-344.
[37] O'Sullivan G, Chew D, Kenny G, et al. The trace element composition of apatite and its application to detrital provenance studies [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 201: 103044. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.103044
[38] Li S Z, Zhao G C, Dai L M, et al. Mesozoic basins in eastern China and their bearing on the deconstruction of the North China Craton [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 47: 64-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.06.008
[39] 邱燕, 王立飞, 黄文凯, 等. 中国海域中新生代沉积盆地[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016: 1-233.
QIU Yan, WANG Lifei, HUANG Wenkai, et al. Meso-Cenozoic Sedimentary Basins in Chinese Waters[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 2016: 1-233.
[40] 姚政权, 石学法. 渤海湾沿岸第四纪海侵研究进展[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2015, 31(2):9-16, 70
YAO Zhengquan, SHI Xuefa. A review of quaternary transgression researches along the Bohai Bay [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2015, 31(2): 9-16, 70.
[41] 王利波, 李军, 赵京涛, 等. 辽东湾中部晚第四纪沉积物物源与沉积环境: 来自碎屑矿物和自生黄铁矿的证据[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(2):39-48
WANG Libo, LI Jun, Zhao Jingtao, et al. Late quaternary sediment provenance and palaeoenvironment in Liaodong Bay, Bohai Sea: evidence from detrital minerals and authigenic pyrite [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(2): 39-48.
[42] 许建廷. 河北省滹沱河流域山区年径流变化情势分析[J]. 水科学与工程技术, 2008(6):3-5 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9900.2008.06.002
XU Jianting. Analysis of annual runoff variation of Hutuo river mountainous basin in Hebei province [J]. Water Sciences and Engineering Technology, 2008(6): 3-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9900.2008.06.002
[43] Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard [J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1-2): 34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004
[44] Vermeesch P, Resentini A, Garzanti E. An R package for statistical provenance analysis [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2016, 336: 14-25. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2016.01.009
[45] 兰嘉庆, 余宛泠. 异方差的游程检验[J]. 中山大学学报: 自然科学版, 2004, 43(S1):9-11
LAN Jiaqing, YU Wanling. Runs test used for heteroscedasticity [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2004, 43(S1): 9-11.
[46] 张硕, 简星, 张巍. 碎屑磷灰石对沉积物源判别的指示[J]. 地球科学进展, 2018, 33(11):1142-1153 doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2018.11.1142.
ZHANG Shuo, JIAN Xing, ZHANG Wei. Sedimentary provenance analysis using detrital apatite: A review [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2018, 33(11): 1142-1153. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2018.11.1142.
[47] 林旭, 赵希涛, 吴中海, 等. 渤海湾周缘主要河流钾长石物源示踪指标研究[J]. 地质科技通报:, 2020, 39(6):10-18
LIN Xu, ZHAO Xitao, WU Zhonghai, et al. Source tracing elements of K-feldspars of main rivers around Bohai Bay Basin [J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 10-18.
[48] 侯江龙, 王登红, 李建康, 等. 河北曲阳地区中佐伟晶岩脉中电气石原位硼同位素分析及其意义[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2017, 39(6):751-760 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2017.06.006
HOU Jianglong, WANG Denghong, LI Jiankang, et al. In-situ boron isotopic analysis and its geological significance of tourmalines from Zhongzuo Pegmatite Veins in Quyang Area of Hebei, China [J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2017, 39(6): 751-760. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2017.06.006
[49] 蔡剑辉, 阎国翰, 许保良, 等. 太行山—大兴安岭东麓晚中生代碱性侵入岩岩石地球化学特征及其意义[J]. 地球学报, 2006, 27(5):447-459 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2006.05.007
CAI Jianhui, YAN Guohan, XU Baoliang, et al. The late Mesozoic alkaline intrusive rocks at the east foot of the Taihang-Da Hinggan Mountains: Lithogeochemical characteristics and their implications [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2006, 27(5): 447-459. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2006.05.007
-



 下载:
下载: