Sedimentary environmental evolution for the past 30 ka of the northern continental slope of the South China Sea
-
摘要:
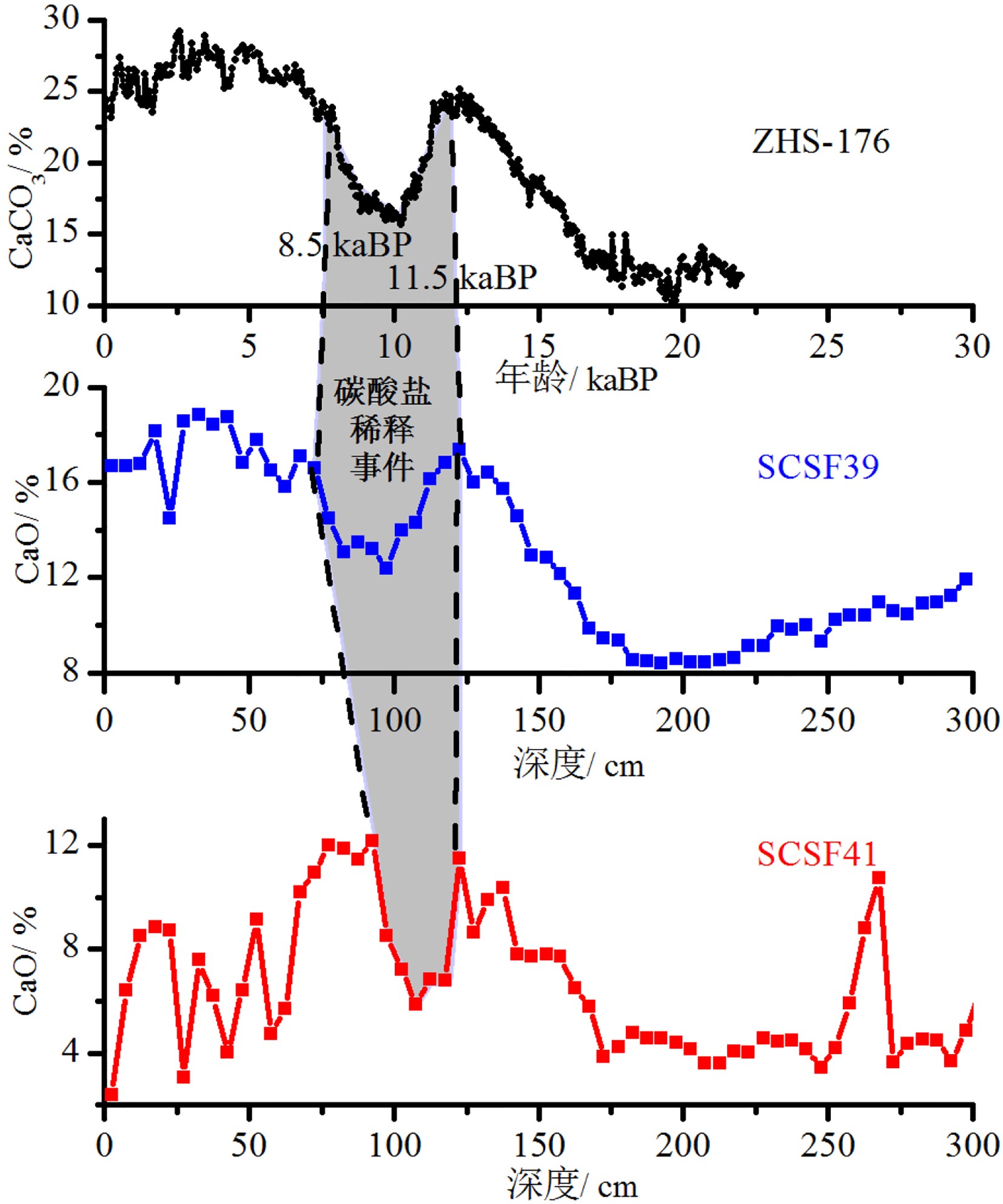
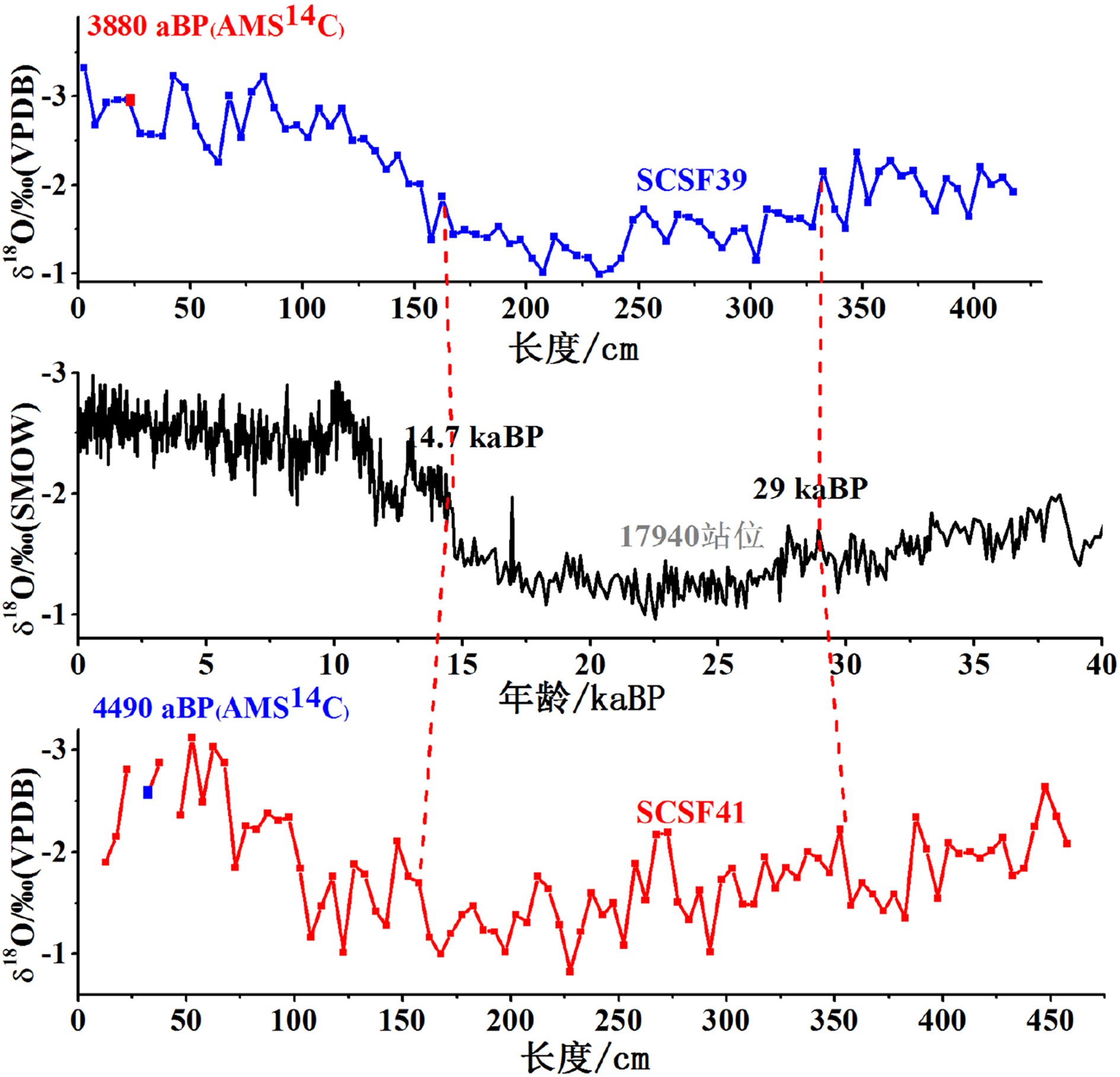
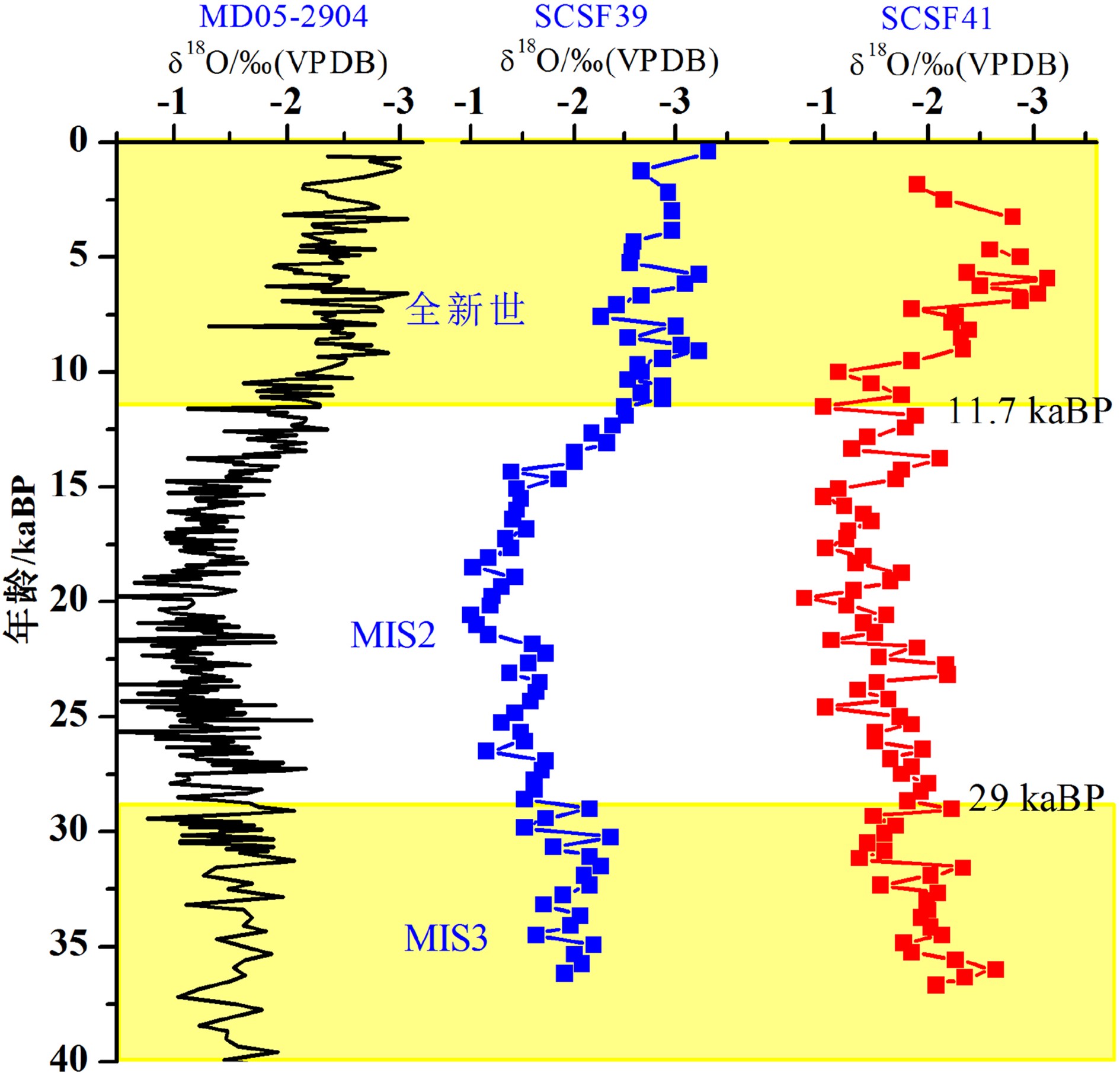
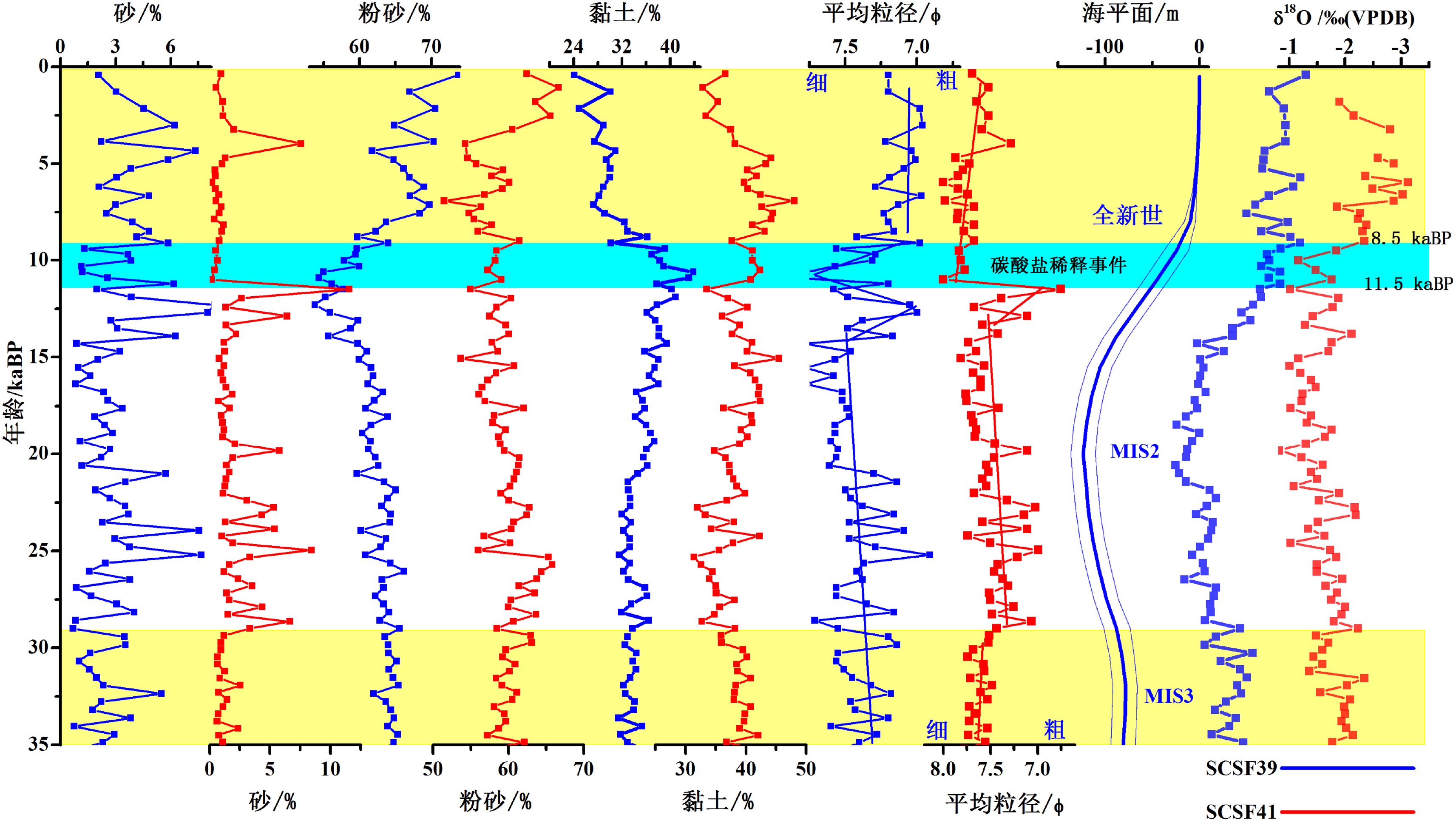
南海是西太地区最大的边缘海,汇集了周边陆地大量碎屑物质。这些陆源碎屑通过复杂的洋流系统经陆坡大量的输送到南海深海海盆中,使陆坡成为研究深海沉积物源汇体系不可缺少的重要环节。但陆坡区域水深变化大,洋流体系复杂,加之冰期间冰期海平面升降和季风的变化,使陆坡沉积环境一直成为研究的难点。为了研究陆坡沉积环境的演变过程,本文选用了南海北部陆坡中部和底部的两个重力柱开展元素地球化学方面的研究,探讨陆坡区域近三万年以来的沉积环境特征。研究发现海平面和季风是影响区域沉积环境的两个重要因素:(1)海平面变化是控制陆坡陆源物质/深海钙质碎屑变化的主要因素;(2)研究区域地层发育有“碳酸盐稀释事件”与东亚夏季风在全新世初期(11.5~8.5 kaBP)增强有关。
Abstract:The South China Sea is the largest marginal sea in the Western Pacific, which receives massive sediments from the surrounding landmasses. Terrestrial sediments are transported into the deep basin via a complex ocean current system, with the continental slope as a key component of the source-to-sink process. However, past changes in sedimentary environment of the continental slope remain rarely understood, because of the drastic variations in water depth and complicated current systems in addition to sea level changes induced by glacial-interglacial cycles and the changes in trade wind. In this research, two gravity cores collected from the northern South China Sea are used to study the sedimentary environmental evolution of the continental slope. One is located in the middle of the slope, and the other at the lower part of the slope. According to the results of element geochemistry, it is revealed that: 1) the sea level change is the key factor which controls the changes in the ratio of terrigenous to biogenic components of the sediments; 2) a carbonate dilution event is found related to the intensification of the East Asian Summer Monsoon during the early Holocene from 11.5 to 8.5 kaBP.
-

-
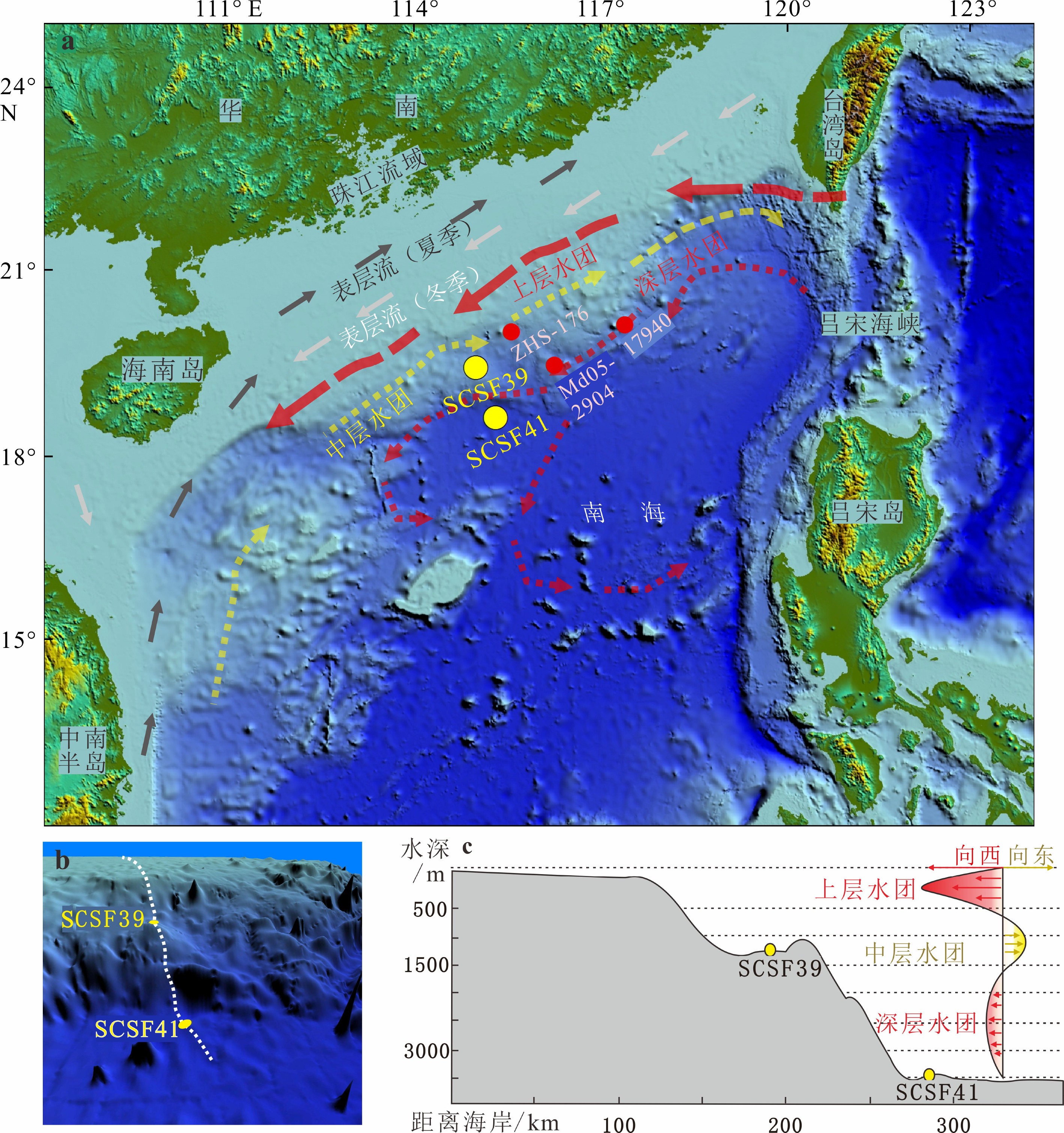
表 1 SCSF39站位和SCSF41站位基本信息
Table 1. Details of Core SCSF39 and SCSF 41
位置 水深/m 获取岩芯长度/cm 岩芯年龄/kaBP 平均沉积速/ (cm/ka) 经度/E 纬度/N SCSF39 114.97° 19.41° 1494 420 36.1 11.6 SCSF41 115.29° 18.61° 3717 460 36.7 12.5 -
[1] Milliman J D, Farnsworth K L. River Discharge to the Coastal Ocean: A Global Synthesis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2011: 1-382.
[2] Liu Z F, Zhao Y L, Colin C, et al. Source-to-sink transport processes of fluvial sediments in the South China Sea [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2016, 153: 238-273. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.08.005
[3] Zhang Y W, Liu Z F, Zhao Y L, et al. Mesoscale eddies transport deep-sea sediments [J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 4: 5937. doi: 10.1038/srep05937
[4] 舒业强, 王强, 俎婷婷. 南海北部陆架陆坡流系研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2018, 61(5):560-571 doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9152-y
SHU Yeqiang, WANG Qiang, ZU Tinging. Progress on shelf and slope circulation in the northern South China Sea [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(5): 560-571. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9152-y
[5] 赵绍华, 刘志飞, 陈全, 等. 南海北部末次冰期以来深水沉积物组成及其堆积速率的时空变化特征[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2017, 60(7):1368-1381 doi: 10.1007/s11430-016-9058-6
ZHAO Shaohua, LIU Zhifei, CHEN Quan, et al. Spatiotemporal variations of deep-sea sediment components and their fluxes since the last glaciation in the northern South China Sea [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2017, 60(7): 1368-1381. doi: 10.1007/s11430-016-9058-6
[6] Becker J J, Sandwell D T, Smith W H, et al. Global bathymetry and elevation data at 30 arc seconds resolution: SRTM30_PLUS [J]. Marine Geodesy, 2009, 32(4): 355-371. doi: 10.1080/01490410903297766
[7] 姚伯初. 南海海盆新生代的构造演化史[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1996, 16(2):1-13
YAO Bochu. Tectonic evolution of the South China Sea in cenozoic [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1996, 16(2): 1-13.
[8] Wang P X, Li Q Y. The South China Sea: Paleoceanography and Sedimentology[M]. Netherlands: Springer, 2009: 1-497.
[9] 刘丛舒, 丁巍伟, 殷绍如, 等. 南海北部陆坡区海底峡谷地貌、沉积特征及控制因素[J]. 海洋学研究, 2019, 37(2):28-43
LIU Congshu, DING Weiwei, YIN Shaoru, et al. Geomorphology, sedimentary characteristics and controlling factors of submarine canyons in the northern continental slope of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2019, 37(2): 28-43.
[10] 俞慕耕, 刘金芳. 南海海流系统与环流形势[J]. 海洋预报, 1993, 10(2):13-17
YU Mugeng, LIU Jinfang. Ocean current system and ocean current situation in the South China Sea [J]. Marine Forecasts, 1993, 10(2): 13-17.
[11] 苏纪兰. 南海环流动力机制研究综述[J]. 海洋学报, 2005, 27(6):1-8
SU Jilan. Overview of the South China Sea circulation and its dynamics [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2005, 27(6): 1-8.
[12] Liu Z Q, Gan J P. Three-dimensional pathways of water masses in the South China Sea: A modeling study [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2017, 122(7): 6039-6054. doi: 10.1002/2016JC012511
[13] Huang E Q, Tian J, Qiao P J, et al. Early interglacial carbonate-dilution events in the South China Sea: Implications for strengthened typhoon activities over subtropical East Asia [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2015, 125: 61-77. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.08.007
[14] Ge Q, Chu F Y, Xue Z, et al. Paleoenvironmental records from the northern South China Sea since the Last Glacial Maximum [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2010, 29(3): 46-62. doi: 10.1007/s13131-010-0036-9
[15] Wang L J, Sarnthein M, Grootes P M, et al. Millennial reoccurrence of century-scale abrupt events of East Asian Monsoon: A possible heat conveyor for the global deglaciation [J]. Paleoceanography, 1999, 14(6): 725-731. doi: 10.1029/1999PA900028
[16] 范维佳, 陈荣华. 南海北部5万年来的表层海水盐度及东亚季风降水[J]. 第四纪研究, 2011, 31(2):227-235 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2011.02.04
FAN Weijia, CHEN Ronghua. Sea Surface salinity and east Asian monsoon precipitation since the last 50000 years in the northern South China Sea [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2011, 31(2): 227-235. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2011.02.04
[17] Wang L, Sarnthein M, Erlenkeuser H, et al. East Asian monsoon climate during the Late Pleistocene: high-resolution sediment records from the South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 1999, 156(1-4): 245-284. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(98)00182-0
[18] 郑洪波, 陈国成, 谢昕, 等. 南海晚第四纪陆源沉积: 粒度组成、动力控制及反映的东亚季风演化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008, 28(3):414-424 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2008.03.005
ZHENG Hongbo, CHEN Guocheng, XIE Xin, et al. Grain size distribution and dynamic control of late Quaternary terrigenous sediments in the South China Sea and their implication for East Asian monsoon evolution [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2008, 28(3): 414-424. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2008.03.005
[19] Liu Z F, Li X J, Colin C, et al. A high-resolution clay mineralogical record in the northern South China Sea since the Last Glacial Maximum, and its time series provenance analysis [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(35): 4058-4068. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-4149-5
[20] Folk R L, Andrews P B, Lewis D W. Detrital sedimentary rock classification and nomenclature for use in New Zealand [J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology & Geophysics, 1970, 13(4): 937-968.
[21] 汪品先. 十五万年来的南海: 南海晚第四纪古海洋学研究阶段报告[M]. 上海: 同济大学出版社, 1995: 1-172.
WANG Pinxian. The Past 150 kyr of the South China Sea: A Periodic Report on the Late Quaternay Paleoceangraphy Research of the South China Sea[M]. Shanghai: Tongji University Press, 1995: 1-172.
[22] Zhao S H, Liu Z F, Colin C, et al. Responses of the East Asian Summer Monsoon in the low-latitude South China Sea to high-latitude millennial-scale climatic changes during the last glaciation: Evidence from a high-resolution clay mineralogical record [J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2018, 33(7): 745-765. doi: 10.1029/2017PA003235
[23] 石学法, 刘升发, 乔淑卿, 等. 东海闽浙沿岸泥质区沉积特征与古环境记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(4):19-30
SHI Xuefa, LIU Shengfa, QIAO Shuqing, et al. Depositional features and palaeoenvironmental records of the mud deposits in Min-Zhe Coastal Mud Area, East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(4): 19-30.
[24] 刘升发, 石学法, 刘焱光, 等. 东海内陆架泥质区表层沉积物常量元素地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2010, 38(1):80-86 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2010.01.011
LIU Shengfa, SHI Xuefa, LIU Yanguang, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of major elements in the surface sediments from the inner shelf mud area of the East China Sea [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2010, 38(1): 80-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2010.01.011
[25] 肖尚斌, 陈木宏, 陆钧, 等. 南海北部陆架柱状沉积物记录的残留沉积[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(3):1-5
XIAO Shangbin, CHEN Muhong, LU Jun, et al. New evidence for remnant deposits recorded by columnar sediments in the shelf of the Northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(3): 1-5.
[26] 田景春, 张翔. 沉积地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016: 1-196.
TIAN Jingchun, ZHANG Xiang. Sedimentary Geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2016: 1-196.
[27] Waelbroeck C, Labeyrie L, Michel E, et al. Sea-level and deep water temperature changes derived from benthic foraminifera isotopic records [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2002, 21(1-3): 295-305. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(01)00101-9
-



 下载:
下载: