Accumulation model of natural gas hydrate in the Beaufort-Mackenzie Delta Basin, the Arctic
-
摘要:
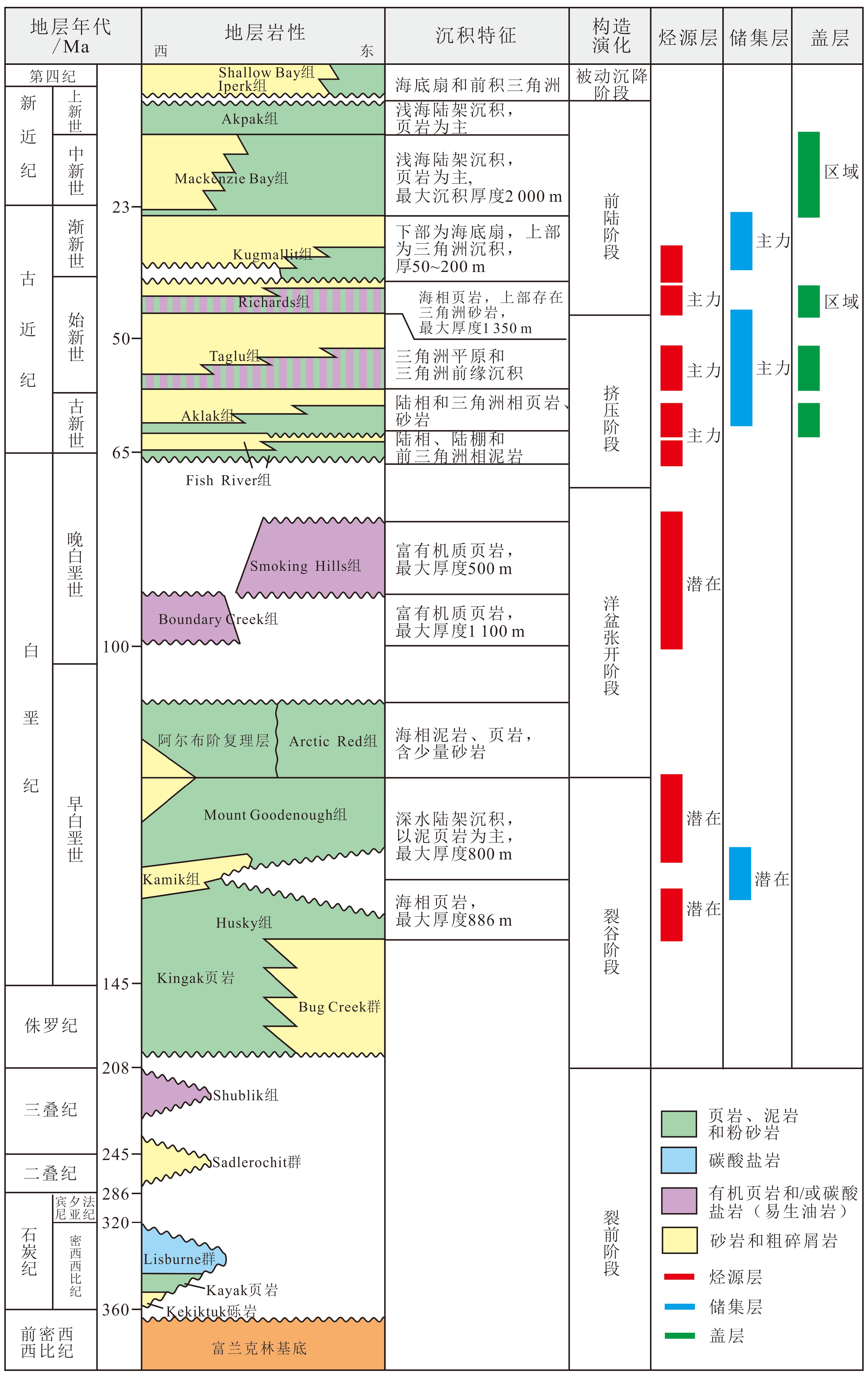
北极波弗特—马更些三角洲盆地常规油气和水合物资源十分丰富,是全球开展天然气水合物调查研究最早的地区之一。对该盆地水合物和常规油气的共生共藏关系的研究,不但对能源资源的勘探具有直接价值,而且对海域工程施工中海底稳定性评价以及全球气候变化和碳循环研究具有重要的理论和实际意义。在大量文献资料综合分析的基础上,系统总结了影响水合物成藏的地质和稳定条件,结合极地冰川演化特征,提出水合物与下伏油气藏渗漏共生并受冻土调节的成藏模式。认为波弗特—马更些三角洲盆地天然气水合物气源主要为下伏含油气系统中的热成因烃气;构造要素(断裂、背斜)密度与水合物富集丰度呈正相关,水合物赋存主要与Iperk、Kugmallit和Richards组的三角洲平原相砂体有关;水合物稳定带之上的冻土带对天然气水合物的成藏起着关键性调节作用。
-
关键词:
- 天然气水合物 /
- 成藏模式 /
- 波弗特―马更些三角洲盆地
Abstract:The Beaufort-Mackenzie Delta is an Arctic basin which contains abundant conventional hydrocarbon and natural gas hydrate. It is also one of the earliest regions in the world to carry out producing test of natural gas hydrate. To study the coexistence relationship between the hydrate and conventional hydrocarbon in the basin has not only direct significance to energy resource exploration, but also important theoretical and practical significance to seabed stability assessment, global climate change and carbon cycle research. In this paper, geological factors and stability conditions for hydrate reservoir generation was systematically summarized based on the large number of data available. Furthermore, combined with the analysis of glacier evolution, it was concluded that the accumulation of natural gas hydrate in the basin is controlled by the leakage of the underlying petroleum system and the change in permafrost zone. It is revealed that the gas source of hydrate in the basin is mainly the thermogenic hydrocarbon gas coming from the buried petroleum system. The activities of tectonic elements, such as faults and folders, were positively correlated with the enrichment of hydrate, and the hydrate occurrence was mainly related to the sand bodies of the delta plain in the Iperk, Kugmallit and Richards sequences. The permafrost above the hydrate stabilization zone plays a key role in the accumulation of gas hydrate.
-

-
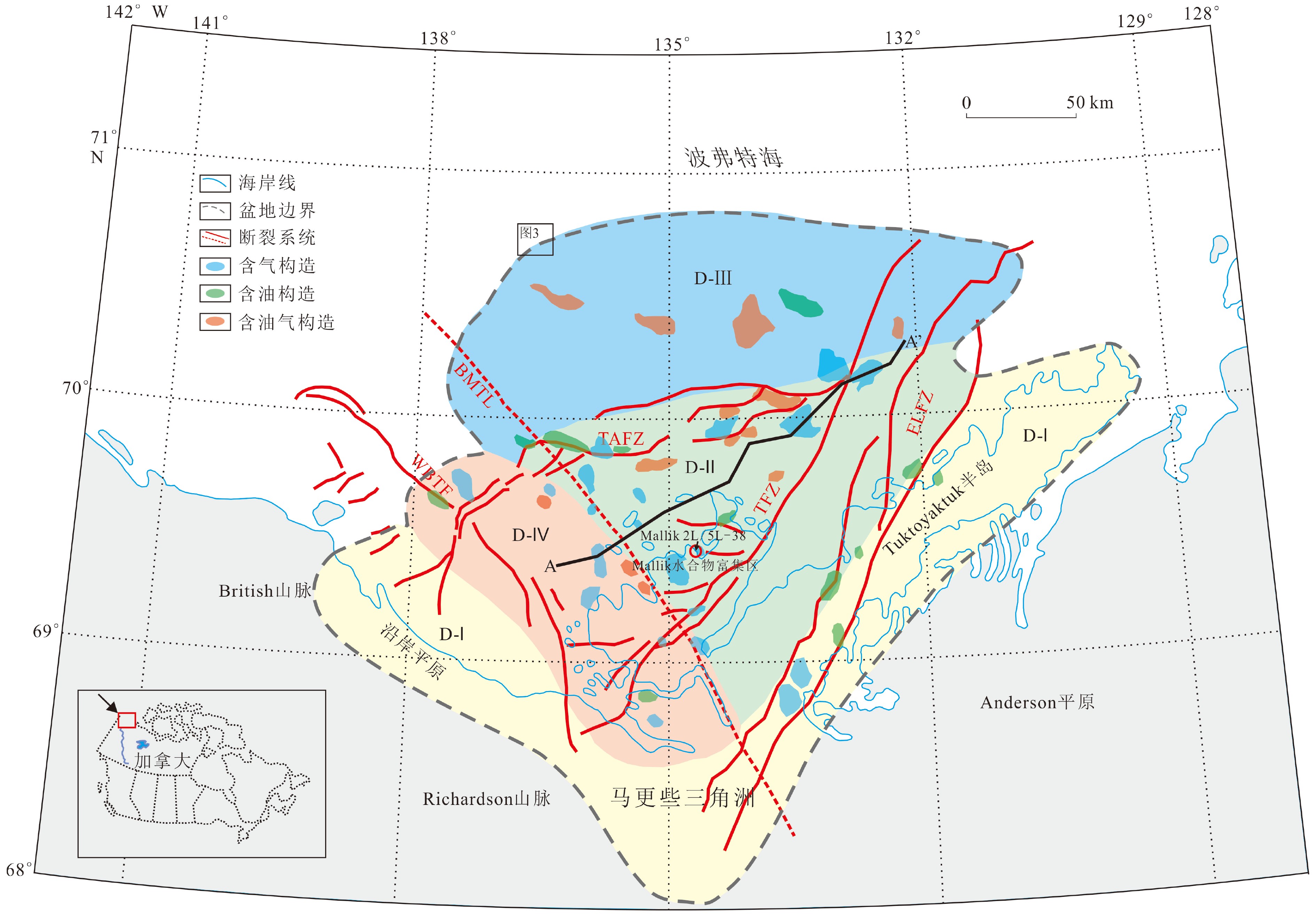
图 1 波弗特—马更些三角洲盆地地理位置及构造单元分布图[20]
Figure 1.
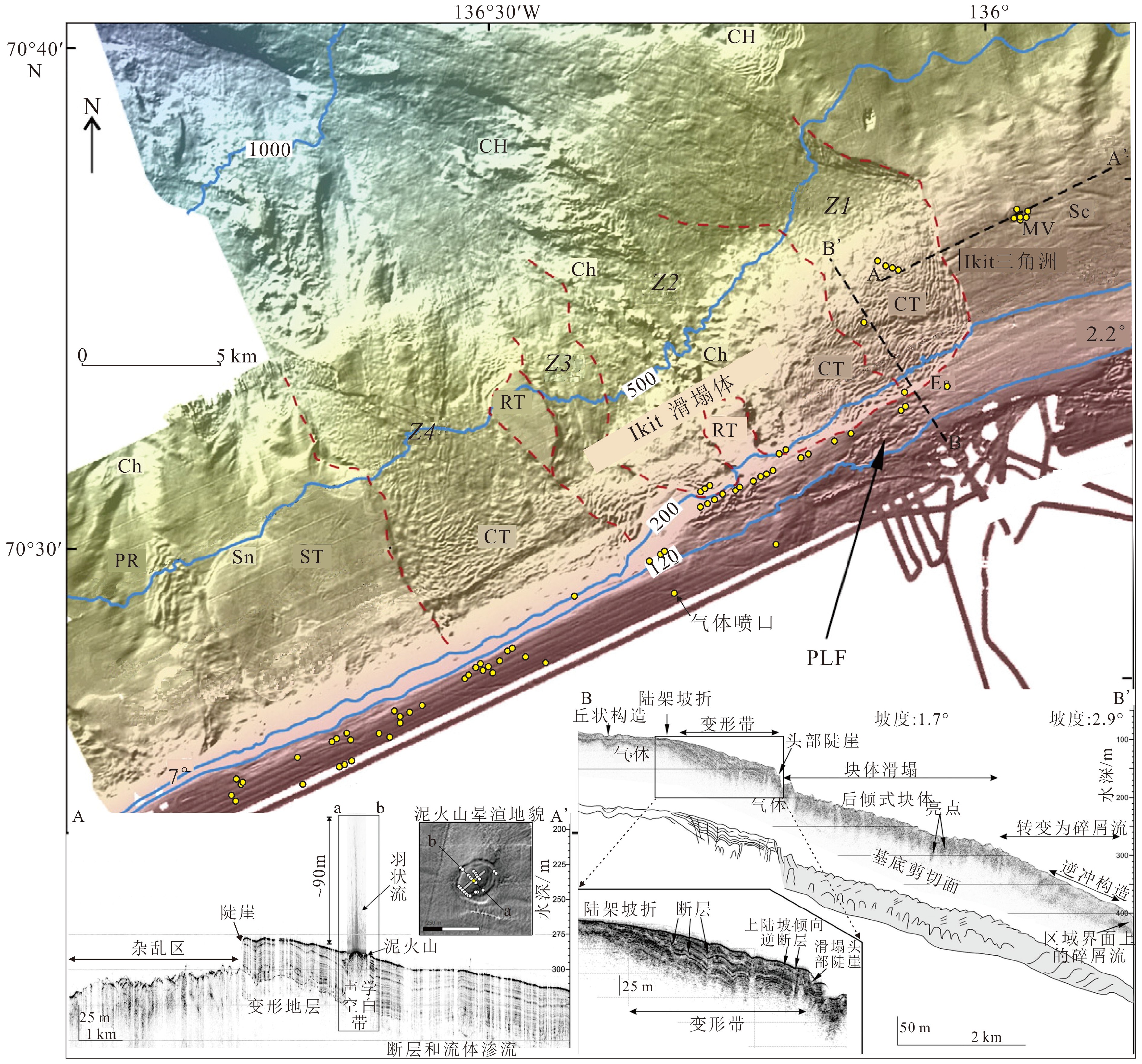
图 3 波弗特海陆架—上陆坡海底块体流搬运痕迹地貌特征及浅地层特征[24]
Figure 3.
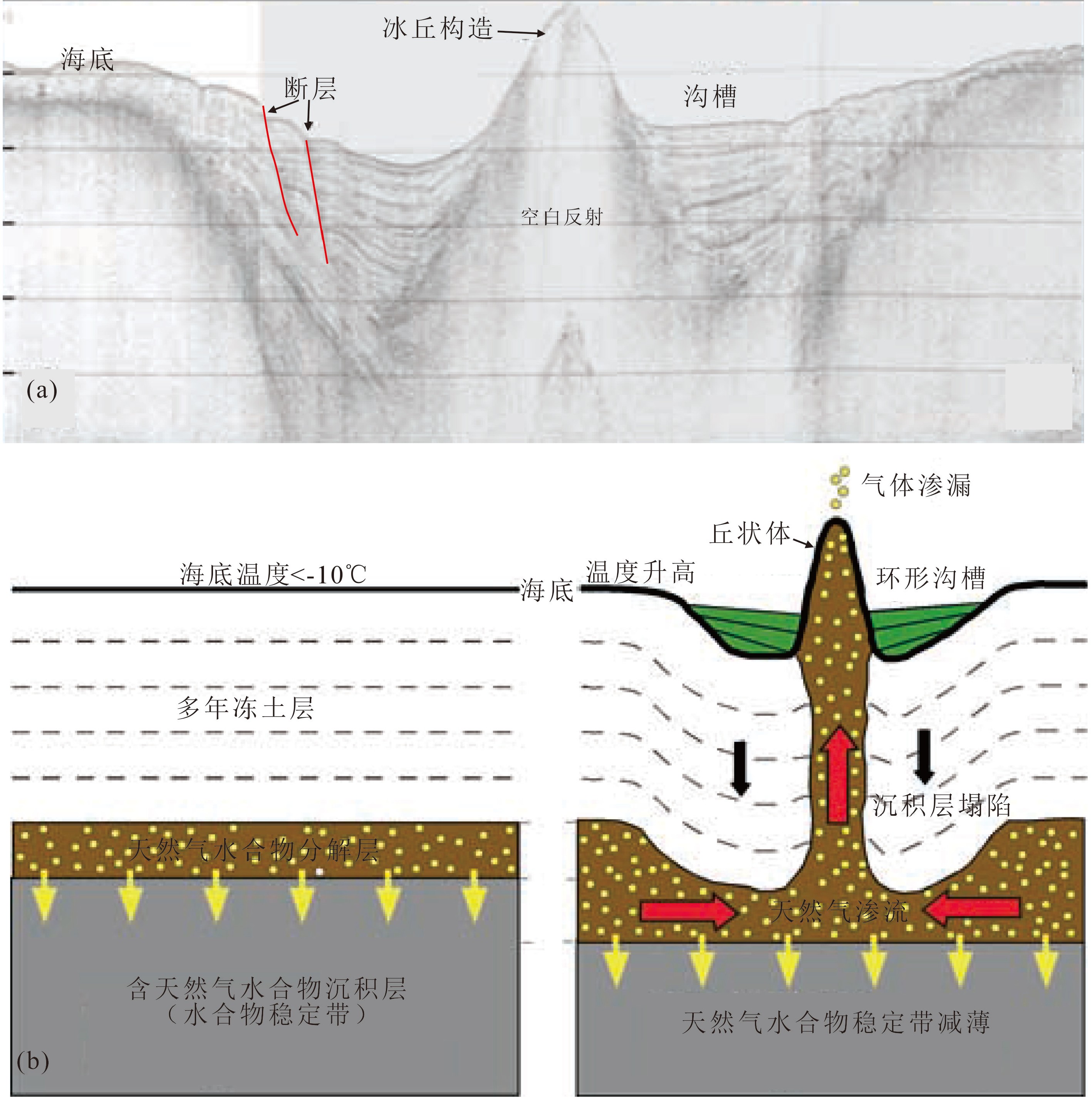
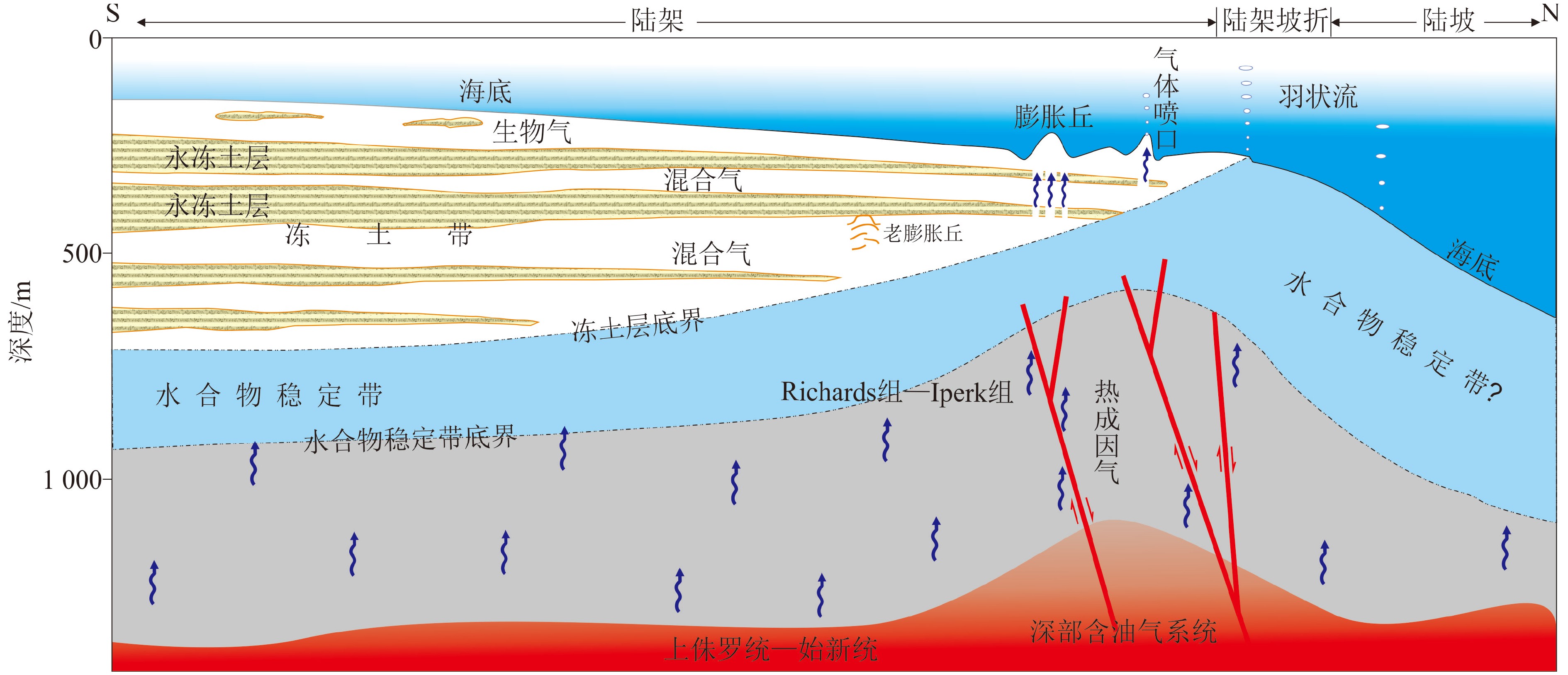
图 4 波弗特海陆架南部的冻胀丘地震反射特征和形成演化模式[27]
Figure 4.
图 5 Mallik 2L-38探井含水合物层的测井异常特征[32]
Figure 5.
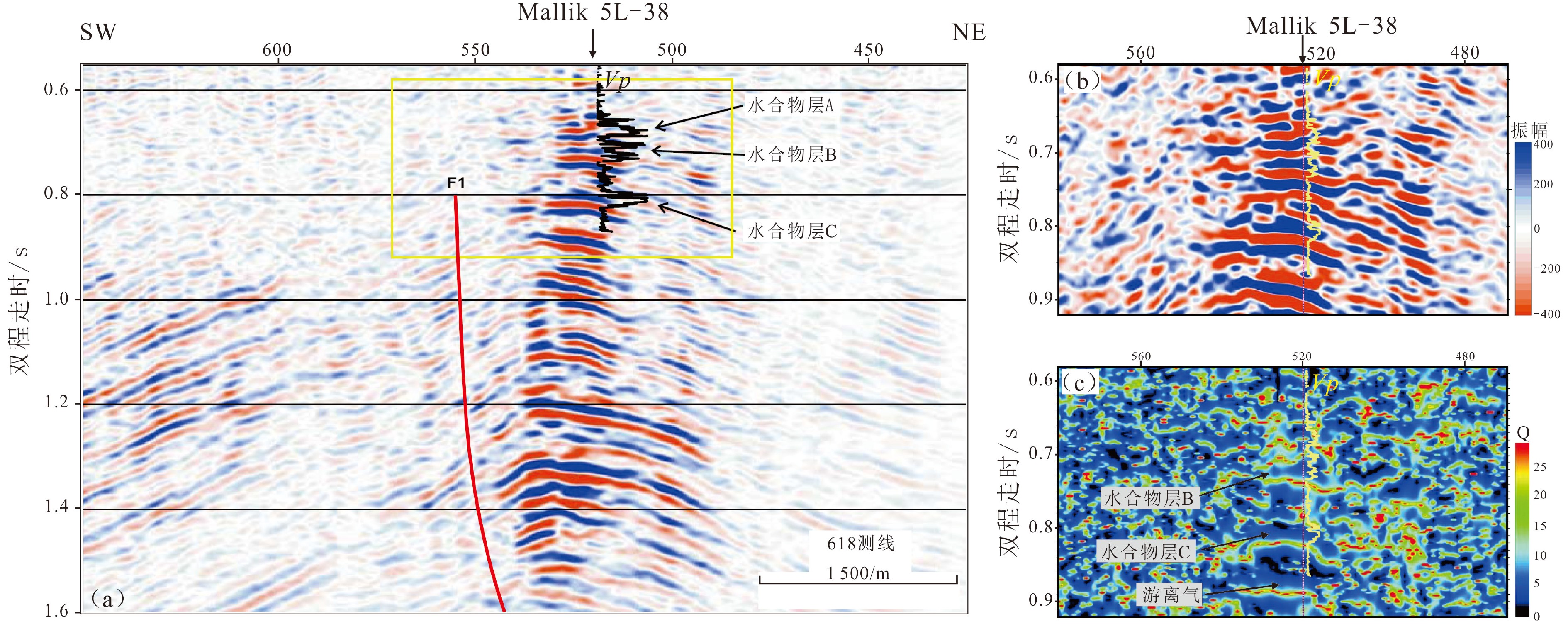
图 6 过Mallik 5L-38井三维地震反射剖面特征[34]
Figure 6.
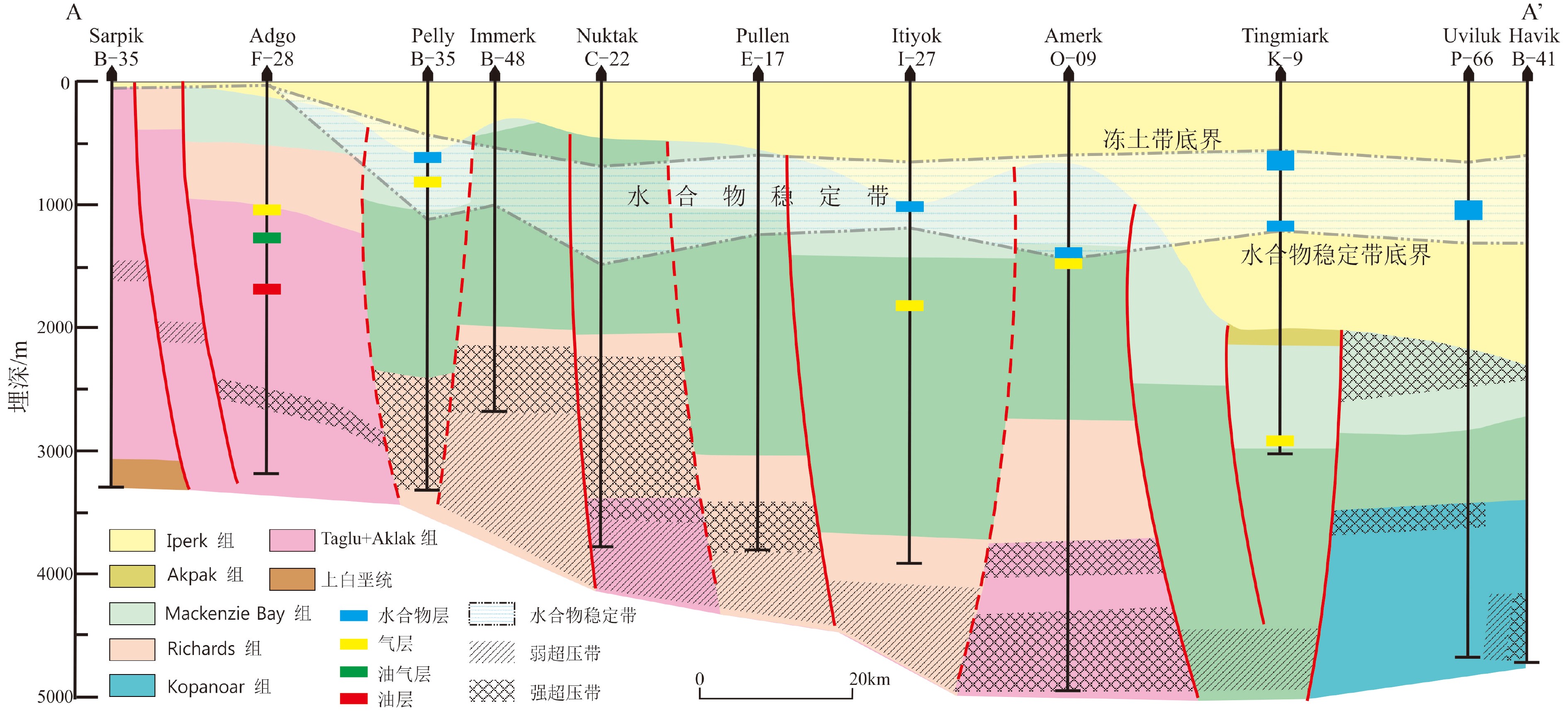
图 7 冻土带、水合物稳定带、水合物层、水合物/游离气接触带和常规油气在地层剖面上的分布关系[37]
Figure 7.
-
[1] Collett T S. Gas hydrate petroleum systems in marine and arctic permafrost environments[C]//GCSSEPM Proceedings. Houston, Texas, USA, 2009.
[2] Collett T S, Johnson A, Knapp C C, et al. Natural Gas Hydrates: Energy Resource Potential and Associated Geologic Hazards[M]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists, 2009: 356-370.
[3] 杨胜雄. 南海天然气水合物成藏理论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019.
YANG Shengxiong. Research on Gas Hydrate Accumulation in South China Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019.
[4] 吴能友, 张海啟, 杨胜雄, 等. 南海神狐海域天然气水合物成藏系统初探[J]. 天然气工业, 2007, 27(9):1-6 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2007.09.001
WU Nengyou, ZHANG Haiqi, YANG Shengxiong, et al. Preliminary Discussion on Natural Gas Hydrate (NGH) reservoir system of Shenhu Area, north slope of South China Sea [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2007, 27(9): 1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2007.09.001
[5] 吴能友, 梁金强, 王宏斌, 等. 海洋天然气水合物成藏系统研究进展[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(3):356-362 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.003
WU Nengyou, LIANG Jinqiang, WANG Hongbin, et al. Marine gas hydrate system: state of the art [J]. Geoscience, 2008, 22(3): 356-362. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.003
[6] 卢振权, 吴能友, 陈建文, 等. 试论天然气水合物成藏系统[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(3):363-375 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.004
LU Zhenquan, WU Nengyou, CHEN Jianwen, et al. Preliminary discussion on gas hydrate geological system [J]. Geoscience, 2008, 22(3): 363-375. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.004
[7] Makogon Y F, Holditch S A, Makogon T Y. Natural gas-hydrates—A potential energy source for the 21st Century [J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2007, 56(1-3): 14-31. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2005.10.009
[8] Matsumoto R, Ryu B J, Lee S R, et al. Occurrence and exploration of gas hydrate in the marginal seas and continental margin of the Asia and Oceania region [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(10): 1751-1767. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.09.009
[9] 张功成, 米立军, 屈红军, 等. 全球深水盆地群分布格局与油气特征[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(3):369-378 doi: 10.7623/syxb201103001
ZHANG Gongcheng, MI Lijun, QU Hongjun, et al. A basic distributional framework of global deepwater basins and hydrocarbon characteristics [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(3): 369-378. doi: 10.7623/syxb201103001
[10] 雷新华, 林功成, 苗永胜, 等. 天然气水合物与传统油气资源共生成藏模式初探[J]. 海相油气地质, 2013, 18(1):47-52 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2013.01.007
LEI Xinhua, LIN Gongcheng, MIAO Yongsheng, et al. Accumulation coexistence models of natural gas hydrate and conventional hydrocarbon: an approach [J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2013, 18(1): 47-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2013.01.007
[11] 刘金龙, 王淑红, 颜文. 海洋天然气水合物与深水油气共生关系探讨[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(2):39-51 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.02.006
LIU Jinlong, WANG Shuhong, YAN Wen. Research on coexistence between marine gas hydrate and deepwater oil [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(2): 39-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.02.006
[12] Collett T S, Lee M W, Agena W F, et al. Permafrost-associated natural gas hydrate occurrences on the Alaska North Slope [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(2): 279-294. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.12.001
[13] 杨楚鹏, 李学杰, 姚永坚, 等. 西南巴伦支海海底天然气渗漏的地球物理—地球化学标志及其成因机制[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(3):135-144
YANG Chupeng, LI Xuejie, YAO Yongjian, et al. The subsurface fluid-flow systems and their genetic mechanism in the southwestern Barents sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(3): 135-144.
[14] 杨楚鹏, 刘杰, 杨睿, 等. 北极阿拉斯加北坡盆地天然气水合物成矿规律与资源潜力[J]. 极地研究, 2019, 31(3):309-321
YANG Chupeng, LIU Jie, YANG Rui, et al. Occurrence and resource potential of gas hydrate in the Alaska north slope basin of the arctic [J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2019, 31(3): 309-321.
[15] Locat J, Lee H J. Submarine landslides: advances and challenges [J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2002, 39(1): 193-212. doi: 10.1139/t01-089
[16] Hornbach M J, Saffer D M, Holbrook W S. Critically pressured free-gas reservoirs below gas-hydrate provinces [J]. Nature, 2004, 427(6970): 142-144. doi: 10.1038/nature02172
[17] Dickens G R. Rethinking the global carbon cycle with a large, dynamic and microbially mediated gas hydrate capacitor [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 213(3-4): 169-183. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00325-X
[18] 刘杰, 孙美静, 杨睿, 等. 马更些三角洲冻土区天然气水合物成藏的地质控制因素[J]. 新能源进展, 2018, 6(1):47-54 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-560X.2018.01.008
LIU Jie, SUN Meijing, YANG Rui, et al. Geologic controls on permafrost-associated gas hydrate occurrence in the Mackenzie delta [J]. Advances in New and Renewable Energy, 2018, 6(1): 47-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-560X.2018.01.008
[19] Osadetz K G, Chen Z H. A re-evaluation of Beaufort Sea-Mackenzie Delta basin gas hydrate resource potential: petroleum system approaches to non-conventional gas resource appraisal and geologically-sourced methane flux [J]. Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, 2010, 58(1): 56-71. doi: 10.2113/gscpgbull.58.1.56
[20] Chen Z H, Issler D R, Osadetz K G, et al. Pore pressure patterns in Tertiary successions and hydrodynamic implications, Beaufort-Mackenzie Basin, Canada [J]. Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, 2010, 58(1): 3-16. doi: 10.2113/gscpgbull.58.1.3
[21] Houseknecht D W, Bird K J. Geology and petroleum potential of the rifted margins of the Canada Basin[M]//Spencer A M, Embry A F, Gautier D L, et al. Arctic Petroleum Geology. Geological Society, London, Memoirs, 2011: 509-526.
[22] Osadetz K G, Dixon J, Dietrich J, et al. A review of Mackenzie Delta-Beaufort Sea petroleum province conventional and non-conventional (gas hydrate) petroleum reserves and undiscovered resources: a contribution to the resource assessment of the proposed Mackenzie Delta-Beaufort Sea Marine Protected Area[M]//Dallimore S R, Collett T S. Beaufort-Mackenzie Basin: A Review of Conventional and Nonconventional (Gas Hydrate) Petroleum Reserves and Undiscovered Resources in Scientific Results from the Mallik 2002 Gas Hydrate Production Research Well Program, Mackenzie Delta, Northwest Territories, Canada. Geological Survey of Canada Bulletin, 2005: 19.
[23] Grantz A, Hart P E. Petroleum prospectivity of the Canada Basin, Arctic Ocean [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 30(1): 126-143. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.11.001
[24] Saint-Ange F, Kuus P, Blasco S, et al. Multiple failure styles related to shallow gas and fluid venting, upper slope Canadian Beaufort Sea, northern Canada [J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 355: 136-149. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.05.014
[25] Mosher D C, Moscardelli L, Shipp R C, et al. Submarine mass movements and their consequences[M]//Mosher D C, Shipp R C, Moscardelli L, et al. Submarine Mass Movements and Their Consequences. Dordrecht, Netherlands: Springer, 2010: 1-8.
[26] Paull C, Dallimore S R, Hughe-Clarke J, et al. Tracking the decomposition of submarine permafrost and gas hydrate under the shelf and slope of the Beaufort Sea[C]//Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Gas Hydrates. Edinburgh, 2012: 12.
[27] Paull C K, Ussler III W, Holbrook W S. Assessing methane release from the colossal Storegga submarine landslide [J]. Geophysical Research Letter, 2007, 34(4): L04601.
[28] Majorowicz J A, Hannigan P K. Stability zone of natural gas hydrates in a permafrost-bearing region of the Beaufort–Mackenzie basin: study of a feasible energy source 1 (Geological Survey of Canada Contribution No. 1999275) [J]. Natural Resources Research, 2000, 9(1): 3-26. doi: 10.1023/A:1010105628952
[29] Collett T S. Seismic -and well-log- inferred gas hydrate accumulations on Richards Island [J]. Bulletin of the Geological Survey of Canada, 1999, 544: 357-376.
[30] Lee M W, Collett T S. Amount of gas hydrate estimated from compressional- and shear -wave velocities at the JAPEX/JNOC/GSC Mallik 2L-38 gas hydrate research well[M]//Dallimore S R, Uchida T, Collett T S. Scientific Results from JAPEX/JNOC/GSC Mallik 2L-38 Gas Hydrate Research Well, Mackenzie Delta, Northwest Territories, Canada. Geology Survey Canada Bulletin, 1999: 313-322.
[31] Guerin G, Goldberg D, Meltser A. Characterization of in situ elastic properties of gas hydrate-bearing sediments on the Blake Ridge [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1999, 104(B8): 17781-17795. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900127
[32] Guerin G, Goldberg D. Sonic waveform attenuation in gas hydrate-bearing sediments from the Mallik 2L-38 research well, Mackenzie Delta, Canada [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2002, 107(B5): 2088. doi: 10.1029/2001JB000556
[33] Bellefleur G, Riedel M, Brent T. Seismic characterization and continuity analysis of gas-hydrate horizons near Mallik research wells, Mackenzie Delta, Canada [J]. The Leading Edge, 2006, 25(5): 599-604. doi: 10.1190/1.2202663
[34] Bellefleur G, Riedel M, Brent T, et al. Implication of seismic attenuation for gas hydrate resource characterization, Mallik, Mackenzie Delta, Canada [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2007, 112(B10): B10311. doi: 10.1029/2007JB004976
[35] Collett T S, Dallimore S R. Hydrocarbon gases associated with permafrost in the Mackenzie Delta, Northwest Territories, Canada [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 1999, 14(5): 607-620. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(98)00087-0
[36] Lorenson T D, Whiticar M J, Waseda A, et al. Gas composition and isotopic geochemistry of cuttings, core and gas hydrate from the JAPEX/JNOC/GSC Mallik 2L-38 gas hydrate research well[M]//Dallimore S R, Collect T S, Uchida T. Scientific Results from JAPEX/JNOC/GSC Mallik 2L-38 Gas Hydrate Research Well, Mackenzie Delta, Northwest Territories, Canada. Geology Survey Canada Bulletin, 1999: 143-163.
[37] Majorowicz J A, Hannigan P K. Natural gas hydrates in the offshore Beaufort–Mackenzie basin—study of a feasible energy source II [J]. Natural Resources Research, 2000, 9(3): 201-214. doi: 10.1023/A:1010179301059
[38] Chen Z H, Osadetz K G, Issler D R, et al. Hydrocarbon migration detected by regional temperature field variations, Beaufort-Mackenzie Basin, Canada [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2008, 92(12): 1639-1653. doi: 10.1306/07300808011
[39] Majorowicz J A, Osadetz K G. Gas hydrate distribution and volume in Canada [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2001, 85(7): 1211-1230.
[40] Bily C, Dick J W L. Naturally occurring gas hydrates in the Mackenzie Delta, N. W. T [J]. Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, 1974, 22(3): 340-352.
[41] Weaver J S, Stewart J M. In situ hydrates under the Beaufort shelf[M]//FRENCH M H. Proceedings of the 4th Canadian Permafrost Conference 1981. National Research Council of Canada, The Roger J. E. Brown Memorial Volume, 1982: 312-319.
[42] Hitchon B, Underschultz J R, Bachu S, et al. Hydrogeology, geopressures and hydrocarbon occurrences, Beaufort-Mackenzie Basin [J]. Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, 1990, 38(2): 215-235.
[43] Dai S, Lee C, Santamarina J C. Formation history and physical properties of sediments from the Mount Elbert Gas Hydrate Stratigraphic Test Well, Alaska North Slope [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(2): 427-438. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.03.005
[44] Allen D M, Michel F A, Judge A S. The permafrost regime in the Mackenzie Delta, Beaufort Sea region, N. W. T. and its significance to the reconstruction of the palaeoclimatic history [J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 1988, 3(1): 3-13. doi: 10.1002/jqs.3390030103
-



 下载:
下载: