Characteristics and classification of the Paleogene reservoirs in Huagang Formation of Gas Field N, East China Sea Basin
-
摘要:
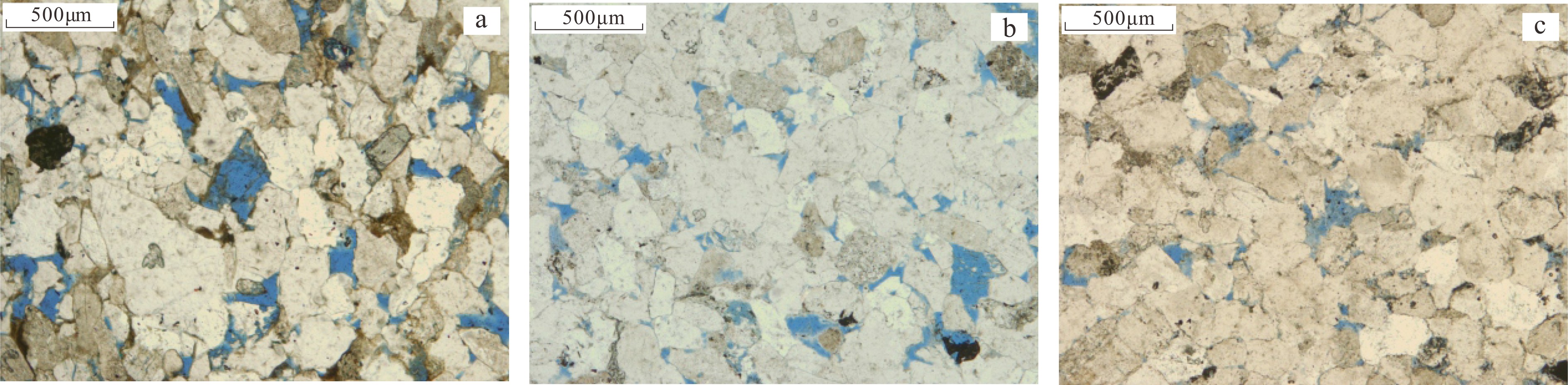
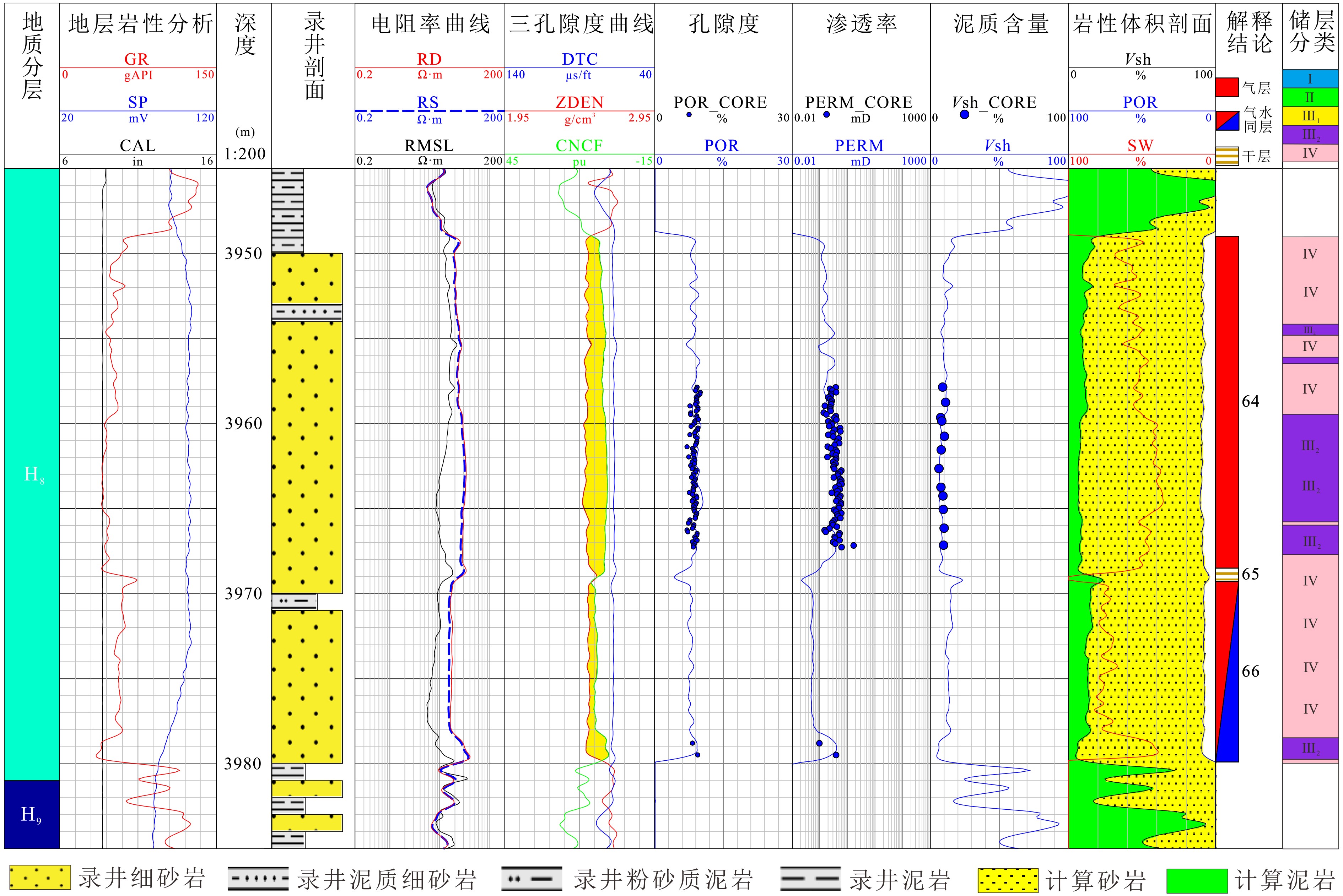
东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷古近系花港组储层为典型的低孔、低渗储层。基于大量岩心物性、粒度、薄片、压汞等资料,对N气田目的层储层岩性、物性和孔隙结构特征进行精细评价。结果表明:N气田花港组储层岩性以细砂岩为主,矿物成分构成稳定,以石英为主,黏土含量低,岩性较纯;随着埋藏变深,孔隙变差,粒间孔减少,溶蚀孔增加,孔喉半径减小,连通性变差;局部发育砂砾岩,且渗透率大于细砂岩一个数量级以上,可作为甜点储层开发。基于实验和试油资料统计结果,建立了一套适用于花港组储层的综合分类评价标准,包含孔隙度、渗透率、饱和度和地质特征4类储层重要参数,分类结果特征鲜明,分类依据科学可靠,为该区域低孔、低渗储层勘探开发提供依据。
Abstract:The Paleogene Huagang Formation in the N gas field of Xihu Sag in the East China Sea Basin is a typical tight reservoir of low-porosity and low-permeability. Based on a large number of testing data for core property, particle size, thin section and mercury testing, the lithology, physical properties and pore structures of the reservoirs in the gas field N are carefully studied in this paper. The Huagang Formation is dominated by fine quartz sandstone with little clay. With the increase in burial depth, the intergranular pores decrease, the dissolution pores increase, and the porosity becomes worse in general, as the pore throat diameter is reduced and the connectivity deteriorated. Glutenite sometimes occurs locally, the permeability of which is more than one order higher than that of the fine sandstone, and thus becomes sweet areas for oil production. Based on the statistical results of testing data, a comprehensive evaluation standard specially applicable to the Huagang reservoir is established, which contains four important reservoir parameters, namely porosity, permeability, saturation and geological features. The classification results are distinctive and reliable. Facts prove that it is an effective tool for exploration and development of tight low-porosity and low-permeability reservoirs in the region.
-

-
表 1 N气田花港组储层矿物成分统计
Table 1. Mineral composition of Huagang reservoir in gas field N
% 层位 石英 长石 岩屑 胶结物 钾长石 斜长石 火成岩 变质岩 沉积岩 方解石 白云石 黏土 其他 花港组上段 64.15 7.79 10.05 6.70 8.17 3.02 1.34 0.23 6.49 1.01 花港组下段 63.60 7.74 9.52 6.79 9.19 3.16 2.24 0.44 7.06 0.93 表 2 东海盆地N气田古近系花港组低渗储层分类标准
Table 2. The classification standard of Huagang low porosity and low permeability reservoir in gas field N of East China Sea Basin
储层分类 Ⅰ(中高渗) Ⅱ(低渗) Ⅲ1(特低渗) Ⅲ2(特低渗) Ⅳ(超低渗) 渗透率 空气渗透率/mD >10 10~1 1~0.5 0.5~0.2 <0.2 覆压渗透率/mD >7 7~0.24 0.25~0.1 0.1~0.026 <0.026 孔隙度 总孔隙度/% >15 15~10 10~6 <6 可动孔隙度/% >12 12~8 8~4 <4 饱和度 束缚水饱和度/% <35 35~50 50~65 >65 地质特征 分选 中、中-差 中-差、差 差 差 差 接触方式 点、点-线 点-线、线 线-点、线 线-点、凹凸-线 线、凹凸-线 孔隙类型 原生粒间孔
少量粒间溶孔原生粒间孔
粒间溶孔大量粒间溶孔
粒内溶孔
少量原生粒间孔大量粒间溶孔
粒内溶孔
铸模孔粒间溶孔
粒内溶孔岩性 中砂岩
砂砾岩砂砾岩
含砾砂岩细砂岩
含砾砂岩细砂岩
粉砂岩粉砂岩
细粉砂岩 -
[1] 邹才能, 张国生, 杨智, 等. 非常规油气概念、特征、潜力及技术——兼论非常规油气地质学[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(4):385-399, 454 doi: 10.11698/PED.2013.04.01
ZOU Caineng, ZHANG Guosheng, YANG Zhi, et al. Geological concepts, characteristics, resource potential and key techniques of unconventional hydrocarbon: On unconventional petroleum geology [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(4): 385-399, 454. doi: 10.11698/PED.2013.04.01
[2] 贾承造. 论非常规油气对经典石油天然气地质学理论的突破及意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(1):1-11 doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(17)30002-2
JIA Chengzao. Breakthrough and significance of unconventional oil and gas to classical petroleum geological theory [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(1): 1-11. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(17)30002-2
[3] 陶士振, 邹才能. 东海盆地西湖凹陷天然气成藏及分布规律[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(4):103-110 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.04.017
TAO Shizhen, ZOU Caineng. Accumulation and distribution of natural gases in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2005, 32(4): 103-110. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.04.017
[4] 曾大乾, 李淑贞. 中国低渗透砂岩储层类型及地质特征[J]. 石油学报, 1994, 15(1):38-46 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.1994.01.014
ZENG Daqian, LI Shuzhen. Types and characteristics of low permeability sandstone reservoirs in China [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1994, 15(1): 38-46. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.1994.01.014
[5] 王会丽. 金湖凹陷低孔低渗储层分布与测井评价方法研究[D]. 中国石油大学硕士学位论文, 2011.
WANG Huili. Study on distribution and logging evaluation methods of low porosity and permeability reservoirs in Jinhu depression[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Petroleum, 2011.
[6] 杨玉卿, 潘福熙, 田洪, 等. 渤中25-1油田沙河街组低孔低渗储层特征及分类评价[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(4):685-693 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.04.006
YANG Yuqing, PAN Fuxi, TIAN Hong, et al. Characteristics and classification and evaluation of low porosity and permeability reservoir in Shahejie formation of BZ25-1 oilfield [J]. Geoscience, 2010, 24(4): 685-693. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.04.006
[7] 赵靖舟, 吴少波, 武富礼. 论低渗透储层的分类与评价标准——以鄂尔多斯盆地为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2007, 19(3):28-31, 53 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2007.03.005
ZHAO Jingzhou, WU Shaobo, WU Fuli. The classification and evaluation criterion of low permeability reservoir: An example from Ordos Basin [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2007, 19(3): 28-31, 53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2007.03.005
[8] 姜艳娇, 孙建孟, 高建申, 等. X区块低孔渗气藏储层特征及分类评价研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(10):164-172 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.10.028
JIANG Yanjiao, SUN Jianmeng, GAO Jianshen, et al. Study on reservoir characteristics and classification evaluation in low porosity and low permeability gas reservoir of X block [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(10): 164-172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.10.028
[9] 刘金水, 廖宗廷, 贾健谊, 等. 东海陆架盆地地质结构及构造演化[J]. 上海地质, 2003, 23(3):1-6
LIU Jinshui, LIAO Zongting, JIA Jianyi, et al. The geological structure and tectonic evolution of the East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Shanghai Geology, 2003, 23(3): 1-6.
[10] 蒋一鸣, 邵龙义, 李帅, 等. 西湖凹陷平湖构造带平湖组沉积体系及层序地层研究[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(1):141-153
JIANG Yiming, SHAO Longyi, LI Shuai, et al. Deposition system and stratigraphy of Pinghu formation in Pinghu tectonic belt, Xihu Sag [J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(1): 141-153.
[11] 姜亮. 东海陆架盆地油气资源勘探现状及含油气远景[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(1):1-5
JIANG Liang. Exploration status and perspective of petroleum resources in East China Sea shelf basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2003, 17(1): 1-5.
[12] 李上卿, 李纯洁. 东海西湖凹陷油气资源分布及勘探潜力分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2003, 25(6):721-728 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2003.06.015
LI Shangqing, LI Chunjie. Analysis on the petroleum resource distribution and exploration potential of the Xihu depression, the East China Sea [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2003, 25(6): 721-728. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2003.06.015
[13] 陈志勇, 葛和平. 西湖凹陷反转构造与油气聚集[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(1):20-24
CHEN Zhiyong, GE Heping. Inversion structures and hydrocarbon accumulation in XIHU sag, east China Sea basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2003, 17(1): 20-24.
[14] 顾惠荣, 贾健谊, 叶加仁. 东海西湖凹陷含油气系统特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2002, 23(3):295-297, 306 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2002.03.021
GU Huirong, JIA Jianyi, YE Jiaren. Characteristics of oil and gas bearing system in Xihu lake depression in the East China Sea [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2002, 23(3): 295-297, 306. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2002.03.021
[15] 祝建军, 王琪, 梁建设, 等. 东海陆架盆地南部新生代地质结构与构造演化特征研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2012, 23(2):222-229
ZHU Jianjun, WANG Qi, LIANG Jianshe, et al. Cenozoic geological structure and tectonic evolution of southern East China Sea shelf basin [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2012, 23(2): 222-229.
[16] 张武, 徐发, 徐国盛, 等. 西湖凹陷某构造花港组致密砂岩储层成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 成都理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2012, 39(2):122-129
ZHANG Wu, XU Fa, XU Guosheng, et al. Diagenesis and pore evolution of Huagang Formation tight sandstone reservoirs in a structure of Xihu depression in East China Sea Basin [J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology: Science & Technology Edition, 2012, 39(2): 122-129.
[17] 刘金水, 曹冰, 徐志星, 等. 西湖凹陷某构造花港组沉积相及致密砂岩储层特征[J]. 成都理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2012, 39(2):130-136
LIU Jinshui, CAO Bing, XU Zhixing, et al. Sedimentary facies and the characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs of Huagang Formation in Xihu depression, East China Sea Basin [J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology: Science & Technology Edition, 2012, 39(2): 130-136.
[18] 张建培, 徐发, 钟韬, 等. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖组-花港组层序地层模式及沉积演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(1):35-41
ZHANG Jianpei, XU Fa, ZHONG Tao, et al. Sequence stratigraphic models and sedimentary evolution of Pinghu and Huagang formations in Xihu trough [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(1): 35-41.
[19] 胡明毅, 柯岭, 梁建设. 西湖凹陷花港组沉积相特征及相模式[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2010, 32(5):1-5 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2010.05.001
HU Mingyi, KE Ling, LIANG Jianshe. The characteristics and pattern of sedimentary facies of Huagang formation in Xihu depression [J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2010, 32(5): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2010.05.001
[20] 王果寿, 周卓明, 肖朝辉, 等. 西湖凹陷春晓区带下第三系平湖组、花港组沉积特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2002, 23(3):257-261, 265 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2002.03.012
WANG Guoshou, ZHOU Zhuoming, XIAO Chaohui, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of Eogene Pinghu formation and Huagang formation in Chunxiao zone of Xihu Lake depression [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2002, 23(3): 257-261, 265. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2002.03.012
[21] 中华人民共和国国土资源部. DZ/T 0252-2013 海上石油天然气储量计算规范[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2013.
Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China. DZ/T 0252-2013 Regulation of offshore petroleum reserves estimation[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2013.
[22] 国家能源局. SY/T 6832-2011 致密砂岩气地质评价方法[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2011.
National Energy Administration. SY/T 6832-2011 Geological evaluating methods for tight sandstone gas[S]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2011.
-




 下载:
下载: