Source and migration direction of oil and gas in Kongqueting area, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin
-
摘要:
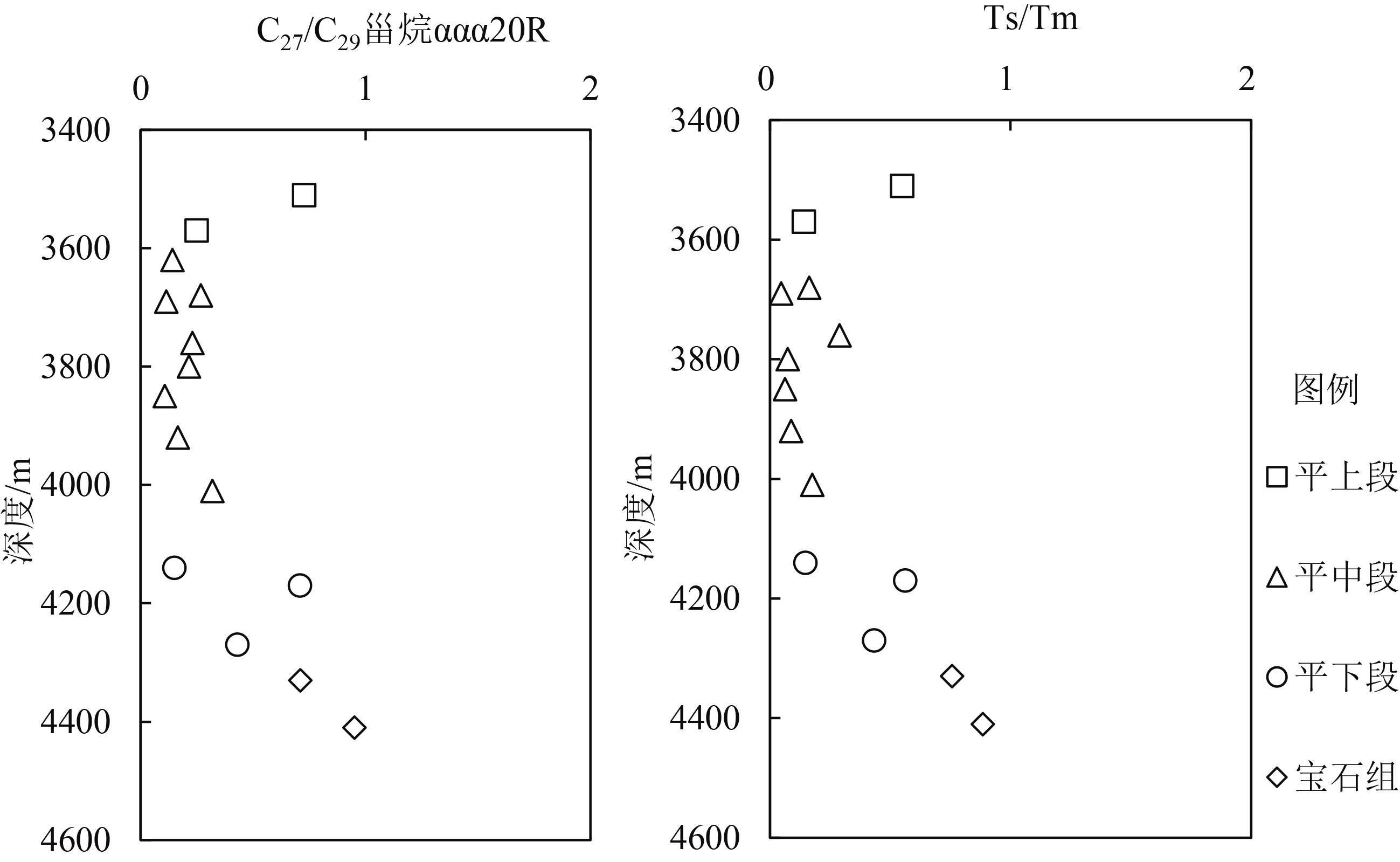
孔雀亭区是西湖凹陷油气勘探重点区带,油气来源及运移方向不清限制了勘探的进一步拓展。基于油气特征及分布研究,通过开展烃源岩及原油生物标志化合物特征对比分析、天然气成熟度计算,综合厘定了油气来源;结合油气运移效应分析明确了原油及天然气运移方向。结果表明,孔雀亭区原油主要来自平湖组下段和宝石组烃源岩,平湖组中段及上段少量贡献,原油自斜坡内生油次洼向高部位运移,是原油优势运聚方向;天然气具有斜坡带本地烃源岩及西次凹双重来源,以西次凹贡献为主,天然气自斜坡低带向高带侧向运移,并沿断层与斜坡带烃源岩自生天然气混合呈现垂向运移特征,斜坡低部位是天然气勘探有利区带。
Abstract:Kongqueting is a key exploration area in the Xihu sag of the East China Sea Shelf Basin. The ambiguity in source and migration direction of oil and gas has brought difficulties in efficient oil and gas exploration. This time, the source of oil and gas is jointly determined by the study of oil and gas characteristics and distribution patterns, the correlation of the biomarkers between source rocks and crude oil, and the calculation of the maturity of natural gas. In combination with the migration effect of oil and gas, the migration direction of crude oil and natural gas are discussed. The results suggest that the crude oil in Kongqueting area mainly comes from the source rocks of the Lower Pinghu Formation and Baoshi Formation, with a little from the Middle Pinghu Formation. Crude oil migrates mainly from the secondary depressions to the higher part of the slope for oil accumulation. In terms of natural gas, there are dual sources, one local source and one the source from the Western Subsag. The natural gas generated from the Western Subsag migrates from low zone to high zone along the slope, and mixed with natural gas generated by local source rock of the slope zone on the way, suggesting a pattern of vertical migration. Therefore, the low part of the slope is a potential area for natural gas exploration.
-
Key words:
- source of oil and gas /
- oil and gas migration /
- Xihu Sag /
- Kongqueting area /
- East China Sea Shelf Basin
-

-
表 1 西湖凹陷孔雀亭区原油物性统计
Table 1. Oil parameters from Kongqueting area
井名 深度/m 密度/ (g/cm3) 凝固点/℃ 硫含量/% 蜡含量/% G2 4150 0.8422 9 0.10 2.11 Z2 4107.5 0.8248 15 0.06 3.14 Z2 4186 0.8152 14 0.07 3.08 Z1 4183 0.8167 5 0.04 3.27 Z1 4548.7 0.8606 29 0.07 10.54 G1 3542.6 0.8345 14 0.04 17.91 G1 3565.6 0.8239 17 0.06 19.53 G1 3810.2 0.7487 −30 0.06 0.07 D2 3949 0.8380 −34 0 0 D2 4317.4 0.8443 12 0.04 9.50 D2 4333 0.8390 −32 0.07 0 G3 2647 0.8315 5 0.02 12.00 G3 3099 0.8105 −1 0.01 7.70 表 2 西湖凹陷孔雀亭区天然气组分及同位素统计
Table 2. Natural gas parameters from Kongqueting area
井号 深度/m 组分/% 同位素/‰ iC4H10/nC4H10 N2/C2H6 成熟度% CH4 C2H6 C3H8 iC4H10 nC4H10 iC5H12 nC5H12 N2 CO2 CH4 C2H6 C3H8 C4H10 G1 3542 83.52 7.61 2.42 0.49 0.37 0.11 0.04 2.98 2.45 − − − − 1.32 0.39 − G1 3565 79.03 8.68 3.54 0.96 0.58 0.23 0.07 4.19 2.72 − − − − 1.66 0.48 − G1 3810 75.96 10.33 5.70 1.80 0.70 0.25 0.12 1.70 3.40 − − − − 2.57 0.16 − G2 4150 89.1 4.48 0.63 0.16 0.10 0.05 0.03 0.36 5.00 −37.1 −22.7 −20.8 −21.7 1.60 0.08 0.79 G4 4093 79.43 8.38 2.84 1.04 0.65 0.28 0.20 0.59 6.29 −34.6 −25.3 −24.5 −25.4 1.60 0.07 1.02 Z2 4111 81.02 7.35 3.03 0.74 0.64 0.22 0.16 0.45 6.19 −37.8 −27.2 −25.4 −24.6 1.16 0.06 0.73 Z2 4186 81.42 7.29 2.97 0.72 0.62 0.22 0.16 0.18 6.19 −28.2 −23.8 −23.7 −23.3 1.16 0.02 1.97 Z1 4183 85.51 6.28 2.30 0.59 0.51 0.18 0.13 0.20 4.11 −35.4 −25.7 −24.4 −24.8 1.16 0.03 0.94 Z1 4548 73.20 8.43 5.83 1.68 1.40 0.49 0.31 0.57 7.79 −37.7 −27.6 −26.3 −26.2 1.20 0.07 0.74 D1 4198 89.82 5.51 1.66 0.44 0.33 0.14 0.09 0 1.99 −33.4 −26.3 −24.3 −23.1 1.32 0 1.16 D1 4810 92.05 5.38 1.51 0.36 0.36 0.17 0.12 0.02 0 −33.6 −28.4 −27.1 −22.7 1.01 0 1.14 表 3 孔雀亭区烃源岩与原油生标参数统计
Table 3. Biomarker of source rock and oil from Kongqueting area
样品类型 甾烷C27/
C29ααα20RTs/Tm 伽马蜡烷/
C30藿烷C29/C30
藿烷C29重排甾
烷/C29规
则甾烷C24四环萜/
C23三环萜C29甾烷ββ/
(αα+ββ)C29甾烷20S/20
(R+S)C31藿烷S/
(S+R)运移效应 烃源岩 平上段 0.79(14)
0.25~2.010.96(13)
0.01~2.660.18(13)
0.01~0.830.7(12)
0.26~2.170.12(14)
0.01~0.240.75(6)
0.24~1.500.39(14)
0.25~0.500.38(14)
0.17~0.500.53(14)
0.36~0.57— 平中段 0.24(16)
0.01~0.540.37(16)
0.05~1.490.07(16)
0.01~0.200.78(16)
0.46~1.220.18(16)
0.12~0.260.95(13)
0.36~3.440.36(16)
0.24~0.530.42(16)
0.28~0.490.56(16)
0.52~0.59— 平下段 0.39(4)
0.15~0.710.33(4)
0.15~0.560.05(2)
0.09~0.100.65(4)
0.61~0.690.16(4)
0.12~0.211.03(2)
0.43~1.680.45(4)
0.43~0.480.46(4)
0.45~0.470.56(4)
0.54~0.57— 宝石组 0.83(2)
0.70~0.950.82(2)
0.76~0.880.14(2)
0.12~0.150.56(2)
0.55~0.570.19(2)
0.19~0.200.25(2)
0.27~0.240.43(2)
0.42~0.430.45(2)
0.46~0.440.5(2)
0.48~0.52— 原油 G2 — 0.31(1) 0.08(1) 0.62(1) — — — — 0.53(1) — Z2 0.91(2)
0.89~0.941.16(2)
1.16~1.160.08(2)
0.08~0.080.63(2)
0.61~0.650.17(2)
0.16~0.17— 0.56(2)
0.56~0.560.45(2)
0.44~0.460.55(2)
0.55~0.5526.19(2)
23.22~29.31Z1 0.65(2)
0.54~0.770.86(2)
0.77~0.940.08(2)
0.07~0.090.61(2)
0.55~0.670.17(2)
0.16~0.18— 0.55(2)
0.54~0.560.44(2)
0.44~0.450.55(2)
0.54~0.5624.05(2)
21.53~26.62D2 0.67(2)
0.65~0.690.51(2)
0.49~0.530.21(2)
0.21~0.210.68(2)
0.66~0.700.13(2)
0.12~0.130.21(2)
0.21~0.210.41(2)
0.39~0.420.41(2)
0.40~0.420.53(2)
0.53~0.54~0.59(2)
~1.89~0.64G3 0.74(3)
0.67~0.850.52(3)
0.36~0.700.08(3)
0.05~0.110.60(3)
0.55~0.650.21(3)
0.21~0.220.27(3)
0.15~0.500.53(3)
0.52~0.540.47(3)
0.45~0.490.56(3)
0.55~0.5611.39(3)
8.14~21.03注:运移效应=参数(C29甾烷ββ/(αα+ββ)−C29甾烷20S/20(R+S))×100/ C29甾烷20S/20(R+S);数据格式: 平均值(样品数量)/最小值-最大值。 -
[1] 周心怀, 高顺莉, 高伟中, 等. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平北斜坡带海陆过渡型岩性油气藏形成与分布预测[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(2):153-164
ZHOU Xinhuai, GAO Shunli, GAO Weizhong, et al. Formation and distribution of marine-continental transitional lithologic reservoirs in Pingbei slope belt, Xihu sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(2): 153-164.
[2] 徐发, 张建培, 张田, 等. 西湖凹陷输导体系特征及其对油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2012, 28(7):24-29, 43
XU Fa, ZHANG Jianpei, ZHANG Tian, et al. Features of migration system in Xihu sag and its control on hydrocarbon accumulation [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2012, 28(7): 24-29, 43.
[3] 单超, 叶加仁, 曹强, 等. 西湖凹陷孔雀亭气田成藏主控因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(1):135-144
SHAN Chao, YE Jiaren, CAO Qiang, et al. Controlling factors for gas accumulation in Kongqueting gas field of Xihu sag [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(1): 135-144.
[4] 刘金水. 西湖凹陷平湖构造带地层压力特征及与油气分布的关系[J]. 成都理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 42(1):60-69
LIU Jinshui. Characteristics of formation pressure and their relationship with hydrocarbon distribution in Pinghu tectonic belt of Xihu sag, East China Sea [J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology: Science & Technology Edition, 2015, 42(1): 60-69.
[5] 刘金水, 赵洪. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带异性气侵的成藏模式[J]. 成都理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 46(4):487-496
LIU Jinshui, ZHAO Hong. Characteristics of differential gas invasion on Pinghu slope of Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin [J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology: Science & Technology Edition, 2019, 46(4): 487-496.
[6] 朱扬明, 周洁, 顾圣啸, 等. 西湖凹陷始新统平湖组煤系烃源岩分子地球化学特征[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(1):32-39 doi: 10.7623/syxb201201004
ZHU Yangming, ZHOU Jie, GU Shengxiao, et al. Molecular geochemistry of Eocene Pinghu formation coal-bearing source rocks in the Xihu depression, East China Sea shelf basin [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(1): 32-39. doi: 10.7623/syxb201201004
[7] 贾健谊, 须雪豪, 孙伯强. 东海西湖凹陷原油与天然气的地球化学特征[J]. 海洋石油, 2000(2):1-7
JIA Jianyi, XU Xuehao, SUN Boqiang. Oil/gas geochemical character in the Xihu trough of the East China Sea [J]. Offshore Oil, 2000(2): 1-7.
[8] 傅宁, 李友川, 陈桂华, 等. 东海平湖油气田油藏地球化学研究[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(4):240-244
FU Ning, LI Youchuan, CHEN Guihua, et al. Reservoir geochemistry in Pinghu field, East China Sea [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2003, 17(4): 240-244.
[9] 曹倩, 宋在超, 周小进, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷原油地化特征及来源分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(2):251-259 doi: 10.11781/sysydz201902251
CAO Qian, SONG Zaichao, ZHOU Xiaojin, et al. Geochemical characteristics and source of crude oil in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(2): 251-259. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201902251
[10] Zhu Y M, Li Y, Zhou J, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Tertiary coal-bearing source rocks in Xihu depression, East China Sea basin [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 35(1): 154-165. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2012.01.005
[11] Su A, Chen H H, Lei M Z, et al. Paleo-pressure evolution and its origin in the Pinghu slope belt of the Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 107: 198-213. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.05.017
[12] 苏奥, 陈红汉. 东海盆地西湖凹陷油岩地球化学特征及原油成因来源[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(6):1072-1082 doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2015.089
SU Ao, CHEN Honghan. Geochemical characteristics of oil and source rock, origin and genesis of oil in Xihu depression, East China Sea Basin [J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2015, 40(6): 1072-1082. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2015.089
[13] 蒋一鸣, 周倩羽, 李帅, 等. 西湖凹陷西部斜坡带平湖组含煤岩系沉积环境再思考[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2016, 28(8):18-25 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2016.08.04
JIANG Yiming, ZHOU Qianyu, LI Shuai, et al. Reconsideration of Pinghu formation coal-bearing rock series sedimentary environment in western slope of Xihu Depression [J]. Coal Geology of China, 2016, 28(8): 18-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2016.08.04
[14] 戴金星. 天然气中烷烃气碳同位素研究的意义[J]. 天然气工业, 2011, 31(12):1-6 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2011.12.001
DAI Jinxing. Significance of the study on carbon isotopes of alkane gases [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2011, 31(12): 1-6. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2011.12.001
[15] 李贤庆, 钟宁宁, 王铁冠, 等. 东海西湖凹陷早第三纪烃源岩生烃组分剖析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 1995, 23(6):24-31
LI Xianqing, ZHONG Ningning, WANG Tieguan, et al. The study on hydrocarbon-generating macerals of lower tertiary source rocks in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin [J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 1995, 23(6): 24-31.
[16] Peters K E, Walters C C, Moldowan J M. The Biomarker Guide: Volume 2, Biomarkers and Isotopes in Petroleum Systems and Earth History[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2005.
[17] 刘文汇, 徐永昌. 煤型气碳同位素演化二阶段分馏模式及机理[J]. 地球化学, 1999, 28(4):359-366 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1999.04.006
LIU Wenhui, XU Yongchang. A two stage model of carbon isotopic fractionation in coal gas [J]. Geochimica, 1999, 28(4): 359-366. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1999.04.006
[18] 苏奥, 陈红汉, 吴悠, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷中西部低渗近致密—致密砂岩气成因、来源及运聚成藏[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(1):184-196 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.01.013
SU Ao, CHEN Honghan, WU You, et al. Genesis, origin and migration-accumulation of Low-Permeable and nearly tight-tight sandstone gas in the central western part of Xihu sag, East China Sea Basin [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2018, 92(1): 184-196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.01.013
[19] 陈中红, 查明, 吴孔友, 等. 准噶尔盆地陆梁地区油气运移方向研究[J]. 石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2003, 27(2):19-22
CHEN Zhonghong, ZHA Ming, WU Kongyou, et al. Hydrocarbon migration direction in Luliang section of Junggar Basin [J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China, 2003, 27(2): 19-22.
[20] 苏奥, 陈红汉, 王存武, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷油气成因及成熟度判别[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(5):521-527 doi: 10.11698/PED.2013.05.02
SU Ao, CHEN Honghan, WANG Cunwu, et al. Genesis and maturity identification of oil and gas in the Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(5): 521-527. doi: 10.11698/PED.2013.05.02
[21] 傅宁, 李友川, 刘东, 等. 东海平湖气田天然气运移地球化学特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(5):34-37 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.05.007
FU Ning, LI Youchuan, LIU Dong, et al. Geochemical characteristics of natural gas migration in Pinghu gas field, East China Sea [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2005, 32(5): 34-37. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.05.007
-




 下载:
下载: