Provenance analysis for surface sediments in different depositional environments of the middle-south Okinawa Trough
-
摘要:
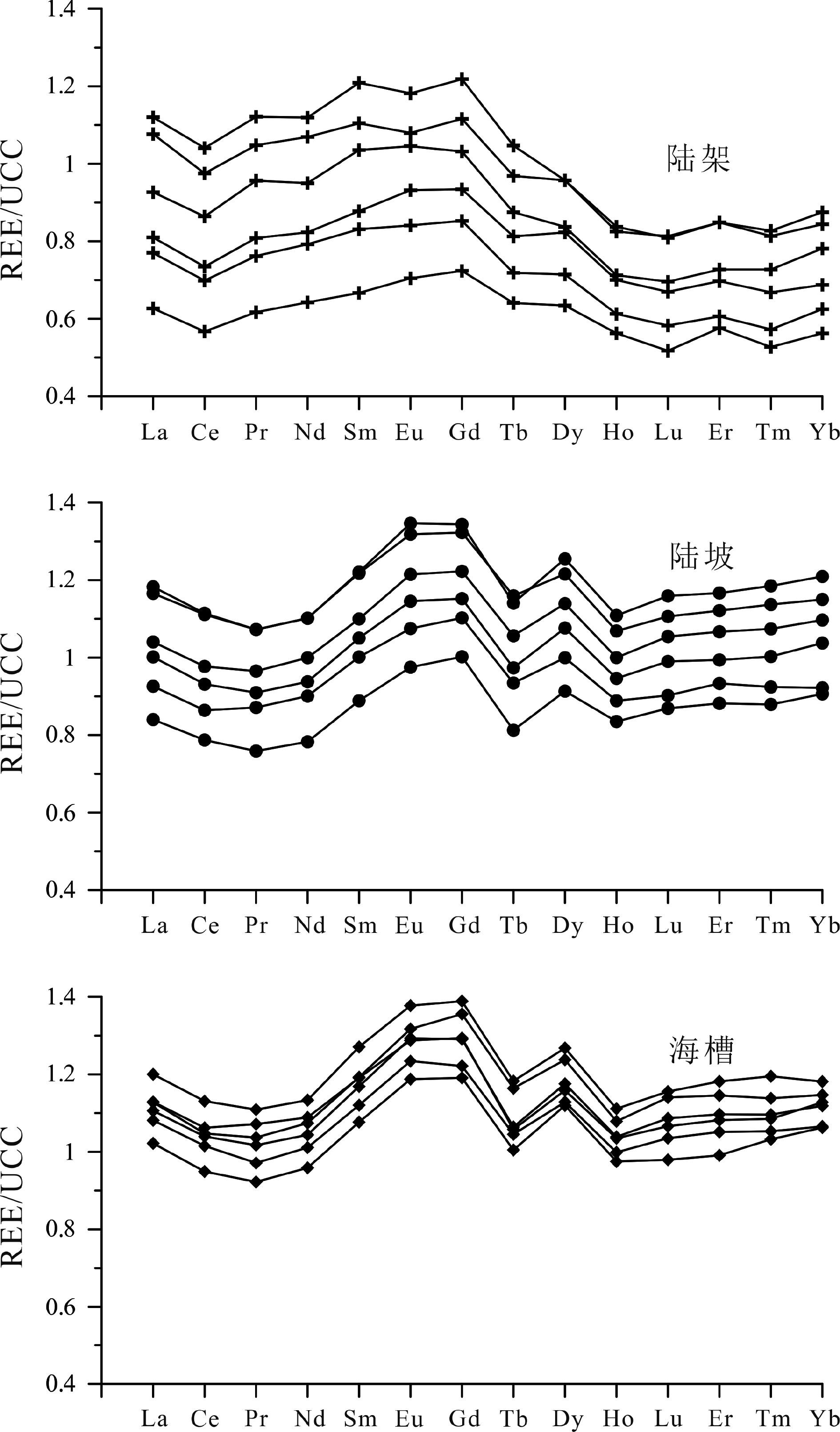
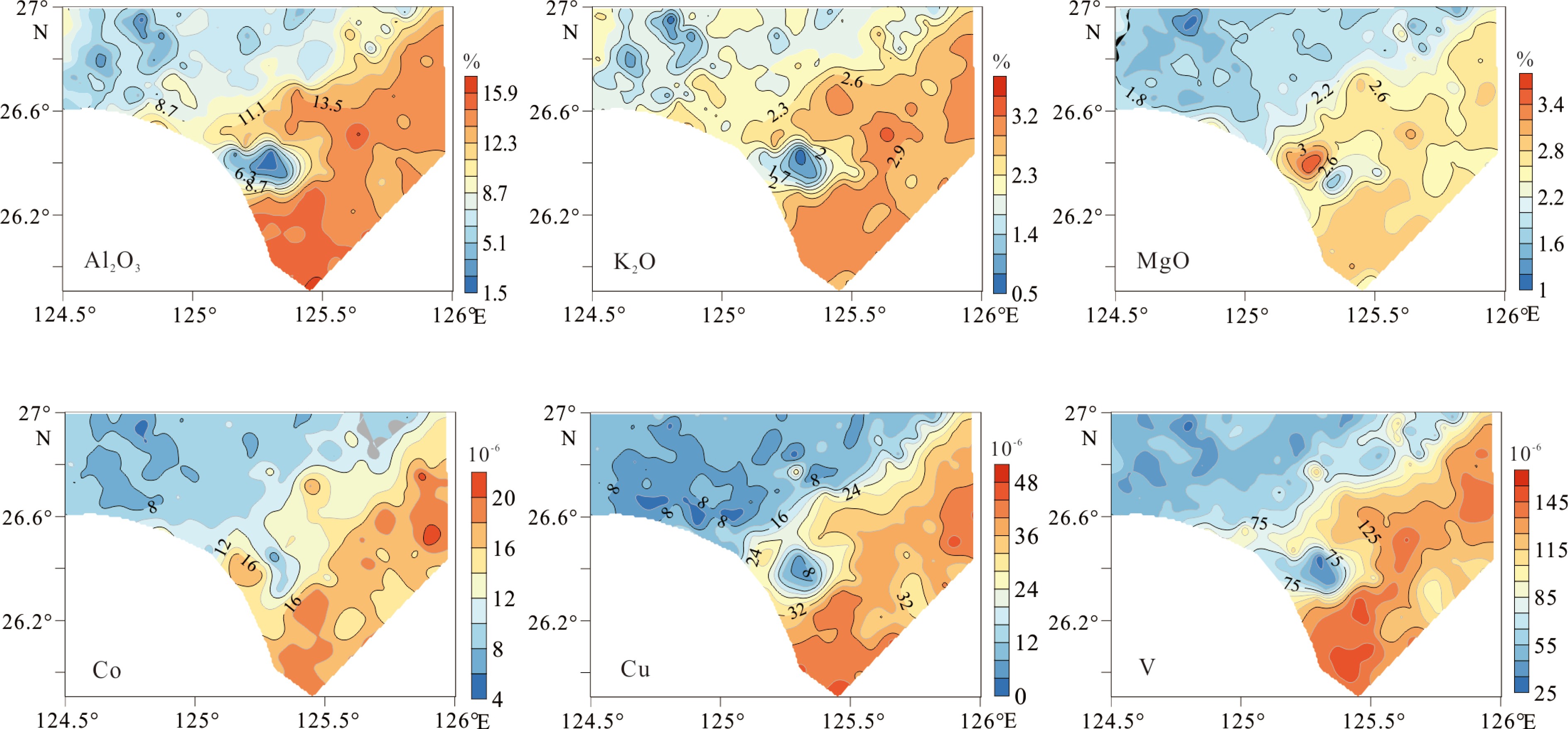
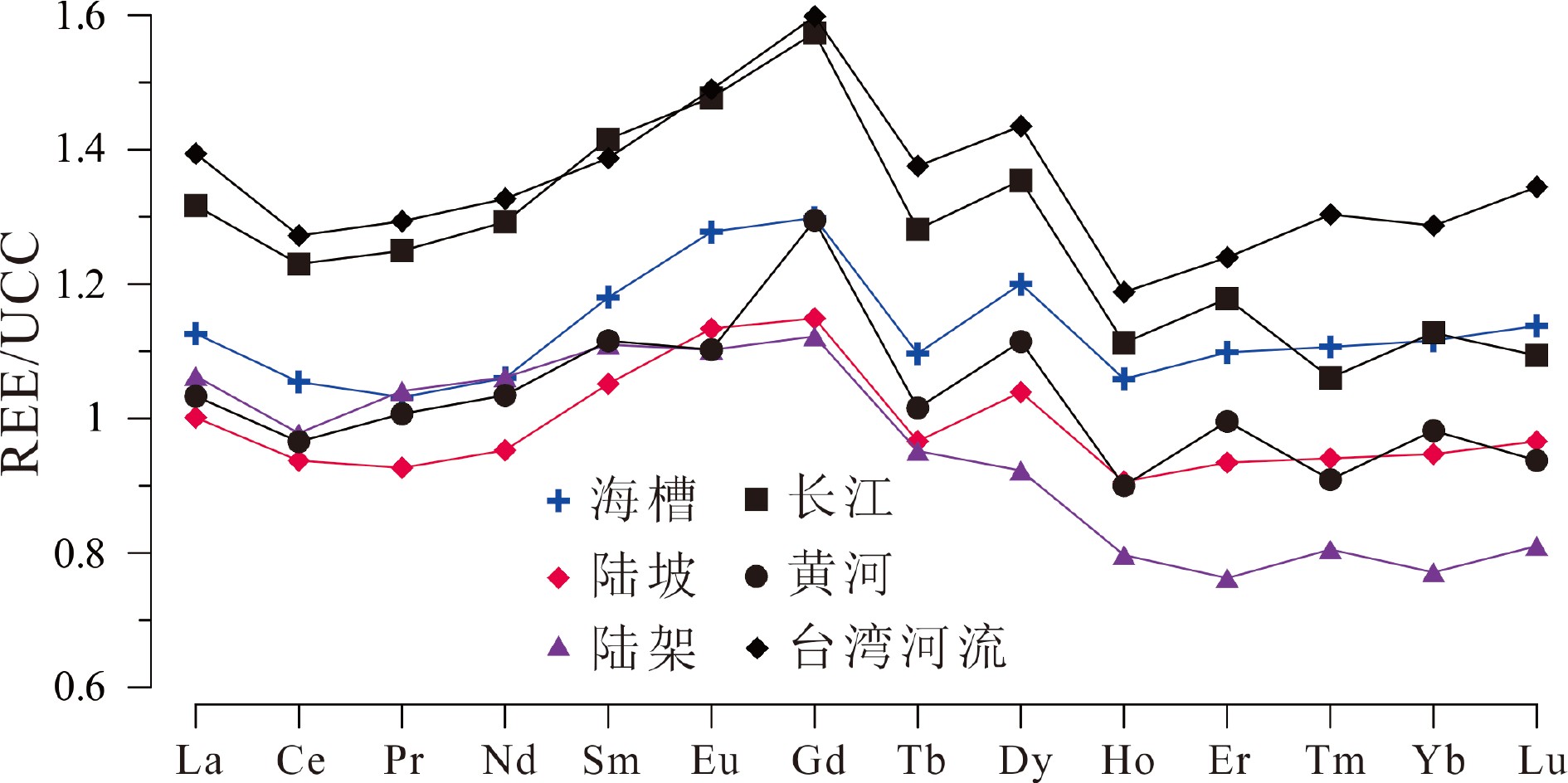
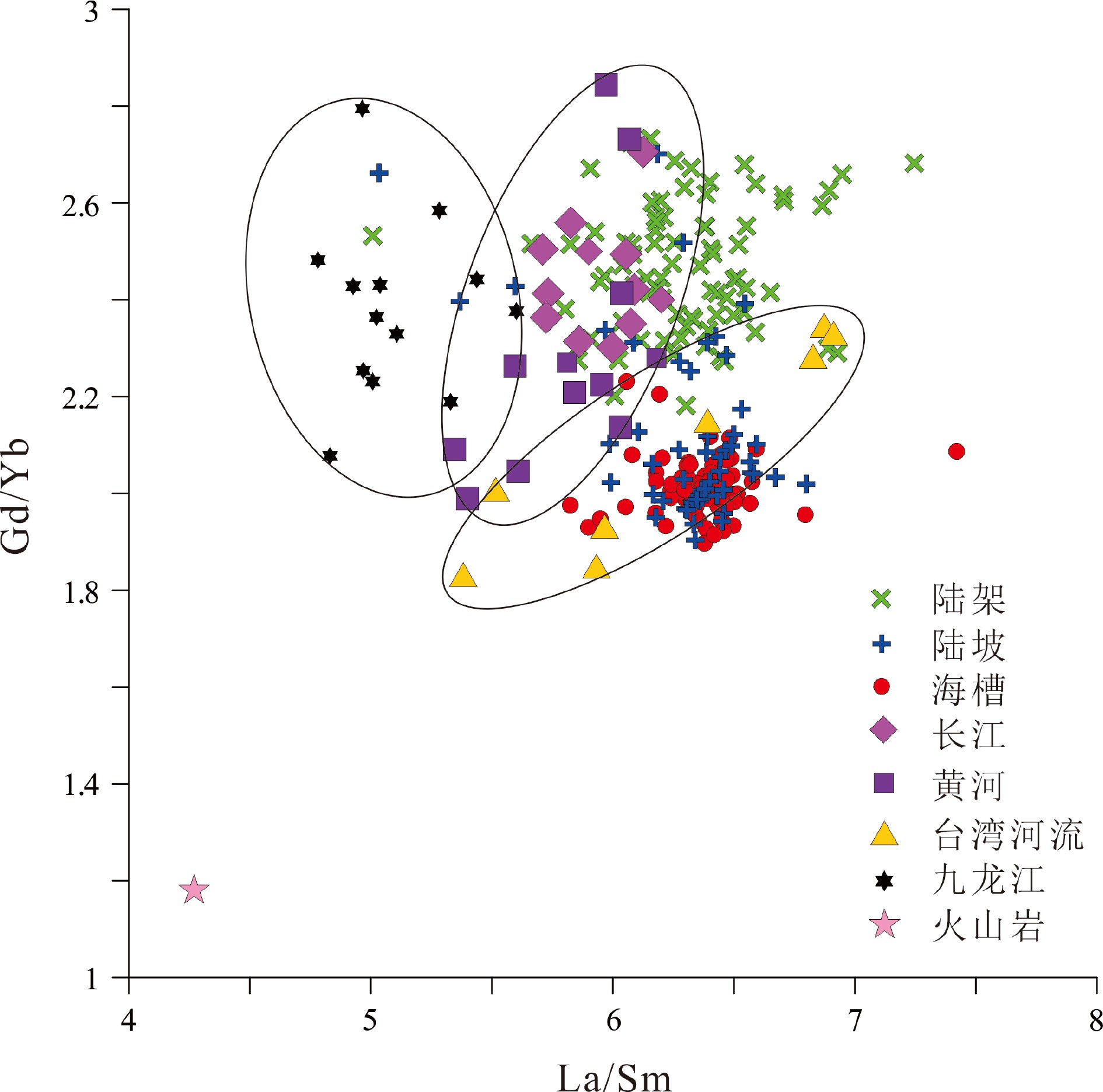
对冲绳海槽中南部3种不同沉积环境(东海外陆架、东海陆坡和冲绳海槽)表层沉积物进行了稀土等元素地球化学分析,结果显示,冲绳海槽和陆坡表层沉积物具有与台湾物质来源类似的稀土元素配分模式,La/Sm-Gd/Yb散点图也显示海槽和陆坡沉积物主要分布在台湾物源端元区,表明冲绳海槽中南部海槽和陆坡表层沉积物主要来源于台湾,而外陆架沉积物明显的重稀土亏损与大陆河流(特别是长江、黄河)沉积物来源较为一致。为进一步判断外陆架表层沉积物来源,对外陆架沉积物重矿物进行分析鉴定,结果显示,外陆架沉积物重矿物以普通角闪石-绿帘石-石榴石-赤褐铁矿为组合特征,与长江沉积物重矿物组成特征类似,其明显缺乏台湾河流来源的典型重矿物锆石、黄河来源典型重矿物云母、浙闽沿岸来源典型重矿物磁铁矿,说明台湾、黄河和浙闽沿岸并非研究区外陆架表层沉积物主要物源。根据以往测年等研究成果,研究区外陆架沉积物年代较老,应为古长江物质经东海现代环流体系不断改造而成。
Abstract:In this paper, surface sediments taken from three different depositional environments, i.e. the outer continental shelf, slope, and trough, of the middle-south Okinawa Trough were analyzed for rare earth elements (REE). The results suggest that the REE distribution patterns of the surface sediments from the continental slope and the Okinawa Trough are quite similar to those from Taiwan. The discrimination plot of La/Sm-Gd/Yb also shows that the surface sediments from continental slope and the Okinawa Trough are mainly located in the diagram close to the provenance end of Taiwan, further supporting the conclusion that the surface sediments of the continental slope and the Okinawa Trough are doubtlessly sourced from Taiwan. The obvious loss of heavy REE in the sediments of the outer continental shelf is consistent with the source of continental river sediments. In order to recognize the source of surface sediments in the outer shelf sedimentary area, the heavy mineral compositions of these sediments were analyzed. The results show that the heavy mineral assemblages of the outer continental shelf sediments are mainly composed of common hornblende, epidote, garnet, limonite, similar to the source composition of the Changjiang river. The outer continental shelf sediments are lack of zircon, mica, and magnetite, typical heavy minerals found in Taiwan, Huanghe river, and Minjiang river sediments respectively, which suggests that Taiwan, Yellow River, and the coast of Zhejiang and Fujian are not the main contributors to the outer continental shelf sediments. According to the results of previous dating data, the sediments of the outer shelf are relatively old, suggesting that the outer shelf sediments should be formed by the rework of the palaeo-Changjiang river materials by the modern circulation system of the East China Sea.
-
Key words:
- provenance /
- rare earth elements /
- heavy minerals /
- surface sediments /
- Okinawa Trough
-

-
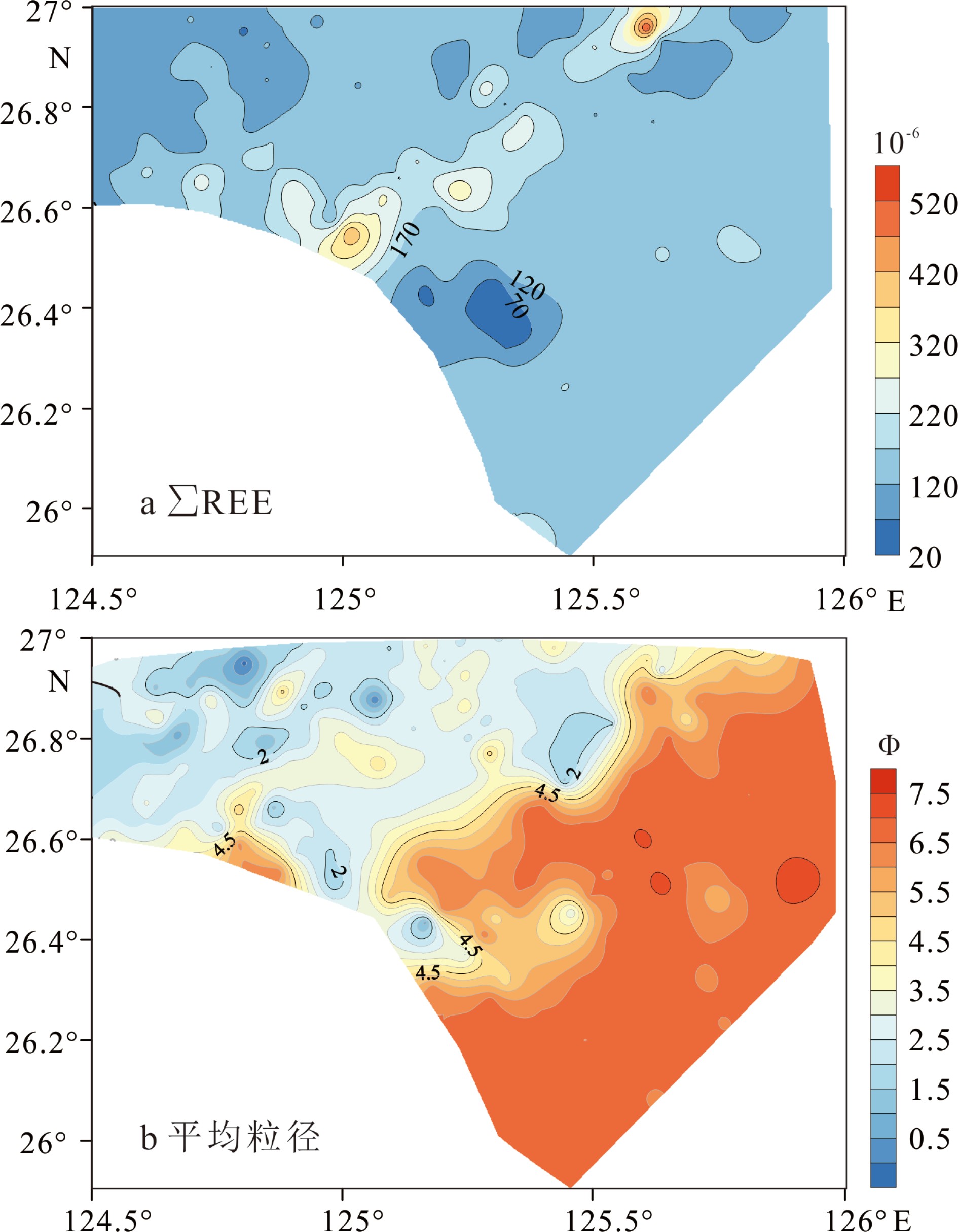
图 2 表层沉积物总稀土元素含量和平均粒径分布 [13]
Figure 2.
表 1 研究区典型样品稀土元素含量
Table 1. REE concentrations of typical samples
μg/g 水深/m La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu 陆架 128.4 37.2 73.2 8.5 31.9 5.7 1.1 4.9 0.71 3.7 0.75 2.0 0.32 2.0 0.32 128.0 32.0 67.6 7.6 28.1 5.0 1.0 4.3 0.61 3.2 0.61 1.7 0.26 1.6 0.25 127.3 31.9 61.9 7.4 27.9 5.1 1.0 4.4 0.63 3.4 0.67 1.9 0.30 1.9 0.29 140.0 26.4 52.2 6.4 24.1 4.4 0.9 3.7 0.52 2.7 0.53 1.4 0.22 1.4 0.21 125.0 22.0 42.4 5.2 19.6 3.6 0.7 3.1 0.44 2.4 0.47 1.3 0.20 1.2 0.18 110.0 23.6 46.3 5.7 21.6 3.9 0.9 3.3 0.47 2.5 0.48 1.3 0.19 1.2 0.18 112.0 28.2 55.4 6.7 25.2 4.6 0.9 4.0 0.58 3.2 0.62 1.7 0.26 1.6 0.25 128.0 28.1 54.2 6.5 24.5 4.4 1.0 3.9 0.55 2.9 0.58 1.6 0.24 1.5 0.22 118.0 38.0 73.8 8.6 31.3 5.4 1.1 4.8 0.71 3.9 0.81 2.4 0.37 2.4 0.36 170.0 28.8 56.7 6.8 25.3 4.5 0.8 3.8 0.52 2.7 0.51 1.4 0.20 1.3 0.20 陆坡 975.5 24.4 48.9 5.5 20.8 4.1 0.9 3.9 0.54 3.3 0.67 2.0 0.29 1.9 0.29 573.9 36.7 73.4 7.9 29.3 5.7 1.1 5.2 0.70 4.1 0.81 2.3 0.33 2.2 0.34 671.7 29.0 57.3 6.2 23.0 4.5 0.9 4.0 0.55 3.3 0.66 2.0 0.27 1.9 0.28 956.6 33.9 67.7 7.3 27.5 5.2 1.1 4.8 0.66 4.0 0.80 2.4 0.34 2.3 0.34 790.5 31.2 62.4 6.8 25.5 5.0 1.1 4.8 0.74 4.5 0.90 2.7 0.37 2.4 0.35 830.0 30.0 60.0 6.6 24.9 4.8 1.0 4.3 0.59 3.5 0.71 2.1 0.30 2.0 0.29 966.1 33.8 66.5 7.2 26.8 5.2 1.1 4.9 0.73 4.4 0.90 2.7 0.38 2.5 0.37 987.1 32.2 63.6 7.0 26.4 5.1 1.1 4.8 0.65 4.1 0.83 2.4 0.36 2.4 0.35 898.1 30.5 60.4 6.6 25.0 4.8 1.0 4.3 0.61 3.6 0.73 2.2 0.31 2.1 0.31 929.3 31.2 61.9 6.7 25.3 4.9 1.0 4.5 0.66 3.9 0.78 2.3 0.33 2.3 0.33 海槽 2112.2 32.7 65.6 7.1 26.8 5.2 1.1 5.0 0.75 4.4 0.88 2.7 0.39 2.6 0.38 2125.6 34.0 68.0 7.4 27.8 5.3 1.1 5.1 0.73 4.3 0.87 2.6 0.37 2.5 0.37 2070.3 28.3 57.2 6.3 24.1 4.8 1.1 5.0 0.74 4.4 0.90 2.7 0.39 2.6 0.37 2079.7 31.0 61.0 6.7 25.2 4.8 1.1 4.6 0.65 3.8 0.78 2.3 0.34 2.3 0.34 2050.7 33.8 67.0 7.4 27.9 5.4 1.2 5.2 0.75 4.3 0.86 2.6 0.38 2.5 0.37 1322.6 33.9 68.0 7.6 28.3 5.4 1.1 4.9 0.68 4.1 0.83 2.5 0.36 2.4 0.36 1701.9 35.1 71.1 7.7 28.5 5.4 1.1 5.1 0.68 4.1 0.82 2.5 0.36 2.5 0.36 1840.3 34.5 69.4 7.9 29.9 5.8 1.2 5.4 0.79 4.8 0.95 2.8 0.40 2.8 0.41 2068.0 35.1 69.7 7.9 30.0 5.8 1.2 5.4 0.76 4.5 0.93 2.8 0.40 2.7 0.40 2058.2 34.7 69.8 8.0 30.3 6.0 1.3 5.5 0.77 4.7 0.96 2.8 0.40 2.8 0.41 表 2 重矿物含量数据统计
Table 2. Statistics on data of heavy mineral provinces
矿物统计 最小值/% 最大值/% 平均值/% 标准偏差 偏度 峰度 角闪石类 19.97 45.06 32.75 5.87 0.04 –0.81 帘石类 5.50 33.57 17.27 4.71 0.39 0.64 金属矿物 1.78 22.00 7.99 4.00 0.97 0.79 云母类 0 1.10 0.14 0.22 2.00 4.13 ZTR 0 2.01 0.75 0.38 1.07 1.48 石榴石 0.93 11.94 4.30 1.97 0.80 1.17 榍石 0 1.85 0.62 0.39 1.17 1.13 辉石类 0 2.00 0.20 0.21 4.49 35.90 岩屑 8.06 53.45 31.20 8.36 0.01 –0.11 -
[1] Milliman J D, Shen H T, Yang Z S, et al. Transport and deposition of river sediment in the Changjiang estuary and adjacent continental shelf [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1985, 4(1-2): 37-45. doi: 10.1016/0278-4343(85)90020-2
[2] 杨文达, 王振宇, 曾久岭. 冲绳海槽轴线地质特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(2):1-6
YANG Wenda, WANG Zhenyu, ZENG Jiuling. Geologic features of the Okinawa trough Axis [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2001, 21(2): 1-6.
[3] 赵月霞, 刘保华, 李西双, 等. 东海陆坡海底峡谷—扇体系沉积特征及物质搬运[J]. 古地理学报, 2011, 13(1):119-126 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2011.01.012
ZHAO Yuexia, LIU Baohua, LI Xishuang, et al. Sedimentary characters and material transportation of submarine canyon-fan systems in slope of the East China Sea [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2011, 13(1): 119-126. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2011.01.012
[4] Milliman J D, Qin Y S, Park Y A. Sediments and sedimentary processes in the Yellow and East China Seas[M]//Taira A, Masuda F. Sedimentary Facies in the Active Plate Margin. Tokyo: Terra Scientific Publishing Company, 1989: 233-249.
[5] Saito Y, Katayama H, Ikehara K, et al. Transgressive and highstand systems tracts and post-glacial transgression, the East China Sea [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1998, 122(1-4): 217-232. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(98)00107-9
[6] Yoo D G, Lee C W, Kim S P, et al. Late Quaternary transgressive and highstand systems tracts in the northern East China Sea mid-shelf [J]. Marine Geology, 2002, 187(3-4): 313-328. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(02)00384-5
[7] Liu Z X, Berné S, Saito Y, et al. Internal architecture and mobility of tidal sand ridges in the East China Sea [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2007, 27(13): 1820-1834. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2007.03.002
[8] Dou Y G, Yang S Y, Liu Z X, et al. Provenance discrimination of siliciclastic sediments in the middle Okinawa Trough since 30 ka: Constraints from rare earth element compositions [J]. Marine Geology, 2010, 275(1-4): 212-220. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2010.06.002
[9] Jian Z M, Wang P X, Saito Y, et al. Holocene variability of the Kuroshio Current in the Okinawa Trough, northwestern Pacific Ocean [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2000, 184(1): 305-319. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00321-6
[10] 郭志刚, 杨作升, 雷坤, 等. 冲绳海槽中南部及其邻近陆架悬浮体的分布、组成和影响因子分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2001, 23(1):66-72
GUO Zhigang, YANG Zuosheng, LEI Kun, et al. The distribution and composition of suspended matters and their influencing factors in the central-southern area of Okinawa Trough and its adjacent shelf sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2001, 23(1): 66-72.
[11] 杨宝菊, 吴永华, 刘季花, 等. 冲绳海槽表层沉积物元素地球化学及其对物源和热液活动的指示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(2):25-37
YANG Baoju, WU Yonghua, LIU Jihua, et al. Elemental geochemistry of surface sediments in Okinawa Trough and its implications for provenance and hydrothermal activity [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(2): 25-37.
[12] 胡思谊, 曾志刚, 殷学博, 等. 冲绳海槽岩心沉积物稀土元素特征及物源指示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 39(1):69-82
HU Siyi, ZENG Zhigang, YIN Xuebo, et al. Characteristics of rare earth elements in the sediment cores from the Okinawa Trough and their implications for sediment provenance [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2018, 39(1): 69-82.
[13] 窦衍光, 陈晓辉, 李军, 等. 东海外陆架-陆坡-冲绳海槽不同沉积单元底质沉积物成因及物源分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(4):21-31
DOU Yanguang, CHEN Xiaohui, LI Jun, et al. Origin and provenance of the surficial sediments in the subenvironments of the East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(4): 21-31.
[14] McLennan S M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks; influence of provenance and sedimentary processes [J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 1989, 21(1): 169-200.
[15] Vital H, Stattegger K, Garbe-Schonberg C D. Composition and trace-element geochemistry of detrital clay and heavy-mineral suites of the lowermost Amazon River: a provenance study [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1999, 69(3): 563-575. doi: 10.2110/jsr.69.563
[16] Xu Z K, Li T G, Chang F M, et al. Sediment provenance discrimination in northern Okinawa Trough during the last 24 ka and paleoenvironmental implication: rare earth elements evidence [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2012, 30(11): 1184-1190. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(12)60202-6
[17] Machida H. The stratigraphy, chronology and distribution of distal marker-tephras in and around Japan [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 1999, 21(1-3): 71-94. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8181(99)00008-9
[18] 翟世奎, 于增慧, 杜同军. 冲绳海槽中部现代海底热液活动在沉积物中的元素地球化学记录[J]. 海洋学报, 2007, 29(1):58-65
ZHAI Shikui, YU Zenghui, DU Tongjun. Elemental geochemical records of modern seafloor hydrothermal activities in sediments from the central Okinawa Trough [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2007, 29(1): 58-65.
[19] Iseki K, Okamura K, Kiyomoto Y. Seasonality and composition of downward particulate fluxes at the continental shelf and Okinawa Trough in the East China Sea [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2003, 50(2): 457-473. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0645(02)00468-X
[20] Katayama H, Watanabe Y. The Huanghe and Changjiang contribution to seasonal variability in terrigenous particulate load to the Okinawa Trough [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2003, 50(2): 475-485. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0645(02)00469-1
[21] Liu J P, Xu K H, Li A C, et al. Flux and fate of Yangtze River sediment delivered to the East China Sea [J]. Geomorphology, 2007, 85(3-4): 208-224. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.03.023
[22] Yang S Y, Wang Z B, Dou Y G, et al. A review of sedimentation since the last glacial maximum on the continental shelf of Eastern China [J]. Geological Society, London, Memoirs, 2014, 41(1): 293-303. doi: 10.1144/M41.21
[23] 张丹丹, 曾志刚, 殷学博. 冲绳海槽中部沉积物物质来源和沉积环境分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(7):92-101
ZHANG Dandan, ZENG Zhigang, YIN Xuebo. Analysis on sediment provenance and environmental changes in the middle Okinawa Trough [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2017, 39(7): 92-101.
[24] Taylor S R, McClennan S M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Blackwell, Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1985: 1-190.
[25] Sholkovitz E R, Elderfield H, Szymczak R, et al. Island weathering: river sources of rare earth elements to the Western Pacific Ocean [J]. Marine Chemistry, 1999, 68(1-2): 39-57. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4203(99)00064-X
[26] Piper D Z, Bau M. Normalized rare earth elements in water, sediments, and wine: identifying sources and environmental redox conditions [J]. American Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 4(10A): 69-83.
[27] Yang S Y, Jung H S, Choi M S, et al. The rare earth element compositions of the Changjiang (Yangtze) and Huanghe (Yellow) river sediments [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 201(2): 407-419. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00715-X
[28] Chen J C, Lo C Y, Lee Y T, et al. Mineralogy and chemistry of cored sediments from active margin off southwestern Taiwan [J]. Geochemical Journal, 2007, 41(5): 303-321. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.41.303
[29] 尚鲁宁, 陈磊, 张训华, 等. 冲绳海槽南部海底热液活动区地形地貌特征及成因分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 39(4):12-22
SHANG Luning, CHEN Lei, ZHANG Xunhua, et al. Topographic features of the hydrothermal field and their genetic mechanisms in southern Okinawa Trough [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 39(4): 12-22.
[30] 蔡宗伟, 翟世奎, 于增慧, 等. 冲绳海槽中、南部热液活动区金属硫化物的地球化学特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2018, 42(11):73-82 doi: 10.11759/hykx20161215001
CAI Zongwei, ZHAI Shikui, YU Zenghui, et al. Geochemical characteristics of hydrothermal sulfide from the middle and southern hydrothermal fields in the Okinawa Trough [J]. Marine Sciences, 2018, 42(11): 73-82. doi: 10.11759/hykx20161215001
[31] 金贵娥, 洪小燕, 汪厦霞, 等. 九龙江河口区稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 台湾海峡, 2010, 29(3):304-313
JIN Guie, HONG Xiaoyan, WANG Xiaxia, et al. Geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements in Jiulongjiang Estuary [J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2010, 29(3): 304-313.
[32] Shinjo R, Kato Y. Geochemical constraints on the origin of bimodal magmatism at the Okinawa Trough, an incipient back-arc basin [J]. Lithos, 2000, 54(3-4): 118-137.
[33] Dou Y G, Yang S Y, Shi X F, et al. Provenance weathering and erosion records in southern Okinawa Trough sediments since 28 ka: Geochemical and Sr–Nd–Pb isotopic evidences [J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 425: 93-109. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.01.029
[34] Wang J Z, Li A C, Xu K H, et al. Clay mineral and grain size studies of sediment provenances and paleoenvironment evolution in the middle Okinawa Trough since 17 ka [J]. Marine Geology, 2015, 366: 49-61. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.04.007
[35] Chen C T A, Kandasamy S, Chang Y P, et al. Geochemical evidence of the indirect pathway of terrestrial particulate material transport to the Okinawa Trough [J]. Quaternary International, 2016, 441: 51-61.
[36] 陈静, 王哲, 王张华, 等. 长江三角洲东西部晚新生代地层中的重矿物差异及其物源意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27(5):700-708 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.05.011
CHEN Jing, WANG Zhe, WANG Zhanghua, et al. Heavy mineral distribution and its provenance implication in late Cenozoic sediments in western and eastern area of the Changjiang river delta [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2007, 27(5): 700-708. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.05.011
[37] 张凯棣, 李安春, 董江, 等. 东海表层沉积物碎屑矿物组合分布特征及其物源环境指示[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(5):902-911
ZHANG Kaili, LI Anchun, DONG Jiang, et al. Detrital mineral distributions in surface sediments of the East China Sea: implications for sediment provenance and sedimentary environment [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(5): 902-911.
[38] Garzanti E, Andò S. Plate tectonics and heavy mineral suites of modern sands [J]. Developments in Sedimentology, 2007, 58: 741-763. doi: 10.1016/S0070-4571(07)58029-5
[39] Heroy D C, Kuehl S A, Goodbred S L Jr. Mineralogy of the Ganges and Brahmaputra Rivers: implications for river switching and Late Quaternary climate change [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2003, 155(3-4): 343-359. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(02)00186-0
[40] 王中波, 杨守业, 李萍, 等. 长江水系沉积物碎屑矿物组成及其示踪意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2006, 24(4):570-578 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2006.04.015
WANG Zhongbo, YANG Shouye, LI Ping, et al. Detrital mineral compositions of the Changjiang River sediments and their tracing implications [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2006, 24(4): 570-578. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2006.04.015
[41] 窦衍光, 王昆山, 王国庆, 等. 长江水下三角洲沉积物碎屑矿物研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2007, 31(4):22-26, 31 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2007.04.006
DOU Yanguang, WANG Kunshan, WANG Guoqing, et al. Research of detrital minerals in the sediment of sub-aqueous Yangtze Delta [J]. Marine Sciences, 2007, 31(4): 22-26, 31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2007.04.006
[42] Yang S Y, Wang Z B, Guo Y, et al. Heavy mineral compositions of the Changjiang (Yangtze River) sediments and their provenance-tracing implication [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 35(1): 56-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.12.002
[43] 林晓彤, 李巍然, 时振波. 黄河物源碎屑沉积物的重矿物特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(3):17-21
LIN Xiaotong, LI Weiran, SHI Zhenbo. Characteristics of mineralogy in the clastic sediments from the Yellow River Provenance, China [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2003, 23(3): 17-21.
[44] 陈心怡, 黄奇瑜, 邵磊. 福建闽江和九龙江现代沉积物重矿物特征及其物源意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2018, 20(4):637-650 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2018.04.046
CHEN Xinyi, HUANG Qiyu, SHAO Lei. Characteristics of heavy minerals in modern sediments of Minjiang and Jiulongjiang Rivers, Fujian Province and their provenance implication [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2018, 20(4): 637-650. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2018.04.046
[45] 邓凯, 杨守业, 王中波, 等. 台湾山溪性小河流碎屑重矿物组成及其示踪意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(3):531-542
DENG Kai, YANG Shouye, WANG Zhongbo, et al. Detrital heavy mineral assemblages in the river sediments from Taiwan and its implications for sediment provenance [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(3): 531-542.
[46] 王中波, 杨守业, 张志珣, 等. 东海陆架中北部沉积物粒度特征及其沉积环境[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(6):1039-1049 doi: 10.11693/hyhz201206003003
WANG Zhongbo, YANG Shouye, ZHANG Zhixun, et al. The grain size compositions of the surface sediments in the East China Sea: Indication for sedimentary environments [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2012, 43(6): 1039-1049. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201206003003
[47] 陈丽蓉. 中国海沉积矿物学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2008: 121-155.
CHEN Lirong. Sedimentary Mineralogy of the China Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2008: 121-155.
-



 下载:
下载: