Water and salt sources and salinization of shallow saline groundwater in the coastal area of Yancheng, Jiangsu
-
摘要:
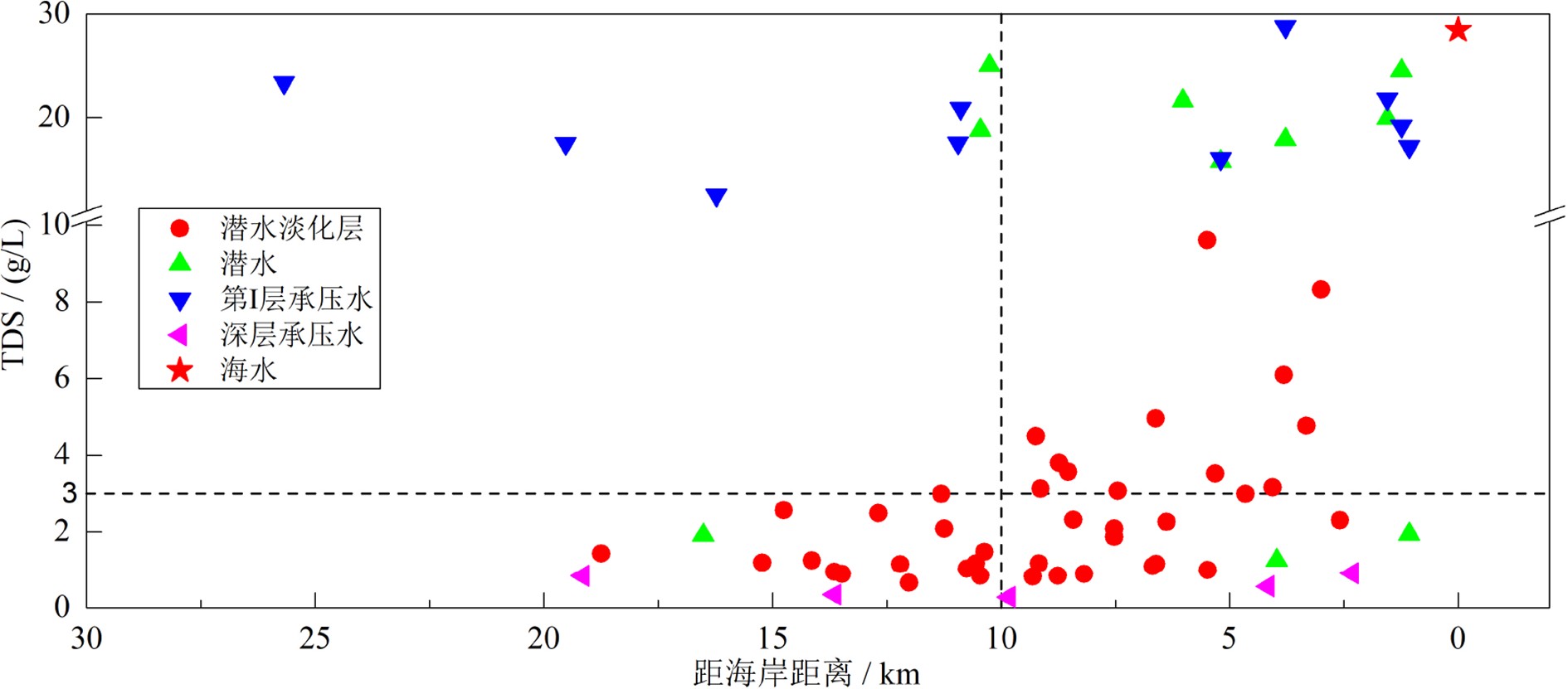
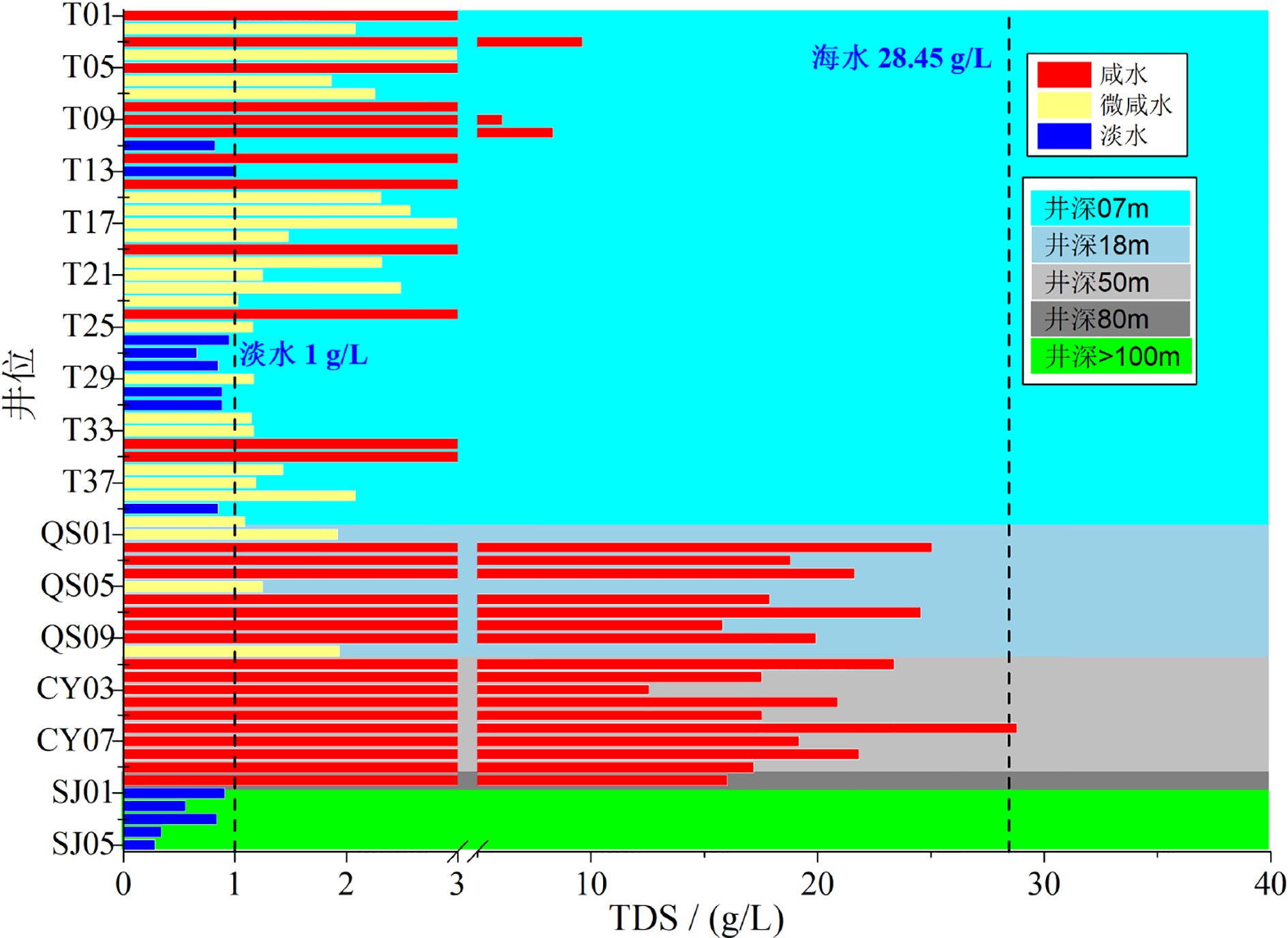
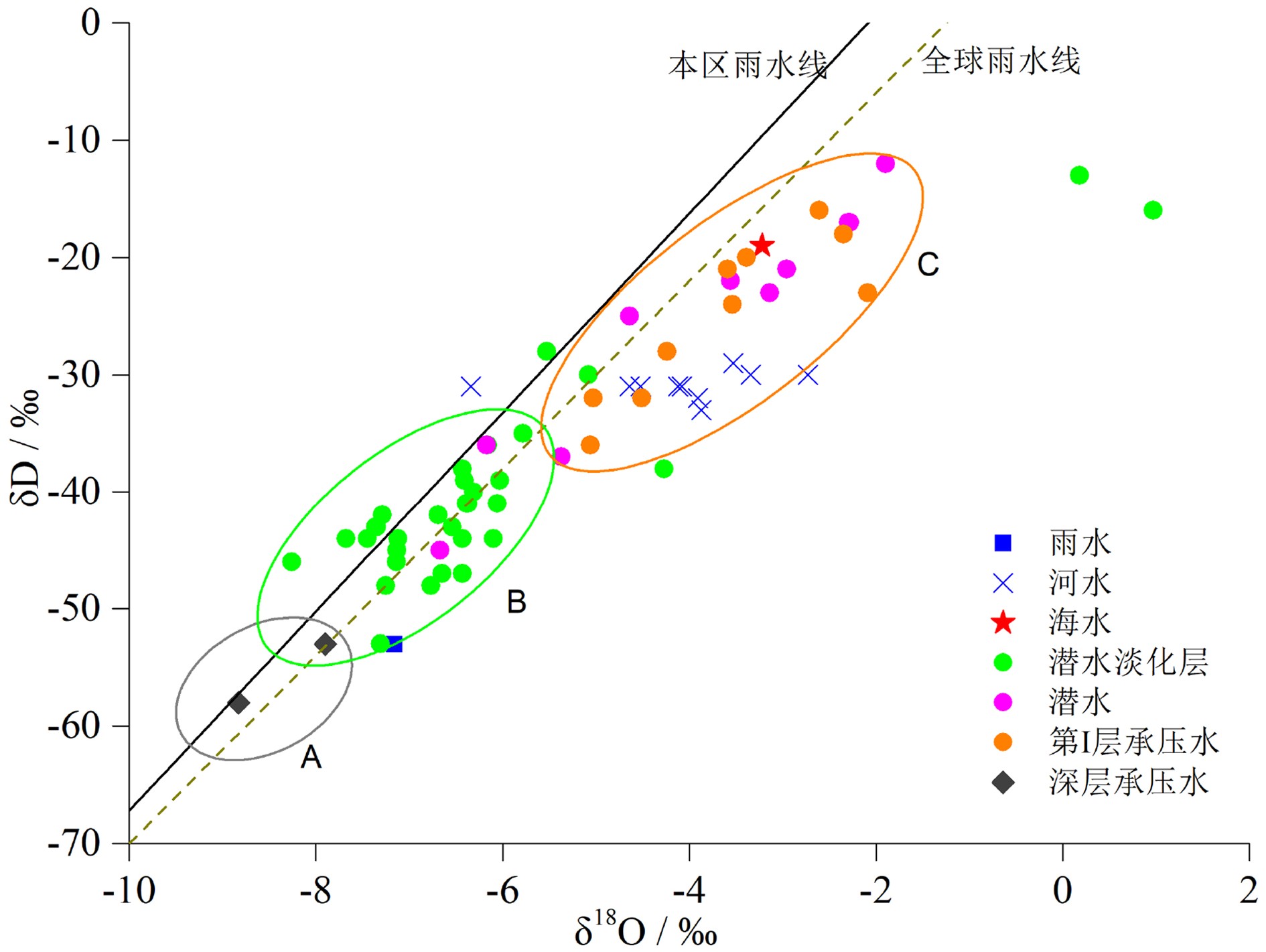
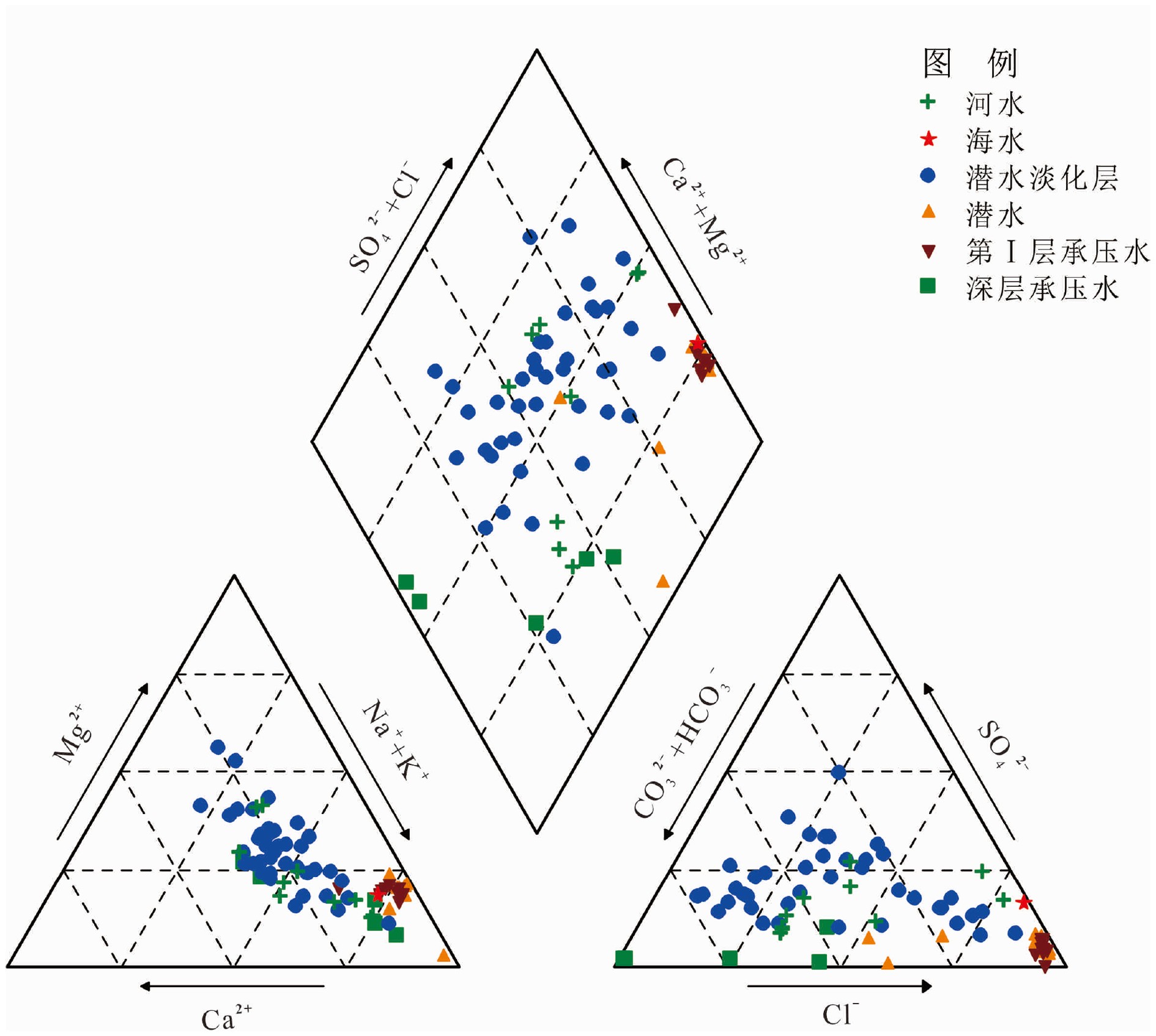
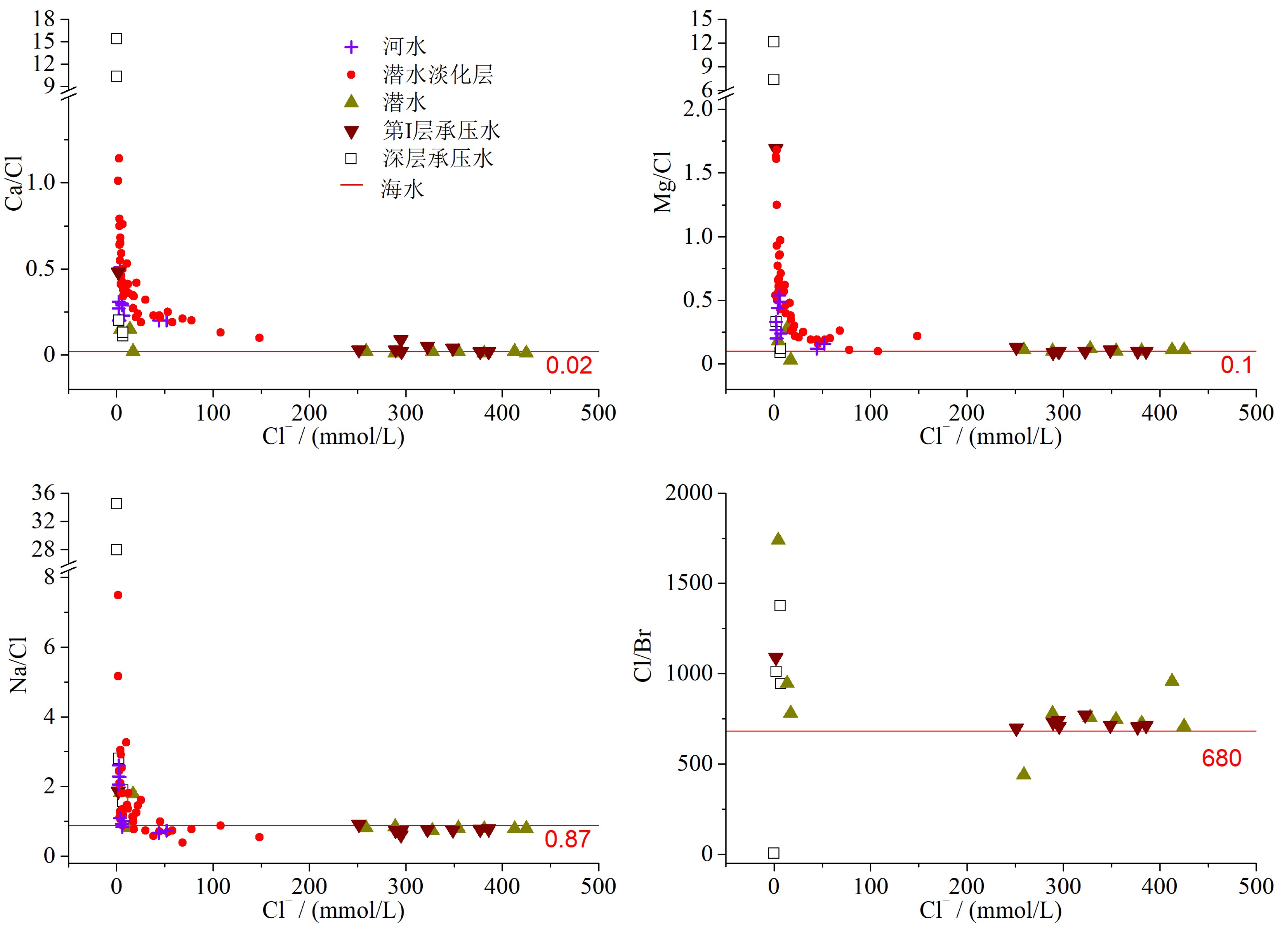
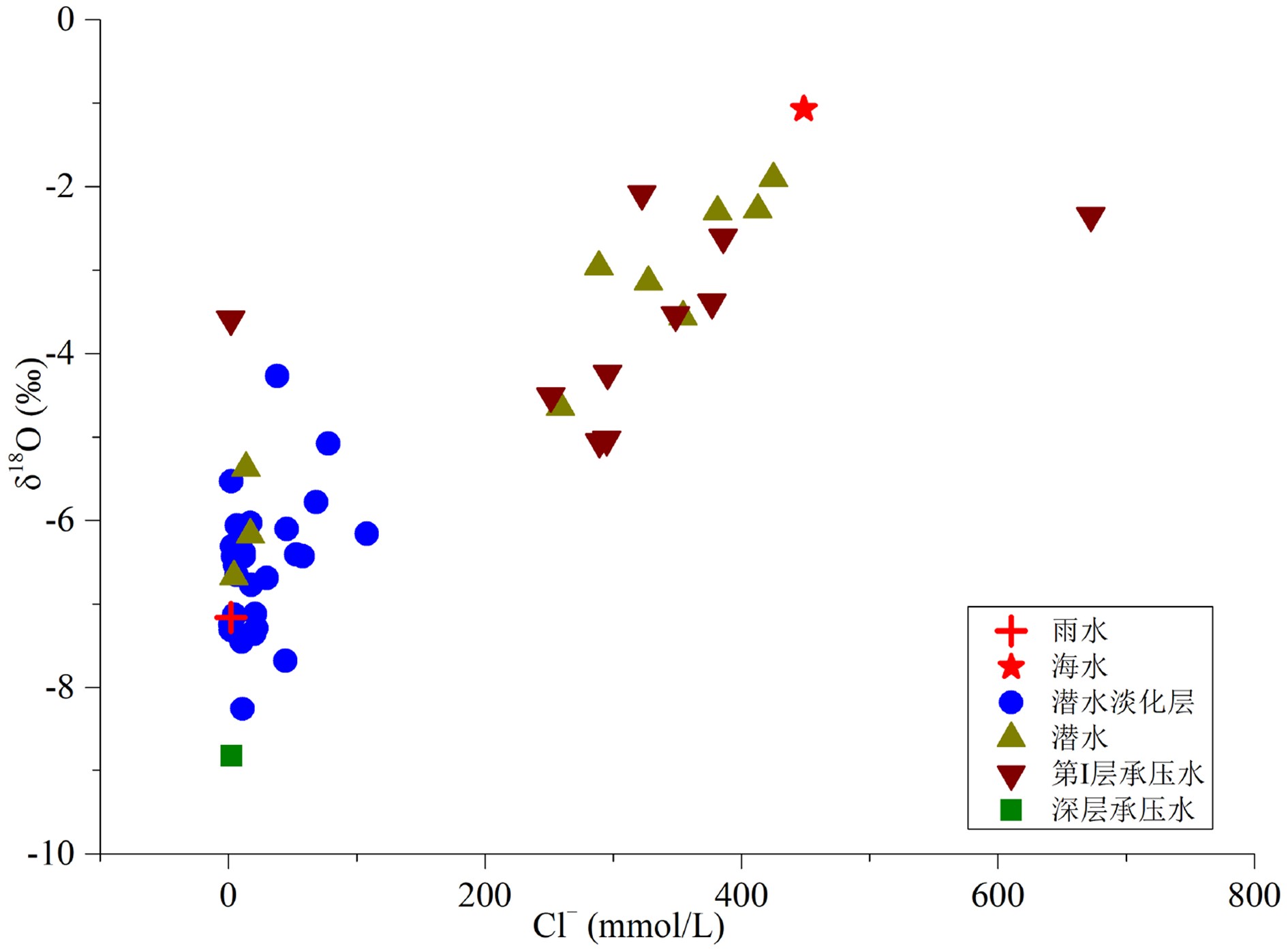
江苏盐城滨海地区浅层地下咸水对区域水资源利用和生态环境保护具有重要影响,为了查明浅层地下咸水的水盐来源及咸化成因,于2018—2019年采集了研究区河水、雨水、海水、地下淡水、微咸水及咸水等不同类型水样,对水样的水化学组成、离子比、Piper三线图、氢氧同位素组成及14C测年结果进行了分析,结果表明:① 潜水与第Ⅰ承压含水层地下水均以咸水为主,潜水含水层上部存在埋深小于10 m的淡化层,向海方向分布有淡水、微咸水、咸水水质类型。② 潜水与第Ⅰ承压含水层地下水主要来源于全新世暖期降水补给,盐分来源于强烈蒸发浓缩后的古残留海水。③ 潜水淡化层地下水主要来源于现代时期降水补给,盐分来源于岩盐和铝硅酸盐矿物的溶解,废黄河口部分地区地下水咸化主要受海水入侵影响。
Abstract:For the purpose to identify the sources of groundwater and salt and the salinization of shallow groundwater in the coastal area of Yancheng, Jiangsu province, different types of water samples are collected, such as the river water, rainwater, seawater, underground fresh water, brackish water, salt water in the study area during the period from 2018 to 2019. The chemical composition and ions ratio, Piper diagram, hydrogen and oxygen isotopic composition and 14C dating results are analyzed. The results suggest that: (1) The phreatic water and the first confined water are dominated by saline water. The upper layer of the phreatic aquifer is less than 10 m in thickness and widely desalinated, which changes seawards from fresh water, brackish water to salty water. (2) The water in the phreatic aquifer and the first confined aquifer mainly come from precipitation replenishment in the Holocene warm period, and salinity mainly come from the ancient residual seawater that has suffered strong evaporation and concentration. (3) Groundwater in the phreatic desalination layer mainly comes from modern precipitation replenishment, and salinity mainly comes from the dissolution of rock salt and aluminosilicate minerals, the salinization of groundwater in some areas of the abandoned Yellow River estuary is mainly affected by seawater intrusion.
-
Key words:
- shallow groundwater /
- hydrochemistry /
- isotope /
- salinization /
- coastal area in Yancheng
-

-
表 1 研究区监测点样品信息
Table 1. Sample information from monitoring points in the study area
井位 位置 距岸线距离/km 取样时间 井深/m EC/ (ms/cm) pH T/℃ TDS/ (mg/L) SJ01 滨海县 2.32 2019.4 120 1565 7.71 — 0.91 SJ02 射阳县 4.16 2019.4 120 1162 8.22 — 0.56 SJ03 大丰市 19.15 2019.4 120 1345.1 8.05 — 0.84 SJ04 东台市 13.64 2019.4 200 653.1 8.01 — 0.34 SJ05 东台市 9.83 2019.4 300 560.4 8.08 — 0.28 QS01 东台市 16.51 2019.4 18 3613 8.78 17.74 1.92 QS02 大丰市 10.25 2019.4 18 41190 7.34 19.45 25.96 QS03 大丰市 10.45 2019.4 18 32480 8.15 19.08 21.70 QS04 射阳县 6.02 2019.4 18 37640 7.53 19.69 22.69 QS05 滨海县 3.97 2019.4 18 2359 8.55 16.88 1.25 QS06 东台市 3.78 2019.4 18 29690 8.08 25.16 18.55 QS07 大丰市 1.24 2019.4 18 40700 8.47 18.91 26.32 QS08 大丰市 5.19 2019.4 18 27620 7.86 18.97 15.79 QS09 射阳县 1.55 2019.4 18 33780 7.22 19.14 20.11 QS10 滨海县 1.07 2019.4 18 3587 8.04 19.28 0.68 CY01 东台市 25.68 2019.4 50 38970 7.21 19.67 0.68 CY02 大丰市 19.52 2019.4 50 30610 7.32 19.37 17.16 CY03 大丰市 16.22 2019.4 50 23560 7.45 20.08 16.95 CY04 射阳县 10.88 2019.4 50 37180 7.34 19.36 22.88 CY05 滨海县 10.94 2019.4 50 31700 7.23 18.82 20.33 CY06 东台市 3.78 2019.4 50 47890 7.53 21.53 41.69 CY07 大丰市 1.24 2019.4 50 34500 7.8 20.29 21.33 CY08 大丰市 5.19 2019.4 80 28670 6.89 19.94 17.34 CY09 射阳县 1.55 2019.4 50 37500 7.54 19.93 23.71 CY10 滨海县 1.07 2019.4 50 29970 7.23 20.51 16.12 T01 滨海县 8.73 2018.6 7 4267 — 20.83 3.80 T02 滨海县 7.52 2018.6 7 2800 — 20.81 2.08 T03 滨海县 5.49 2018.6 7 10100 — 18.22 9.61 T04 滨海县 4.65 2018.6 7 4700 — 20.88 2.99 T05 滨海县 3.32 2018.6 7 7130 — 23.94 4.77 T06 滨海县 7.52 2018.6 7 — — 19.28 1.87 T07 滨海县 6.38 2018.6 7 — — 20.32 2.26 T08 滨海县 5.31 2018.6 7 — — 20.14 3.52 T09 滨海县 3.81 2018.6 7 — — 20.30 6.09 T10 滨海县 3.00 2018.6 7 — — 18.70 8.32 T11 射阳县 9.30 2018.6 7 1130 6.56 20.40 0.82 T12 射阳县 7.44 2018.6 7 2880 6.05 19.90 3.07 T13 射阳县 5.48 2018.6 7 1268 5.75 24.40 0.99 T14 射阳县 4.06 2018.6 7 4330 6.43 18.80 3.16 T15 射阳县 2.58 2018.6 7 2285 5.92 20.37 2.31 T16 射阳县 14.75 2018.6 7 2780 9.20 21.42 2.57 T17 射阳县 11.30 2018.6 7 4349 7.01 19.52 2.99 T18 射阳县 10.36 2018.6 7 1940 8.85 18.55 1.48 T19 射阳县 9.24 2018.6 7 4560 7.68 19.36 4.50 T20 射阳县 8.42 2018.6 7 2220 7.41 20.05 2.32 T21 大丰市 14.13 2018.6 7 1643 7.49 19.70 1.25 T22 大丰市 12.68 2018.6 7 2359 7.77 18.54 2.49 T23 大丰市 10.75 2018.6 7 1409 7.90 19.60 1.03 T24 大丰市 8.53 2018.6 7 1640 7.37 19.35 3.57 T25 大丰市 6.60 2018.6 7 2780 9.20 19.24 1.16 T26 大丰市 13.64 2018.6 7 1255 7.60 18.91 0.95 T27 大丰市 12.01 2018.6 7 1405 8.30 18.94 0.66 T28 大丰市 10.45 2018.6 7 1407 7.54 18.15 0.85 T29 大丰市 9.17 2018.6 7 1859 8.14 17.48 1.17 T30 大丰市 8.18 2018.6 7 1299 6.09 19.57 0.89 T31 东台市 13.47 2018.6 7 1500 7.75 19.07 0.89 T32 东台市 12.20 2018.6 7 2003 7.86 17.96 1.15 T33 东台市 10.55 2018.6 7 1680 7.90 19.54 1.17 T34 东台市 9.13 2018.6 7 3840 8.26 19.07 3.13 T35 东台市 6.61 2018.6 7 5150 7.20 19.98 4.96 T36 东台市 18.74 2018.6 7 1850 7.28 18.50 1.43 T37 东台市 15.22 2018.6 7 1669 7.06 19.20 1.19 T38 东台市 11.24 2018.6 7 1320 6.65 20.50 2.08 T39 东台市 8.76 2018.6 7 1290 7.10 18.30 0.85 T40 东台市 6.68 2018.6 7 1990 8.44 18.43 1.09 HH01 废黄河口 0.03 2018.6 4830 — — 3.32 HH02 废黄河口 11.22 2018.6 1217 — — 0.76 HH03 废黄河口 22.30 2018.6 700 — — 0.38 SY01 射阳河 0.02 2018.6 5602 7.01 — 4.33 SY02 射阳河 9.91 2018.6 1119 8.15 — 0.74 SY03 射阳河 16.24 2018.6 1023 7.13 — 0.56 SY04 射阳河 19.47 2018.6 961 7.36 — 0.77 SY05 射阳河 27.04 2018.6 912 7.05 — 0.47 SY06 射阳河 53.67 2018.6 736 6.84 — 0.39 SY07 射阳河 95.58 2018.6 740 6.84 — 0.41 Sea 海滩 0 2018.6 39000 7.84 — 28.45 注:空格表示地表水体没有井深参数,“—”表示该参数没有测试。 -
[1] 薛春汀, 刘健, 孔祥淮. 全新世淮河三角洲初步研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2010, 30(5):892-901 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2010.05.06
XUE Chunting, LIU Jian, KONG Xianghuai. Preliminary study of holocene Huaihe river delta on west coastal plain of Yellow Sea, China [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2010, 30(5): 892-901. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2010.05.06
[2] 薛春汀, 周永青, 朱雄华. 晚更新世末至公元前7世纪的黄河流向和黄河三角洲[J]. 海洋学报, 2004, 26(1):48-61
XUE Chunting, ZHOU Yongqing, ZHU Xionghua. The Huanghe river course and delta from end of late pleistocene to the 7th century BC [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2004, 26(1): 48-61.
[3] 张忍顺. 苏北黄河三角洲及滨海平原的成陆过程[J]. 地理学报, 1984, 39(2):173-184 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1984.02.005
ZHANG Renshun. Land-forming history of the Huanghe river delta and coastal plain of north Jiangsu [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1984, 39(2): 173-184. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1984.02.005
[4] 张旸, 陈沈良. 苏北废黄河三角洲海岸时空演变遥感分析[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2009, 27(2):166-175 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2009.02.006
ZHANG Yang, CHEN Shenliang. Remote sensing analysis of spatial and temporal changes of the coastal area in the abandoned Huanghe river delta in the northern Jiangsu province [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2009, 27(2): 166-175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2009.02.006
[5] 付昌昌. 淮河流域沿海平原深层地下水水化学特征及咸水成因[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2015.
FU Changchang. The hydrochemical characteristics and processes for salinity sources of the deep confined groundwater in the coastal plain of Huai river basin[D]. Master Dissertation of Jilin University, 2015.
[6] Lee K S, Wenner D B, Lee I. Using H- and O-isotopic data for estimating the relative contributions of rainy and dry season precipitation to groundwater: example from Cheju island, Korea [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1999, 222(1-4): 65-74. doi: 10.1016/S0022-1694(99)00099-2
[7] Mehta S, Fryar A E, Banner J L. Controls on the regional-scale salinization of the Ogallala aquifer, southern high plains, Texas, USA [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2000, 15(6): 849-864. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(99)00098-0
[8] 刘贯群, 朱利文, 孙运晓. 大沽河下游地区地下咸水的水化学特征及成因[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2019, 49(5):84-92
LIU Guanqun, ZHU Liwen, SUN Yunxiao. Hydrochemical characteristics and origins of salt groundwater in the lower reaches of Dagu river [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2019, 49(5): 84-92.
[9] 侯国华, 高茂生, 党显璋. 唐山曹妃甸浅层地下水水化学特征及咸化成因[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(6):49-57
HOU Guohua, GAO Maosheng, DANG Xianzhang. Hydrochemical characteristics and salinization causes of shallow groundwater in Caofeidian, Tangshan city [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(6): 49-57.
[10] 沈照理. 水文地球化学基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1993: 86-90.
SHEN Zhaoli. Fundamentals of Hydrogeochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1993: 86-90.
[11] Wang Y, Jiao J J. Origin of groundwater salinity and hydrogeochemical processes in the confined quaternary aquifer of the Pearl River delta, China [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2012, 438-439: 112-124. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.03.008
[12] 杨巧凤, 王瑞久, 徐素宁, 等. 莱州湾沿岸寿光、莱州和龙口地下水的稳定同位素与地球化学[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(4):801-817 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.04.014
YANG Qiaofeng, WANG Ruijiu, XU Suning, et al. Hydrogeochemistry and stable isotopes of groundwater from Shouguang, Laizhou and Longkou in the south coast aquifer of Laizhou bay [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(4): 801-817. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.04.014
[13] Kim Y, Lee K S, Koh D C, et al. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic evidence of groundwater salinization in a coastal aquifer: a case study in Jeju volcanic island, Korea [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2003, 270(3-4): 282-294. doi: 10.1016/S0022-1694(02)00307-4
[14] Schiavo M A, Hauser S, Povinec P P. Stable isotopes of water as a tool to study groundwater–seawater interactions in coastal south-eastern Sicily [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2009, 364(1-2): 40-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.10.005
[15] 章斌, 郭占荣, 高爱国, 等. 用氢氧稳定同位素评价闽江河口区地下水输入[J]. 水科学进展, 2012, 23(4):539-548
ZHANG Bin, GUO Zhanrong, GAO Aiguo, et al. Estimating groundwater discharge into Minjiang river estuary based on stable isotopes deuterium and oxygen-18 [J]. Advances in Water Science, 2012, 23(4): 539-548.
[16] Han D M, Song X F, Currell M J, et al. Chemical and isotopic constraints on evolution of groundwater salinization in the coastal plain aquifer of Laizhou bay, China [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2014, 508: 12-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.10.040
[17] Han D M, Kohfahl C, Song X F, et al. Geochemical and isotopic evidence for palaeo-seawater intrusion into the south coast aquifer of Laizhou bay, China [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2011, 26(5): 863-883. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.02.007
[18] 姜月华, 贾军元, 许乃政, 等. 苏锡常地区地下水同位素组成特征及其意义[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2008, 51(6):778-787 doi: 10.1007/s11430-008-0055-y
JIANG Yuehua, JIA Junyuan, XU Naizhen, et al. Isotopic characteristics of groundwater in Changzhou, Wuxi and Suzhou area and their implications [J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2008, 51(6): 778-787. doi: 10.1007/s11430-008-0055-y
[19] 赵继昌, 梁静, 蔡鹤生. 苏北平原地下咸淡水形成与含水介质的关系[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1993(3):25-27
ZHAO Jichang, LIANG Jing, CAI Hesheng. Relation between formation of salt-fresh water and water-bearing medium in the plain of Su Bei [J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 1993(3): 25-27.
[20] 张岩, 付昌昌, 毛磊, 等. 江苏盐城地区地下水水化学特征及形成机理[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2017, 26(4):598-605 doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201704013
ZHANG Yan, FU Changchang, MAO Lei, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of the groundwater in Yancheng, Jiangsu province [J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2017, 26(4): 598-605. doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201704013
[21] 葛勤. 沿海地区弱透水层孔隙水水化学形成与演化: 以苏北平原为例[D]. 中国地质大学博士学位论文, 2018.
GE Qin. The formation and geochemical evolution of porewater in the coastal clay-rich aquitards: a case study in north Jiangsu coastal plain[D]. Doctor Dissertation of China University of Geosciences, 2018.
[22] Clark I D, Fritz P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology[M]. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press/Lewis Publishers, 1997: 206-215.
[23] 康博. 江苏沿海地区地下水演化与合理开发利用研究[D]. 吉林大学博士学位论文, 2017.
KANG Bo. The study of groundwater evolution and rational exploitation and utilizing in Jiangsu coastal area[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Jilin University, 2017.
[24] 中国地质调查局. 水文地质手册[M]. 2版. 北京: 地质出版社, 2012: 102.
China Geological Survey. Handbook of Hydrogeology[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2012: 102.
[25] 许乃政, 刘红樱, 魏峰, 等. 江苏洋口港地区地下水的环境同位素组成及其形成演化研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2015, 35(12):3862-3871
XU Naizheng, LIU Hongying, WEI Feng, et al. Study on the environmental isotope compositions and their evolution in groundwater of Yoco port in Jiangsu province, China [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015, 35(12): 3862-3871.
[26] Liu Y Z, Wu Q, Lin P, et al. Restudy of the storage and migration model of the quaternary groundwater in Beijing plain area [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2012, 55(7): 1147-1158. doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4417-0
[27] Leybourne M I, Goodfellow W D. Br/Cl ratios and O, H, C, and B isotopic constraints on the origin of saline waters from eastern Canada [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(9): 2209-2223. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.02.011
[28] Panno S V, Hackley K C, Hwang H H, et al. Characterization and Identification of Na-Cl sources in ground water [J]. Ground Water, 2006, 44(2): 176-187. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2005.00127.x
[29] Edmunds W M. Geochemistry's vital contribution to solving water resource problems [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2009, 24(6): 1058-1073. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.02.021
-




 下载:
下载: