Archaeozoic buried-hill reservoir of Bozhong 19-6 condensate field: Main controlling factors and development model
-
摘要:
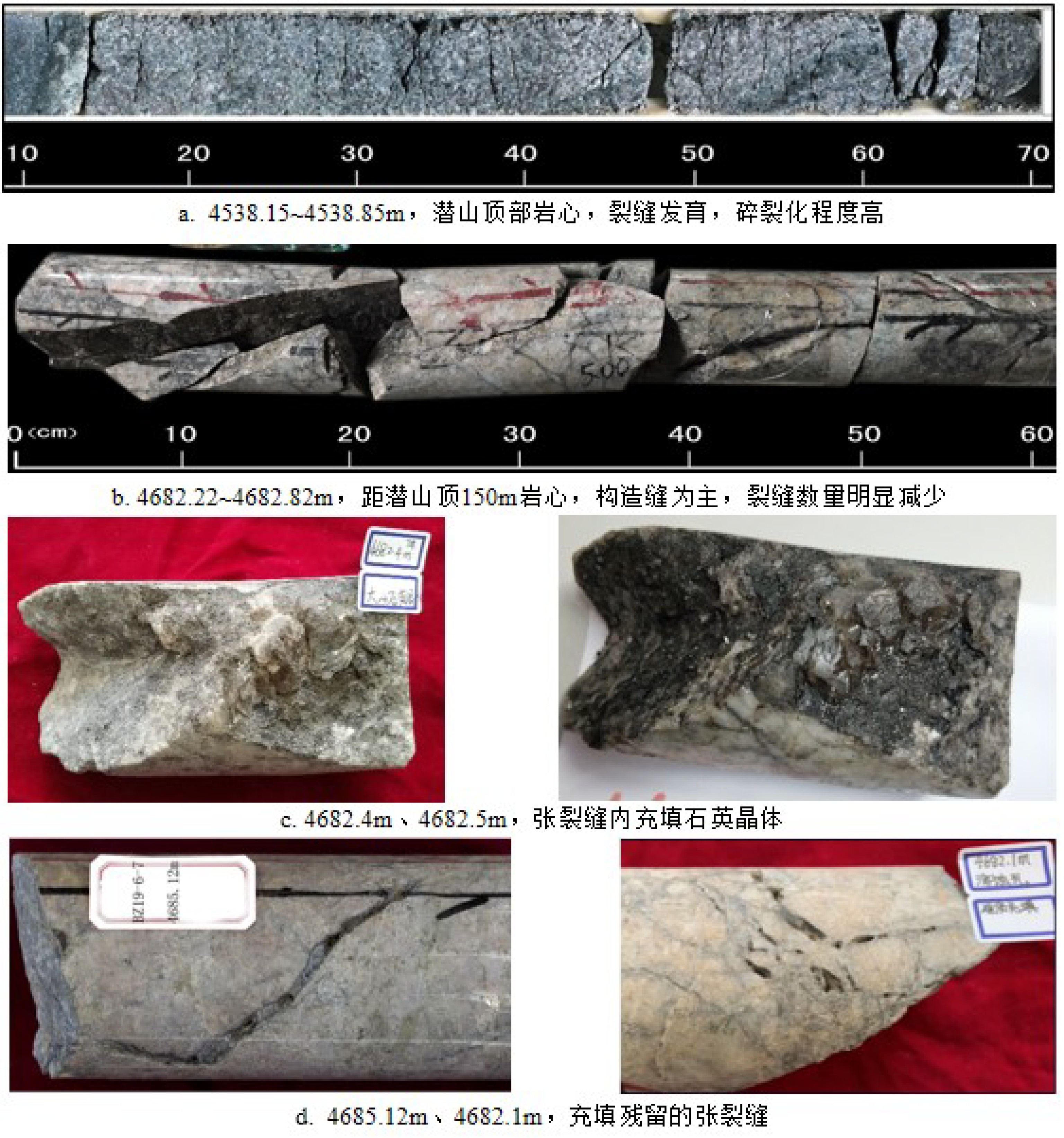
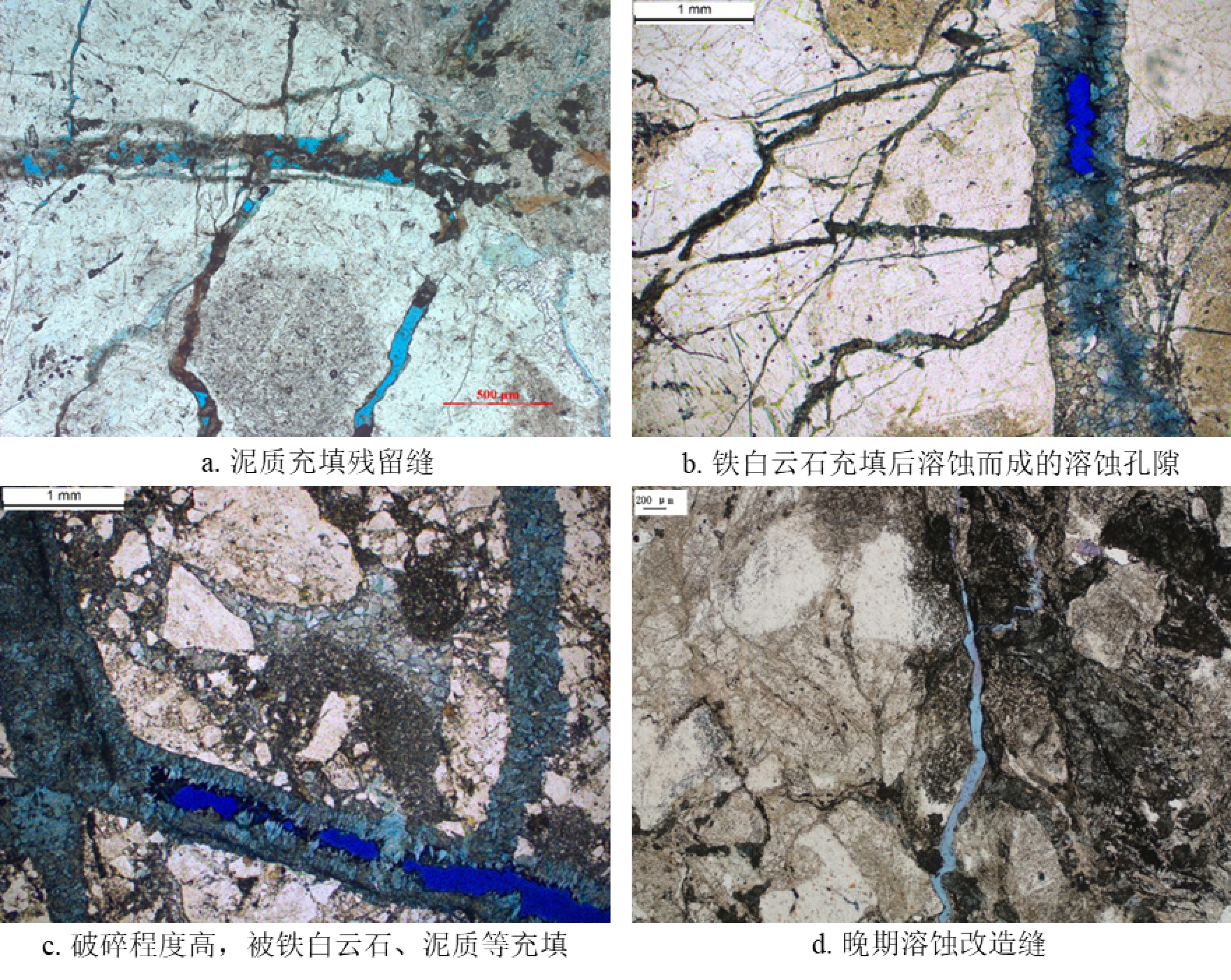
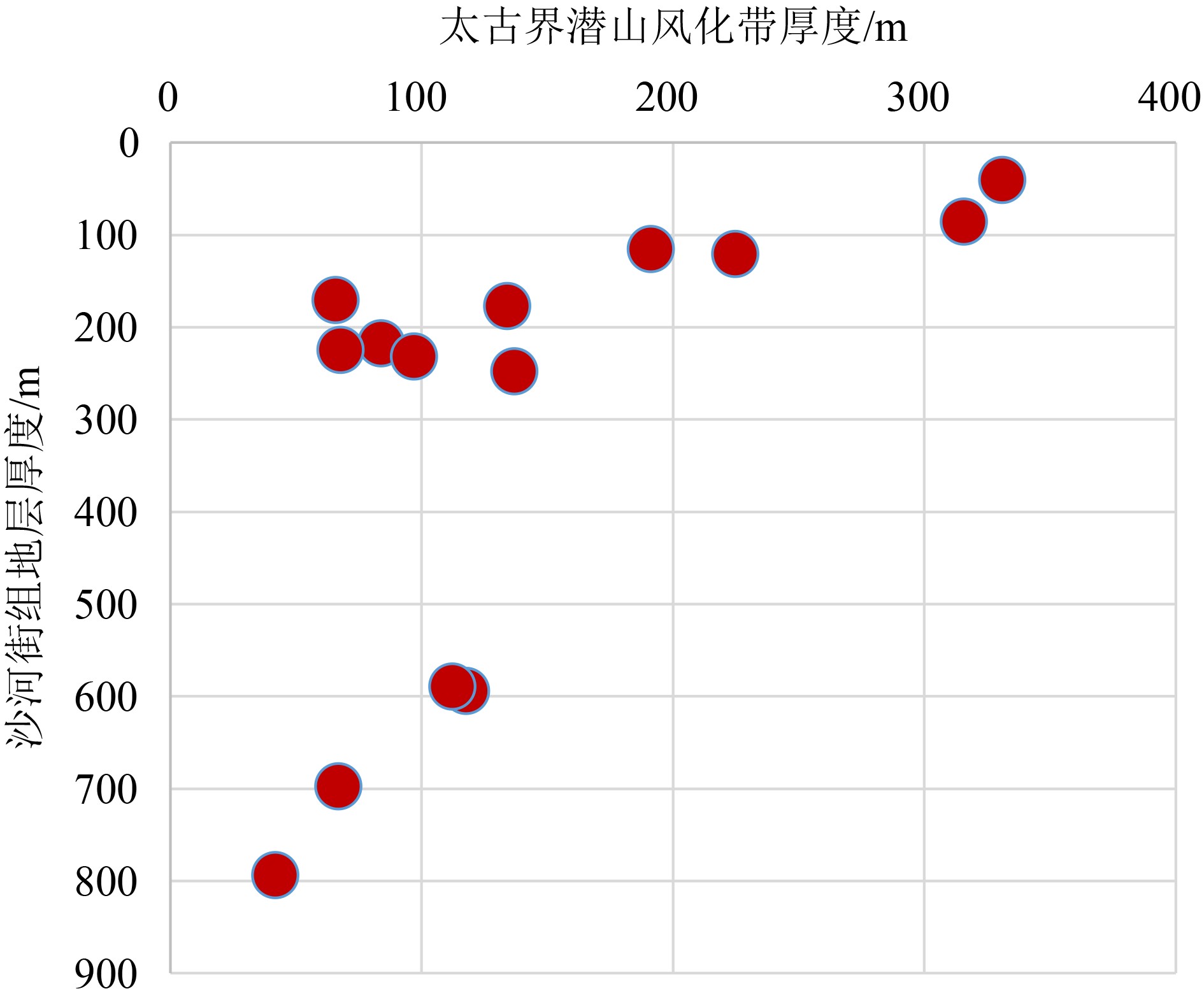
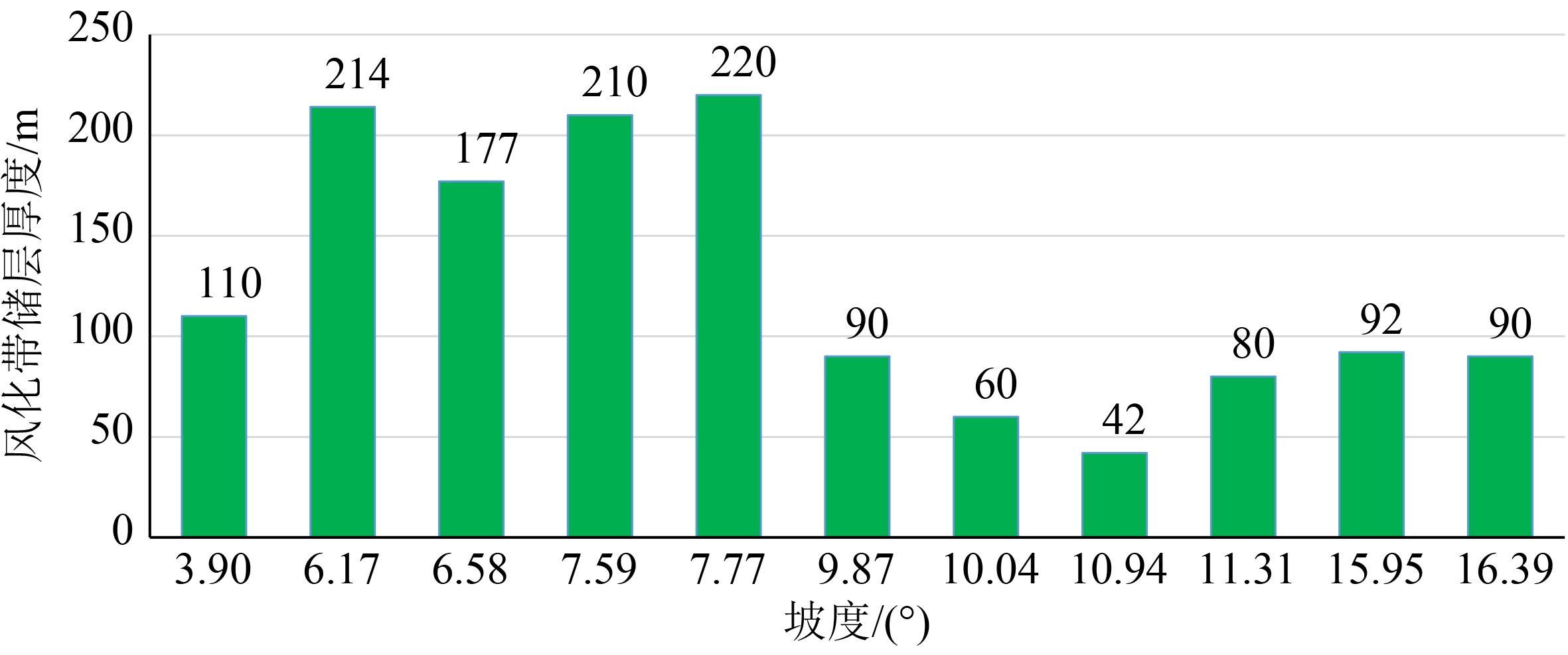
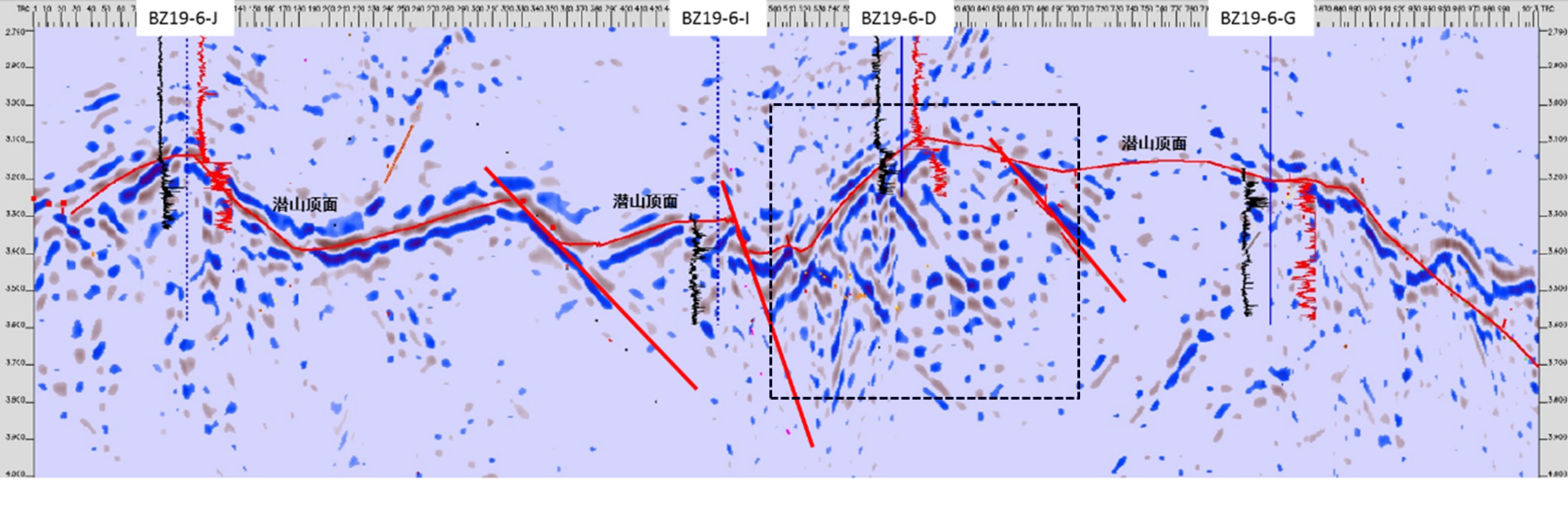
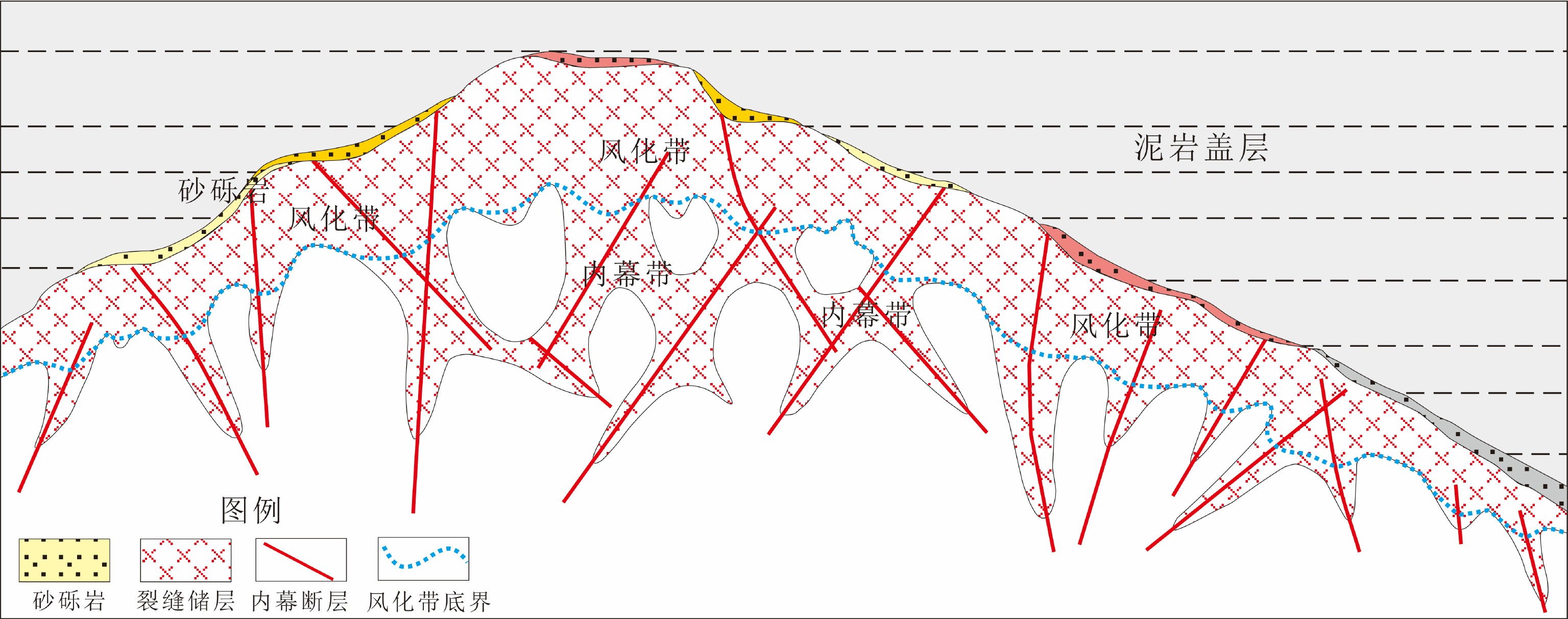
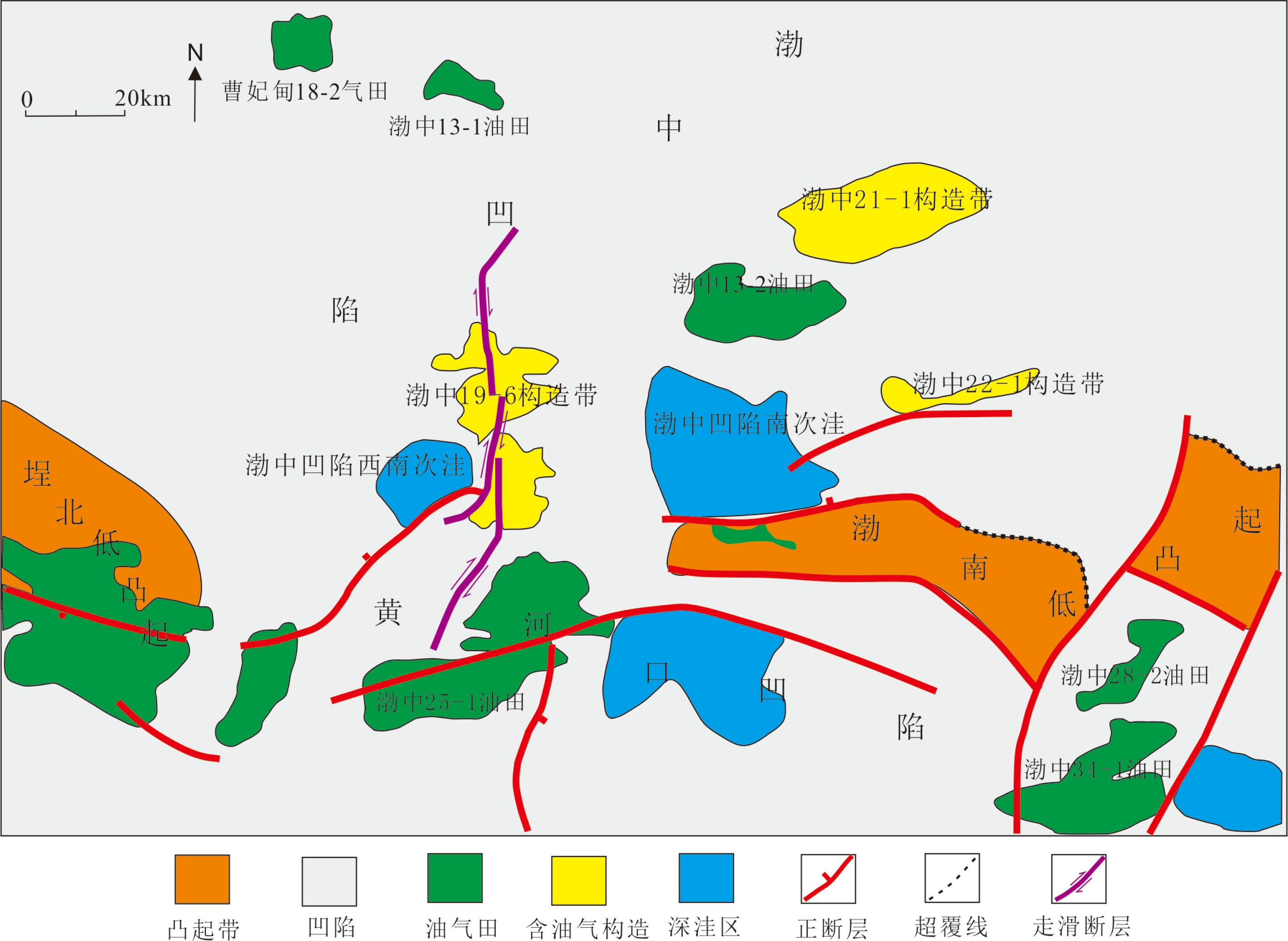
综合运用岩心、测井、地震、野外露头及生产测试资料对渤中19-6太古宇潜山储层发育特征及主控因素进行了分析。研究发现渤中19-6太古宇潜山储层主要受岩石类型、构造运动和风化淋滤等因素影响,储层纵向分为风化带和内幕带,其储层发育主控因素及储层空间分布模式差异明显。其中,风化带受构造和风化淋滤作用双重控制,发育构造缝、风化缝、溶蚀孔隙等储集空间类型,裂缝整体发育呈网状,储层连通性好。受宏观古地貌控制,风化带厚度从古构造高部位向构造低部位呈逐渐减薄的“似层状”分布模式。同时,受岩石类型、局部断层、沟-脊微地貌以及坡度等因素的影响,风化带厚度局部增厚或减薄。潜山内幕带主要受内幕高角度断层控制,基本不受风化作用影响,储集空间以构造缝为主。通过内幕高角度断层的识别和刻画,认为内幕带储层沿高角度断层带状、漏斗型分布。上述认识对于渤中19-6凝析气田开发方案的编制,特别是为潜山储量动用及注采井网部署奠定了重要基础。
Abstract:In order to reveal the distribution pattern of the Archaeozoic buried hill reservoirs in the Bozhong 19-6 condensate field, integrated study is carried out with cores, well logs, well testing data, seismic data in addition to outcrops. The Archaeozoic buried hill reservoir consists of weathered crust reservoirs and internal rock reservoirs, which have obvious differences in controlling factors and distribution patterns. The formation of weathered crust reservoir mainly depends upon structural deformation and weathering, of which the thickness is dependent on the ancient landform. It usually becomes thinner from the paleosrtuctural high to the structural low. Rock types, local faults, microreliefs and topographic slopes are also the controlling factors needed to be considered. However, the inner part reservoir is mainly controlled by the high-angle faults, and the main reservoir space is provided by structural fractures.
-
Key words:
- Archaeozoic buried hill /
- control factors /
- paleogeomorphology /
- weathered zone /
- inner hill /
- geological model /
- Bozhong19-6
-

-
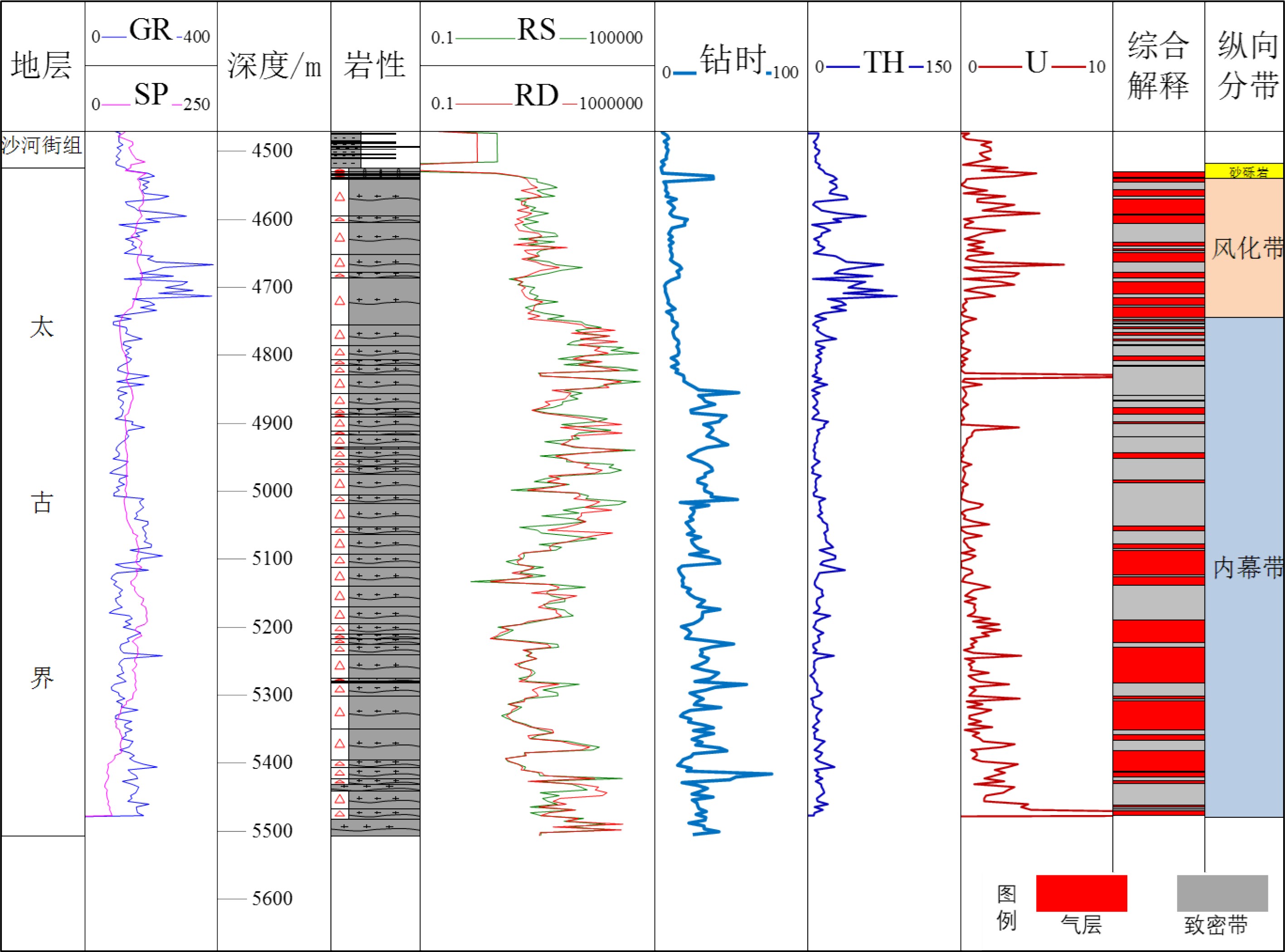
表 1 渤中19-6太古宇潜山风化带分带标准
Table 1. Standards for classification of weathering zone in Bozhong19-6 field
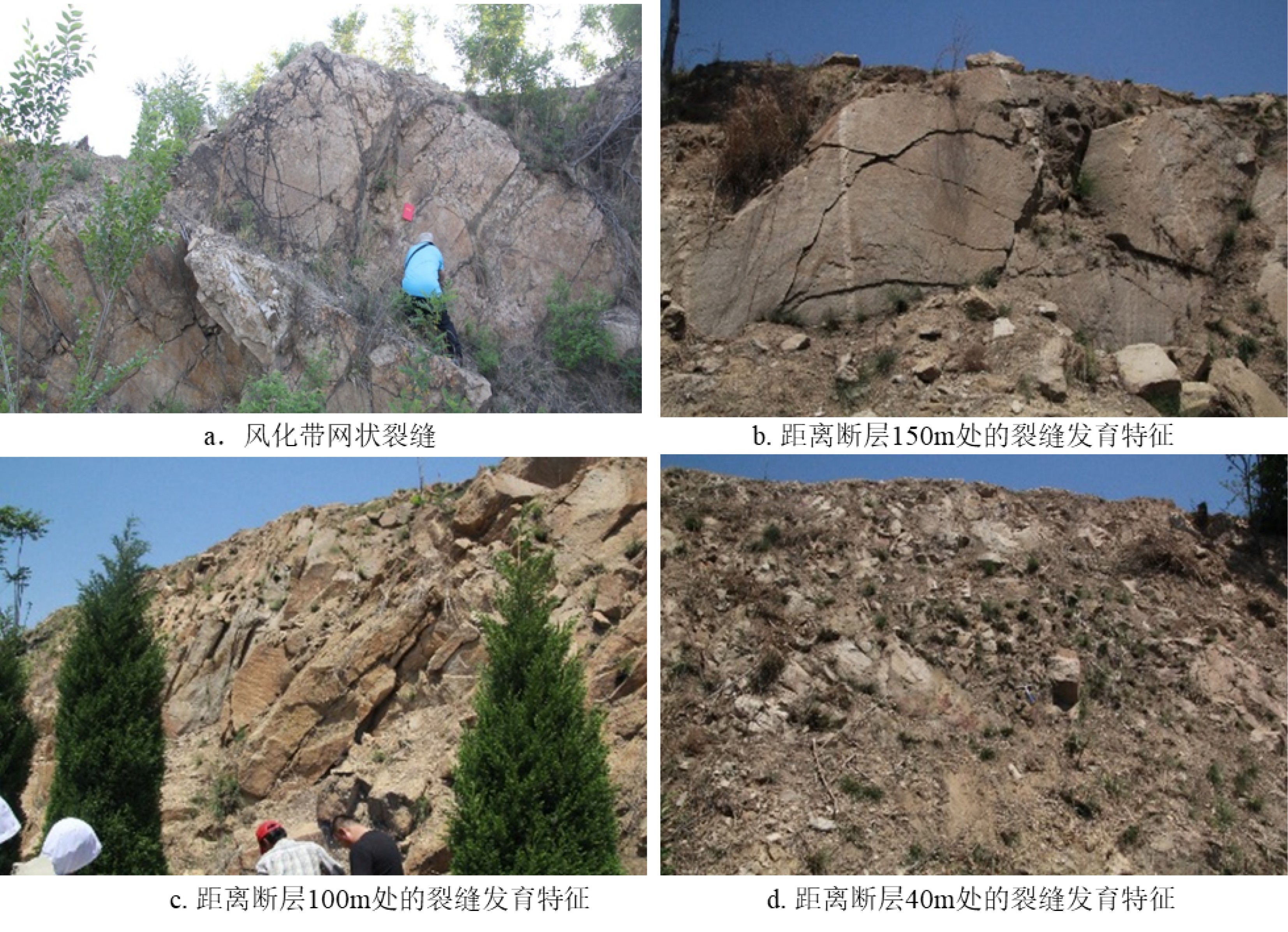
钻时/(min/m) RS/(Ω·m) RD/(Ω·m) 裂缝密度/(条/m) 孔隙度/% 净毛比% 风化带 8~29 75~930 180~1100 3~6 2.4~6.5 0.33~0.62 内幕带 12~52 440~6200 700~22000 0.8~1.2 1.7~3.9 <0.35 表 2 新泰变质岩露头断层附近裂缝发育密度统计
Table 2. Fracture density on the metamorphic outcrop fault near Xintai
与断层距离/m 20 40 100 150 200 裂缝密度/(条/m) 破碎带 20~30 5~15 <10 <5 -
[1] 徐长贵, 于海波, 王军, 等. 渤海海域渤中19-6大型凝析气田形成条件与成藏特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(1):25-38
XU Changgui, YU Haibo, WANG Jun, et al. Formation conditions and accumulation characteristics of Bozhong 19-6 large condensate gas fields in offshore Bohai Bay Basin [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(1): 25-38.
[2] 谢玉洪, 张功成, 沈朴, 等. 渤海湾盆地渤中凹陷大气田形成条件与勘探方向[J]. 石油学报, 2018, 39(11):1199-1210 doi: 10.7623/syxb201811001
XIE Yuhong, ZHANG Gongcheng, SHEN Pu, et al. Formation conditions and exploration direction of large gas field in Bozhong sag of Bohai Bay Basin [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(11): 1199-1210. doi: 10.7623/syxb201811001
[3] 侯明才, 曹海洋, 李慧勇, 等. 渤海海域渤中19-6构造带深层潜山储层特征及其控制因素[J]. 地质勘探, 2018, 39(1):33-44
HOU Mingcai, CAO Haiyang, LI Huiyong, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of deep buried-hill reservoirs in the BZ19-6 structural belt, Bohai Sea area [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2018, 39(1): 33-44.
[4] 张鹏飞, 刘惠民, 王永诗, 等. 济阳坳陷太古界潜山储集体发育模式[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 41(6):20-29
ZHANG Pengfei, LIU Huimin, WANG Yongshi, et al. Development model of Archaeozoic buried hill reservoir in Jiyang Depression [J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2017, 41(6): 20-29.
[5] 张鹏飞, 刘惠民, 曹忠祥, 等. 太古宇潜山风化壳储层发育主控因素分析: 以鲁西-济阳地区为例[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2015, 45(5):1289-1298
ZHANG Pengfei, LIU Huimin, CAO Zhongxiang, et al. Analysis on main controlling factors of Archaeozoic weathering crust reservoir: With Jiyang and Luxi Area as an example [J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2015, 45(5): 1289-1298.
[6] 邹华耀, 赵春明, 尹志军. 辽东湾JZS潜山变质岩风化壳识别及储集特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(4):599-607
ZOU Huayao, ZHAO Chunming, YIN Zhijun. Development and distribution of the metamorphite-weathering crust and its feature of reservoir-property for the JZS Buried Hill, Liaodongwan Area [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2015, 26(4): 599-607.
[7] 伍劲, 高先志, 周伟, 等. 柴达木盆地东坪地区基岩风化壳与油气成藏[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2018, 39(6):666-672
WU Jin, GAO Xianzhi, ZHOU Wei, et al. Base rock weathering crusts and petroleum accumulation in Dongping Area, Qaidam Basin [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2018, 39(6): 666-672.
[8] 付淑清, 王钧, 熊海仙, 等. 南岭保护区石坑崆花岗岩风化壳理化特征与环境分析[J]. 生态科学, 2018, 37(5):174-179
FU Shuqing, WANG Jun, XIONG Haixian, et al. Physical, chemical characteristics of Shikengkong granite weathered crust and potential environments analysis in Nanling area [J]. Ecological Science, 2018, 37(5): 174-179.
[9] 李治, 秦启荣, 李朋波, 等. 准噶尔腹部火山岩风化壳储层特征及其影响因素[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2018, 33(4):589-596 doi: 10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2018.04.012
LI Zhi, QIN Qirong, LI Pengbo, et al. Reservoir characteristics and influence factor of weathering volcanic crust: A case study of Carboniferous System of Shixi Oilfield in the center of Junggar Basin [J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2018, 33(4): 589-596. doi: 10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2018.04.012
[10] 张顺, 王丽静, 张博远, 等. 松辽盆地安达古隆起风化壳特征及控藏机制[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2019, 38(1):9-16
ZHANG Shun, WANG Lijing, ZHANG Boyuan, et al. Characteristics of the weathered crust and reservoir-controlling mechanism for Anda Palaeohigh in Songliao Basin [J]. Petroleum Geology and Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2019, 38(1): 9-16.
[11] 陈志海, 牟珍宝, 孙钰. 越南白虎油田缝洞型基岩油藏特征与开发对策[J]. 中外能源, 2009, 14(9):45-49
CHEN Zhihai, MU Zhenbao, SUN Yu. Characteristics and development strategy of fracture-cavern basement oil reservoir in White Tiger Field, Vietnam [J]. Sino-Global Energy, 2009, 14(9): 45-49.
[12] 张鹏飞, 曹忠祥, 刘慧民, 等. 太古界潜山内幕储层发育主控因素分析: 以鲁西-济阳地区为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2016, 45(1):96-104
ZHANG Pengfei, CAO Zhongxiang, LIU Huimin, et al. Main controlling factors of Archaeozoic inner buried hill reservoir: with Luxi and Jiyang area as an example [J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2016, 45(1): 96-104.
[13] 谢文彦, 孟卫工, 张占文, 等. 辽河坳陷潜山内幕多期裂缝油藏成藏模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2006, 33(6):649-652 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2006.06.001
XIE Wenyan, MENG Weigong, ZHANG Zhanwen, et al. Formation model of multi-stage fracture reservoirs inside the buried hills in Liaohe Depression [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2006, 33(6): 649-652. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2006.06.001
[14] 马志宏. 辽河坳陷太古宇变质岩内幕油藏成藏特征[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2013, 20(2):25-29 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2013.02.006
MA Zhihong. Formation features of interior reservoir in metamorphic rock of Archean Eonothem, Liaohe depression [J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2013, 20(2): 25-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2013.02.006
[15] 任芳祥, 龚姚进, 谷团, 等. 潜山内幕油藏裂缝发育段井眼信息响应特征研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(9):1781-1792
REN Fangxiang, GONG Yaojin, GU Tuan, et al. Research on the response characteristics of wellbore multi-information in the fracture developed section of the buried hill inside reservoirs [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2015, 26(9): 1781-1792.
[16] 高先志, 陈振岩, 邹志文, 等. 辽河西部凹陷兴隆台高潜山内幕油气藏形成条件和成藏特征[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 31(6):6-9
GAO Zhixiang, CHEN Zhenyan, ZOU Zhiwen, et al. Forming conditions and accumulation features of oil pools within the inner of highly buried-hills of Xinglongtai in west sag of Liaohe Depression [J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2007, 31(6): 6-9.
[17] 宋柏荣, 胡英杰, 边少之, 等. 辽河坳陷兴隆台潜山结晶基岩油气储层特征[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(1):77-82 doi: 10.7623/syxb201101011
SONG Bairong, HU Yingjie, BIAN Shaozhi, et al. Reservoir characteristics of the crystal basement in the Xinglongtai buried-hill, Liaohe Depression [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(1): 77-82. doi: 10.7623/syxb201101011
[18] Cuong T X, Warren J K. Bach ho field, a fractured granitic basement reservoir, cuu long basin, offshore SE Vietnam: a “buried-hill” play [J]. Journal of Petroleum Geology, 2009, 32(2): 129-156. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-5457.2009.00440.x
[19] 李家强. 层拉平方法在沉积前古地貌恢复中的应用[J]. 油气地球物理, 2008, 6(2):46-49
LI Jiaqiang. Application of bedding flattening in the process of rebuilding paleogeomorpholog before basin deposition: A case study in Dongying sag, Jiyang Depression [J]. Petroleum Geophysics, 2008, 6(2): 46-49.
[20] 聂妍. 潜山微小断层的表征方法[J]. 中国科技论文, 2019, 14(1):28-32, 50 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2019.01.006
NIE Yan. Research on small faults description of buried hill [J]. China Sciencepaper, 2019, 14(1): 28-32, 50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2019.01.006
-



 下载:
下载: