Late Cenozoic climate changes in the Huanghuai Plain
-
摘要:
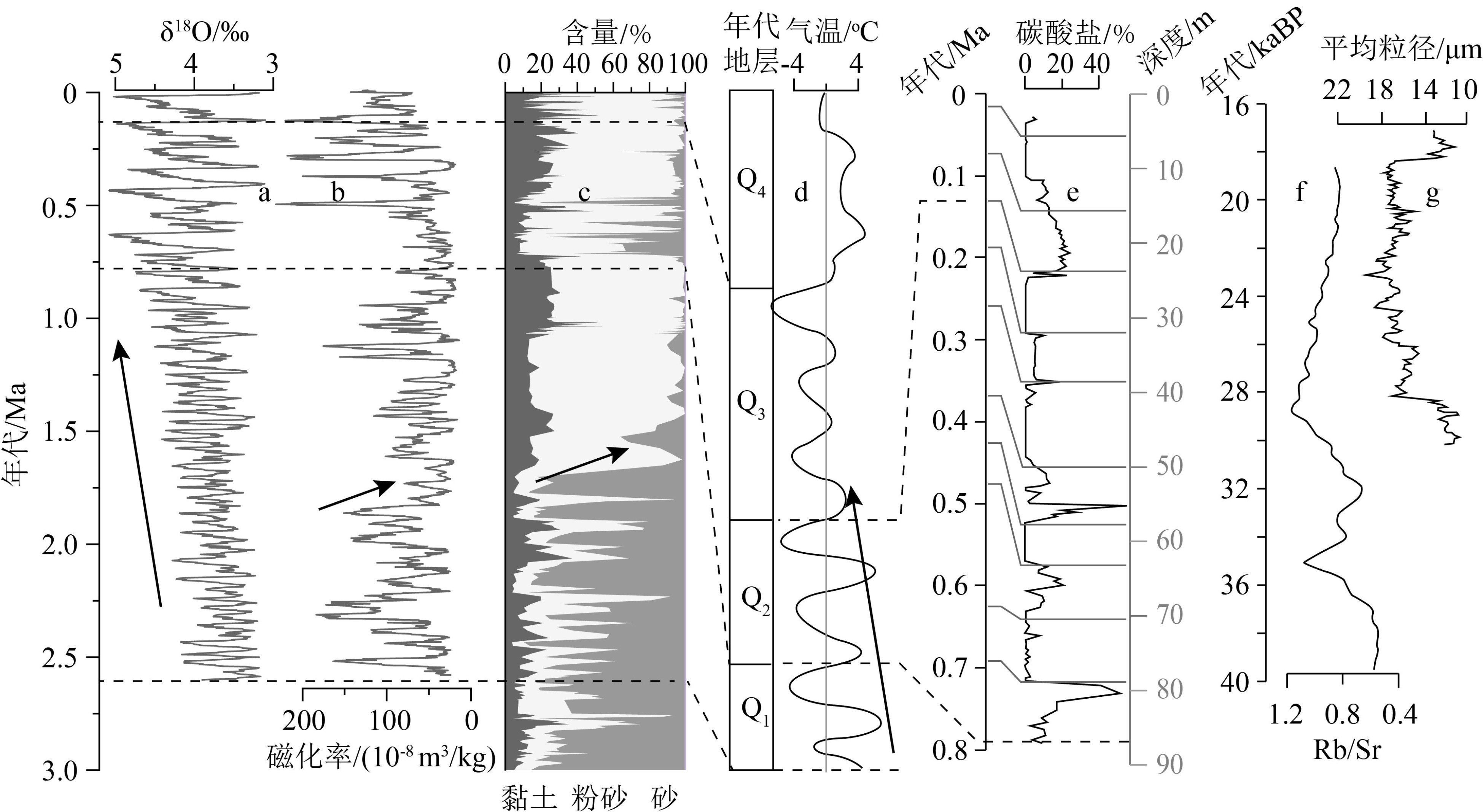
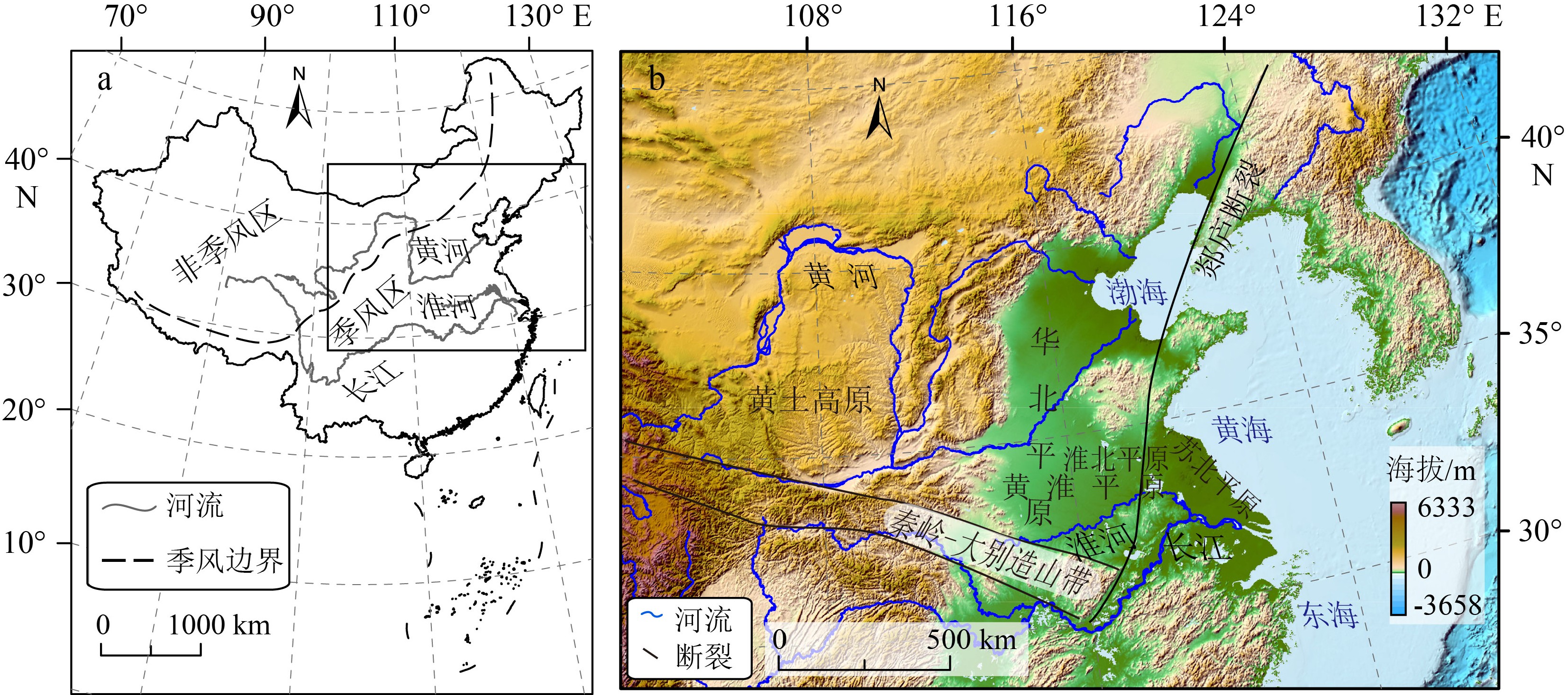
通过梳理黄淮平原内的黄土、湖沼和石笋等剖面及钻孔沉积记录,探讨了该区晚新生代以来的气候变化特征,并对比分析了该区气候变化的时空差异。结果表明,新近纪期间东亚季风系统开始逐渐建立,研究区气候带由干旱区转为湿润区。晚新生代以来,黄淮平原区构造尺度气候变化符合东亚气候变化的一般趋势,即经历了较显著的阶段性冷干化演变。第四纪期间,黄淮平原区气候表现出典型的轨道尺度冷暖波动(冰期-间冰期旋回),可能是在全球宏观气候背景下对东亚季风强弱变化的响应。然而在千年尺度,受区域地形等局地因素的影响,黄淮平原区全新世气候变化在空间上表现出一定的差异性和穿时性。
Abstract:Based on the published records of loess, lacustrine-marsh deposits, stalagmite and other archives, this paper attempts to explore the characteristics of Late Cenozoic climate changes and to make comparative analyzes of the similarities and differences of climate changes on different spatiotemporal scales in the Huanghuai Plain. The results show that the East Asian monsoon system began to establish in Neogene, and as the result this area changed its climate zone from a previous arid area to a humid area. Since late Cenozoic, the pattern of climate change in the Huanghuai Plain has been consistent with the general trend of East Asian region in the tectonic timescale, which has experienced a drastic change from warm and humid to cold and dry. During the Quaternary period, the climate changes showed typical orbit-scale cold and warm fluctuations or glacial-interglacial cycles in the study area, possibly as a response to the changes of the intensity of the East Asian monsoon under the global climate background. However, due to the influence of local factors such as regional topography, the Holocene climate change shows a certain degree of spatial differentiation and diachroneity in the Huanghuai Plain on a millennium scale.
-
Key words:
- climate change /
- sedimentary record /
- late Cenozoic /
- Huanghuai Plain
-

-
[1] Zachos J C, Dickens G R, Zeebe R E. An early Cenozoic perspective on greenhouse warming and carbon-cycle dynamics [J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7176): 279-283. doi: 10.1038/nature06588
[2] Li J J, Fang X M, Song C H, et al. Late Miocene–Quaternary rapid stepwise uplift of the NE Xizang Plateau and its effects on climatic and environmental changes [J]. Quaternary Research, 2014, 81(3): 400-423. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2014.01.002
[3] 程海, 张海伟, 赵景耀, 等. 中国石笋古气候研究的回顾与展望[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2019, 62(10):1489-1513 doi: 10.1007/s11430-019-9478-3
CHENG Hai, ZHANG Haiwei, ZHAO Jingyao, et al. Chinese stalagmite paleoclimate researches: A review and perspective [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2019, 62(10): 1489-1513. doi: 10.1007/s11430-019-9478-3
[4] 姚檀栋, 秦大河, 王宁练, 等. 冰芯气候环境记录研究: 从科学到政策[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2020, 35(4):466-474
YAO Tandong, QIN Dahe, WANG Ninglian, et al. Study on climatic and environmental changes recorded in ice cores: from science to policy [J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Science, 2020, 35(4): 466-474.
[5] Hays J D, Imbrie J, Shackleton N J. Variations in the Earth’s orbit: Pacemaker of the Ice Ages [J]. Science, 1976, 194(4270): 1121-1132. doi: 10.1126/science.194.4270.1121
[6] Lisiecki L E, Raymo M E. A pliocene-pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ18O records [J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2005, 20(1): PA1003. doi: 10.1029/2004PA001071
[7] Tian J, Zhao Q H, Wang P X, et al. Astronomically modulated Neogene sediment records from the South China Sea [J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2008, 23(3): PA3210. doi: 10.1029/2007PA001552
[8] Ren H J, Sigman D M, Martínez-García A, et al. Impact of glacial/interglacial sea level change on the ocean nitrogen cycle [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(33): E6759-E6766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1701315114
[9] Stuiver M, Grootes P M, Braziunas T F. The GISP2 δ18O climate record of the past 16, 500 years and the role of the sun, ocean, and volcanoes [J]. Quaternary Research, 1995, 44(3): 341-354. doi: 10.1006/qres.1995.1079
[10] Yan Y Z, Bender M L, Brook E J, et al. Two-million-year-old snapshots of atmospheric gases from Antarctic ice [J]. Nature, 2019, 574(7780): 663-666. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1692-3
[11] Liu T S, Ding Z L. Chinese loess and the paleomonsoon [J]. Annual Reviews of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1998, 26: 111-145. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.26.1.111
[12] Song Y G, Fang X M, Torii M, et al. Late Neogene rock magnetic record of climatic variation from Chinese eolian sediments related to uplift of the Xizang Plateau [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2007, 30(2): 324-332. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2006.10.004
[13] Li X M, Peng T J, Ma Z H, et al. Late Miocene–Pliocene climate evolution recorded by the red clay covered on the Xiaoshuizi planation surface, NE Xizang Plateau [J]. Climate of the Past, 2019, 15(2): 405-421. doi: 10.5194/cp-15-405-2019
[14] Dykoski C A, Edwards R L, Cheng H, et al. A high-resolution, absolute-dated Holocene and deglacial Asian monsoon record from Dongge Cave, China [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 233(1-2): 71-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.01.036
[15] Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al. Millennial- and orbital-scale changes in the East Asian monsoon over the past 224, 000 years [J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7182): 1090-1093. doi: 10.1038/nature06692
[16] Cheng H, Edwards R L, Broecker W S, et al. Ice age terminations [J]. Science, 2009, 326(5950): 248-252. doi: 10.1126/science.1177840
[17] Cheng H, Edwards R L, Sinha A, et al. The Asian monsoon over the past 640,000 years and ice age terminations [J]. Nature, 2016, 534(7609): 640-646. doi: 10.1038/nature18591
[18] Cook E R, Anchukaitis K J, Buckley B M, et al. Asian monsoon failure and megadrought during the last millennium [J]. Science, 2010, 328(5977): 486-489. doi: 10.1126/science.1185188
[19] Liu Y, Tian H, Song H M, et al. Tree ring precipitation reconstruction in the Chifeng-Weichang region, China, and East Asian summer monsoon variation since A. D. 1777 [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2010, 115(D6): D06103. doi: 10.1029/2009JD012330
[20] Gou X H, Yang T, Gao L L, et al. A 457-year reconstruction of precipitation in the southeastern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, China using tree-ring records [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(10): 1107-1114. doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5539-7
[21] 李吉均, 文世宣, 张青松, 等. 青藏高原隆起的时代、幅度和形式的探讨[J]. 中国科学, 1979, 22(11):1314-1328
LI Jijun, WEN Shixuan, ZHANG Qingsong, et al. A discussion on the period, amplitude and type of the uplift of the Qinghai-Xizang plateau [J]. Scientia Sinica, 1979, 22(11): 1314-1328.
[22] 张林源. 青藏高原上升对我国第四纪环境演变的影响[J]. 兰州大学学报, 1981(3):142-155
ZHANG Linyuan. The influence of the uplift of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau on the Quaternary environmental evolution in China [J]. Journal of Lanzhou University, 1981(3): 142-155.
[23] 刘东生, 丁梦林. 晚第三纪以来中国古环境的特征及其发展历史[J]. 地球科学—武汉地质学院学报, 1983(4):15-28
LIU Dongsheng, DING Menglin. The characteristics and evolution of paleoenvironment of China since Late Tertiary [J]. Earth Science—Journal of Wuhan College of Geology, 1983(4): 15-28.
[24] Wang P X. Progress in Late Cenozoic palaeoclimatology of China: a brief review[M]//Whyte R O. The Evolution of the East Asian Environment. Hong Kong, China: Centre of Asian Studies, University of Hong Kong, 1984, 165-187.
[25] Wang Y B, Bekeschus B, Handorf D, et al. Coherent tropical-subtropical Holocene see-saw moisture patterns in the Eastern Hemisphere monsoon systems [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2017, 169: 231-242. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2017.06.006
[26] 刘东生, 张新时, 熊尚发, 等. 青藏高原冰期环境与冰期全球降温[J]. 第四纪研究, 1999, 19(5):386-396
LIU Dongsheng, ZHANG Xinshi, XIONG Shangfa, et al. Qinghai-Xizang plateau glacial environment and global cooling [J]. Quaternary Science, 1999, 19(5): 386-396.
[27] 姚檀栋, 刘晓东, 王宁练. 青藏高原地区的气候变化幅度问题[J]. 科学通报, 2000, 45(13):1236-1243 doi: 10.1007/BF02886087
YAO Tandong, LIU Xiaodong, WANG Ninglian, et al. Amplitude of climatic changes in Qinghai-Xizang Plateau [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45(13): 1236-1243. doi: 10.1007/BF02886087
[28] Chou C, Chiang J C H, Lan C H, et al. Increase in the range between wet and dry season precipitation [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2013, 6(4): 263-267. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1744
[29] 施雅风, 沈永平, 李栋梁, 等. 中国西北气候由暖干向暖湿转型的特征和趋势探讨[J]. 第四纪研究, 2003, 23(2):152-164 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2003.02.005
SHI Yafeng, SHEN Yongping, LI Dongliang, et al. Discussion on the present climate change from warm-dry to warm wet in northwest China [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2003, 23(2): 152-164. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2003.02.005
[30] 陈发虎, 黄伟, 靳立亚, 等. 全球变暖背景下中亚干旱区降水变化特征及其空间差异[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 54(12):1812-1821 doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4333-8
CHEN Fahu, HUANG Wei, JIN Liya, et al. Spatiotemporal precipitation variations in the arid Central Asia in the context of global warming [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2011, 54(12): 1812-1821. doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4333-8
[31] 张百平. 中国南北过渡带研究的十大科学问题[J]. 地理科学进展, 2019, 38(3):305-311 doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.03.001
ZHANG Baiping. Ten major scientific issues concerning the study of China's north-south transitional zone [J]. Progress in Geography, 2019, 38(3): 305-311. doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.03.001
[32] 赵希涛, 唐领余, 沈才明, 等. 江苏建湖庆丰剖面全新世气候变迁和海面变化[J]. 海洋学报, 1994, 16(1):78-88
ZHAO Xitao, TANG Lingyu, SHEN Caiming, et al. Climate evolution and sea level changes based on Qingfeng Section, Jianhu, Jiangsu [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1994, 16(1): 78-88.
[33] 秦小光, 张磊, 穆燕. 中国东部南北方过渡带淮河半湿润区全新世气候变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2015, 35(6):1509-1524 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.06.20
QIN Xiaoguang, ZHANG Lei, MU Yan. The Holocene climatic changes of the Huaihe River semi-humid region in the North and South Transition Zone of the eastern China [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2015, 35(6): 1509-1524. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.06.20
[34] 毛瑞雪, 蔡演军, 马乐, 等. 河南马沟洞石笋记录的早中全新世气候和环境变化[J]. 地球环境学报, 2016, 7(3):254-268 doi: 10.7515/JEE201603004
MAO Ruixue, CAI Yanjun, MA Le, et al. Early to mid-Holocene paleoclimatic changes recorded by the stalagmites from the Magou Cave, Henan Province [J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2016, 7(3): 254-268. doi: 10.7515/JEE201603004
[35] Zhang L, Liu J Q, Qin X G, et al. Magnetostratigraphy and paleoenvironmental events recorded in a late Cenozoic sedimentary succession in Huaibei Plain, East China [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2018, 200: 52-64. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.09.041
[36] Qiu Z D, Li C K. Evolution of Chinese mammalian faunal regions and elevation of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau [J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2005, 48(8): 1246-1258. doi: 10.1360/03yd0523
[37] An Z S, Wu G X, Li J P, et al. Global monsoon dynamics and climate change [J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2015, 43: 29-77. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-060313-054623
[38] Sun X J, Wang P X. How old is the Asian monsoon system?: Palaeobotanical records from China [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2005, 222(3-4): 181-222. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.03.005
[39] 鹿化煜, 郭正堂. 晚新生代东亚气候变化: 进展与问题[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2014, 57(1):70-79 doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4790-3
LU Huayu, GUO Zhengtang. Evolution of the monsoon and dry climate in East Asia during late Cenozoic: A review [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2014, 57(1): 70-79. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4790-3
[40] 张光业. 河南省第四纪古地理的演变[J]. 河南大学学报, 1985, 15(3):11-22
ZHANG Guangye. Evolution of quaternary paleogeograpy of Henan province, China [J]. Journal of Henan University, 1985, 15(3): 11-22.
[41] 王鸿桢. 中国古地理图集[M]. 北京: 地图出版社, 1985: 121-130.
WANG Hongzhen. Atlas of the Palaeogeography of China[M]. Beijing: Cartographic Press, 1985: 121-130.
[42] 金权, 王平, 王松根. 安徽淮河中游平原晚新生代孢粉组合及古气候[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1987, 7(4):93-109
JIN Quan, WANG Ping, WANG Songgen. The sporo-pollen assemblages and palaeoclimate in the middle course area of the Huaihe River during late Cenozoic [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1987, 7(4): 93-109.
[43] 于振江, 黄多成. 淮北平原上第三系划分和孢粉序列[J]. 地层学杂志, 1993, 17(3):202-209
YU Zhenjiang, HUANG Duocheng. Division of the upper tertiary of the Huaibei plain and sporo pollen sequence [J]. Journal of Stratigrapy, 1993, 17(3): 202-209.
[44] 宋雪芳. 苏北盆地XH-2孔晚中新世以来古植被与古气候研究[D]. 南京师范大学硕士学位论文, 2016.
SONG Xuefang. Paleo-vegetation and paleo-climate records from the XH-2 core in Northern Jiangsu Basin since late Miocene[D]. Master Dissertation of Nanjing Normal University, 2016
[45] 张茂恒, 李吉均, 舒强, 等. 兴化XH-1孔记录的苏北盆地晚新生代沉积体系及环境变化过程[J]. 地理研究, 2011, 30(3):513-522
ZHANG Maoheng, LI Jijun, SHU Qiang, et al. The sediments sequence and environmental oscillation of the core XH-1 in Subei Basin since late Cenozoic [J]. Geographical Research, 2011, 30(3): 513-522.
[46] Raymo M E. The initiation of northern Hemisphere glaciation [J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1994, 22: 353-383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.22.050194.002033
[47] 鹿化煜, 王珧. 触发和驱动第四纪冰期的机制是什么?[J]. 科学通报, 2016, 61(11):1164-1172 doi: 10.1360/N972015-01294
LU Huayu, WANG Yao. What causes the ice ages in the late Pliocene and Pleistocene? [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(11): 1164-1172. doi: 10.1360/N972015-01294
[48] 石钦周. 对 《河南省平原区第四纪下限的探讨》 一文的几点看法[J]. 河南地质, 1989, 7(3):73-78
SHI Qinzhou. Several views on the article "Discussion on the lower boundary of the Quaternary in the plain area of Henan Province" [J]. Henan Geology, 1989, 7(3): 73-78.
[49] 于振江, 黄多成. 安徽省淮北平原第四纪孢粉序列[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1993, 13(1):21-32
YU Zhenjiang, HUANG Duocheng. Quaternary palynological sequence in Huaibei Plain, Anhui province [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1993, 13(1): 21-32.
[50] 杨競红, 王颖, 张振克, 等. 苏北平原2.58 Ma以来的海陆环境演变历史: 宝应钻孔沉积物的常量元素记录[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26(3):340-352 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.03.005
YANG Jinghong, WANG Ying, ZHANG Zhenke, et al. Major element records of land-sea interaction and evolution in the past 2.58 Ma from the Baoying borehole sediments, Northern Jiangsu Plain, China [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2006, 26(3): 340-352. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.03.005
[51] 刘奇, 宋传中, 崔王, 等. 淮河源区中更新世黄土堆积的元素地球化学特征及其古气候意义[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2007, 29(4):356-361 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2007.04.004
LIU Qi, SONG Chuanzhong, CUI Wang, et al. Geochemical changes in Source Area of Huaihe river and its implications for variations of paleoclimate in middle Pleistocene [J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2007, 29(4): 356-361. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2007.04.004
[52] 朱芸, 陈晔, 舒强, 等. 苏北盆地XH1钻孔中更新世以来的彩度指标记录及其气候环境变化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(2):23-31
ZHU Yun, CHEN Ye, SHU Qiang, et al. Chroma index record of core XH1 at northern Jiangsu Basin and the climate since mid-Pleistocene [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(2): 23-31.
[53] 舒强, 萧家仪, 赵志军, 等. 苏北盆地XH-1钻孔0.78 Ma以来的气候环境变化记录[J]. 地层学杂志, 2010, 34(1):27-34
SHU Qiang, XIAO Jiayi, ZHAO Zhijun, et al. Environmental records in XH-1 core in northern Jiangsu Basin since about 780 kaBP [J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2010, 34(1): 27-34.
[54] 牛旭亚. 中更新世以来苏北盆地XH-2孔的古植被与古气候研究[D]. 南京师范大学硕士学位论文, 2013.
NIU Xuya. Study on climate and vegetation changes in core XH-2 in northern Jiangsu Basin since middle Pleistocene[D]. Master Dissertation of Nanjing Normal University, 2013.
[55] 杨俊峰, 侯林晓, 晁红丽, 等. 黄淮平原西南部130~13 kaBP 气候环境及盆地演化: 以河南信阳胡族铺剖面为例[C]//河南地球科学通报2011年卷(上册). 郑州: 河南人民出版社, 2011: 20-25.
YANG Junfeng, HOU Linxiao, CHAO Hongli, et al. Climate and basin evolution of the southwestern Huanghuai Plain during 130~13 kaBP take the Huzupu profile in Xinyang, Henan as an example[C]//Acta Geological Sinica of Henan 2011 (Volume 1). Zhengzhou: Henan People’s Publishing House, 2011: 20-25.
[56] 萧家仪, 王丹, 吕海波, 等. 苏北盆地晚更新世以来的孢粉记录与气候地层学的初步研究[J]. 古生物学报, 2005, 44(4):591-598 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-6616.2005.04.010
XIAO Jiayi, WANG Dan, LV Haibo, et al. A study of pollen and climatic stratigraphy in the northern Jiangsu Basin since late Pleistocene [J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 2005, 44(4): 591-598. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-6616.2005.04.010
[57] 刘玉, 杨佩佩, 舒强. 苏北盆地晚更新世晚期湖泊沉积记录的气候环境变化[J]. 地球与环境, 2021, 49(1): 1-8.
LIU Yu, YANG Peipei, SHU Qiang. Paleoclimatic and paleoenvironmental changes in late stage of late pleistocene inferred from lacustrine sediment in Subei basin[J]. Earth and Environment, 2021, 49(1): 1-8.
[58] 张唯唯, 舒强, 陈晔, 等. 苏北盆地里下河地区30~15 cal.kaBP期间地球化学元素变化特征及古气候意义[J]. 地球与环境, 2014, 42(5):583-588
ZHANG Weiwei, SHU Qiang, CHEN Ye, et al. Characteristics of geochemical element variation and paleoclimatical significance in the Subei Basin during 30~15 cal. kaBP [J]. Earth and Environment, 2014, 42(5): 583-588.
[59] 陈景荣, 舒强, 赵志军, 等. 苏北盆地湖沼沉积记录的30~17 cal.kaBP期间的气候变化[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(2):75-79, 85
CHEN Jingrong, SHU Qiang, ZHAO Zhijun, et al. Climate change records of lacustrine deposits of Subei Basin in eastern China, 30~17 cal.kaBP [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(2): 75-79, 85.
[60] 骆丁, 肖渊甫, 叶思源, 等. 宁波平原晚第四纪的古气候变化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(5):155-161
LUO Ding, XIAO Yuanfu, YE Siyuan, et al. Palaeoclimatic changes during late Quaternary in Ningbo Plain [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(5): 155-161.
[61] 施雅风, 孔昭宸, 王苏民, 等. 中国全新世大暖期的气候波动与重要事件[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 1994, 37(3):353-365
SHI Yafeng, KONG Zhaochen, WANG Sumin, et al. The climatic fluctuation and important events of Holocene megathermal in China [J]. Science in China Series B, 1994, 37(3): 353-365.
[62] 侯光良, 方修琦. 中国全新世气温变化特征[J]. 地理科学进展, 2011, 30(9):1075-1080 doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2011.09.001
HOU Guangliang, FANG Xiuqi. Characteristics of holocene temperature change in China [J]. Progress in Geography, 2011, 30(9): 1075-1080. doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2011.09.001
[63] 闫慧, 申怀飞, 李中轩. 河南省全新世环境演变研究概述[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2011, 34(1):73-78 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7148.2011.01.013
YAN Hui, SHEN Huaifei, LI Zhongxuan. Holocene environmental change in Henan Province [J]. Meteorological and Environmental Sciences, 2011, 34(1): 73-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7148.2011.01.013
[64] 杨瑞霞, 李志飞, 张莉, 等. 河南嵩山东麓邓家剖面元素的地球化学特征及环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(2):129-134
YANG Ruixia, LI Zhifei, ZHANG Li, et al. Elements distribution of the Dengjia loess section, central Henan and its environmental implications [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(2): 129-134.
[65] Li K F, Gao W H. Holocene climate change in Henan area: A synthesis of proxy records [J]. Quaternary International, 2019, 521: 185-193. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2019.05.026
[66] Li X Y, Huang C C, Pang J L, et al. Dust source of the Holocene loess-soil and pedogenic environmental changes in the upper Huaihe River [J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2009, 19(1): 107-117. doi: 10.1007/s11442-009-0107-z
[67] 舒强, 赵志军, 陈晔, 等. 江苏兴化DS浅孔沉积物地球化学元素与粒度所揭示的古环境意义[J]. 地理科学, 2009, 29(6):923-928
SHU Qiang, ZHAO Zhijun, CHEN Ye, et al. Palaeoenvironmental significance of geochemistry elements and grain size of DS core sediments in Xinghua, Jiangsu Province [J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2009, 29(6): 923-928.
[68] 舒强, 陈晔, 赵志军, 等. 江淮平原地区晚冰期以来的气候与环境变化记录[J]. 地理科学, 2013, 33(11):1377-1382
SHU Qiang, CHEN Ye, ZHAO Zhijun, et al. Paleoclimatic and paleoenvironmental evolution since the Late Glacial epoch in Jianghuai Plain [J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2013, 33(11): 1377-1382.
[69] 刘钧枢. 郑州地区全新世古气候变化初探[J]. 西安地质学院学报, 1994, 16(4):48-54
LIU Junshu. A preliminary probe into the Holocene palaeoclimate variations in the Zheng Zhou area [J]. Journal of Xi’an College of Geology, 1994, 16(4): 48-54.
[70] 陈月秋. 江苏两万年来的古气候与海平面变化[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 1992(4):1-5
CHEN Yueqiu. Paleoclimate and sea level changes during the past 20000 years in Jiangsu Province [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 1992(4): 1-5.
[71] 张本昀, 李容全. 洛阳盆地全新世气候环境[J]. 北京师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 1997, 33(2):275-280
ZHANG Benyun, LI Rongquan. The environmental changes of Luoyang Basin in Holocene [J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University: Natural Science, 1997, 33(2): 275-280.
[72] 孙雄伟, 夏正楷. 河南洛阳寺河南剖面中全新世以来的孢粉分析及环境变化[J]. 北京大学学报: 自然科学版, 2005, 41(2):289-294
SUN Xiongwei, XIA Zhengkai. Paleoenvironment changes since mid-Holocene revealed by a palynological sequence from Sihenan profile in Luoyang, Henan Province [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2005, 41(2): 289-294.
[73] 黄润, 朱诚, 郑朝贵. 安徽淮河流域全新世环境演变对新石器遗址分布的影响[J]. 地理学报, 2005, 60(5):742-750 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2005.05.005
HUANG Run, ZHU Cheng, ZHENG Chaogui. Distribution of neolithic sites and environmental change in Huaihe River Basin, Anhui province [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2005, 60(5): 742-750. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2005.05.005
[74] 吴小爽. 江苏建湖地区末次冰盛期以来的古植物群和古地理[D]. 南京师范大学硕士学位论文, 2018.
WU Xiaoshuang. Paleophyte and paleogeographic environment since the last glacial maximum in the Jianhu area, Jiangsu Province[D]. Master Dissertation of Nanjing Normal University, 2018.
[75] 程瑜, 李向前, 赵增玉, 等. 全新世以来苏北平原里下河南部地区的沉积记录和环境演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(1):49-58
CHENG Yu, LI Xiangqian, ZHAO Zengyu, et al. Sedimentary and environment evolutionary records of the southern Lixiahe area in the Subei Plain during Holocene [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(1): 49-58.
[76] 赵琳, 马春梅, 张广胜, 等. 安徽蚌埠禹会村遗址地层的孢粉记录研究[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2013, 30(4):405-414
ZHAO Lin, MA Chunmei, ZHANG Guangsheng, et al. Sporo-pollen record of the Yuhuicun site in Bengbu, Anhui Province [J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 2013, 30(4): 405-414.
[77] Guo Z T, Sun B, Zhang Z S, et al. A major reorganization of Asian climate by the early Miocene [J]. Climate of the Past, 2008, 4(3): 153-174. doi: 10.5194/cp-4-153-2008
[78] Sun J M, Ye J, Wu W Y, et al. Late Oligocece-Miocene mid-latitude aridification and wind patterns in the Asian interior [J]. Geology, 2010, 38(6): 515-518. doi: 10.1130/G30776.1
[79] Lu H Y, Wang X Y, Li L P. Aeolian sediment evidence that global cooling has driven late Cenozoic stepwise aridification in central Asia [J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 2010, 342(1): 29-44. doi: 10.1144/SP342.4
[80] Zhang J, Li J J, Guo B H, et al. Magnetostratigraphic age and monsoonal evolution recorded by the thickest Quaternary loess deposit of the Lanzhou region, western Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 139: 17-29. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.02.025
[81] Miao Y F, Song C H, Fang X M, et al. Late Cenozoic genus Fupingopollenites development and its implications for the Asian summer monsoon evolution [J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 29(1): 320-333. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.12.007
[82] 赵辰辰, 王永波, 胥勤勉. 2.5 Ma以来中国陆地孢粉记录反映的古气候变化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(4):175-191
ZHAO Chenchen, WANG Yongbo, XU Qinmian. Climate changes on Chinese continent since 2.5 Ma: Evidence from fossil pollen records [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(4): 175-191.
[83] Chen F H, Yu Z C, Yang M L, et al. Holocene moisture evolution in arid central Asia and its out-of-phase relationship with Asian monsoon history [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2008, 27(3-4): 351-364. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2007.10.017
[84] Chen F H, Jia J, Chen J H, et al. A persistent Holocene wetting trend in arid central Asia, with wettest conditions in the late Holocene, revealed by multi-proxy analyses of loess-paleosol sequences in Xinjiang, China [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 146: 134-146. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.06.002
[85] 姚付龙, 朱诚, 马春梅, 等. 长江三角洲西部地区13200cal aB.P.以来环境演变及对长江两岸文化交流与传播影响研究[J]. 地层学杂志, 2018, 42(3):278-287
YAO Fulong, ZHU Cheng, MA Chunmei, et al. Environmental evolution in the western region of the Yangtze River delta since 13200 cal a B. P. and its effects on cultural exchange between both sides of the Yangtze River [J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2018, 42(3): 278-287.
[86] An Z S, Porter S C, Kutzbach J E, et al. Asynchronous Holocene optimum of the East Asian monsoon [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2000, 19(8): 743-762. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(99)00031-1
[87] Zhou X, Sun L G, Zhan T, et al. Time-transgressive onset of the Holocene Optimum in the East Asian monsoon region [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 456: 39-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.09.052
[88] 赵艳, 刘耀亮, 郭正堂, 等. 全新世气候渐变导致中亚地区植被突变[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2017, 60(7):1317-1327 doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9047-7
ZHAO Yan, LIU Yaoliang, GUO Zhengtang, et al. Abrupt vegetation shifts caused by gradual climate changes in central Asia during the Holocene [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2017, 60(7): 1317-1327. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9047-7
[89] 杨小平, 梁鹏, 张德国, 等. 中国东部沙漠/沙地全新世地层序列及其古环境[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2019, 62(8):1302-1315 doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9304-y
YANG Xiaoping, LIANG Peng, ZHANG Deguo, et al. Holocene aeolian stratigraphic sequences in the eastern portion of the desert belt (sand seas and sandy lands) in northern China and their palaeoenvironmental implications [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2019, 62(8): 1302-1315. doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9304-y
[90] 李曼玥, 张生瑞, 许清海, 等. 华北平原末次冰盛期以来典型时段古环境格局[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2019, 62(8):1279-1287 doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9264-2
LI Manyue, ZHANG Shengrui, XU Qinghai, et al. Spatial patterns of vegetation and climate in the North China Plain during the Last Glacial Maximum and Holocene climatic optimum [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2019, 62(8): 1279-1287. doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9264-2
[91] 杨石岭, 董欣欣, 肖举乐. 末次冰盛期以来东亚季风变化历史: 中国北方的地质记录[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2019, 62(8):1181-1192 doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9254-8
YANG Shiling, DONG Xinxin, XIAO Jule. The East Asian Monsoon since the Last Glacial Maximum: Evidence from geological records in northern China [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2019, 62(8): 1181-1192. doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9254-8
-



 下载:
下载: