Geochemical and clay mineral characteristics of the Holocene sediments on the west coast of Bohai Bay and their implications for environmental and climatic changes
-
摘要:
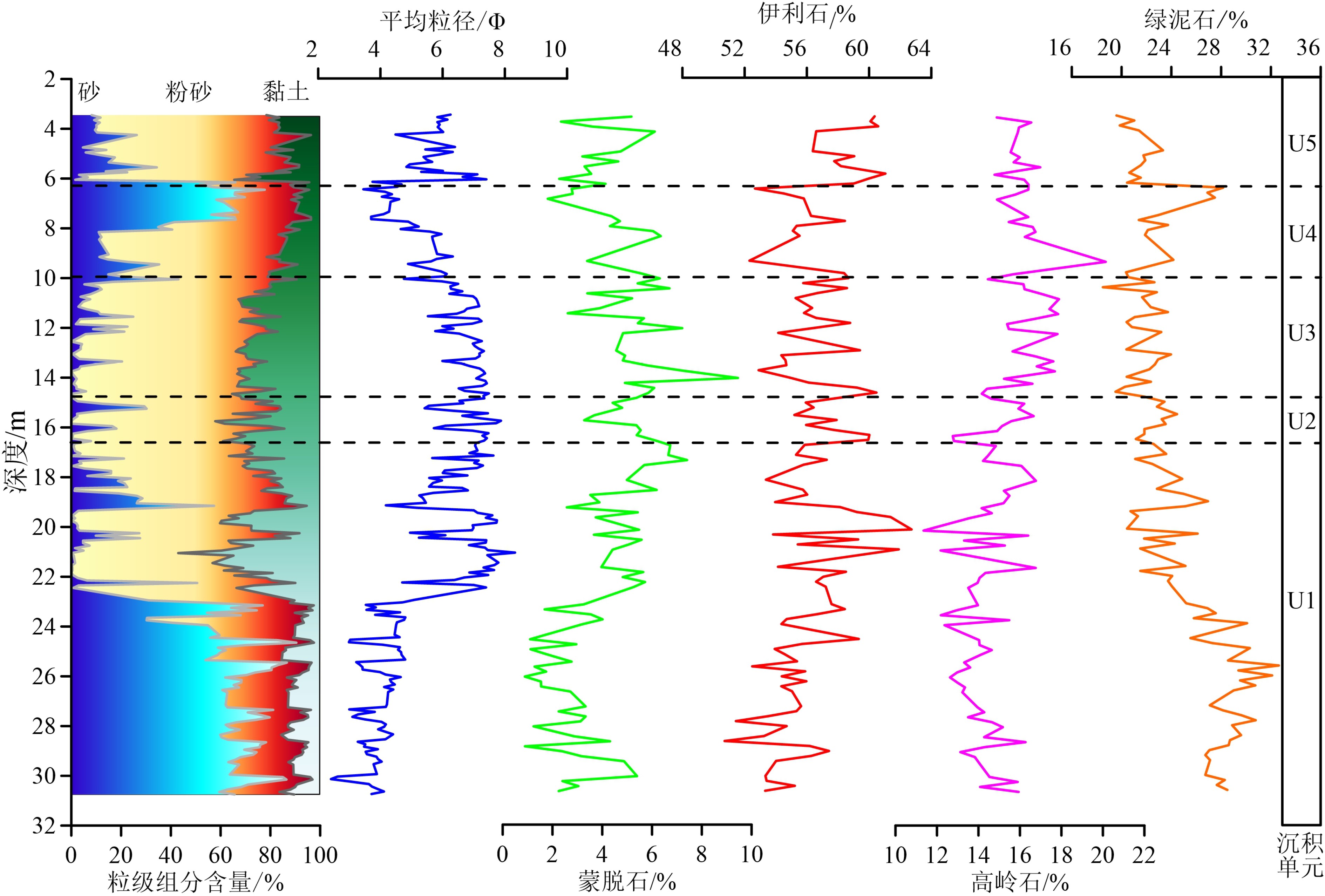
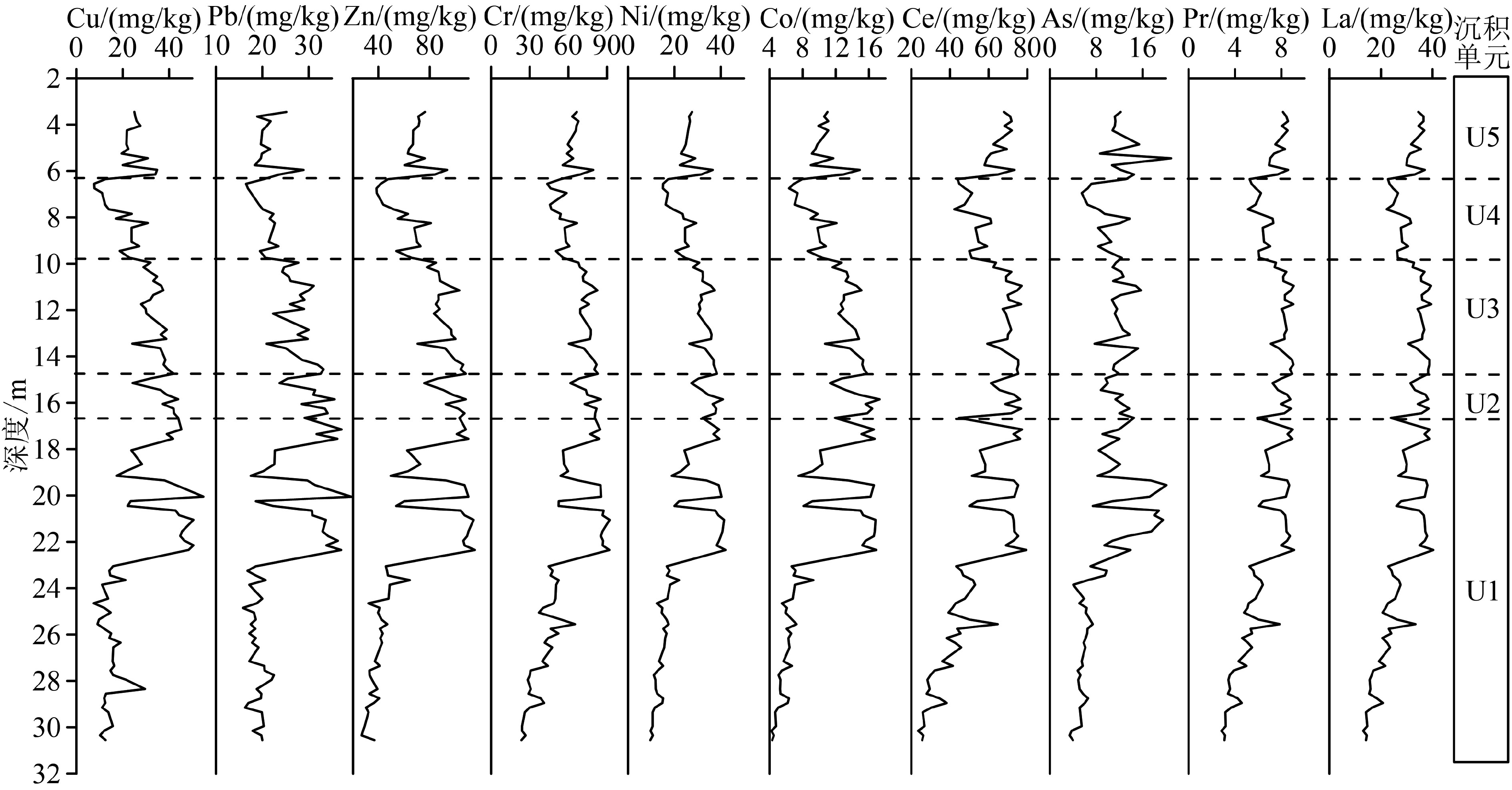
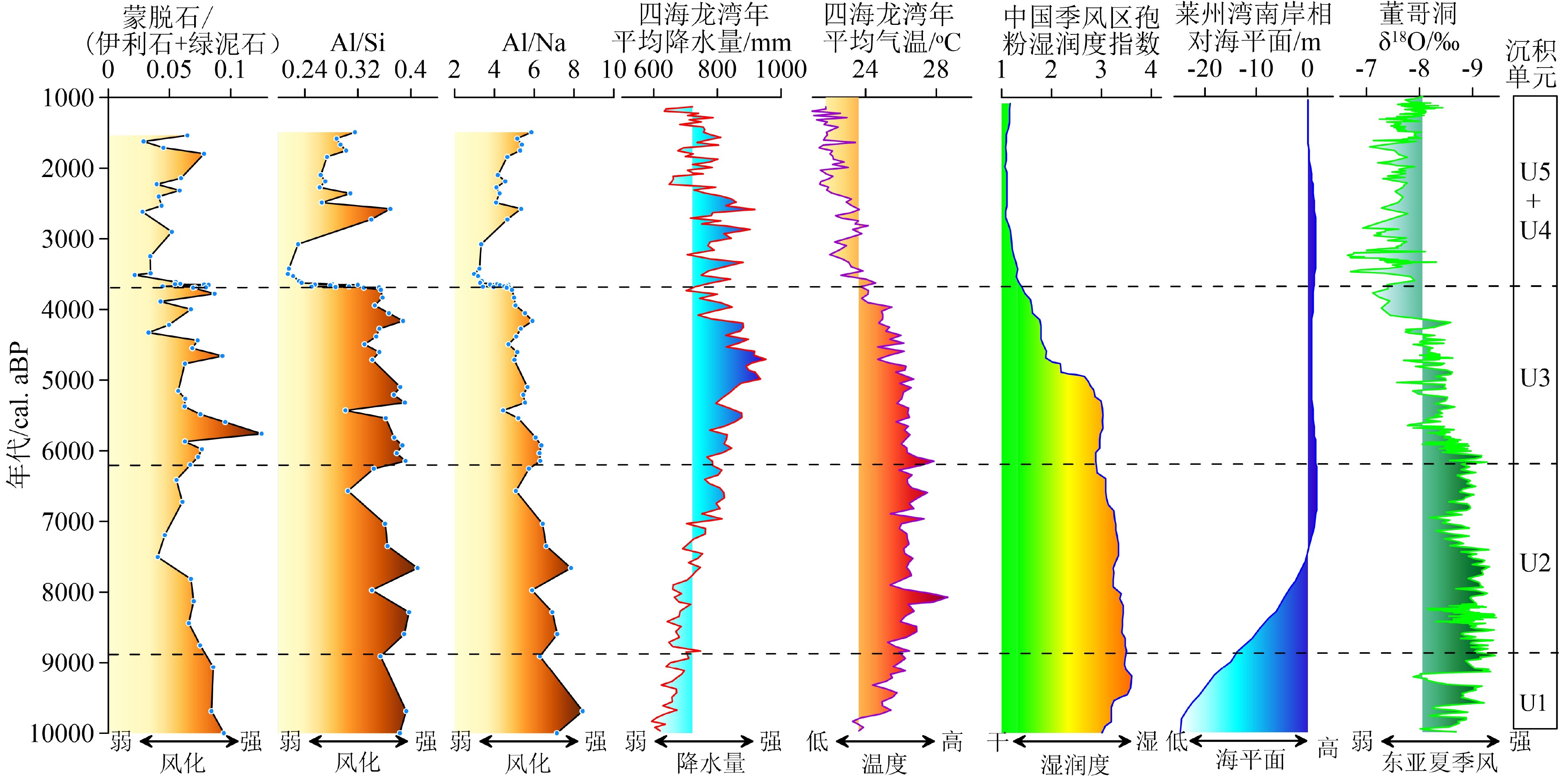
通过对渤海湾西岸BXZK11孔沉积物黏土矿物、地球化学元素组分、粒度分析以及AMS14C年代测定并与研究区周边6个具有较好年龄控制的钻孔剖面对比,结合黏土矿物蒙脱石/(伊利石+绿泥石)比值以及元素Al/Si和Al/Na比值对气候变化的响应,探讨了渤海湾西岸地区全新世以来沉积环境以及气候变化过程。结果表明,末次盛冰期到8830 cal. aBP,海平面快速上升,海水临近研究区,沉积物以黄河古河道沉积为主,气候温凉略湿;8830~6255 cal. aBP,海侵范围达到最大,研究区主要为潮坪-浅海环境,气候温暖湿润;6255~3650 cal. aBP,海平面逐渐降低,沉积环境为前三角洲沉积,沉积物为黄河三角洲的一期超级叶瓣,气候转为温凉稍湿;3650~2780 cal. aBP,海平面趋于稳定,三角洲不断进积,为三角洲前缘环境,气候向凉干方向变化;2780 cal. aBP至今,古黄河三角洲不断进积,该区变成三角洲平原环境,气候凉干与现今相似。
Abstract:Based on the data of clay mineralogy, element geochemistry, grain size and AMS14C dating from the core of BXZK11 collected from the west coast of Bohai Bay and the correlation made with six well dated core profiles surrounding the study area, in addition to the smectite/(illite+chlorite) ratio, Al/Si ratio and Al/Na ratio analysis results, the sedimentary environmental and climatic changes since the beginning of Holocene are discussed for the region in this paper. The results suggest that owing to the rapid sea level rising during the period from the Last Glacial Maximun to 8830 cal. aBP, the sea water was quite close to the study area, the sedimentary environment had been dominated by the paleo-channel of the Yellow River, and a cool and slightly humid climate. During the period of 8830 to 6255 cal. aBP when the transgression reached its peak, the study area had been dominated by tidal flat and shallow sea and a warm and humid climate. From 6255 cal. aBP to 3650 cal. aBP, as the sea level was gradually dropping, this area had been occupied by a prodelta deposit, as one of the super lobes of the Yellow River Delta, under a cool and slightly humid climate. In the period from 3650 to 2780 cal. aBP, the sea level had remained stable to keep the delta continuously progradating as a delta front, while the climate changed to cool and dry. Since 2780 cal. aBP, the ancient Yellow River Delta has been continuously expanding, and the study area become a wide deltaic plain and the climate is cool and dry, similar to that of the present.
-
Key words:
- clay minerals /
- geochemistry /
- sedimentary environment /
- Holocene /
- the west coast of Bohai Bay
-

-
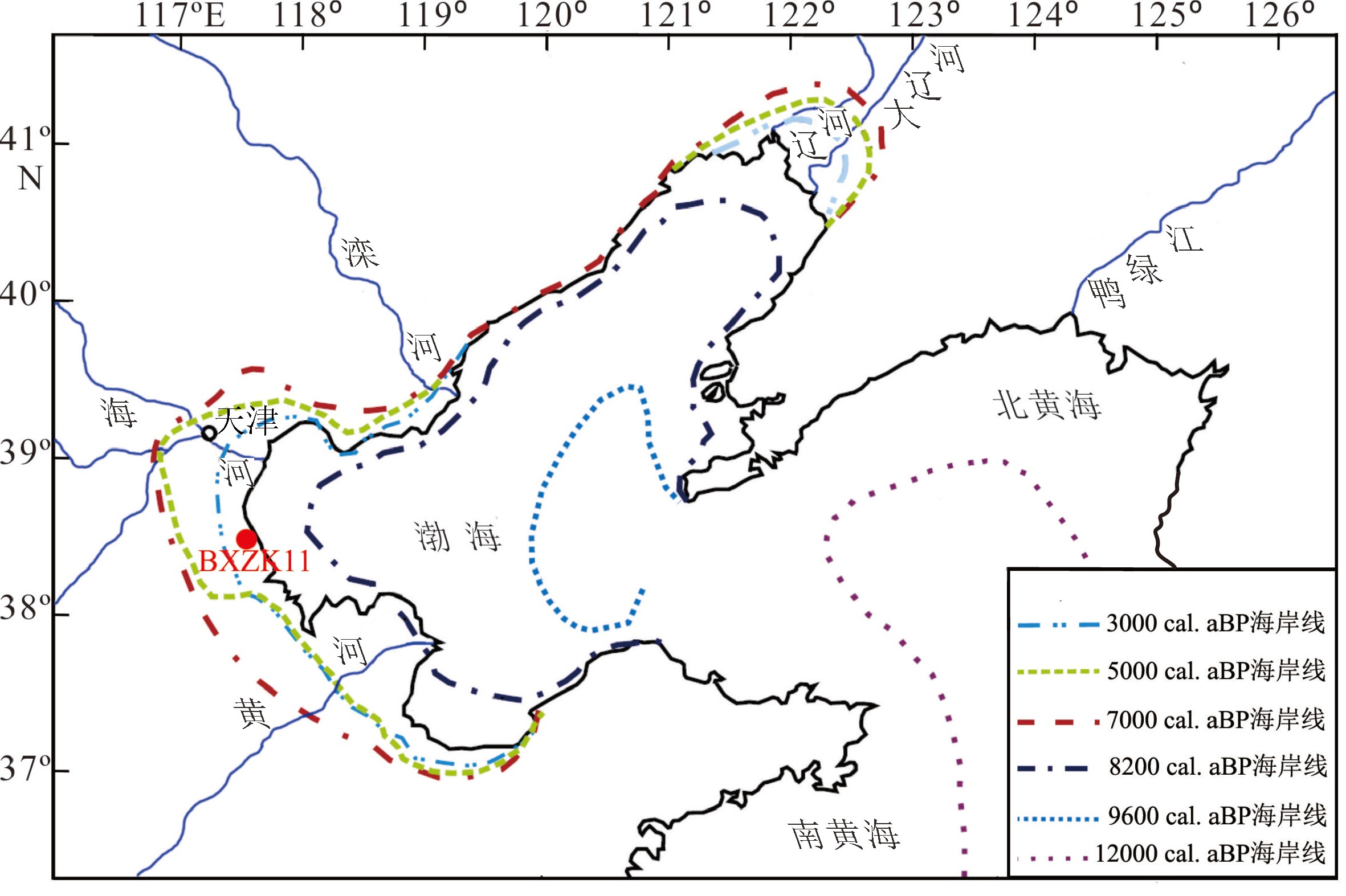
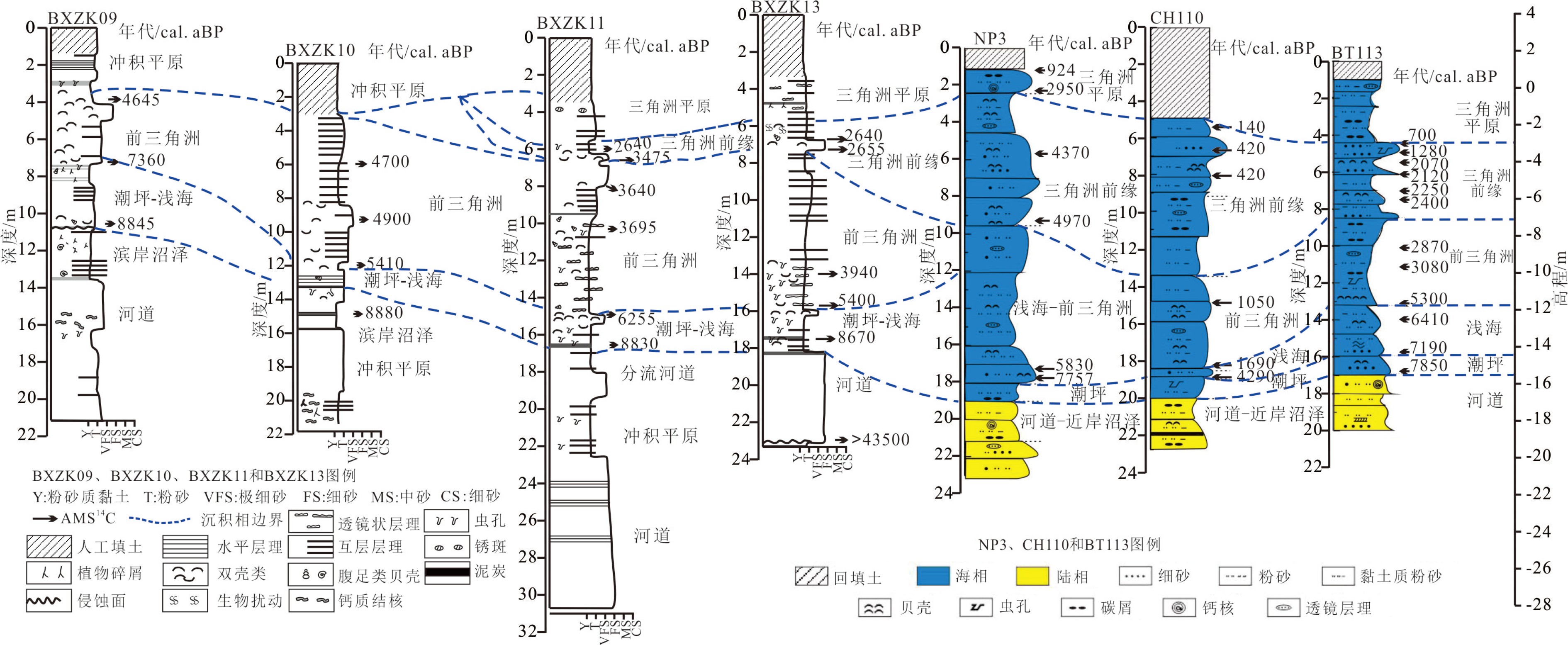
图 7 钻孔位置和北黄海与渤海海域12000 cal. aBP以来的海岸线变化[53]
Figure 7.
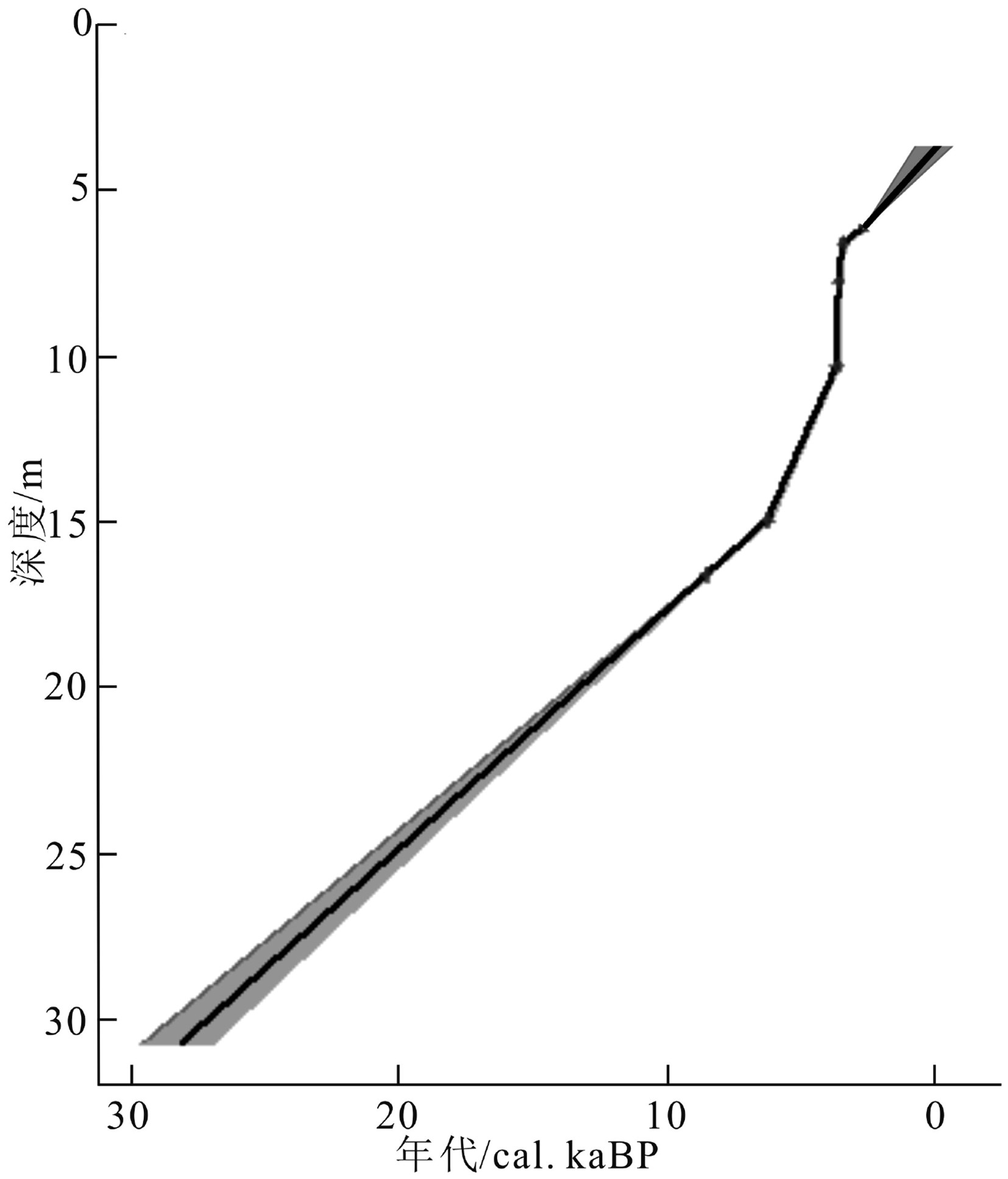
表 1 BXZK11孔14C年代测试数据
Table 1. AMS 14C dating of core BXZK11
样品编号 实验室编号 深度/m 材料 δ13C/‰ 惯用年龄/aBP 校正年龄/cal. aBP 中值 范围(1σ) BXZK11S1 462377 6.1 Potamocorbula laevis −2 2700±30 2640 2568~2730 BXZK11S5 485924 6.58 Potamocorbula ustulata −1.5 3400±30 3475 3400~3543 BXZK11S6 485925 7.76 Estellarca olivacea −1.7 3540±30 3640 3555~3716 BXZK11S4 470414 10.3 Nassarius sp. −2.5 3580±30 3695 3609~3776 BXZK11S2 462378 14.95 Anomia sp. 0.7 5660±30 6255 6190~6306 BXZK11S3 462379 16.6 植物碎屑 −27.9 7950±30 8830 8717~8975 -
[1] Driscoll N W, Nittrouer C. Source to sink studies [J]. Margins, 2002, 11: 1-14.
[2] Berglund B E. Human impact and climate changes-synchronous events and a causal link? [J]. Quaternary International, 2003, 105(1): 7-12.
[3] Dobrzańska H, Jerem E, Kalicki T. The Geoarchaeology of River Valleys[M]. Budapest: Archaeolingua, 2004: 1-216.
[4] 王强, 李凤林. 渤海湾西岸第四纪海陆变迁[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1983, 3(4):83-89
WANG Qiang, LI Fenglin. The changes of marine-cotinental conditions in the west coast of the Bohai Gulf during Quaternary [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1983, 3(4): 83-89.
[5] 成国栋, 薛春汀. 黄河三角洲沉积地质学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997: 73-139.
CHENG Guodong, XUE Chunting. Sediment Geology of Huanghe River Delta[M]. Beijing: Geology Publishing House, 1997: 73-139.
[6] 胥勤勉, 袁桂邦, 张金起, 等. 渤海湾沿岸晚第四纪地层划分及地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(8):1352-1367
XU Qinmian, YUAN Guibang, ZHANG Jinqi, et al. Stratigraphic division of the late Quaternary strata along the coast of Bohai Bay and its geology significance [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85(8): 1352-1367.
[7] 阎玉忠, 王宏, 李凤林, 等. 渤海湾西岸BQ1孔揭示的沉积环境与海面波动[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25(3):357-382 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.03.006
YAN Yuzhong, WANG Hong, LI Fenglin, et al. Sedimentary environment and sea-level fluctuations revealed by Borehole BQ1 on the west coast of the Bohai Bay, China [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006, 25(3): 357-382. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.03.006
[8] 陈永胜, 王宏, 裴艳东, 等. 渤海湾西岸晚第四纪海相地层划分及地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(3):747-759
CHEN Yongsheng, WANG Hong, PEI Yandong, et al. Division and its geological significance of the late quaternary marine sedimentary beds in the west coast of Bohai Bay, China [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2012, 42(3): 747-759.
[9] 陈永胜, 王宏, 李建芬, 等. 渤海湾西岸BT113孔35 ka以来的沉积环境演化与海陆作用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(S1):205-216
CHEN Yongsheng, WANG Hong, LI Jianfen, et al. Sedimentary environment since 35 ka and terrestrial-marine interaction revealed by borehole BT113 in the western coast of Bohai Bay, China [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2012, 42(S1): 205-216.
[10] 王宏, 陈永胜, 田立柱, 等. 渤海湾全新世贝壳堤与牡蛎礁: 古气候与海面变化[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(9):1405-1411 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.09.009
WANG Hong, CHEN Yongsheng, TIAN Lizhu, et al. Holocene cheniers and oyster reefs in Bohai Bay: palaeoclimate and sea level changes [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2011, 30(9): 1405-1411. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.09.009
[11] 李凤林, 王宏, 阎玉忠, 等. 渤海湾西岸滨海平原晚第四纪以来的沉积间断[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2004, 27(3):177-183 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2004.03.008
LI Fenglin, WANG Hong, YAN Yuzhong, et al. The significance of the depositional hiatuses on the coastal plain of west Bohai Bay since the late Quaternary period [J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2004, 27(3): 177-183. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2004.03.008
[12] 李建芬, 王宏, 李凤林, 等. 渤海湾牡蛎礁平原中部兴坨剖面全新世地质环境变迁[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(2):169-176 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.02.011
LI Jianfen, WANG Hong, LI Fenglin, et al. Holocene geo-environmental changes at the Xingtuo section in the central part of the Oyster Reef plain, Bohai Bay [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2004, 23(2): 169-176. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.02.011
[13] 范昌福, 李建芬, 王宏, 等. 渤海湾西北岸大吴庄牡蛎礁测年与古环境变化[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2005, 28(2):124-129 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2005.02.011
FAN Changfu, LI Jianfeng, WANG Hong, et al. Age and paleoenvironmental change of Dawuzhuang Oyster Reef on the northwest coast of Bohai Bay [J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2005, 28(2): 124-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2005.02.011
[14] 范昌福, 王宏, 裴艳东, 等. 渤海湾西北岸滨海湖埋藏牡蛎礁古生态环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28(1):33-41
FAN Changfu, WANG Hong, PEI Yandong, et al. Palaeoecological environment revealed by the buried Binhaihu Oyster Reef on the northwest coast of Bohai Bay [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2008, 28(1): 33-41.
[15] 商志文, 范昌福, 李冬玲, 等. 硅藻组合指示的渤海湾西北岸两个牡蛎礁体生长环境的差异[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(5):33-39
SHANG Zhiwen, FAN Changfu, LI Dongling, et al. Revealing paleo-environment difference of two oyster reefs by diatom assemblages in the northwest coast of Bohai Bay [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(5): 33-39.
[16] 商志文, 田立柱, 王宏, 等. 渤海湾西北部CH19孔全新统硅藻组合、年代学与古环境[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(5):675-681 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.05.006
SHANG Zhiwen, TIAN Lizhu, WANG Hong, et al. Holocene diatom assemblages, chronology and palaeoenvironment of the borehole CH19 in the northwestern Bohai Bay, China [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2010, 29(5): 675-681. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.05.006
[17] Fan C F, Koeniger P, Wang H, et al. Ligamental increments of the mid-Holocene pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas are reliable independent proxies for seasonality in the western Bohai Sea, China [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2011, 299(3-4): 437-448.
[18] Xu Q M, Yang J L, Yuan G B, et al. Stratigraphic sequence and episodes of the ancient Huanghe Delta along the southwestern Bohai Bay since the LGM [J]. Marine Geology, 2015, 367: 69-82.
[19] Tian L Z, Chen Y P, Jiang X Y, et al. Post-glacial sequence and sedimentation in the western Bohai Sea, China, and its linkage to global sea-level changes [J]. Marine Geology, 2017, 388: 12-24.
[20] He L, Xue C T, Ye S Y, et al. New evidence on the spatial-temporal distribution of superlobes in the Yellow River Delta Complex [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2019, 214: 117-138.
[21] 张树山, 任振纪, 刘春源. 晚更新世以来渤海湾沿岸的海进海退及古气候环境[J]. 河北师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 1996, 20(3):96-102
ZHANG Shushan, REN Zhenji, LIU Chunyuan. Trimsgression, regression and ancient climatic environment in the littoral of Bohai Sea since Pleistocene epoch [J]. Journal of Heibei Normal University: Natural Science, 1996, 20(3): 96-102.
[22] 李凤林, 阎玉忠, 商志文, 等. 渤海西岸全新世气候演化与海陆变迁[J]. 地质学刊, 2014, 38(2):173-186 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2014.02.173
LI Fenglin, YAN Yuzhong, SHANG Zhiwen, et al. Holocene climate evolution and land-sea changes on west Bohai Sea [J]. Journal of Geology, 2014, 38(2): 173-186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2014.02.173
[23] 王玥铭, 窦衍光, 李军, 等. 16 ka以来冲绳海槽中南部沉积物物源演化及其对古气候的响应[J]. 沉积学报, 2018, 36(6):1157-1168
WANG Yueming, DOU Yanguang, LI Jun, et al. Sediment provenance change and its response to paleochimate change in the middle Okinawa Trough since 16 ka [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2018, 36(6): 1157-1168.
[24] Singer A. The paleoclimatic interpretation of clay minerals in sediments-A review [J]. Earth-Science Review, 1984, 21(4): 251-293.
[25] Chamley H. Clay Sedimentology[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1989.
[26] 刘志飞, 赵玉龙, 李建如, 等. 南海西部越南岸外晚第四纪黏土矿物记录: 物源分析与东亚季风演化[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 2007, 50(11):1674-1684
LIU Zhifei, ZHAO Yulong, LI Jianru, et al. Late Quaternary clay minerals off Middle Vietnam in the western South China Sea: implications for source analysis and East Asian monsoon evolution [J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2007, 50(11): 1674-1684.
[27] 刘志飞, COLIN C, TRENTESAUX A, 等. 南海南部晚第四纪东亚季风演化的粘土矿物记录[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 2005, 48(1):84-92
LIU Zhifei, COLIN C, TRENTESAUX A, et al. Clay mineral records of East Asian monsoon evolution during late Quaternary in the southern South China Sea [J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2005, 48(1): 84-92.
[28] Liu J G, Li T G, Xiang R, et al. Influence of the Kuroshio Current intrusion on Holocene environmental transformation in the South China Sea [J]. The Holocene, 2013, 23(6): 850-859.
[29] Liu Z F, Wang H, Hantoro W S, et al. Climatic and tectonic controls on chemical weathering in tropical Southeast Asia (Malay Peninsula, Borneo, and Sumatra) [J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 291: 1-12.
[30] Zhang Q, Chen M H, Liu J G, et al. Clay mineral assemblages at IODP Site U1340 in the Bering Sea and their paleoclimatic significance [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2015, 58(5): 707-717.
[31] Chamley H, Diester-Haass L. Upper Miocene to Pleistocene climates in northwest Africa deduced from terrigenous components of Site 397 sediments (DSDP Leg 47A). In: von Rad U, Ryan W B F. Et al. Initial Reports Deep Sea Drilling Project[M]. Washington D C: U. S. Government Printing Office, 1979, 47(1): 641-646.
[32] Ehrmann W. Implications of late Eocene to early Miocene clay mineral assemblages in McMurdo Sound (Ross Sea, Antarctica) on paleoclimate and ice dynamics [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1998, 139(3-4): 213-231.
[33] Franke D, Ehrmann W. Neogene clay mineral assemblages in the AND-2A drill core (McMurdo Sound, Antarctica) and their implications for environmental change [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2010, 286(1-2): 55-65.
[34] Wei G J, Li X H, Liu Y, et al. Geochemical record of chemical weathering and monsoon climate change since the early Miocene in the South China Sea [J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2006, 21(4): PA4214.
[35] Yang S L, Ding F, Ding Z L. Pleistocene chemical weathering history of Asian arid and semi-arid regions recorded in loess deposits of China and Tajikistan [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(7): 1695-1709.
[36] Jiang H C, Guo G X, Cai X M, et al. Geochemical evidence of windblown origin of the Late Cenozoic lacustrine sediments in Beijing and implications for weathering and climate change [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2016, 446: 32-43.
[37] 王强, 袁桂邦, 张熟, 等. 渤海湾西岸贝壳堤堆积与海陆相互作用[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27(5):775-786 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.05.019
WANG Qiang, YUAN Guibang, ZHANG Shu, et al. Shelly ridge accumulation and sea-land interaction on the West Coast of the Bohai bay [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2007, 27(5): 775-786. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.05.019
[38] 陈永胜, 王福, 田立柱, 等. 渤海湾西岸全新世沉积速率对河流供给的响应[J]. 地质通报, 2014, 33(10):1582-1590 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.10.015
CHEN Yongsheng, WANG Fu, TIAN Lizhu, et al. Holocene sedimentation rates and their response to fluvial supply on the west coast of Bohai Bay [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, 33(10): 1582-1590. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.10.015
[39] Zhao G M, Ye S Y, He L, et al. Historical change of carbon burial in Late Quaternary sediments of the ancient Yellow River delta on the west coast of Bohai Bay, China [J]. Catena, 2020, 193: 104619.
[40] 中国科学院海洋研究所海洋地质研究室. 渤海地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985.
Department of Marine Geology, Institute of Oceanography, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Geology of Bohai Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985.
[41] 方晶, 王福, 肖美美, 等. 岩芯EC、pH、泥分含量和有孔虫丰度对沉积环境的判读—以渤海湾西岸CZ61孔为例[J]. 第四纪研究, 2018, 36(6):1523-1526
FANG Jing, WANG Fu, XIAO Meimei, et al. Analysis of paleoenvironment based on EC, pH, mud content and foraminifera numbers: Taking drilled core CZ61 collected from west coast of Bohai Bay as examples [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2018, 36(6): 1523-1526.
[42] 刘翀, 方晶, 王福, 等. 沉积物粘土混浊水电导率与pH值相关性研究: 以渤海湾西岸平原XZ、MD钻孔为例[J]. 第四纪研究, 2015, 35(2):319-325 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.02.07
LIU Chong, FANG Jing, WANG Fu, et al. The correlation between electric conductivity and pH of the STICS-water: A case study of cores XZ and MD on the plain of west Bohai Bay [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2015, 35(2): 319-325. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.02.07
[43] Xue C T. Missing evidence for stepwise postglacial sea level rise and an approach to more precise determination of former sea levels on East China Sea Shelf [J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 348: 52-62.
[44] 赵松龄, 杨光复, 苍树溪, 等. 关于渤海湾西岸海相地层与海岸线问题[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1978, 9(1):15-25
ZHAO Songling, YANG Guangfu, CANG Shuxi, et al. On the marine stratigraphy and coastlines of the western coast of the Gulf of Bohai [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1978, 9(1): 15-25.
[45] 李建芬, 商志文, 王福, 等. 渤海湾西岸全新世海面变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2015, 35(2):243-264 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.02.01
LI Jianfeng, SHANG Zhiwen, WANG Fu, et al. Holocene sea level change on the west coast of the Bohai Bay [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2015, 35(2): 243-264. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.02.01
[46] Southon J, Kashgarian M, Fontugne M, et al. Marine reservoir corrections for the Indian ocean and Southeast Asia [J]. Radiocarbon, 2002, 44(1): 167-180.
[47] Reimer P J, Bard E, Bayliss A, et al. IntCal 13 and Marine 13 radiocarbon age calibration curves 0-50, 000 years cal BP [J]. Radiocarbon, 2013, 55(4): 1869-1874.
[48] 赵东波. 常用沉积物粒度分类命名方法探讨[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2009, 25(8):41-44, 46 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2009.08.009
ZHAO Dongbo. Discussion on general methods of the grain-size classification and nomenclature of sediments [J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2009, 25(8): 41-44, 46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2009.08.009
[49] 蓝先洪, 张志珣, 王中波, 等. 东海陆架晚更新世以来沉积物常量元素的分布及其地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2014, 44(6):1883-1891
LAN Xianhong, ZHANG Zhixun, WANG Zhongbo, et al. Content distributions and its geological implication of major elements in sediments from the continental shelf of the East China Sea during the late Pleistocene [J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2014, 44(6): 1883-1891.
[50] Moore D M, Reynolds R C Jr. X-Ray Diffraction and the Identification and Analysis of Clay Minerals[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1997: 1-332.
[51] Biscaye P E. Mineralogy and sedimentation of recent deep-sea clay in the Atlantic Ocean and adjacent seas and oceans [J]. GSA Bulletin, 1965, 76(7): 803-832.
[52] 陈永胜, 李建芬, 王福, 等. 渤海湾西岸现代岸线钻孔记录的全新世沉积环境与相对海面变化[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2016, 46(2):499-517
CHEN Yongsheng, LI Jianfen, WANG Fu, et al. Records of Holocene sedimentation environment and relative sea level by the boreholes collected along the present shoreline of the west coast of Bohai Bay, China [J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2016, 46(2): 499-517.
[53] Xue C T, Qin Y C, Ye S Y, et al. Evolution of Holocene ebb-tidal clinoform off the Shandong Peninsula on East China Sea shelf [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 177: 478-496.
[54] 董红梅, 宋友桂. 黏土矿物在古环境重建中的应用[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(6):119-130
DONG Hongmei, SONG Yougui. Clay mineralogy and its application to paleoenvironmental reconstruction [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(6): 119-130.
[55] Rateev M A, Gorbunova Z N, Lisitzyn A P, et al. The distribution of clay minerals in the oceans [J]. Sedimentolgy, 1969, 13: 21-43.
[56] 刘大为, 张可欣, 裴艳东, 等. 渤海湾西岸QG01钻孔沉积物黏土矿物分布及古气候替代指标研究[J]. 海洋学研究, 2018, 36(3):28-36 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2018.03.003
LIU Dawei, ZHANG Kexin, PEI Yandong, et al. The study of clay mineral assembalges and paleoclimatic proxies of borehole QG01 in the werstern coast of Bohai Bay, China [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2018, 36(3): 28-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2018.03.003
[57] 杨作升. 黄河、长江、珠江沉积物中黏土的矿物组合、化学风化特征及其与物源区气候环境的关系[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1988, 19(4):336-346
YANG Zuosheng. Mineralogical assemblages and chemical characteristics of clays from sediments of the Huanghe, Changjiang, Zhujiang Rivers and their relationship to the climate environment in their sediment source areas [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1988, 19(4): 336-346.
[58] 黄湘通, 郑洪波, 杨守业, 等. 长江三角洲DY03孔沉积物元素地球化学及其物源示踪意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2009, 29(2):299-307 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2009.02.14
HUANG Xiangtong, ZHENG Hongbo, YANG Shouye, et al. Investigation of sedimentary geochemistry of core DY03 in the Yangtze Delta: Implications to tracing provenance [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2009, 29(2): 299-307. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2009.02.14
[59] 钟巍, 李吉均, 方小敏, 等. 临夏盆地王家山剖面沉积物地球化学元素特征与季风演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1997, 17(4):55-62
ZHONG Wei, LI Jijun, FANG Xiaomin, et al. Geochemical features of the sediment in Wangjiashan section in Linxia Basin and monsoon evolution [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1997, 17(4): 55-62.
[60] Liu Y X, Huang H J, Qi Y L, et al. Holocene coastal morphologies and shoreline reconstruction for the southwestern coast of the Bohai Sea, China [J]. Quaternary Research, 2016, 86(2): 114-161.
[61] Zhao Y, Yu Z C, Chen F H, et al. Vegetation response to Holocene climate change in monsoon-influenced region of China [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2009, 97(1-4): 242-256.
[62] Wang Y L, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al. The Holocene Asian monsoon: links to solar changes and North Atlantic climate [J]. Science, 2005, 308(5723): 854-857.
[63] Stebich M, Rehfeld K, Schlütz F, et al. Holocene vegetation and climate dynamics of ne china based on the pollen record from Sihailongwan maar lake [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2015, 124: 275-289.
[64] 王绍武. 全新世大暖期[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2011, 7(5):383-384 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1719.2011.05.013
WANG Shaowu. Megathermal [J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2011, 7(5): 383-384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1719.2011.05.013
[65] 巩晓燕, 魏明建, 张玉华. 华北地区全新世气候时空变化特征研究述评[J]. 首都师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 27(4):73-78
GONG Xiaoyan, WEI Mingjian, ZHANG Yuhua. General research on the spatio-temporal trait of climate change in North China in Holocene [J]. Journal of Capital Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2006, 27(4): 73-78.
[66] 施雅风, 孔昭宸, 王苏民, 等. 中国全新世大暖期的气候波动与重要事件[J]. 中国科学B辑, 1992, 22(12):1300-1308 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9240.1992.12.003
SHI Yafeng, KONG Zhaochen, WANG Sumin, et al. The climate fluctuations and important events of Holocene Megathermal in China [J]. Science in China (Series B), 1992, 22(12): 1300-1308. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9240.1992.12.003
[67] 申改慧, 丁国强, 阳小兰, 等. 白洋淀地区全新世以来的气候环境变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2018, 38(3):756-768 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2018.03.20
SHEN Gaihui, DING Guoqiang, YANG Xiaolan, et al. Holocene climate and environmental change in the Baiyangdian area [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2018, 38(3): 756-768. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2018.03.20
[68] 许清海, 肖举乐, 中村俊夫, 等. 孢粉资料定量重建全新世以来岱海盆地的古气候[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(4):99-108
XU Qinghai, XIAO Jule, NAKAMURA T, et al. Quantitative reconstructed climatic changes of Daihai basin by pollen data [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2003, 23(4): 99-108.
-




 下载:
下载: