Surface sediments and their geotechnical characteristics in the development area of deepwater gas field LS17-2
-
摘要:
陵水17-2气田位于中国南海琼东南盆地,是中国海油自营勘探发现的第一个深水高产气田,探明储量规模超千亿立方米。在水深200~1600 m区域,采用工程调查船与自主式水下潜器调查结合的方式,进行地球物理资料采集、海底表层取样及钻探取样,并对多波束测深、后向散射强度、侧扫声呐、浅地层剖面、室内测试分析等数据进行综合分析,研究了海底表层沉积物类型、分布规律及工程地质特性。按照海底地形地貌特征,陵水17-2深水气田开发区可划分为陆架区、缓坡区和滑塌区;陆架区表层沉积物以黏土和粉质黏土为主,不同站位物理力学性质差异较大,局部夹砂层;缓坡区和滑塌区具有高含水率、低密度、高孔隙比、高液限、高可塑性、低强度等典型深水沉积特点。区域内海底泥面至泥面之下0.3 m,土质不排水抗剪强度为0~4 kPa,非常有利于海底电缆、海底管道、脐带缆的铺设。缓坡区浅层土质条件非常适合吸力式、防沉板及抓力锚施工,滑塌区浅层土质条件适合防沉板、抓力锚及打入桩基础施工。研究成果将对琼东南盆地深水油气田开发工程的设计和安装施工具有指导意义。
Abstract:The gas field LS17-2, the first deep-water and high-yield gas field discovered independently by CNOOC in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea, is a large gas field with a proven reserve more than 100 billion cubic meters. Studied in this paper are the geophysical data, such as multi-beam echo sounder data, backscatter strength data, side scan sonar data, and sub-bottom profiler data as well as seabed surface sampling and drilling data, collected by the engineering survey vessels and autonomous underwater vehicles within the development zone of the gas field LS17-2 in the water depth between 200 m and 1600 m. Types, distribution patterns and geotechnical properties of subsurface sediments are described. The bathymetry data suggests that the study area of the development zone of the gas field LS17-2 could be subdivided into three subareas, i.e. the shelf subarea, gentle slope subarea and slumping subarea. The seabed sediments are predominated by clay and silty clay, with sandy deposits in some places. The geotechnical characteristics are quite different in different sampling locations. The geotechnical characteristics of seabed sediments within the gentle slope subarea and slumping subarea are typical deep-water sediments, characterized by high water content, low density, high void ratio, high liquid limit, high plasticity and low strength. The undrained shear strength of the soil layers between seabed and the layer about 0.3 m below seabed varies between 0~4 kPa, and it is conducive to the laying of submarine cables, submarine pipelines and umbilical cables. Soil conditions in the shallow part are suitable for the foundation of suction type, mud mat and grab anchor in the gentle slope subarea, and for the types of mud mat, grab anchor and driven piles in the slumping subarea. The research results are believed useful as a reference to the design and installation of subsea facilities for the coming deep-water oil and gas field development projects in the Qiongdongnan Basin.
-
Key words:
- surface sediment /
- backscatter strength /
- sediment types /
- geotechnical characteristics
-

-
图 4 图2区域后向散射强度平面图及底质分区
Figure 4.
图 5 陆架区后向散射强度图及其底质分类结果(图4中A区)
Figure 5.
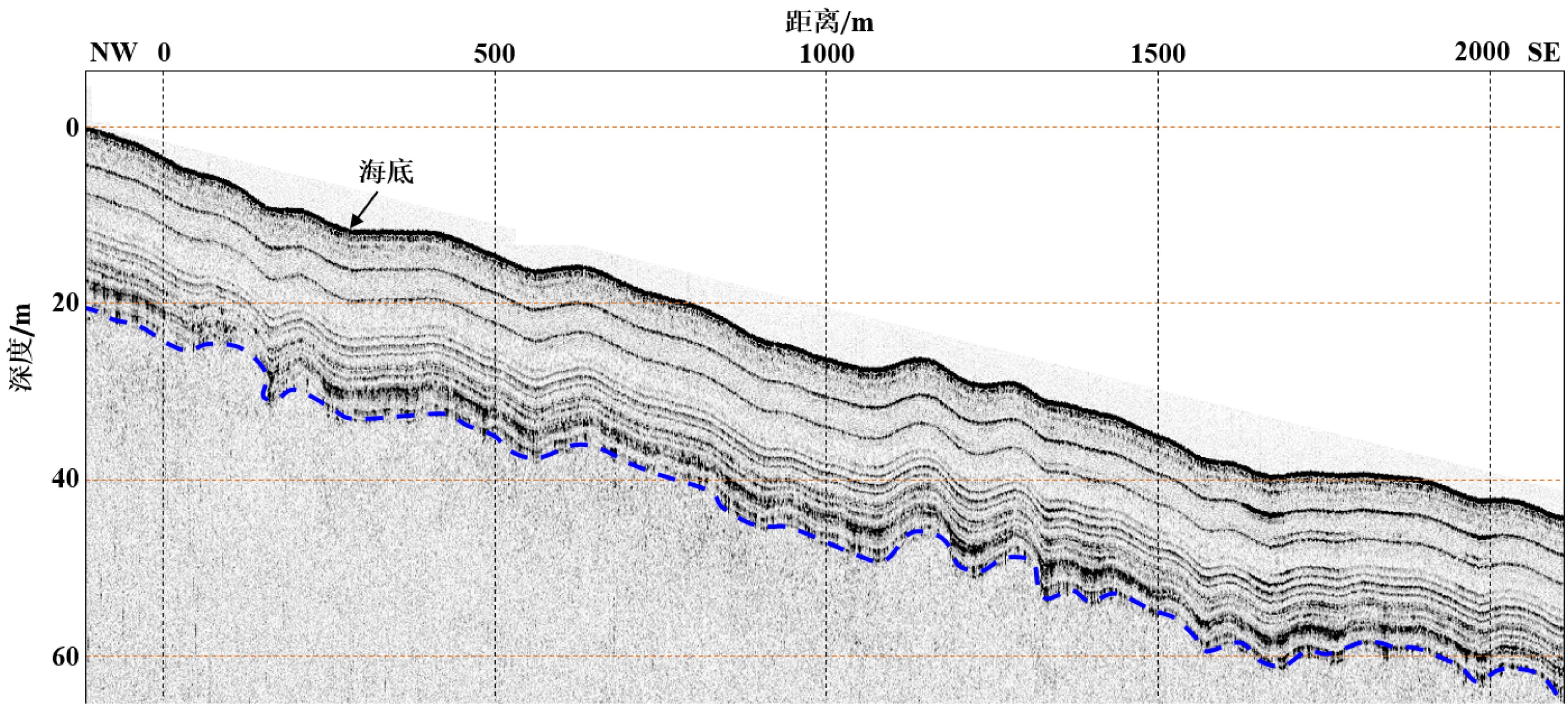
图 6 过海底洼地的浅地层剖面图(图4中L1)
Figure 6.
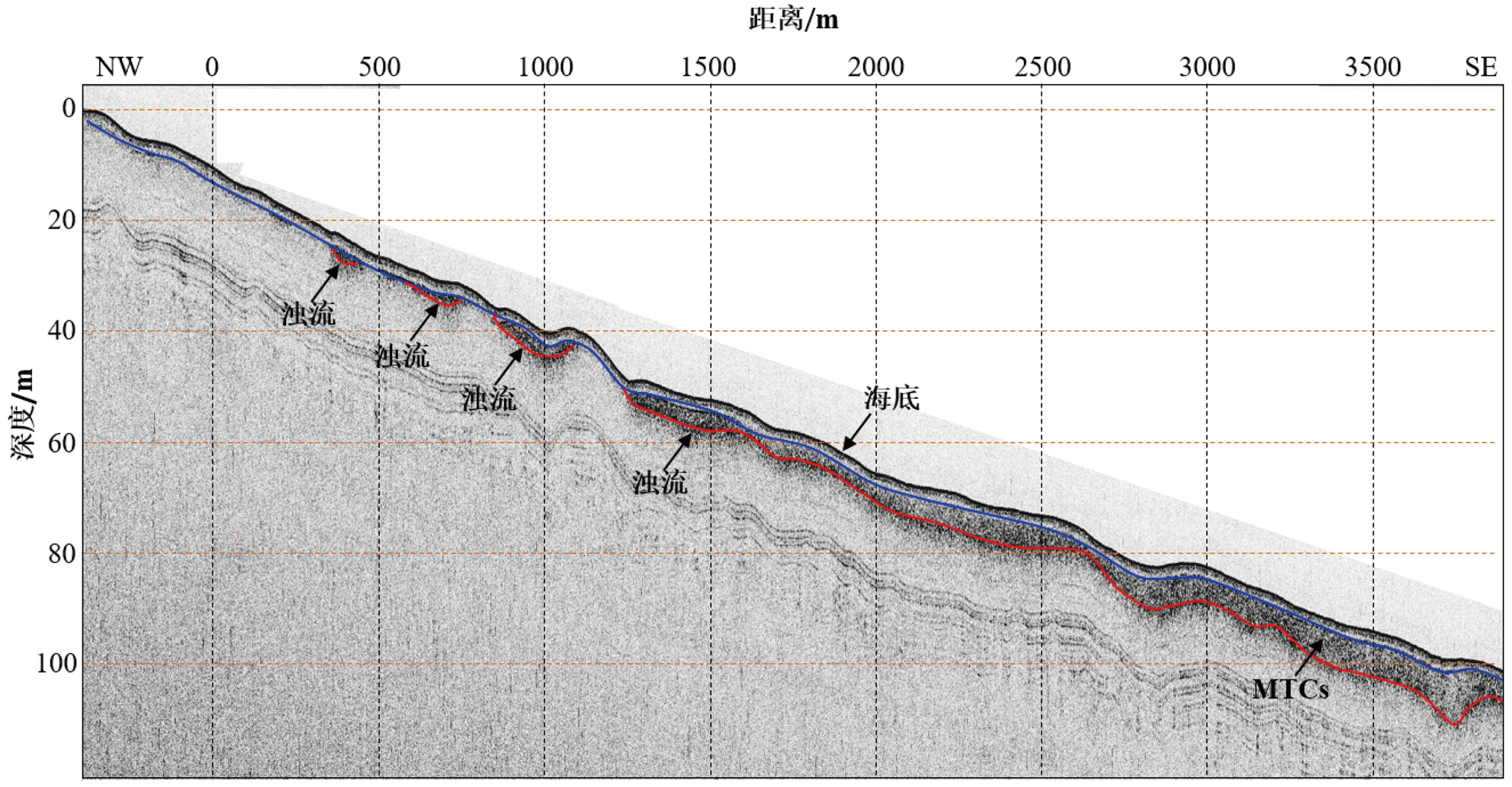
图 7 过滑坡堆积物的浅地层剖面图(图4中L2)
Figure 7.
图 8 滑塌区边缘的浅地层剖面记录中的浊流沉积(图4中L3)
Figure 8.
图 9 浅地层剖面记录中的缓坡区、滑塌区过渡带(图4中L4)
Figure 9.
图 10 海底底质详细分区(图4中C区)
Figure 10.
表 1 陵水17-2深水气田开发区沉积物物理力学性质汇总
Table 1. A summary of physico-mechanic properties of sediments within LS17-2 deepwater gas field development area
所在区域 土质类型 深度/m 含水量/% 容重/(kN/m3) 碳酸盐含量/% 中值粒径/mm 液限/% 塑性指数/% 不排水抗剪强度/kPa 陆架区
(水深<250 m)黏土/粉质黏土 0~5.0 30~70 15.5~18.5 7~30 0.006~0.32 30~60 10~30 2~43 缓坡区
(水深<1000 m)黏土 0~5.0 60~106 14.0~16.5 15~20 0.005~0.01 50~90 22~55 2~9 缓坡区
(水深>1000 m)黏土 0~1.0 100~120 13.5~14.5 17~29 0.008~0.009 70~110 40~70 1.5~7.5 黏土 1.0~5.0 110~140 13.0~14.0 10~18 0.005~0.009 70~110 30~70 4.0~15.0 MTCs沉积区
(水深>1000 m)黏土 0~1.0 100~120 13.5~14.5 17~29 0.008~0.009 70~110 40~70 1.5~7.5 1.0~5.0 60~110 13.5~16.3 10~18 0.005~0.009 50~90 20~50 4.0~15.0 浊流体系沉积区
(水深>1000 m)黏土 0~1.0 100~120 13.5~14.5 17~29 0.008~0.009 70~110 40~70 1.5~7.5 1.0~5.0 70~140 13.0~17.3 7~28 0.005~0.009 70~110 30~70 4.0~15.0 -
[1] 李新仲, 谭越. 海上油气田开发工程模式探讨[J]. 石油工程建设, 2015, 41(1):1-4 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2206.2015.01.001
LI Xinzhong, TAN Yue. Discussion on development engineering modes for offshore oil and gas fields [J]. Petroleum Engineering Construction, 2015, 41(1): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2206.2015.01.001
[2] 王丽勤, 侯金林, 庞然, 等. 深水油气田开发工程中的基础应用探讨[J]. 海洋石油, 2011, 31(4):87-92 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2011.04.087
WANG Liqin, HOU Jinlin, PANG Ran, et al. The application of foundations in deepwater oil and gas field development engineering [J]. Offshore Oil, 2011, 31(4): 87-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2011.04.087
[3] 王桂林, 段梦兰, 冯玮, 等. 深海油气田开发模式及控制因素分析[J]. 海洋工程, 2011, 29(3):139-145 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2011.03.021
WANG Guilin, DUAN Menglan, FENG Wei, et al. Analysis of control factors in deepwater oil & gas field development [J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2011, 29(3): 139-145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2011.03.021
[4] 刘乐军, 傅命佐, 李家钢, 等. 荔湾3-1气田海底管道深水段地质灾害特征[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2014, 32(2):162-174 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2014.02.006
LIU Lejun, FU Mingzuo, LI Jiagang, et al. Geologic Hazards in the deep pipeline routing area of the Liwan 3-1 gas field in the South China Sea [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2014, 32(2): 162-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2014.02.006
[5] 冯文科, 石要红, 陈玲辉. 南海北部外陆架和上陆坡海底滑坡稳定性研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1994, 14(2):81-94
FENG Wenke, SHI Yaohong, CHEN Linghui. Research for seafloor landslide stability on the outer continental shelf and the upper continental slope in the northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1994, 14(2): 81-94.
[6] 吴时国, 陈珊珊, 王志君, 等. 大陆边缘深水区海底滑坡及其不稳定性风险评估[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(3):430-437 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.013
WU Shiguo, CHEN Shanshan, WANG Zhijun, et al. Submarine landslide and risk evaluation on its instability in the deepwater continental margin [J]. Geoscience, 2008, 22(3): 430-437. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.013
[7] 孙运宝, 吴时国, 王志君, 等. 南海北部白云大型海底滑坡的几何形态与变形特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28(6):69-77
SUN Yunbao, WU Shiguo, WANG Zhijun, et al. The geometry and deformation characteristics of Baiyun submarine Landslide [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2008, 28(6): 69-77.
[8] 王大伟, 吴时国, 秦志亮, 等. 南海陆坡大型块体搬运体系的结构与识别特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(5):65-72
WANG Dawei, WU Shiguo, QIN Zhiliang, et al. Architecture and identification of large quaternary mass transport depositions in the slope of South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(5): 65-72.
[9] Wang W W, Wang D W, Wu S G, et al. Submarine landslides on the north continental slope of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2018, 17(1): 83-100. doi: 10.1007/s11802-018-3491-0
[10] 杨文达, 张异彪, 李斌. 南海琼东南深水海区地质灾害类型与特征[J]. 海洋石油, 2011, 31(1):1-7 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2011.01.001
YANG Wenda, ZHANG Yibiao, LI Bin. Types and characteristics of deepwater geologic hazard in Qiongdongnan of the South China Sea [J]. Offshore Oil, 2011, 31(1): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2011.01.001
[11] 杨文达, 李斌, 胡津荧, 等. 三维地震资料在深水油气勘探井场地质灾害评价中的运用: 以南海琼东南海区为例[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(1):83-90
YANG Wenda, LI Bin, HU Jinying, et al. Using 3D Seismic data to evaluate deepwater geohazards for well site investigation: a case of Qiongdongnan Block in South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(1): 83-90.
[12] 阎贫, 王彦林, 郑红波. 南海北部白云凹陷-东沙岛西南海区的浅地层探测与深水沉积特点[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2011, 30(2):115-122 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2011.02.017
YAN Pin, WANG Yanlin, ZHENG Hongbo. Characteristics of deep water sedimentation revealed by sub-bottom profiler survey over the Baiyun Sag: southwest Dongsha Island Waters in the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(2): 115-122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2011.02.017
[13] 陈泓君, 彭学超, 朱本铎, 等. 南海1: 100万海南岛幅海洋区域地质调查与编图成果综述[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(6):83-96
CHEN Hongjun, PEN Xuechao, ZHU Benduo, et al. A brief review of 1: 1 000 000 marine geological survey and mapping results of the Hainan sheet in the South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(6): 83-96.
[14] 罗进华, 朱培民. 琼东南盆地陆坡区重力流沉积体系超高精度解析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6):42-50
LUO Jinhua, ZHU Peimin. Gravity induced deposits in the continental slope of Qiongdongnan basin based on ultrahigh resolution AUV data [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(6): 42-50.
[15] Silva A J, Baxter C D P, Larosa P T, et al. Investigation of mass wasting on the continental slope and rise [J]. Marine Geology, 2004, 203(3-4): 355-366. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00315-3
[16] Haflidason H, Sejrup H P, Nygård A, et al. The Storegga Slide: architecture, geometry and slide development [J]. Marine Geology, 2004, 213(1-4): 201-234. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2004.10.007
[17] Sultan N, Voisset M, Marsset B, et al. Potential role of compressional structures in generating submarine slope failures in the Niger Delta [J]. Marine Geology, 2007, 237(3-4): 169-190. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2006.11.002
[18] 谢玉洪. 南海北部自营深水天然气勘探重大突破及其启示[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(10):1-8
XIE Yuhong. A major breakthrough in deepwater natural gas exploration in a self-run oil/gas field in the northern South China Sea and its enlightenment [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(10): 1-8.
[19] 杨进, 李文龙, 胡志强, 等. 深水钻井水下井口稳定性研究进展[J]. 中国海上油气, 2020, 32(4):124-130
YANG Jin, LI Wenlong, HU Zhiqiang, et al. Research progresses on subsea wellhead stability of deep water drilling [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2020, 32(4): 124-130.
[20] 郑利军, 段梦兰, 刘军鹏, 等. 水下生产系统选型影响因素研究[J]. 石油矿场机械, 2012, 41(6):67-71 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3482.2012.06.017
ZHENG Lijun, DUAN Menglan, LIU Junpeng, et al. Study of influencing factors on subsea production system selection [J]. Oil Field Equipment, 2012, 41(6): 67-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3482.2012.06.017
[21] 赵党, 郝双户, 何宁. 海底管道稳定性分析[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2013, 35(5):99-102 doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2013.05.023
ZHAO Dang, HAO Shuanghu, HE Ning. Survey on on-bottom stability design of submarine pipelines [J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2013, 35(5): 99-102. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2013.05.023
[22] 朱海山, 李达, 魏澈, 等. 南海陵水17-2深水气田开发工程方案研究[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(4):170-177
ZHU Haishan, LI Da, WEI Che, et al. Research on LS17-2 deep water gas field development engineering scenario in South China Sea [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(4): 170-177.
[23] 吴自银, 阳凡林, 李守军, 等. 高分辨率海底地形地貌: 可视计算与科学应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017.
WU Ziyin, YANG Fanlin, LI Shoujun, et al. High Resolution Submarine Geomorphology Visual Computation and Scientific Applications[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2017.
[24] 纪雪. 基于多波束数据的海底底质及地形复杂度分类研究[D]. 国家海洋局第一海洋研究所硕士学位论文, 2017.
JI Xue. Classification of seabed sediment and terrain complexity based on multibeam data[D]. Master Dissertation of the First Institute of Oceanography, State Bureau of Oceanic Administration, 2017.
[25] 罗伟东, 郭军. 基于多波束背向散射数据的海底底质分类[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(8):57-62
LUO Weidong, GUO Jun. Seabed sediment classification based on multibeam backscatter data [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2017, 33(8): 57-62.
[26] 唐秋华, 纪雪, 丁继胜, 等. 多波束声学底质分类研究进展与展望[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2019, 37(1):1-10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2019.01.001
TANG Qiuhua, JI Xue, DING Jisheng, et al. Research progress and prospect of acoustic seabed classification using multibeam echo sounder [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2019, 37(1): 1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2019.01.001
[27] 金绍华, 翟京生, 刘雁春, 等. Simrad EM多波束反向散射强度数据精处理研究[J]. 测绘科学, 2010, 35(2):106-108
JIN Shaohua, ZHAI Jingsheng, LIU Yanchun, et al. Study on processing of Simrad EM multibeam backscatter data [J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2010, 35(2): 106-108.
[28] 杨词银. 基于侧扫声纳成像的海底底质识别研究[D]. 中国科学院声学研究所博士学位论文, 2005.
YANG Ciyin. Seabed sediment classification based on side scan sonar imagery[D]. Doctor Dissertation of the Institute of Acoustics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2005.
[29] 张楷涵, 袁飞, 程恩. 侧扫声呐图像噪声模型的分析[J]. 厦门大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 57(3):390-395
ZHANG Kaihan, YUAN Fei, CHENG En. Analysis of side-scan sonar image noise model [J]. Journal of Xiamen University: Natural Science, 2018, 57(3): 390-395.
[30] 赵永祯, 唐劲松, 钟何平. 基于声纳图像纹理特征的海底底质分类方法研究[J]. 海洋测绘, 2015, 35(3):60-63
ZHAO Yongzhen, TANG Jinsong, ZHONG Heping. Seabed sediment classification based on texture features of sonar imagery [J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2015, 35(3): 60-63.
[31] 罗进华, 蒋锦朋, 朱培民. 基于数学形态学的侧扫声呐图像轮廓自动提取[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(5):150-157
LUO Jinhua, JIANG Jinpeng, ZHU Peimin. Automatic extraction of the side-scan sonar imagery outlines based on mathematical morphology [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2016, 38(5): 150-157.
[32] 刘玉萍, 丁龙翔, 杨志成, 等. 利用浅剖资料进行海底底质分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(1):66-72
LIU Yuping, DING Longxiang, YANG Zhicheng, et al. Seabed sediment analysis using sub-bottom profile data [J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(1): 66-72.
[33] 国家海洋局. GB/T 12763.8-2007 海洋调查规范 第8部分 海洋地质地球物理调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017.
State Oceanic Administration. GB/T 12763.8-2007 Specifications for oceanographic survey: Part 8: marine geology and geophysics survey[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2017.
[34] Prior D B, Bornhold B D, Johns M W. Depositional characteristics of a submarine debris flow [J]. The Journal of Geology, 1984, 92(6): 707-727. doi: 10.1086/628907
[35] 陈泓君, 詹文欢, 温明明, 等. 南海西北部琼东南盆地陆架坡折带类型及沉积作用特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2015, 31(8):1-9
CHEN Hongjun, ZHAN Wenhuan, WEN Mingming, et al. Characteristics of shelf break and sedimentaion process at the Qiongdongnan basin, Northwestern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2015, 31(8): 1-9.
-




 下载:
下载: