The characteristics and genesis of bottom cyclic steps in the Lingshui Sag of Qiongdongnan Basin
-
摘要:
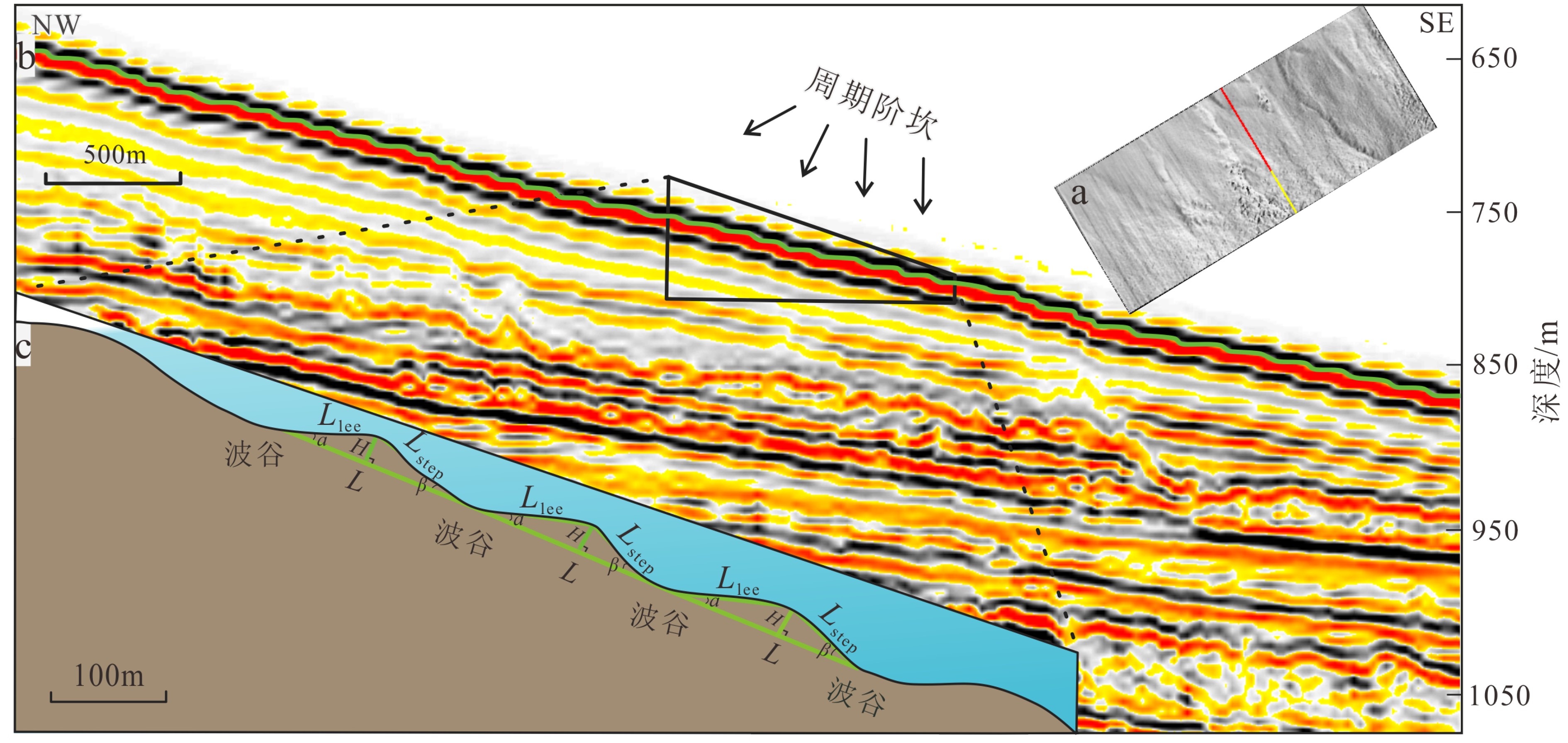
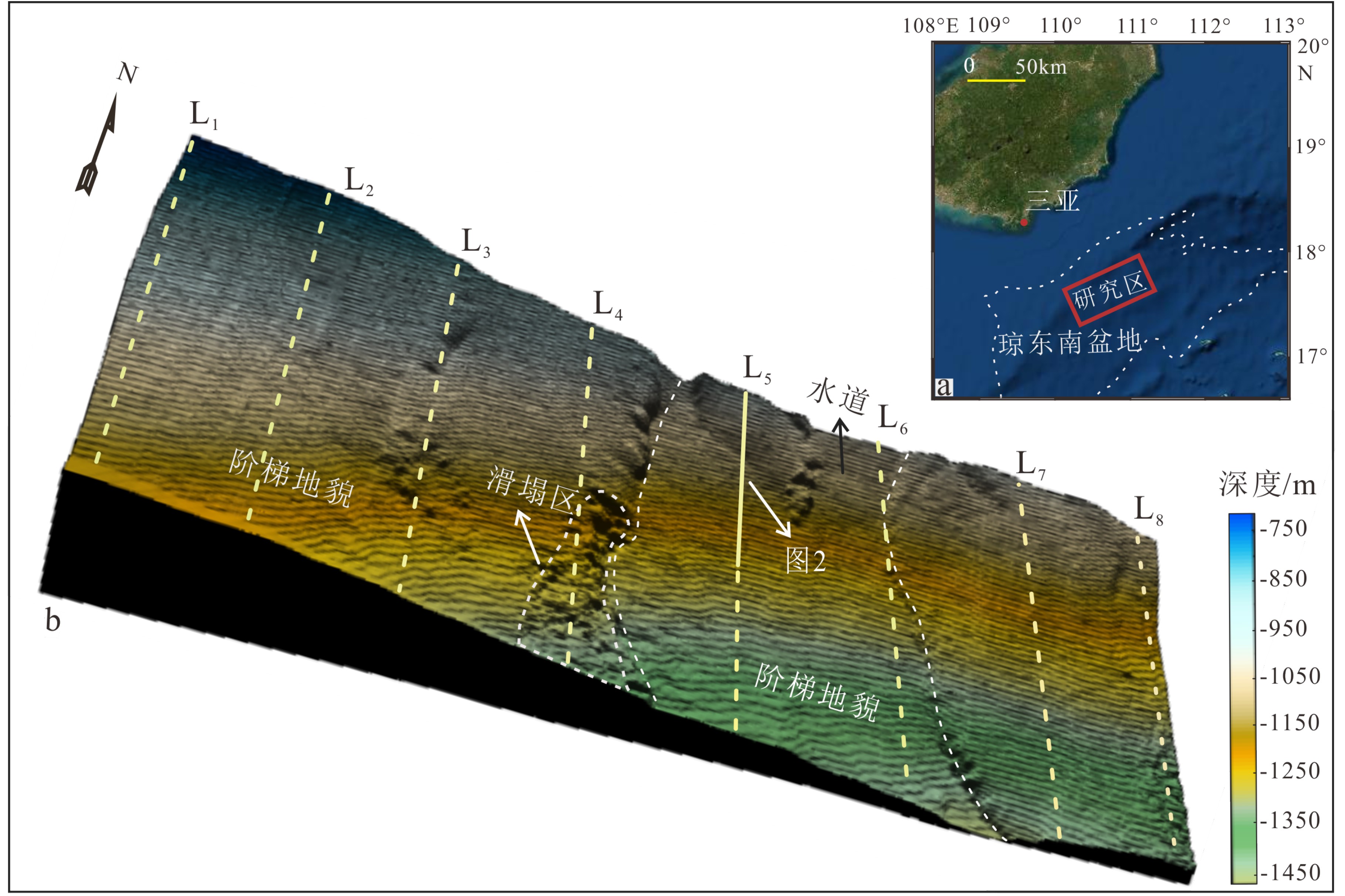
海底周期阶坎底形一直是海洋地质关注的热点。本文基于285 km2三维地震资料对琼东南盆地海底周期阶坎底形几何构型(波长、波高、迎流面长度、背流面长度、迎流面夹角和背流面夹角)及形成机理进行了分析。研究区位于上陆坡(2°~14°),发育一条NE-SW水道,宽 6.5 km,深 35 m。水道内外均发育周期阶坎,剖面上具有波状特征。周期阶坎的波长(20~160 m)随深度增加而变长,波高(4~10 m)随深度增加而减小,迎流面长度(20~140 m)比背流面长度(10~40 m)长,迎流面夹角(0.1°~0.15°)平缓,背流面夹角(0.2°~0.8°)陡峭。初步认为,研究区周期阶坎底形由持续稳定的浊流形成,且以沉积型周期阶坎为主。
Abstract:Cyclic steps, as a kind of bedforms on the deep sea bottom, are one of the hot research spots in deep sea geology nowadays. Based on the 285 km2 of 3D seismic data collected from the Qiongdongnan Basin, the characteristics of cyclic steps, such as the wavelength, wave height, length of lee side, length of steep side, angle of lee side and angle of steep side, as well as their forming mechanisms are carefully analyzed in this paper. The study area is located on the upper slope (2°~14°), with a NE-SW channel of 6.5 km in width and 35 m in depth. Cyclic steps are developed on both inner and outer sides of the channel, with wavy patterns on profile. Wavelength (20~160 m) increases, while wave height (4~10 m) decreases with depth, the length of the leeward side (20~140 m) is longer than that of the windward (10~40 m), the leeward side is gentle (0.05°~0.06°), but windward side steep (0.1°~0.35°). It is suggested that most of the cyclic steps be formed by the deposition of a continuous and stable turbidity current.
-
Key words:
- cyclic steps /
- channel /
- supercritical turbidity current /
- Qiongdongnan Basin
-

-
图 3 波长随深度变化曲线图 (测线位置见图1b)
Figure 3.
-
[1] Parker G. Interaction between basic research and applied engineering: A personal perspective [J]. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 1996, 34(3): 291-316. doi: 10.1080/00221689609498482
[2] 钟广法, 朱本铎, 王嘹亮. 南海浊流地貌[J]. 科技导报, 2020, 38(18):75-82
ZHONG Guangfa, ZHU Benduo, WANG Liaoliang. Turbidity current related landforms in the South China Sea [J]. Science & Technology Review, 2020, 38(18): 75-82.
[3] Zhong G F, Cartigny M J B, Kuang Z G, et al. Cyclic steps along the South Taiwan Shoal and West Penghu submarine canyons on the northeastern continental slope of the South China Sea [J]. GSA Bulletin, 2015, 127(5-6): 804-824. doi: 10.1130/B31003.1
[4] 许小勇, 吕福亮, 王大伟, 等. 周期性阶坎的特征及其对深水沉积研究的意义[J]. 海相油气地质, 2018, 23(4):1-14 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2018.04.001
XU Xiaoyong, LÜ Fuliang, WANG Dawei, et al. Cyclic steps and significance to deep water sedimentation [J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2018, 23(4): 1-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2018.04.001
[5] 高红芳, 钟和贤, 孙美静, 等. 南海海盆东南部大型深水浊积扇体系及其成因的构造控制[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(5):1395-1406
GAO Hongfang, ZHONG Hexian, SUN Meijing, et al. The large deep-water turbidity fan system in southeastern South China Sea Basin: Formation and tectonic constraint [J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(5): 1395-1406.
[6] Wynn R B, Piper D J W, Gee M J R. Generation and migration of coarse-grained sediment waves in turbidity current channels and channel-lobe transition zones [J]. Marine Geology, 2002, 192(1-3): 59-78. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(02)00549-2
[7] 曾小明, 潘燕, 于佳, 等. 陵水凹陷北坡低密度浊流海底扇沉积特征[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2015, 15(33):48-53, 78 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.33.008
ZENG Xiaoming, PAN Yan, YU Jia, et al. Low-density turbidity submarine fan sedimentary characteristics in north slope of Lingshui sag [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2015, 15(33): 48-53, 78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.33.008
[8] 何家雄, 陈胜红, 马文宏, 等. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地深水油气成藏条件早期预测与评价[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2008, 19(6):780-789 doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2008.06.780
HE Jiaxiong, CHEN Shenghong, MA Wenhong, et al. Early forecast and evaluation on petroleum accumulation conditions in deep basin in northern continental margin of the South China Sea [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2008, 19(6): 780-789. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2008.06.780
[9] 吴时国, 秦志亮, 王大伟, 等. 南海北部陆坡块体搬运沉积体系的地震响应与成因机制[J]. 地球物理学报, 2011, 54(12):3184-3195 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.018
WU Shiguo, QIN Zhiliang, WANG Dawei, et al. Seismic characteristics and triggering mechanism analysis of mass transport deposits in the northern continental slope of the South China Sea [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(12): 3184-3195. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.018
[10] Fildani A, Hubbard S M, Covault J A, et al. Erosion at inception of deep-sea channels [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 41: 48-61. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2012.03.006
[11] Heiniö P, Davies R J. Trails of depressions and sediment waves along submarine channels on the continental margin of Espirito Santo Basin, Brazil [J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2009, 121(5-6): 698-711. doi: 10.1130/B26190.1
[12] Cartigny M J B, Postma G, van den Berg J H, et al. A comparative study of sediment waves and cyclic steps based on geometries, internal structures and numerical modeling [J]. Marine Geology, 2011, 280(1-4): 40-56. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2010.11.006
[13] Fielding C R. Upper flow regime sheets, lenses and scour fills: extending the range of architectural elements for fluvial sediment bodies [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2006, 190(1-4): 227-240. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2006.05.009
[14] Kostic S. Modeling of submarine cyclic steps: Controls on their formation, migration, and architecture [J]. Geosphere, 2011, 7(2): 294-304. doi: 10.1130/GES00601.1
[15] Gong C L, Chen L Q, West L. Asymmetrical, inversely graded, upstream-migrating cyclic steps in marine settings: Late Miocene-early Pliocene Fish Creek-Vallecito Basin, southern California [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2017, 360: 35-46. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2017.09.002
[16] Li L, Gong C L. Gradual transition from net erosional to net depositional cyclic steps along the submarine distributary channel Thalweg in the Rio Muni Basin: A joint 3-D seismic and numerical approach [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 2018, 123(9): 2087-2106. doi: 10.1029/2017JF004513
[17] Lamb M P, Parsons J D, Mullenbach B L, et al. Evidence for superelevation, channel incision, and formation of cyclic steps by turbidity currents in Eel Canyon, California [J]. GSA Bulletin, 2008, 120(3-4): 463-475. doi: 10.1130/B26184.1
[18] 谈明轩, 朱筱敏, 刘伟, 等. 旋回阶梯底形的动力地貌及其相关沉积物发育特征[J]. 地质论评, 2017, 63(6):1512-1522
TAN Mingxuan, ZHU Xiaomin, LIU Wei, et al. The morphodynamics of cyclic steps and sedimentary characteristics of associated deposits [J]. Geological Review, 2017, 63(6): 1512-1522.
[19] 王大伟, 孙悦, 司少文, 等. 海底周期阶坎研究进展与挑战[J]. 地球科学进展, 2020, 35(9):890-901
WANG Dawei, SUN Yue, SI Shaowen, et al. Research progress and challenges of submarine cyclic steps [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2020, 35(9): 890-901.
[20] 肖彬. 深水水道沉积体系及成因机制研究[D]. 长江大学博士学位论文, 2014.
XIAO Bin. Sedimentary system and formation mechanism of deep-water channel complex[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Yangtze University, 2014.
[21] 王大伟, 白宏新, 吴时国. 浊流及其相关的深水底形研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2018, 33(1):52-65 doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2018.01.0052
WANG Dawei, BAI Hongxin, WU Shiguo. The research progress of turbidity currents and related deep-water bedforms [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2018, 33(1): 52-65. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2018.01.0052
[22] 朱筱敏. 沉积岩石学[M]. 4版. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2008.
ZHU Xiaomin. Sedimentary Petrology[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2008.
[23] 操应长, 杨田, 王艳忠, 等. 超临界沉积物重力流形成演化及特征[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(6):607-621 doi: 10.7623/syxb201706001
CAO Yingchang, YANG Tian, WANG Yanzhong, et al. Formation, evolution and sedimentary characteristics of supercritical sediment gravity-flow [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(6): 607-621. doi: 10.7623/syxb201706001
[24] Kostic S, Parker G. The response of turbidity currents to a canyon-fan transition: internal hydraulic jumps and depositional signatures [J]. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 2006, 44(5): 631-653. doi: 10.1080/00221686.2006.9521713
[25] 张兴阳, 何幼斌, 罗顺社, 等. 内波单独作用形成的深水沉积物波[J]. 古地理学报, 2002, 4(1):83-89 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2002.01.010
ZHANG Xingyang, HE Youbin, LUO Shunshe, et al. Deep-water sediment waves formed by internal waves [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2002, 4(1): 83-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2002.01.010
[26] 钟广法, 李前裕, 郝沪军, 等. 深水沉积物波及其在南海研究之现状[J]. 地球科学进展, 2007, 22(9):907-913 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2007.09.004
ZHONG Guangfa, LI Qianyu, HAO Hujun, et al. Current status of deep-water sediment wave studies and the South China Sea perspectives [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2007, 22(9): 907-913. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2007.09.004
[27] Spinewine B, Sequeiros O E, Garcia M H, et al. Experiments on wedge-shaped deep sea sedimentary deposits in minibasins and/or on channel levees emplaced by turbidity currents. Part II. Morphodynamic evolution of the wedge and of the associated bedforms [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2009, 79(8): 608-628. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2009.065
[28] 王海荣, 王英民, 邱燕, 等. 南海北部大陆边缘深水环境的沉积物波[J]. 自然科学进展, 2007, 17(9):1235-1243 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008x.2007.09.012
WANG Hairong, WANG Yingmin, QIU Yan, et al. Sediment waves in the deep water environment of the northern continental margin of the South China Sea [J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2007, 17(9): 1235-1243. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008x.2007.09.012
[29] Middleton G V, Hampton M A. Part I. Sediment gravity flows: mechanics of flow and deposition [J]. Turbidites & Deep Water Sedimentation, 1973.
[30] 胡日军. 南海北部外陆架区海底沙波动态分析[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2006.
HU Rijun. Dynamical analysis of seafloor sandwaves in the outer continental shelf of the northern South China Sea[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2006.
[31] 张洪运. 南海北部陆架坡折附近的海底沙波的形态特征、活动规律和成因机制[D]. 中国科学院大学(中国科学院海洋研究所)博士学位论文, 2019.
ZHANG Hongyun. Sand waves near the shelf break of northern South China Sea: morphology, mobility and mechanism[D]. Doctor Dissertation of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2019.
[32] Symons W O, Sumner E J, Talling P J, et al. Large-scale sediment waves and scours on the modern seafloor and their implications for the prevalence of supercritical flows [J]. Marine Geology, 2016, 371: 130-148. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.11.009
[33] 李爽, 李伟, 詹文欢. 南海东北部陆缘浊流活动的地貌记录及其形成机制分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(1):111-121
LI Shuang, LI Wei, ZHAN Wenhuan. Geomorphological records of turbidity current activity in the northeastern margin of the South China Sea and analysis of triggering mechanism [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(1): 111-121.
[34] 鲁勇. 多坡道的浊流流动及沉积的实验研究[D]. 安徽工业大学硕士学位论文, 2019.
LU Yong. Experimental study on the flow and deposition of turbidity currents with multiple slope transitions[D]. Master Dissertation of Anhui University of Technology, 2019.
[35] 丁巍伟, 李家彪, 韩喜球, 等. 南海东北部海底沉积物波的形态、粒度特征及物源、成因分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2010, 32(2):96-105
DING Weiwei, LI Jiabiao, HAN Xiqiu, et al. Geomorphology, grain-size charicteristics, matter source and forming mechanism of sediment waves on the ocean bottom of the northeast South China Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2010, 32(2): 96-105.
[36] Fildani A, Normark W R, Kostic S, et al. Channel formation by flow stripping: Large-scale scour features along the Monterey East Channel and their relation to sediment waves [J]. Sedimentology, 2006, 53(6): 1265-1287. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.2006.00812.x
[37] Jalili Ghazizadeh M, Fallahi H, Jabbari E. Characteristics of water surface profile over rectangular side weir for supercritical flows [J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 2021, 147(5): 04021011. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0001551
-



 下载:
下载: