Submarine stability evaluation of the Philippine Sea of the Western Pacific based on microgeomorphologic features
-
摘要:
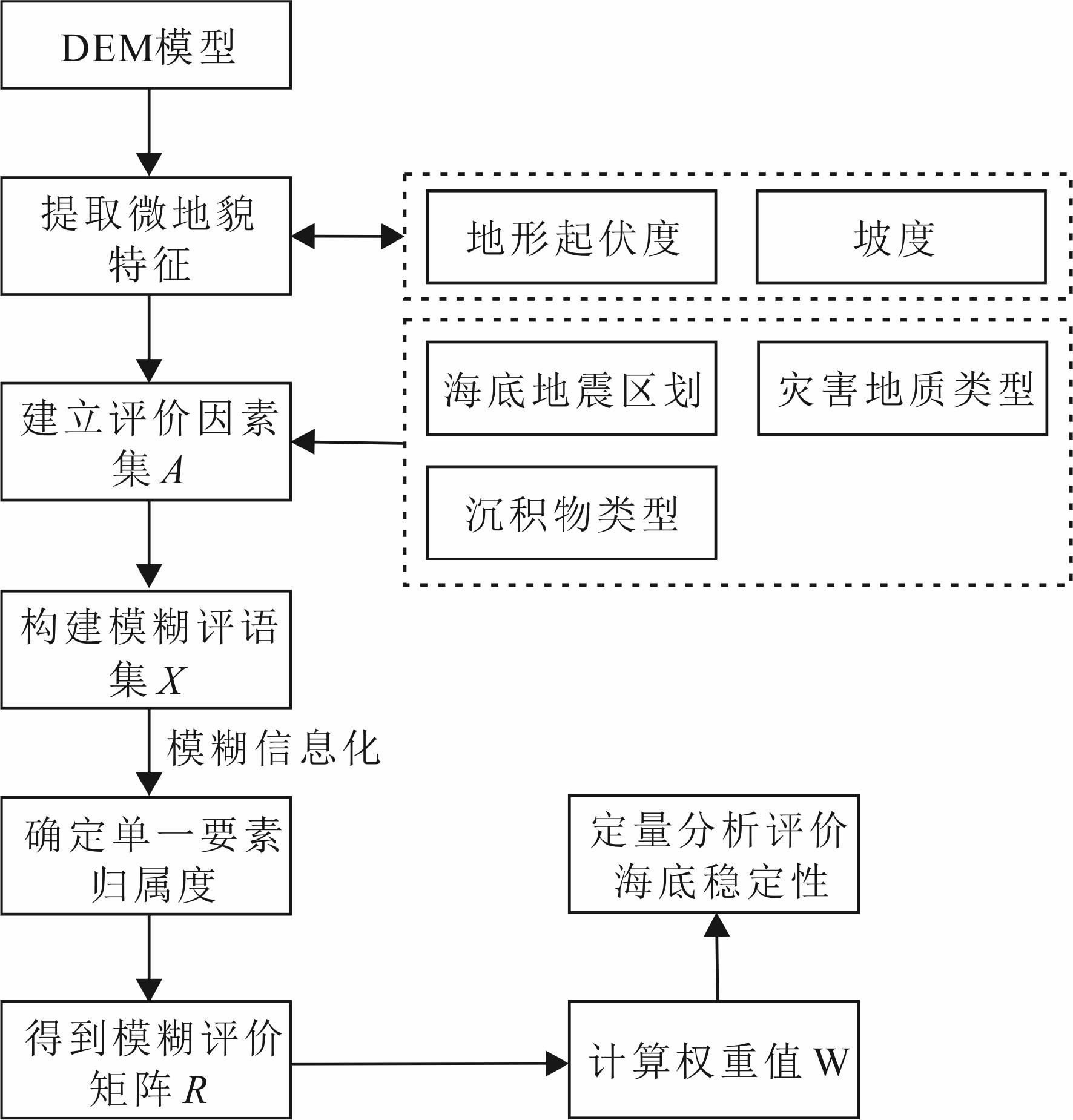
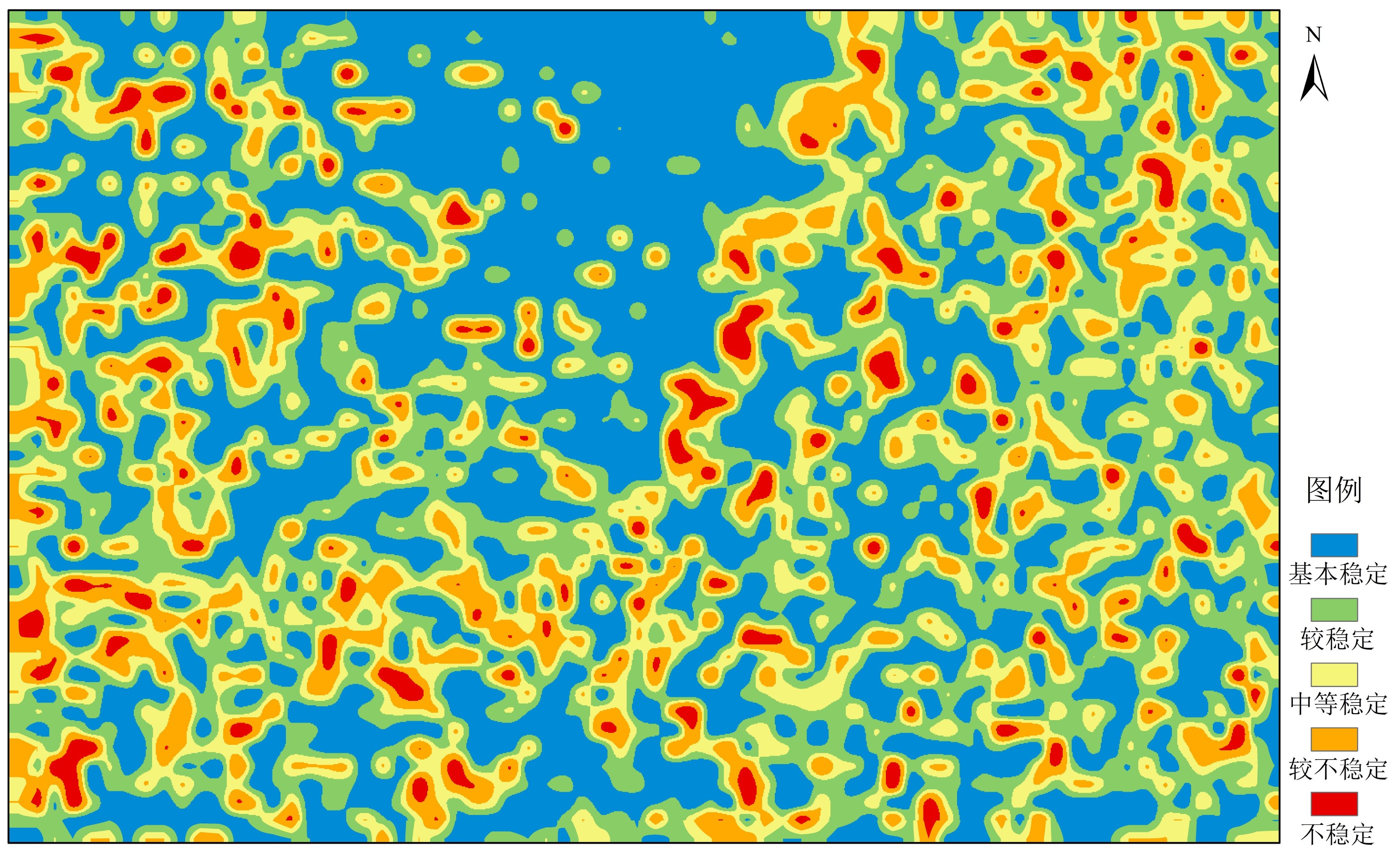
随着海洋战略地位的逐步提高,深远海海底资源开发和海洋工程建设将面临巨大挑战,主要是受限于技术手段,高精度调查资料难以获取,无法全面准确地进行海底稳定性评价。针对这一问题,本文提出了基于微地貌特征的深远海海底稳定性评价方法。基于已有的研究工作,本文选取西太平洋菲律宾海中南部某区域为研究区,利用ArcGIS平台建立研究区DEM(Digital Elevation Model),提取宏、微观地貌因子,结合全球地震数据、研究区底质类型和潜在地质灾害分布特征,运用模糊数学方法评价研究区海底稳定性,并绘制海底稳定性区划图。结果显示,对区域3220个评价单元进行稳定性分析,可将研究区海底稳定性划分为5个等级,包括基本稳定、较稳定、中等稳定、较不稳定和不稳定。其中,稳定区主要集中在较为平坦的中北部,不稳定区多发育在九州-帕劳海岭、海山、山间盆地等大规模地貌单元发育区,分析揭示,研究区海底稳定性与微地貌特征密切相关。因此,本文提出的基于微地貌特征的海底稳定性评价方法,能够很好地服务于深远海海底稳定性评价。
Abstract:In addition to underwater resource development, submarine construction and engineering have become great concerns to marine geoscientists. Both of them require accurate sea-bottom stability evaluation. However, mainly due to the limitation of offshore technology, it is difficult for the time being to acquire high-precision data for accurate and comprehensive evaluation of the stability. In order to solve this problem, a method for stability evaluation of submarine engineering is proposed in this paper based on microgeomorphologic features. Based on the existing research, this paper selected a region in the south-central Philippines Sea of the Western Pacific as the target area, and a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) using ArcGIS is established to extract macro and micro geomorphological factors. Combined with seismic data, bottom sediments and distribution pattern of geo-hazards in the study area, the fuzzy mathematical evaluation method was adopted to evaluate the submarine stability, and an evaluation map was compiled. The results show that by analysis of the stability for 3220 evaluation units in the region, the seabed can be divided into 5 grades according to its stability, including stable, basic stable, relatively stable, relatively unstable and unstable. The stable areas are mainly located in the central and northern part where the sea bottom is flat, while the unstable areas occur in the large-scale geomorphic units such as the Kyushu-Palau Ridge, seamounts and intermontane basins. It is revealed that the stability of the seabed of the study area is closely related to the change in topography and landform. The practice proves that the submarine stability evaluation method based on micro-geomorphic features proposed in this paper is useful and efficient, and may well serve the stability evaluation required in similar regions.
-
Key words:
- stability evaluation /
- micromorphology /
- geomorphic factor /
- fuzzy evaluation /
- Philippine Sea
-

-
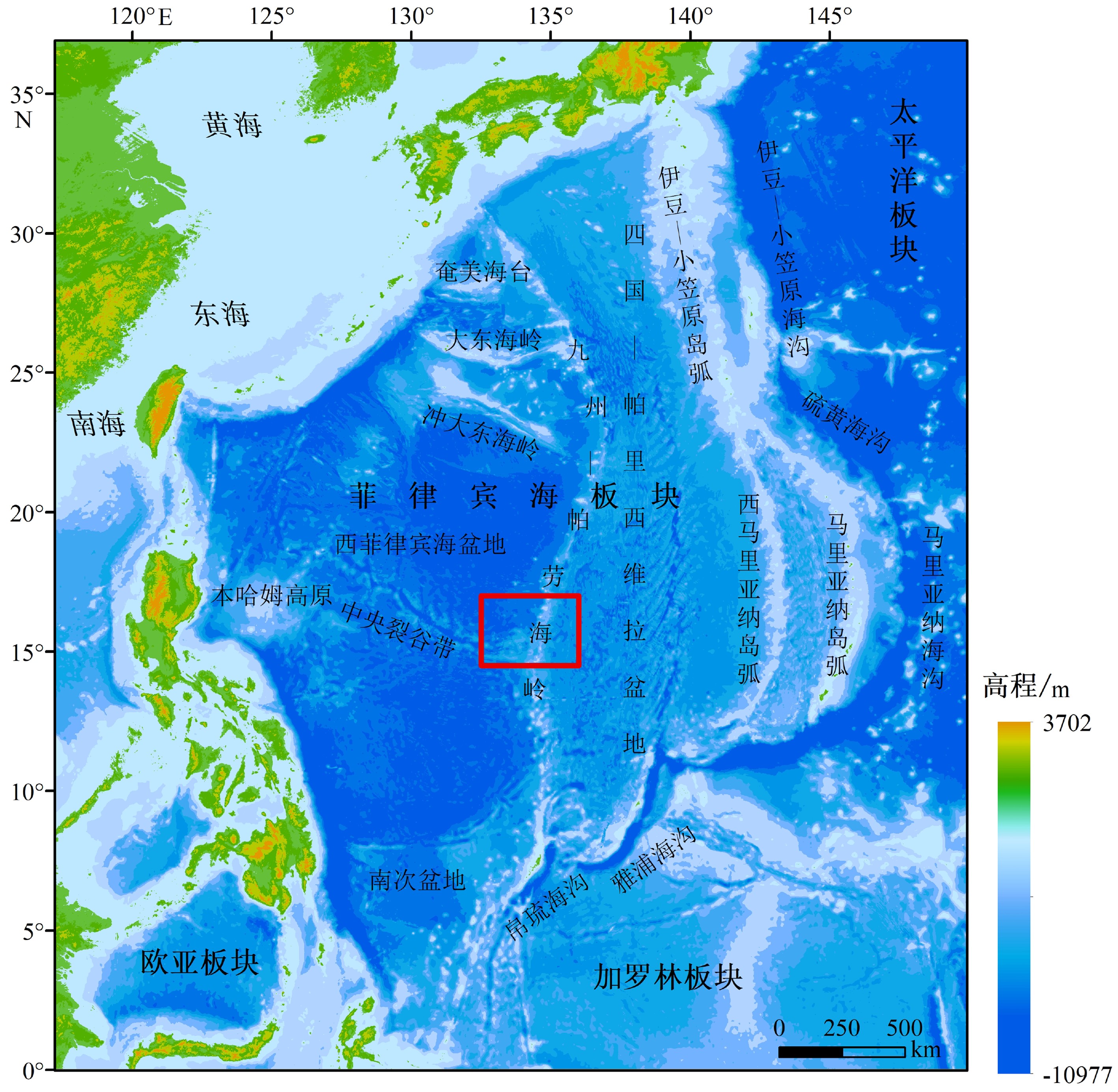
图 1 菲律宾海板块海底地形地貌与研究区位置图[22]
Figure 1.
地形因子 概念 公式 坡度 描述地表单元陡缓程度,表示地面在某点的倾斜度 tanα=△h/△dα—坡度,△h—高程差(m),△d—水平距离(m) 地形起伏度 区域最高点与最低点海拔高度的差值,反映地形起伏特征[25] RAi=Zimax—Zimin,RAi—地形起伏度(m),Zimax—区域内最大高程值(m),Zimin—区域内最小高程值(m) 表 2 海底稳定性评价指标体系
Table 2. Evaluation index system for seabed stability
指标体系 地震区划 灾害地质 微观地貌因子(坡度) 宏观地貌因子(地形起伏度) 底质类型 1级 地震动峰加速度值=0.05 g,相当于5级地震区 海底火山 0°~3° 0~19 m 基岩 2级 地震动峰加速度值=0.1 g,相当于6级地震区 裂谷 3°~7° 19~45 m 铁锰结壳 3级 地震动峰加速度值=0.15 g,相当于7级地震区 海底滑坡 7°~15° 45~77 m 含铁锰结核的远洋黏土 4级 地震动峰加速度值=0.2 g,相当于8级地震区 陡坎 15°~25° 77~120 m 远洋黏土 5级 地震动峰加速度值≥0.3 g,相当于9级地震区 崩塌 >25° >120 m 硅藻软泥 表 3 海底稳定性评价指标隶属度值
Table 3. Membership value of evaluation index of seabed stability
稳定性
等级评价指标 地震区划 灾害地质 微观地貌因子 宏观地貌因子 底质类型 基本稳定 1级 1级 1级 1级 1级 v1 0.15 0.15 0.15 0.15 0.15 较稳定 2级 2级 2级 2级 2级 v2 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.30 中等稳定 3级 3级 3级 3级 3级 v3 0.55 0.55 0.55 0.55 0.55 较不稳定 4级 4级 4级 4级 4级 v4 0.80 0.80 0.80 0.80 0.80 不稳定 5级 5级 5级 5级 5级 v5 0.85 0.85 0.85 0.85 0.85 表 4 评价指标权重值
Table 4. The weight value of the evaluation index
评价指标 地震区划 灾害地质 微观地貌因子 宏观地貌因子 底质类型 权重值 0.0882 0.4412 0.2206 0.1471 0.1029 -
[1] 陈连增, 雷波. 中国海洋科学技术发展70年[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(10):3-22
CHEN Lianzeng, LEI Bo. Marine science and technology development over the past 70 years in China [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2019, 41(10): 3-22.
[2] 夏真. 海洋地质学的军事战略意义[J]. 南海地质研究, 2010:83-90
XIA Zhen. The significance of marine geology in military strategy [J]. Gresearch of Eological South China Sea, 2010: 83-90.
[3] 汪品先. 大洋钻探与中国的海洋地质[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(1):7-14
WANG Pinxian. Ocean drilling and marine geology in China [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(1): 7-14.
[4] 杜军, 李培英, 李萍, 等. 基于海洋灾害地质评价基础上的我国近海海底稳定性区划[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(5):124-129
DU Jun, LI Peiying, LI Ping, et al. The seabed stability zonation based on the marine geohazards evaluation in China [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2014, 36(5): 124-129.
[5] 马秀冬, 李萍, 徐元芹, 等. 冲绳海槽中段海底灾害地质类型及海底稳定性评价[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2018, 36(1):79-87 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2018.01.007
MA Xiudong, LI Ping, XU Yuanqin, et al. Submarine geohazards types and seabed stability evaluation of the middle part of the Okinawa Trough [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2018, 36(1): 79-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2018.01.007
[6] MacKillop K, Fenton G, Mosher D, et al. Assessing submarine slope stability through deterministic and probabilistic approaches: a case study on the west-central scotia slope [J]. Geosciences, 2019, 9(1): 18.
[7] Bellwald B, Urlaub M, Hjelstuen B O, et al. NE Atlantic continental slope stability from a numerical modeling perspective [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2019, 203: 248-265. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.11.019
[8] Ionov V Y, Kalinin E V, Fomenko I K, et al. Regional slope stability assessment along the Caucasian shelf of the Black Sea[M]//Krastel S, Behrmann J H, Völker D, et al. Submarine Mass Movements and Their Consequences: 6th International Symposium. Cham: Springer, 2014, 37: 201-212.
[9] Dimakis P, Elverhøi A, Høeg K, et al. Submarine slope stability on high-latitude glaciated Svalbard–Barents Sea margin [J]. Marine Geology, 2000, 162(2-4): 303-316. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(99)00076-6
[10] Ten Brink U S, Andrews B D, Miller N C. Seismicity and sedimentation rate effects on submarine slope stability [J]. Geology, 2018, 44(7): 563-566.
[11] Lehner F K, Schöepfer M P J. Slope stability and exact solutions for cohesive critical Coulomb wedges from Mohr diagrams [J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2018, 116: 234-240. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2018.04.021
[12] 胡光海, 刘振夏, 房俊伟. 国内外海底斜坡稳定性研究概况[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2006, 24(1):130-136 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2006.01.017
HU Guanghai, LIU Zhenxia, FANG Junwei. A review of submarine slope stability studies at home and abroad [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2006, 24(1): 130-136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2006.01.017
[13] Guo X S, Zheng D F, Nian T K, et al. Large-scale seafloor stability evaluation of the northern continental slope of South China Sea [J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2020, 38(7): 804-817.
[14] 徐元芹, 李萍, 刘乐军, 等. 河北南堡-曹妃甸海域工程地质条件及海底稳定性评价[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(5):103-114
XU Yuanqin, LI Ping, LIU Lejun, et al. Engineering geological conditions and seabed stability assessment of Nanpu-Caofeidian, Hebei Province [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2017, 39(5): 103-114.
[15] 宋晓帅, 于开宁, 吴振, 等. 莱州湾海岸带工程地质环境质量分区[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(2):79-89
SONG Xiaoshuai, YU Kaining, WU Zhen, et al. Engineering geological environment quality division of Laizhou Bay coastal zone [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(2): 79-89.
[16] 李常珍, 李乃胜, 林美华. 菲律宾海的地势特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2000, 24(6):47 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2000.06.014
LI Changzhen, LI Naisheng, LIN Meihua. Terrain features of the Philippine Sea [J]. Marine Sciences, 2000, 24(6): 47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2000.06.014
[17] Macpherson C G, Hall R. Tectonic setting of Eocene boninite magmatism in the Izu–Bonin–Mariana forearc [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 186(2): 215-230. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00248-5
[18] Takahashi N, Suyehiro K, Shinohara M. Implications from the seismic crustal structure of the northern Izu-Bonin arc [J]. The Island Arc, 1998, 7(3): 383-394. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1738.1998.00197.x
[19] Ark J O, Hori T, Kaneda Y. Seismotectonic implications of the Kyushu-Palau Ridge subducting beneath the westernmost Nankai Forearc [J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2009, 61(8): 1013-1018. doi: 10.1186/BF03352951
[20] Nishizawa A, Kaneda K, Katagiri Y, et al. Variation in crustal structure along the Kyushu-Palau Ridge at 15-21 N on the Philippine Sea plate based on seismic refraction profiles [J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2007, 59(6): e17-e20. doi: 10.1186/BF03352711
[21] Yamashita M, Tsuru T, Takahashi N, et al. Fault configuration produced by initial arc rifting in the Parece Vela Basin as deduced from seismic reflection data [J]. Island Arc, 2007, 16(3): 338-347. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1738.2007.00594.x
[22] 张斌, 李广雪, 黄继峰. 菲律宾海构造地貌特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(2):79-88
ZHANG Bin, LI Guangxue, HUANG Jifeng. The tectonic geomorphology of the Philippine sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(2): 79-88.
[23] 闫满存, 王光谦, 李保生, 等. 基于模糊数学的广东沿海陆地地质环境区划[J]. 地理学与国土研究, 2000, 16(4):41-48
YAN Mancun, WANG Guangqian, LI Baosheng, et al. Land Geoenvironmental Regionalization of Guangdong Coast by Fuzzy [J]. Geography and Territorial Research, 2000, 16(4): 41-48.
[24] 郭芳芳, 杨农, 孟晖, 等. 地形起伏度和坡度分析在区域滑坡灾害评价中的应用[J]. 中国地质, 2008, 35(1):131-143 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.01.014
GUO Fangfang, YANG Nong, MENG Hui, et al. Application of the relief amplitude and slope analysis to regional landslide hazard assessments [J]. Geology in China, 2008, 35(1): 131-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.01.014
[25] 兰燕, 王明华, 刘珊红, 等. 逐点内插法建立DEM的研究[J]. 测绘科学, 2009, 34(1):214-216 doi: 10.3771/j.issn.1009-2307.2009.01.077
LAN Yan, WANG Minghua, LIU Shanhong, et al. Study on building DEM based on point-by-point interpolation algorithm [J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2009, 34(1): 214-216. doi: 10.3771/j.issn.1009-2307.2009.01.077
[26] 涂汉明, 刘振东. 中国地势起伏度最佳统计单元的求证[J]. 湖北大学学报:自然科学版, 1990, 12(3):266-271
XU Hanming, LIU Zhendong. Demonstrating on optimum statistic unit of relief amplitude in China [J]. Journal of Hubei University (Natural Science), 1990, 12(3): 266-271.
[27] 陈曦, 曾亚武, 刘伟, 等. 岩体基本质量分级模糊综合评价法研究[J]. 武汉大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 52(6):511-522
CHEN Xi, ZENG Yawu, LIU Wei, et al. Research on classification of rock mass basic quality based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method [J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2019, 52(6): 511-522.
[28] 马林伟, 吴时国. 海底滑坡过程的分段模拟研究[C]//国家安全地球物理丛书(十五)——丝路环境与地球物理. 西安: 西安地图出版社, 2019: 65-69.
MA Linwei, WU Shiguo. Subsection simulation of submarine landslide process[C]//National Security Geophysics Series (xv) - Silk Road Environment and Geophysics. Xi'an: Xi'an Map Publishing House, 2019: 65-69.
[29] Whelan N T, Cohmen J M, Suhayda J N, et al. Acoustical penetration and shear strength in gas-charged sediment [J]. Marine Geotechnology, 1977, 2: 147-159. doi: 10.1080/10641197709379776
[30] 马云, 李三忠, 夏真, 等. 南海北部神狐陆坡区灾害地质因素特征[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2014, 39(9):1364-1372
MA Yun, LI Sanzhong, XIA Zhen, et al. Characteristics of hazardous geological factors on Shenhu continental slope in the Northern South China Sea [J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2014, 39(9): 1364-1372.
[31] Sultan N, Voisset M, Marsset B, et al. Potential role of compressional structures in generating submarine slope failures in the Niger Delta [J]. Marine Geology, 2006, 237(3-4): 169-190.
[32] 许文锋, 车爱兰, 王治, 等. 地震荷载作用下海底滑坡特征及其机理[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2011, 45(5):782-786
XU Wenfeng, CHE Ailan, WANG Zhi, et al. Destruction characteristic of seabed landslide during earthquake motion and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2011, 45(5): 782-786.
[33] Imbo Y, De Batist M, Canals M, et al. The Gebra Slide: a submarine slide on the trinity peninsula margin, Antarctica [J]. Marine Geology, 2003, 193(3-4): 235-252. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(02)00664-3
[34] 朱友生. 南海北部陆架边缘区域地质灾害类型特征及分布规律[J]. 中国海上油气, 2017, 29(3):107-115
ZHU Yousheng. Features and distribution pattern of the geological hazards in the northern continental shelf margins of South China Sea [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2017, 29(3): 107-115.
[35] 谢先得, 朱照宇, 覃慕陶, 等. 广东沿海地质环境与地质灾害[M]. 广州: 广东科技出版社, 2003.
XIE Xiande, ZHU Zhaoyu, QIN Mutao, et al. Geological Environment and Geological Hazards Along the Coast of Guangdong Province[M]. Guangzhou: Guangdong Science and Technology Press, 2003.
[36] 杜军, 李培英, 魏巍, 等. 中国海岸带灾害地质稳定性区划[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2008, 17(4):1-6 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2008.04.001
DU Jun, LI Peiying, WEI Wei, et al. Stability zoning of hazard geology in coastal zone of China [J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2008, 17(4): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2008.04.001
[37] 蔡鹤生, 周爱国, 唐朝晖. 地质环境质量评价中的专家-层次分析定权法[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 1998, 23(3):299-302
CAI Hesheng, ZHOU Aiguo, TANG Zhaohui. Expert-analytic hierarchy weighting process in geological environmental quality assessment [J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1998, 23(3): 299-302.
-



 下载:
下载: