Two distribution patterns of the marine-continental transitional source rocks in the southern South China Sea
-
摘要:
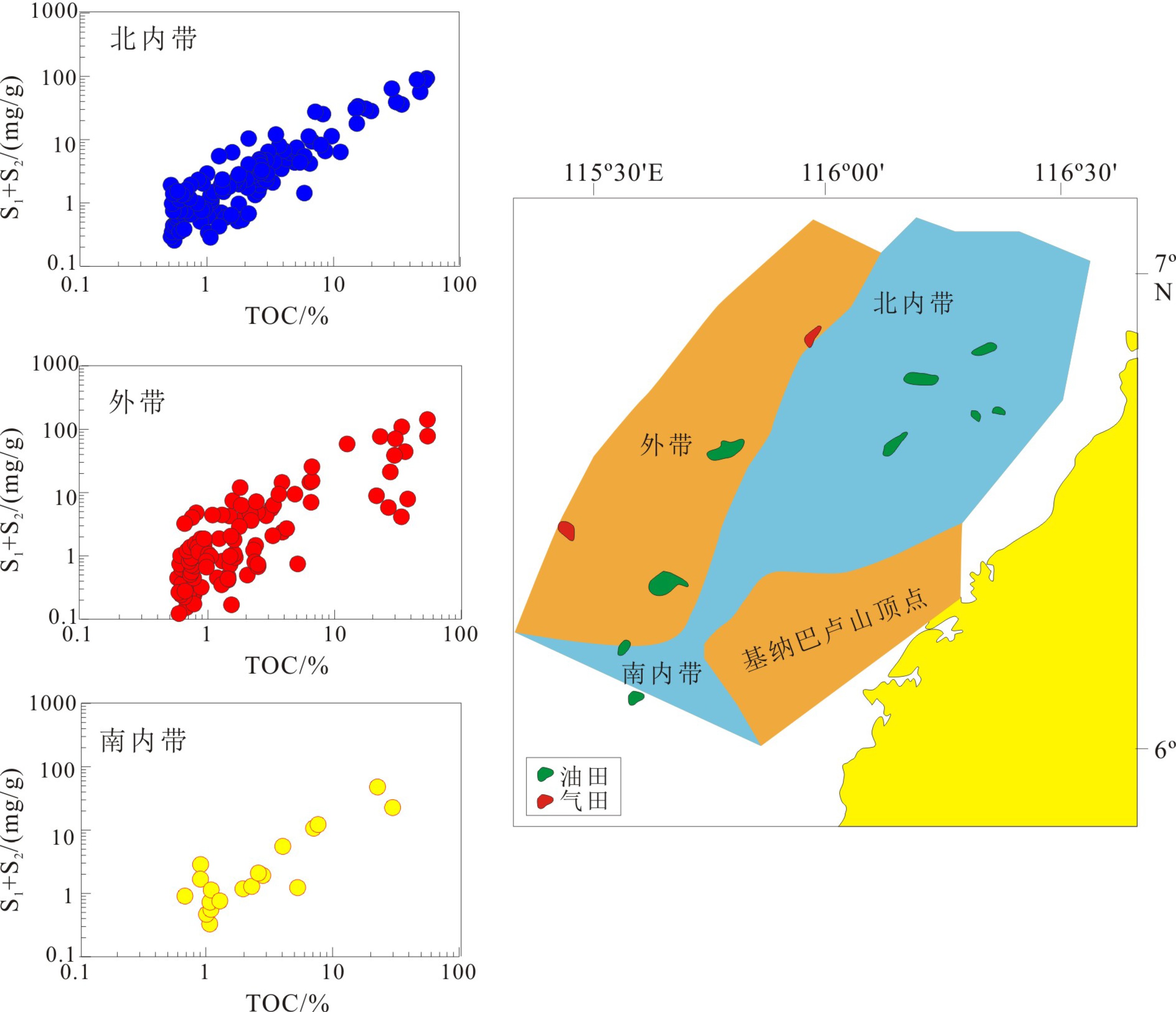
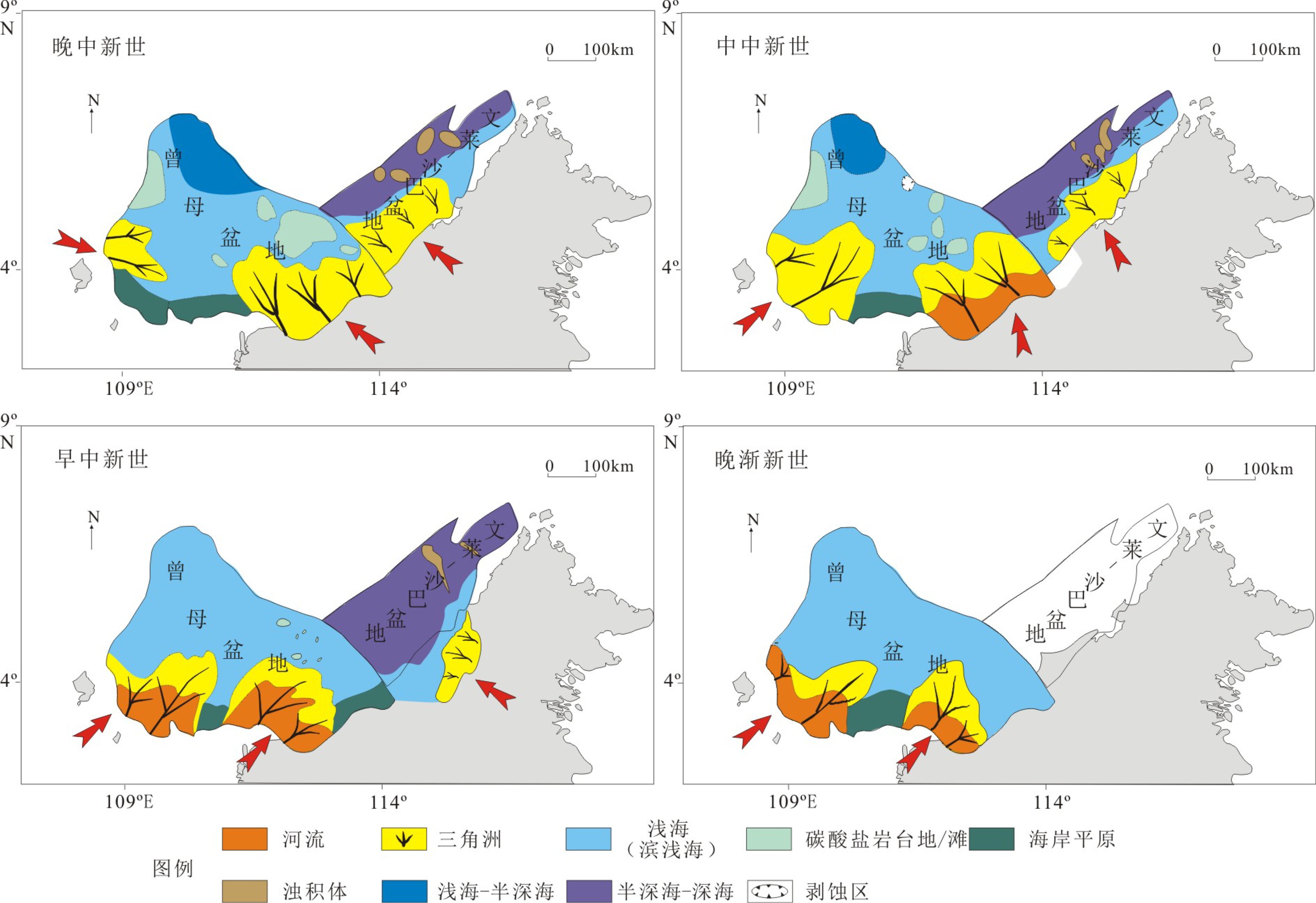
位于南海南部的曾母盆地和文莱-沙巴盆地是南海中南部油气资源最为富集的两个盆地,可采储量相当,但含油气性和油气分布差异巨大。本文在油源对比的基础上,结合古气候、古植被、沉积演化与沉积相带差异,总结了曾母盆地和文莱-沙巴盆地海陆过渡相烃源岩的分布模式。研究认为,曾母盆地近岸一侧原油和文莱-沙巴盆地原油为煤系烃源岩来源,曾母盆地远岸一侧原油为陆源海相烃源岩来源。受古气候、古植被控制,煤系烃源岩具有较强生油能力,受沉积相带控制,曾母盆地和文莱-沙巴盆地海陆过渡相烃源岩存在两种分布模式,分别为“三角洲煤系-陆源海相”烃源岩分布模式和“三角洲-浊积含煤”分布模式。烃源岩分布模式进而控制了油气分布,曾母盆地的原油集中分布于三角洲平原及近岸地区,而文莱-沙巴盆地煤系烃源岩分布受浊积岩分布控制而广泛分布,这可能是文莱-沙巴盆地满盆富油的重要原因。
Abstract:As the largest oil and gas basins in the Southern South China Sea, the Zengmu and Baram-Sabah basins have roughly similar recoverable reserves but great differences in oil and gas ratio, and distribution patterns. Based on the data of oil source correlation, combined with the data of paleoclimate, paleovegetation, depositional evolution and faices differentiation, two distribution patterns for marine-continental transitional source rocks has been concluded by this paper. It suggests that the oil from shore side of the Zengmu Basin and the Baram-Sabah Basin are mainly generated from coaly source rocks, while the oil from offshore Zengmu Basin from terrestrially sourced marine deposits. Up to the paleoclimate and paleovegetation, the coaly source rock has rather strong ability of oil generation. Based on the depositional facies of source rocks, two distribution patterns for the marine-continental transitional source rocks have been recognized by the authors for the first time, which are the “deltaic coaly facies -terrestrially sourced marine facies source rocks” and the “deltaic- turbidite -coaly source rocks”. Under the control of the type of source rocks, the oil in the Zengmu Basin is enriched in the delta plain and inshore region, while the oil in the Baram-Sabah Basin has a wide coverage.
-

-
[1] 赵志刚. 南海中南部主要盆地油气地质特征[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(4):45-56
ZHAO Zhigang. Hydrocarbon geology characteristics of the main basins in mid-southern South China Sea [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(4): 45-56.
[2] 王龙, 谢晓军, 刘世翔, 等. 南海南部主要盆地油气分布规律及主控因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(10):1546-1554
WANG Long, XIE Xiaojun, LIU Shixiang, et al. Analysis of hydrocarbon accumulation and diversity of the major basins in mid-southern part of the South China Sea [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(10): 1546-1554.
[3] Abdullah Wan Hasiah, Chai Peng Lee, Patrick Gou, et al. Coal-bearing strata of Labuan: Mode of occurrences, organic petrographic characteristics and stratigraphic associations [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 76(20): 334-345.
[4] Say-Gee Sia, Wan Hasiah Abdullah, Zainey Konjing, et al. The age, palaeoclimate, palaeovegetation, coal seam architecture/mire types, paleodepositional environments and thermal maturity of syn-collision paralic coal from Mukah, Sarawak, Malaysia [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 81(25): 1-19.
[5] Olayinka S Togunwa, Wan Hasiah Abdullah, Mohammed Hail Hakimi, et al. Organic geochemical and petrographic characteristics of Neogene organic-rich sediments from the onshore West Baram Delta Province, Sarawak Basin: Implications for source rocks and hydrocarbon generation potential [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015.
[6] Wan Hasiah Abdullah. Organic petrological characteristics of limnic and paralic coals of Sarawak [J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Malaysia, 2002(45): 65-69.
[7] Curiale J, Morelos J, Lambiase J, et al. Brunei Darussalam: Characteristics of selected petroleums and source rocks [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2000, 31(12): 1475-1493. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(00)00084-X
[8] 王登, 徐耀辉, 文志刚, 等. 曾母盆地东巴林坚坳陷烃源岩评价及油源探讨[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2013, 32(5):583-590
WANG Deng, XU Yaohui, WEN Zhigang, et al. Evaluation of source rocks and oil-source correlation in east Balingian depression of Zengmu Basin [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2013, 32(5): 583-590.
[9] Awang Sapawi Awang Jamil, Mona Liza Anwar, Eric Seah Peng Kiang. Geochemistry of selected crude oils from Sabah and Sarawak [J]. Geol. Soc. Malaysia, 1991(28): 123-149.
[10] 张功成, 李友川, 刘世翔, 等. “源热共控”中国海油气田“近岸油、远岸气”有序分布[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2014, 19(5):1-22 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2014.05.001
ZHANG Gongcheng, LI Youchuan, LIU Shixiang, et al. “Co-control of source rock and heat” in orderly distribution of “near-shore oil and far-shore gas” in China’s offshore and adjacent area [J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2014, 19(5): 1-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2014.05.001
[11] Leong K M. The Petroleum Geology and Resources of Malaysia[M]. Kualar Lumpur: PetroNas (Petroliam Nasional Berhad), 2000.
[12] Aarssen B G K V, Cox H C, Hoogendoorn P, et al. A cadinene biopolymer in fossil and extant dammar resins as a source for cadinanes and bicadinanes in crude oils from South East Asia [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1990, 54(11): 3021-3031. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(90)90119-6
[13] 刘焕杰, 桑树勋, 施健. 成煤环境的比较沉积学研究: 海南岛红树林潮坪与红树林泥炭[M]. 中国矿业大学出版社, 1997: 105-113.
LIU Huanjie, SANG Shuxun, SHI Jian. Comparative Sedimentology Research on Coal-Forming Enviroments: Mangrove Tidal Flats and Mangrove Peats in The Hainan Island of The South China Sea, China[M]. China University of Mining and Technology Press, 1997: 105-113.
[14] 兰蕾. 南海南部盆地烃源岩特征及其对含油气性的影响[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4):23-29
LAN Lei. Controlling factors for different hydrocarbon distribution in Basins in Southern South China Sea [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(4): 23-29.
[15] Meor H Amir Hassan, Howard D Johnson, Peter A Allison, et al. Sedimentology and stratigraphic development of the Upper Nyalau Formation (Early Miocene), Sarawak, Malaysia: A mixed wave- and tide-influenced coastal system [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 76(1): 301-311.
[16] 郭佳, 谢晓军, 刘世翔, 等. 南海曾母盆地新生代沉积体系特征[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2016, 21(4):99-107 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2016.04.0011
GUO Jia, XIE Xiaojun, LIU Shixiang, et al. Cenozoic sedimentary systems in Zengmu Basin, South China Sea [J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2016, 21(4): 99-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2016.04.0011
[17] 刘世翔, 张功成, 赵志刚, 等. 南海构造旋回对曾母盆地油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2016, 21(2):37-44 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2016.02.005
LIU Shixiang, ZHANG Gongcheng, ZHAO Zhigang, et al. Control of tectonic cycle in South China Sea over hydrocarbon accumulation in the Zengmu Basin [J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2016, 21(2): 37-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2016.02.005
[18] 张泉兴, 张启明. 莺-琼盆地梅山组海相烃源岩的树脂化合物[J]. 中国海上油气, 1992, 6(3):1-10
ZHANG Quanxing, ZHANG Qiming. The marine hydrocarbon source rock’s resinite compounds of Meishan group of Yinggehai-Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. China’s Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 1992, 6(3): 1-10.
[19] Simoneit B R T. Diterpenoid compounds and other lipids in deep-sea sediments and their geochemical significance [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1977, 41(4): 463-476. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(77)90285-X
[20] Andrew B Cullen. Transverse segmentation of the Baram-Balabac Basin, NW Borneo: Refining the model of Borneo's tectonic evolution [J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 2010, 16(1): 3-29. doi: 10.1144/1354-079309-828
[21] Mohammed Hail Hakimi, Wan Hasiah Abdullah, Say-Gee Sia, et al. Organic geochemical and petrographic characteristics of Tertiary coals in the north-west Sarawak, Malaysia: Implications for palaeoenvironmental conditions and hydrocarbon generation potential [J]. Marine & Petroleum Geology, 2013, 48: 31-46.
-




 下载:
下载: