Hydrodynamic characteristics of Longkou Bay and its response to artificial island groups
-
摘要:
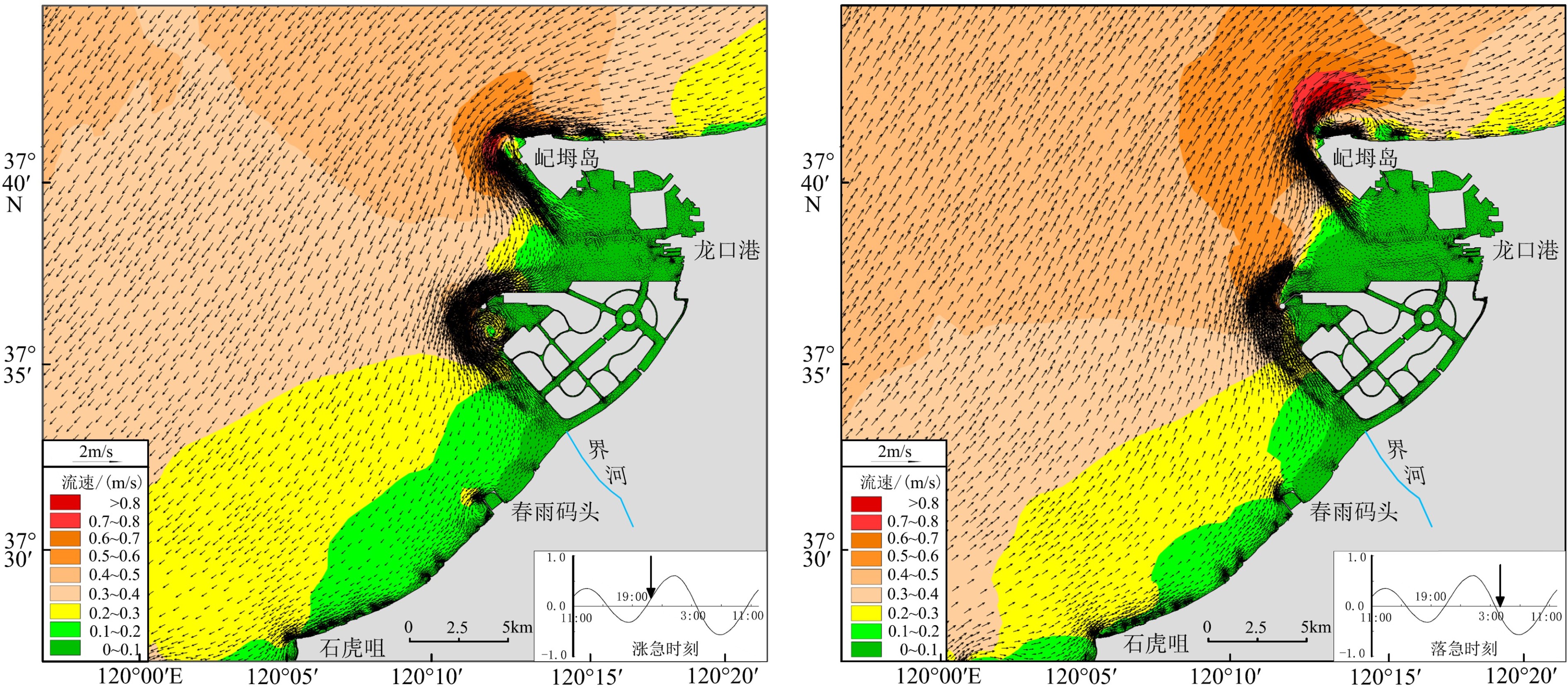
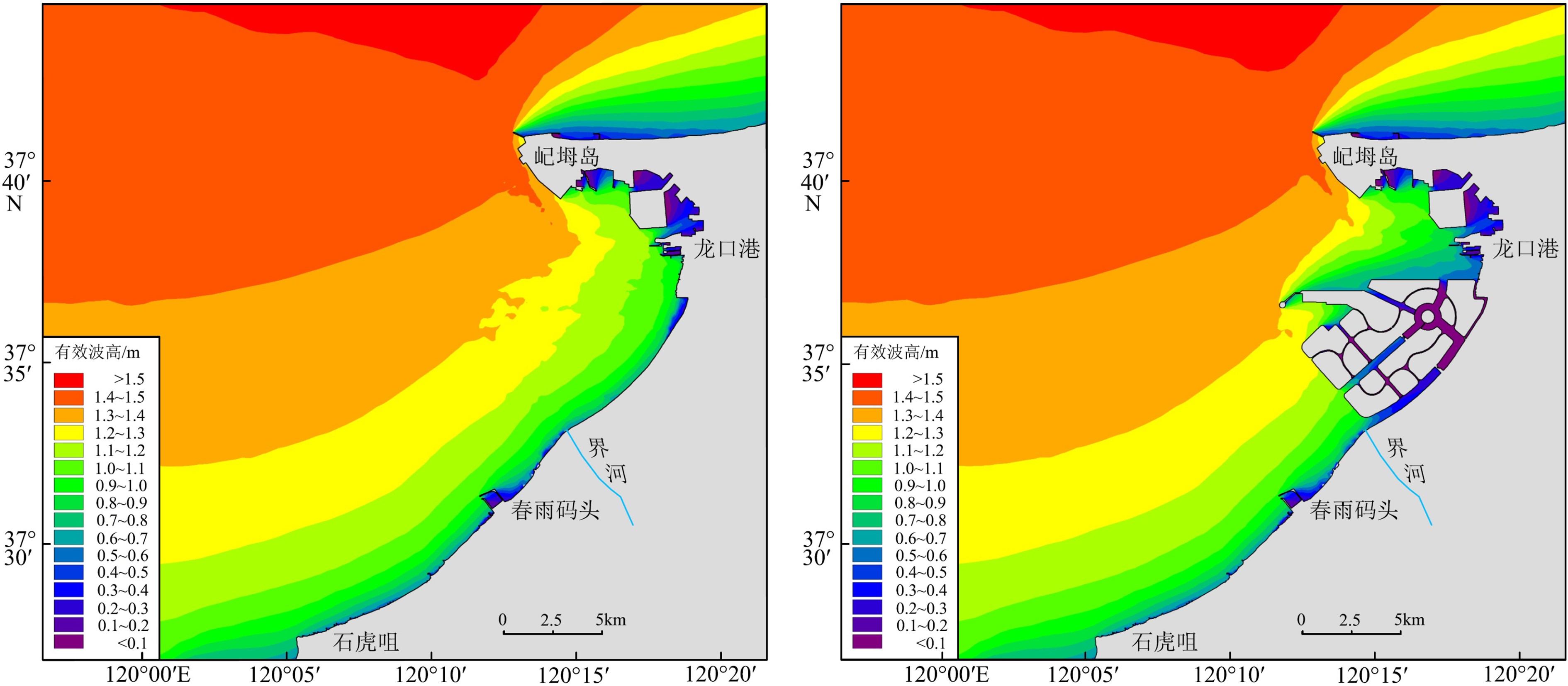
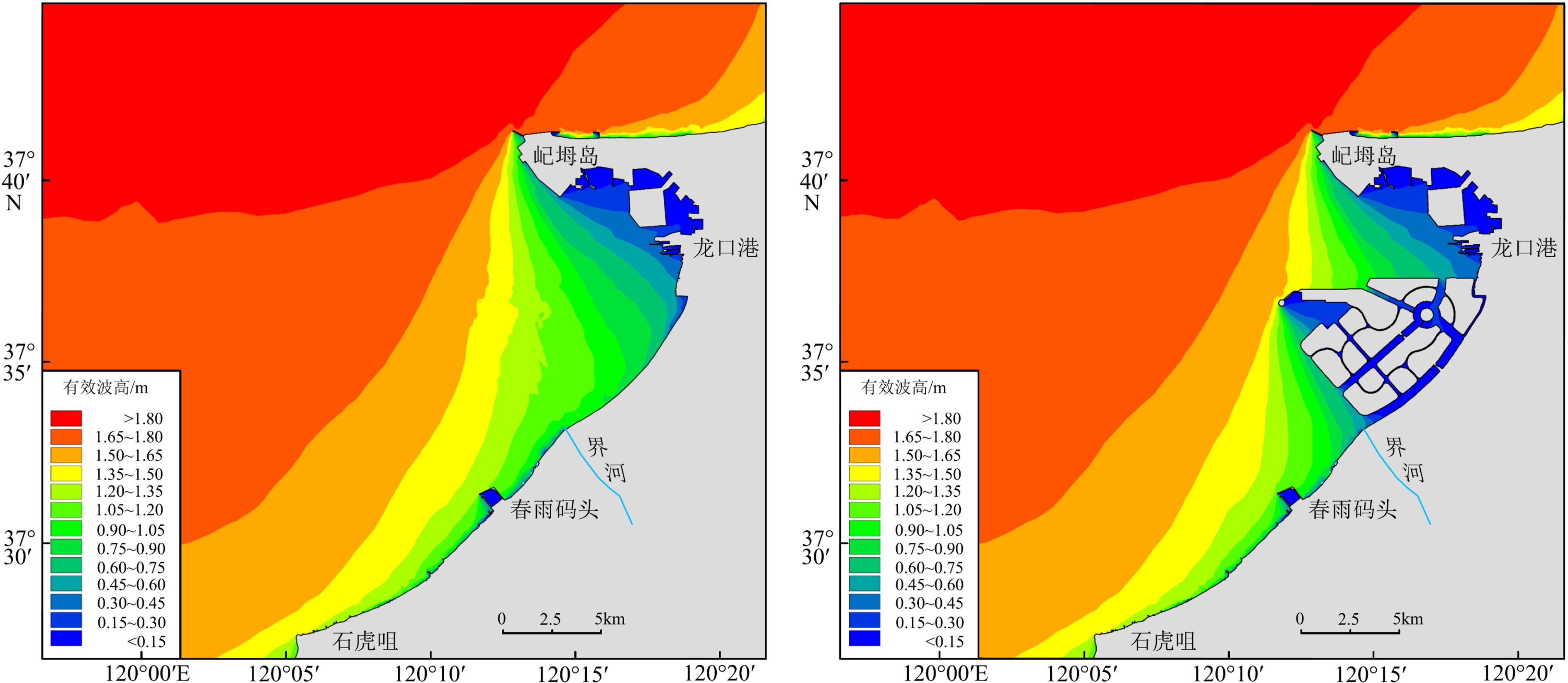
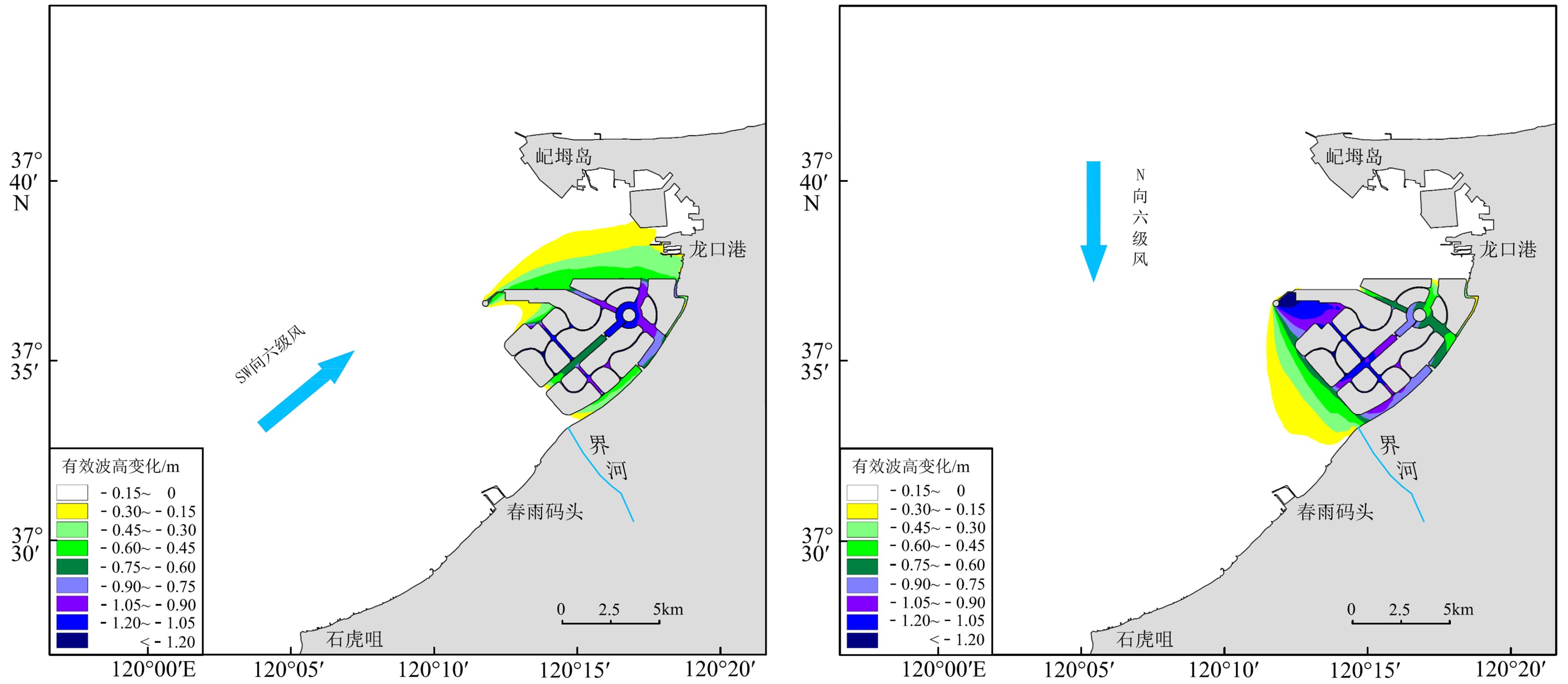
基于龙口湾及附近海域的水文实测资料,利用Mike21数学模型模拟了人工岛建设前后的潮流、波浪、纳潮量及水交换率等水动力特征,探讨了人工岛群建设对龙口湾水动力环境的影响。结果表明,人工岛建设显著改变了龙口湾潮流场特征及水体运动路径,湾内受到人工岛的阻挡,流速普遍减小,局部区域潮流运动形式由往复流变为旋转流,流向变化较大,余流形成多个涡旋;湾外由于堤头挑流作用导致局部区域流速增大且余流流速增大,潮流运动形式未发生明显改变。受人工岛的掩蔽作用,人工岛及附近区域的波浪有效波高普遍减小。龙口湾潮位出现北部最大潮差变小、南部最大潮差增大的格局,壅水作用导致人工岛内部水道潮差变化明显。人工岛建设直接占据了龙口湾海域面积,导致其纳潮量明显减小,水交换率呈现南部和北部增大、人工岛北侧以及内部水道减小的特征,人工岛造成的水动力环境的改变是影响水交换率变化的主要原因。人工岛群建设导致龙口湾内的潮流、波浪、纳潮量以及水交换等水动力特征减弱,是引起龙口湾水动力条件变化的根本因素。
Abstract:With the hydrological data from Longkou Bay and adjacent waters, hydrodynamic patterns of current, wave, tidal prism and water exchange rate before and after the construction of artificial island groups are simulated using the numerical model Mike21. On this basis, the impact of the construction of artificial islands onto the hydrodynamic environment of Longkou Bay is discussed. The results show that the construction of artificial islands has significantly changed the characteristics of current field in Longkou Bay in addition to water movement path. Flow velocity within the bay is generally reduced due to the obstruction of artificial islands, and the local tidal current movement has changed from the reciprocating flow to a rotating flow. The flow direction also changed greatly, and the residual flow forms multiple vortices. As the local regional velocity increases, the residual flow velocity also increased outside the bay due to the rippling effect of dike heads, which result in the increase in tidal current. There is no obvious change in the form of flow movement. Due to the masking effect of the artificial islands, the significant wave height at the artificial islands and their surrounding areas generally decreases. In Longkou Bay, the maximum tidal range decreases in the north and increases in the south, and the change of tidal range is most obvious due to backwater. The construction of artificial islands has directly occupied the area of Longkou Bay, resulting in the decrease of tidal capacity, the increase of water exchange rate in the south and north, and the decrease of water channel in the north and in the area inside the artificial islands. The change of hydrodynamic environment caused by artificial islands is the main reason to the change in water exchange rate. The construction of artificial islands has weakened the hydrodynamic characteristics such as tidal current, wave, tidal capacity and water exchange of Longkou Bay, which is fundamental to the change of hydrodynamic conditions in the bay.
-
Key words:
- numerical simulation /
- hydrodynamics /
- artificial islands /
- Longkou bay
-

-
表 1 人工岛建设前后纳潮量
Table 1. Tidal prism before and after construction of artificial island
潮况 建设前纳潮量/m3 建设后纳潮量/m3 变化量/m3 变化率/% 大潮 1.3620×108 1.1749×108 −1.8710×107 −13.74 小潮 9.1227×107 7.8660×107 −1.2567×107 −13.78 平均 1.1371×108 9.8075×107 −1.5635×107 −13.75 表 2 人工岛建设前后代表点潮位变化
Table 2. Tide changes before and after construction of artificial island (spring tide)
位置 站号 工程前最大潮差/m 工程后最大潮差/m 最大潮差变化/m 人工岛北 1 1.080 1.063 −0.017 2 1.076 1.063 −0.013 人工岛西 3 1.095 1.087 −0.008 4 1.100 1.094 −0.006 5 1.109 1.104 −0.005 人工岛南 6 1.107 1.121 0.014 7 1.118 1.126 0.008 8 1.138 1.139 0.001 人工岛内 9 1.085 1.066 −0.019 10 1.092 1.139 0.046 11 1.091 1.070 −0.021 12 1.097 1.144 0.047 表 3 不同海湾纳潮量变化对比
Table 3. Variation of tide prism in different bays
-
[1] 史经昊, 李广雪, 周春艳. 海湾沉积环境对人类活动的响应[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(4):11-18
SHI Jinghao, LI Guangxue, ZHOU Chunyan. Preliminary study on human influence on sedimentary environment of a bay [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(4): 11-18.
[2] 张盼. 莱州湾西南部现代沉积环境研究[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2014.
ZHANG Pan. A study on modern sedimentary environment in Southwestern Laizhou Bay[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2014.
[3] Barnes B B, Hu C M. Island building in the South China Sea: detection of turbidity plumes and artificial islands using Landsat and MODIS data [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 33194. doi: 10.1038/srep33194
[4] 林元军, 吴家鸣. 人工岛工程建设对海洋环境影响的数值分析方法探讨[J]. 广东造船, 2008(4):35-37 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6622.2008.04.014
LIN Yuanjun, WU Jiaming. Numerical methods for analyzing influence of artificial island project on marine environment [J]. Guangdong Shipbuilding, 2008(4): 35-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6622.2008.04.014
[5] Kassas M. Coastal processes with engineering applications [J]. The Environmentalist, 2004, 24(1): 60-61. doi: 10.1023/B:ENVR.0000046451.85342.a9
[6] Neumann B, Vafeidis A T, Zimmermann J, et al. Future coastal population growth and exposure to sea-level rise and coastal flooding-a global assessment [J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(3): e0131375.
[7] Jiang S H, Hu R J, Feng X L, et al. Influence of the construction of the Yantai West Port on the dynamic sedimentary environment [J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2018, 36(1): 43-51.
[8] Hu S L, Kot S C. Numerical model of tides in pearl river estuary with moving boundary [J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1997, 123(1): 21-29. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1997)123:1(21)
[9] Byun D S, Wang X H, Holloway P E. Tidal characteristic adjustment due to dyke and seawall construction in the Mokpo Coastal Zone, Korea [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2004, 59(2): 185-196. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2003.08.007
[10] 丁若雪, 顾介康. 基于MIKE21的瓯江口水动力特征与水流数值模拟研究[J]. 中国水运, 2017, 17(9):200-203
DING Ruoxue, GU Jiekang. Hydrodynamic characteristics and flow numerical simulation of Oujiang Estuary based on MIKE21 [J]. China Water Transport, 2017, 17(9): 200-203.
[11] 李雨. 潮流数值模拟在斯里兰卡汉班托塔港人工岛设计中的研究应用[J]. 中国水运, 2018, 18(5):70-72, 94
LI Yu. Research and application of tidal flow numerical simulation in artificial island design of Hambantota port, Sri Lanka [J]. China Water Transport, 2018, 18(5): 70-72, 94.
[12] 谭晓煜, 高佳. 三亚新机场人工岛工程前后潮流变化模拟研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2019, 21(2):1-15
TAN Xiaoyu, GAO Jia. Impact of the Sanya new airport artificial islands project on tidal dynamics of the Hongtang Bay [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2019, 21(2): 1-15.
[13] Rtimi R, Sottolichio A, Tassi P. Hydrodynamics of a hyper-tidal estuary influenced by the world's second largest tidal power station (Rance estuary, France) [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2021, 250: 107143. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.107143
[14] Cornett A, Cousineau J, Nistor I. Assessment of hydrodynamic impacts from tidal power lagoons in the Bay of Fundy [J]. International Journal of Marine Energy, 2013, 1: 33-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ijome.2013.05.006
[15] Hoefel F, Elgar S. Wave-induced sediment transport and sandbar migration [J]. Science, 2003, 299(5614): 1885-1887. doi: 10.1126/science.1081448
[16] Torres-Freyermuth A, Medellín G, Salles P. Human impact on the spatiotemporal evolution of beach resilience on the Northwestern Yucatan Coast [J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2021, 8: 111.
[17] Hendriyono W, Wibowo M, Subarkah A, et al. Wave model for the design of sustainable coastal infrastructures at an industrial site in Tuban, East Java [J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2020, 1625(1): 012049.
[18] Gou H, Luo F, Li R J, et al. Modeling study on the hydrodynamic environmental impact caused by the sea for regional construction near the Yanwo Island in Zhoushan, China [J]. Water, 2019, 11(8): 1674. doi: 10.3390/w11081674
[19] 陈静, 王永学. 岸线变迁对大连湾内湾海域纳潮量的影响[J]. 海洋通报, 2016, 35(4):390-395 doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2016.04.005
CHEN Jing, WANG Yongxue. Effect of the coastline changes on the tidal prism water quality of Dalian inner bays [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2016, 35(4): 390-395. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2016.04.005
[20] 孙永根, 高俊国, 朱晓明. 钦州保税港区填海造地工程对海洋环境的影响[J]. 海洋科学, 2012, 36(12):84-89
SUN Yonggen, GAO Junguo, ZHU Xiaoming. Effect of reclamation engineering in Qinzhou Bond Harbor on marine environment of Qinzhou Bay [J]. Marine Sciences, 2012, 36(12): 84-89.
[21] 王金华, 夏云峰, 杜峰, 等. 马尔代夫国际机场改扩建工程对潟湖水动力影响研究[J]. 施工技术, 2019, 48(4):28-31
WANG Jinhua, XIA Yunfeng, DU Feng, et al. Impact research of reconstruction and extension project of maldives international airport on the hydrodynamics of the lagoon [J]. Construction Technology, 2019, 48(4): 28-31.
[22] Rusdiansyah A, Tang Y L, He Z G, et al. The impacts of the large-scale hydraulic structures on tidal dynamics in open-type bay: numerical study in Jakarta Bay [J]. Ocean Dynamics, 2018, 68(9): 1141-1154. doi: 10.1007/s10236-018-1183-3
[23] Xiao K, Li H L, Song D H, et al. Field measurements for investigating the dynamics of the tidal prism during a spring-neap tidal cycle in Jiaozhou Bay, China [J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2019, 35(2): 335-347. doi: 10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-17-00121.1
[24] Wang C, Zhang X Q, Sun Y L. Numerical simulation of water exchange characteristics of the Jiaozhou bay based on a three-dimensional Lagrangian model [J]. China Ocean Engineering, 2009, 23(2): 277-290.
[25] Yuan Y, Jalón-Rojas I, Wang X H. Response of water-exchange capacity to human interventions in Jiaozhou Bay, China [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2021, 249: 107088. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.107088
[26] 袁德奎, 李广, 王道生, 等. 围填海工程对渤海湾水交换能力影响的数值模拟[J]. 天津大学学报: 自然科学与工程技术版, 2015, 48(7):605-613
YUAN Dekui, LI Guang, WANG Daosheng, et al. Numerical simulation of effects of land reclamation on water exchange capability of Bohai Bay [J]. Journal of Tianjin University: Science and Technology, 2015, 48(7): 605-613.
[27] Ranasinghe R, Larson M, Savioli J. Shoreline response to a single shore-parallel submerged breakwater [J]. Coastal Engineering, 2010, 57(11-12): 1006-1017. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2010.06.002
[28] 王春玲, 武雅洁, 董启涛, 等. 日照豪迈码头港池布局对泥沙输移影响研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2019, 49(7):110-117
WANG Chunling, WU Yajie, DONG Qitao, et al. Study on the impacts of the sediment transport on the Rizhao Haomai Harbor’s Layout [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2019, 49(7): 110-117.
[29] 匡翠萍, 钱从锐, 姚凯华, 等. 潮流与泥沙输运对黄骅港工程的响应分析[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 42(10):1516-1522
KUANG Cuiping, QIAN Congrui, YAO Kaihua, et al. Responses of tidal current and sediment transport to Huanghua Port [J]. Journal of Tongji University: Natural Science, 2014, 42(10): 1516-1522.
[30] Chen J Y, Chen S L. Estuarine and coastal challenges in China [J]. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2002, 20(2): 174-181. doi: 10.1007/BF02849656
[31] Li T H, Han P, Zhao Z J. Impact analysis of coastal engineering projects on mangrove wetland area change with remote sensing [J]. China Ocean Engineering, 2008, 22(2): 347-358.
[32] Chen Y P, Wei Y Q, Peng L H. Ecological technology model and path of seaport reclamation construction [J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2018, 165: 244-257.
[33] Li K Y, Liu X B, Zhao X G, et al. Effects of reclamation projects on marine ecological environment in Tianjin harbor industrial zone [J]. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2010, 2: 792-799. doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2010.10.090
[34] 刘星池, 王永学, 陈静. 人工岛群分阶段建设对附近水沙环境影响的数值研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2017, 36(3):302-310 doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2017.03.008
LIU Xingchi, WANG Yongxue, CHEN Jing. Study on the water-sediment environment of artificial islands constructed in stages by numerical simulation [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2017, 36(3): 302-310. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2017.03.008
[35] 安永宁, 吴建政, 朱龙海, 等. 龙口湾冲淤特性对人工岛群建设的响应[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2010, 26(10):24-30
AN Yongning, WU Jianzheng, ZHU Longhai, et al. Response of erosion-deposition pattern to artificial islands construction in Longkou Bay [J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2010, 26(10): 24-30.
[36] 刘波, 胡日军, 李毅, 等. 夏季潮流作用下龙口湾海域悬浮泥沙时空变化特征及其输运机制[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(3):20-30
LIU Bo, HU Rijun, LI Yi, et al. Spatio-temporal variation characteristics and transport mechanism of suspended sediments in Longkou bay under the influence of summer tidal current [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(3): 20-30.
[37] 任鹏, 孙志高, 赵全升, 等. 龙口湾表层沉积物碎屑矿物分布特征及影响因素[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2016, 35(2):279-284 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2016.02.007
REN Peng, SUN Zhigao, ZHAO Quansheng, et al. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of detrital mineralsin surficial sediments of the Longkou Bay [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2016, 35(2): 279-284. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2016.02.007
[38] 韩彬, 宋转玲, 曹磊, 等. 龙口湾近岸海域水质状况调查与评价[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2010, 28(2):186-192 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2010.02.008
HAN Bin, SONG Zhuanling, CAO Lei, et al. Survey and assessment of coastal seawater quality in Longkou Bay [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2010, 28(2): 186-192. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2010.02.008
[39] Li D, Tang C, Hou X Y, et al. Rapid morphological changes caused by intensive coastal development in Longkou Bay, China [J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2019, 35(3): 615-624. doi: 10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-18-00095.1
[40] 任鹏, 孙志高, 王传远, 等. 人工岛建设对龙口湾表层沉积物粒度及黏土矿物组成特征的影响[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2016, 34(4):578-587 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2016.04.014
REN Peng, SUN Zhigao, WANG Chuanyuan, et al. Impacts of construction of artificial islands on the flow-sediment regulation scheme on grain and clay compositions in the Longkou Bay [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2016, 34(4): 578-587. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2016.04.014
[41] 冯兴如, 杨德周, 尹宝树. FVCOM在龙口海域潮汐潮流模拟中的应用研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2010, 34(6):94-99
FENG Xingru, YANG Dezhou, YIN Baoshu. Application of FVCOM in tidal modeling of the seas adjacent to Longkou City [J]. Marine Sciences, 2010, 34(6): 94-99.
[42] 中国海湾志编纂委员会. 中国海湾志(第三分册)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1991.
China Bay Record Committee. The Bay Chorography in China: Bays in the South Shandong Peninsula and Jiangsu Province[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1993: 73-94.
[43] 许婷. 丹麦MIKE21模型概述及应用实例[J]. 水利科技与经济, 2010, 16(8):867-869 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7175.2010.08.013
XU Ting. Calculation principle and application example of a two-dimensional flow model-MIKE21 HD [J]. Water Conservancy Science and Technology and Economy, 2010, 16(8): 867-869. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7175.2010.08.013
[44] 赵博. 莱州三山岛: 刁龙嘴近岸海域冲淤特征及影响因素研究[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2014.
ZHAO Bo. Study on characteristic and influence factors of erosion and deposition in Sanshan Island: Diaolongzui Area, Laizhou[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2014.
[45] 邱桔斐, 马越, 徐新华. 长江口外海域波浪场数值模拟[J]. 水运工程, 2011(10):11-14 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2011.10.003
QIU Jufei, MA Yue, XU Xinhua. Numerical simulation of wave field around the Yangtze River estuary [J]. Port & Waterway Engineering, 2011(10): 11-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2011.10.003
[46] 秦晓, 纪平, 赵懿珺. 东山湾水动力数值模拟及其纳潮量和水交换周期计算[J]. 水利水电技术, 2020, 51(6):93-99
QIN Xiao, JI Ping, ZHAO Yijun. Hydrodynamic numerical simulation on Dongshan Bay and calculation of its tidal prism and water exchange cycle [J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2020, 51(6): 93-99.
[47] 叶海桃, 王义刚, 曹兵. 三沙湾纳潮量及湾内外的水交换[J]. 河海大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 35(1):96-98
YE Haitao, WANG Yigang, CAO Bing. Tidal prism of Sansha Bay and its water exchange with the open sea [J]. Journal of Hohai University: Natural Sciences, 2007, 35(1): 96-98.
[48] 王宏, 陈丕茂, 贾晓平, 等. 海水交换能力的研究进展[J]. 南方水产, 2008, 4(2):75-80
WANG Hong, CHEN Peimao, JIA Xiaoping, et al. Advance in the research on water exchange in the sea area [J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2008, 4(2): 75-80.
[49] 董礼先, 苏纪兰. 象山港水交换数值研究Ⅰ. 对流-扩散型的水交换模式[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1999, 30(4):410-415 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1999.04.010
DONG Lixian, SU Jilan. Numerical study of the water exchange in the Xiangshan Bay I. Advection-diffusion water exchange model [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1999, 30(4): 410-415. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1999.04.010
[50] 黄祖珂, 黄磊. 潮汐原理与计算[M]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学出版社, 2005.
HUANG Zuke, HUANG Lei. Tidal Principle and Calculation[M]. Qingdao: China Ocean University Press, 2005.
[51] 陆志妹. 近岸水域波浪与结构物相互作用的数值模拟[D]. 上海交通大学硕士学位论文, 2007.
LU Zhimei. Numerical simulation of wave interaction with structures in the coastal zone[D]. Master Dissertation of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2007.
[52] 李文丹, 李孟国, 韩西军, 等. 港珠澳大桥珠澳口岸人工岛工程二维潮流泥沙数学模型研究[J]. 中国港湾建设, 2011(5):27-30, 39 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3688.2011.05.006
LI Wendan, LI Mengguo, HAN Xijun, et al. 2-D tidal current and sediment modeling of Zhuhai-Macao artificial island of Hongkong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge [J]. China Harbour Engineering, 2011(5): 27-30, 39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3688.2011.05.006
[53] 朱雅琴, 张法星, 许唯临. 舌形挑流鼻坎水力特性研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2004(5):397-402, 408 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2004.05.019
ZHU Yaqin, ZHANG faxing, XU Welin. Research on hydraulic characteristics of flip bucket with Tongue-type [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2004(5): 397-402, 408. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2004.05.019
[54] 李池鸿, 顾晨, 杨之彦, 等. 基于MIKE 21的码头潮流数学模型研究[J]. 港工技术, 2019, 56(S1):1-6
LI Chihong, GU Chen, YANG Zhiyan, et al. Study on the mathematical model of wharf tidal based on MIKE 21 [J]. Port Engineering Technology, 2019, 56(S1): 1-6.
[55] 李瑞杰, 江森汇, 郑俊, 等. 日照港码头结构消浪的数值模拟[J]. 河海大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 39(2):190-194
LI Ruijie, JIANG Senhui, ZHENG Jun, et al. Numerical simulation of wave dissipation on dock structure of Rizhao Port [J]. Journal of Hohai University: Natural Sciences, 2011, 39(2): 190-194.
[56] 刘功鹏. 山东莱州湾海域波浪数值模拟研究[J]. 水利水电快报, 2020, 41(4):57-60
LIU Gongpeng. Numerical simulation of waves in Shandong Laizhou Bay [J]. Express Water Resources & Hydropower Information, 2020, 41(4): 57-60.
[57] 顾杰, 马悦, 王佳元, 等. 洋河-葡萄岛岸段养滩工程波浪响应特征研究[J]. 水动力学研究与进展, 2017, 32(1):18-24
GU Jie, MA Yue, WANG Jiayuan, et al. Wave responses to beach nourishment at coast between Yang River and Putao Island [J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2017, 32(1): 18-24.
[58] 张蔚, 严以新, 郑金海, 等. 珠江三角洲年际潮差长期变化趋势[J]. 水科学进展, 2010, 21(1):77-83
ZHANG Wei, YAN Yixin, ZHENG Jinhai, et al. Interannual tidal range trend in Pearl River Delta [J]. Advances in Water Science, 2010, 21(1): 77-83.
[59] 蒋陈娟, 周佳楠, 杨清书. 珠江磨刀门河口潮汐动力变化对人类活动的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(6):66-76
JIANG Chenjuan, ZHOU Jianan, YANG Qingshu. Effects of human intervention on tidal dynamics in the Modaomen Estuary, Pearl River [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(6): 66-76.
[60] 金中武, 卢金友, 吴华莉. 铜锣峡壅水作用机理研究[J]. 水动力学研究与进展, 2014, 29(5):552-564
JIN Zhongwu, LU Jinyou, WU Huali. Study on the mechanison of backwater effect in Tongluoxia Gorge [J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2014, 29(5): 552-564.
[61] 张莞君, 迟万清, 胡泽建, 等. 青岛胶州湾大桥建设对周边海域水动力环境影响的数值研究[J]. 海岸工程, 2015, 34(2):40-50 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2015.02.005
ZHANG Wanjun, CHI Wanqing, HU Zejian, et al. Numerical study on the effect of the Jiaozhou bay bridge construction on the hydrodynamic conditions in the surrounding sea area [J]. Coastal Engineering, 2015, 34(2): 40-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2015.02.005
[62] 姜胜辉, 朱龙海, 胡日军, 等. 围填海工程对莱州湾水动力条件的影响[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2015, 45(10):74-80
JIANG Shenghui, ZHU Longhai, HU Rijun, et al. The hydrodynamic response to reclamation in Laizhou Bay [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2015, 45(10): 74-80.
[63] 王勇智, 孙惠凤, 谷东起, 等. 罗源湾多年围填海工程对水动力环境的累积影响研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2015, 45(3):16-24
WANG Yongzhi, SUN Huifeng, GU Dongqi, et al. Research on Cumulative effects of coastal reclamation on hydrodynamic environment in Luoyuan Bay [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2015, 45(3): 16-24.
[64] 刘明, 席小慧, 雷利元, 等. 锦州湾围填海工程对海湾水交换能力的影响[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 2013, 28(1):110-114 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1388.2013.01.021
LIU Ming, XI Xiaohui, LEI Liyuan, et al. The effects of coastal reclamation on hydrodynamics in Jinzhou Bay [J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 2013, 28(1): 110-114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1388.2013.01.021
[65] 朱金龙, 朱淑香, 魏潇, 等. 围填海影响下的芝罘湾水动力变化的数值研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2020(6):61-71
ZHU Jinlong, ZHU Shuxiang, WEI Xiao, et al. Numerical simulation study on hydrodynamic changes of Zhifu Bay under the influence of reclamation [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2020(6): 61-71.
[66] 张志飞, 诸裕良, 何杰. 多年围填海工程对湛江湾水动力环境的影响[J]. 水利水运工程学报, 2016(3):96-104
ZHANG Zhifei, ZHU Yuliang, HE Jie. Influences of long term reclamation works on hydrodynamic environment in Zhanjiang bay [J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2016(3): 96-104.
[67] 曾相明, 管卫兵, 潘冲. 象山港多年围填海工程对水动力影响的累积效应[J]. 海洋学研究, 2011, 29(1):73-83 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2011.01.011
ZENG Xiangming, GUAN Weibing, PAN Chong. Cumulative influence of long term reclamation on hydrodynamics in the Xiangshangang Bay [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2011, 29(1): 73-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2011.01.011
[68] 胡建宇. 罗源湾海水与外海水的交换研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 1998, 17(3):51-54
HU Jianyu. Study on the sea water exchange between the open sea and Luoyuan Bay [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 1998, 17(3): 51-54.
-




 下载:
下载: