Tempo-spatial variation of wetlands at the Yellow River Mouth and its control factors
-
摘要:
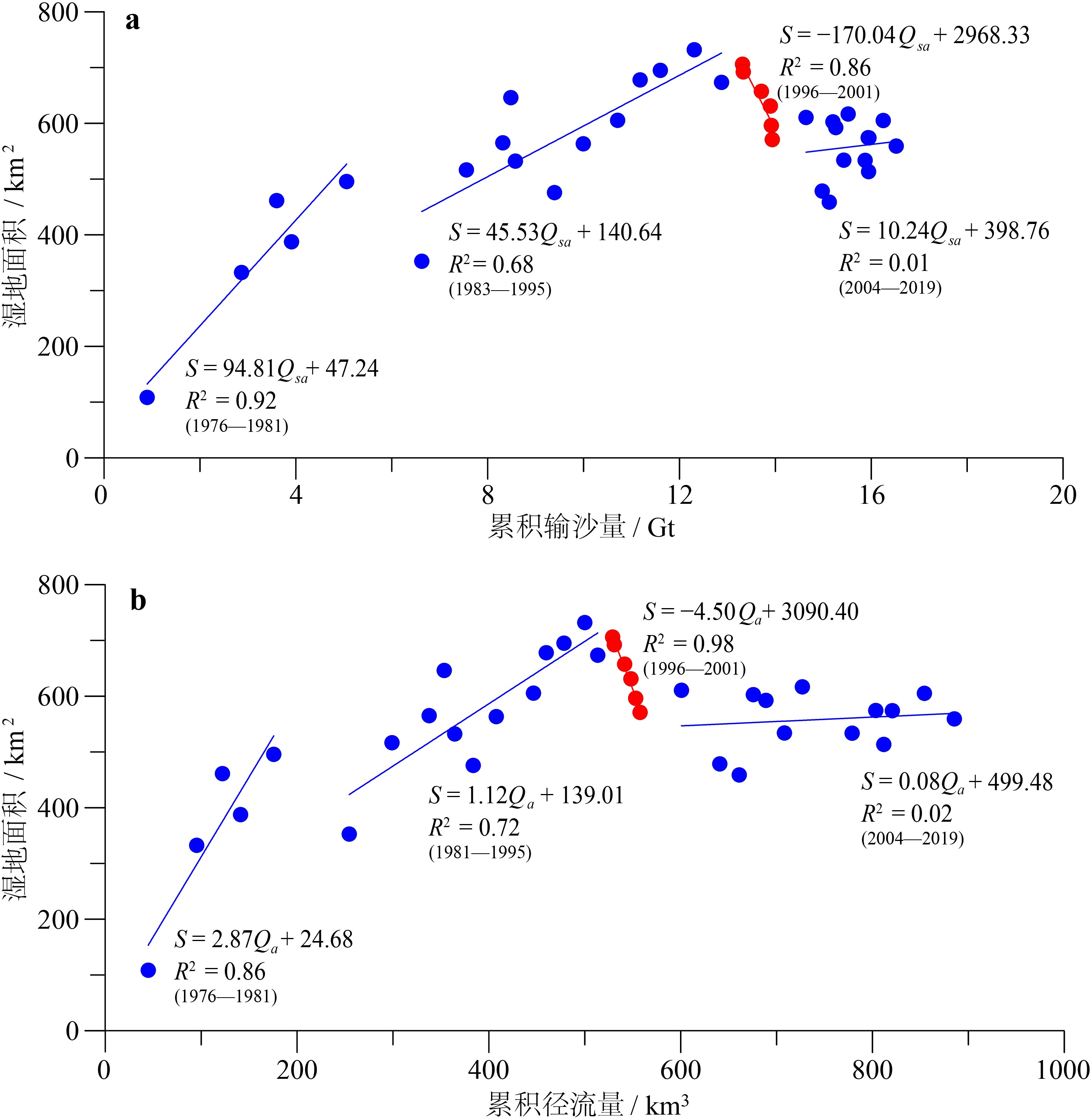
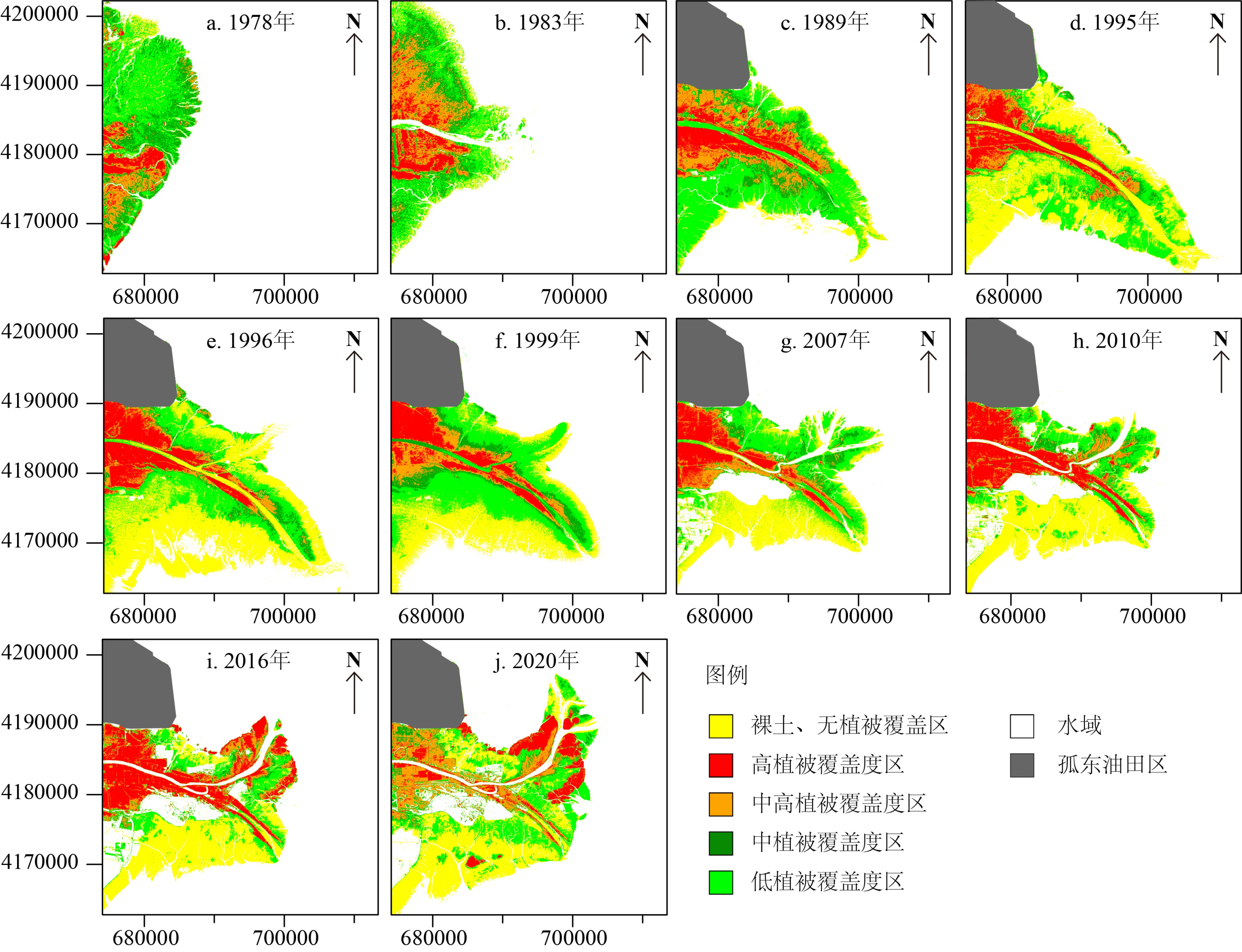
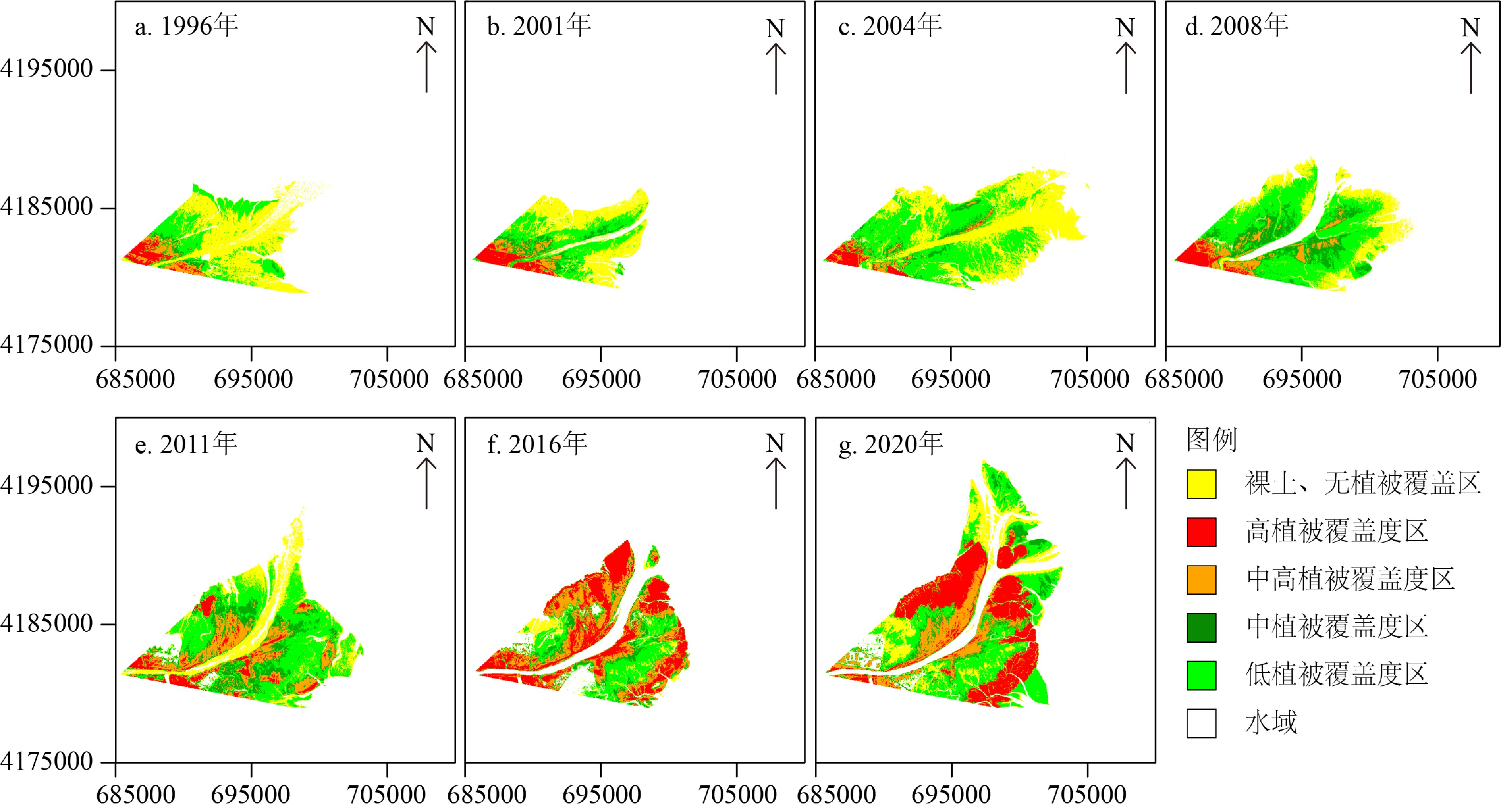
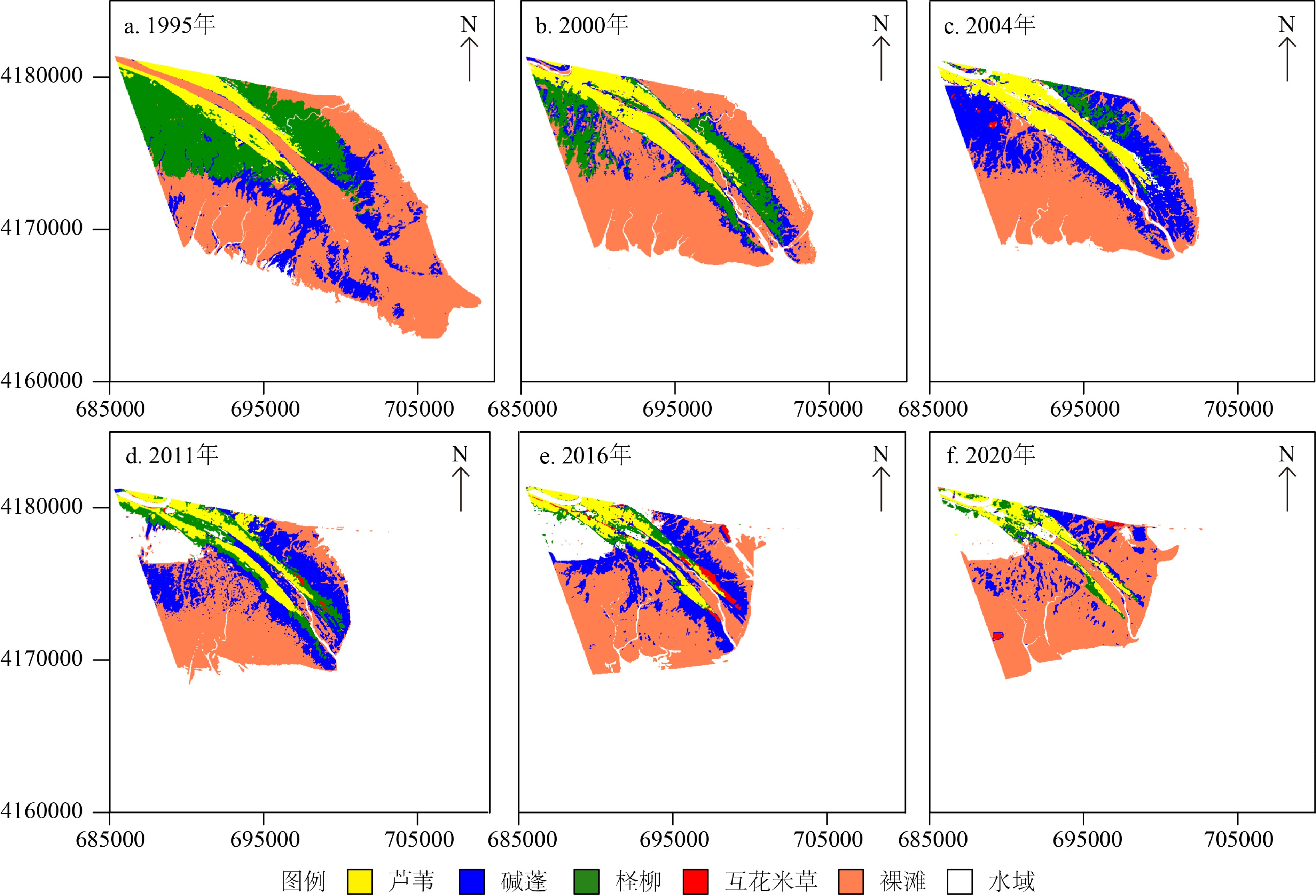
基于1976—2020年Landsat卫星长时间序列遥感影像开展研究工作,结合黄河水沙资料、河口沉积动力机制研究及人类活动影响,研究了黄河口湿地植被时空变化过程,对比揭示了清8汊(行水)和清水沟(废弃)不同流路湿地演化的差异,探讨黄河口湿地植被时空变化的影响因素。结果表明:① 黄河口湿地在发育过程中呈现了显著的阶段性和空间差异性变化,总体上经历了快速增加、稳定增长、快速蚀退、相对稳定四个阶段。② 现行清8河口湿地变化的主控因素为黄河入海径流量和输沙量,湿地面积与入海水沙量呈显著正相关,植被覆盖与黄河改道、调水调沙等人类活动密切相关。③ 废弃清水沟叶瓣湿地时空变化的主控因素为海洋动力作用下的海岸侵蚀。1996年废弃之后湿地面积随海岸侵蚀加剧而快速减少,同时潮汐不对称导致废弃河道再充填以及海水入侵在一定程度上改变了河道两侧湿地植被的生境,植被覆盖面积总体上逐渐减小。
Abstract:Based on the long-term series data retrieved from the Landsat remote sensing images (1976—2020), this paper is devoted to the study of tempo-spatial variations of wetlands in the present Yellow River deltaic lobe since the last channel shifting in 1976. Significant differences in the distribution pattern of wetlands are observed for the present (Q8) and the abandoned (Qingshuigou) river mouths. The wetlands in the current deltaic lobe have experienced four stages of temporal and spatial variations with time, i.e the stages of rapid accretion, stable growing, rapid erosion and relatively stable. The wetland growth at the present active Q8 river mouth is primarily dominated by the water and sediment discharges from the upper reach of the river associated with sedimentation off the river mouth, particularly after the water-sediment regulation since 2002. In contrast, the spatial-temporal variation of the abandoned Qingshuigou wetlands is dominated by tidal and wave erosion induced by estuary dynamics. The wetland retreats rapidly together with the increasing coastal erosion and channel refilling, by which vegetation habitat on both sides of the abandoned channel are destroyed. In combination with the Yellow River’s water and sediment discharge, the dynamic mechanism dominating the wetland evolution is discussed in this paper, that is important to the countermeasures for future conservation and restoration of wetlands.
-
Key words:
- wetland evolution /
- sediment transport /
- human activities /
- ocean dynamics /
- Yellow River Delta
-

-
表 1 Landsat遥感影像数据信息(1976—2020)
Table 1. Information of Landsat imagery (1976—2020)
日期 传感器 波段数 分辨率/m 日期 传感器 波段数 分辨率/m 1976-08-31 MSS 4 79 1998-09-10 TM 7 30 1978-08-30 MSS 4 79 1999-08-28 TM 7 30 1979-08-25 MSS 4 79 2000-09-15 TM 7 30 1980-07-14 MSS 4 79 2001-09-02 TM 7 30 1981-09-19 MSS 4 79 2004-09-10 TM 7 30 1983-07-07 MSS 4 79 2006-10-26 ETM+ 8 30 1984-09-11 MSS 4 79 2007-09-11 ETM+ 8 30 1985-09-06 TM 7 30 2008-09-05 TM 7 30 1986-08-08 TM 7 30 2009-08-23 TM 7 30 1987-08-11 TM 7 30 2010-09-11 TM 7 30 1988-06-10 TM 7 30 2011-09-22 ETM+ 8 30 1989-09-01 TM 7 30 2013-09-03 OLI 11 30 1991-09-23 TM 7 30 2015-06-05 OLI 11 30 1992-08-24 TM 7 30 2016-08-26 OLI 11 30 1993-09-28 TM 7 30 2017-09-30 OLI 11 30 1994-10-17 TM 7 30 2018-09-17 OLI 11 30 1995-09-18 TM 7 30 2019-08-19 OLI 11 30 1996-08-19 TM 7 30 2020-10-24 OLI 11 30 1997-09-07 TM 7 30 表 3 不同传感器中NDVI各波段对应值
Table 3. Band of NDVI in different Landsat sensors
传感器波段 MSS TM ETM+ OLI RED 3 3 3 4 NIR 4 4 4 5 表 4 不同传感器中MNDWI各波段对应值
Table 4. Band of MNDWI in different Landsat sensors
传感器波段 TM ETM+ OLI GREEN 2 2 3 MIR 5 5 6 表 5 植被覆盖度等级划分标准
Table 5. Rank of fractional vegetation cover
序号 植被覆盖度 覆盖等级 1 Fvc<10% 裸土或无植被覆盖 2 10%≤Fvc≤30% 低植被覆盖度 3 30%≤Fvc≤50% 中植被覆盖度 4 50%≤Fvc≤80% 中高植被覆盖度 5 Fvc>80% 高植被覆盖度 -
[1] 孙广友. 中国湿地科学的进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 2000, 15(6):666-672 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2000.06.008
SUN Guangyou. Development and prospect of wetland science in China [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2000, 15(6): 666-672. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2000.06.008
[2] 段晓男, 王效科, 尹弢, 等. 湿地生态系统固碳潜力研究进展[J]. 生态环境, 2006, 15(5):1091-1095
DUAN Xiaonan, WANG Xiaoke, YIN Tao, et al. Advance in the studies on carbon sequestration potential of wetland ecosystem [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2006, 15(5): 1091-1095.
[3] Schimel D S. Terrestrial ecosystems and the carbon cycle [J]. Global Change Biology, 1995, 1(1): 77-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.1995.tb00008.x
[4] 陈亮, 何厚军, 申源, 等. 黄河三角洲湿地遥感监测与生态评估技术研究[M]. 郑州: 黄河水利出版社, 2015.
CHEN Liang, HE Houjun, SHEN Yuan, et al. Research on Remote Sensing Monitoring and Ecological Assessment Technology of Wetland in Yellow River Delta[M]. Zhengzhou: The Yellow River Water Conservancy Press, 2015.
[5] 安树青. 湿地生态工程: 湿地资源利用与保护的优化模式[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2003.
AN Shuqing. Ecological Engineering of Wetland: Optimized Model for Utilization and Protection of Wetland Resources[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2003.
[6] Wu X, Wang H J, Bi N S, et al. Evolution of a tide-dominated abandoned channel: a case of the abandoned Qingshuigou course, Yellow River [J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 422: 106116. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106116
[7] Wang H J, Yang Z S, Saito Y, et al. Interannual and seasonal variation of the Huanghe (Yellow River) water discharge over the past 50 years: Connections to impacts from ENSO events and dams [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2006, 50(3-4): 212-225. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2006.01.005
[8] Wang H J, Yang Z S, Saito Y, et al. Stepwise decreases of the Huanghe (Yellow River) sediment load (1950–2005): Impacts of climate change and human activities [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2007, 57(3-4): 331-354. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2007.01.003
[9] Wu X, Bi N S, Xu J P, et al. Stepwise morphological evolution of the active Yellow River (Huanghe) delta lobe (1976—2013): dominant roles of riverine discharge and sediment grain size [J]. Geomorphology, 2017, 292: 115-127. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.04.042
[10] 徐振田, Ali S, 张莎, 等. 基于Landsat数据的黄河三角洲湿地提取及近30年动态研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2020(3):70-79
XU Zhentian, Ali S, ZHANG Sha, et al. Mapping the wetland in Yellow River delta and its dynamics in recent 30 years based on Landsat data [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2020(3): 70-79.
[11] Beck P S A, Atzberger C, Høgda K A, et al. Improved monitoring of vegetation dynamics at very high latitudes: a new method using MODIS NDVI [J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2006, 100(3): 321-334. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2005.10.021
[12] 贾维花, 廉丽姝, 吕宜平. 基于TM数据的黄河三角洲地区植被覆盖度提取[J]. 地理信息世界, 2012, 10(6):62-66, 74 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1586.2012.06.013
JIA Weihua, LIAN Lishu, LV Yiping. The derivation of vegetation fraction based on TM data in Yellow River delta [J]. Geomatics World, 2012, 10(6): 62-66, 74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1586.2012.06.013
[13] 李苗苗, 吴炳方, 颜长珍, 等. 密云水库上游植被覆盖度的遥感估算[J]. 资源科学, 2004, 26(4):153-159 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2004.04.022
LI Miaomiao, WU Bingfang, YAN Changzhen, et al. Estimation of vegetation fraction in the upper basin of Miyun reservoir by remote sensing [J]. Resources Science, 2004, 26(4): 153-159. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2004.04.022
[14] Wu X, Bi N S, Yuan P, et al. Sediment dispersal and accumulation off the present Huanghe (Yellow River) delta as impacted by the water-sediment regulation scheme [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2015, 111: 126-138. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2015.11.003
[15] 刘波, 彭相楷, 束龙仓, 等. 黄河三角洲清水沟湿地三次生态补水对地下水的影响分析[J]. 湿地科学, 2015, 13(4):393-399
LIU Bo, PENG Xiangkai, SHU Longcang, et al. An analysis of effect of three water ecological diversions on groundwater of Qingshuigou wetlands in the Yellow River delta [J]. Wetland Science, 2015, 13(4): 393-399.
[16] 李晓敏, 张杰, 马毅, 等. 基于无人机高光谱的外来入侵种互花米草遥感监测方法研究: 以黄河三角洲为研究区[J]. 海洋科学, 2017, 41(4):98-107 doi: 10.11759/hykx20161102002
LI Xiaomin, ZHANG Jie, MA Yi, et al. Study on monitoring alien invasive species Spartina alterniflora using unmanned aerial vehicle hyperspectral remote sensing- a case study of the Yellow River delta [J]. Marine Sciences, 2017, 41(4): 98-107. doi: 10.11759/hykx20161102002
-




 下载:
下载: