Trace elements geochemistry of marine sediments and its implications for gas hydrate exploration
-
摘要:
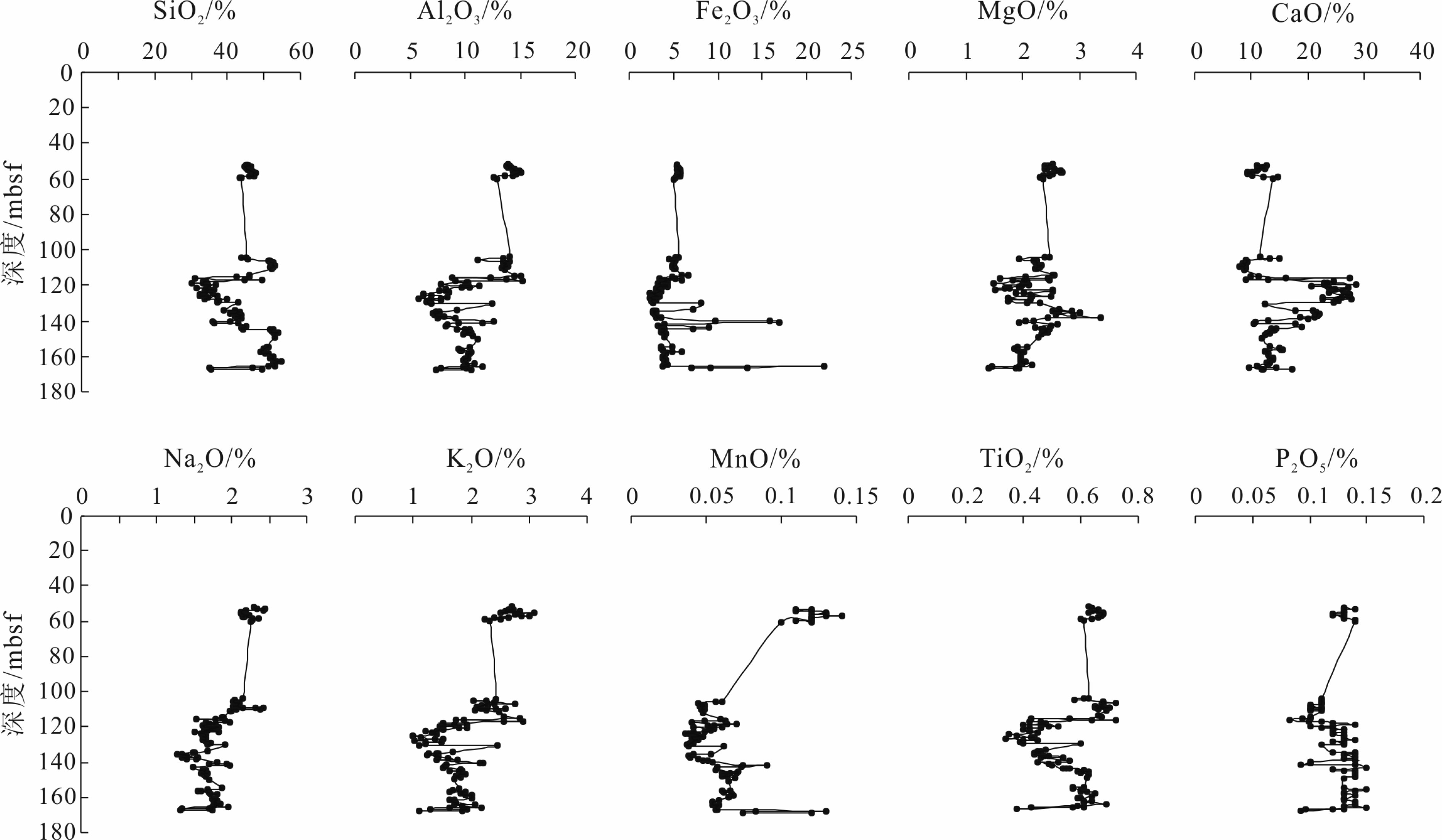
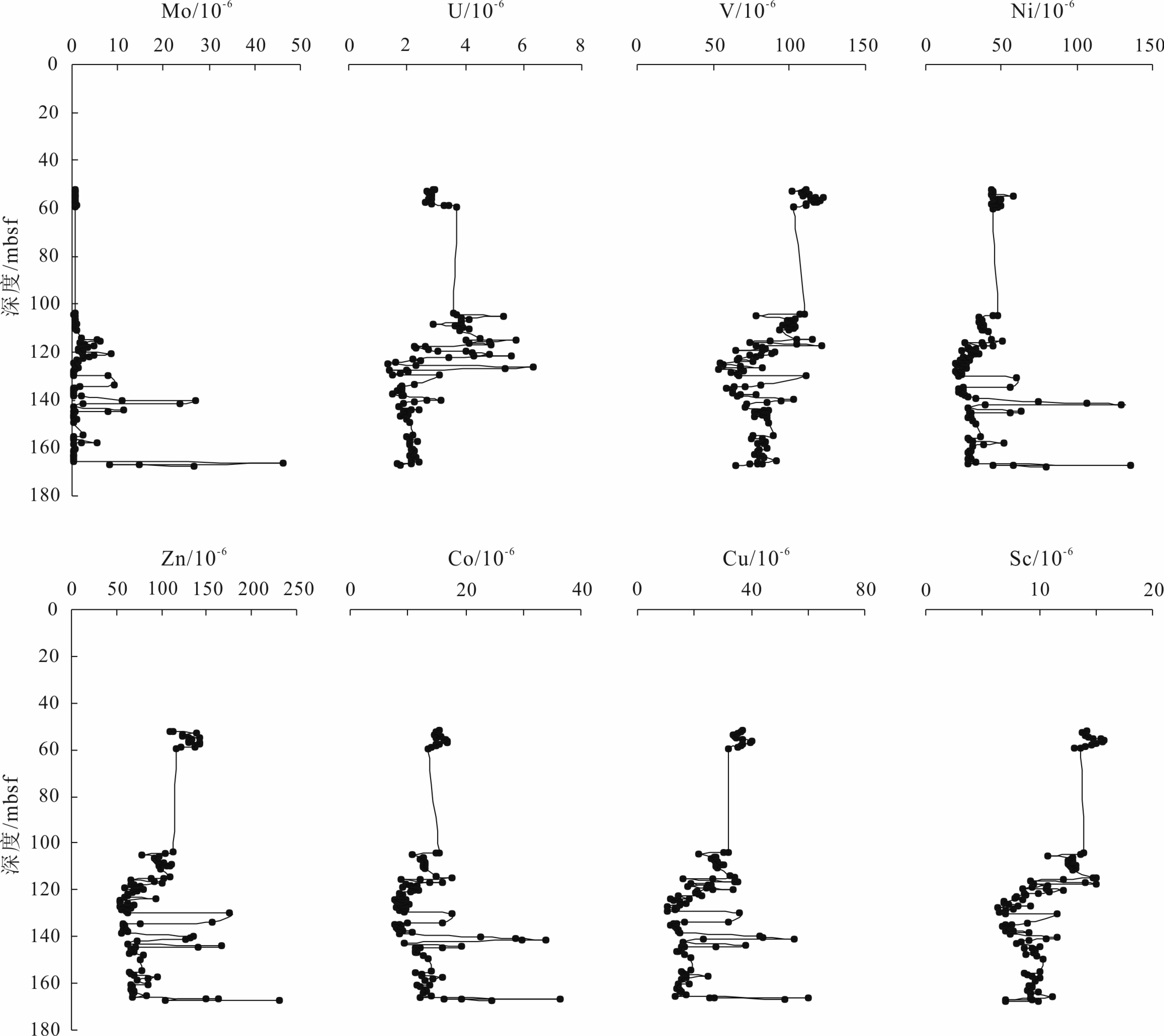
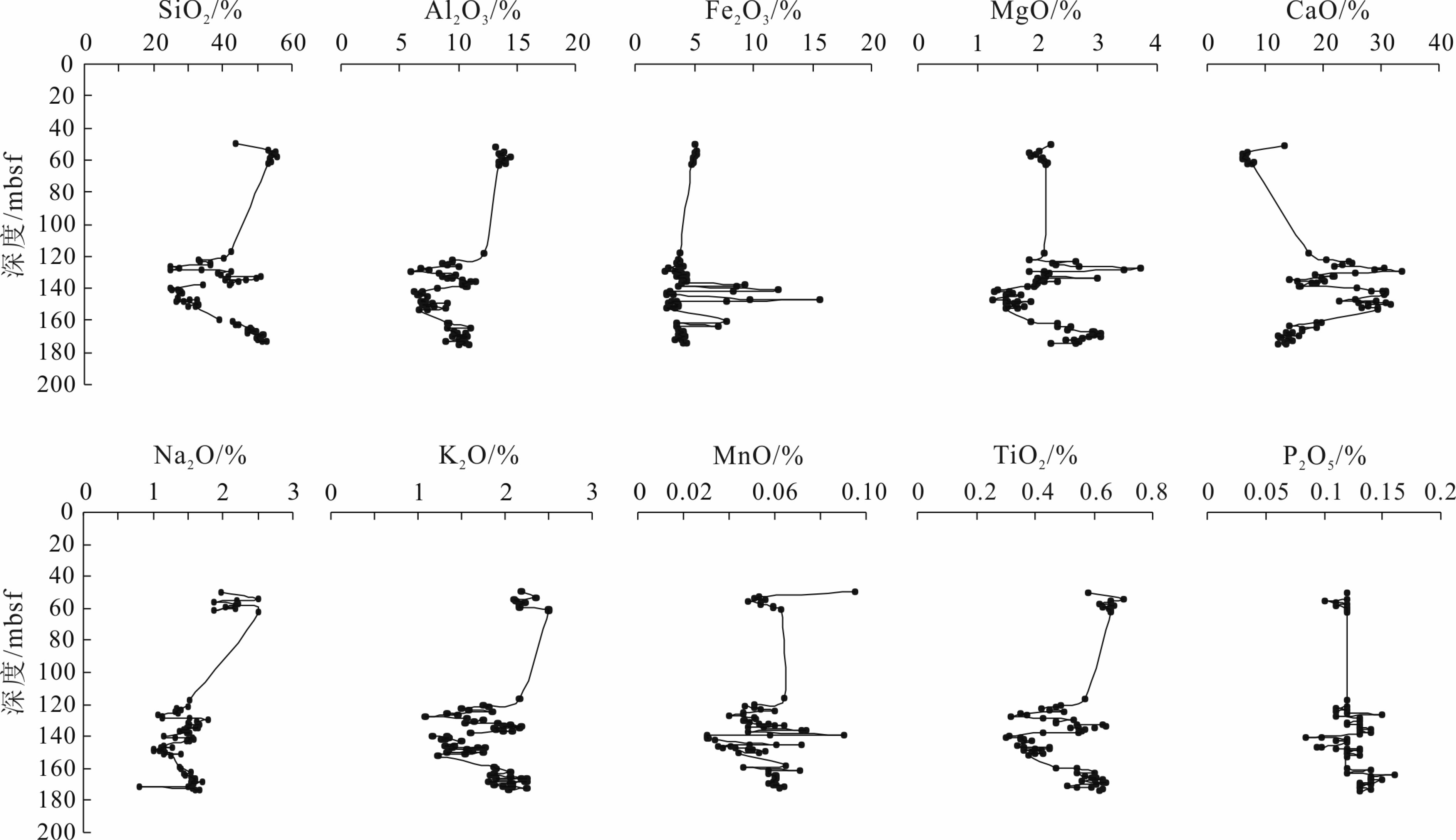
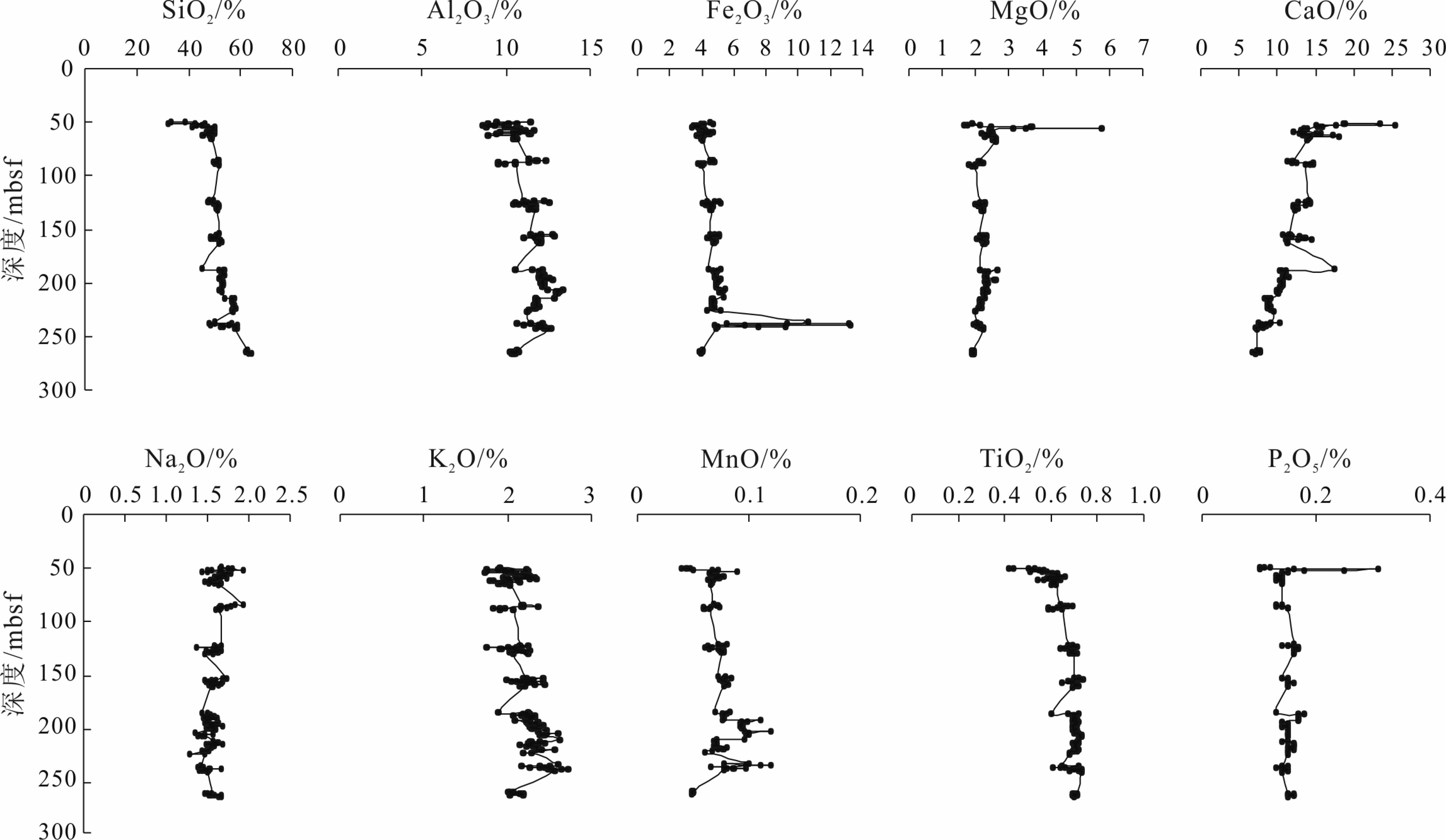
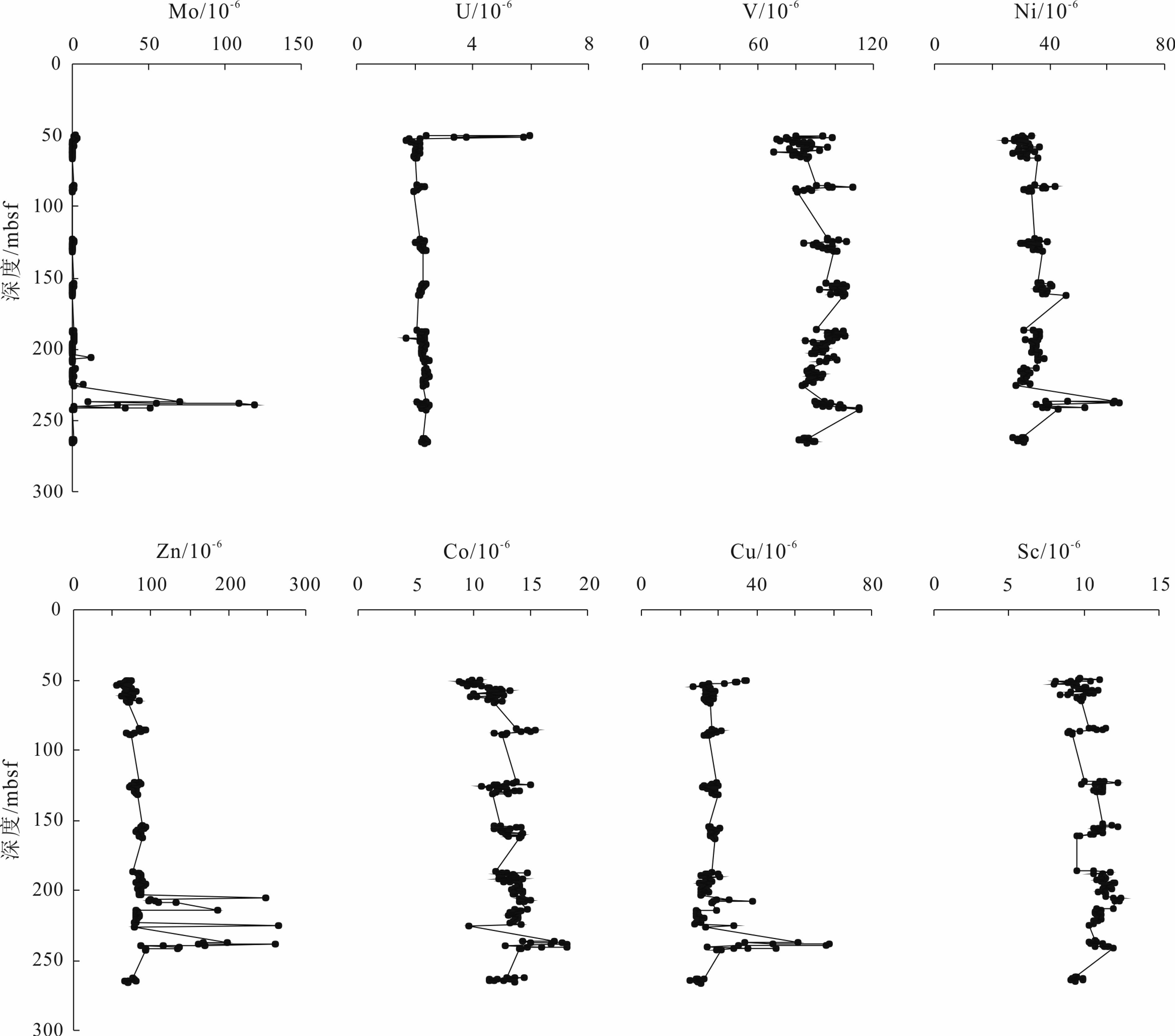
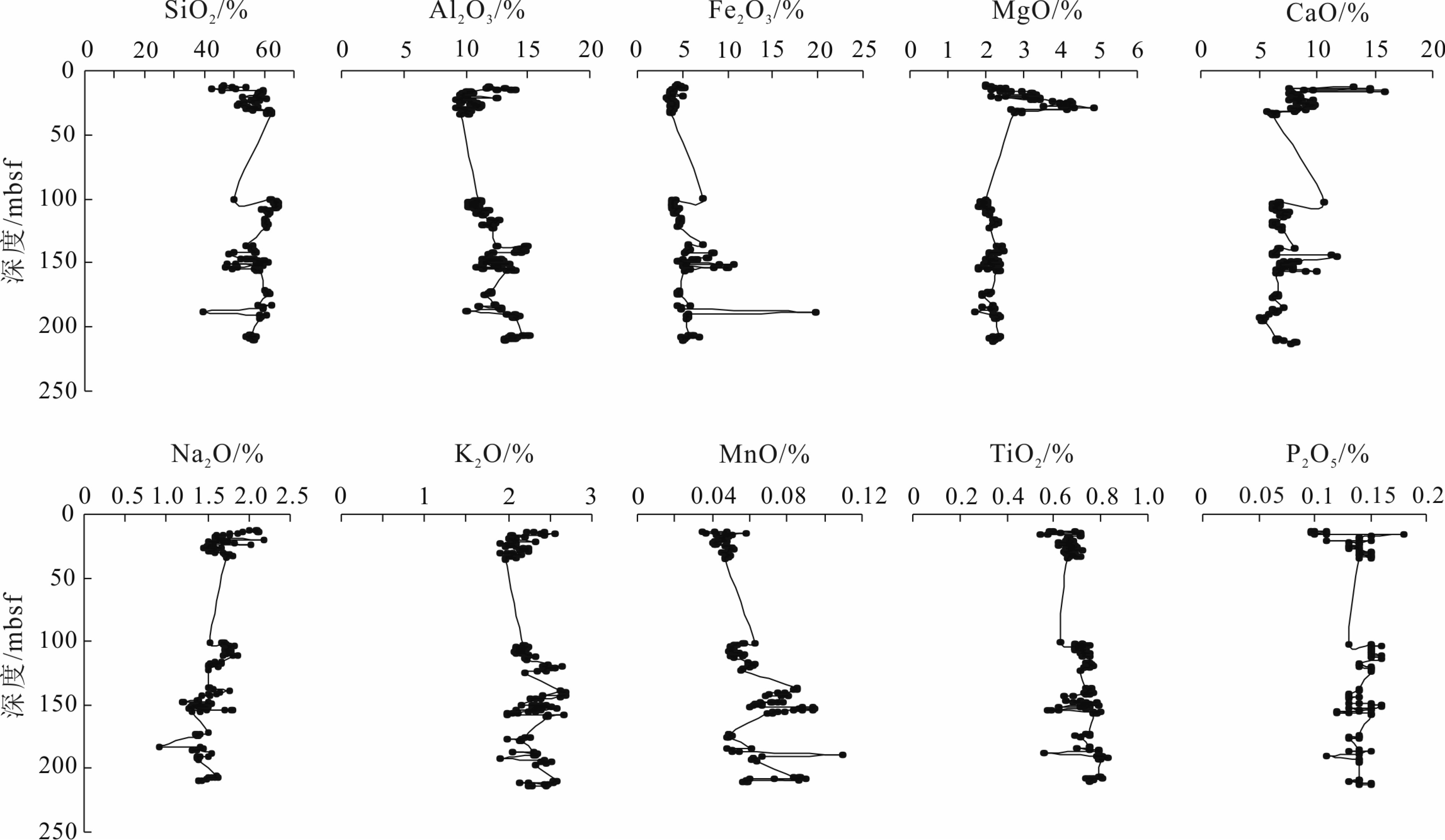
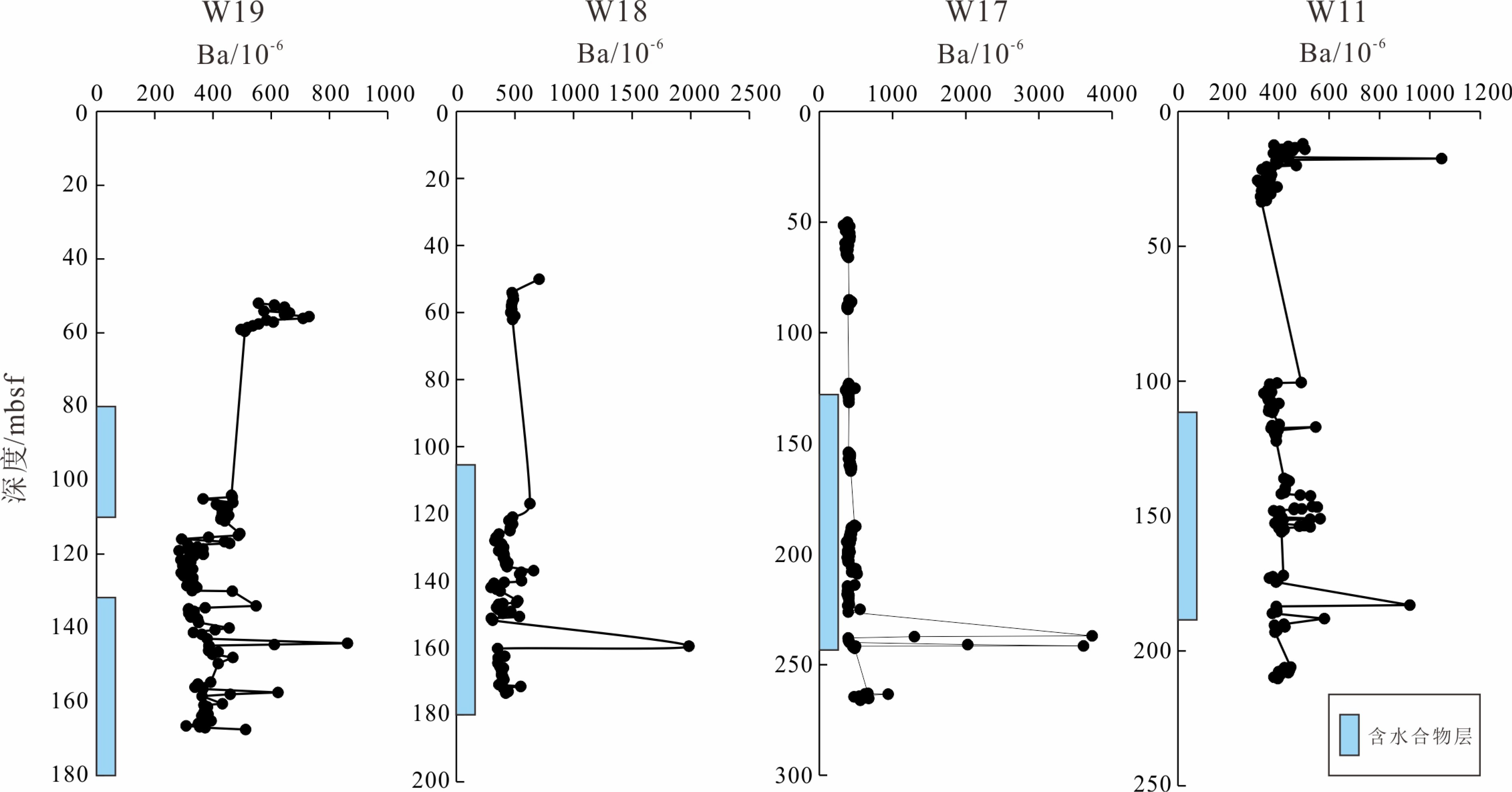
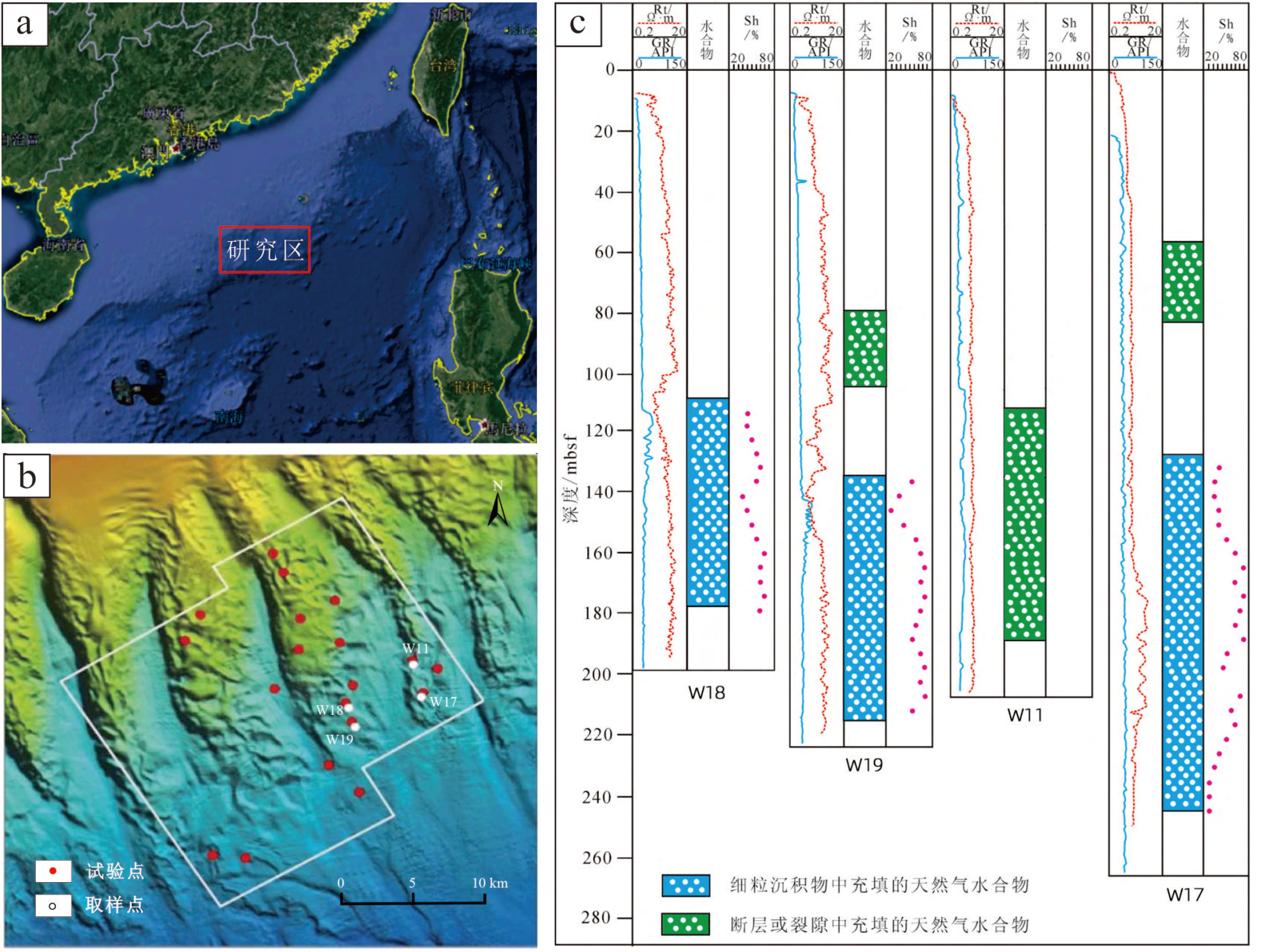
天然气水合物与资源和全球环境变化等重大科学问题密切相关。前期关于甲烷渗漏区地球化学特征的研究主要集中于浅表层沉积物(<20 m),而浅层沉积物(>20 m)地球化学特征知之甚少。为探讨海洋浅层沉积物微量元素特征与天然气水合物勘探的相关关系,对南海神狐海域沉积物进行了4个站位的钻探取样,分析了样品主、微量元素和有机碳地球化学特征,并采用氧化还原状态以及Mo与TOC相关关系的分析方法进行探讨。结果显示,沉积物主量元素特征主要受到陆源碎屑物质输入的主导,与天然气水合物富集无明显关系。水合物赋存段及附近沉积物中Ba和Mo元素高度富集,存在明显的“Ba峰”和“Mo峰”,主要是由于天然气水合物分解释放大量甲烷产生的硫化环境所导致。因此,沉积物中的Ba和Mo富集特征可作为识别可能存在天然气水合物分布的重要地球化学指标。
Abstract:Gas hydrate is closely related to some major scientific issues such as energy supply and global environmental changes, and has become one of the hotspots of the world. Previous studies of the geochemical characteristics of methane seepage areas were mainly focused on shallow sediments, while the geochemical characteristics of deep sediments are ignored to certain extent. In order to explore the relationship between gas hydrate and the characteristics of trace elements in deeper sediments, 4 holes have been drilled and sampled at the Shenhu area of the South China Sea. Main, trace elements and organic carbon geochemical characteristics of the samples are analyzed and the oxidation-reduction state and their correlation with Mo and TOC discussed. The results suggest that the major elements in the sediments mainly come from terrigenous clastic material input, without obvious relationship with the process of gas hydrate enrichment. In the area rich in natural gas hydrate, Ba and Mo elements are always highly enriched showing obvious "Ba peaks" and "Mo peaks" owing to the sulfidation environment caused by the decomposition of natural gas hydrates. Therefore, the enrichment of Ba and Mo in the sediments can be used as important geochemical indicators to possible presence of gas hydrate accumulation.
-
Key words:
- trace elements /
- gas hydrate drilling /
- marine sediments /
- the South China Sea
-

-
[1] Dickens G R, O'Neil J R, Rea D K, et al. Dissociation of oceanic methane hydrate as a cause of the carbon isotope excursion at the end of the Paleocene [J]. Paleoceanography, 1995, 10(6): 965-971. doi: 10.1029/95PA02087
[2] Hesselbo S P, Gröcke D R, Jenkyns H C, et al. Massive dissociation of gas hydrate during a Jurassic oceanic anoxic event [J]. Nature, 2000, 406(6794): 392-395. doi: 10.1038/35019044
[3] Milkov A V, Sassen R. Preliminary assessment of resources and economic potential of individual gas hydrate accumulations in the Gulf of Mexico continental slope [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2003, 20(2): 111-128. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(03)00024-2
[4] Maslin M, Owen M, Day S, et al. Linking continental-slope failures and climate change: Testing the clathrate gun hypothesis [J]. Geology, 2004, 32(1): 53-56. doi: 10.1130/G20114.1
[5] Wellsbury P, Goodman K, Cragg B A, et al. The geomicrobiology of deep marine sediments from Blake ridge containing methane hydrate (sites 994, 995, and 997)[M]//Paull C K, Matsumoto R, Wallace P, et al. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program Scientific Results. College Station, TX: Ocean Drilling Program, 2000, 164: 379-391.
[6] 邓希光, 吴庐山, 付少英, 等. 南海北部天然气水合物研究进展[J]. 海洋学研究, 2008, 26(2):67-74 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2008.02.010
DENG Xiguang, WU Lushan, FU Shaoying, et al. The research advances of natural gas hydrates in northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Marine Science, 2008, 26(2): 67-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2008.02.010
[7] 吴能友, 梁金强, 王宏斌, 等. 海洋天然气水合物成藏系统研究进展[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(3):356-362 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.003
WU Nengyou, LIANG Jinqiang, WANG Hongbin, et al. Marine gas hydrate system: state of the art [J]. Geoscience, 2008, 22(3): 356-362. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.003
[8] 姚伯初, 杨木壮, 吴时国, 等. 中国海域的天然气水合物资源[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(3):333-341 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.001
YAO Bochu, YANG Muzhuang, WU Shiguo, et al. The gas hydrate resources in the China seas [J]. Geoscience, 2008, 22(3): 333-341. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.001
[9] 何家雄, 卢振权, 张伟, 等. 南海北部珠江口盆地深水区天然气水合物成因类型及成矿成藏模式[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(5):1024-1034 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.05.005
HE Jiaxiong, LU Zhengquan, ZHANG Wei, et al. Biogenetic and Sub-biogenetic gas resource and genetic types of natural gas hydrates in Pearl River Mouth Basin, Northern Area of South China Sea [J]. Geoscience, 2015, 29(5): 1024-1034. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.05.005
[10] Deng Y N, Chen F, Hu Y, et al. Methane seepage patterns during the middle Pleistocene inferred from molybdenum enrichments of seep carbonates in the South China Sea [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 125: 103701. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103701
[11] Chen F, Hu Y, Feng D, et al. Evidence of intense methane seepages from molybdenum enrichments in gas hydrate-bearing sediments of the northern South China Sea [J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 443: 173-181. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.09.029
[12] 邓义楠, 方允鑫, 张欣, 等. 南海琼东南海域沉积物的微量元素地球化学特征及其对天然气水合物的指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(5):70-81
DENG Yi’nan, FANG Yunxin, ZHANG Xin, et al. Trace element geochemistry of sediments in Qiongdongnan area, the South China Sea, and its implications for gas hydrates [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(5): 70-81.
[13] 冯东, 陈多福. 海底沉积物孔隙水钡循环对天然气渗漏的指示[J]. 地球科学进展, 2007, 22(1):49-57 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2007.01.007
FENG Dong, CHEN Duofu. Barium Cycling in pore water of seafloor sediment: indicator of methane fluxes [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2007, 22(1): 49-57. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2007.01.007
[14] 吴庐山, 杨胜雄, 梁金强, 等. 南海北部琼东南海域HQ-48PC站位地球化学特征及对天然气水合物的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(3):534-544 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.03.018
WU Lushan, YANG Shengxiong, LIANG Jinqiang, et al. Geochemical characteristics of sediments at Site HQ-48PC in Qiongdongnan Area, the North of the South China Sea, and their implication for gas hydrates [J]. Geoscience, 2010, 24(3): 534-544. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.03.018
[15] Sato H, Hayashi K I, Ogawa Y, et al. Geochemistry of deep sea sediments at cold seep sites in the Nankai Trough: insights into the effect of anaerobic oxidation of methane [J]. Marine Geology, 2012, 323-325: 47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2012.07.013
[16] Feng D, Chen D F. Authigenic carbonates from an active cold seep of the northern South China Sea: New insights into fluid sources and past seepage activity [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2015, 122: 74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2015.02.003
[17] Ge L, Jiang S Y, Swennen R, et al. Chemical environments of cold seep carbonate formation on the northern continental slope of South China Sea: evidence from trace and rare earth element geochemistry [J]. Marine Geology, 2010, 277(1-4): 21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2010.08.008
[18] Hu Y, Feng D, Peckmann J, et al. New insights into cerium anomalies and mechanisms of trace metal enrichment in authigenic carbonate from hydrocarbon seeps [J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 381: 55-66. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.05.014
[19] Liang Q Y, Hu Y, Feng D, et al. Authigenic carbonates from newly discovered active cold seeps on the northwestern slope of the South China Sea: Constraints on fluid sources, formation environments, and seepage dynamics [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2017, 124: 31-41. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2017.04.015
[20] Zhang G X, Liang J Q, Lu J A, et al. Geological features, controlling factors and potential prospects of the gas hydrate occurrence in the east part of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 67: 356-367. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.05.021
[21] Feng D, Qiu J W, Hu Y, et al. Cold seep systems in the South China Sea: an overview [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 168: 3-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.09.021
[22] 张伟, 梁金强, 苏丕波, 等. 南海北部陆坡高饱和度天然气水合物气源运聚通道控藏作用[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(1):1-14 doi: 10.12029/gc20180101
ZHANG Wei, LIANG Jinqiang, SU Pibo, et al. Migrating pathways of hydrocarbons and their controlling effects associated with high saturation gas hydrate in Shenhu area, northern South China Sea [J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(1): 1-14. doi: 10.12029/gc20180101
[23] Dickens G R. Rethinking the global carbon cycle with a large, dynamic and microbially mediated gas hydrate capacitor [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 213(3-4): 169-183. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00325-X
[24] 冯东, 陈多福, 苏正, 等. 海底甲烷缺氧氧化与冷泉碳酸盐岩沉淀动力学研究进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(3):125-131
FENG Dong, CHEN Duofu, SU Zheng, et al. Anaerobic oxidation of methane and seep carbonate precipitation kinetics at seafloor [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(3): 125-131.
[25] Dickens G R. Sulfate profiles and barium fronts in sediment on the Blake Ridge: present and past methane fluxes through a large gas hydrate reservoir [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(4): 529-543. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00556-1
[26] Riedinger N, Kasten S, Gröger J, et al. Active and buried authigenic barite fronts in sediments from the Eastern Cape basin [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 241(3-4): 876-887. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.10.032
[27] Aloisi G, Wallmann K, Bollwerk S M, et al. The effect of dissolved barium on biogeochemical processes at cold seeps [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(8): 1735-1748.
[28] Torres M E, Bohrmann G, Dubé T E, et al. Formation of modern and Paleozoic stratiform barite at cold methane seeps on continental margins [J]. Geology, 2003, 31(10): 897-900. doi: 10.1130/G19652.1
[29] Berner R A. Diagenetic models of dissolved species in the interstitial waters of compacting sediments [J]. American Journal of Science, 1975, 275(1): 88-96. doi: 10.2475/ajs.275.1.88
[30] Helz G R, Miller C V, Charnock J M, et al. Mechanism of molybdenum removal from the sea and its concentration in black shales: EXAFS evidence [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(19): 3631-3642. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(96)00195-0
[31] Helz G R, Bura-Nakić E, Mikac N, et al. New model for molybdenum behavior in euxinic waters [J]. Chemical Geology, 2011, 284(3-4): 323-332. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.03.012
[32] Zheng Y, Anderson R F, Van Geen A, et al. Authigenic molybdenum formation in marine sediments: a link to pore water sulfide in the Santa Barbara Basin [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(24): 4165-4178. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00495-6
[33] Tribovillard N, Algeo T J, Lyons T, et al. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: an update [J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 232(1-2): 12-32. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.02.012
[34] Algeo T J, Maynard J B. Trace-element behavior and redox facies in core shales of Upper Pennsylvanian Kansas-type cyclothems [J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 206(3-4): 289-318. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2003.12.009
[35] Boetius A, Ravenschlag K, Schubert C J, et al. A marine microbial consortium apparently mediating anaerobic oxidation of methane [J]. Nature, 2000, 407(6804): 623-626. doi: 10.1038/35036572
[36] Algeo T J, Tribovillard N. Environmental analysis of paleoceanographic systems based on molybdenum-uranium covariation [J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 268(3-4): 211-225. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.09.001
[37] Ferré B, Jansson P G, Moser M, et al. Reduced methane seepage from Arctic sediments during cold bottom-water conditions [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2020, 13(2): 144-148. doi: 10.1038/s41561-019-0515-3
[38] Crémière A, Lepland A, Chand S, et al. Timescales of methane seepage on the Norwegian margin following collapse of the Scandinavian Ice Sheet [J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 11509. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11509
-



 下载:
下载: