Numerical modeling of the coupling between strike-slip faulting and sedimentation: A case from the Yangjiang Sag of northern South China Sea
-
摘要:
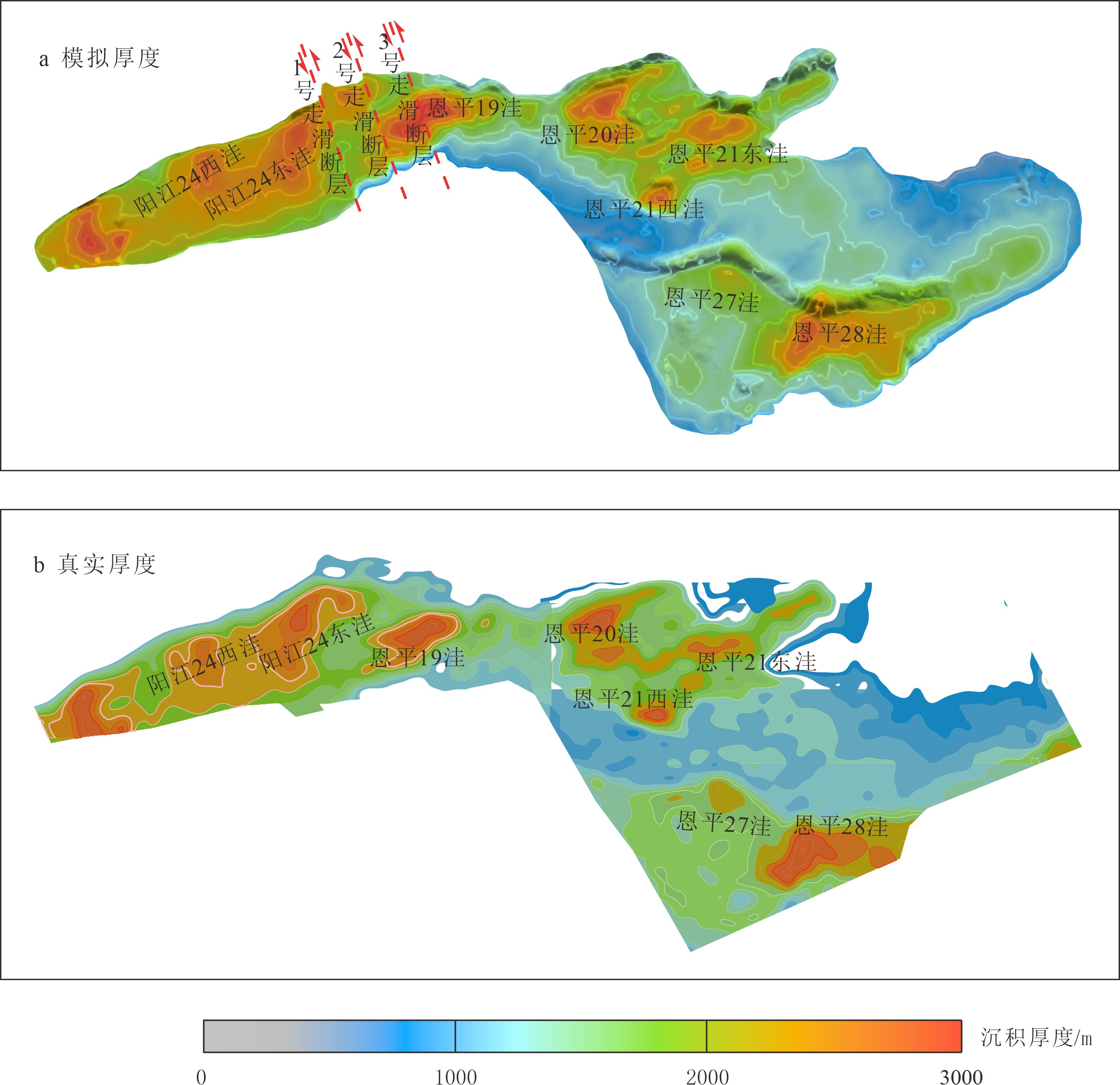
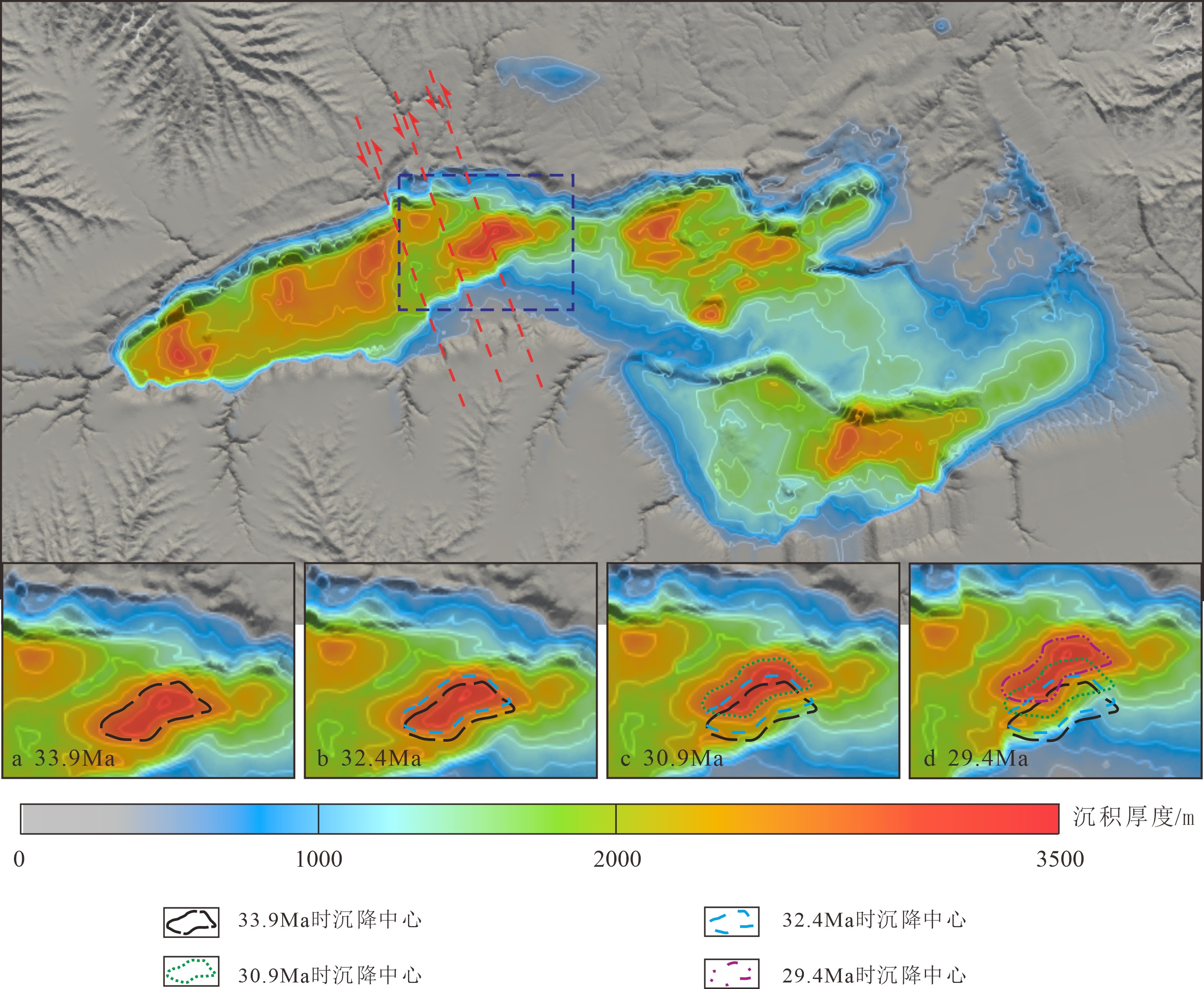
以构造变形为核心的内动力过程和以沉积“源–汇”过程为核心的外动力过程,如何动态塑造盆地精细地貌景观,是油气精准勘探必须突破的关键技术。本研究以南海北部陆缘珠江口盆地的阳江凹陷为例,试图探索NW向阳江–一统暗沙深大断裂带对周缘新生代沉降中心分布的控制作用。为此,本文采用Badlands沉积数值模拟方法,定量分析阳江–一统暗沙断裂带的运动学特征,模拟阳江凹陷新生代地层构造-沉积耦合过程。模拟结果显示,阳江–一统暗沙断裂带在始新世末期是一条左行走滑断裂带,其走滑过程主要可分为两个阶段。其中,在早期慢走滑阶段,走滑位移量约800 m,沿断裂带走滑方向,恩平19洼的沉降中心发生迁移;在后期快走滑阶段,走滑位移量约1200 m,模拟剖面可识别出明显的花状构造,恩平19洼的沉降中心加速向北迁移,并发生逆时针旋转。
-
关键词:
- 运动学性质 /
- 数值模拟 /
- 阳江–一统暗沙断裂带 /
- 阳江凹陷
Abstract:To dynamically shape the fine geomorphic landscape of a basin is a key technology required in efficient oil and gas exploration. In this paper, the Yangjiang Sag in the Pearl River Mouth Basin on the northern margin of the South China Sea is selected as a case to explore the NW-trending Yangjiang-Yitong’ansha Blind Fault Zone(YYBFZ) and its control over the distribution patterns of Cenozoic depocenters in its periphery. Badlands’ numerical sedimentation simulation is used to quantitatively analyze the kinematic characteristics of the YYBFZ for further understanding the Cenozoic tectono-sedimentary coupling process of the Yangjiang Sag. The simulation results suggest that the YYBFZ was a sinistral strike-slip fault zone formed by the end of Eocene, and the strike slip process can be divided into two stages. The early stage is a slow strike slip stage, with a strike-slip displacement of about 800 m, and the depocenters of the Enping 19 Subsag migrate along the slip direction of the fault; In the late stage, however, the slip was fast and the displacement of the strike slip may reach the figure about 1200 m, and along the simulation section, obvious flower-like structures are observed. At the same time, the depocenters of the Enping 19 Subsag accelerated its move northward with rotation anticlockwise.
-

-
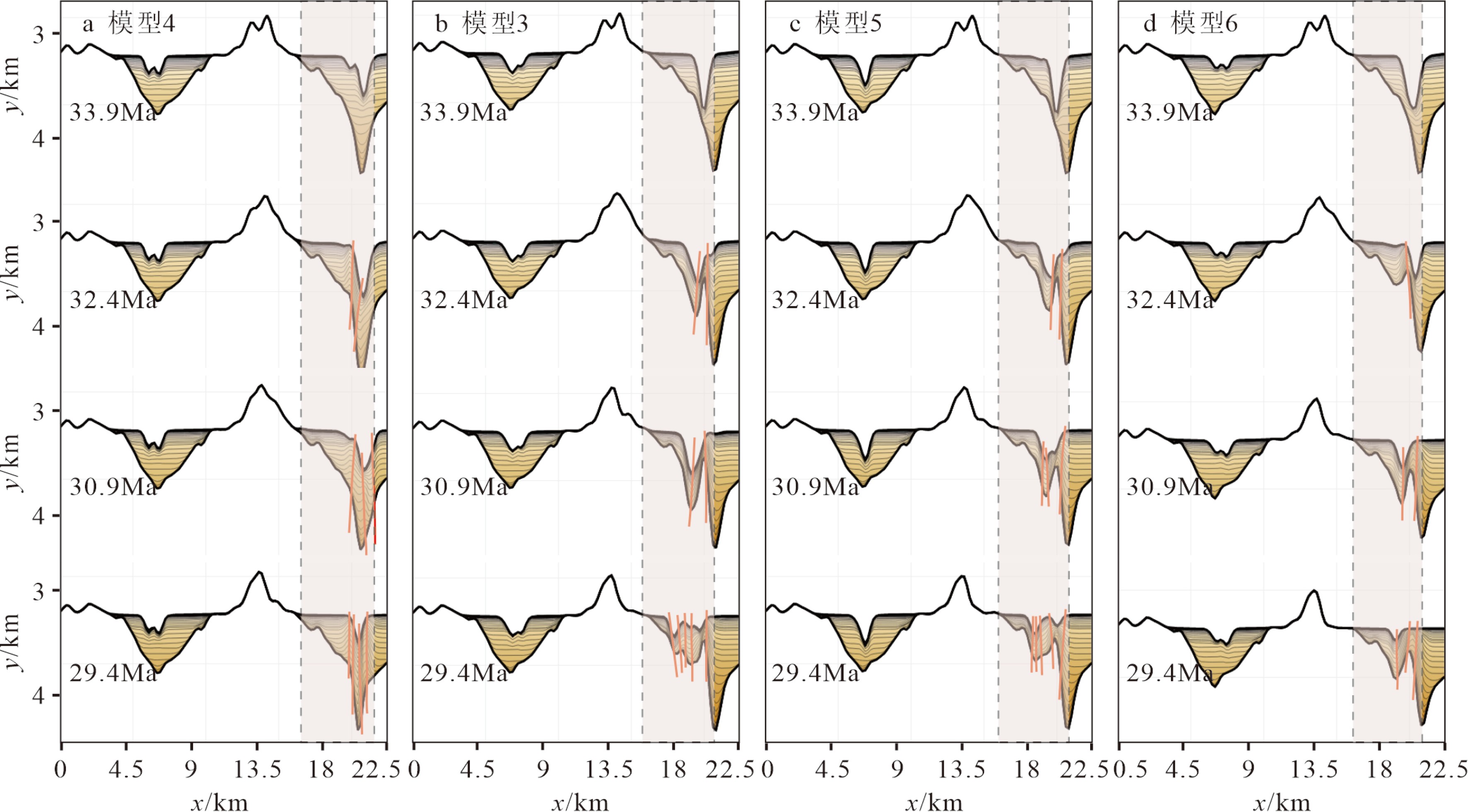
表 1 模型参数
Table 1. Model parameters
模型 模型1 模型2 模型3 模型4 模型5 模型6 性质 非走滑 右行 左行 左行 左行 左行 走滑量/m 2000 2000 2000 1500 2500 3000 侵蚀系数/a−1 3×10−7 3×10−7 3×10−7 3×10−7 3×10−7 3×10−7 降水量/(m/a) 1 1 1 1 1 1 -
[1] 姜衍, 张向涛, 龙祖烈, 等. 南海北部珠江口盆地烃源岩成因: 阳江凹陷的资源潜力[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1):90-107
JIANG Yan, ZHANG Xiangtao, LONG Zulie, et al. Formation of source rocks in the Pearl River mouth basin, northern south China sea: resource potential of the Yangjiang Sag [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 90-107.
[2] 杜晓东, 刘军, 徐乐意, 等. 南海北缘东部揭阳凹陷的东沙运动: 对油气成藏的影响[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1):201-210
DU Xiaodong, LIU Jun, XU Leyi, et al. The Dongsha movement in the Jieyang Sag at the Northern South China Sea Margin: control on hydrocarbon traps [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 201-210.
[3] 朱定伟, 彭光荣, 张忠涛, 等. 油气"穿断运移"模式、评价方法与应用: 以珠江口盆地恩平凹陷为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1):140-147
ZHU Dingwei, PENG Guangrong, ZHANG Zhongtao, et al. Model of oil-gas cross-fault migration, evaluation and application: a case in the Enping sag of pearl river mouth basin [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 140-147.
[4] 刘雨晴, 吴智平, 程燕君, 等. 南海北缘古近纪裂陷结构时空差异及控制因素: 以珠江口盆地为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2019, 48(2):367-376
LIU Yuqing, WU Zhiping, CHENG Yanjun, et al. Spatial and temporal difference of Paleogene rift structure and its controlling factors in the northern South China Sea: a case study of Pearl River Mouth basin [J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2019, 48(2): 367-376.
[5] 李三忠, 索艳慧, 刘鑫, 等. 南海的盆地群与盆地动力学[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(6):55-78
LI Sanzhong, SUO Yanhui, LIU Xin, et al. Basin dynamics and basin groups of the South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(6): 55-78.
[6] 程世秀, 李三忠, 索艳慧, 等. 南海北部新生代盆地群构造特征及其成因[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(6):79-93
CHENG Shixiu, LI Sanzhong, SUO Yanhui, et al. Cenozoic tectonics and dynamics of basin groups of the northern South China sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(6): 79-93.
[7] Tang X Y, Yang S C, Zhu J Z, et al. Tectonic subsidence of the Zhu 1 sub-basin in the pearl river mouth basin, northern South China Sea [J]. Frontiers of Earth Science, 2017, 11(4): 729-739. doi: 10.1007/s11707-016-0610-3
[8] Li Y J, Jiang Z L, Liang S, et al. Hydrocarbon generation in the lacustrine mudstones of the Wenchang formation in the Baiyun sag of the pearl river mouth basin, northern South China Sea [J]. Energy & Fuels, 2016, 30(1): 626-637.
[9] 吕宝凤, 殷征欣, 蔡周荣, 等. 南海北部新生代构造演化序列及其油气成藏意义[J]. 地质学报, 2012, 86(8):1249-1261 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.08.008
LV Baofeng, YIN Zhengxin, CAI Zhourong, et al. Cenozoic tectonic evolution sequence in northern South China Sea and its oil/gas singificance [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(8): 1249-1261. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.08.008
[10] Ma B S, Qi J F, Chen W C, et al. Fault interaction and evolution during two‐phase rifting in the Xijiang sag, pearl river mouth basin, northern South China Sea [J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55(2): 1128-1147. doi: 10.1002/gj.3474
[11] 李三忠, 索艳慧, 刘鑫, 等. 南海的基本构造特征与成因模型: 问题与进展及论争[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(6):35-53
LI Sanzhong, SUO Yanhui, LIU Xin, et al. Basic strcutural pattern and tectonic models of the South China Sea: problems, advances and controversies [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(6): 35-53.
[12] 吕彩丽, 张功成, 杨东升. 珠江口盆地珠二坳陷文昌组构造差异性与动力学成因机制[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(6):333-341
LV Caili, ZHANG Gongcheng, YANG Dongsheng. Differential structure and dynamic mechanism of Wenchang formation in the Zhu H depression of the Pearl River mouth basin [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(6): 333-341.
[13] 陈汉宗, 吴湘杰, 周蒂, 等. 珠江口盆地中新生代主要断裂特征和动力背景分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2005, 24(2):52-61 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2005.02.007
CHEN Hanzong, WU Xiangjie, ZHOU Di, et al. Meso-cenozoic faults in Zhujiang river mouth basin and their geodynamic background [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2005, 24(2): 52-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2005.02.007
[14] Li Y H, Zhu R W, Liu H L, et al. The cenozoic activities of Yangjiang-Yitongdong fault: insights from analysis of the tectonic characteristics and evolution processes in western Zhujiang (Pearl) river mouth basin [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2019, 38(9): 87-101. doi: 10.1007/s13131-019-1477-x
[15] 刘欣颖, 吴静, 朱定伟, 等. 珠江口盆地多期走滑构造与叠合型拉分盆地: 以阳江东凹为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1):6-19
LIU Xinying, WU Jing, ZHU Dingwei, et al. Superimposition of Strike-slip Faults and Pull-apart Basins in the Pearl River mouth basin: a case study from the eastern Yangjiang sag [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 6-19.
[16] 高阳东, 张向涛, 彭光荣, 等. 珠江口盆地成盆-成烃-成藏: 代序[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1):1-5
GAO Yangdong, ZHANG Xiangtao, PENG Guangrong, et al. Basin formation, hydrocarbon maturation and oil accumulation of the Pearl River mouth basin: preface [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 1-5.
[17] 陆蕾蕾, 姜素华, 索艳慧, 等. 南海珠江口盆地走滑构造与油气成藏机制[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1):108-122
LU Leilei, JIANG Suhua, SUO Yanhui, et al. Relationship Between Strike-slip structure and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Pearl River mouth basin in the northern South China Sea [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 108-122.
[18] 杨海长, 徐建永, 武爱俊, 等. 珠三坳陷阳江凹陷构造特征及其对油气成藏的影响[J]. 海洋石油, 2011, 31(2):20-24 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2011.02.020
YANG Haichang, XU Jianyong, WU Aijun, et al. Structural features and impact on hydrocarbon accumulation in Yangjiang Sag of Zhu Ⅲ depression [J]. Offshore Oil, 2011, 31(2): 20-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2011.02.020
[19] 李辉, 陈胜红, 张迎朝, 等. 珠江口盆地珠三坳陷断裂特征与油气成藏[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(3):115-124
LI Hui, CHEN Shenghong, ZHANG Yingzhao, et al. Faults in the Zhu-3 depression of pearl river mouth basin and their control over hydrocarbon accumulation [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(3): 115-124.
[20] 彭光荣, 张向涛, 许新明, 等. 南海北部珠江口盆地阳江凹陷油气勘探重要发现与认识[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(3):267-279 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.03.001
PENG Guangrong, ZHANG Xiangtao, XU Xinming, et al. Important discoveries and understandings of oil and gas exploration in Yangjiang sag of the Pearl River mouth basin, northern South China Sea [J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(3): 267-279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.03.001
[21] 田立新, 张向涛, 彭光荣, 等. 珠江口盆地阳江凹陷石油地质特征及成藏主控因素[J]. 中国海上油气, 2020, 32(1):13-22
TIAN Lixin, ZHANG Xiangtao, PENG Guangrong, et al. Petroleum geological characteristics and main controlling factors of the Yangjiang sag in Pearl River mouth basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2020, 32(1): 13-22.
[22] 陈雯雯. 珠江口盆地珠Ⅲ坳陷北部文昌组沉积相研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2012.
CHEN Wenwen. Study on Wenchang formation in northern Zhu Ⅲ depression of Pearl River mouth basin[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2012.
[23] 占华旺, 蔡国富, 张志伟, 等. 南海北缘古近纪断裂活动规律及控盆特征: 以阳江东凹为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1):20-39
ZHAN Huawang, CAI Guofu, ZHANG Zhiwei, et al. Paleogene fault activity and basin controlling characteristics in the northern south China sea margin: a case study of the eastern Yangjiang sag [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 20-39.
[24] 汪晓萌, 彭光荣, 吴静, 等. 珠江口盆地恩平21洼文昌组沉积期原型盆地及其对优质烃源岩的控制[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1):158-167
WANG Xiaomeng, PENG Guangrong, WU Jing, et al. Prototype basin and its control on high-quality source rocks during the depositional period of Wenchang formation in Enping 21 sub-sag, Pearl River mouth basin [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 158-167.
[25] 姜华, 王华, 李俊良, 等. 珠江口盆地珠三坳陷层序地层样式分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(1):87-93
JIANG Hua, WANG Hua, LI Junliang, et al. Analysis on sequence formation styles of Zhu-3 depression in Pearl River mouth basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(1): 87-93.
[26] 李思田, 林畅松, 张启明, 等. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地幕式裂陷的动力过程及10 Ma以来的构造事件[J]. 科学通报, 1999, 44(1):10-23 doi: 10.1007/BF03182877
LI Sitian, LIN Changsong, ZHANG Qiming, et al. Episodic rifting of continental marginal basins and tectonic events since 10 Ma in the South China Sea [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1999, 44(1): 10-23. doi: 10.1007/BF03182877
[27] 杜晓东, 彭光荣, 吴静, 等. 珠江口盆地阳江东凹断层特征及其对油气成藏的影响[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2020, 41(4):414-421
DU Xiaodong, PENG Guangrong, WU Jing, et al. Faults and its impacts on petroleum accumulation in eastern Yangjiang Sag, Pearl River mouth basin [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2020, 41(4): 414-421.
[28] Peng J W, Pang X Q, Xiao S, et al. Secondary migration of hydrocarbons in the Zhujiang formation in the Huixi half-Graben, Pearl River mouth basin, South China Sea [J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2016, 53(2): 189-201. doi: 10.1139/cjes-2015-0076
[29] Lyu C F, Chen G J, Du G C, et al. Diagenesis and reservoir quality evolution of shelf-margin sandstones in Pearl River mouth basin, South China Sea [J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Technology, 2014, 4(1): 1-19.
[30] Su M, Alves T M, Li W, et al. Reassessing two contrasting late Miocene-Holocene stratigraphic frameworks for the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 102: 899-913. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.12.034
[31] Wang X D, Zhang X T, Lin H M, et al. Paleogene geological framework and tectonic evolution of the central anticlinal zone in Lufeng 13 sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Petroleum Research, 2019, 4(3): 238-249. doi: 10.1016/j.ptlrs.2019.05.002
[32] 刘志峰, 刘志鹏, 肖伶俐, 等. 珠三坳陷北部珠海组—韩江组沉积演化及储盖组合[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2013, 29(9):25-31
LIU Zhifeng, LIU Zhipeng, XIAO Lingli, et al. Facies evolution and reservoir-seal assemblages in the Zhuhai and Hanjiang formations, north of Zhu Ⅲ depression, Pearl River mouth basin [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2013, 29(9): 25-31.
[33] 方竞男. 珠江口盆地第三系沉积体系演变与生储盖组合[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2013.
FANG Jingnan. Evolution of sedimentary system and source-reservoir-caprock association in tertiary of Pearl River Mouth Basin[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2013.
[34] 于海洋, 索艳慧, 杜晓东, 等. 珠江口盆地渐-中新世古气候及物源特征: 以阳江东凹为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1):53-63
YU Haiyang, SUO Yanhui, DU Xiaodong, et al. Oligocene-Miocene provenance and paleoclimate of the Pearl River Mouth basin: a case study of the eastern Yangjiang Sag [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 53-63.
[35] 梁卫, 彭光荣, 朱定伟, 等. 珠江口盆地阳江东凹古近系构造特征与勘探潜力[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1):168-178
LIANG Wei, PENG Guangrong, ZHU Dingwei, et al. Paleogene structures and exploration potential in the Eastern Yangjiang Sag, Pearl River mouth basin [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 168-178.
[36] 杨悦, 彭光荣, 朱定伟, 等. 珠江口盆地阳江东凹裂陷期沉积环境及其构造控制[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1):79-89
YANG Yue, PENG Guangrong, ZHU Dingwei, et al. Syn-rifting sedimentary environment and its tectonic control in the eastern Yangjiang Sag of the Pearl River mouth basin [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 79-89.
[37] 刘军, 彭光荣, 朱定伟, 等. 珠江口盆地阳江凹陷东部地区断控成藏条件[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1):123-130
LIU Jun, PENG Guangrong, ZHU Dingwei, et al. Fault-controlled hydrocarbon accumulation in the eastern Yangjiang Sag, Pearl River mouth basin [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 123-130.
[38] 蔡国富, 张向涛, 彭光荣, 等. 南海北部阳江-一统暗沙断裂带与新近纪岩浆活动[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1):40-52
CAI Guofu, ZHANG Xiangtao, PENG Guangrong, et al. Neogene volcanism and tectonics along the Yangjiang-Yitong'ansha fault zone in the northern South China Sea margin [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 40-52.
[39] 宋海斌, 郝天珧, 江为为, 等. 南海地球物理场特征与基底断裂体系研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2002, 17(1):24-34 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2002.01.003
SONG Haibin, HAO Tianyao, JIANG Weiwei, et al. Researches on geophysical field characteristics and basement fault system of South China Sea [J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2002, 17(1): 24-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2002.01.003
[40] 鲁宝亮, 王璞珺, 张功成, 等. 南海北部陆缘盆地基底结构及其油气勘探意义[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(4):580-587 doi: 10.7623/syxb201104004
LU Baoliang, WANG Pujun, ZHANG Gongcheng, et al. Basement structures of an epicontinental basin in the northern South China Sea and their significance in petroleum prospect [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(4): 580-587. doi: 10.7623/syxb201104004
[41] Salles T, Hardiman L. Badlands: An open-source, flexible and parallel framework to study landscape dynamics [J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2016, 91: 77-89.
[42] Salles T. Badlands: A parallel basin and landscape dynamics model [J]. Softwarex, 2016, 5: 195-202. doi: 10.1016/j.softx.2016.08.005
[43] Braun J, Sambridge M. Modelling landscape evolution on geological time scales: a new method based on irregular spatial discretization [J]. Basin Research, 1997, 9(1): 27-52. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2117.1997.00030.x
[44] Tucker G, Lancaster S, Gasparini N, et al. The channel-hillslope integrated landscape development model (CHILD)[M]//Harmon R S, Doe W W. Landscape Erosion and Evolution Modeling. Boston, MA: Springer, 2001: 319-388.
[45] 刘泽, 李三忠, Bukhari S W H, 等. 动态古地貌再造: Badlands软件在盆地分析中的应用[J]. 古地理学报, 2020, 22(1):29-38 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2020.01.003
LIU Ze, LI Sanzhong, Bukhari S W H, et al. Reconstruction of dynamic palaeogeomorphy: Application of Badlands software in basin analysis [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2020, 22(1): 29-38. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2020.01.003
[46] Chen A, Darbon J, Morel J M. Landscape evolution models: A review of their fundamental equations [J]. Geomorphology, 2014, 219: 68-86. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.04.037
[47] Pelletier J D. Fluvial and slope‐wash erosion of soil‐mantled landscapes: detachment‐or transport‐limited? [J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2012, 37(1): 37-51. doi: 10.1002/esp.2187
[48] Fernandes N F, Dietrich W E. Hillslope evolution by diffusive processes: the timescale for equilibrium adjustments [J]. Water Resources Research, 1997, 33(6): 1307-1318. doi: 10.1029/97WR00534
[49] Perron J T, Kirchner J W, Dietrich W E. Formation of evenly spaced ridges and valleys [J]. Nature, 2009, 460(7254): 502-505. doi: 10.1038/nature08174
[50] Lague D, Hovius N, Davy P. Discharge, discharge variability, and the bedrock channel profile [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2016, 110(F4): F04006.
[51] Whipple K X, Tucker G E. Dynamics of the stream-power river incision model: implications for height limits of mountain ranges, landscape response timescales, and research needs [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1999, 104(B8): 17661-17674. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900120
[52] Tucker G E, Hancock G R. Modelling landscape evolution [J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2010, 35(1): 28-50. doi: 10.1002/esp.1952
[53] Howard A D. Thresholds in river regimes[M]//Coates D R, Vitek J D. Thresholds in Geomorphology. London: George Allen and Unwin Ltd., 1980: 227-258.
[54] Wickert A D. Open-source modular solutions for flexural isostasy: gFlex v1.0 [J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2016, 9(3): 997-1017. doi: 10.5194/gmd-9-997-2016
[55] Tucker G E, Slingerland R L. Erosional dynamics, flexural isostasy, and long-lived escarpments: A numerical modeling study [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1994, 99(B6): 12229-12243. doi: 10.1029/94JB00320
[56] Ruetenik G. Long-term landscape evolution modeling: the role of dynamic topography, flexural isostasy, and sea level[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Syracuse University, 2017.
[57] Hodgetts D, Egan S S, Williams G D. Flexural modelling of continental lithosphere deformation: a comparison of 2D and 3D techniques [J]. Tectonophysics, 1998, 294(1-2): 1-20. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(98)00084-5
[58] 杜文波, 邱燕, 黄文凯, 等. 南海西缘曾母西断裂构造特征及其对盆地沉积发育的控制作用[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(2):100-108
DU Wenbo, QIU Yan, HUANG Wenkai, et al. Zengmu Xi fault on the western-border of South China Sea and its control over the sedimentation of the Basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(2): 100-108.
[59] 胡小猛, 郭家秀, 胡向阳. 汾河地堑湖盆第四纪地貌—沉积特征的构造控制[J]. 地理学报, 2010, 65(1):73-81 doi: 10.11821/xb201001008
HU Xiaomeng, GUO Jiaxiu, HU Xiangyang. The development of morpho-sediment of quaternary in Fenhe river Graben basins and the neotectonic movement [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2010, 65(1): 73-81. doi: 10.11821/xb201001008
[60] 李磊, 王英民, 张莲美, 等. 尼日尔三角洲坡脚逆冲带沉积样式及构造控制[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2008, 33(5):643-650 doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2008.079
LI Lei, WANG Yingmin, ZHANG Lianmei, et al. Sedimentary patterns and structural control across toe thrust belts, Niger Delta [J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2008, 33(5): 643-650. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2008.079
[61] 姜雪, 刘丽芳, 孙和风, 等. 气候与构造控制下湖相优质烃源岩的差异分布: 以渤中凹陷为例[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(2):165-175 doi: 10.7623/syxb201902004
JIANG Xue, LIU Lifang, SUN Hefeng, et al. Differential distribution of high-quality lacustrine source rocks controlled by climate and tectonic: a case study from Bozhong sag [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(2): 165-175. doi: 10.7623/syxb201902004
[62] 高红芳, 钟和贤, 孙美静, 等. 南海海盆东南部大型深水浊积扇体系及其成因的构造控制[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(5):1395-1406
GAO Hongfang, ZHONG Hexian, SUN Meijing, et al. The large deep-water turbidity fan system in southeastern South China Sea Basin: Formation and tectonic constraint [J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(5): 1395-1406.
[63] Haq B U, Hardenbol J, Vail P R. Chronology of Fluctuating Sea Levels Since the Triassic [J]. Science, 1987, 235(4793): 1156-1167. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4793.1156
[64] 许志琴, 杨经绥, 张建新, 等. 阿尔金断裂两侧构造单元的对比及岩石圈剪切机制[J]. 地质学报, 1999, 73(3):193-205 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.1999.03.001
XU Zhiqin, YANG Jingsui, ZHANG Jianxin, et al. A comparison between the tectonic units on the two sides of the Altun Sinistral Strike-slip fault and the Mechanism of lithospheric Shearing [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1999, 73(3): 193-205. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.1999.03.001
[65] 李海兵, 许志琴, 杨经绥, 等. 阿尔金断裂带最大累积走滑位移量: 900km?[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(10):1288-1298 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.10.007
LI Haibing, XU Zhiqin, YANG Jingsui, et al. The maximum cumulative strike-slip displacement of the Altyn Tagh Fault: 900 km? [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2007, 26(10): 1288-1298. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.10.007
[66] Zhang Y Q, Wei S, Dong S W. Cenozoic deformation history of the Tancheng–Lujiang Fault Zone, north China, and dynamic implications [J]. Island Arc, 2003, 12(3): 281-293. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1738.2003.00395.x
[67] Hsiao L Y, Graham S A, Tilander N. Seismic reflection imaging of a major strike-slip fault zone in a rift system: Paleogene structure and evolution of the Tan-Lu fault system, Liaodong Bay, Bohai, offshore China [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2004, 88(1): 71-97. doi: 10.1306/09090302019
[68] Liu Y J, Neubauer F, Genser J, et al. Geochronology of the initiation and displacement of the Altyn Strike-Slip Fault, western China [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2007, 29(2): 243-252.
[69] Gilder S A, Coe R S, Wu H R, et al. Cretaceous and Tertiary paleomagnetic results from Southeast China and their tectonic implications [J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1993, 117(3-4): 637-652.
[70] Gilder S A, Leloup P H, Courtillot V, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Tancheng-Lujiang (Tan-Lu) fault via Middle Triassic to Early Cenozoic paleomagnetic data [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1999, 104(B7): 15365-15390. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900123
[71] 万天丰, 朱鸿. 郯庐断裂带的最大左行走滑断距及其形成时期[J]. 高校地质学报, 1996, 2(1):14-27
WAN Tianfeng, ZHU Hong. The maximum sinistral Strike slip and its Forming age of Tancheng-Lujiang Fault zone [J]. Geological Journal of Universities, 1996, 2(1): 14-27.
[72] 吴奎, 何京, 张中巧, 等. 基于构造物理模拟实验的走滑量求取[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2019, 54(4):891-900
WU Kui, HE Jing, ZHANG Zhongqiao, et al. Strike-slip fault displacement calculation based on structure physical simulation [J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2019, 54(4): 891-900.
[73] 马晓倩, 刘军, 朱定伟, 等. 多期走滑拉分盆地的沉积响应: 以南海北部珠江口盆地为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1):64-78
MA Xiaoqian, LIU Jun, ZHU Dingwei, et al. Sedimentary response of multi-stage pull-apart basin: insights from the Pearl River Mouth Basin in the Northern South China Sea margin [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 64-78.
[74] 吴静, 朱定伟, 赵鹏, 等. 断裂复合汇聚脊对新近系油气远距离富集的控制作用: 以珠江口盆地阳江东凹与恩平凹陷为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1):131-139
WU Jing, ZHU Dingwei, ZHAO Peng, et al. Controls of faulted composite accumulation ridge on the Long distance migration and accumulation of Neogene hydrocarbon: a case study of the Eastern Yangjiang Sag and the Enping Sag in the Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 131-139.
[75] 林鹤鸣, 刘培, 汪旭东, 等. 珠一坳陷始新世文昌组沉积期构造转换对源-汇体系的控制[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1):188-200
LIN Heming, LIU Pei, WANG Xudong, et al. Influences of structural transformation on source-to-sink system during the depositional period of Wenchang formation of Eocene in the Zhu Ⅰ depression [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 188-200.
[76] 肖坤泽, 童亨茂. 走滑断层研究进展及启示[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(2):151-166 doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.02.015
XIAO Kunze, TONG Hengmao. Progress on strike-slip fault research and its significance [J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 26(2): 151-166. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.02.015
-




 下载:
下载: