Transportion of suspended sediment in the southern mud area of Bohai Bay in summer: Characteristics and mechanism
-
摘要:
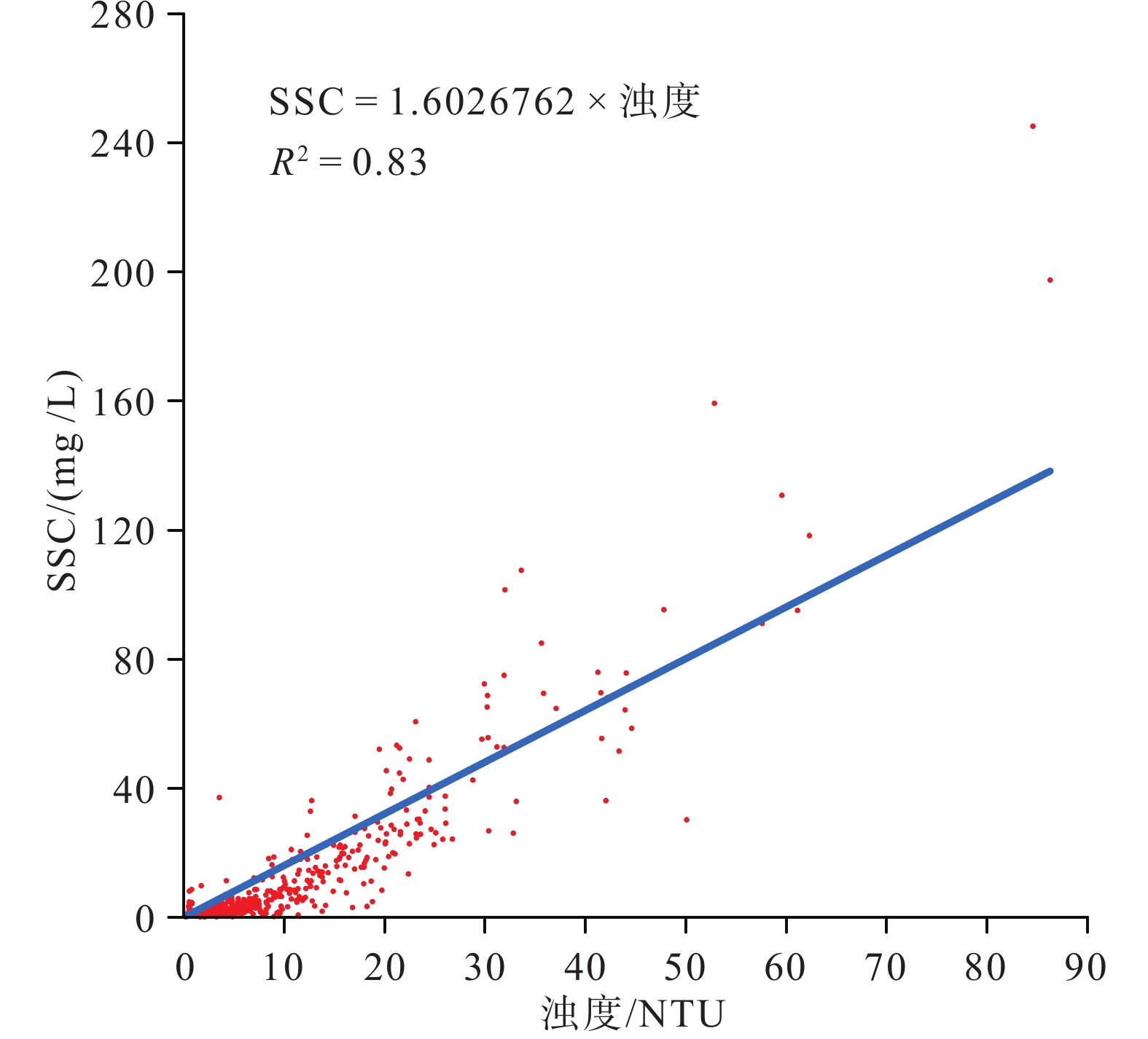
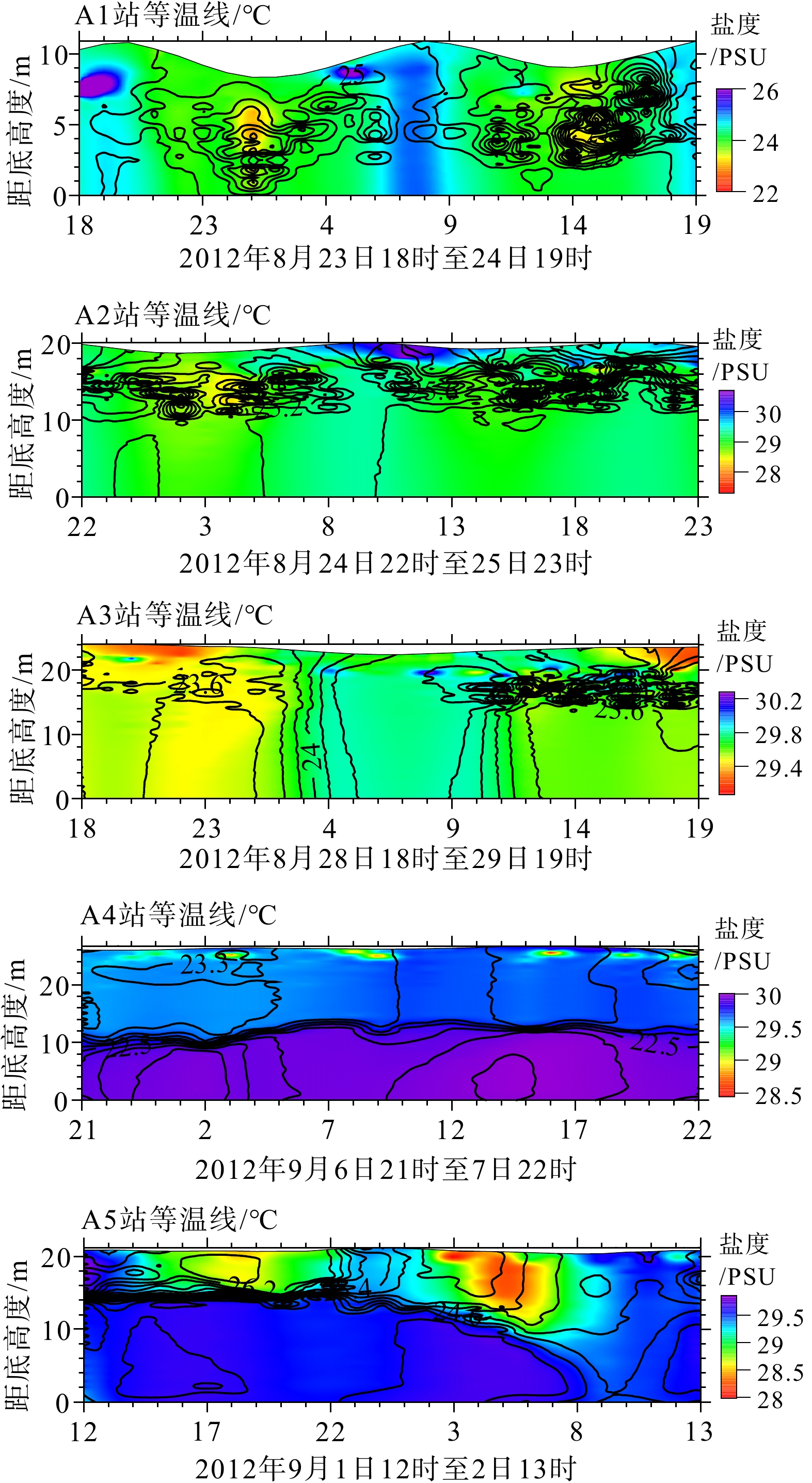
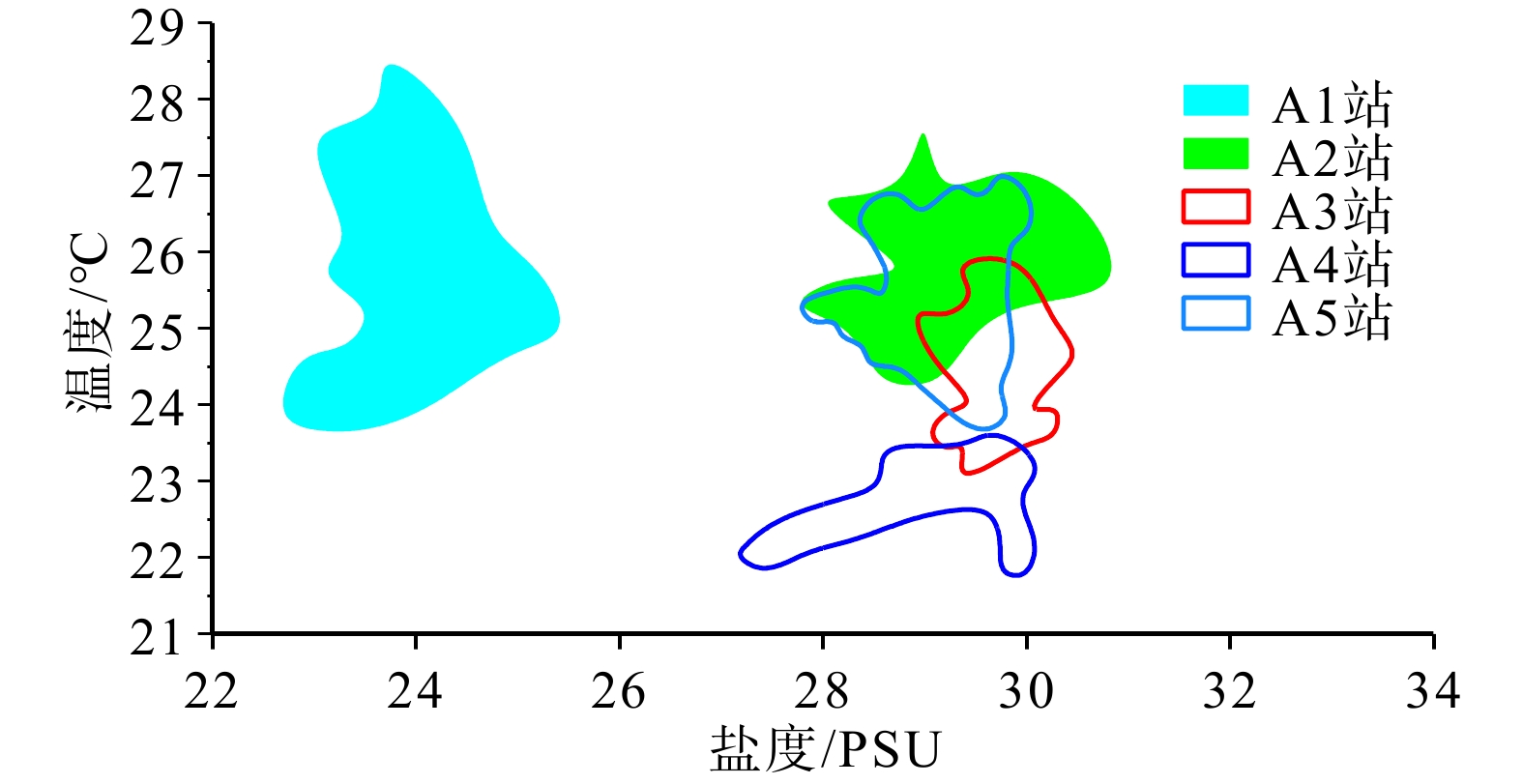
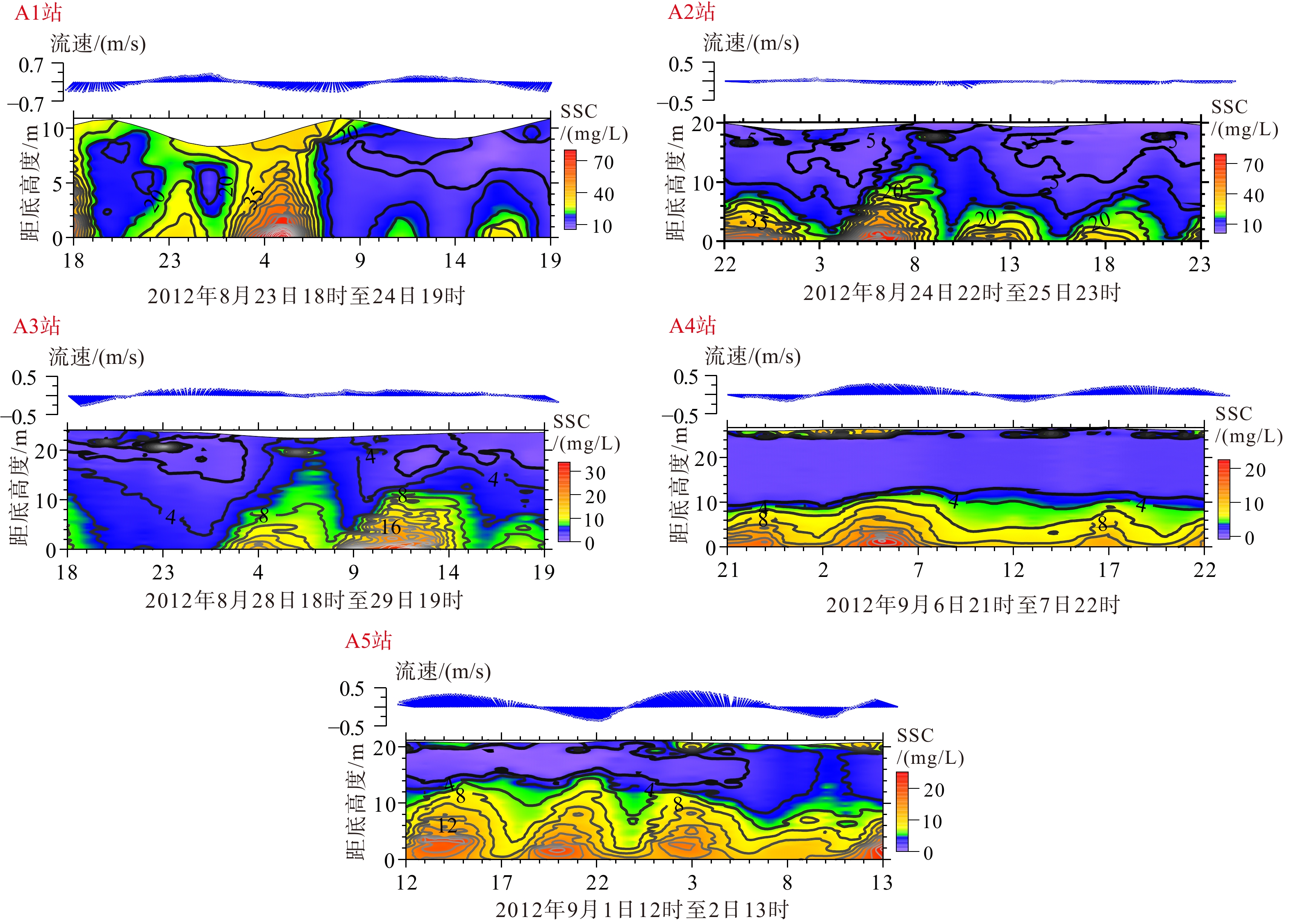
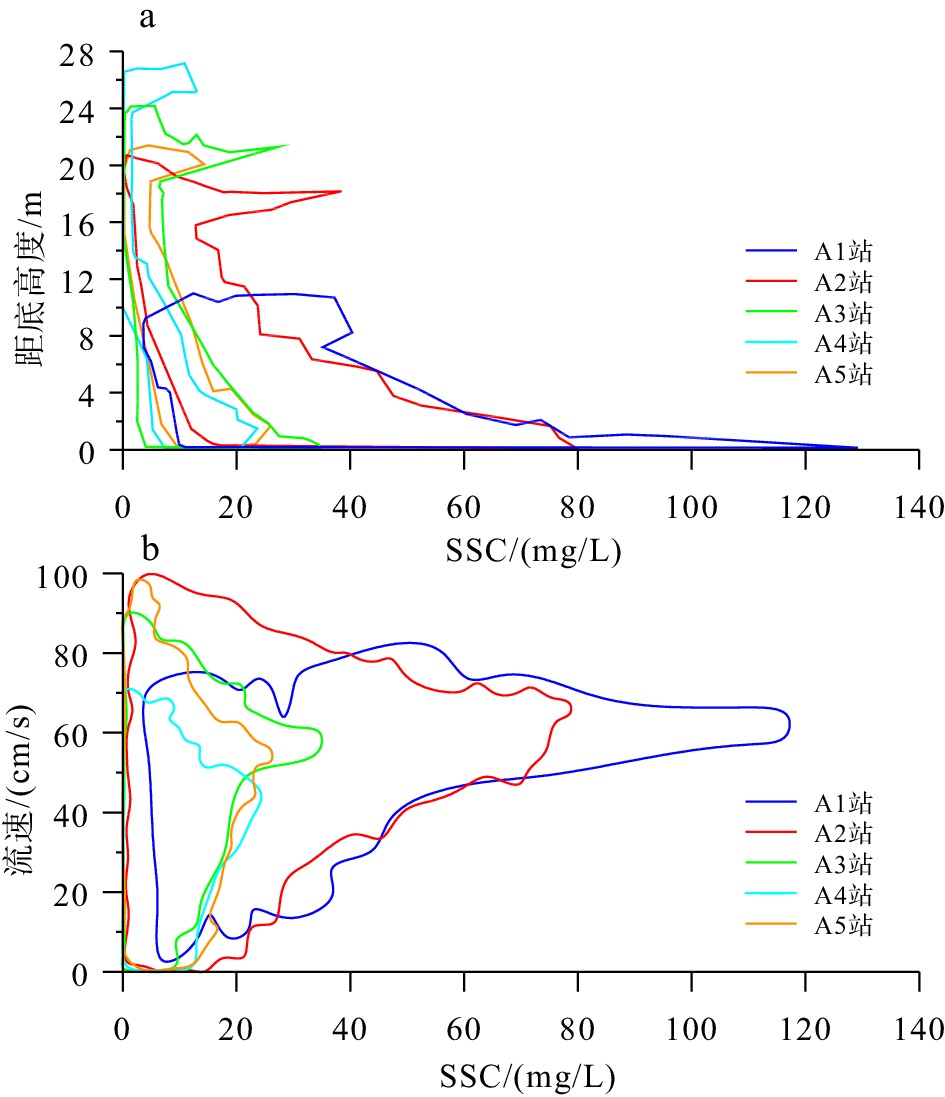
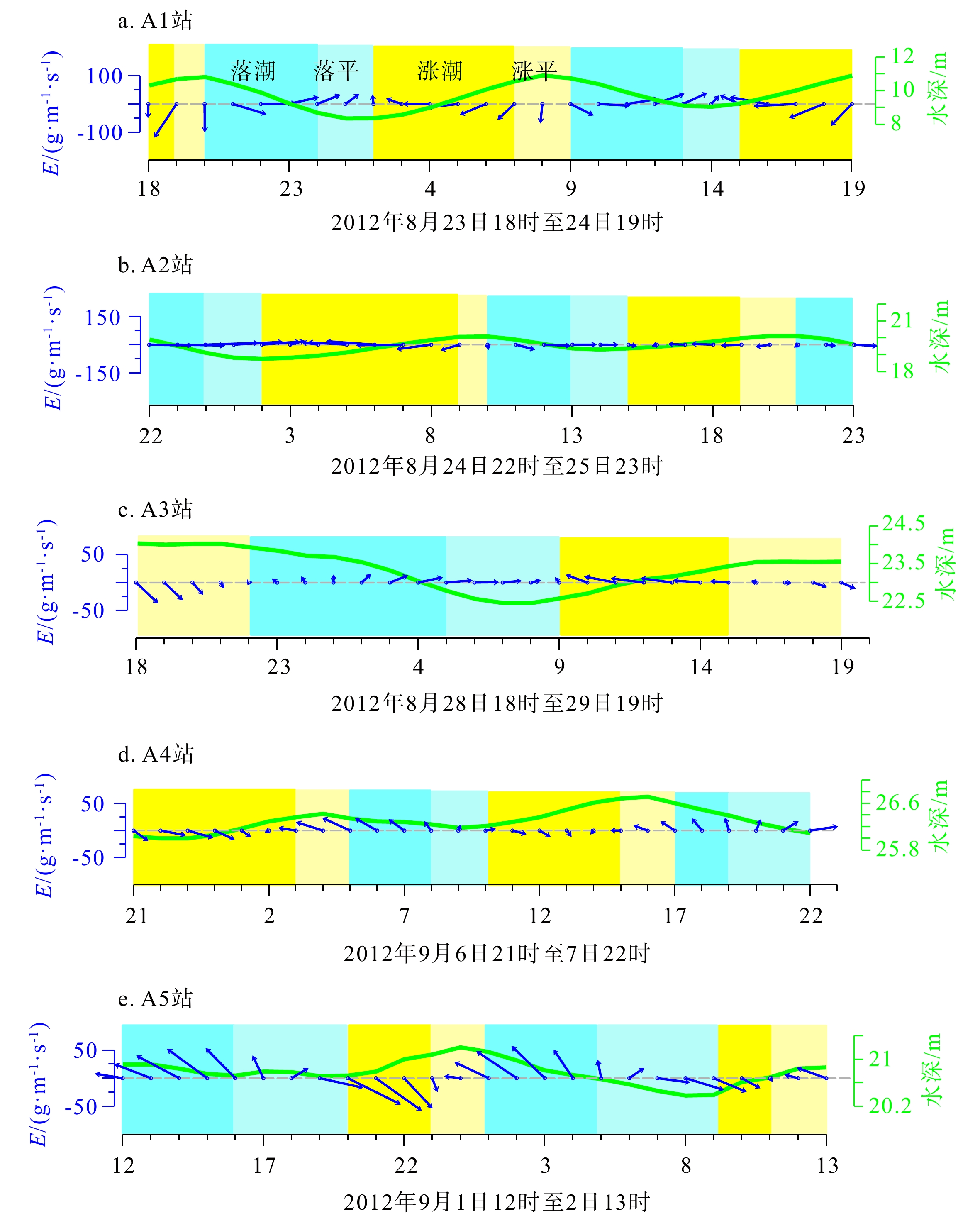
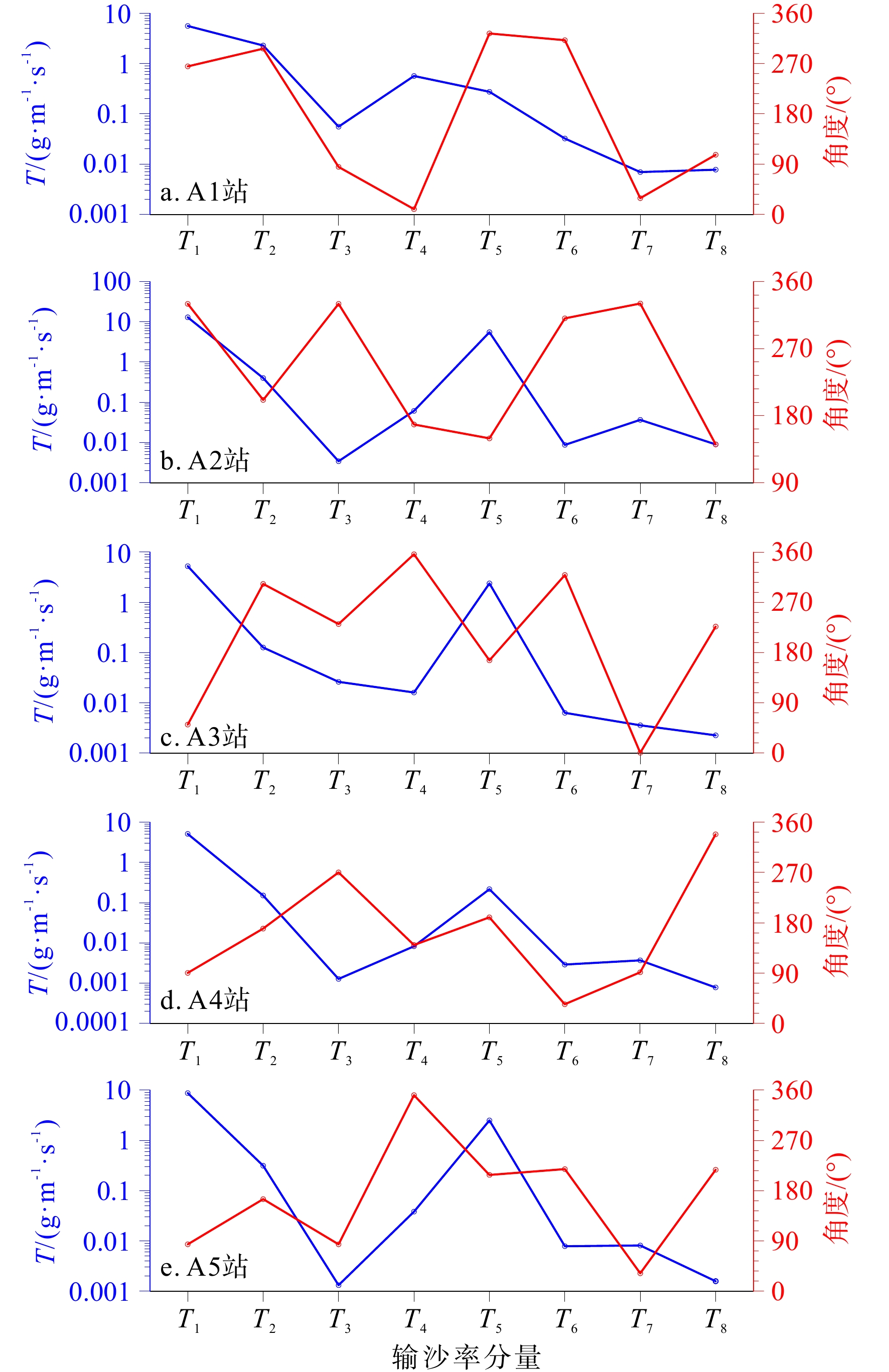
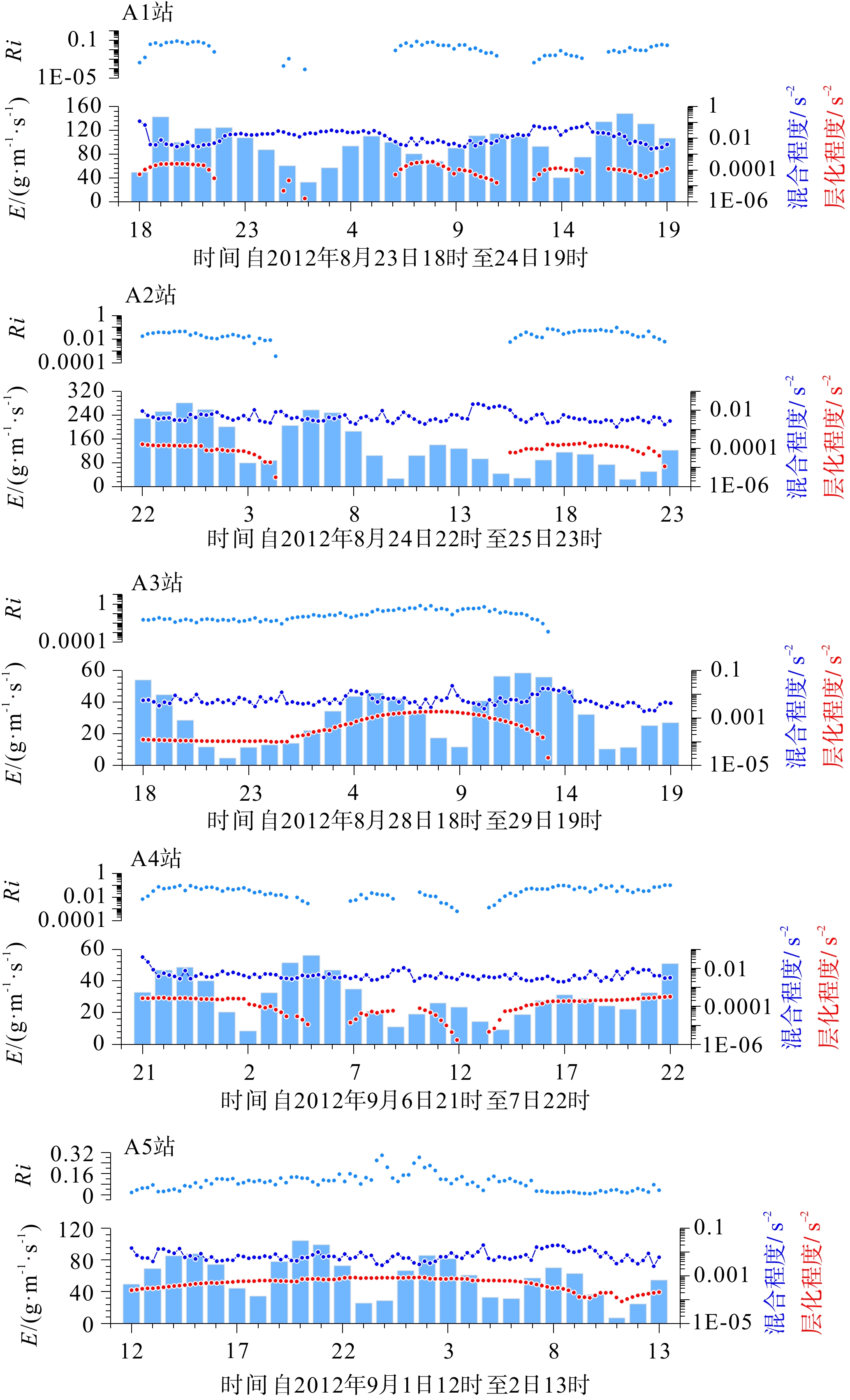
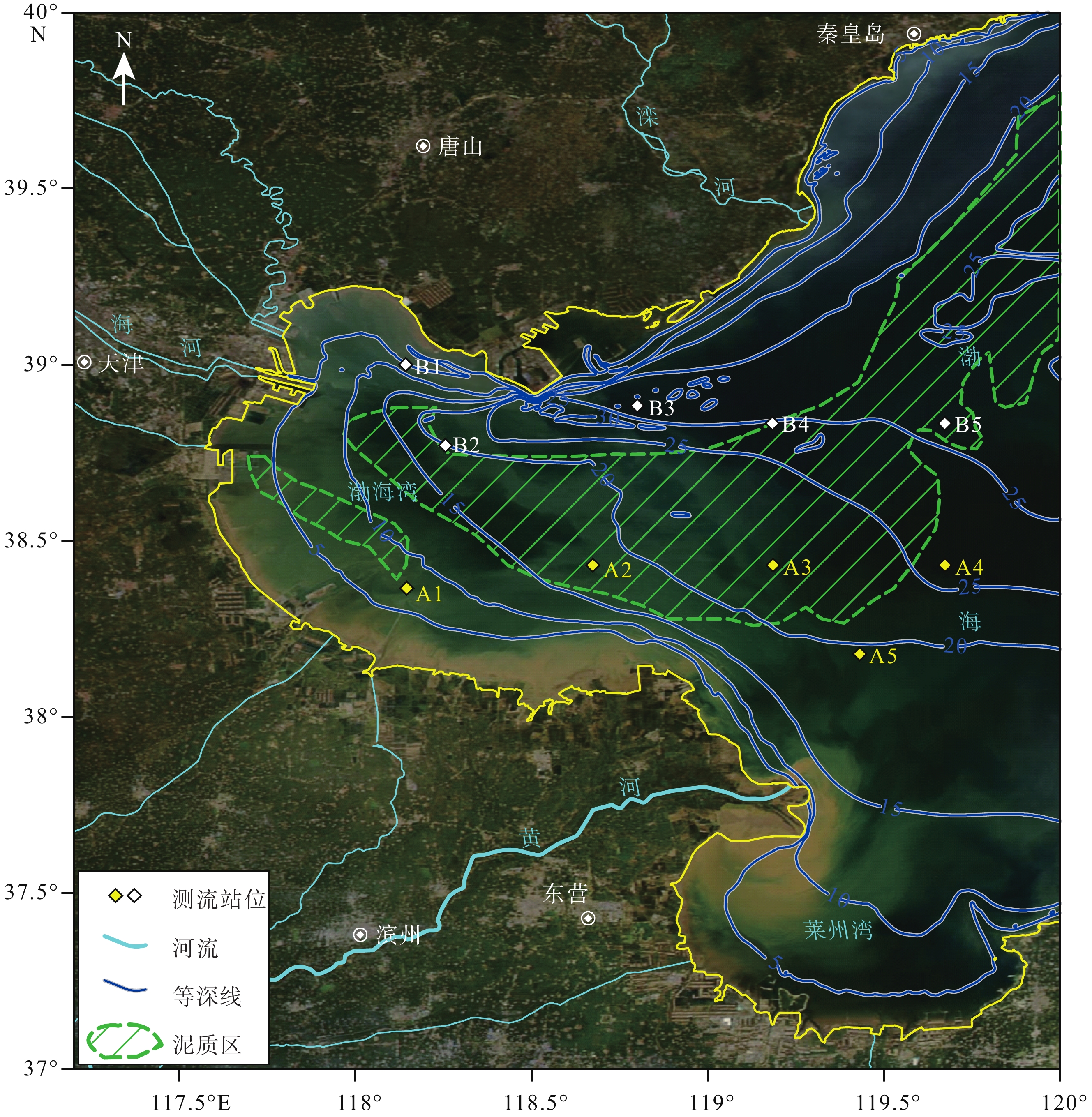
为了解渤海湾泥质区南部近岸及毗邻海域夏季悬浮体输运格局,分别在湾内、湾口、湾口外和黄河口外NE向剖面处设置站位,进行25 h海流、温盐连续观测及悬浮体浓度(SSC)测定。结果显示,高温淡水以羽状流的方式自近岸向渤海中部传输,高浊度悬浮体多出现在涨急和落急的流速较高时期,较高的SSC值多出现在距底5 m水深范围,其中湾内和湾口两站的底层SSC值最高,分别可达约130 和80 mg/L,黄河口外NE向剖面20 m以深海域SSC值最小,均低于40 mg/L。单宽输沙率具有潮周期性特点:湾内A1站涨潮和涨平期以向湾内近岸输沙为主,落潮和落平期以向湾外输沙为主,潮平均单宽输沙率为7.8 g·m−1·s−1,方向为280°;湾口A2站涨落潮流输沙方向相反,整体以SE向朝湾外近岸输沙为主,潮平均单宽输沙率为7.2 g·m−1·s−1,方向为328°。湾外A3站涨潮和涨平时期输沙方向基本相反,大小相当,落潮和落平时期输沙方向以偏E和偏NE向为主,潮平均单宽输沙率为4.7 g·m−1·s−1,方向为77°。黄河口SE向的两个站位涨潮时输沙偏SE向,涨平时输沙偏NW向,落潮时输沙偏NW向,落平时输沙偏N向和偏NE向,两站的潮平均单宽输沙率方向以偏N向为主,A4站的潮平均单宽输沙率为5.2 g·m−1·s−1,方向为94°,A5站潮平均单宽输沙率为7.7 g·m−1·s−1,方向为102°。潮平均单宽输沙率以拉格朗日输沙贡献最显著,在湾口泥质区南部和东南部水深15~25 m的海域,垂向净环流的影响较大,有抵消一部分拉格朗日输沙率的作用,且对潮平均单宽输沙率的影响比湾内和25 m以深海域的大,其他分量数量级较小,对潮平均单宽输沙率贡献较小。水体以混合为主,水体层化程度加强对各站位悬浮体输运均有一定的抑制作用。
Abstract:To understand the transport pattern of suspended sediment in summer in the coastal and adjacent waters of the southern muddy area of Bohai Bay, observation stations were deployed in the bay, the bay mouth, and at the N-E-directed section off the Huanghe (Yellow) River estuary, in which current, thermohaline, and suspended sediment concentration (SSC) were observed in-situ continuously in 25 h. Results show that warm fresh waters travelled from shore to the middle of Bohai Sea in the form of plume flow. High turbidity suspension occurred mostly during periods of maximum flood and maximum ebb, and high SSC value appeared mostly in 5m above sea bottom. The bottom SSC values in the bay and bay mouth stations are the highest, reaching about 130 and 80 mg/L, respectively. The SSC value at 20 m-deep sea area outside the Huanghe River estuary was the lowest at below 40 mg/L. The average single-width sediment transport rate at Station A1 in the bay was 7.8 g·m−1·s−1 toward 280°. However, the sand transport direction of the ebb and flow tide at Station A2 in the bay mouth was opposite, and the sand transport direction was mainly southeastward to the outside of the bay. The average single width sand transport rate of the tide was 7.2 g·m−1·s−1 toward 328°. The sediment transport directions of Station A3 outside the bay during flood tide and flood slack were generally opposite to each other on similar scales, and the sediment transport directions were mainly east-to-northeastward during ebb tide and ebb slack. The tidal averaged sediment transport rate per unit width was 4.7 g·m−1·s−1, and the direction was 77°. At the two stations in SE of the Huanghe River estuary, the sediment transport was in southeastward in flood tide, northeastward in flood slack, northwestward in ebb tide, and north-northeastward in ebb slack. The average single-width sediment transport in the two stations was mainly northward. The average sediment transport rate per unit width of Station A4 was 5.2 g·m−1·s−1, and the direction of transport was 94°. The tidal averaged sediment transport rate per unit width at Station A5 is 7.7 g·m−1·s−1, and the direction of transport was 102°. The Lagrange sediment transport rate contributed most significantly to the tidal averaged sediment transport rate per unit width. In the southern and southeastern parts of the bay-mouth mud area, the vertical net circulation showed a large impact on the Lagrange sediment transport rate, which could offset partially the Lagrange sediment transport rate, thus affecting more obviously the tidal averaged sediment transport rate per unit width than those in the bay and the sea area deeper than 25 m. Other directional components of velocity had smaller orders of magnitude and contributed less to the tidal averaged sediment transport rate per unit width.
-

-
[1] 中国科学院海洋研究所海洋地质研究室. 渤海地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985
Department of Marine Geology, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The Bohai Sea Geological[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985.
[2] 秦蕴珊, 廖先贵. 渤海湾海底沉积作用的初步探讨[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1962, 4(3-4):199-207
QIN Yunshan, LIAO Xiangui. A preliminary study on seabed sedimentation in Bohai Bay [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1962, 4(3-4): 199-207.
[3] Wang Y, Li R H, Wen Z H, et al. The summer spring-neap variation of the water thermohaline-turbidity structure and its dynamical mechanism in the southern Bohai Strait [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 90: 52-59. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.04.004
[4] 庞家珍, 司书亭. 黄河河口演变I. 近代历史变迁[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1979, 10(2):136-141
PANG Jiazhen, SI Shuting. The estuary changes of Huanghe River I. Changes in modern time [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1979, 10(2): 136-141.
[5] 杨作升, 戴慧敏, 王开荣. 1950-2000年黄河入海水沙的逐日变化及其影响因素[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2005, 35(2):237-244
YANG Zuosheng, DAI Huimin, WANG Kairong. Daily variations of water discharge and sediment discharge into the sea from Yellow River from 1950 to 2000 and relevant influential factors that generate these changes [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2005, 35(2): 237-244.
[6] Wang H J, Bi N S, Wang Y, et al. Tide-modulated hyperpycnal flows off the Huanghe (Yellow River) mouth, China [J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2010, 35(11): 1315-1329. doi: 10.1002/esp.2032
[7] Wang H J, Bi N S, Saito Y, et al. Recent changes in sediment delivery by the Huanghe (Yellow River) to the sea: Causes and environmental implications in its estuary [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2010, 391(3-4): 302-313. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.07.030
[8] 庞家珍, 司书亭. 黄河河口演变Ⅱ. 河口水文特征及泥沙淤积分布[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1980, 11(4):295-305
PANG Jiazhen, SI Shuting. Fluvial process of the Huanghe River estuary Ⅱ. Hydrographical character and the region of sediment silting [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1980, 11(4): 295-305.
[9] 杨作升, 孙宝喜, 沈渭铨. 黄河口毗邻海域细粒级沉积物特征及沉积物入海后的运移[J]. 山东海洋学院学报, 1985, 15(2):121-129
YANG Zuosheng, SUN Baoxi, SHEN Weiquan. Characteristics of fine-grained sediment of the shelf area adjacent to the mouth of the Huanghe River and sediment dispersion in that region [J]. Journal of Shandong College of Oceanology, 1985, 15(2): 121-129.
[10] Wang H J, Yang Z S, Saito Y, et al. Interannual and seasonal variation of the Huanghe (Yellow River) water discharge over the past 50 years: connections to impacts from ENSO events and dams [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2006, 50(3-4): 212-225. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2006.01.005
[11] Yang Z S, Ji Y J, Bi N S, et al. Sediment transport off the Huanghe (Yellow River) delta and in the adjacent Bohai Sea in winter and seasonal comparison [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 93(3): 173-181. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2010.06.005
[12] Wang H J, Yang Z S, Saito Y, et al. Stepwise decreases of the Huanghe (Yellow River) sediment load (1950-2005): impacts of climate change and human activities [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2007, 57(3-4): 331-354. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2007.01.003
[13] Ren M E, Shi Y L. Sediment discharge of the Yellow River (China) and its effect on the sedimentation of the Bohai and the Yellow Sea [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1986, 6(6): 785-810. doi: 10.1016/0278-4343(86)90037-3
[14] Jiang W S, Pohlmann T, Sündermann J, et al. A modelling study of SPM transport in the Bohai Sea [J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2000, 24(3-4): 175-200. doi: 10.1016/S0924-7963(99)00071-8
[15] Bi N S, Yang Z S, Wang H J, et al. Seasonal variation of suspended-sediment transport through the southern Bohai Strait [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 93(3): 239-247. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.03.007
[16] 李建伟. 渤海湾西南部海域海底沉积物分布特征研究[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2011
LI Jianwei. Research on distribution characteristics of bed sediments in Southwest of Bohai Bay[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2011.
[17] 余佳, 王厚杰, 毕乃双, 等. 基于MODIS L1B数据的黄海悬浮体季节性分布的反演[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(1):1-9
YU Jia, WANG Houjie, BI Naishuang, et al. Seasonal distribution and variation of suspended sediment in the Yellow Sea in 2010 based on retrieved monthly data from MODIS L1B imagery [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(1): 1-9.
[18] 肖合辉, 王厚杰, 毕乃双, 等. 渤黄海海域悬浮体季节性分布及主要运移路径[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(2):11-21
XIAO Hehui, WANG Houjie, BI Naishuang, et al. Seasonal variation of suspended sediment in the Bohai and Yellow Sea and the pathway of sediment transport [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(2): 11-21.
[19] Wang Y, Wang H J, Bi N S, et al. Numerical modeling of hyperpycnal flows in an idealized river mouth [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 93(3): 228-238. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.02.011
[20] Shi W, Wang M H, Jiang L D. Spring-neap tidal effects on satellite ocean color observations in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2011, 116(C12): C12032. doi: 10.1029/2011JC007234
[21] Kirk J T O. Effects of suspensoids (turbidity) on penetration of solar radiation in aquatic ecosystems [J]. Hydrobiologia, 1985, 125(1): 195-208. doi: 10.1007/BF00045935
[22] Liu C G, Wang J L, Feng J F, et al. Effects of suspended particles on the growth of two dominant phytoplankton species of Bohai Bay, China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2013, 74(1): 220-224. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.06.054
[23] Song G D, Liu S M. Phosphorus speciation and distribution in surface sediments of the Yellow Sea and East China Sea and potential impacts on ecosystem [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2015, 34(4): 84-91. doi: 10.1007/s13131-015-0653-4
[24] Duan L Q, Song J M, Xu Y Y, et al. The distribution, enrichment and source of potential harmful elements in surface sediments of Bohai Bay, North China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 183(1-3): 155-164. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.07.005
[25] 冯剑丰, 王秀明, 孟伟庆, 等. 天津近岸海域夏季大型底栖生物群落结构变化特征[J]. 生态学报, 2011, 31(20):5875-5885
FENG Jianfeng, WANG Xiuming, MENG Weiqing, et al. Variation characteristics of macrobenthic communities structure in Tianjin coastal region in summer [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(20): 5875-5885.
[26] 秦延文, 张雷, 郑丙辉, 等. 渤海湾岸线变化(2003-2011年)对近岸海域水质的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2012, 32(9):2149-2159
QIN Yanwen, ZHANG Lei, ZHENG Binghui, et al. Impact of shoreline changes on the costal water quality of Bohai Bay(2003-2011) [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2012, 32(9): 2149-2159.
[27] 蔡文倩, 刘录三, 乔飞, 等. 渤海湾大型底栖生物群落结构变化及原因探讨[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(9):3104-3109
CAI Wenqian, LIU Lusan, QIAO Fei, et al. Study on the changes of macrobenthos communities and their causes in Bohai Bay [J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(9): 3104-3109.
[28] 李广雪, 杨子赓, 刘勇. 中国东部海域海底沉积物成因环境图[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005.
LI Guangxue, YANG Zigeng, LIU Yong. Formation Environment of the Seafloor Sediment in the East China Seas[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005.
[29] 李秉天. 渤海地形演变对潮波系统影响的数值研究[D]. 国家海洋局第一海洋研究所硕士学位论文, 2014
LI Bingtian. Numerical study on impact of Bohai Sea topography changes on the tidal wave system[D]. Master Dissertation of First Institute of Oceanography, MNR, 2014.
[30] 江文胜, 汪景庸, 赵建中, 等. 渤海湾环流的一次观测和分析[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 1997, 27(1):25-34
JIANG Wensheng, WANG Jingyong, ZHAO Jianzhong, et al. An observation of current in Bohai gulf and its analysis [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 1997, 27(1): 25-34.
[31] 杨作升, 郭志刚, 王兆祥, 等. 黄东海陆架悬浮体向其东部深海区输送的宏观格局[J]. 海洋学报, 1992, 14(2):81-90
YANG Zuosheng, GUO Zhigang, WANG Zhaoxiang, et al. Macroscopic pattern of suspension transport from the Yellow Sea and East China Sea to the eastern deep sea area [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1992, 14(2): 81-90.
[32] 吴德安, 张忍顺, 严以新, 等. 辐射沙洲东大港潮流水道悬沙输移机制分析[J]. 河海大学学报:自然科学版, 2006, 34(2):216-222
WU Dean, ZHANG Renshun, YAN Yixin, et al. Mechanism of suspended sediment transport in Dongdagang tidal channel of radial sand ridges [J]. Journal of Hohai University:Natural Sciences, 2006, 34(2): 216-222.
[33] Zhang D L, Anthes R A. A high-resolution model of the planetary boundary layer-sensitivity tests and comparisons with SESAME-79 data [J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 1982, 21(11): 1594-1609. doi: 10.1175/1520-0450(1982)021<1594:AHRMOT>2.0.CO;2
[34] Kundu P K, Beardsley R C. Evidence of a critical Richardson number in moored measurements during the upwelling season off northern California [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Ocean, 1991, 96(C3): 4855-4868. doi: 10.1029/90JC02108
[35] Wright L D, Friedrichs C T, Scully M E. Pulsational gravity-driven sediment transport on two energetic shelves [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2002, 22(17): 2443-2460. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(02)00133-4
[36] 孟令鹏, 胡日军, 李毅, 等. 福宁湾海域冬季大潮期悬浮泥沙输运特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(3):61-73
MENG Lingpeng, HU Rijun, LI Yi, et al. Transport characteristics of suspended sediment in Funing Bay during spring tide in winter [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(3): 61-73.
-



 下载:
下载: