Semi-quantitative study on reservoir configuration in grey theory—A case study of H3 sand unit of Huagang Formation in A Structure, Xihu Sag
-
摘要:
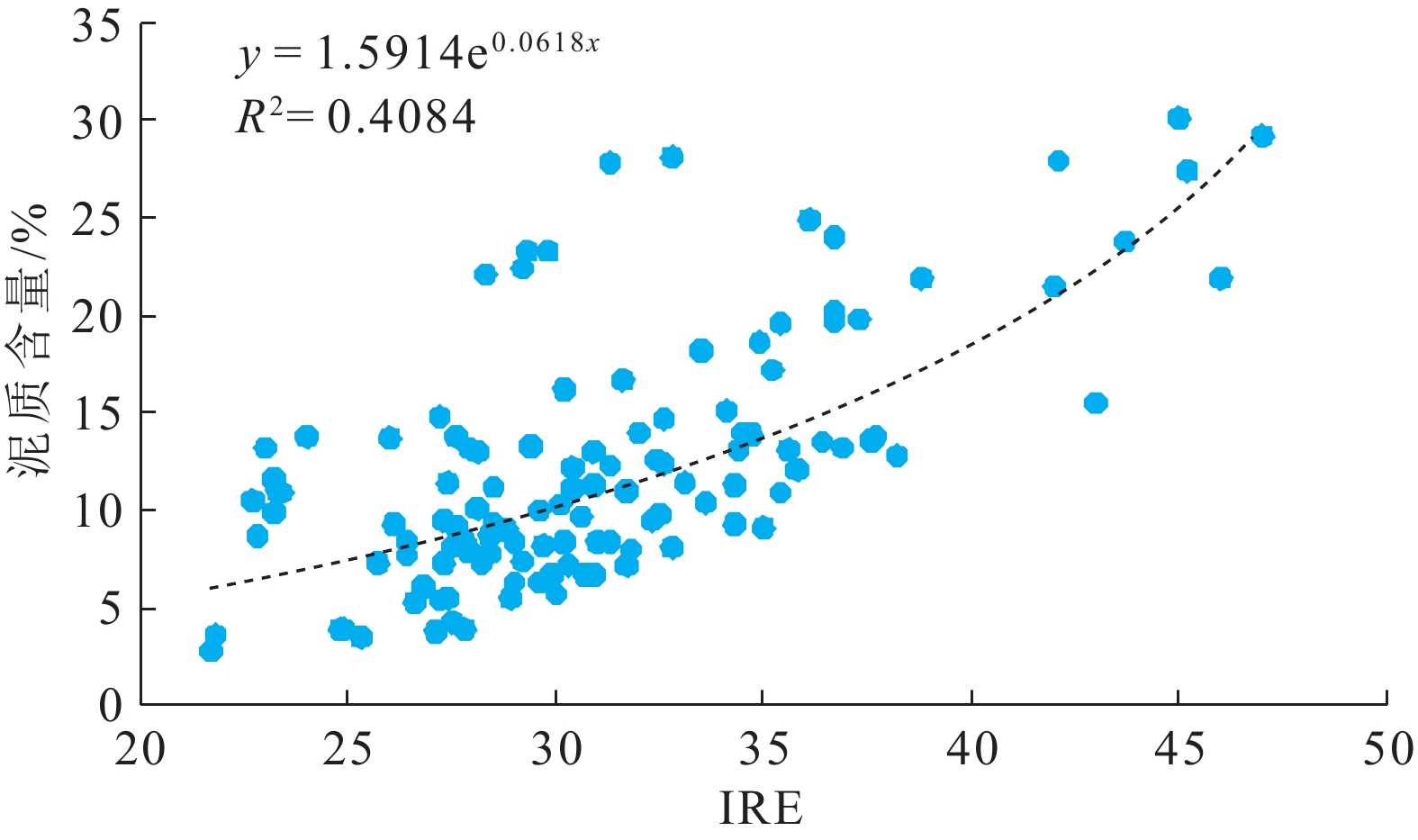
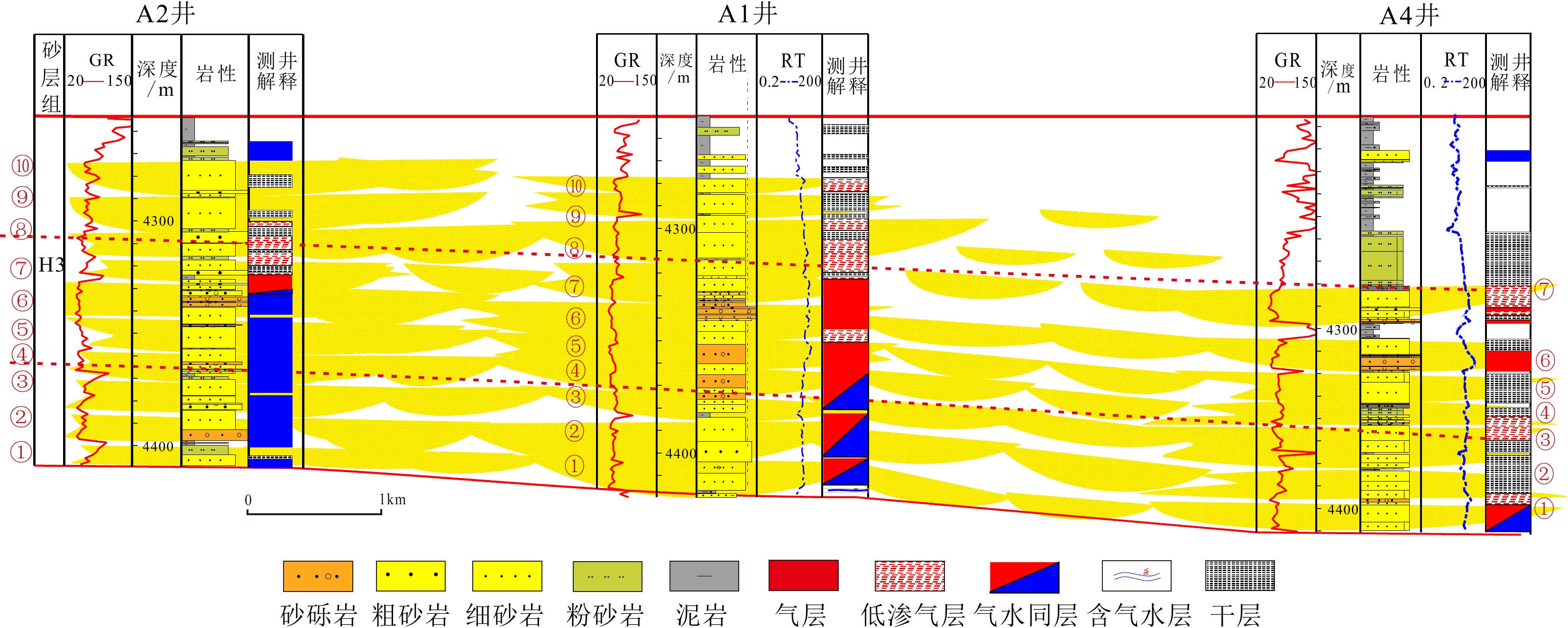
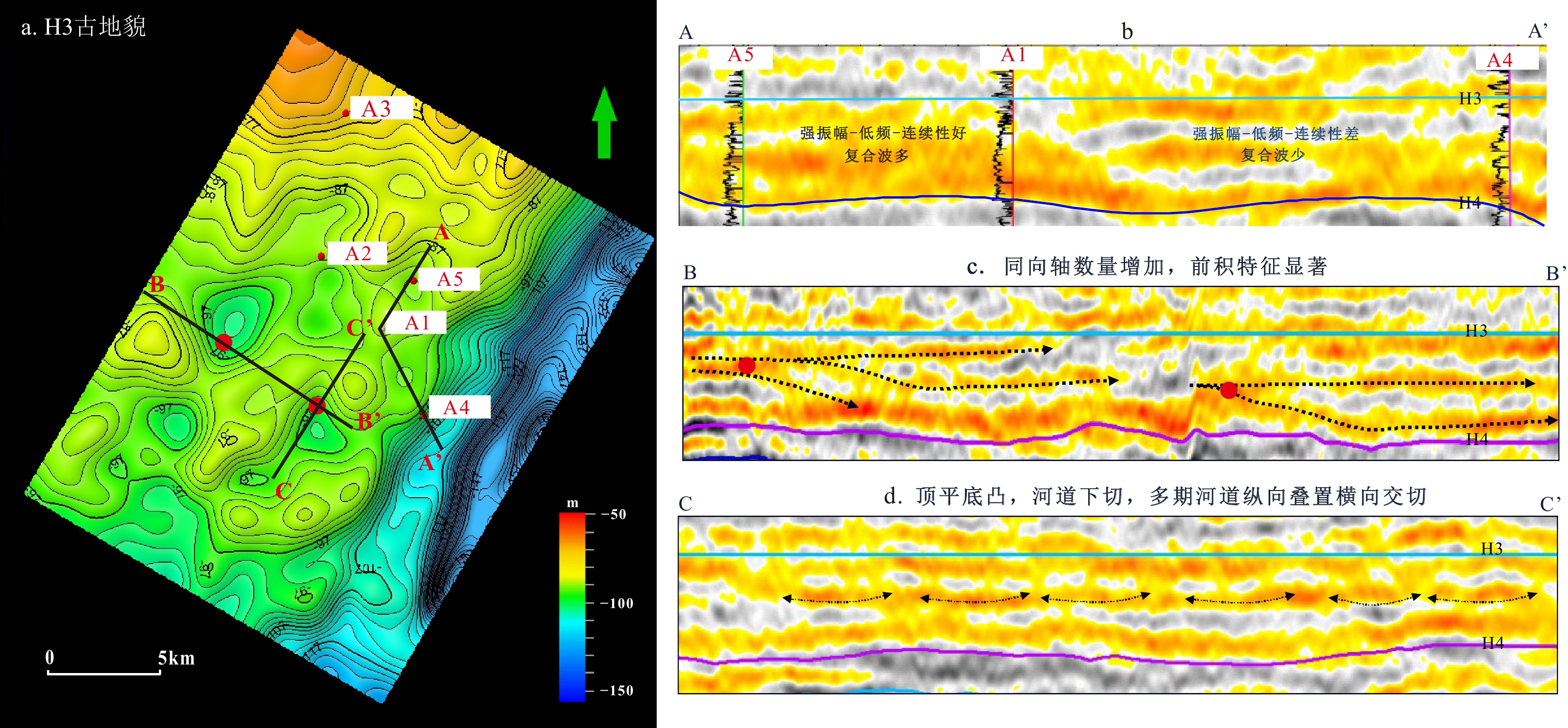
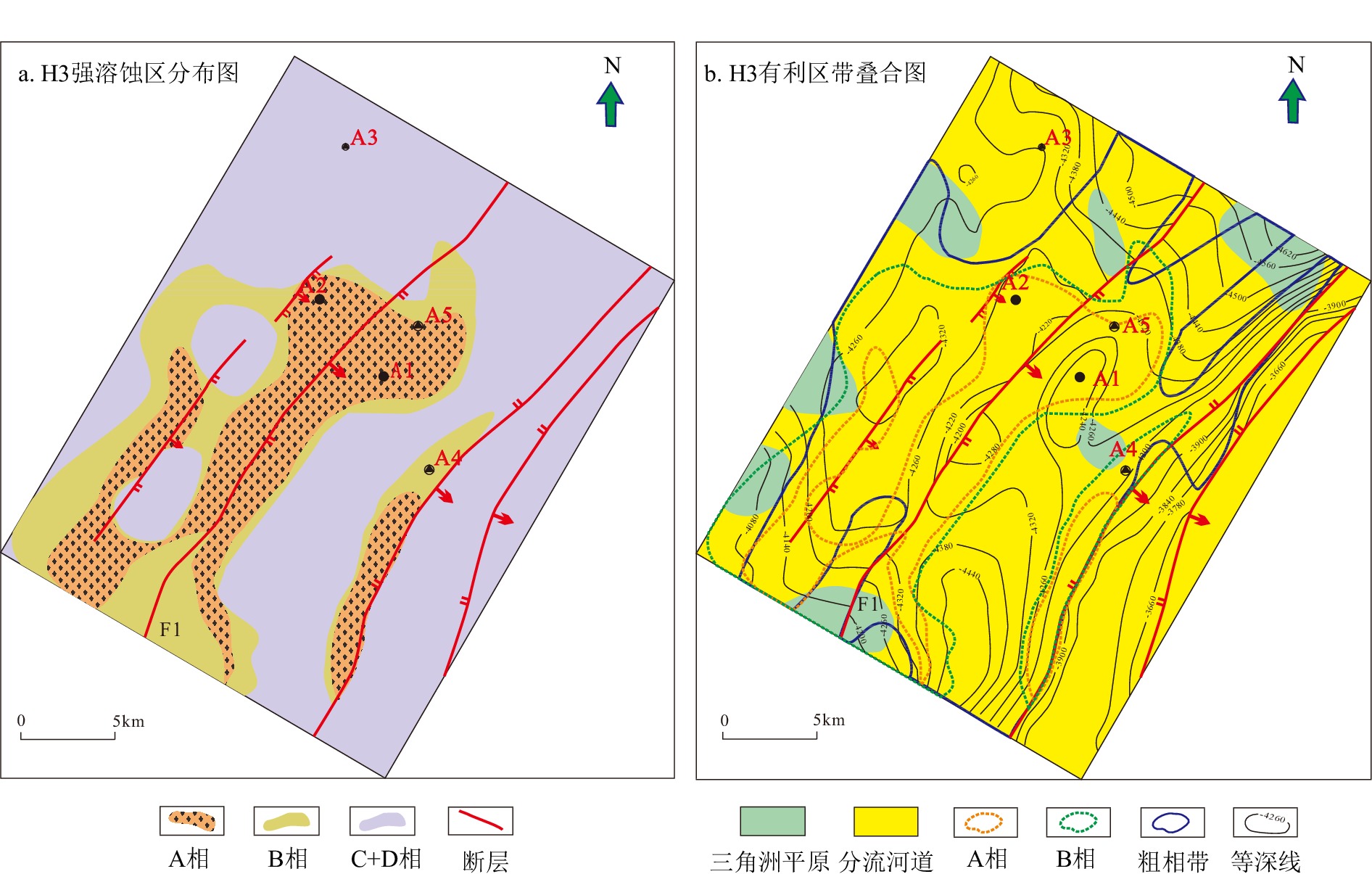
A构造位于西湖凹陷中北部,花港组H3砂层组为主力目的层,其储层横向分布相对稳定,但储层砂体厚度大,非均质性强,骨架河道的雕刻不清制约了优质储层的预测。利用灰色理论,定量计算西湖凹陷A构造花港组隔夹层综合评价指标IRE,识别厚层砂岩中的隔夹层类型,划分河道期次,识别骨架河道。此外,计算河道宽厚比和砂地比,半定量表征河道连通性及展布特征,预测优质储层发育区。结果表明,西湖凹陷A构造花港组发育两种类型隔夹层:落淤层夹层和泥岩层隔层,其中落淤层IRE值为24~45,泥岩层IRE值为51~110,在H3砂层组识别出3大套共10期单河道砂体。工区单河道宽厚比为38.87,折算出各期河道展布范围为1.1~2.3 km,河道砂体几乎都呈叠拼式展布。在地震复合微相指导下,对花港组早期河道进行识别和追踪,结合沉积微相、粗粒相带及成岩相分布特征,认为A构造南部有利储层更为发育。
Abstract:Using grey theory, we calculated quantitatively the comprehensive evaluation index IRE of the interlayer in Huagang Formation (Fm) of the A Structure in the Xihu Sag, China Sea, from which the type of interlayer in thick-bedded sandstone was identified and the channel period was divided. Combing logging data and lithofacies associations, we clarified the strength of hydrodynamic force, divided the reservoir types, and then defined influencing factors of high-quality reservoir development. In addition, based on single channel identification and classification, the average thickness of single interlaced strata was determined, and the river width-thickness ratio and sand-soil ratio were calculated to semi-quantitatively characterize the river connectivity and distribution characteristics. Based on the influencing factors and channel distribution characteristics of high-quality reservoirs, the development area of high-quality reservoirs was predicted. Results show that there are two types of interlayers in Huagang Fm of the A Structure, namely, desilting stratum and mudstone interlayer. The desilting stratum with low IRE was 24~45, and that of the mudstone layer was 51~110, much greater, thus the three sets of single channel sand bodies in 10 stages were identified in the H3 sand unit of Huagang Fm. The width-thickness ratio of single channel in the work area was 38.87, and the range of channel distribution in each period was calculated to be 1.1~2.3 km. The channel sand bodies are almost overlapped. Under the guidance of seismic composite microfacies, the early channel of Huagang Fm was identified and tracked. Combined with the distribution characteristics of sedimentary microfacies, coarse-grained facies zoning, and diagenesis development, we considered that the favorable reservoirs are more developed in the south area of the A Structure.
-
Key words:
- grey theory /
- interlayer /
- reservoir configuration /
- high quality reservoirs
-

-
表 2 IRE与储层类型定量关系
Table 2. Quantitative relationship between IRE and reservoir type
隔夹层类型 IRE 岩相组合 水动力强弱 渗透率/10−3 μm2 储层类型 落淤层 24~37 块状含砾砂岩–中粗砂岩–块状中砂岩 高能水道 0.3~79
(均值 21)I类 落淤层 35~45 少量砂质砾岩–少量块状中粗砂岩–大量块状细砂+平行细砂 低能水道 0.5~8
(均值1.2)II1类 泥岩层 51~110 平行中细砂岩–粉细砂 低能水道 0~1
(均值0.4)II2类 表 3 A构造H3 IRE值与隔夹层类型划分
Table 3. The IRE value of A Structure and the corresponding interlayer type
砂层期次 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 A1井 IRE 36~42 41~45 54~70 30~39 26~34 24~29 27~30 31~42 34~43 51~72 隔夹层类型 落淤层 落淤层 泥岩层 落淤层 落淤层 落淤层 泥岩层 落淤层 落淤层 泥岩层 A2井 IRE 37~46 30~33 44~70 24~29 27~30 41~60 31~42 34~53 41~52 43~104 隔夹层类型 落淤层 落淤层 泥岩层 落淤层 落淤层 泥岩层 落淤层 泥岩层 泥岩层 泥岩层 A4井 IRE 43~49 47~53 42~82 42~47 31~42 45~77 41~76 53~67 隔夹层类型 泥岩层 泥岩层 泥岩层 落淤层 落淤层 泥岩层 泥岩层 泥岩层 A5井 IRE 43~50 36~55 37~45 38~47 39~43 43~50 42~71 52~60 47~56 43~92 隔夹层类型 落淤层 落淤层 泥岩层 落淤层 落淤层 落淤层 泥岩层 落淤层 泥岩层 泥岩层 表 4 强溶蚀区划分依据
Table 4. Identification criterion for the division of diagenetic facies in strong dissolution area
成岩储集相 A相 B相 C相 D相 岩石类型 中、粗砂岩
含砾砂岩中–细砂岩
含砾砂岩细砂岩 粉–细砂岩、泥砾砂岩、钙质砂岩 沉积微相 辫状河道主体 河道侧缘 泥质杂基/% 0~4 2~5 1~7 1~13 孔隙度/% 6~11 5~10 3.5~10 2.2~9 渗透率/10−3 μm2 >1 0.5~1 0.2~0.5 <0.2 视压实率/% 85~99 80~94 40~95 40~93 视胶结率/% <6 1~8.5 1~17 1~68 视溶蚀率/% 4~20 2.3~10 0.5~9 0~8 DTS/(μs/ft) 95~105 90~115 GR/API ≤55 >55 RT/(Ω·m) ≥45 <45 ZDEN/(g/cm) ≤2.52 >2.52 储集性能 好 较好 差 致密 -
[1] 于兴河, 马兴详, 穆龙新, 等. 辫状河储层地质模式及层次界面分析[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004.
YU Xinghe, MA Xingxiang, MU Longxin, et al. Reservoir Geology Model and Analysis of Hierarchy Surface[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004.
[2] Lynds R, Hajek E. Conceptual model for predicting mudstone dimensions in sandy braided-river reservoirs [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2006, 90(8): 1273-1288. doi: 10.1306/03080605051
[3] 印森林, 吴胜和, 冯文杰, 等. 冲积扇储集层内部隔夹层样式: 以克拉玛依油田一中区克下组为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(6):757-763 doi: 10.11698/PED.2013.06.18
YIN Senlin, WU Shenghe, FENG Wenjie, et al. Patterns of inter-layers in the alluvial fan reservoirs: A case study on Triassic Lower Karamay Formation, Yizhong Area, Karamay Oilfield, NW China [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(6): 757-763. doi: 10.11698/PED.2013.06.18
[4] 渠芳, 陈清华, 连承波. 河流相储层构型及其对油水分布的控制[J]. 中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2008, 32(3):14-18
QU Fang, CHEN Qinghua, LIAN Chengbo. Fluvial facies reservoir architecture and its control over the distribution of oil and water [J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2008, 32(3): 14-18.
[5] Thorne C R, Russell A P G, Alam M K. Planform pattern and channel evolution of the Brahmaputra river, Bangladesh[M]//Best J L, Bristow C S. Braided Rivers. London: Geological Society of London, 1993: 257-276.
[6] 陈清华, 曾明, 章凤奇, 等. 河流相储层单一河道的识别及其对油田开发的意义[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2004, 11(3):13-15 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2004.03.005
CHEN Qinghua, ZENG Ming, ZHANG Fengqi, et al. Identification of single channel in fluvial reservoir and its significance to the oilfield development [J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2004, 11(3): 13-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2004.03.005
[7] 白振强. 辫状河砂体三维构型地质建模研究[J]. 西南石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 32(6):21-24
BAI Zhenqiang. Study on the 3D architecture geological modeling of braided fluvial sandbody [J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University:Science & Technology Edition, 2010, 32(6): 21-24.
[8] 蒋一鸣, 何新建, 张绍亮. 东海陆架盆地“反转改造”构造迁移演化特征: 以西湖凹陷边缘构造为例[J]. 长江大学学报:自科版, 2016, 13(26):1-7
JIANG Yiming, HE Xinjian, ZHANG Shaoliang. The characteristics of “Inverse-transform” tectonic migration evolution of the East China Sea Shelf basin: by taking the marginal structure of Xihu sag for example [J]. Journal of Yangtze University:Natural Science Edition, 2016, 13(26): 1-7.
[9] 郭真, 刘池洋, 田建锋. 东海陆架盆地龙井运动构造影响及其发育背景[J]. 西北大学学报:自然科学版, 2015, 45(5):801-810
GUO Zhen, LIU Chiyang, TIAN Jianfeng. Longjing movement structural effect and developmental background in East China Sea basin [J]. Journal of Northwest University:Natural Science Edition, 2015, 45(5): 801-810.
[10] 李顺利, 许磊, 于兴河, 等. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷渐新世海侵作用与潮控体系沉积特征[J]. 古地理学报, 2018, 20(6):1023-1032 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2018.06.075
LI Shunli, XU Lei, YU Xinghe, et al. Marine transgressions and characteristics of tide-dominated sedimentary systems in the Oligocene, Xihu sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2018, 20(6): 1023-1032. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2018.06.075
[11] 张建培, 余逸凡, 张田, 等. 东海西湖凹陷深盆气勘探前景探讨[J]. 中国海上油气, 2013, 25(2):24-29, 35
ZHANG Jianpei, YU Yifan, ZHANG Tian, et al. A discussion on the exploration potential of deep basin gas in Xihu sag, East China Sea [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2013, 25(2): 24-29, 35.
[12] 王果寿, 周卓明, 肖朝辉, 等. 西湖凹陷春晓区带下第三系平湖组、花港组沉积特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2002, 23(3):257-261, 265 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2002.03.012
WANG Guoshou, ZHOU Zhuoming, XIAO Chaohui, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of Eugene Pinghu formation and Huagang formation in Chunxiao Zone of Xihu lake depression [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2002, 23(3): 257-261, 265. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2002.03.012
[13] 张银国. 东海西湖凹陷花港组油气地质条件与油气分布规律[J]. 石油实验地质, 2010, 32(3):223-226,231 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2010.03.004
ZHANG Yinguo. Petroleum geology and hydrocarbon distribution pattern of Huagang Formation in the Xihu sag of the East China Sea [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2010, 32(3): 223-226,231. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2010.03.004
[14] 陈哲, 张昌民, 侯国伟, 等. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖组断层组合样式及其控砂机制[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(4):824-837 doi: 10.11743/ogg20200415
CHEN Zhe, ZHANG Changmin, HOU Guowei, et al. Fault distribution patterns and their control on sand bodies in Pinghu Formation of Xihu Sag in East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(4): 824-837. doi: 10.11743/ogg20200415
[15] 苏奥, 贺聪, 陈红汉, 等. 构造反转对西湖凹陷中部油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 特种油气藏, 2016, 23(3):75-78,147 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2016.03.017
SU Ao, HE Cong, CHEN Honghan, et al. Effect of tectonic inversion on hydrocarbon accumulation in the central area of Xihu depression [J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2016, 23(3): 75-78,147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2016.03.017
[16] 梁若冰, 李玉珍, 李纯洁, 等. 平湖油气田地质特征与勘探方向[J]. 海洋石油, 2008, 28(2):7-13, 57 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2008.02.002
LIANG Ruobing, LI Yuzhen, LI Chunjie, et al. Geological characteristics and exploration targets of Pinghu oilfield [J]. Offshore Oil, 2008, 28(2): 7-13, 57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2008.02.002
[17] 钟志洪, 张建培, 孙珍, 等. 西湖凹陷黄岩区地质演化及断层对油气运聚的影响[J]. 海洋石油, 2003, 23(S1):30-35
ZHONG Zhihong, ZHANG Jianpei, SUN Zhen, et al. Geological evolution of Huangyan area in Xihu sag and the influence of oil and gas migration in fault zone [J]. Offshore Oil, 2003, 23(S1): 30-35.
[18] 秦兰芝, 刘金水, 李帅, 等. 东海西湖凹陷中央反转带花港组锆石特征及物源指示意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(4):498-504, 526 doi: 10.11781/sysydz201704498
QIN Lanzhi, LIU Jinshui, LI Shuai, et al. Characteristics of zircon in the Huagang Formation of the central inversion zone of Xihu Sag and its provenance indication [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(4): 498-504, 526. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201704498
[19] 陈波, 李文俊, 丁芳, 等. 基于地震波形结构特征的分流河道砂体储层构型[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2021, 35(6):1-6 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2021.06.001
CHEN Bo, LI Wenjun, DING Fang, et al. Reservoir configuration of distributary channel sand body based on the structural features of seismic waveforms [J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2021, 35(6): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2021.06.001
[20] 刘玉娟, 郑彬, 李红英, 等. 渤海A油田大厚层油藏储层构型研究[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2018, 32(6):16-20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2018.06.004
LIU Yujuan, ZHENG Bin, LI Hongying, et al. Study on reservoir configuration of large thick reservoirs in Bohai A Oilfield [J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2018, 32(6): 16-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2018.06.004
[21] 孙天建, 穆龙新, 赵国良. 砂质辫状河储集层隔夹层类型及其表征方法: 以苏丹穆格莱特盆地Hegli油田为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(2):112-120
SUN Tianjian, MU Longxin, ZHAO Guoliang. Classification and characterization of barrier-intercalation in sandy braided river reservoirs: Taking Hegli Oilfield of Muglad Basin in Sudan as an example [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(2): 112-120.
[22] 宋子齐, 谭成仟, 曲政. 利用灰色理论精细评价油气储层的方法[J]. 石油学报, 1996, 17(1):25-31 doi: 10.7623/syxb199601004
SONG Ziqi, TAN Chengqian, QU Zheng. Utilizing exact grey theory to evaluate oil and gas formation [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1996, 17(1): 25-31. doi: 10.7623/syxb199601004
[23] Bridge J S. Fluvial facies models: Recent developments[M]//Posamentier H W, Walker R G. Facies Models Revisited. Tulsa: Society for Sedimentary Geology, 2006: 83-168.
[24] Bridge J S, Tye R S. Interpreting the dimensions of ancient fluvial channel bars, channels, and channel belts from wireline-logs and cores [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2000, 84(8): 1205-1228.
[25] Kelly S. Scaling and hierarchy in braided rivers and their deposits: Examples and implications for reservoir modelling[M]//Smith G H S, Best J L, Bristow C S, et al. Braided Rivers: Process, Deposits, Ecology and Management. Oxford, UK: International Association of Sedimentologists, 2006: 75-106.
[26] 金振奎, 杨有星, 尚建林, 等. 辫状河砂体构型及定量参数研究: 以阜康、柳林和延安地区辫状河露头为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(3):311-317
JIN Zhenkui, YANG Youxing, SHANG Jianlin, et al. Sandbody architecture and quantitative parameters of single channel sandbodies of braided river: cases from outcrops of braided river in Fukang, Liulin and Yanan areas [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25(3): 311-317.
-




 下载:
下载: