Variation of clay mineral input in the Parece Vela Basin since the last 2.1 Ma and the response to the mid-Pleistocene climate transition
-
摘要:
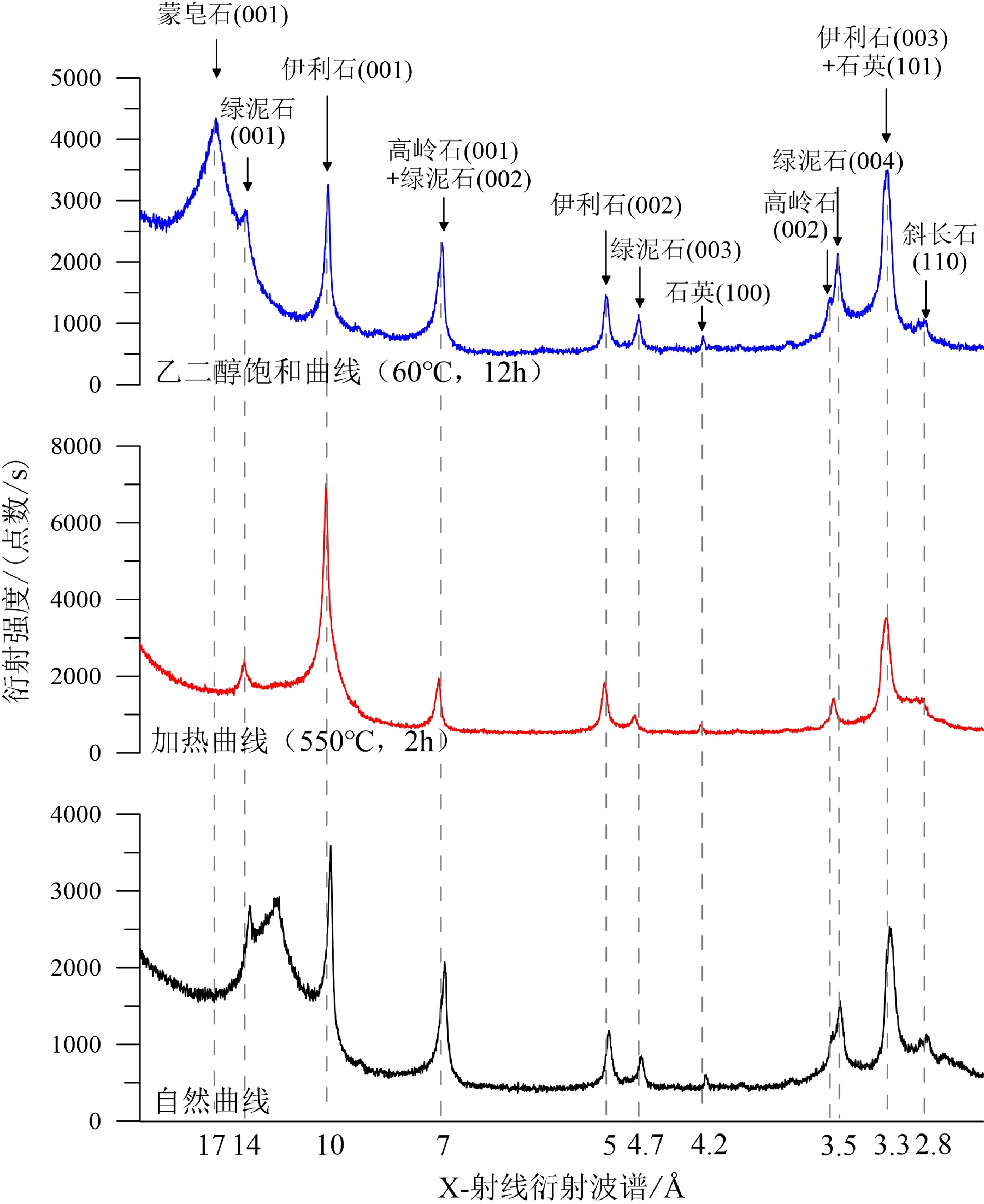
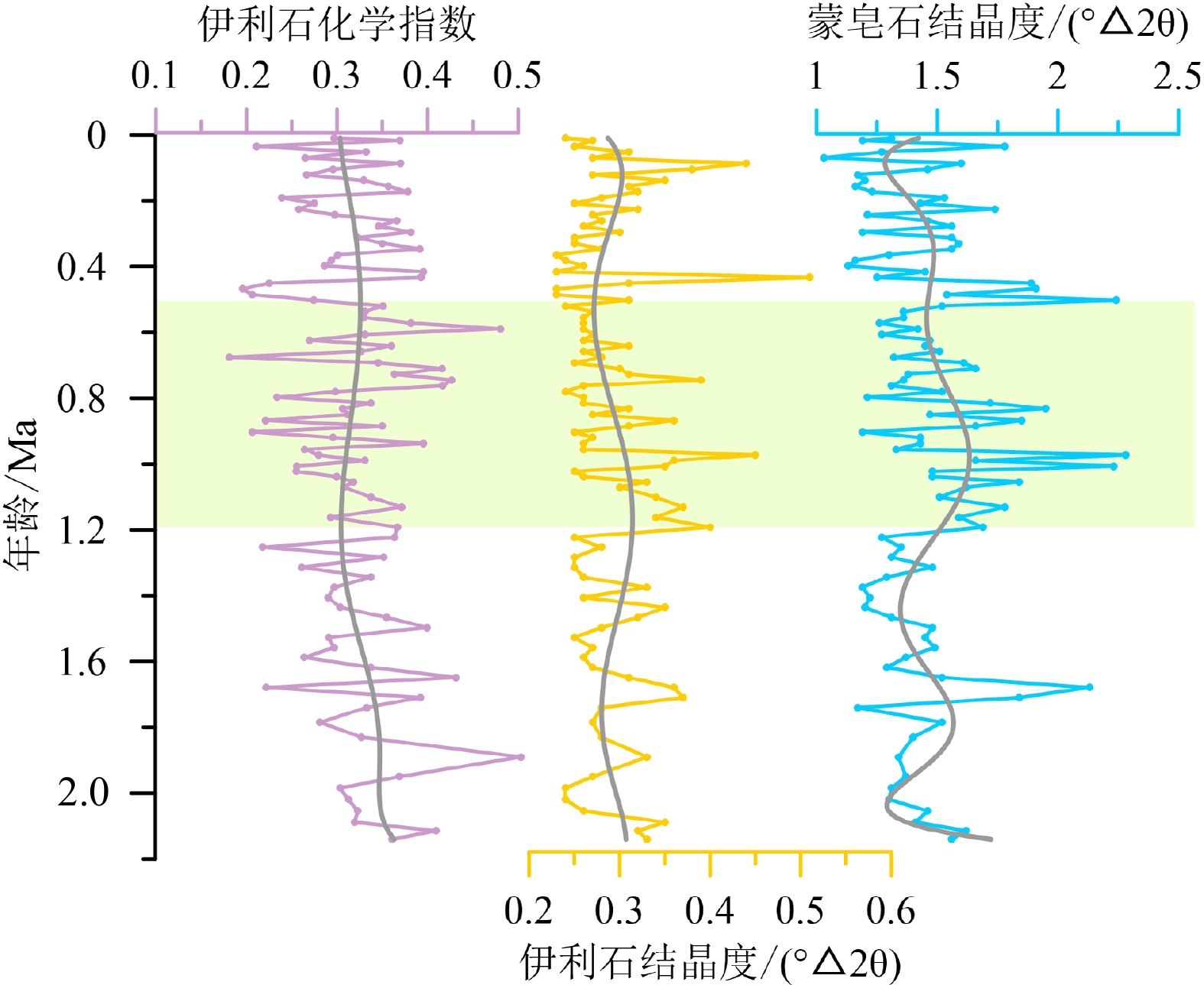
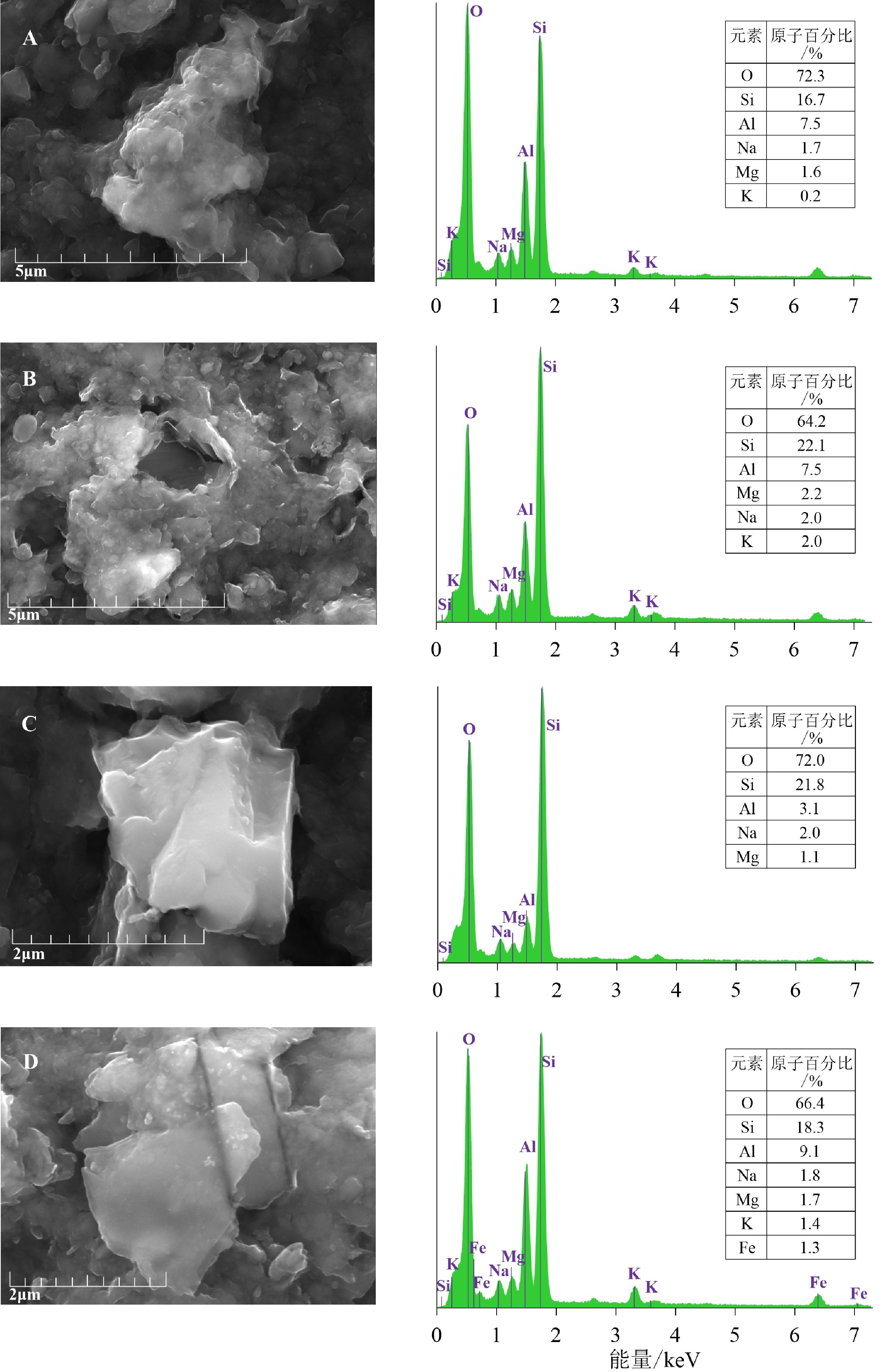
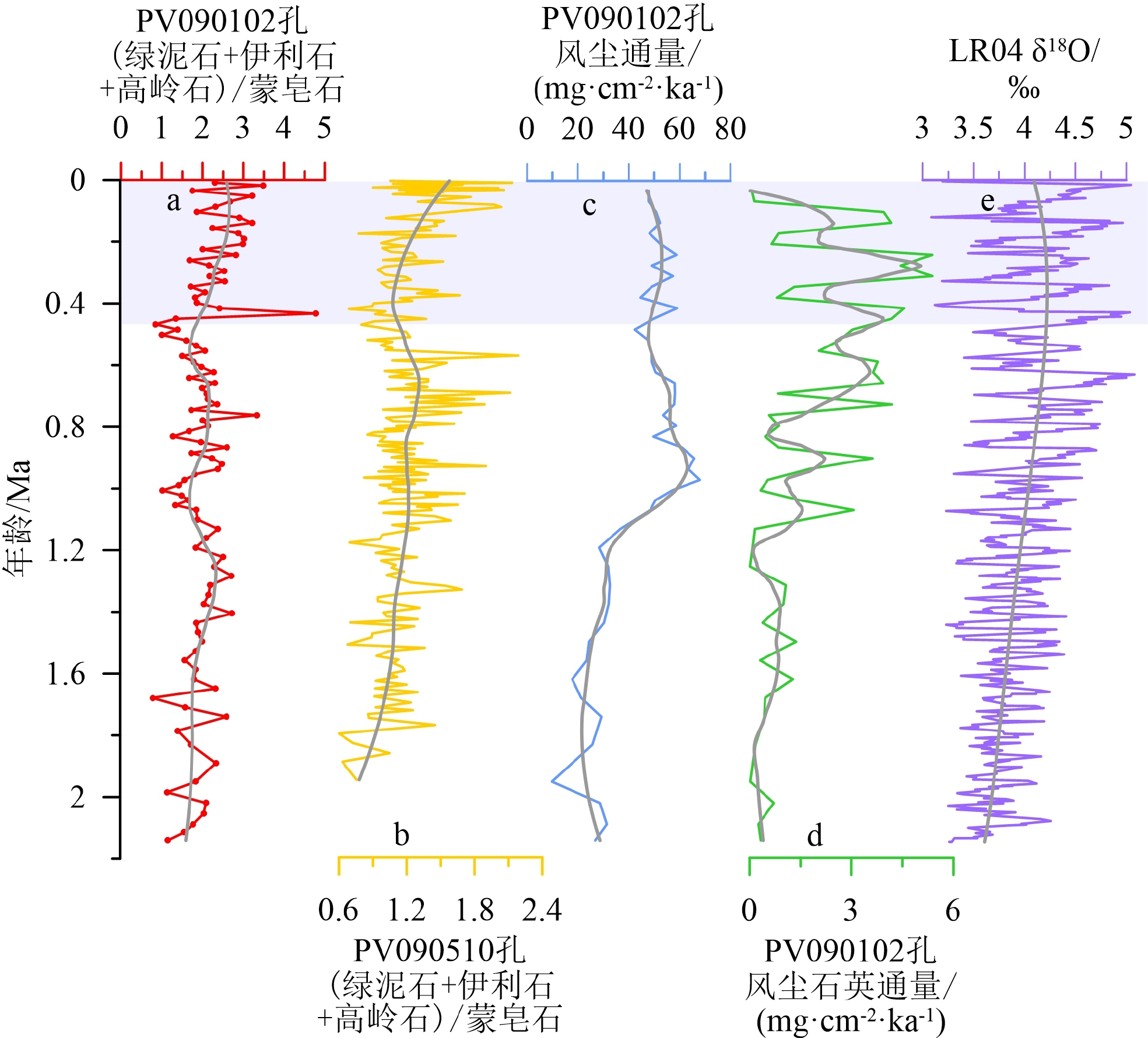
对帕里西维拉海盆PV090102孔2.1 Ma以来沉积物中黏土矿物的含量、特征参数和形貌特征进行了分析,结果表明,黏土矿物以伊利石(48%)和蒙皂石(34%)为主,绿泥石(13%)和高岭石(6%)含量较低。伊利石结晶度平均为0.29°△2θ,表明其形成于气候寒冷且水解作用弱的陆地源区;伊利石化学指数平均为0.32,表明该孔伊利石为富Fe-Mg伊利石,且经历了较强的物理风化。黏土矿物的组合特征和形貌特征表明,蒙皂石主要来源于周围火山岛弧,伊利石、绿泥石和高岭石主要来源于亚洲大陆风尘。在中更新世气候转型期,伊利石通量、绿泥石通量和高岭石通量均呈增加趋势,这与该孔总的风尘通量和风尘石英通量的变化趋势一致,且与亚洲大陆干旱化一致,表明其响应了中更新世气候转型期亚洲内陆的干旱变化,因而可以作为亚洲内陆干湿变化的示踪指标。此外,第四纪以来PV090102孔蒙皂石通量的变化与该孔火山物质通量的变化趋势具有很好的一致性,因而可以作为火山物质输入西菲律宾海的替代指标。
Abstract:The composition and morphology of clay minerals collected from Core PV090102 in the Parece Vela Basin over the last 2.1 Ma were analyzed. Results show that the clays are mainly composed of illite (48% on average) and smectite (34%), and chlorite (13%) and kaolinite (6%). The illite crystallinity (0.29°Δ2θ) indicates that illite is mainly derived from cold and dry terrestrial regions; and the illite chemical index (0.32) implies that illite is rich in Fe-Mg and has experienced strong physical weathering. The clay mineral assemblage and morphological characteristics reflect that smectite is mainly derived from surrounding volcanic islands, while illite, chlorite, and kaolinite from Asian dust. The mass accumulation rates (MARs) of illite, chlorite, and kaolinite in Core PV090102 increased during mid-Pleistocene, which is consistent with the increase of MARs of eolian dust quartz in the Parece Vela Basin and Asia continent, suggesting that the MARs of illite, chlorite, and kaolinite in the Parece Vela Basin responded to the aridification in Asia during the mid-Pleistocene. Therefore, the MARs of illite, chlorite, and kaolinite in the Parece Vela Basin can be used to trace the paleoclimate change of Asian continent. In addition, variation of smectite MARs in Core PV090102 since the Quaternary is very consistent with the trend of volcanic material MARs in this core, and thus the variation can be used as a proxy of volcanic material input into the West Philippine Sea.
-
Key words:
- clay minerals /
- provenance /
- mid-Pleistocene /
- Parece Vela Basin
-

-
[1] Scott R B, Kroenke L, Zakariadze G, et al. Evolution of the South Philippine Sea: deep sea drilling project leg 59 results[C]//Kroenke L, Scott R B, Balshaw K, et al. Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project. Washington: U. S. Government Printing Office, 1981: 803-815.
[2] Jiang F Q, Zhu X, Li T G, et al. Increased dust deposition in the Parece Vela Basin since the mid- Pleistocene inferred from radiogenic Sr and Nd isotopes [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2019, 173: 83-95. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.12.011
[3] Wan S M, Yu Z J, Clift P D, et al. History of Asian eolian input to the West Philippine Sea over the last one million years [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 326-328: 152-159. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2012.02.015
[4] Ming J, Li A C, Huang J, et al. Assemblage characteristics of clay minerals and its implications to evolution of eolian dust input to the Parece Vela Basin since 1.95 Ma [J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2014, 32(1): 174-186. doi: 10.1007/s00343-014-3066-x
[5] Yu Z J, Wan S M, Colin C, et al. Co-evolution of monsoonal precipitation in East Asia and the tropical Pacific ENSO system since 2.36 Ma: new insights from high-resolution clay mineral records in the West Philippine Sea [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 446: 45-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.04.022
[6] 周宇. 近2Ma帕里西—维拉海盆的风尘记录[D]. 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所)硕士学位论文, 2014: 30
ZHOU Yu. Asian dust record in the Parece Vela Basin over the last 2 Ma[D]. Master Dissertation of Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2014: 30.
[7] 石学法, 陈丽蓉, 李坤业, 等. 西菲律宾海西部海域粘土沉积物的成因矿物学研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1995, 15(2):61-72 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1995.02.007
SHI Xuefa, CHEN Lirong, LI Kunye, et al. Study on minerageny of the clay sediment in the west of Philippine Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1995, 15(2): 61-72. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1995.02.007
[8] 刘华华, 蒋富清, 周烨, 等. 晚更新世以来奄美三角盆地黏土矿物的来源及其对古气候的指示[J]. 地球科学进展, 2016, 31(3):286-297 doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2016.03.0286.
LIU Huahua, JIANG Fuqing, ZHOU Ye, et al. Provenance of clay minerals in the Amami Sankaku Basin and their paleoclimate implications since Late Pleistocene [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2016, 31(3): 286-297. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2016.03.0286.
[9] 杨佳毅, 蒋富清, 颜钰, 等. 上新世以来伊豆-小笠原海脊黏土矿物的来源与古气候意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(4):73-83
YANG Jiayi, JIANG Fuqing, YAN Yu, et al. Provenance and paleoclimatic significance of clay minerals from Izu-Ogasawara Ridge since Pliocene [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(4): 73-83.
[10] 靳宁, 李安春, 刘海志, 等. 帕里西维拉海盆西北部表层沉积物中粘土矿物的分布特征及物源分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2007, 38(6):504-511 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814x.2007.06.004
JIN Ning, LI Anchun, LIU Haizhi, et al. Clay minerals in surface sediment of the northwest Parece Vela Basin: distribution and provenance [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2007, 38(6): 504-511. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814x.2007.06.004
[11] Seo I, Lee Y I, Yoo C M, et al. Sr-Nd isotope composition and clay mineral assemblages in eolian dust from the central Philippine Sea over the last 600 kyr: Implications for the transport mechanism of Asian dust [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2014, 119(19): 11492-11504. doi: 10.1002/2014JD022025
[12] 肖春晖, 王永红, 林间. 近1Ma以来帕里西维拉海盆沉积物物源和古气候: 粒度和黏土矿物特征的指示[J]. 沉积学报, 2022, 40(2):508-524
XIAO Chunhui, WANG Yonghong, LIN Jian. Provenance and paleoclimate of sediments in the Parece Vela Basin in past 1 Ma: inferences from grain -size and clay mineral distribution [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2022, 40(2): 508-524.
[13] Kawabe M, Fujio S, Yanagimoto D, et al. Water masses and currents of deep circulation southwest of the Shatsky Rise in the western North Pacific [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers, 2009, 56(10): 1675-1687. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2009.06.003
[14] Lee I, Ogawa Y. Bottom-current deposits in the Miocene-Pliocene Misaki Formation, Izu forearc area, Japan [J]. Island Arc, 1998, 7(3): 315-329. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1738.1998.00192.x
[15] 孟庆勇, 李安春, 蒋富清, 等. 近2 Ma来东菲律宾海地球磁场相对强度变化的沉积记录[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2010, 41(4):606-613 doi: 10.11693/hyhz201004021021
MENG Qingyong, LI Anchun, JIANG Fuqing, et al. A geomagnetic paleointensity record over the last 2Ma from the east Philippine Sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2010, 41(4): 606-613. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201004021021
[16] Biscaye P E. Mineralogy and sedimentation of recent deep-sea clay in the Atlantic ocean and adjacent seas and oceans [J]. GSA Bulletin, 1965, 76(7): 803-825. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1965)76[803:MASORD]2.0.CO;2
[17] Ehrmann W. Implications of Late Eocene to early Miocene clay mineral assemblages in McMurdo Sound (Ross Sea, Antarctica) on paleoclimate and ice dynamics [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1998, 139(3-4): 213-231. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(97)00138-7
[18] Chamley H. Clay Sedimentology[M]. Berlin: Springer, 1989: 1-623.
[19] 杨雅秀, 张乃娴, 苏昭冰, 等. 中国粘土矿物[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1994: 143-150
YANG Yaxiu, ZHANG Naixian, SU Zhaobing, et al. Clay Minerals of China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1994: 143-150.
[20] 师育新, 戴雪荣, 李节通, 等. 末次间冰期兰州黄土记录中的粘土矿物及其环境意义探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1997, 17(1):87-94 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1997.01.013
SHI Yuxin, DAI Xuerong, LI Jietong, et al. Origin and significance of clay minerals in the last interglacial loess in Lanzhou area, North Central China [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1997, 17(1): 87-94. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1997.01.013
[21] 师育新, 戴雪荣, 宋之光, 等. 我国不同气候带黄土中粘土矿物组合特征分析[J]. 沉积学报, 2005, 23(4):690-695 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.04.019
SHI Yuxin, DAI Xuerong, SONG Zhiguang, et al. Characteristics of clay mineral assemblages and their spatial distribution of Chinese loess in different climatic zones [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2005, 23(4): 690-695. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.04.019
[22] 郑洪汉. 中国黄土中粘土矿物的古气候记录[J]. 第四纪研究, 1985, 6(2):41-47
ZHENG Honghan. Paleoclimatic records of clay minerals in loess, China [J]. Quaternary Sinica, 1985, 6(2): 41-47.
[23] Wan S M, Li A C, Clift P D, et al. Development of the East Asian monsoon: Mineralogical and sedimentologic records in the northern South China Sea since 20 Ma [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2007, 254(3-4): 561-582. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2007.07.009
[24] Liu Z F, Tuo S T, Colin C, et al. Detrital fine-grained sediment contribution from Taiwan to the northern South China Sea and its relation to regional ocean circulation [J]. Marine Geology, 2008, 255(3-4): 149-155. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2008.08.003
[25] 李传顺, 石学法, 高树基, 等. 台湾河流沉积物的黏土矿物组成特征与物质来源[J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57(6):673-681 doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4824-1
LI Chuanshun, SHI Xuefa, GAO Shuji, et al. Clay mineral composition and their sources for the fluvial sediments of Taiwanese rivers [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(6): 673-681. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4824-1
[26] 郑智睿. 南冲绳海槽表层沉积物中黏土矿物之研究[D]. 台湾大学海洋研究所硕士学位论文, 2008: 23-46
ZHENG Zhirui. Clay mineral distribution in surface sediments of the southern Okinawa Trough[D]. Master Dissertation of Institute of Oceanography, National Taiwan University, 2008: 23-46.
[27] Xu K H, Milliman J D, Li A C, et al. Yangtze- and Taiwan-derived sediments on the inner shelf of East China Sea [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2009, 29(18): 2240-2256. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2009.08.017
[28] Nagel U, Müller G, Schumann D, et al. Mineralogy of sediments cored during deep sea drilling project legs 58-60 in the north and south Philippine Sea: results of X-ray diffraction analyses[C]//Hussong D M, Uyeda S, Blanchet R, et al. Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project. Washington: U. S. Government Printing Office, 1981: 415-435.
[29] Underwood M B, Orr R, Pickering K, et al. Provenance and dispersal patterns of sediments in the turbidite wedge of Nankai Trough[C]//Hill I A, Taira A, Firth J V, et al. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program. Scientific Results, 1993: 15-34.
[30] Shen X Y, Wan S M, France-Lanord C, et al. History of Asian eolian input to the Sea of Japan since 15 Ma: Links to Xizang uplift or global cooling? [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2017, 474: 296-308. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2017.06.053
[31] 张德玉. 马里亚纳海槽区粘土矿物组成及分布特征[J]. 黄渤海海洋, 1994, 12(2):32-39
ZHANG Deyu. Clay mineral composition and distribution in the Mariana Trough [J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 1994, 12(2): 32-39.
[32] Liu Z F, Zhao Y L, Colin C, et al. Chemical weathering in Luzon, Philippines from clay mineralogy and major-element geochemistry of river sediments [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2009, 24(11): 2195-2205. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.09.025
[33] 秦蕴珊, 赵一阳, 陈丽蓉, 等. 东海地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1987: 81-92
QIN Yunshan, ZHAO Yiyang, CHEN Lirong, et al. Geology of the East China Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1987: 81-92.
[34] Ji J F, Chen J, Lu H Y. Origin of illite in the loess from the Luochuan area, Loess Plateau, Central China [J]. Clay Minerals, 1999, 34(4): 525-532. doi: 10.1180/000985599546398
[35] Aoki S, Kohyama N, Ishizuka T. Sedimentary history and chemical characteristics of clay minerals in cores from the distal part of the Bengal Fan (ODP 116) [J]. Marine Geology, 1991, 99(1-2): 175-185. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(91)90090-Q
[36] Aoki S, Kohyama N. The vertical change in clay mineral composition and chemical characteristics of smectite in sediment cores from the southern part of the Central Pacific Basin [J]. Marine Geology, 1991, 98(1): 41-49. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(91)90034-2
[37] Aoki S, Kohyama N. Modern sedimentation in the Japan Trench: implications of the mineralogy and chemistry of clays sampled from sediment traps [J]. Marine Geology, 1992, 108(2): 197-208. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(92)90172-E
[38] Windom H L. Lithogenous material in marine sediments[M]//Riley J P, Chester R. Chemical Oceanography. 2nd ed. London: Academic Press, 1976: 103-135.
[39] Kolla V, Nadler L, Bonatti E. Clay mineral distributions in surface sediments of the Philippine Sea [J]. Oceanologica Acta, 1980, 3(2): 245-250.
[40] Yan Y, Jiang F Q, Zeng Z G, et al. Response of eolian quartz flux and grain size in the Parece Vela Basin sediment to the mid-Pleistocene transition [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2022, 236: 105332. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2022.105332
[41] Cai M T, Fang X M, Wu F L, et al. Pliocene-Pleistocene stepwise drying of Central Asia: Evidence from paleomagnetism and sporopollen record of the deep borehole SG-3 in the western Qaidam Basin, NE Xizang Plateau [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2012, 94-95: 72-81. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2012.07.002
[42] Han W X, Fang X M, Berger A. Xizang forcing of mid-Pleistocene synchronous enhancement of East Asian winter and summer monsoons revealed by Chinese loess record [J]. Quaternary Research, 2012, 78(2): 174-184. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2012.05.001
[43] Lisiecki L E, Raymo M E. A Pliocene-Pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ18O records [J]. Paleoceanography, 2005, 20(1): PA1003.
[44] Patterson D B, Farley K A, Norman M D. 4He as a tracer of continental dust: A 1.9 million year record of aeolian flux to the west equatorial Pacific Ocean [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(5): 615-625. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00077-0
[45] Martínez-García A, Rosell-Melé A, Jaccard S L, et al. Southern Ocean dust–climate coupling over the past four million years [J]. Nature, 2011, 476(7360): 312-315. doi: 10.1038/nature10310
-




 下载:
下载: