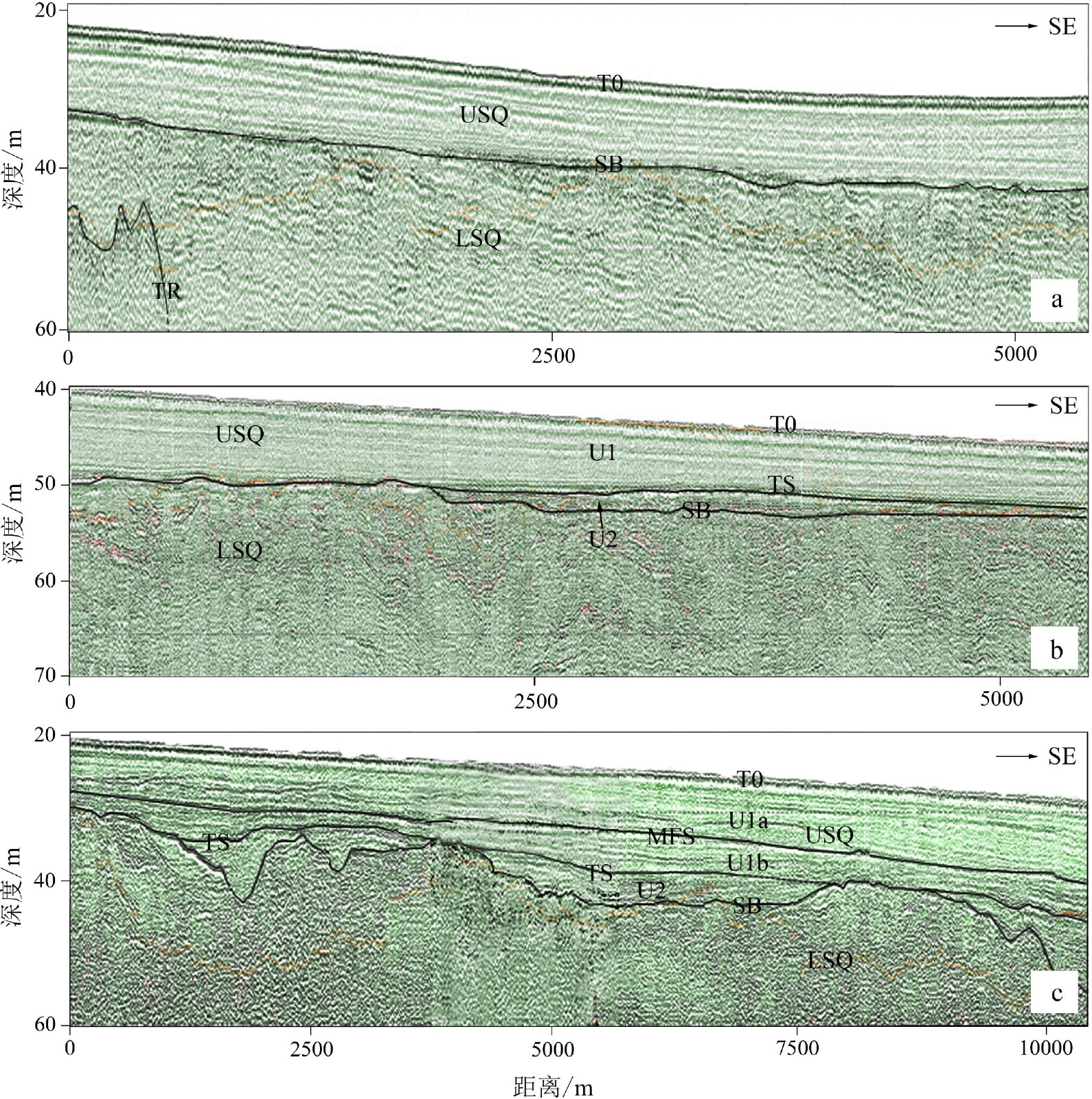
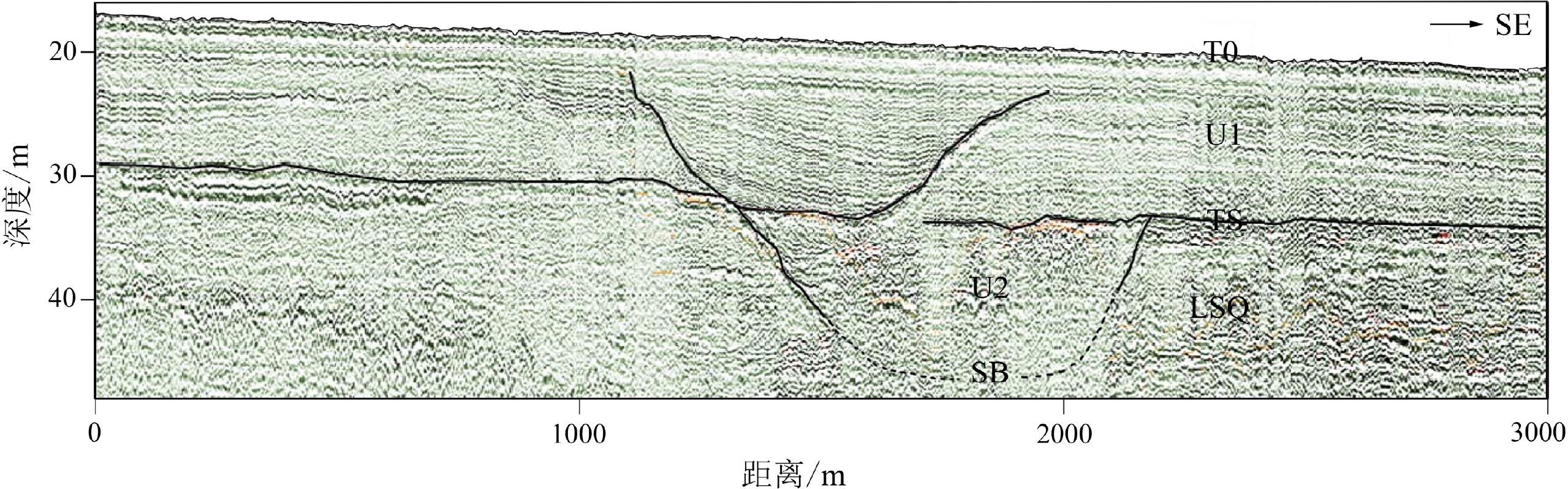
Seismic stratigraphy and buried special geomorphological features in shallow strata off middle and south Fujian Province, China
-
摘要:
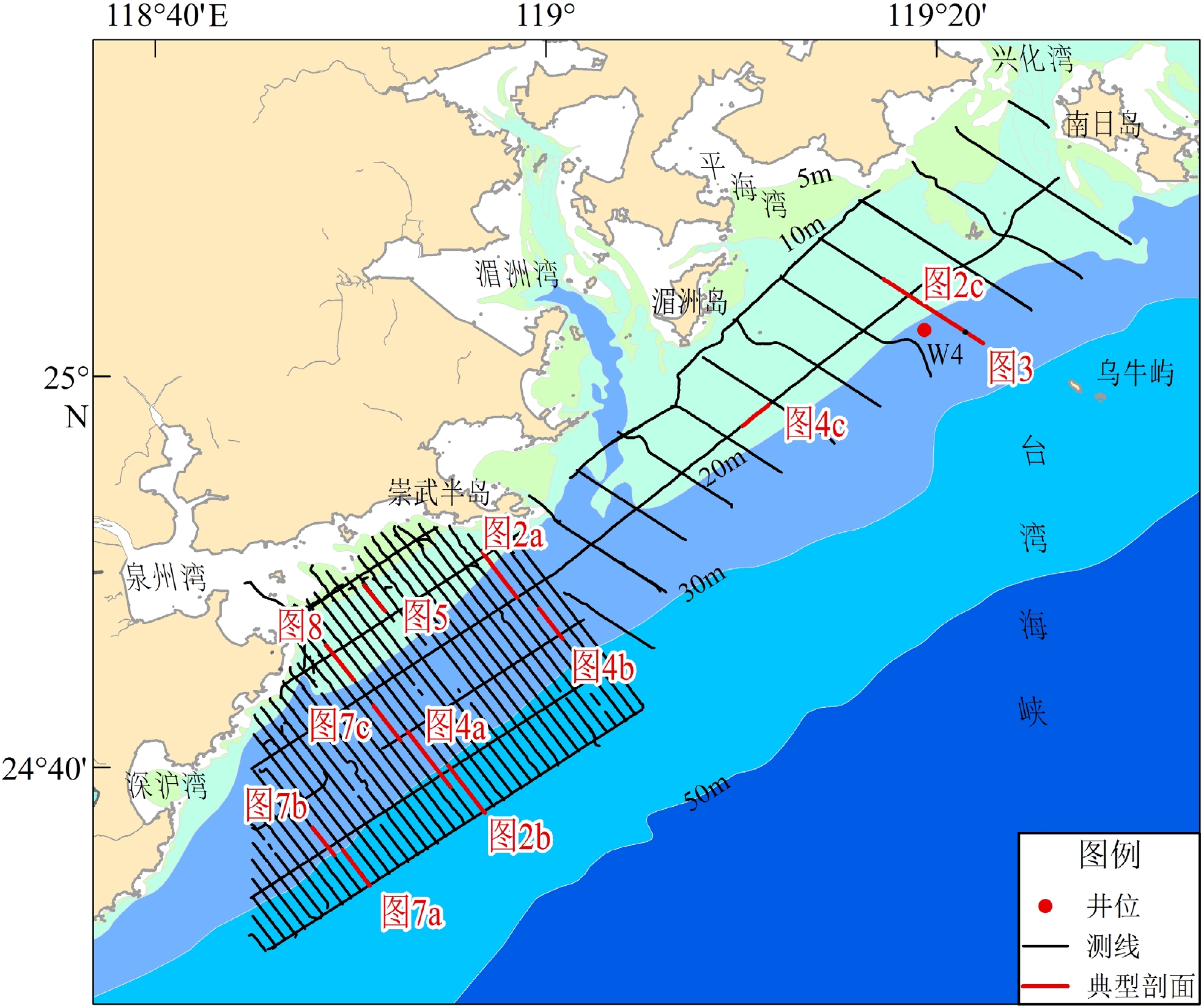
在闽中南近海台湾海峡中西部的湄洲湾和泉州湾采用拖筏震源进行高分辨率单道浅地震调查,测线网格在南部海域为1 km×5 km,北部为约5 km×8 km。有两个区域性的强反射界面:海底面和陆相强侵蚀面。局部可以辨识海侵面、最大海泛面和基岩面。除了在晚更新世古河道等负地形区外,陆相强侵蚀面与海侵面重合,该强侵蚀面将地震剖面分隔为上层序和下层序,而海侵面又将上层序划分为全新世海相和晚更新世古河道充填相层。其中,全新世海相层为主体,全区有分布,部分海域可以分成上亚层和下亚层。在晚更新世末次低海面时期,研究区南部发育古晋江南河道和北河道,最宽分别约7~8 km和2 km,北部为密集的溪沟地貌,宽约1 km;推测随着海平面上升,古晋江河道发生堆积退缩,直至消失,时间为约12.0~9.6 kaBP,而后掩埋于全新世海相层之下。在研究区最南部,有19 条长度1 km以上的潮流沙脊埋藏于全新世海相层内,高约1~7 m,长约1.5~10 km,大体相互平行,主要发育年代可能在约10 kaBP。沙脊分为单脊型和多脊型,前者又分为单脊孤立型和单脊多列型,后者分为简单多脊型和超复多脊型,沙脊高度与下伏亚层的厚度基本上呈正相关。泉州湾口外发育小型河道和水下三角洲,主要浅埋于全新世海相层内,形成于全新世。这些埋藏特殊地貌的发育,除北部海域的溪沟外,均与晋江水沙有关。
Abstract:High-resolution shallow-seismic profiles using boomer in inshore area off Meizhou Bay and Quanzhou Bay, the middle of the western Taiwan Strait were analyzed. The survey grids are 1 km×5 km in the southern area and about 5 km×8 km in the northern. The seismic profiles reveal two regional strong reflectors: T0 (sea bottom) and SB (subaerial erosion surface); and three locally recognizable: TS (transgressive surface), MFS (maximum flooding surface), and TR (rock surface). Apart from paleo-negative topography, such as river channels of MIS 2, SB coincides with TS. In addition, the seismic profiles can be divided at SB into upper sequence (USQ) and lower sequence (LSQ). The USQ is subdivided at TS into unit U1 (marine Holocene) and U2 (infillings of paleo-channel of MIS 2). During the last low sea level, the south and north channels of paleo-Jinjiang River were developed in the southern study area in 7~8 km and 2 km, the widest width, respectively. In the northern study area were developed quite dense gullies, about 1 km wide, which might be related to complicated paleo-ground and streams from Meizhou Bay region varying strongly in season. Considering sea level curves, as sea level rising, the south channels were gradually submerged landward about 12.0~9.6 kaBP. In addition, 19 buried linear tidal sand ridges in NE-SW direction within unit U1 in the southernmost part of the study area were recognized. The sand ridges are about 1~7 m high, 1.5–10 km long, and usually in intervals of several-hundred meters to about 1 km. They were mainly formed at about 10 kaBP. In terms of the profile shapes and internal structures, they could be divided into single-crest sand ridges and multiple-crests sand ridges. The former ones are in turn subdivided into isolated single-crest ridges and single-crest ridges of multiple-lines, while the latter ones, into simple multiple-crests ridges and overlapped multiple-crests ridges. A small river channel and a subaqueous delta were mainly buried inside U1 just outside Quanzhou Bay mouth. They were formed during the Holocene. The development of all these buried special geomorphological features, but gullies in the northern area, were related with sand and water discharges of paleo-Jinjiang River.
-

-
图 3 W4井与相邻地震剖面对比图[10]
Figure 3.
表 1 沙脊典型(最大)高度和下伏U1b厚度
Table 1. Typical (maximum) height of sand ridges and thickness of their underlain U1b
沙脊编号 TS深度/m 海底深度/m 沙脊高度/m U1b厚度/m 沙脊分区 SR17 47.2 37.7 5.7 3.2 南小区 SR15 45.5 37.2 4.7 1.2 南小区 SR10-4 44.4 33.7 7.2 1.2 南小区 SR07 42.0 32.7 4.4 1.6 南小区 SR05 40.7 27.7 2.0 ~0* 东北小区 SR04 40.0 27.7 3.6 0.4 东北小区 SR01 36.0 25.9 3.6 1.6 西北小区 注:*:~0是指U1b的厚度在剖面中难以分辨出,估计约为0 m。 -
[1] 许江, 朱嘉, 张异彪, 等. 平潭海域地震层序及地层层序特征[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2010, 25(2):396-402 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.02.004
XU Jiang, ZHU Jia, ZHANG Yibiao, et al. Characteristics of seismic sequence and stratigraphic sequence in the Pingtan sea area [J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2010, 25(2): 396-402. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.02.004
[2] 蔡锋, 曹超, 周兴华, 等. 中国近海海洋: 海底地形地貌[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2013: 22-23, 177-180
CAI Feng, CAO Chao, ZHOU Xinghua, et al. China Offshore Oceanography-Topography and Geomorphology[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2013: 22-23, 177-180.
[3] 卢惠泉, 吴承强, 许艳. 闽江口外潮流沙脊群特征与成因[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(2):27-36
LU Huiquan, WU Chengqiang, XU Yan. Characteristics and origin of the tidal sand ridges off the Minjiang River estuary, southeastern China [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(2): 27-36.
[4] 刘阿成, 唐建忠, 吴巍, 等. 闽江口外海域晚第四纪地震层序和古河道演变[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2019, 50(1):61-73 doi: 10.11693/hyhz20180400087
LIU A’cheng, TANG Jianzhong, WU Wei, et al. Seismic sequences and evolution of paleo-river channels of late Quaternary off Minjiang River estuary, southeast China [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2019, 50(1): 61-73. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20180400087
[5] 刘阿成, 张杰, 唐建忠. 闽江口外海域全新统地震地层学特征和沉积作用[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(11):49-61
LIU A’cheng, ZHANG Jie, TANG Jianzhong. Characteristics of seismic stratigraphy and sedimentation of the Holocene off the Minjiang River estuary, southeast China [J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(11): 49-61.
[6] 刘阿成, 张杰, 唐建忠. 闽江口外海域MIS5和MIS3的地震地层学特征和古环境[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2022, 41(1):109-119
LIU A’cheng, ZHANG Jie, TANG Jianzhong. Characteristics of seismic stratigraphy and paleoenvironment during MIS 5 and MIS 3 off the Minjiang Estuary, Southeast China [J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2022, 41(1): 109-119.
[7] 陈承惠, 蓝东兆, 于永芬, 等. 台湾海峡西部海域晚第四纪地层[J]. 第四纪研究, 1990(4):301-307 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1990.04.002
CHEN Chenghui, LAN Dongzhao, YU Yongfen, et al. Late quaternary stratigraphy in the western Taiwan Strait [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1990(4): 301-307. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1990.04.002
[8] Liu J P, Xu K H, Li A C, et al. Flux and fate of Yangtze River sediment delivered to the East China Sea [J]. Geomorphology, 2007, 85(3-4): 208-224. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.03.023
[9] 许江, 赵绍华, 李海东, 等. 闽南海岸带浅层地震层序特征[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2011, 26(2):498-504 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2011.02.014
XU Jiang, ZHAO Shaohua, LI Haidong, et al. Characteristics of Min-nan offshore shallow seismic sequence [J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2011, 26(2): 498-504. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2011.02.014
[10] 杜文波, 黄文凯, 朱红涛, 等. 台湾海峡西部海域沉积体系、地层架构与油气勘探前景[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(5):1542-1553
DU Wenbo, HUANG Wenkai, ZHU Hongtao, et al. Sedimentary system, stratigraphic architecture and petroleum exploration prospect in the western Taiwan Strait [J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(5): 1542-1553.
[11] 彭学超, 姚伯初. 台湾海峡西部地震地层分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1993, 13(2):49-63
PENG Xuechao, YAO Bochu. Seismic stratigraphic analysis of the western Taiwan Strait [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1993, 13(2): 49-63.
[12] 周勐佳, 吴自银, 马胜中, 等. 台湾海峡晚更新世以来的高分辨率地震地层学研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(9):76-88
ZHOU Mengjia, WU Ziyin, MA Shengzhong, et al. High resolution seismic stratigraphy research in the Taiwan Strait since late Pleistocene [J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(9): 76-88.
[13] 吴自银, 温珍河. 中国东部海域海底地貌图[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019.
WU Zhiyin, WEN Zhenhe. Submarine geomorphologic map of Eastern China Seas[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019.
[14] 吴自银, 温珍河. 中国东部海域海底沉积物类型图[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019.
WU Zhiyin, WEN Zhenhe. Submarine sediment type map of Eastern China Seas[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019.
[15] 曾成开, 朱永其, 王秀昌. 台湾海峡的底质类型与沉积分区[J]. 台湾海峡, 1982, 1(1):54-61
ZENG Chengkai, ZHU Yongqi, WANG Xiuchang. Bottom material types and sedimentation districts in Taiwan Strait [J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 1982, 1(1): 54-61.
[16] 《中国海湾志》编纂委员会. 中国海湾志: 第八分册: 福建省南部海湾[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1993: 1-74.
Compiling Commission of Chinese Bays Annals. Chinese Bays Annals: Volume Eight: Bays of southern Fujian Province[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1993: 1-74.
[17] Tang C, Zhou D, Endler R, et al. Sedimentary development of the Pearl River Estuary based on seismic stratigraphy [J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2010, 82(S1): S3-S16.
[18] 刘阿成, 陆琦, 吴巍. 南黄海太阳沙西侧海域晚第四系地震层序和沉积环境演变[J]. 海洋学研究, 2017, 35(2):11-22 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2017.02.002
LIU A’cheng, LU Qi, WU Wei. Seismic sequences and sedimentary environment evolution of Late Quaternary west of Taiyangsha Ridge in the South Yellow Sea [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2017, 35(2): 11-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2017.02.002
[19] 曾从盛. 闽东北沿海晚第四纪海侵与海面变动[J]. 福建师范大学学报:自然科学版, 1997, 13(4):94-101
ZENG Congsheng. Transgressions and sea level changes along the northeast coast of Fujian during the Late Quaternary [J]. Journal of Fujian Teachers University:Natural Science, 1997, 13(4): 94-101.
[20] 徐家声. 黄海晚更新统表层与全新统底层的沉积相及其界面特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1989, 9(1):53-62 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1989.01.008
XU Jiasheng. Characteristics of stratigraphic boundary between Late Pleistocene and early Holocene serieses and their sedimentary facies in the Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1989, 9(1): 53-62. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1989.01.008
[21] 王雨灼. 福建省第四纪地层的划分[J]. 福建地质, 1990, 9(4):289-306
WANG Yuzhuo. The classification of quaternary strata in Fujian Province [J]. Geology of Fujian, 1990, 9(4): 289-306.
[22] 王律江, 鲁一江, 钱建兴, 等. 南海北部晚第四纪同位素地层学及历史[C]//南海晚第四纪古海洋学研究. 青岛: 青岛海洋大学出版社, 1992: 11-22.
WANG Lvjiang, LU Yijiang, QIAN Jianxing et al. Late Quaternary oxygen isotope stratigraphy and sedimentation history of the northern South China Sea[C]//Contributions to late Quaternary paleoceanography of the South China Sea. Qingdao: Qingdao Ocean University Press, 1992: 11-22.
[23] 夏东兴, 刘振夏. 潮流脊的形成机制和发育条件[J]. 海洋学报, 1984, 6(3):361-367
XIA Dongxing, LIU Zhenxia. Formation mechanism and development conditions of tidal sand ridges [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1984, 6(3): 361-367.
[24] Dyer K R, Huntley D A. The origin, classification and modelling of sand banks and ridges [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1999, 19(10): 1285-1330. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(99)00028-X
[25] Houbolt J J H C. Recent sediments in the Southern Bight of the North Sea [J]. Geologie en Mijnbouw, 1968, 47(4): 245-273.
[26] Caston V N D. Linaer sand banks in the southern North Sea [J]. Sedimentology, 1972, 18(1-2): 63-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1972.tb00003.x
[27] Kenyon N H, Belderson R H, Stride A H, et al. Offshore tidal sand-banks as indicators of net sand transport and as potential deposits[M]//Nio S D, Shüttenhelm R T E, Van Weering T C E. Holocene Marine Sedimentation in the North Sea Basin. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Pub. , 1981: 257-268.
[28] Huthnance J M. On one mechanism forming linear sand banks [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1982, 14(1): 79-99. doi: 10.1016/S0302-3524(82)80068-6
[29] 印萍. 东海陆架冰后期潮流沙脊地貌与内部结构特征[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2003, 21(2):181-187 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2003.02.007
YIN Ping. Geomorphology and internal structure of postglacial tidal sand ridges on the East China Sea shelf [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2003, 21(2): 181-187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2003.02.007
[30] 刘振夏, 余华, 熊应乾, 等. 东海和凯尔特海潮流沙脊的对比研究[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2005, 23(1):35-42 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2005.01.005
LIU Zhenxia, YU Hua, XIONG Yingqian, et al. A comparative study on tidal sand ridges in the East China Sea and Celtic Sea [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2005, 23(1): 35-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2005.01.005
[31] 吴自银, 金翔龙, 李家彪, 等, 东海外陆架线状沙脊群[J]. 科学通报, 2006, 51(1): 93-103
WU Ziyin, JIN Xianglong, LI Jiabiao, et al. Linear sand ridges on the outer shelf of the East China Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(21): 2517-2528.
[32] 吴自银, 金翔龙, 曹振轶, 等. 东海陆架沙脊分布及其形成演化[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2010, 53(1):101-112
WU Ziyin, JIN Xianglong, CAO Zhenyi, et al. Distribution, formation and evolution of sand ridges on the East China Sea shelf [J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2010, 53(1): 101-112.
[33] 王颖. 黄海陆架辐射沙脊群[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002: 8-9.
WANG Ying. Radiative Sandy Ridge Field on Continental Shelf of the Yellow Sea[M]. Beijing: China Environment Press, 2002: 8-9.
[34] Simarro G, Guillén J, Puig P, et al. Sediment dynamics over sand ridges on a tideless mid-outer continental shelf [J]. Marine Geology, 2015, 361: 25-40. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.12.005
[35] 蔡爱智, 石谦. 台湾海峡成因初探[M]. 厦门: 厦门大学出版社, 2009: 20-22.
CAI Aizhi, SHI Qian. Preliminary Inquiring into Formation Causes of Taiwan Strait[M]. Xiamen: Xiamen University Press, 2009: 20-22.
[36] 赵希涛, 耿秀山, 张景文. 中国东部20000年来的海平面变化[J]. 海洋学报, 1979, 1(2):269-281
ZHAO Xitao, GENG Xiushan, ZHANG Jingwen. Sea level chances of the eastern China during the past 20000 years [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1979, 1(2): 269-281.
[37] 王鹏, 贾凯, 吴建政, 等. 渤海沙脊和沙席分布及与M2潮流的关系[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(2):23-32
WANG Peng, JIA Kai, WU Jianzheng, et al. Distribution pattern of sand ridges and sand sheets in Bohai Sea and the relationship with M2 tidal current [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(2): 23-32.
[38] 陈新忠. 台湾海峡及其两岸沿海的潮流[J]. 海洋通报, 1983, 2(2):16-24
CHEN Xinzhong. On the distribution of the tidal currents in the Taiwan Strait [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1983, 2(2): 16-24.
[39] 吴頔, 王勇智, 孙永根. 台湾海峡M2分潮潮汐潮流特征分布及机制研究[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2020, 39(4):460-468 doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2020.04.002
WU Di, WANG Yongzhi, SUN Yonggen. Distribution and mechanism of M2 tide and tidal current in Taiwan Strait [J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2020, 39(4): 460-468. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2020.04.002
-



 下载:
下载: