Distribution and provenance of detrital minerals in surface sediments of the northeastern East China Sea
-
摘要:
为深入了解东海外陆架表层沉积物物质来源及沉积环境特征,运用粒度和矿物学研究手段,对济州岛西南海域180个表层沉积物样品进行沉积物类型和碎屑矿物组成分析,探讨了矿物分布特征与沉积环境的相互关系,进一步明确表层沉积物的输运模式、物质来源及环流系统对其分布的影响。结果表明,研究区重矿物共34种,以普通角闪石、绿帘石和钛铁氧化物类矿物为主,橄榄石和变质岩矿物是区别内陆架沉积的标志性矿物。轻矿物共13种,以普遍发育的海绿石为特征。根据碎屑矿物组合分布特征,将研究区分为Ⅰ、Ⅱ两个矿物组合区,并进一步将Ⅱ区划分为两个矿物组合亚区。中部现代沉积区(Ⅰ区)矿物组合为普通角闪石-绿帘石-自生黄铁矿-钛铁氧化物类矿物-片状矿物,表现为现代陆源沉积特征,物质来源以黄河为主,生物沉积和自生沉积也是该区重要的沉积方式。外围残留沉积区(Ⅱ区)为沉积作用缓慢的弱还原环境,Ⅱ-1亚区矿物组合为普通角闪石-绿帘石-钛铁氧化物类矿物-石榴石-橄榄石,认为是以古长江的残留前积沉积为基底,受到Ⅰ区影响,接受了少量悬浮再悬浮的现代陆源沉积,同时又具有区域独特性。Ⅱ-2亚区矿物组合为绿帘石-普通角闪石-钛铁氧化物类矿物-石榴石,认为是古长江的残留沉积,在中部冷涡作用下,很少有现代物质的加入,区内不排除在当地环境生长的生物体作用下与Ⅰ区互相调整的物质。本研究为今后在东海外陆架深入开展沉积学、矿物学及环境演化研究提供了新的参考。
Abstract:In order to understand the source of surface sediments and the characteristics of the depositional environment on the East China Sea Shelf, 180 surface sediment samples from the southwest waters of Jeju Island were analyzed in terms of sediment types and detrital mineral compositions by means of grain size and mineralogy. The relationship between the distribution characteristics of minerals and the depositional environment was discussed. Based on the sedimentary dynamics method, the influence of the transport mode, material source and circulation system of the surface sediments on its distribution was clarified. Thirty-four heavy minerals were identified, mainly common amphibole, epidote, and metallic minerals. Olivine and metamorphic rock minerals are the landmark minerals distinguished from inland shelf deposits. Thirteen light minerals were identified, which are characterized by commonly developed glauconite. According to the distribution characteristics of clastic mineral assemblage, the study area could be divided into two mineral assemblages named as Zone Ⅰ and Zone Ⅱ, correspondingly. Zone Ⅰ occupied in the central modern sedimentary zone characteristic of ordinary amphibole, epidote, authigenic pyrite, metallic minerals, and sheet minerals, showing colors of modern terrigenous sediments from mainly the Yellow River, biological, and authigenic sediments. Zone Ⅱ covered the peripheral residual sedimentary zone characteristic of weak reductive environment with slow sedimentation rate. Zone Ⅱ could be divided into two subzones. Subzone Ⅱ-1 features ordinary amphibole, epidote, metallic minerals, garnet, and olivine, indicating the origin of the ancient Yangtze River on the basement of foreset sediments with the influence of Zone Ⅰ, receiving a small amount of modern terrigenous suspended or resuspended sediments with own regional uniqueness. Subzone Ⅱ-2 contains epidote, ordinary hornblende, metal minerals, and garnet etc, reflecting residual sediments of the ancient Yangtze River. Under the action of the central cold vortex, few modern materials could be added. Meanwhile, local organic substances in local environment that are mutually exchanged with zone Ⅰ cannot be excluded from the area. The research content of this paper provides a new reference for further studies on sedimentology, mineralogy and environmental evolution on the East China Sea Shelf.
-

-
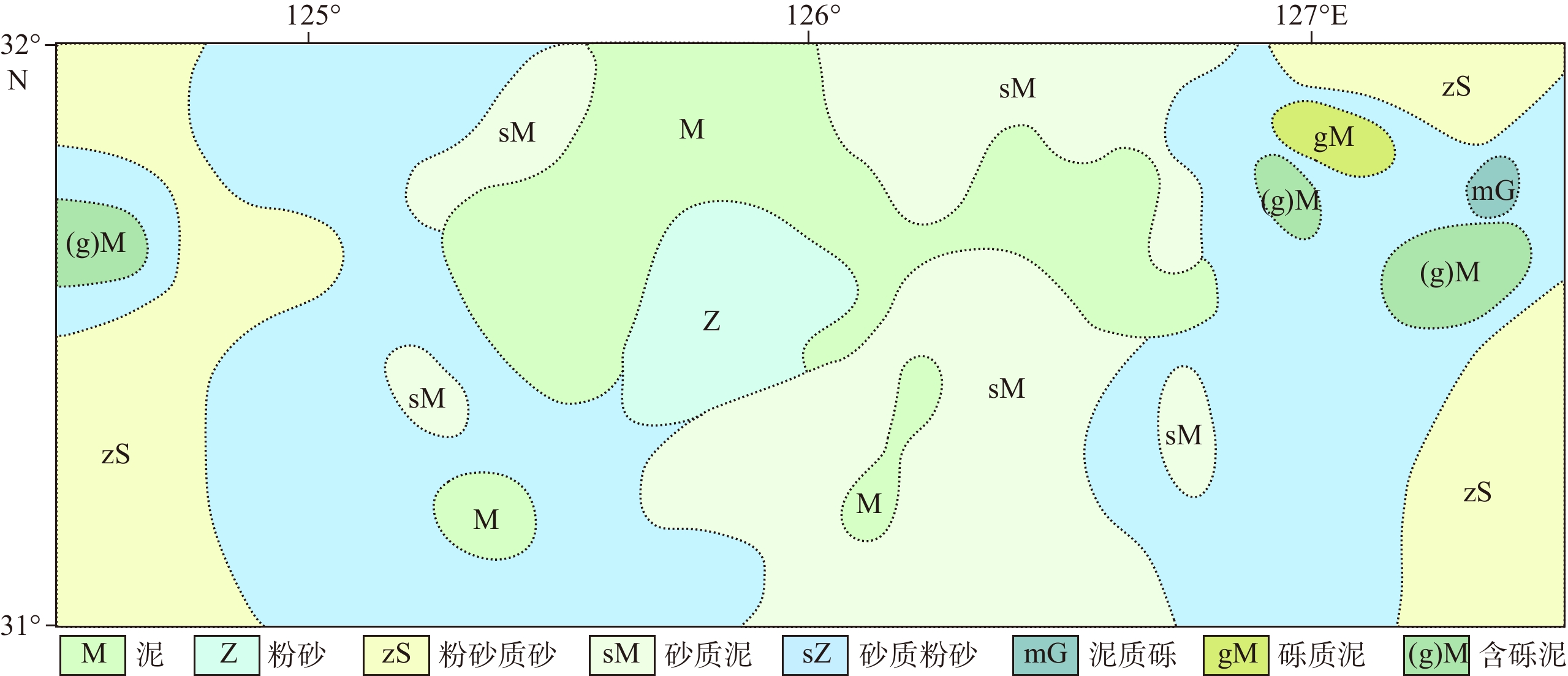
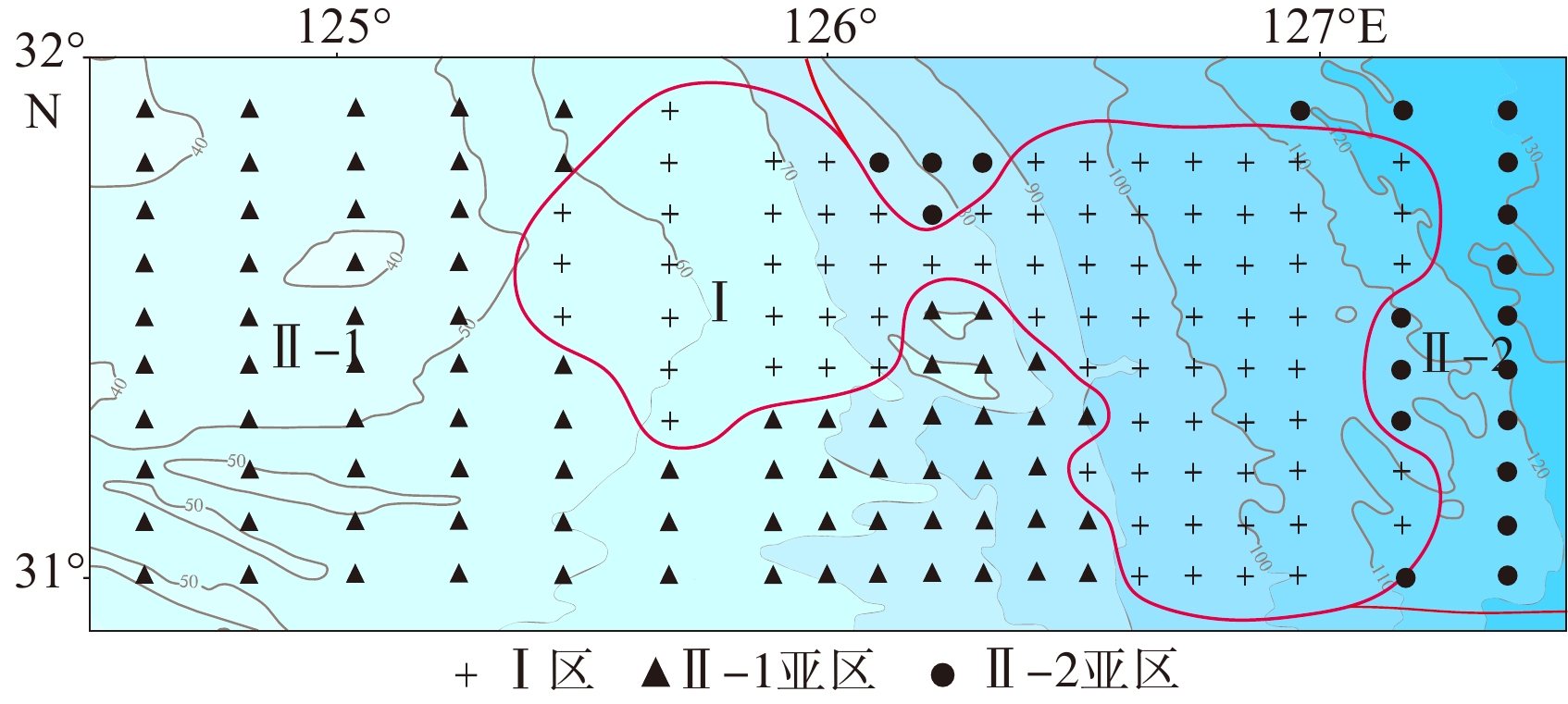
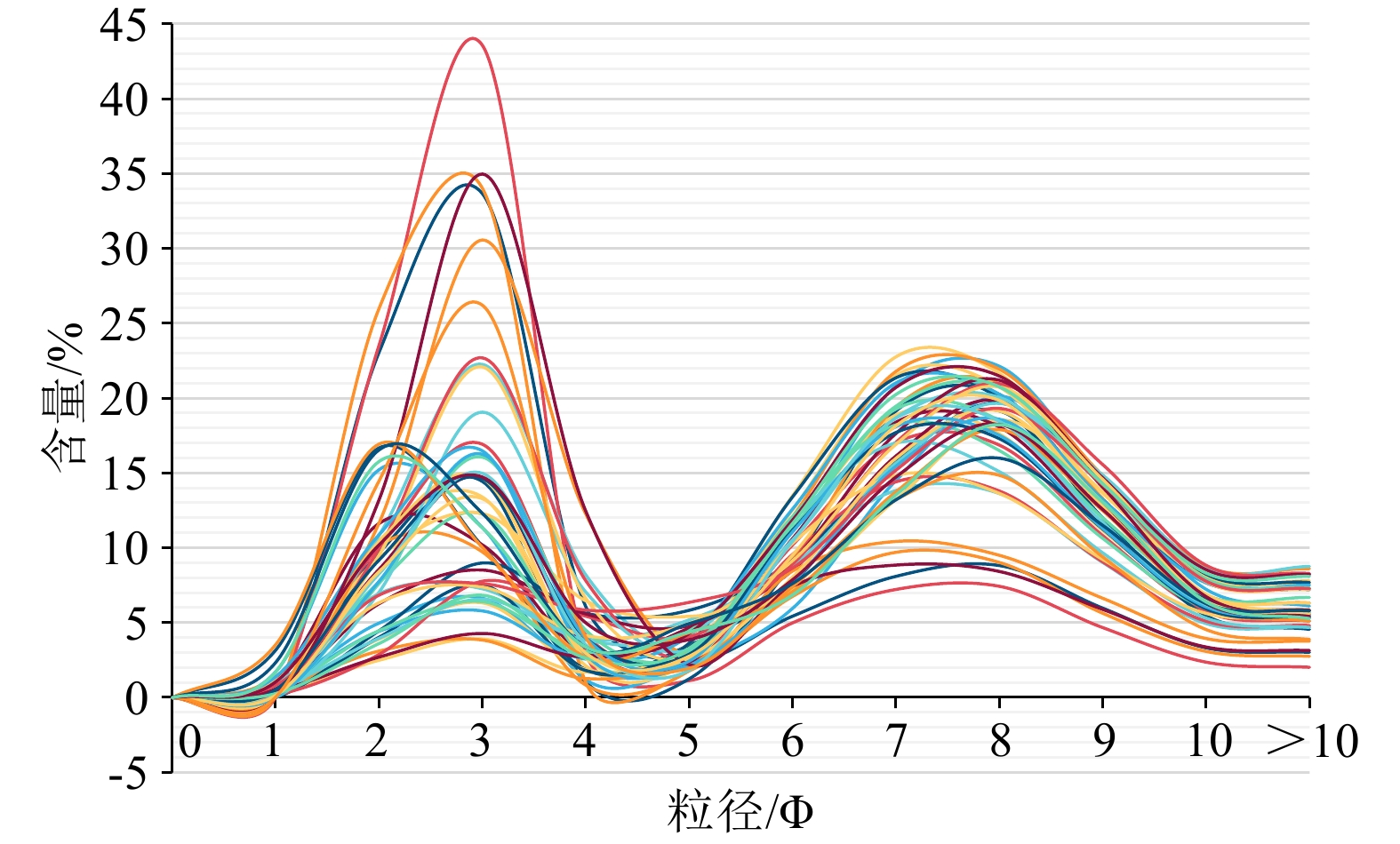
图 1 研究区及地质背景[9]
Figure 1.
表 1 研究区沉积物中主要重矿物含量统计
Table 1. Statistics of major heavy minerals in sediment of the study area
矿物种类 矿物颗粒百分比/%(180) 平均值 最大值 最小值 出现率 Ⅰ
(75)Ⅱ-1
(90)Ⅱ-2
(15)普通角闪石 29.25 47.80 2.64 100 25.97 32.34 27.07 绿帘石 25.63 44.11 3.81 100 23.62 26.85 28.34 闪石类 31.84 51.26 4.99 100 28.41 35.23 28.61 帘石类 28.63 49.22 4.69 100 26.11 30.52 29.93 钛铁氧化物 7.70 33.87 1.26 100 6.11 9.50 4.78 片状矿物 2.95 28.75 0.20 91.11 5.15 1.26 2.03 辉石类 0.42 1.23 0.25 33.89 0.40 0.44 0.41 锆石 0.71 11.18 0.22 4.44 0.57 0.86 0.36 榍石 1.36 3.87 0.19 98.33 1.18 1.56 1.03 石榴石 1.95 5.06 0.29 98.33 1.75 2.07 2.26 橄榄石 1.67 7.67 0.20 14.44 0.55 2.01 0.00 ZTR 1.31 12.06 0.21 96.11 1.10 1.43 1.00 变质岩矿物 0.48 1.24 0.23 41.67 0.16 0.23 0.25 自生黄铁矿 5.24 34.59 0.21 21.67 6.58 0.75 0.00 注:表内除全区列出最小值、最大值和平均值外,其余各列均为平均值;Ⅰ、Ⅱ-1和Ⅱ-2代表研究区分区号,在本文2.4章节阐述了分区依据;括号内代表各列样品个数。 表 2 研究区沉积物中主要轻矿物含量统计
Table 2. Statistics of major light minerals in sediment of the study area
矿物种类 矿物颗粒百分比%(180) 平均值 最大值 最小值 出现率 Ⅰ
(75)Ⅱ-1
(90)Ⅱ-2
(15)石英 16.42 45.05 0.94 100 9.06 22.47 16.95 斜长石 29.92 59.26 3.44 98.89 18.04 39.28 31.57 钾长石 1.63 11.76 0.30 77.78 1.26 1.89 1.54 黑云母 1.01 36.44 0.25 41.67 1.37 0.40 0.31 白云母 0.94 6.65 0.25 70.56 1.26 0.55 0.50 风化云母 0.82 4.44 0.25 70.56 0.99 0.67 0.52 海绿石 1.47 5.37 0.26 87.78 1.02 1.71 1.85 生物碎屑 39.68 91.82 0.29 93.33 62.94 18.02 38.49 注:表内除全区列出最小值、最大值和平均值外,其余各列均为平均值;Ⅰ、Ⅱ-1和Ⅱ-2代表研究区分区号;括号内代表各列样品个数。 -
[1] 张凯棣, 李安春, 董江, 等. 东海表层沉积物碎屑矿物组合分布特征及其物源环境指示[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(5):902-911 doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2016.05.009
ZHANG Kaidi, LI Anchun, DONG Jiang, et al. Detrital mineral distributions in surface sediments of the East China Sea: Implications for sediment provenance and sedimentary environment [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(5): 902-911. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2016.05.009
[2] Morton A C, Hallsworth C. Identifying provenance-specific features of detrital heavy mineral assemblages in sandstones [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1994, 90(3-4): 241-256. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(94)90041-8
[3] 金秉福, 宫立新, 宋键. 大沽河泥沙来源的重矿物分析及其环境意义[J]. 海洋科学, 2010, 34(10):71-76
JIN Bingfu, GONG Lixin, SONG Jian. Heavy mineral analysis in the sediment originated from the Daguhe River and its environmental significance [J]. Marine Sciences, 2010, 34(10): 71-76.
[4] 梅西, 李学杰, 密蓓蓓, 等. 中国海域表层沉积物分布规律及沉积分异模式[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(5):1447-1462
MEI Xi, LI Xuejie, MI Beibei, et al. Distribution regularity and sedimentary differentiation patterns of China seas surface sediments [J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(5): 1447-1462.
[5] 陈丽蓉. 中国海沉积矿物学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2008: 121-155
CHEN Lirong. Sedimentary Mineralogy of the China Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2008: 121-155.
[6] 王昆山, 石学法, 林振宏. 南黄海和东海北部陆架重矿物组合分区及来源[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2003, 21(1):31-40 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2003.01.004
WANG Kunshan, SHI Xuefa, LIN Zhenhong. Assemblages, provinces and provenances of heavy minerals on the shelf of the southern Yellow Sea and northern East China Sea [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2003, 21(1): 31-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2003.01.004
[7] 林晓彤. 东海外缘沉积物来源的判识分析[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2003
LIN Xiaotong. Discriminant analysis of the sediment provenance in outer East China Sea[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2003.
[8] 王中波, 杨守业, 张志珣, 等. 东海西北部陆架表层沉积物重矿物组合及其沉积环境指示[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(6):114-125
WANG Zhongbo, YANG Shouye, ZHANG Zhixun, et al. The heavy mineral assemblages of the surface sediments on the northeast shelf of the East China Sea and their environmental implication [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2012, 34(6): 114-125.
[9] 戴慧敏. 济州岛西南泥质区不同粒级沉积物的元素地球化学特征及物源分析[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2005
DAI Huimin. Study on geochemistry characteristics and sources in the mud area southwest of Cheju Island[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2005.
[10] 王中波, 杨守业, 王红霞, 等. 南黄海表层沉积物碎屑石榴石化学组成及物源示踪应用[J]. 地球科学进展, 2012, 27(S1):514
WANG Zhongbo, YANG Shouye, WANG Hongxia, et al. Detrital garnet compositions of the surface sediments in the South Yellow Sea and their tracing implications [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2012, 27(S1): 514.
[11] Yuan D L, Hsueh Y. Dynamics of the cross-shelf circulation in the Yellow and East China Seas in winter [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2010, 57(19-20): 1745-1761. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2010.04.002
[12] Yang Z S, Milliman J D. Fine-grained sediments of Changjiang and Huanghe Rivers and sediment sources of East China Sea[C]//Proceedings of the International Symposium on Sedimentation on the Continental Shelf, with Special Reference to the East China Sea. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1983: 405-415.
[13] Milliman J D, Beardsley R C, Yang Z S, et al. Modern Huanghe-derived muds on the outer shelf of the East China Sea: identification and potential transport mechanisms [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1985, 4(1-2): 175-188. doi: 10.1016/0278-4343(85)90028-7
[14] 李双林, 李绍全, 孟祥君. 东海陆架晚第四纪沉积物化学成分及物源示踪[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2002, 22(4):21-28
LI Shuanglin, LI Shaoquan, MENG Xiangjun. Chemical composition and source tracing of late quaternary sediments in the East China Sea shelf [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2002, 22(4): 21-28.
[15] 杨作升, 范德江, 郭志刚, 等. 东海陆架北部泥质区表层沉积物碳酸盐粒级分布与物源分析[J]. 沉积学报, 2002, 20(1):1-6 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.01.001
YANG Zuosheng, FAN Dejiang, GUO Zhigang, et al. Distribution of the carbonate clast size and the provenance analyses of the surface sediments in the northern East China Sea [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2002, 20(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.01.001
[16] 刘健, 李绍全, 王圣洁, 等. 末次冰消期以来黄海海平面变化与黄海暖流的形成[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1999, 19(1):13-24 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1999.01.003
LIU Jian, LI Shaoquan, WANG Shengjie, et al. Sea level changes of the Yellow Sea and formation of the Yellow Sea warm current since the Last Deglaciation [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1999, 19(1): 13-24. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1999.01.003
[17] 颜彬, 谢敬谦, 黄博, 等. 广东近岸海域矿物特征指数分布及指示意义[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(11):1-8
YAN Bin, XIE Jingqian, HUANG Bo, et al. Detrital mineral indexes of the bottom sediments of Guangdong coastal water: distribution and implications [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2017, 33(11): 1-8.
[18] 刘金庆, 宋红瑛, 印萍, 等. 威海南部近岸泥质区晚更新世以来的重矿物组合特征及对物源的指示[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(3):129-140
LIU Jinqing, SONG Hongying, YIN Ping, et al. Characteristics of heavy mineral assemblage and its indication of provenance in the mud area off the southern coast of Weihai since the Late Pleistocene [J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(3): 129-140.
[19] 刘忠诚. 辽东湾海岸带沉积物碎屑矿物分析及其环境意义[D]. 鲁东大学硕士学位论文, 2014
LIU Zhongcheng. Detrital mineralogy and its environmental indicative significance of the sediments of Coastal zone in Liaodong Bay[D]. Master Dissertation of Ludong University, 2014.
[20] 何起祥. 海洋沉积作用的物源控制[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2011, 27(1):8-13
HE Qixiang. Sediment source and its bearing on marine sedimentations [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2011, 27(1): 8-13.
[21] 李家彪. 东海区域地质[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2008
Li Jiabiao. East China Sea Regional Geology[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2008.
[22] 郭志刚, 杨作升, 张东奇, 等. 冬、夏季东海北部悬浮体分布及海流对悬浮体输运的阻隔作用[J]. 海洋学报, 2002, 24(5):71-80
GUO Zhigang, YANG Zuosheng, ZHANG Dongqi, et al. Seasonal distribution of suspended matter in the northern East China Sea and barrier effect of current circulation on its transport [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2002, 24(5): 71-80.
[23] 孙效功, 方明, 黄伟. 黄、东海陆架区悬浮体输运的时空变化规律[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2000, 31(6):581-587 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2000.06.001
SUN Xiaogong, FANG Ming, HUANG Wei. Spatial and temporal variations in suspended particulate matter transport on the Yellow and East China Sea shelf [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2000, 31(6): 581-587. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2000.06.001
[24] 胡敦欣, 韩舞鹰, 章申, 等. 长江、珠江口及邻近海域陆海相互作用[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2001
HU Dunxin, HAN Wuying, ZHANG Shen, et al. Land-Ocean Interaction in Yangtze River, Pearl River Estuary and Adjacent Waters[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2001.
[25] 金翔龙. 东海海洋地质[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1992
JIN Xianglong. Marine Geology of the East China Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1992.
[26] 刘振夏, 夏东兴. 中国近海潮流沉积沙体[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2004
LIU Zhenxia, XIA Dongxing. Tidal Sands in the China Seas[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2004.
[27] 金秉福, 林振宏, 时振波, 等. 东海外陆架晚更新世沉积物中的有用重矿物及其资源潜力[J]. 古地理学报, 2004, 6(3):372-379 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2004.03.012
JIN Bingfu, LIN Zhenhong, SHI Zhenbo, et al. Valuable heavy minerals and their resource potential on outer shelf in East China Sea during the Late Pleistocene [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2004, 6(3): 372-379. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2004.03.012
[28] 陈丽蓉, 申顺喜, 徐文强, 等. 中国海的碎屑矿物组合及其分布模式的探讨[J]. 沉积学报, 1986, 4(3):87-96
CHEN Lirong, SHEN Shunxi, XU Wenqiang, et al. An approach to the detrital assemblages and their distribution patterns in the sediments of the China Sea [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1986, 4(3): 87-96.
[29] 杨作升, 郭志刚, 王兆祥, 等. 黄东海陆架悬浮体向其东部深海区输送的宏观格局[J]. 海洋学报, 1992, 14(2):81-90
YANG Zuosheng, GUO Zhigang, WANG Zhaoxiang, et al. The macroscopic pattern of the transport of suspended matter from the Yellow-East China Sea shelf to its eastern deep-sea area [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1992, 14(2): 81-90.
[30] 郭志刚, 杨作升, 雷坤, 等. 东海陆架北部泥质区沉积动力过程的季节性变化[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 1999, 29(3):507-513
GUO Zhigang, YANG Zuosheng, LEI Kun, et al. Seasonal variation of the sedimentary dynamic processes for the mud area in the northern East China Sea [J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 1999, 29(3): 507-513.
[31] 杨作升, 郭志刚, 王兆祥, 等. 黄东海陆架悬浮体向其东部深海区输送的宏观格局[J]. 海洋学报(中文版), 1992(2): 81-90
YANG Zuosheng, GUO Zhigang, WANG Zhaoxiang, et al. The macroscopic pattern of the transport of suspended matter from the Yellow-East China Sea shelf to its eastern deep-sea area[J].Acta Oceanologica Sinica(Chinese Version), 1992(2): 81-90
[32] 秦蕴珊, 李凡, 徐善民, 等. 南黄海海水中悬浮体的研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1989, 20(2):101-112 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1989.02.002
QIN Yunshan, LI Fan, XU Shanmin, et al. Suspended matter in the South Yellow Sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1989, 20(2): 101-112. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1989.02.002
[33] 陈丽蓉, 徐文强, 申顺喜. 东海沉积物的矿物组合及其分布特征[J]. 科学通报, 1979(15):709-712
CHEN Lirong, XU Wenqiang, SHEN Shunxi. Mineral composition and their distribution patterns in the sediments of the East China Sea [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1979(15): 709-712.
[34] Milliman J D, Shen H T, Yang Z S, et al. Transport and deposition of river sediment in the Changjiang estuary and adjacent continental shelf [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1985, 4(1-2): 37-45. doi: 10.1016/0278-4343(85)90020-2
[35] Zhang J. Heavy metal compositions of suspended sediments in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) estuary: significance of riverine transport to the ocean [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1999, 19(12): 1521-1543. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(99)00029-1
[36] 郭志刚, 杨作升, 范德江, 等. 长江口泥质区的季节性沉积效应[J]. 地理学报, 2003, 58(4):591-597 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2003.04.014
GUO Zhigang, YANG Zuosheng, FAN Dejiang, et al. Seasonal sedimentary effect on the Changjiang estuary mud area [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2003, 58(4): 591-597. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2003.04.014
[37] 刘世东, 乔璐璐, 李广雪, 等. 东海内陆架悬浮体输运、通量及季节变化[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2018, 49(1):24-39
LIU Shidong, QIAO Lulu, LI Guangxue, et al. Transport and flux of suspended sediment and its seasonal variation over the inner shelf of the East China Sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2018, 49(1): 24-39.
[38] 徐方建, 李安春, 黄敬利. 东海陆架浙-闽沿岸泥质沉积研究进展[J]. 海洋通报, 2012, 31(1):97-104 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2012.01.017
XU Fangjian, LI Anchun, HUANG Jingli. Research progress in the mud deposits along the Zhe-Min coast of the East China Sea continental shelf [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2012, 31(1): 97-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2012.01.017
[39] 王濮, 潘兆橹, 翁玲宝. 系统矿物学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1982
WANG Pu, PAN Zhaolu, WENG Lingbao. Systematic Mineralogy[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 1982.
-




 下载:
下载: