Progress and prospects of research on the Quaternary sedimentary environment in the eastern shelf of China
-
摘要:
中国东部陆架位于亚洲大陆与西太平洋的过渡区域,是连接全球最大的沉积源-汇系统的重要纽带,记录了东亚构造变形、亚洲季风系统形成与演化、海平面变化及东亚重大水系变迁等诸多重要信息。在总结前人研究的基础上,结合最近20年来中国海洋专项获得的数据资料和研究成果,综述了中国东部陆架区第四纪以海侵-海退变化为主要特征的沉积环境变化,探讨了陆架沉积环境变化与区域构造、海平面和东亚季风气候变化的联系;基于目前在长江、黄河流域及东部陆架区开展的沉积物源-汇研究,讨论了长江和黄河贯通入海的可能时代及控制因素;提出新生代以来陆架地质环境演变与东亚构造历史、季风系统演化、海平面变化、重大水系调整及陆架有机碳埋藏的耦合机制研究是未来在中国东部陆架实施科学钻探的重点科学目标。
Abstract:The eastern shelf of China is located in the transitional zone between the Asian continent and the western Pacific Ocean. It is an important link connecting the largest sedimentary source-sink system in the world, and bears many important information on tectonic deformation in East Asia, the formation and evolution of the Asian monsoon system, sea level changes and major water system changes in East Asia. Based on the review of previous studies and the new data obtained from marine projects in China during the last two decades, this paper reviews the Quaternary sedimentary environmental changes in the eastern shelf of China, mainly focusing on changes in marine transgression and regression cycles, and discusses the connection between the Quaternary sedimentary environment in eastern shelf of China and regional tectonic, sea level and East Asian monsoon climate changes. Based on the previous sedimentary source-sink studies in the Yangtze and Yellow River basins and the shelf area, we discuss the timing of penetrating into the sea of the Yangtze and Yellow rivers and controlling factors. We propose that the coupling mechanism of the geological environment evolution in the eastern shelf of China with Asian tectonic deformation, monsoon system evolution, sea-level change, major water system adjustment and carbon burial since the Cenozoic is a key scientific goal for future scientific drilling in the eastern shelf of China.
-

-
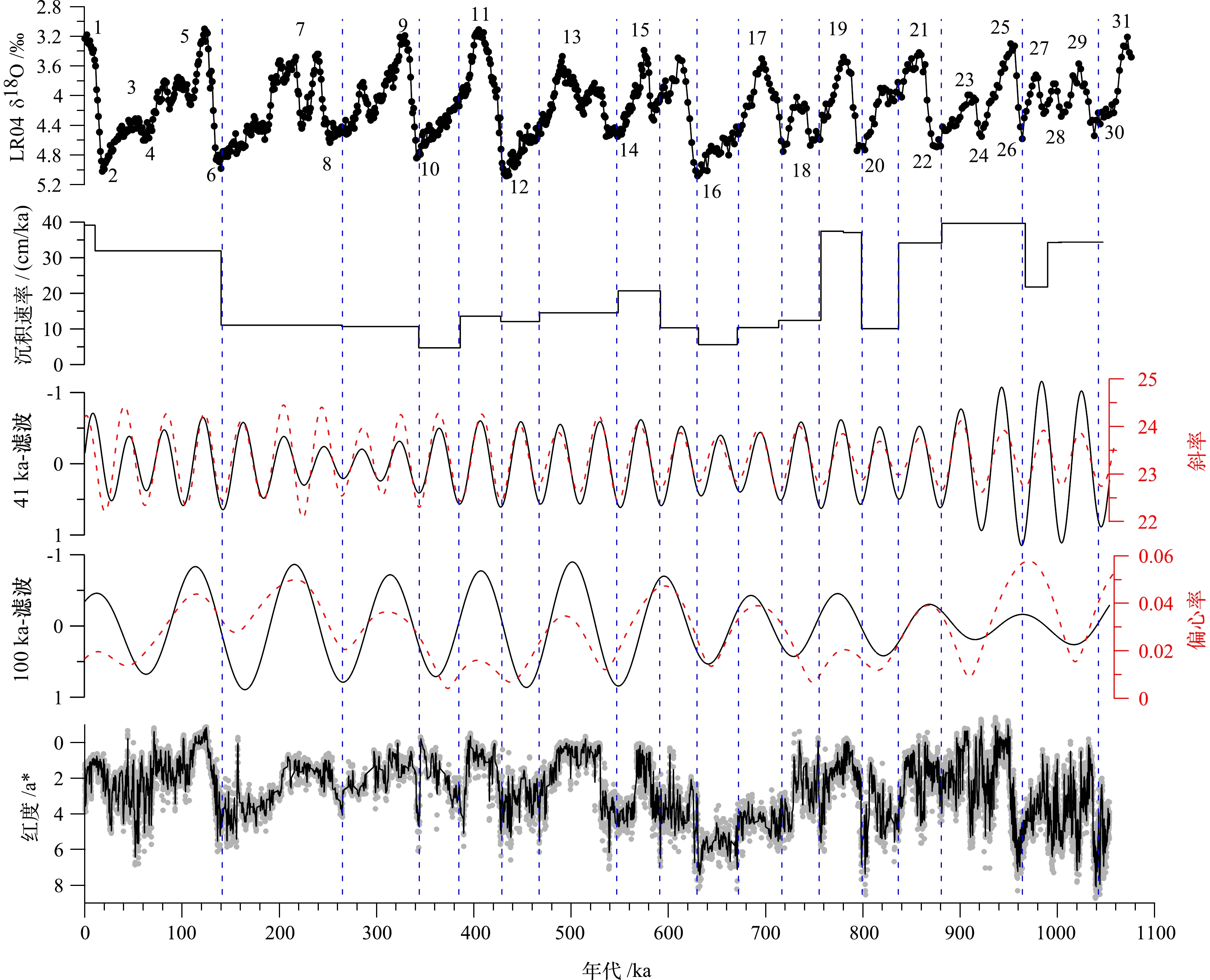
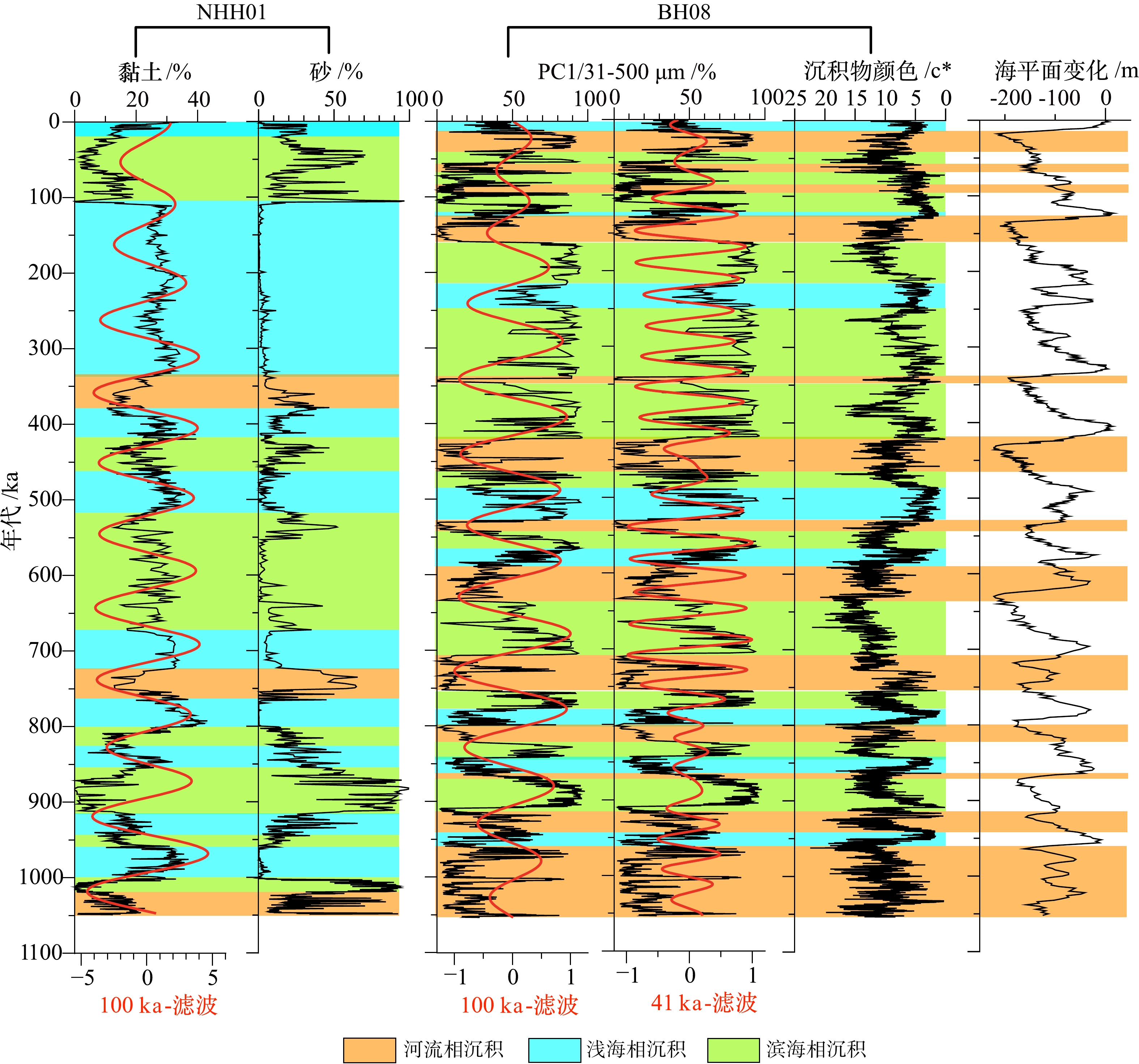
图 2 渤海BH08钻孔天文调谐方法建立的年代框架[34]
Figure 2.
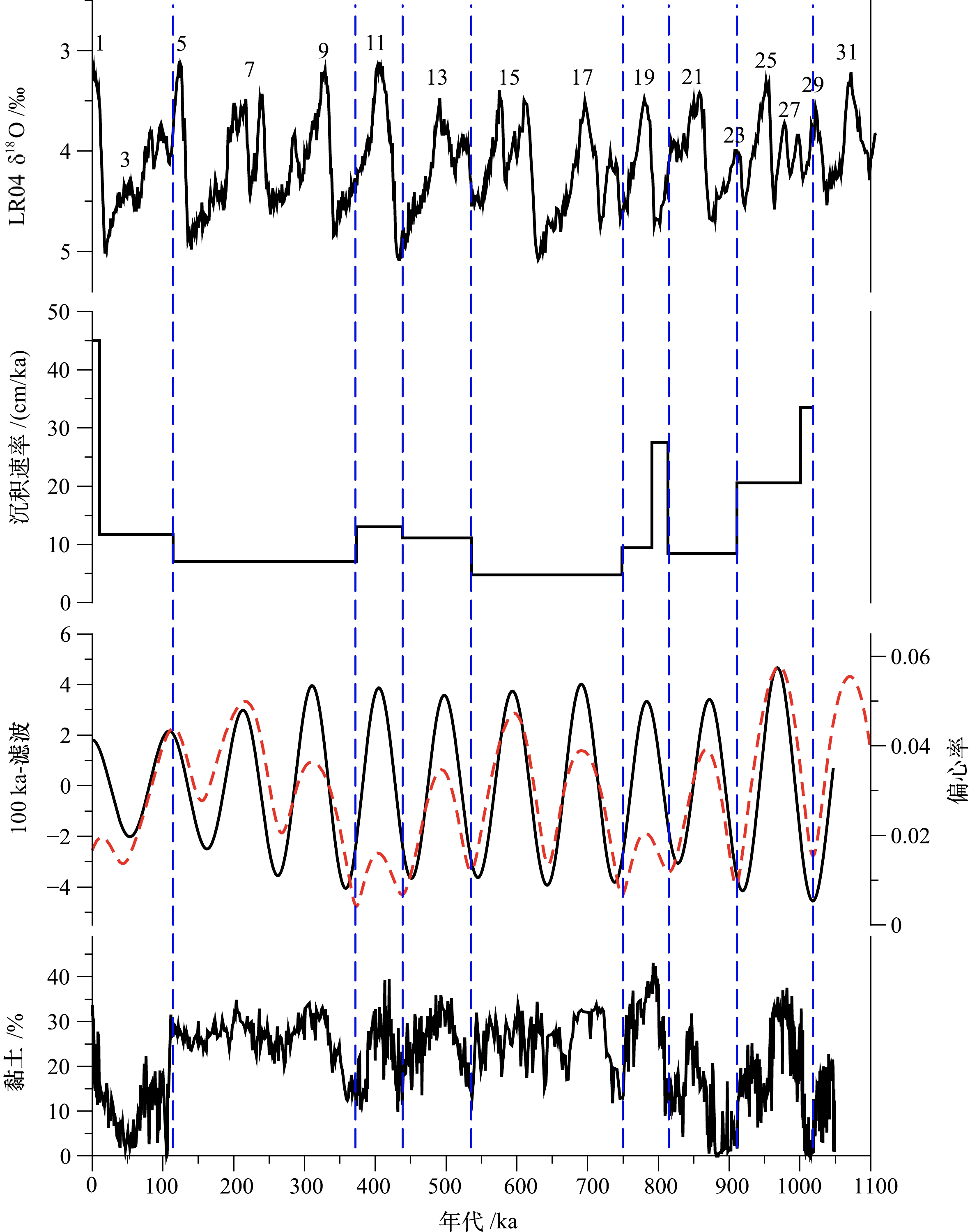
图 3 黄海NHH01钻孔天文调谐方法建立的年代框架[49]
Figure 3.
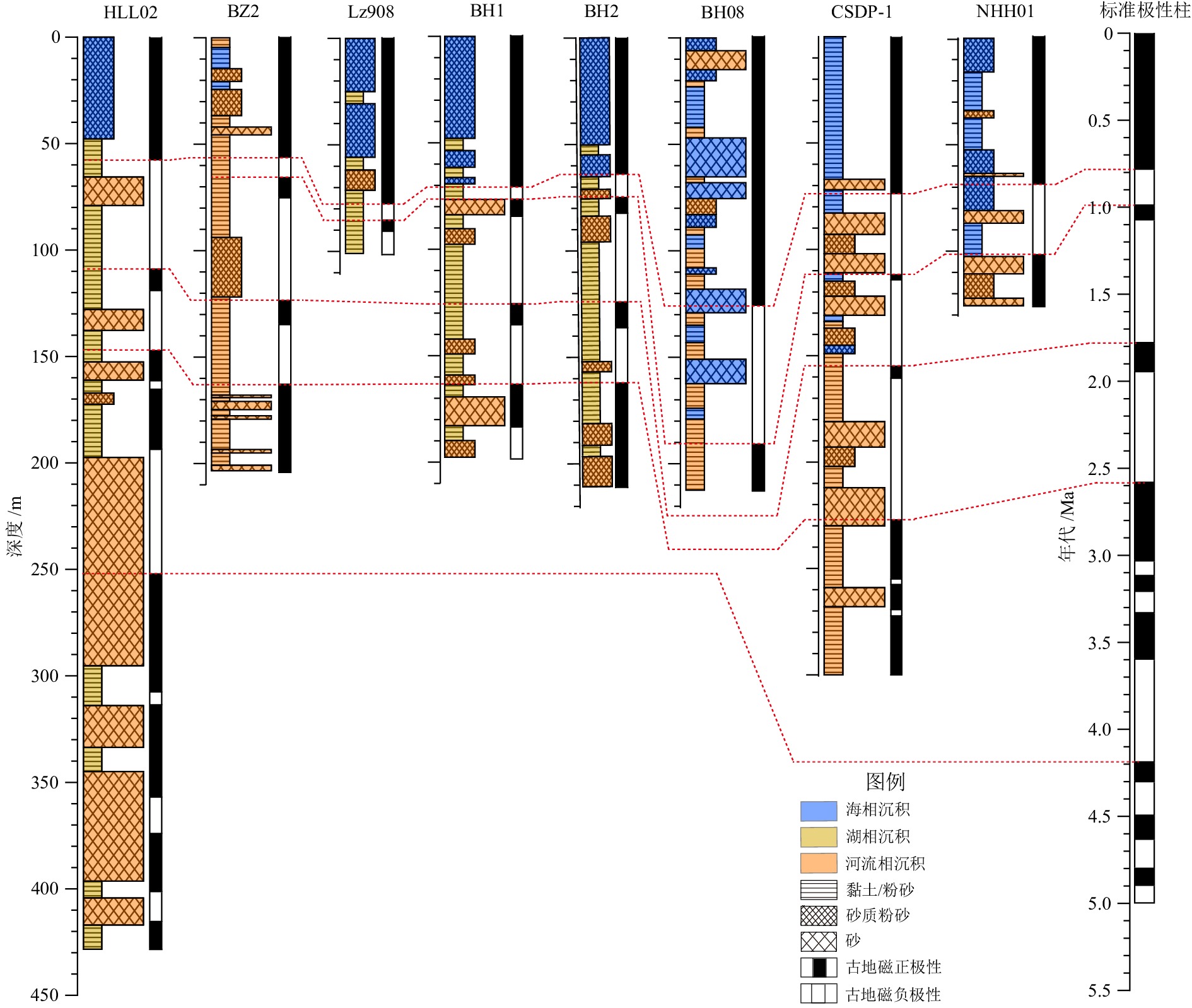
图 4 中国渤、黄海海域及沿岸第四纪沉积环境对比[49]
Figure 4.
图 6 渤、黄海陆架轨道尺度沉积环境变化[49]
Figure 6.
图 7 渤海BH08钻孔沉积粒度揭示的海平面与东亚夏季风变化[92]
Figure 7.
表 1 文中提及的中国东部陆架主要钻孔岩心信息
Table 1. Detailed information of cores on the coastal area and the eastern shelf of China mentioned in text
区域 钻孔 纬度/(°) 经度/(°) 长度/m 水深/m 底界年龄/Ma 文献来源 渤海 BC-1 39.15 119.9 240.5 24 0.24 [25] BH08 38.28 120 212.4 28 1 [34] BH1 37.28 119.1 198.8 4 3 [29] BH2 37.17 119.07 228.2 陆上 3 [29] BZ1 38.85 117.38 204.5 陆上 2.2 [26] BZ2 39.03 117.14 203.6 陆上 3.2 [27] CK3 38.15 117.54 500 陆上 6.6 [28] G2 39.07 117.63 1226 陆上 8.5 [35] G3 38.83 117.43 905 陆上 8 [36] G4 38.04 117.6 400 陆上 5.2 [28] HLL02 37.03 119.13 425 陆上 5 [29] JXC-1 40.4 121.05 70.3 22 1.2 [31] Lz908 37.15 118.97 101.3 陆上 0.12 [20] MT04 39.27 118.83 383 陆上 3.2 [30] TJC-1 38.73 118.95 200.3 26 2.28 [32] YKC-2 40.43 121.61 70.2 13 0.7 [31] YRD-1101 38.04 118.6 200.3 1.8 1.9 [37] 黄海 CSDP-1 34.3 122.37 300.1 52.5 3.5 [33] CSDP-2 34.56 121.26 2 809.9 22 5* [38] DLC70-3 36.33 123.53 71.2 72 0.8 [39] EY02-2 34.5 123.5 70 79 0.89 [40] NHH01 35.22 123.22 125.6 73 1 [41] QC1 32.52 122.5 117.2 29.5 1 [42] QC2 34.3 122.27 108.8 49.1 1.9 [42] 东海 CJ-1 31.13 121.75 172.3 陆上 0.89 [43] ECS-DZ1 30.48 112.05 153.6 12 2 [44] EY02-1 30.73 126.57 70 90 0.26 [40] FX 31.20 121.25 102 陆上 0.12 [17] MFC 31.24 121.46 112 陆上 0.12 [17] SFK-1 29.1 125.3 88.3 82.9 0.15 [45] ZK9 30.88 122.42 50 12.5 0.013 [46] 注:*为上部550 m沉积的底界年代。 -
[1] Milliman J D, Farnsworth K L. River Discharge to the Coastal Ocean: A Global Synthesis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2011: 1-384.
[2] Johnson K S, Chavez F P, Friederich G E. Continental-shelf sediment as a primary source of iron for coastal phytoplankton [J]. Nature, 1999, 398(6729): 697-700. doi: 10.1038/19511
[3] Blair N E, Aller R C. The fate of terrestrial organic carbon in the marine environment [J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2012, 4: 401-423. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-120709-142717
[4] 石学法, 乔淑卿, 杨守业, 等. 亚洲大陆边缘沉积学研究进展(2011-2020)[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2021, 40(2):319-336
SHI Xuefa, QIAO Shuqing, YANG Shouye, et al. Progress in sedimentology research of the Asian continental margin (2011-2020) [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2021, 40(2): 319-336.
[5] 汪品先. 亚洲形变与全球变冷: 探索气候与构造的关系[J]. 第四纪研究, 1998, 18(3):213-221 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1998.03.004
WANG Pinxian. Deformation of Asia and global cooling: searching links between climate and tectonics [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1998, 18(3): 213-221. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1998.03.004
[6] Guo Z T, Ruddiman W F, Hao Q Z, et al. Onset of Asian desertification by 22 Myr ago inferred from loess deposits in China [J]. Nature, 2002, 416(6877): 159-163. doi: 10.1038/416159a
[7] Zheng H B, Clift P D, Wang P, et al. Pre-Miocene birth of the Yangtze River [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(19): 7556-7561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216241110
[8] Zhang J, Wan S M, Clift P D, et al. History of Yellow River and Yangtze River delivering sediment to the Yellow Sea since 3.5 Ma: tectonic or climate forcing? [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2019, 216: 74-88. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.06.002
[9] Xiao G Q, Sun Y Q, Yang J L, et al. Early Pleistocene integration of the Yellow River I: detrital-zircon evidence from the North China Plain [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 546: 109691. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.109691
[10] Shackleton N J. Oxygen isotopes, ice volume and sea level [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1987, 6(3-4): 183-190. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(87)90003-5
[11] Rohling E J, Grant K, Bolshaw M, et al. Antarctic temperature and global sea level closely coupled over the past five glacial cycles [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2009, 2(7): 500-504. doi: 10.1038/ngeo557
[12] 赵松龄, 杨光复, 苍树溪, 等. 关于渤海湾西岸海相地层与海岸线问题[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1978, 9(1):15-25
ZHAO Songling, YANG Guangfu, CANG Shuxi, et al. On the marine stratigraphy and coastlines of the western coast of the Gulf of Bohai [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1978, 9(1): 15-25.
[13] 汪品先, 闵秋宝, 卞云华, 等. 我国东部第四纪海侵地层的初步研究[J]. 地质学报, 1981, 55(1):1-13
WANG Pinxian, MIN Qiubao, BIAN Yunhua, et al. Strata of Quaternary transgressions in East China: a preliminary study [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1981, 55(1): 1-13.
[14] 王强, 李凤林. 渤海湾西岸第四纪海陆变迁[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1983, 3(4):83-89 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1983.04.013
WANG Qiang, LI Fenglin. The changes of marine-continental conditions in the West coast of the Bohai Gulf during Quaternary [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1983, 3(4): 83-89. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1983.04.013
[15] 汪品先, 闵秋宝. 我国第四纪海侵研究中的几个基本问题[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1985, 5(1):15-25 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1985.01.003
WANG Pinxian, MIN Qiubao. Quaternary marine transgressions in China: some basic questions [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1985, 5(1): 15-25. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1985.01.003
[16] 王张华, 丘金波, 冉莉华, 等. 长江三角洲南部地区晚更新世年代地层和海水进退[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(4):1-8 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2004.04.001
WANG Zhanghua, QIU Jinbo, RAN Lihua, et al. Chronostratigraphy and transgression/regression during Late Pleistocene in the southern Changjiang (Yangtze) River delta plain [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2004, 24(4): 1-8. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2004.04.001
[17] Zhao B C, Wang Z H, Chen J, et al. Marine sediment records and relative sea level change during Late Pleistocene in the Changjiang delta area and adjacent continental shelf [J]. Quaternary International, 2008, 186(1): 164-172. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2007.08.006
[18] Liu J, Saito Y, Wang H, et al. Stratigraphic development during the Late Pleistocene and Holocene offshore of the Yellow River delta, Bohai Sea [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 36(4-5): 318-331. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.06.007
[19] Yao Z Q, Guo Z T, Xiao G Q, et al. Sedimentary history of the western Bohai coastal plain since the late Pliocene: implications on tectonic, climatic and sea-level changes [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 54-55: 192-202. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.04.013
[20] Yi L, Lai Z P, Yu H J, et al. Chronologies of sedimentary changes in the South Bohai Sea, China: constraints from luminescence and radiocarbon dating [J]. Boreas, 2013, 42(2): 267-284. doi: 10.1111/j.1502-3885.2012.00271.x
[21] Shi X F, Yao Z Q, Liu Q S, et al. Sedimentary architecture of the Bohai Sea China over the last 1 Ma and implications for sea-level changes [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 451: 10-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.07.002
[22] Wang P X. Cenozoic deformation and the history of sea-land interactions in Asia[M]//Clift P, Kuhnt W, Wang P, et al. Continent-Ocean Interactions within East Asian Marginal Seas. Washington: American Geophysical Union, 2004: 1-22.
[23] 杨守业. 亚洲主要河流的沉积地球化学示踪研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2006, 21(6):648-655 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2006.06.013
YANG Shouye. Advances in sedimentary geochemistry and tracing applications of Asian rivers [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2006, 21(6): 648-655. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2006.06.013
[24] 郑洪波, 汪品先, 刘志飞, 等. 东亚东倾地形格局的形成与季风系统演化历史寻踪: 综合大洋钻探计划683号航次建议书简介[J]. 地球科学进展, 2008, 23(11):1150-1160 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2008.11.005
ZHENG Hongbo, WANG Pinxian, LIU Zhifei, et al. Carving the history of East Asia’s East-tilting topography and East Asian monsoon-an introduction to IODP proposal 683 [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2008, 23(11): 1150-1160. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2008.11.005
[25] Qin Y S, Zhao Y Y, Chen L R, et al. Geology of Bohai Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1990.
[26] 肖国桥, 郭正堂, 陈宇坤, 等. 渤海湾西岸BZ1钻孔的磁性地层学研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008, 28(5):909-916 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2008.05.014
XIAO Guoqiao, GUO Zhengtang, CHEN Yukun, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of BZ1 borehole in West coast of Bohai Bay, northern China [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2008, 28(5): 909-916. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2008.05.014
[27] 姚政权, 郭正堂, 陈宇坤, 等. 渤海湾海陆交互相沉积的磁性地层学[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(1):9-15 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2006.01.002
YAO Zhengquan, GUO Zhengtang, CHEN Yukun, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of marine-terrigenous facies deposits in Bohai Bay [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(1): 9-15. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2006.01.002
[28] Xu Q M, Yang J L, Hu Y Z, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of two deep boreholes in southwestern Bohai Bay: tectonic implications and constraints on the ages of volcanic layers [J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2018, 43: 102-114. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2017.08.006
[29] Yi L, Deng C L, Tian L Z, et al. Plio-Pleistocene evolution of Bohai Basin (East Asia): demise of Bohai Paleolake and transition to marine environment [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 29403. doi: 10.1038/srep29403
[30] 胥勤勉, 袁桂邦, 秦雅飞, 等. 滦河三角洲南部MT04孔磁性地层研究及其构造与气候耦合关系的探讨[J]. 第四纪研究, 2014, 34(3):540-552 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2014.03.08
XU Qinmian, YUAN Guibang, QIN Yafei, et al. Magnetostratigraphy and discussion of coupling relationship between tectonic movement and climate change of MT04 borehole in southern Luanhe River delta [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2014, 34(3): 540-552. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2014.03.08
[31] 王忠蕾, 郑洪波, 梅西, 等. 辽东湾北部钻孔磁性地层年代框架及地质意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2020, 40(3):616-632 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2020.03.03
WANG Zhonglei, ZHENG Hongbo, MEI Xi, et al. Magnetic stratigraphy of boreholes in the north of Liaodong Bay and its significance [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2020, 40(3): 616-632. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2020.03.03
[32] 李翔, 李日辉, 陈晓辉, 等. 渤海西部TJC-1孔磁性地层研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2016, 36(1):208-215 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2016.20
LI Xiang, LI Rihui, CHEN Xiaohui, et al. Quaternary magnetostratigraphy recorded in the sediments of core TJC-1 in the western Bohai Sea [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2016, 36(1): 208-215. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2016.20
[33] Liu J X, Liu Q S, Zhang X H, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of a long Quaternary sediment core in the South Yellow Sea [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 144: 1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.05.025
[34] Yao Z Q, Shi X F, Liu Q S, et al. Paleomagnetic and astronomical dating of sediment core BH08 from the Bohai Sea, China: implications for glacial-interglacial sedimentation [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2014, 393: 90-101. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.11.012
[35] 肖国强, 杨吉龙, 赵长荣, 等. 天津滨海地区G2孔磁性地层年代及其构造指示[J]. 地质通报, 2014, 33(10):1642-1650 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.10.024
XIAO Guoqiang, YANG Jilong, ZHAO Changrong, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of drill hole G2 in the Tianjin coastal area and its tectonic significance [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, 33(10): 1642-1650. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.10.024
[36] Yang J L, Liang M Y, Algeo T J, et al. Upper Miocene-Quaternary magnetostratigraphy and magnetic susceptibility from the Bohai Bay Basin (eastern China) and implications for regional volcanic and basinal subsidence history [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 538: 109469. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2019.109469
[37] Liu J, Wang H, Wang F F, et al. Sedimentary evolution during the last ~ 1.9 Ma near the western margin of the modern Bohai Sea [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2016, 451: 84-96. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.03.012
[38] 刘健, 段宗奇, 梅西, 等. 南黄海中部隆起晚新近纪—第四纪沉积序列的地层划分与沉积演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(5):25-43
LIU Jian, DUAN Zongqi, MEI Xi, et al. Stratigraphic classification and sedimentary evolution of the Late Neogene to Quaternary sequence on the Central Uplift of the South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(5): 25-43.
[39] Mei X, Li R H, Zhang X H, et al. Evolution of the Yellow Sea warm current and the Yellow Sea cold water mass since the Middle Pleistocene [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2016, 442: 48-60. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.11.018
[40] 葛淑兰, 石学法, 朱日祥, 等. 南黄海EY02-2孔磁性地层及古环境意义[J]. 科学通报, 2006, 51(7):855-865
GE Shulan, SHI Xuefa, ZHU Rixiang, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of borehole EY02-2 in the southern Yellow Sea and its paleoenvironmental significance [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(7): 855-865.
[41] Liu J X, Shi X F, Liu Q S, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of a greigite-bearing core from the south yellow sea: implications for remagnetization and sedimentation [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2014, 119(10): 7425-7441. doi: 10.1002/2014JB011206
[42] 郑光膺. 南黄海第四纪层型地层对比[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989: 1-262
ZHENG Guangying. Comparison of Sandwich Stratum of Quaternary in the South Yellow Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989: 1-262.
[43] Duan Z Q, Liu Q S, Shi X F, et al. Reconstruction of high-resolution magnetostratigraphy of the Changjiang (Yangtze) River Delta, China [J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2016, 204(2): 948-960. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggv497
[44] Yi L, Ye X Y, Chen J B, et al. Magnetostratigraphy and luminescence dating on a sedimentary sequence from northern East China Sea: constraints on evolutionary history of eastern marginal seas of China since the Early Pleistocene [J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 349: 316-326. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.07.038
[45] Jiang Z X, Jin C S, Wang Z B, et al. Chronostratigraphic framework of the East China Sea since MIS 6 from geomagnetic paleointensity and environmental magnetic records [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2020, 185: 103092. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2019.103092
[46] Wang Z H, Xu H, Zhan Q, et al. Lithological and palynological evidence of Late Quaternary depositional environments in the subaqueous Yangtze delta, China [J]. Quaternary Research, 2010, 73(3): 550-562. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2009.11.001
[47] Chen Z Y, Chen Z L, Zhang W G. Quaternary stratigraphy and trace-element indices of the Yangtze Delta, eastern China, with special reference to marine transgressions [J]. Quaternary Research, 1997, 47(2): 181-191. doi: 10.1006/qres.1996.1878
[48] Lisiecki L E, Raymo M E. A Pliocene-Pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ18O records [J]. Paleoceanography, 2005, 20(1): PA1003.
[49] Shi X F, Yao Z Q, Liu J X, et al. Dominant role of sea level on the sedimentary environmental evolution in the Bohai and Yellow Seas over the last 1 million years [J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2021, 9: 638221. doi: 10.3389/feart.2021.638221
[50] McKee B A, Nittrouer C A, DeMaster D J. Concepts of sediment deposition and accumulation applied to the continental shelf near the mouth of the Yangtze River [J]. Geology, 1983, 11(11): 631-633. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1983)11<631:COSDAA>2.0.CO;2
[51] Shan X, Shi X F, Clift P D, et al. Carbon isotope and rare earth element composition of Late Quaternary sediment gravity flow deposits on the mid shelf of East China Sea: implications for provenance and origin of hybrid event beds [J]. Sedimentology, 2019, 66(5): 1861-1895. doi: 10.1111/sed.12561
[52] 阎玉忠, 王宏, 李凤林, 等. 渤海湾西岸晚更新世沉积的差异性特征[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26(3):181-191
YAN Yuzhong, WANG Hong, LI Fenglin, et al. Different depositional processes of boreholes BQ1 and BQ2 in the Late Pleistocene on the West coast of Bohai Bay [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2006, 26(3): 181-191.
[53] 王强, 张玉发, 袁桂邦, 等. MIS 3阶段以来河北黄骅北部地区海侵与气候期对比[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008, 28(1):79-95 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2008.01.009
WANG Qiang, ZHANG Yufa, YUAN Guibang, et al. Since MIS 3 stage the correlation between transgression and climatic changes in the North Huanghua area, Hebei [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2008, 28(1): 79-95. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2008.01.009
[54] 刘健, 王红, 李绍全, 等. 南黄海北部泥质沉积区冰后期海侵沉积记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(3):1-10 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2004.03.001
LIU Jian, WANG Hong, LI Shaoquan, et al. Postglacial transgressive sedimentary records of muddy sedimentary areas in the North of the South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2004, 24(3): 1-10. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2004.03.001
[55] Yi L, Yu H J, Ortiz J D, et al. Late Quaternary linkage of sedimentary records to three astronomical rhythms and the Asian monsoon, inferred from a coastal borehole in the South Bohai Sea, China [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 329-330: 101-117. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2012.02.020
[56] 庄振业, 许卫东, 刘东生, 等. 渤海南部S3孔晚第四纪海相地层的划分及环境演变[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1999, 19(2):27-35
ZHUANG Zhenye, XU Weidong, LIU Dongsheng, et al. Division and environmental evolution of Late Quaternary marine beds of S3 hole in the Bohai Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1999, 19(2): 27-35.
[57] 王中波, 张江勇, 梅西, 等. 中国陆架海MIS 5(74 ~ 128 ka)以来地层及其沉积环境[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(5):1370-1394
WANG Zhongbo, ZHANG Jiangyong, MEI Xi, et al. The stratigraphy and depositional environments of China’s sea shelves since MIS 5 (74-128) ka [J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(5): 1370-1394.
[58] Yi L, Yu H J, Ortiz J D, et al. A reconstruction of Late Pleistocene relative sea level in the South Bohai Sea, China, based on sediment grain-size analysis [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2012, 281: 88-100. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2012.08.007
[59] Gradstein F M, Ogg J G, Schmitz M D, et al. The Geologic Time Scale[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2012: 1-1144.
[60] Liu J, Zhang X H, Mei X, et al. The sedimentary succession of the last ~ 3.50 Myr in the western South Yellow Sea: paleoenvironmental and tectonic implications[J]. Marine Geology, 2018, 399: 47-65.
[61] 李从先, 范代读, 杨守业, 等. 中国河口三角洲地区晚第四纪下切河谷层序特征和形成[J]. 古地理学报, 2008, 10(1):87-97 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2008.01.010
LI Congxian, FAN Daidu, YANG Shouye, et al. Characteristics and Formation of the Late Quaternary incised-valley sequences in estuary and delta areas in China [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2008, 10(1): 87-97. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2008.01.010
[62] Fan D D, Shang S, Burr G. Sea level implications from Late Quaternary/Holocene paleosols from the Oujiang Delta, China [J]. Radiocarbon, 2019, 61(1): 83-99. doi: 10.1017/RDC.2018.77
[63] Wellner R W, Bartek L R. The effect of sea level, climate, and shelf physiography on the development of incised-valley complexes: a modern example from the East China Sea [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2003, 73(6): 926-940. doi: 10.1306/041603730926
[64] 李从先, 陈庆强, 范代读, 等. 末次盛冰期以来长江三角洲地区的沉积相和古地理[J]. 古地理学报, 1999, 1(4):12-25 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.1999.04.002
LI Congxian, CHEN Qingqiang, FAN Daidu, et al. Palaeogeography and Palaeoenvironment in Changjiang delta since last glaciation [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 1999, 1(4): 12-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.1999.04.002
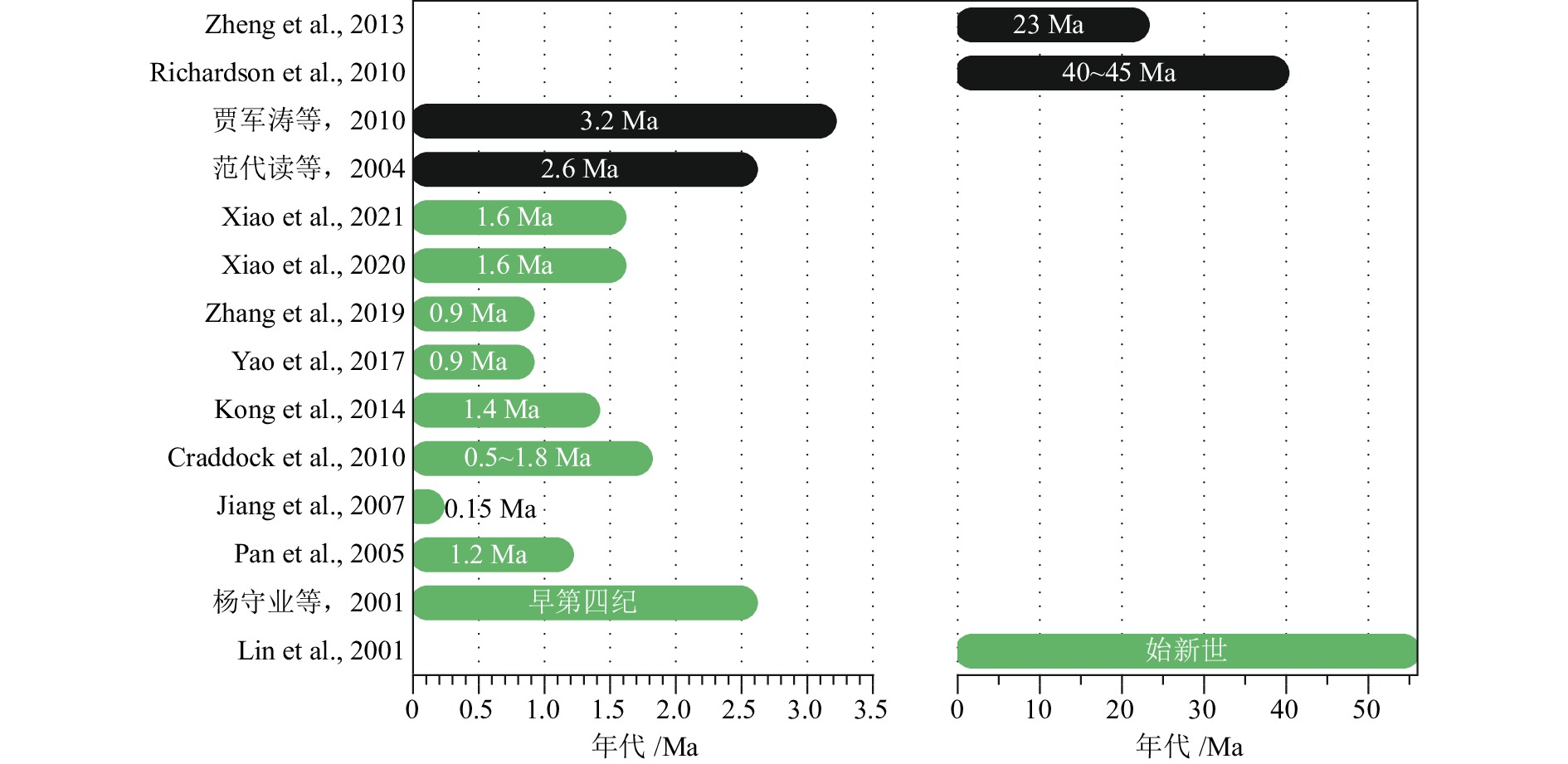
[65] Lin A M, Yang Z Y, Sun Z M, et al. How and when did the Yellow River develop its square bend? [J]. Geology, 2001, 29(10): 951-954. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0951:HAWDTY>2.0.CO;2
[66] Richardson N J, Densmore A L, Seward D, et al. Did incision of the Three Gorges begin in the Eocene? [J]. Geology, 2010, 38(6): 551-554. doi: 10.1130/G30527.1
[67] 范代读, 李从先, Yokoyama K, 等. 长江三角洲晚新生代地层独居石年龄谱与长江贯通时间研究[J]. 中国科学D辑 地球科学, 2005, 48(10):1718-1727 doi: 10.1360/01yd0447
FAN Daidu, LI Congxian, Yokoyama K, et al. Monazite age spectra in the Late Cenozoic strata of the Changjiang delta and its implication on the Changjiang run-through time [J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2005, 48(10): 1718-1727. doi: 10.1360/01yd0447
[68] 贾军涛, 郑洪波, 黄湘通, 等. 长江三角洲晚新生代沉积物碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄及其对长江贯通的指示[J]. 科学通报, 2010, 55(15):1520-1528 doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3091-x
JIA Juntao, ZHENG Hongbo, HUANG Xiangtong, et al. Detrital zircon U-Pb ages of Late Cenozoic sediments from the Yangtze delta: implication for the evolution of the Yangtze River [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(15): 1520-1528. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3091-x
[69] Craddock W H, Kirby E, Harkins N W, et al. Rapid fluvial incision along the Yellow River during Headward Basin integration [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2010, 3(3): 209-213. doi: 10.1038/ngeo777
[70] Jiang F C, Fu J L, Wang S B, et al. Formation of the Yellow River, inferred from loess–palaeosol sequence in Mangshan and lacustrine sediments in Sanmen Gorge, China [J]. Quaternary International, 2007, 175(1): 62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2007.03.022
[71] Pan B T, Wang J P, Gao H S, et al. Paleomagnetic dating of the topmost terrace in Kouma, Henan and its indication to the Yellow River’s running through Sanmen Gorges [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(7): 657-664. doi: 10.1360/03wd0290
[72] Kong P, Jia J, Zheng Y. Time constraints for the Yellow River traversing the Sanmen Gorge [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2014, 15(2): 395-407. doi: 10.1002/2013GC004912
[73] Xiao G Q, Pan Q, Zhao Q Y, et al. Early Pleistocene integration of the Yellow River II: evidence from the Plio-Pleistocene sedimentary record of the Fenwei Basin [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2021, 577: 110550. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2021.110550
[74] 杨守业, 蔡进功, 李从先, 等. 黄河贯通时间的新探索[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(2):15-20 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2001.02.003
YANG Shouye, CAI Jingong, LI Congxian, et al. New discussion about the run-through time of the Yellow River [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2001, 21(2): 15-20. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2001.02.003
[75] Yao Z Q, Shi X F, Qiao S Q, et al. Persistent effects of the Yellow River on the Chinese marginal seas began at least ~880 ka ago [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 2827. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03140-x
[76] Coe A L. The Sedimentary Record of Sea-Level Change[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003: 1-288.
[77] Limarino C, Tripaldi A, Marenssi S, et al. Tectonic, sea-level, and climatic controls on Late Paleozoic sedimentation in the western basins of Argentina [J]. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 2006, 22(3-4): 205-226. doi: 10.1016/j.jsames.2006.09.009
[78] Komatsubara J. Fluvial architecture and sequence stratigraphy of the Eocene to Oligocene Iwaki Formation, northeast Japan: channel-fills related to the sea-level change [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2004, 168(1-2): 109-123. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2004.03.005
[79] Chappell J, Shackleton N J. Oxygen isotopes and sea level [J]. Nature, 1986, 324(6093): 137-140. doi: 10.1038/324137a0
[80] 韦桃源, 陈中原, 魏子新, 等. 长江河口区第四纪沉积物中的地球化学元素分布特征及其古环境意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26(3):397-405 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.03.011
WEI Taoyuan, CHEN Zhongyuan, WEI Zixin, et al. The distribution of geochemical trace elements in the Quaternary sediments of the Changjiang River mouth and the paleoenvironmental implications [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2006, 26(3): 397-405. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.03.011
[81] 秦蕴珊, 赵一阳, 陈丽蓉, 等. 黄海地质[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1989: 1-289
QIN Yunshan, ZHAO Yiyang, CHEN Lirong, et al. Geology of Yellow Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1989: 1-289.
[82] Chen Z Y, Stanley D J. Quaternary subsidence and river channel migration in the Yangtze delta plain, eastern China [J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 1995, 11(3): 927-945.
[83] Allen M B, Macdonald D I M, Xun Z, et al. Early Cenozoic two-phase extension and Late Cenozoic thermal subsidence and inversion of the Bohai Basin, northern China [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1997, 14(7-8): 951-972. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(97)00027-5
[84] Yokoyama T, Koizumi I. Marine transgressions on the Pleistocene pecangan Formation in the Sangiran area, central Java, Indonesia [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1989, 72: 177-193. doi: 10.1016/0031-0182(89)90141-7
[85] Kitaba I, Harada M, Hyodo M, et al. MIS 21 and the Mid-Pleistocene climate transition: climate and sea- level variation from a sediment core in Osaka Bay, Japan [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2011, 299(1-2): 227-239. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2010.11.004
[86] Miller K G, Kominz M A, Browning J V, et al. The Phanerozoic record of global sea-level change [J]. Science, 2005, 310(5752): 1293-1298. doi: 10.1126/science.1116412
[87] McCarthy F M G, Katz M E, Kotthoff U, et al. Sea-level control of New Jersey margin architecture: palynological evidence from Integrated Ocean Drilling Program Expedition 313 [J]. Geosphere, 2013, 9(6): 1457-1487. doi: 10.1130/GES00853.1
[88] Naish T, Kamp P J J, Alloway B V, et al. Integrated tephrochronology and magnetostratigraphy for cyclothemic marine strata, Wanganui Basin: implications for the Pliocene-Pleistocene boundary in New Zealand [J]. Quaternary International, 1996, 34-36: 29-48. doi: 10.1016/1040-6182(95)00067-4
[89] Katz M E, Browning J V, Miller K G, et al. Paleobathymetry and sequence stratigraphic interpretations from benthic foraminifera: insights on New Jersey shelf architecture, IODP Expedition 313 [J]. Geosphere, 2013, 9(6): 1488-1513. doi: 10.1130/GES00872.1
[90] Miller K G, Sugarman P J, Browning J V, et al. Pleistocene sequence stratigraphy of the shallow continental shelf, offshore New Jersey: constraints of Integrated Ocean Drilling Program Leg 313 core holes [J]. Geosphere, 2013, 9(1): 74-95. doi: 10.1130/GES00795.1
[91] Reynolds D J, Steckler M S, Coakley B J. The role of the sediment load in sequence stratigraphy: the influence of flexural isostasy and compaction [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 1991, 96(B4): 6931-6949. doi: 10.1029/90JB01914
[92] Yao Z Q, Shi X F, Liu Y G, et al. Sea-level and climate signatures recorded in orbitally-forced continental margin deposits over the last 1 Myr: New perspectives from the Bohai Sea [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 550: 109736. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.109736
[93] Cheng H, Edwards R L, Sinha A, et al. The Asian monsoon over the past 640, 000 years and ice age terminations [J]. Nature, 2016, 534(7609): 640-646. doi: 10.1038/nature18591
[94] Laskar J, Robutel P, Joutel F, et al. A long-term numerical solution for the insolation quantities of the Earth [J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2004, 428(1): 261-285.
[95] Zhao D B, Wan S M, Clift P D, et al. Provenance, sea-level and monsoon climate controls on silicate weathering of Yellow River sediment in the northern Okinawa Trough during Late Last Glaciation [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2018, 490: 227-239. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.11.002
[96] 石学法. 大洋钻探与中国边缘海沉积地质学[J]. 海洋科学, 1996, 25(3):47-50
SHI Xuefa. Ocean drilling and sedimentary geology of China marginal seas [J]. Marine Sciences, 1996, 25(3): 47-50.
[97] 郑洪波. IODP中的海陆对比和海陆相互作用[J]. 地球科学进展, 2003, 18(5):722-729 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2003.05.012
ZHENG Hongbo. Land-ocean comparison and interactions in IODP [J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 2003, 18(5): 722-729. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2003.05.012
[98] 赵美训, 丁杨, 于蒙. 中国边缘海沉积有机质来源及其碳汇意义[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2017, 47(9):70-76
ZHAO Meixun, DING Yang, YU Meng. Sources of sedimentary organic matter in China marginal Sea surface sediments and implications of carbon sink [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2017, 47(9): 70-76.
-




 下载:
下载: