Controlling factors on the effectiveness of turbidite fan reservoir of the Meishan Formation, Qiongdongnan Basin
-
摘要:
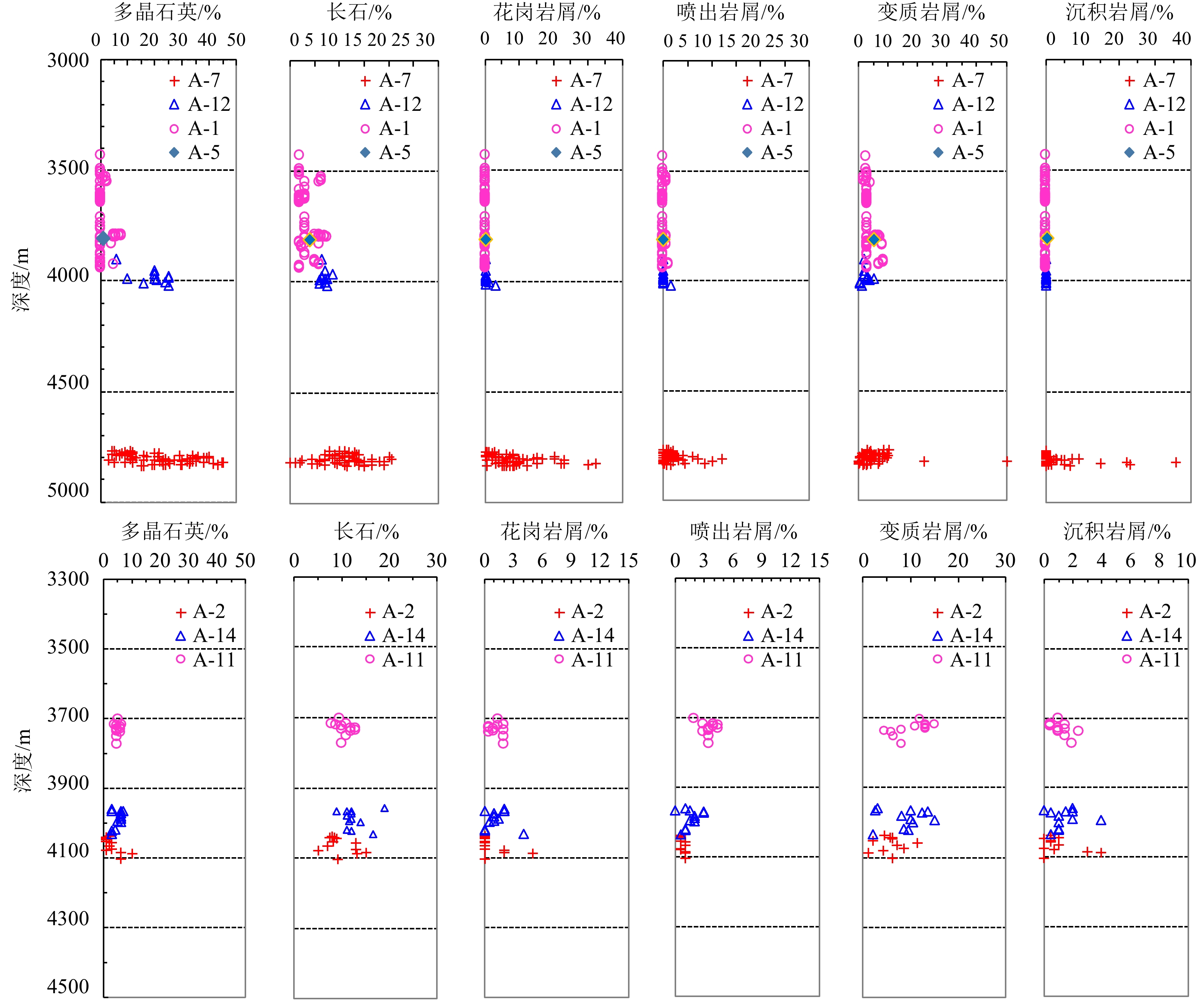
琼东南盆地中新统梅山组浊积扇是该地区天然气最主要的贡献者之一,其沉积机理、储层主控因素分析及储层预测方法技术的提高直接影响着该区天然气增储上产。本文根据大量的岩心及井壁取心等实测资料,对该区钻井揭示的海底扇储层进行了系统分析。研究表明,琼东南盆地梅山组浊积扇类型及其内部组成、底流改造是影响和制约储层预测成功率的关键,其中断控陡坡根部盆底扇、深洼盆底扇和峡谷切割深洼盆底扇是储层相对发育的浊积扇类型,底流改造对处于敞流环境的中扇、外扇储层品质改善至关重要。对于深水环境的浊积扇储层而言,沉积因素,如岩性侧封、储层上倾尖灭构成这类岩性圈闭有效性的主要原因,对于峡谷切割型深洼盆底扇需要重点考虑岩性侧封,对于深洼盆底扇需要重点考虑上倾尖灭。研究成果可广泛应用于深水浊积扇储层预测。
Abstract:The turbidite fan of Miocene Meishan Formation in Qiongdongnan Basin is one of the main contributors of natural gas in the area. To increase the natural gas reserve and production in this area, the sedimentary mechanism, the controlling factors and prediction methods were studied. According to a large number of DST, geological fluid sampling, core and rotary sidewall coring measured data, and relevant enterprise standards, the turbidite fan reservoir of the could be divided into four levels of grade: high-quality, good, effective, and tight. The four levels correspond to high production, commercial production capacity, merely productive capacity, and dry layer. Results show that the type of turbidite fans and its internal composition, bottom current reformation, and reservoir effectiveness are key factors on reservoir prediction success. Fault-terrace basin floor fans, basin floor fans cut by canyon, and integral basin floor fans are three types of relatively good reservoirs; and bottom current reworking is important to improve the reservoir of middle fan and outer fan in open flow environment. For the basin floor fan cut by canyon, the lithological side seal needs to be focused in the future. For the integral basin floor fans, the reservoir pinch out shall be considered too. At present, the rate of reservoir prediction of the Meishan turbidite fans in this area is very low. The methods developed in this study shall be of great value to improve the success rate of reservoir prediction.
-
Key words:
- turbidite fan /
- reservoir /
- main controlling factors /
- reservoir effectiveness /
- Meishan Formation /
- Qiongdongnan Basin
-

-
表 1 琼东南盆地梅山组天然气储层分类标准
Table 1. Classification standard of natural gas reservoir in the Meishan Formation of the Qiongdongnan Basin
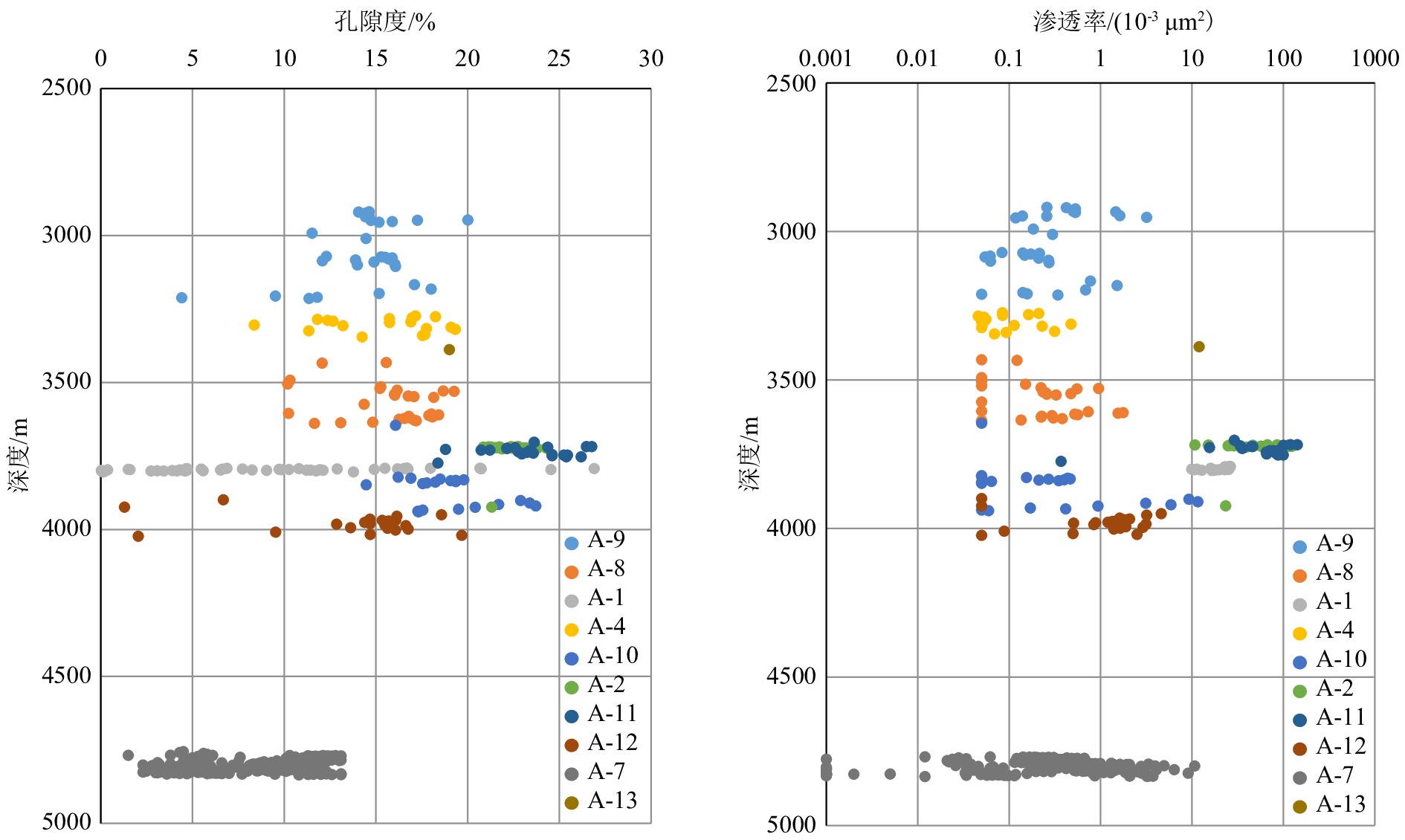
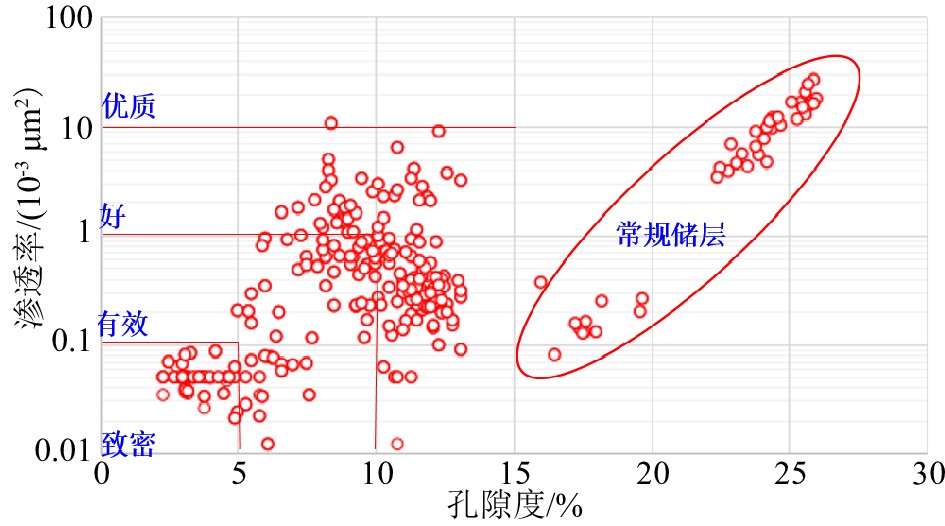
中石油分类 本次研究分类 储层分类 孔隙度/% 渗透率/(10−3 μm2) 评价 分类 评价 I >20 >1000 最好 优质储层 高产 II 15~20 100~1000 好 III 10~15 10~100 较好 IV 5~10 1~10 较差 好储层 商业产能 V <5 0.1~1 差 有效储层 少量地层流体 <0.1 致密层 泥浆滤液 表 2 琼东南盆地梅山组已钻盆底扇储层厚度统计
Table 2. Statistics in the thickness that drilled into the basin-floor fan reservoir in the Meishan Formation of Qiongdongnan Basin
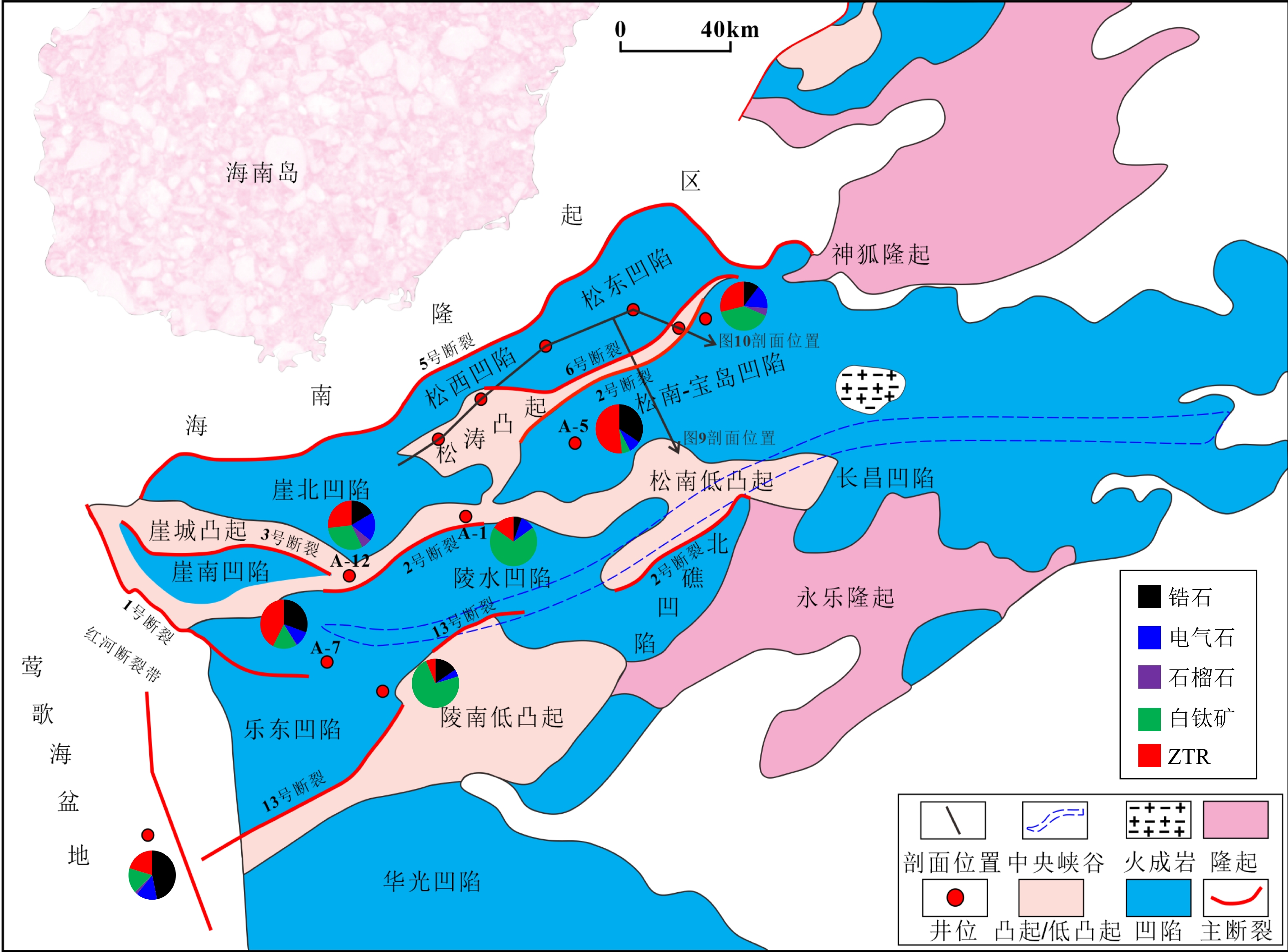
浊积扇类型 各种类型储层厚度占比/% 大类 亚类 优质+好 有效 致密 盆
底
扇深洼盆底扇
峡谷切割深洼盆底扇85 5 10 断控缓坡根部盆底扇 76 5 19 断控陡坡根部盆底扇 10 87.5 2.5 斜坡扇 5 15 80 陆棚扇 0 13 87 表 3 A-8井梅山组海底扇储层实测物性特征
Table 3. Measured physical property data of submarine fan reservoir of Well A-8
序号 井深
/m沉积相 孔隙度
/%渗透率
/(10−3 μm2)泥质含量
/%描述 1 3 639 内扇浊积沟道 11.6 ﹤0.05 25 致密储层
小孔喉占比高2 3 615 内扇上部沉积 16.8 0.52 12 有效储层
中大孔喉普遍存在,但占比不高3 3 550.5 外扇沉积 18.2 3.33 9 好储层
中等孔喉占比很高表 4 B-1井梅山组海底扇储层实测物性特征
Table 4. Measured physical property data of submarine fan reservoir of Well B-1
序号 井壁取芯 压汞资料 深度/m 岩性 照片 孔隙度/% 渗透率/(10−3μm2) 储层
类型孔隙度/% 渗透率
/(10−3μm2)压汞曲线及孔喉半径 1 3899 中砂岩 
6.7
6.1<0.05
8.17致密 6 0.0438 
2 3950 中砂岩 
18.6
18.44.61
13好-优质 17.9 4.85 3 3968 粗砂岩 
16.1
15.62.08
4.85好-优质 15.7 2.46 4 3980.5 中砂岩 
14.7 0.88 好-优质 15.2 2.79 
5 3994 含砾
粗砂岩
13.6 1.89 好-优质 12.8 2.19 6 4002 中砂岩 
16.1 1.4 好-优质 15.7 1.77 7 4017 粗砂岩 
14.7 0.5 有效 14.7 0.75 -
[1] 王振峰. 深水重要油气储层: 琼东南盆地中央峡谷体系[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(4):646-653
WANG Zhenfeng. Important deepwater hydrocarbon reservoirs: the central canyon system in the Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(4): 646-653.
[2] 解习农, 陈志宏, 孙志鹏, 等. 南海西北陆缘深水沉积体系内部构成特征[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2012, 37(4):627-634
XIE Xinong, CHEN Zhihong, SUN Zhipeng, et al. Depositional architecture characteristics of deepwater depositional systems on the continental margins of northwestern South China Sea [J]. Earth Science:Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2012, 37(4): 627-634.
[3] 李建平, 廖计华, 方勇. 基于露头和岩心的深水重力流沉积新认识及其油气地质意义[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(6):30-37
LI Jianping, LIAO Jihua, FANG Yong. New understanding of deep-water gravity flow deposition and its significance in petroleum geology based on outcrops and cores [J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(6): 30-37.
[4] 魏魁生, 崔旱云, 叶淑芬, 等. 琼东南盆地高精度层序地层学研究[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2001, 26(1):59-66
WEI Kuisheng, CUI Hanyun, YE Shufen, et al. High-precision sequence stratigraphy in Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. Earth Science:Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2001, 26(1): 59-66.
[5] Xie X N, Müller R D, Ren J Y, et al. Stratigraphic architecture and evolution of the continental slope system in offshore Hainan, northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2008, 247(3-4): 129-144. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2007.08.005
[6] 吴时国, 秦蕴珊. 南海北部陆坡深水沉积体系研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(5):922-930
WU Shiguo, QIN Yunshan. The research of deepwater depositional system in the northern South China Sea [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(5): 922-930.
[7] 雷超, 任建业, 李绪深, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区结构构造特征与油气勘探潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2011, 38(5):560-569
LEI Chao, REN Jianye, LI Xushen, et al. Structural characteristics and petroleum exploration potential in the deep-water area of the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2011, 38(5): 560-569.
[8] 何云龙, 解习农, 陆永潮, 等. 琼东南盆地深水块体流构成及其沉积特征[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2011, 36(5):905-913
HE Yunlong, XIE Xinong, LU Yongchao, et al. Architecture and characteristics of mass transport deposits (MTDs) in Qiongdongnan Basin in northern South China Sea [J]. Earth Science:Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2011, 36(5): 905-913.
[9] Shanmugam G. Submarine fans: a critical retrospective (1950-2015) [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2016, 5(2): 110-184. doi: 10.1016/j.jop.2015.08.011
[10] Posamentier H W, Kolla V, 刘化清. 深水浊流沉积综述[J]. 沉积学报, 2019, 37(5):879-903
Posamentier H W, Kolla V, LIU Huaqing. An overview of deep-water turbidite deposition [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2019, 37(5): 879-903.
[11] 傅焓埔, 刘群, 胡修棉. 水下沉积物重力流与海底扇相模式研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2020, 35(2):124-136
FU Hanpu, LIU Qun, HU Xiumian. Review on subaqueous sediment gravity flow and submarine fan [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2020, 35(2): 124-136.
[12] Chen H, Stow D A V, Xie X N, et al. Depositional architecture and evolution of basin-floor fan systems since the Late Miocene in the Northwest Sub-Basin, South China Sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 126: 104803. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104803
[13] 李建平, 刘子玉, 谢晓军, 等. 深水重力流沉积机理新认识及其在北海G油田发现中的应用[J]. 中国海上油气, 2021, 33(1):23-31
LI Jianping, LIU Ziyu, XIE Xiaojun, et al. New understanding of deep-water gravity flow deposition mechanism and its application in the discovery of G oilfield in North Sea [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2021, 33(1): 23-31.
[14] Reading H G, Richards M. Turbidite systems in deep-water basin margins classified by grain size and feeder system [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1994, 78(5): 792-822.
[15] Scott R A, Smyth H R, Moton A C, 等. 油气勘探开发中的沉积物源研究[M]. 李胜利, 李顺利, 单新, 等译. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2018: 1-472
Scott R A, Smyth H R, Moton A C, 等. 油气勘探开发中的沉积物源研究[M]. 李胜利, 李顺利, 单新, 等译. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2018: 1-472. [Scott R A, Smyth H R, Moton A C, et al. Sediment Provenance Studies in Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production[M]. LI Shengli, LI Shunli, SHAN Xin, et al, trans. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2018: 1-472.
[16] Shanmugam G. Deep-Water Processes and Facies Models: Implications for Sandstone Petroleum Reservoirs[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2006: 1-474.
[17] Chen H, Xie X N, Mao K N, et al. Depositional characteristics and formation mechanisms of deep-water canyon systems along the northern South China Sea margin [J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2020, 31(4): 808-819. doi: 10.1007/s12583-020-1284-z
[18] Purvis K, Kao J, Flanagan K, et al. Complex reservoir geometries in a deep water clastic sequence, Gryphon Field, UKCS: injection structures, geological modelling and reservoir simulation [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2002, 19(2): 161-179. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(02)00003-X
[19] Mayall M, Jones E, Casey M. Turbidite channel reservoirs – Key elements in facies prediction and effective development [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2006, 23(8): 821-841. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2006.08.001
[20] 王英民, 王海荣, 邱燕, 等. 深水沉积的动力学机制和响应[J]. 沉积学报, 2007, 25(4):495-504
WANG Yingmin, WANG Hairong, QIU Yan, et al. Process of dynamics and its response of deep-water sedimentation [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2007, 25(4): 495-504.
[21] Brackenridge R E, Hernández-Molina F J, Stow D A V, et al. A Pliocene mixed contourite-turbidite system offshore the Algarve Margin, Gulf of Cadiz: seismic response, margin evolution and reservoir implications [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 46: 36-50. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.05.015
[22] Alonso B, Ercilla G, Casas D, et al. Contourite vs gravity-flow deposits of the Pleistocene Faro Drift (Gulf of Cadiz): sedimentological and mineralogical approaches [J]. Marine Geology, 2016, 377: 77-94. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.12.016
[23] 苏明, 李俊良, 姜涛, 等. 琼东南盆地中央峡谷的形态及成因[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(4):85-93
SU Ming, LI Junliang, JIANG Tao, et al. Morphological features and formation mechanism of central canyon in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(4): 85-93.
-



 下载:
下载: