Productivity evolution in the antarctic Weddell Sea and its paleoceanographic implication since MIS 5
-
摘要:
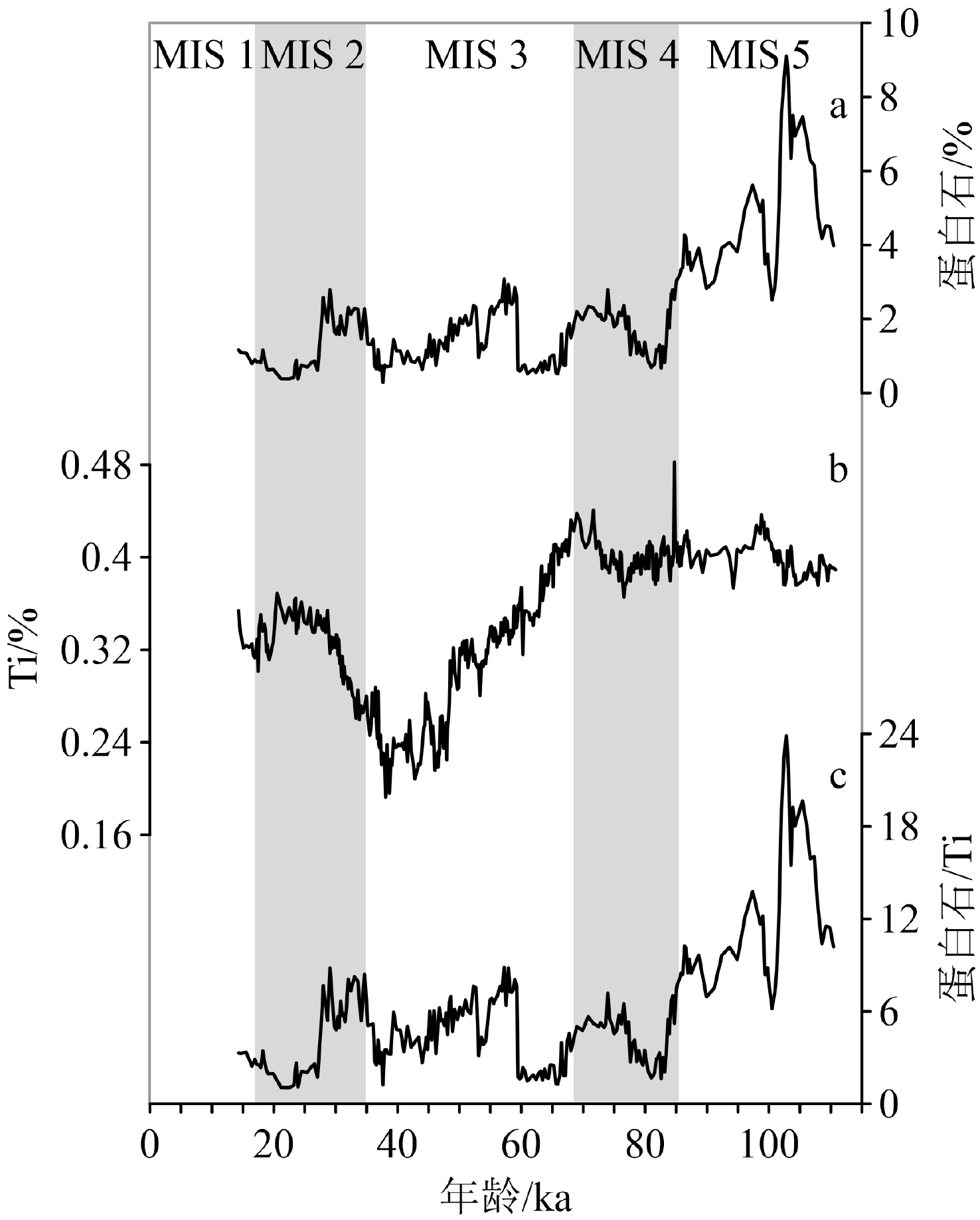
南大洋有关大气二氧化碳分压(pCO2)冰期旋回机制的最新假说表明,冰期南极带生产力降低指示的深部流通状况减弱对CO2的封存,以及亚南极带生产力升高对CO2的固定能够圆满解释冰期大气pCO2的降低。显然,测试该假说合理性的关键是验证冰期旋回中南极带与亚南极带呈“镜像”关系的生产力演化特征。通过沉积物岩芯中生源蛋白石含量重建了MIS 5期以来南极威德尔海(南极带)生产力演化。结果显示,南极威德尔海生产力呈现暖期(MIS 5和3期)高、冷期(MIS 4和2期)低的冰期旋回特征以及总体降低的长期演化趋势。联合该生产力记录与搜集的南大洋其他海区多个生产力记录,确证了南极带与亚南极带“镜像”的生产力演化模式。进一步,通过该生产力记录与其潜在环境影响因素的对比,发现西风带经向移动和海冰张缩通过影响深部流通状况,进而控制深部营养物进入表层的可利用性,最终驱动MIS 5期以来威德尔海生产力演化的冰期旋回和长期趋势。南极威德尔海的深部流通状况对CO2的“收押”与释放很可能贡献了MIS 5期以来大气pCO2演化的冰期旋回和长期趋势。该研究确证了上述南大洋有关大气pCO2冰期旋回机制假说的合理性,表明南大洋在全球气候演化中扮演重要角色。
Abstract:The latest hypothesis on the mechanism of glacial/interglacial variation in atmospheric partial pressure of carbon dioxide (pCO2-atm) in the Southern Ocean suggests that the decrease of pCO2-atm during glaciation can be satisfactorily explained by CO2 sequestration via the reduced deep ventilation indicated by the decrease in the Antarctic zone productivity, and the CO2 fixation by the increase in the subantarctic zone productivity. Obviously, verifying the mirror-image relation between productivity evolution in the Antarctic zone and the subantarctic zone in glacial cycles is the key to examine this hypothesis. The productivity evolution in the Weddell Sea (in Antarctic Zone) since MIS 5 was reconstructed based on the biogenic opal content from sediment cores. The results indicate that the productivity in the Weddell Sea showed glacial-interglacial variations, with high productivity during warm periods (MIS 5 and 3) and low productivity during cold periods (MIS 4 and 2), and a long-term decreasing trend was also observed. By combining our productivity records with those of other areas in the Southern Ocean, the mirror-image model of productivity evolution in the Antarctic and subantarctic zones was confirmed. Furthermore, comparison between the productivity records and potential environmental influence factors indicated that the meridional movement of Westerlies as well as the expansion and retreat of sea ice controlled the nutrient availability from deep water into surface by affecting deep convection, and ultimately drove glacial-interglacial and long-term variations of productivity in the Weddell Sea since MIS 5. The sequestration and release of CO2 due to variation of deep convection in the Weddell Sea probably contributed to the long-term trend and glacial-interglacial cycles of pCO2-atm since MIS 5. This research confirms that the above hypothesis about the mechanism for glacial-interglacial pCO2-atm cycles in the Southern Ocean is reasonable, indicating that the Southern Ocean plays an important role in global climate evolution.
-
Key words:
- biogenic opal /
- pCO2-atm /
- deep ocean ventilation /
- sea ice /
- Westerlies /
- Antarctic Zone
-

-
[1] Sabine C L, Feely R A, Gruber N, et al. The oceanic sink for anthropogenic CO2 [J]. Science, 2004, 305(5682): 367-371. doi: 10.1126/science.1097403
[2] Frölicher T L, Sarmiento J L, Paynter D J, et al. Dominance of the Southern Ocean in anthropogenic carbon and heat uptake in CMIP5 models [J]. Journal of Climate, 2015, 28(2): 862-886. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00117.1
[3] Lüthi D, Le Floch M, Bereiter B, et al. High-resolution carbon dioxide concentration record 650, 000-800, 000 years before present [J]. Nature, 2008, 453(7193): 379-382. doi: 10.1038/nature06949
[4] Toggweiler J R, Russell J L, Carson S R. Midlatitude westerlies, atmospheric CO2, and climate change during the ice ages [J]. Paleoceanography, 2006, 21(2): PA2005.
[5] Watson A J, Garabato A C N. The role of Southern Ocean mixing and upwelling in glacial-interglacial atmospheric CO2 change [J]. Tellus B:Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 2006, 58(1): 73-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0889.2005.00167.x
[6] Watson A J, Vallis G K, Nikurashin M. Southern Ocean buoyancy forcing of ocean ventilation and glacial atmospheric CO2 [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2015, 8(11): 861-864. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2538
[7] Jaccard S L, Hayes C T, Martinez-Garcia A, et al. Two modes of change in Southern Ocean productivity over the past million years [J]. Science, 2013, 339(6126): 1419-1423. doi: 10.1126/science.1227545
[8] Hoppema M, Fahrbach E, Stoll M H C, et al. Annual uptake of atmospheric CO2 by the Weddell Sea derived from a surface layer balance, including estimations of entrainment and new production [J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 1999, 19(4): 219-233. doi: 10.1016/S0924-7963(98)00091-8
[9] Brown P J, Jullion L, Landschützer P, et al. Carbon dynamics of the Weddell Gyre, Southern Ocean [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2015, 29(3): 288-306. doi: 10.1002/2014GB005006
[10] Hoppema M. Weddell Sea turned from source to sink for atmospheric CO2 between pre-industrial time and present [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2004, 40(3-4): 219-231. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2003.08.001
[11] Hauck J, Völker C. Rising atmospheric CO2 leads to large impact of biology on Southern Ocean CO2 uptake via changes of the Revelle factor [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(5): 1459-1464. doi: 10.1002/2015GL063070
[12] Brzezinski M A, Pride C J, Franck V M, et al. A switch from Si(OH)4 to NO3− depletion in the glacial Southern Ocean [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2002, 29(12): 5-1-5-4.
[13] Gilbert I M, Pudsey C J, Murray J W. A sediment record of cyclic bottom-current variability from the northwest Weddell Sea [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1998, 115(1-4): 185-214. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(97)00093-6
[14] Pudsey C J, Barker P F, Hamilton N. Weddell Sea abyssal sediments a record of Antarctic Bottom Water flow [J]. Marine Geology, 1988, 81(1-4): 289-314. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(88)90032-1
[15] Carsey F D. Microwave observation of the Weddell Polynya [J]. Monthly Weather Review, 1980, 108(12): 2032-2044. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1980)108<2032:MOOTWP>2.0.CO;2
[16] Marshall J, Speer K. Closure of the meridional overturning circulation through Southern Ocean upwelling [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2012, 5(3): 171-180. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1391
[17] Marinov I, Gnanadesikan A, Toggweiler J R, et al. The southern ocean biogeochemical divide [J]. Nature, 2006, 441(7096): 964-967. doi: 10.1038/nature04883
[18] Orsi A H, Nowlin W D Jr, Whitworth T III. On the circulation and stratification of the Weddell Gyre [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers, 1993, 40(1): 169-203. doi: 10.1016/0967-0637(93)90060-G
[19] Vernet M, Geibert W, Hoppema M, et al. The Weddell Gyre, Southern Ocean: present knowledge and future challenges [J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2019, 57(3): 623-708. doi: 10.1029/2018RG000604
[20] Müller P J, Schneider R. An automated leaching method for the determination of opal in sediments and particulate matter [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers, 1993, 40(3): 425-444. doi: 10.1016/0967-0637(93)90140-X
[21] Mortlock R A, Froelich P N. A simple method for the rapid determination of biogenic opal in pelagic marine sediments [J]. Deep Sea Research Part A. Oceanographic Research Papers, 1989, 36(9): 1415-1426. doi: 10.1016/0198-0149(89)90092-7
[22] Lisiecki L E, Raymo M E. A Pliocene-Pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ18O records [J]. Paleoceanography, 2005, 20(1): PA1003.
[23] Lu L J, Zheng X F, Chen Z, et al. One-to-one coupling between southern ocean productivity and Antarctica climate [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(13): e2022GL098761.
[24] Weber M E, Kuhn G, Sprenk D, et al. Dust transport from Patagonia to Antarctica–a new stratigraphic approach from the Scotia Sea and its implications for the last glacial cycle [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2012, 36: 177-188. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.01.016
[25] Lambert F, Bigler M, Steffensen J P, et al. The calcium-dust relationship in high-resolution data from Dome C, Antarctica [J]. Climate of the Past Discussions, 2011, 7(2): 1113-1137.
[26] Skinner L C, Fallon S, Waelbroeck C, et al. Ventilation of the deep Southern Ocean and deglacial CO2 rise [J]. Science, 2010, 328(5982): 1147-1151. doi: 10.1126/science.1183627
[27] Pugh R S, McCave I N, Hillenbrand C D, et al. Circum-Antarctic age modelling of Quaternary marine cores under the Antarctic Circumpolar Current: ice-core dust–magnetic correlation [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2009, 284(1-2): 113-123. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2009.04.016
[28] Fischer H, Fundel F, Ruth U, et al. Reconstruction of millennial changes in transport, dust emission and regional differences in sea ice coverage using the deep EPICA ice cores from the Atlantic and Indian Ocean sector of Antarctica [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 260(1-2): 340-354. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2007.06.014
[29] Röthlisberger R, Bigler M, Wolff E W, et al. Ice core evidence for the extent of past atmospheric CO2 change due to iron fertilisation [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 31(16): L16207. doi: 10.1029/2004GL020338
[30] Lunt D J, Valdes P J. Dust transport to Dome C, Antarctica, at the Last Glacial Maximum and present day [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2001, 28(2): 295-298. doi: 10.1029/2000GL012170
[31] Li F Y, Ginoux P, Ramaswamy V. Transport of Patagonian dust to Antarctica [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2010, 115(D18): D18217. doi: 10.1029/2009JD012356
[32] Barker P F, Kennett J P, Scientific P. Weddell Sea palaeoceanography: preliminary results of ODP leg 113 [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1988, 67(1-2): 75-102. doi: 10.1016/0031-0182(88)90123-X
[33] Van der Weijden C H. Pitfalls of normalization of marine geochemical data using a common divisor [J]. Marine Geology, 2002, 184(3-4): 167-187. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(01)00297-3
[34] Wedepohl K H. Environmental influences on the chemical composition of shales and clays [J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 1971, 8: 307-333. doi: 10.1016/0079-1946(71)90020-6
[35] Murray R W, Leinen M, Isern A R. Biogenic flux of Al to sediment in the central equatorial Pacific Ocean: Evidence for increased productivity during glacial periods [J]. Paleoceanography, 1993, 8(5): 651-670. doi: 10.1029/93PA02195
[36] Murray R W, Leinen M. Scavenged excess aluminum and its relationship to bulk titanium in biogenic sediment from the central equatorial Pacific Ocean [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(20): 3869-3878. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(96)00236-0
[37] Sayles F L, Martin W R, Chase Z, et al. Benthic remineralization and burial of biogenic SiO2, CaCO3, organic carbon, and detrital material in the Southern Ocean along a transect at 170° West [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2001, 48(19-20): 4323-4383. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0645(01)00091-1
[38] Pondaven P, Ragueneau O, Tréguer P, et al. Resolving the ‘opal paradox’ in the Southern Ocean [J]. Nature, 2000, 405(6783): 168-172. doi: 10.1038/35012046
[39] Martínez-García A, Sigman D M, Ren H J, et al. Iron fertilization of the Subantarctic Ocean during the last ice age [J]. Science, 2014, 343(6177): 1347-1350. doi: 10.1126/science.1246848
[40] Weber M E, Bailey I, Hemming S R, et al. Antiphased dust deposition and productivity in the Antarctic Zone over 1.5 million years [J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 2044. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29642-5
[41] Nürnberg C C, Bohrmann G, Schlüter M, et al. Barium accumulation in the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean: Results from 190, 000 year records [J]. Paleoceanography, 1997, 12(4): 594-603. doi: 10.1029/97PA01130
[42] Kim S, Lee J I, McKay R M, et al. Late pleistocene paleoceanographic changes in the Ross Sea–Glacial-interglacial variations in paleoproductivity, nutrient utilization, and deep-water formation [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 239: 106356. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106356
[43] Kohfeld K E, Quéré C L, Harrison S P, et al. Role of marine biology in glacial-interglacial CO2 cycles [J]. Science, 2005, 308(5718): 74-78. doi: 10.1126/science.1105375
[44] Toyos M H, Winckler G, Arz H W, et al. Variations in export production, lithogenic sediment transport and iron fertilization in the Pacific sector of the Drake Passage over the past 400 kyr [J]. Climate of the Past, 2022, 18(1): 147-166. doi: 10.5194/cp-18-147-2022
[45] Romero O E, Kim J H, Bárcena M A, et al. High-latitude forcing of diatom productivity in the southern Agulhas Plateau during the past 350 kyr [J]. Paleoceanography, 2015, 30(2): 118-132. doi: 10.1002/2014PA002636
[46] Amsler H E, Thöle L M, Stimac I, et al. Bottom water oxygenation changes in the Southwestern Indian Ocean as an indicator for enhanced respired carbon storage since the last glacial inception [J]. Climate of the Past, 2022, 18(8): 1797-1813. doi: 10.5194/cp-18-1797-2022
[47] Anderson R F, Barker S, Fleisher M, et al. Biological response to millennial variability of dust and nutrient supply in the Subantarctic South Atlantic Ocean [J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2014, 372(2019): 20130054. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2013.0054
[48] Trull T W, Bray S G, Manganini S J, et al. Moored sediment trap measurements of carbon export in the Subantarctic and Polar Frontal Zones of the Southern Ocean, south of Australia [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2001, 106(C12): 31489-31509. doi: 10.1029/2000JC000308
[49] Boyd P W, Jickells T, Law C S, et al. Mesoscale iron enrichment experiments 1993-2005: synthesis and future directions [J]. Science, 2007, 315(5812): 612-617. doi: 10.1126/science.1131669
[50] Anderson R F, Ali S, Bradtmiller L I, et al. Wind-driven upwelling in the Southern Ocean and the deglacial rise in atmospheric CO2 [J]. Science, 2009, 323(5920): 1443-1448. doi: 10.1126/science.1167441
[51] Petrou K, Kranz S A, Trimborn S, et al. Southern Ocean phytoplankton physiology in a changing climate [J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2016, 203: 135-150. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2016.05.004
[52] Chadwick M, Crosta X, Esper O, et al. Compilation of Southern Ocean sea-ice records covering the last glacial-interglacial cycle (12-130 ka) [J]. Climate of the Past, 2022, 18(8): 1815-1829. doi: 10.5194/cp-18-1815-2022
[53] Gran H H. On the conditions for the production of plankton in the sea [J]. Rapp. proc. verb. reun. cons. int. explor. Mer, 1931, 75: 37-46.
[54] Martin J H, Gordon M, Fitzwater S E. The case for iron [J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1991, 36(8): 1793-1802. doi: 10.4319/lo.1991.36.8.1793
[55] Martínez-Garcia A, Rosell-Melé A, Jaccard S L, et al. Southern Ocean dust-climate coupling over the past four million years [J]. Nature, 2011, 476(7360): 312-315. doi: 10.1038/nature10310
[56] Toggweiler J R, Samuels B. Is the magnitude of the deep outflow from the Atlantic Ocean actually governed by Southern Hemisphere winds?[M]//Heimann M. The Global Carbon Cycle. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1993: 303-331.
[57] Wu S Z, Lembke-Jene L, Lamy F, et al. Orbital- and millennial-scale Antarctic Circumpolar Current variability in Drake Passage over the past 140, 000 years [J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 3948. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24264-9
[58] Wolff E W, Barbante C, Becagli S, et al. Changes in environment over the last 800, 000 years from chemical analysis of the EPICA Dome C ice core [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2010, 29(1-2): 285-295. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2009.06.013
[59] Lange M A, Ackley S F, Wadhams P, et al. Development of sea ice in the Weddell Sea [J]. Annals of Glaciology, 1989, 12: 92-96. doi: 10.3189/S0260305500007023
[60] Haumann F A, Gruber N, Münnich M, et al. Sea-ice transport driving Southern Ocean salinity and its recent trends [J]. Nature, 2016, 537(7618): 89-92. doi: 10.1038/nature19101
[61] Garibotti I A, Vernet M, Ferrario M E, et al. Phytoplankton spatial distribution patterns along the western Antarctic Peninsula (Southern Ocean) [J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2003, 261: 21-39. doi: 10.3354/meps261021
[62] Sigman D M, Boyle E A. Glacial/interglacial variations in atmospheric carbon dioxide [J]. Nature, 2000, 407(6806): 859-869. doi: 10.1038/35038000
[63] Ullermann J, Lamy F, Ninnemann U, et al. Pacific-Atlantic Circumpolar Deep Water coupling during the last 500 ka [J]. Paleoceanography, 2016, 31(6): 639-650. doi: 10.1002/2016PA002932
[64] Hodell D A, Venz K A, Charles C D, et al. Pleistocene vertical carbon isotope and carbonate gradients in the South Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2003, 4(1): 1-19.
[65] Bereiter B, Eggleston S, Schmitt J, et al. Revision of the EPICA Dome C CO2 record from 800 to 600 kyr before present [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(2): 542-549. doi: 10.1002/2014GL061957
[66] Sigman D M, Hain M P, Haug G H. The polar ocean and glacial cycles in atmospheric CO2 concentration [J]. Nature, 2010, 466(7302): 47-55. doi: 10.1038/nature09149
-




 下载:
下载: