Characteristics of phosphatization and its effects on the geochemical compositions of basalts from the Mid-Pacific Mountains
-
摘要:
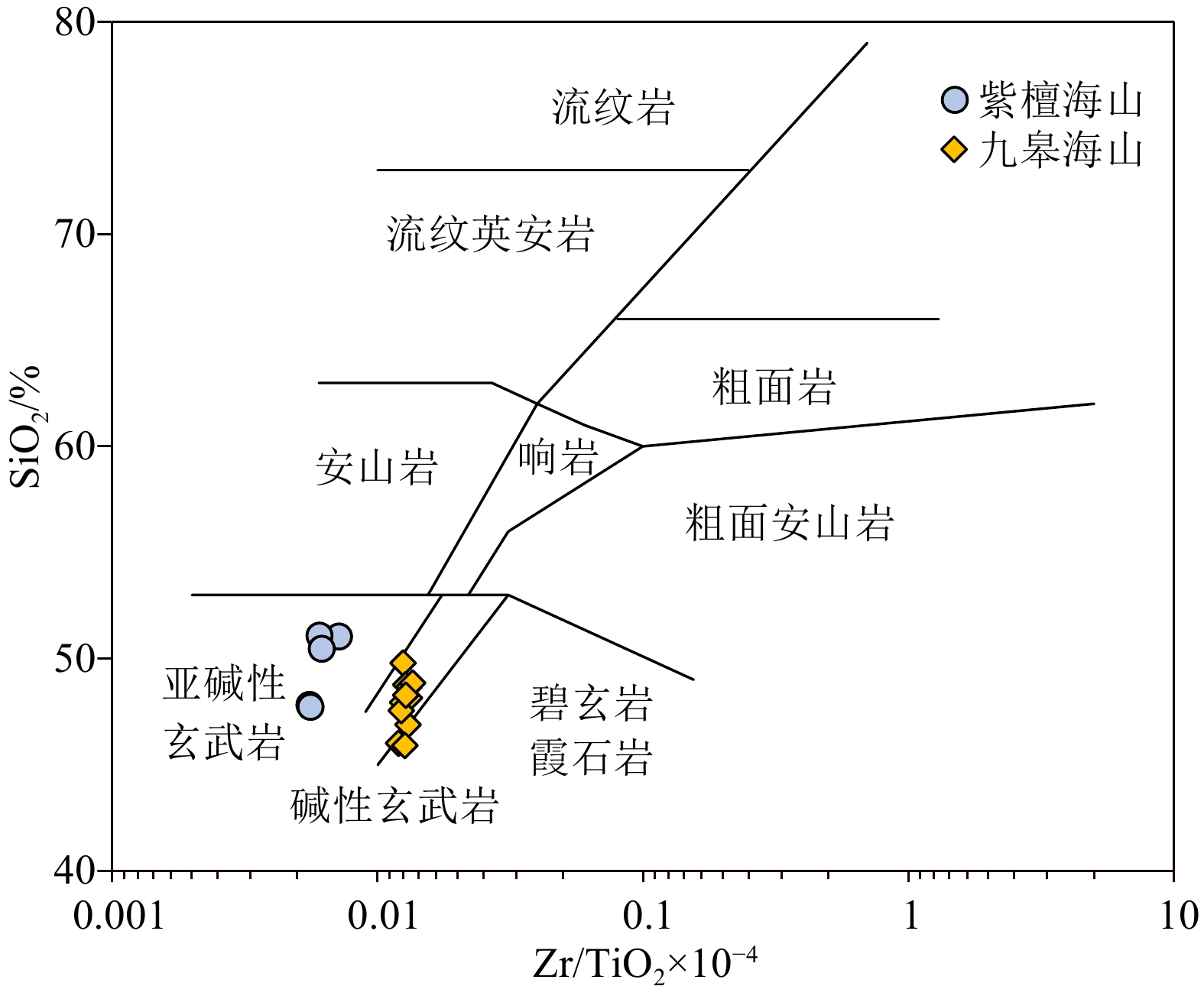
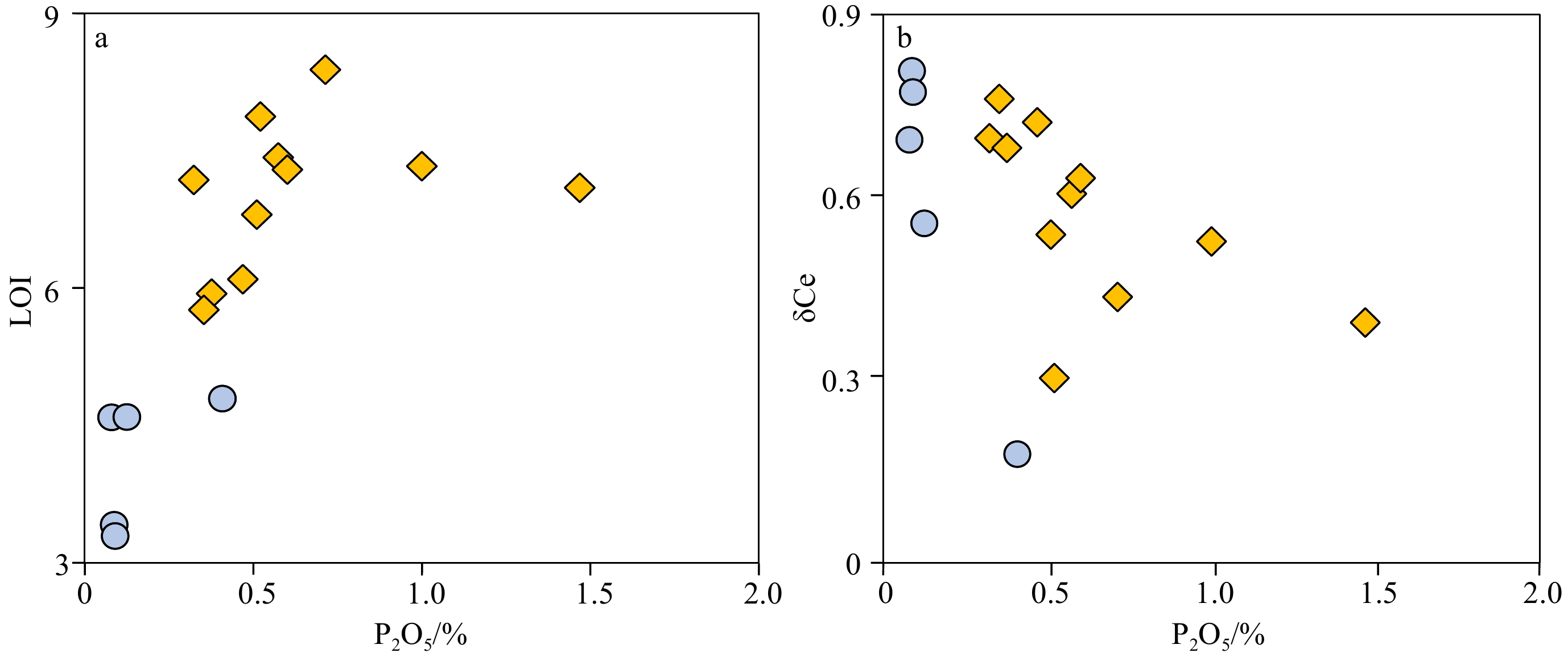
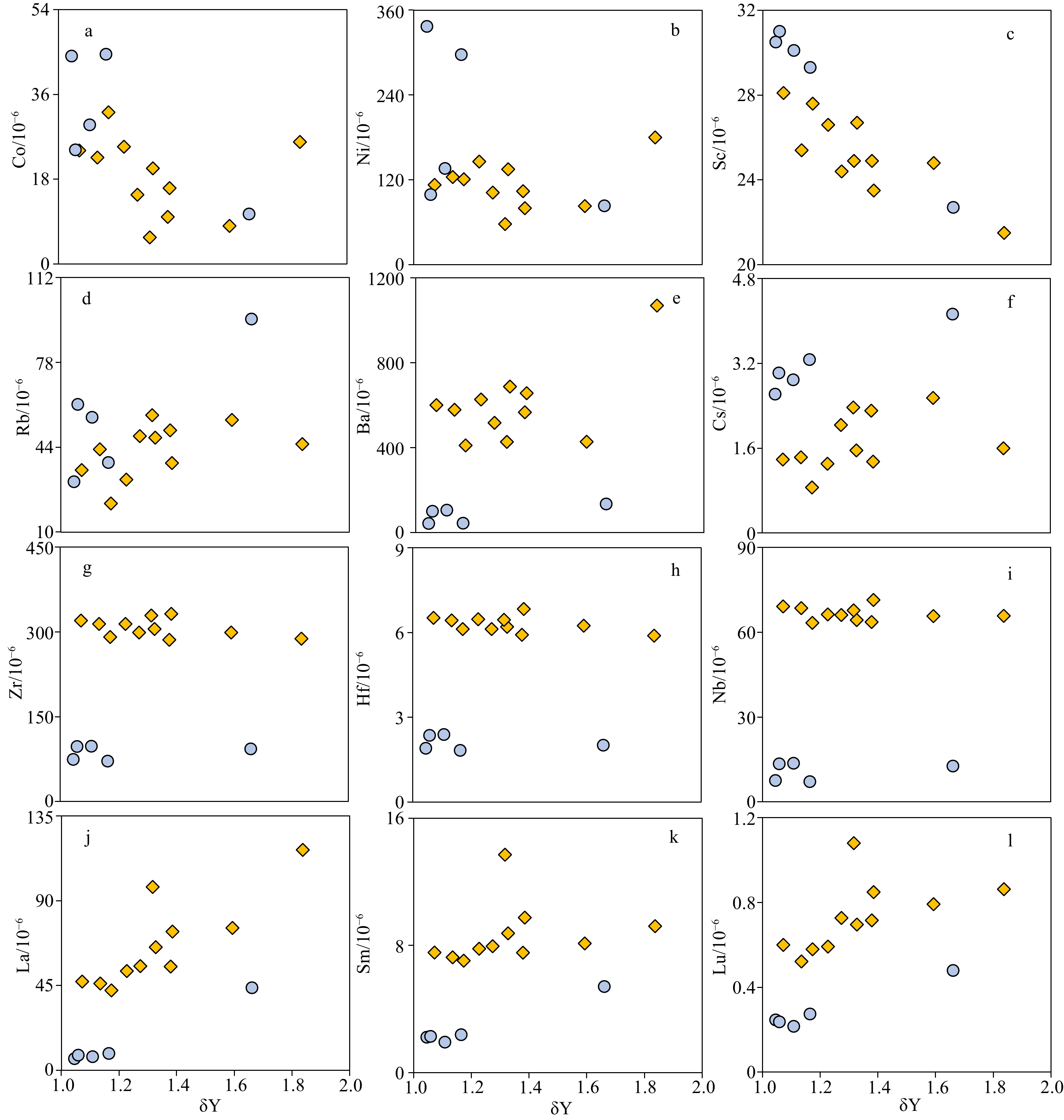
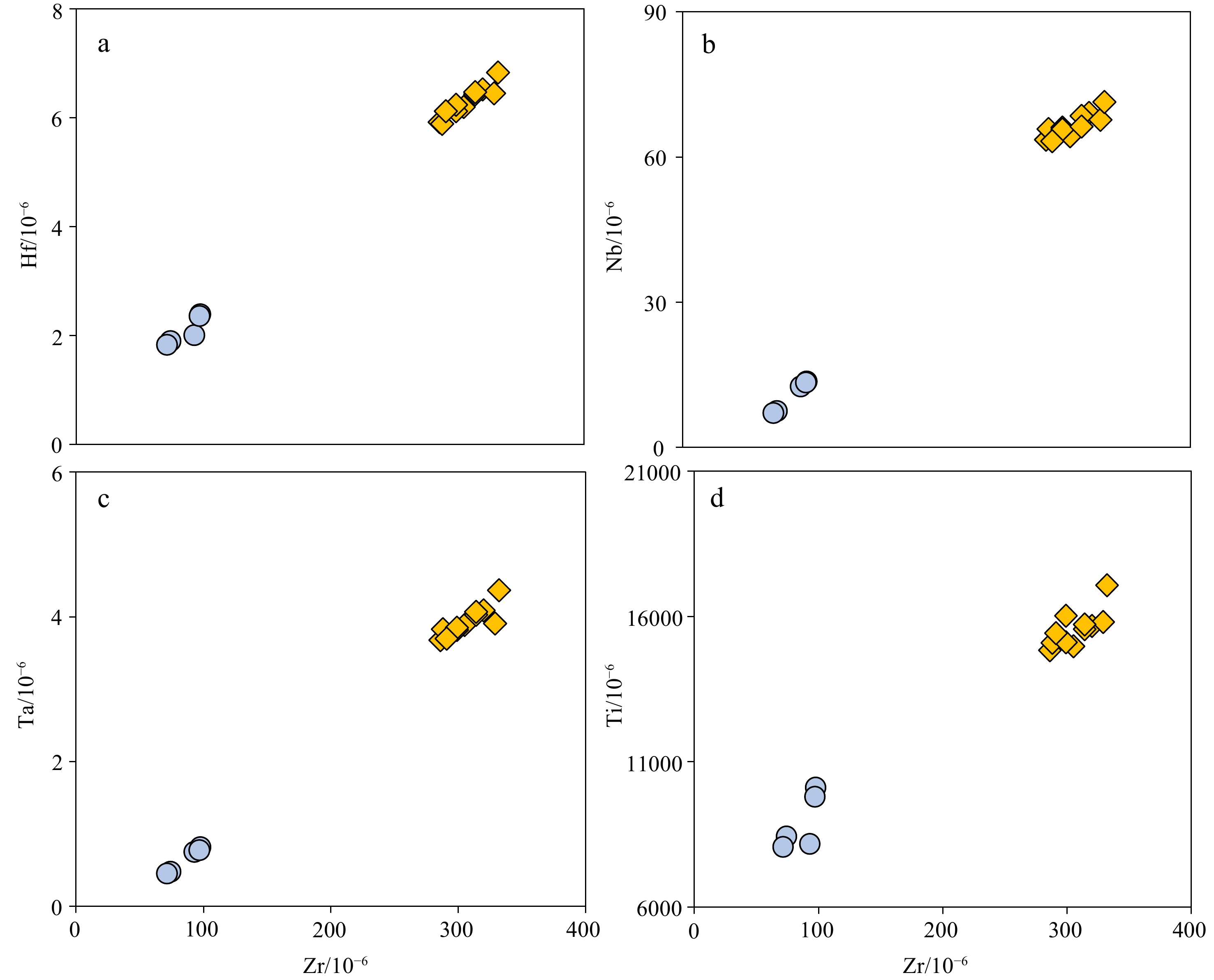
大洋玄武岩是研究地幔不均一性、岩浆起源与演化的重要对象。然而,由于其长期与周围的海水相互作用,极易发生蚀变和次生变化。磷酸盐化是大洋玄武岩最常见的次生变化之一,会影响到其全岩地球化学成分,且目前仍没有去除磷酸盐化的有效方法。因此,研究磷酸盐化特征以及评估其对玄武岩全岩地球化学成分的影响至关重要。本文以中太平洋海山群(九皋和紫檀海山)玄武岩为研究对象,通过能谱面扫描元素分布图、主量元素以及微量元素揭示玄武岩的磷酸盐化特征,评估磷酸盐化对其全岩主微量元素的影响。面扫描元素分布图显示,中太平洋海山群玄武岩的磷酸盐化作用主要发生在玄武岩气孔和裂隙周围,以交代早期的碳酸盐化基质,形成细小的磷酸盐矿物,呈浸染状分布在玄武岩基质中为特点,并且磷酸盐化会不同程度地改变玄武岩的主量元素和微量元素成分:比如磷酸盐化会使玄武岩的MgO、CaO、Na2O、MnO含量降低,K2O和Fe2O3T含量升高,同时也会对相容元素(如Cr、Co、Ni等)、大离子亲石元素(Rb、Ba、Cs等)和稀土元素造成不同程度的影响。值得注意的是,在磷酸盐化过程中,玄武岩的Al2O3、SiO2和高场强元素(Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf和Ti)几乎不受影响。
Abstract:Oceanic basalts are ideal samples in deciphering geodynamics, mantle heterogeneity, and magma origin and evolution. However, due to its long-term interaction with the surrounding seawater, it is easy to undergo alteration and secondary alteration. Phosphatization is one of the most common secondary alteration in oceanic basalts, which can affect the geochemical compositions of basalt and there is no effective method to eliminate it yet. Therefore, it is important to evaluate the effect of phosphatization on the geochemical compositions of basalt. The mapping of element distribution by energy spectrum surface scanning with energy dispersive spectrometer, and analyses of major and trace elements of the phosphatized basalts from the Mid-Pacific Mountains were conducted. The elemental mapping shows that the phosphatization occurred mainly around the vesicles and fissures of basalts. It metasomatized the early-formed carbonated matrix by which fine phosphate minerals were formed. Phosphatization would change the major elements and trace elements of basalt. For example, phosphatization could decrease the contents of MgO, CaO, Na2O and MnO, and increase the contents of K2O and Fe2O3T in the basalt. Meanwhile, it also affected the compatible elements (such as Cr, Co, Ni, etc.), large ion lithophile elements (Rb, Ba, Cs, etc.), and rare earth elements. It is noted that Al2O3, SiO2, and high field strength elements (Nb, Ta, Zr, Hf and Ti) of the basalts are nearly unaffected the the phosphatization.
-
Key words:
- basalts /
- phosphatization /
- geochemical compositions /
- seamount groups /
- Mid-Pacific Mountains
-

-
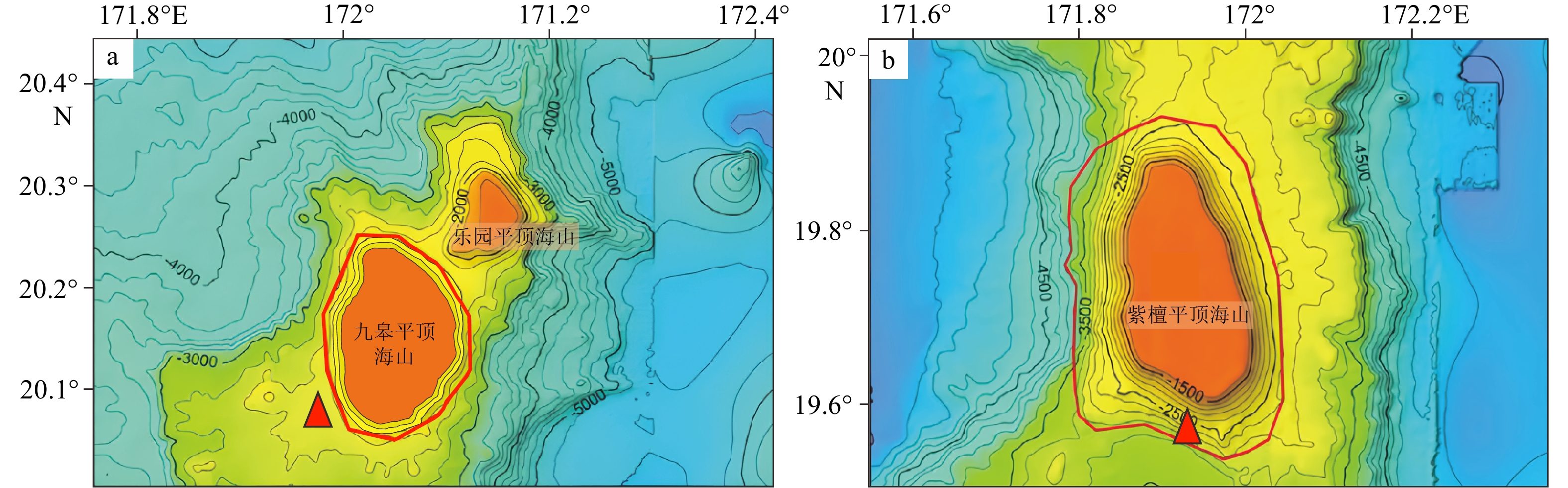
表 1 九皋和紫檀海山玄武岩主量元素地球化学数据
Table 1. Major elements of the Jiugao and Zitan basalts
% 海山 样品编号 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3T MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 LOI SUM 九皋
海山CWD16-1.1 49.80 2.29 17.75 12.77 0.07 2.91 3.16 1.31 1.95 0.57 7.43 100.01 CWD16-1.2 47.94 2.32 17.89 11.40 0.19 2.42 5.18 1.55 2.06 1.47 7.10 99.51 CWD16-1.3 48.16 2.31 17.36 12.65 0.09 3.18 4.49 1.59 2.25 0.51 6.80 99.38 CWD16-1.4 46.90 2.46 18.85 12.76 0.10 3.53 6.20 1.51 1.39 0.47 6.09 100.27 CWD16-1.5 48.78 2.34 17.79 13.30 0.09 3.04 3.90 1.23 1.87 0.60 7.29 100.23 CWD16-1.6 48.67 2.39 18.29 12.21 0.11 3.05 3.75 1.42 2.06 0.32 7.18 99.46 CWD16-2.1 47.56 2.43 18.15 13.61 0.07 2.34 3.14 1.08 1.88 0.71 8.39 99.36 CWD16-2.2 48.85 2.43 17.21 14.19 0.04 2.50 2.94 1.01 2.42 0.52 7.87 99.98 CWD16-2.4 48.29 2.46 18.58 11.49 0.19 3.35 6.26 1.63 1.29 0.38 5.94 99.84 CWD16-2.5 46.02 2.42 16.73 13.23 0.14 5.22 8.10 1.11 0.95 0.35 5.76 100.03 CWD16-2.6 45.92 2.62 18.90 13.51 0.09 2.08 4.93 1.47 1.47 1.00 7.33 99.30 CWD10-2② 47.81 1.34 15.13 12.57 0.10 7.58 7.98 1.88 0.82 0.08 4.58 99.87 CWD10-3 47.75 1.28 15.30 13.05 0.10 7.41 7.26 1.84 1.06 0.13 4.59 99.75 紫檀
海山CWD12-1① 51.03 1.30 15.20 14.19 0.02 2.88 4.88 1.86 3.57 0.41 4.79 100.13 CWD12-2 51.08 1.62 17.85 11.65 0.06 2.42 6.58 2.63 2.01 0.09 3.41 99.39 CWD12-3② 50.46 1.57 17.17 12.75 0.07 2.51 6.89 2.53 2.12 0.09 3.29 99.44 表 2 九皋和紫檀玄武岩微量元素地球化学数据
Table 2. Trace elements of the Jiugao and Zitan basalts
海山 样品编号 Sc V Cr Co Ni Ga Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Cs Ba La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu 九皋海山 CWD16-1.1 24.9 103 319 10 104 18.4 50.8 627 64.1 286 63.6 2.31 567 55.1 58.9 9.93 40.3 7.54 2.31 CWD16-1.2 21.5 118 321 25.9 180 18.5 45.3 763 109 288 65.8 1.6 1070 117 64.9 13.4 54 9.21 2.78 CWD16-1.3 26.7 135 359 20.3 135 18.1 47.9 782 66.3 305 64.3 1.56 688 65.4 61.9 11.7 47.6 8.76 2.67 CWD16-1.4 28.1 212 350 24.1 113 17.9 34.9 735 44 320 69.1 1.39 601 47.1 64.2 9.7 39.1 7.55 2.4 CWD16-1.5 24.4 111 330 14.7 102 18.1 48.5 638 59.4 299 66.1 2.04 517 55.3 63.2 10.5 42.3 7.95 2.45 CWD16-1.6 25.4 156 335 22.6 124 18.5 43.2 704 43.4 314 68.5 1.43 579 46.1 60.2 9.38 38 7.25 2.26 CWD16-2.1 24.8 91 263 8.1 82.9 17.4 55 553 83.9 299 65.7 2.55 428 75.6 53.5 11.5 46.9 8.13 2.44 CWD16-2.2 24.9 120 326 5.67 57.6 14.4 56.9 499 107 329 67.7 2.37 427 97.3 52.6 17.9 74.6 13.7 3.92 CWD16-2.4 26.6 159 356 24.9 146 17.4 31.1 758 52.1 314 66.3 1.31 627 52.7 65.6 10.2 41.3 7.79 2.48 CWD16-2.5 27.6 243 258 32.2 121 18.4 21.5 619 46.3 291 63.3 0.86 411 42.4 61.3 8.86 36 7.04 2.24 CWD16-2.6 23.5 175 372 16.1 80.1 16.1 37.7 769 81.3 332 71.4 1.35 657 73.6 68.3 13.2 53.6 9.75 2.93 紫檀海山 CWD10-2② 30.5 220 418 44.1 337 17.3 30.2 141 18.7 74.2 7.52 2.62 41.9 6.15 9.38 1.72 8.32 2.22 0.842 CWD10-3 29.3 187 495 44.5 297 17.3 37.9 142 22.8 71.4 7.13 3.27 43.5 8.89 9.61 1.94 9.21 2.38 0.87 CWD12-1① 22.7 67 256 10.6 83.2 16.7 95.4 228 61.1 93 12.6 4.13 134 43.8 12.5 6.51 28.6 5.41 1.59 CWD12-2 30.1 162 186 29.5 136 20.2 56 224 16.3 97.7 13.6 2.89 105 7.25 11.7 1.68 7.74 1.91 0.79 CWD12-3② 31 171 185 24.2 99 20 61.2 221 18.4 97 13.4 3.02 99.8 8 12.8 1.99 9.22 2.28 0.875 海山 样品编号 Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Hf Ta Pb Th U δEu δCe δY (La/Sm)N ∑REE 九
皋
海
山CWD16-1.1 8.48 1.25 7.56 1.67 4.78 0.71 4.42 0.716 5.92 3.68 10.9 4.98 1.15 0.88 0.61 1.38 4.6 203.67 CWD16-1.2 11.2 1.56 9.52 2.16 6.15 0.88 5.32 0.863 5.89 3.83 16.6 4.95 1.04 0.84 0.39 1.84 7.99 298.94 CWD16-1.3 9.73 1.41 8.28 1.76 4.88 0.714 4.4 0.696 6.2 3.89 13.7 5.21 1.04 0.88 0.54 1.33 4.7 229.9 CWD16-1.4 7.75 1.17 6.88 1.43 4.01 0.602 3.81 0.6 6.52 4.09 12.1 5.47 0.94 0.96 0.72 1.07 3.92 196.3 CWD16-1.5 8.7 1.29 7.65 1.66 4.75 0.71 4.45 0.727 6.12 3.82 20 5.06 0.96 0.9 0.63 1.27 4.38 211.64 CWD16-1.6 7.49 1.11 6.42 1.33 3.67 0.535 3.33 0.522 6.43 4.03 17.7 5.4 0.84 0.94 0.7 1.13 4 187.6 CWD16-2.1 9.82 1.39 8.39 1.93 5.45 0.791 4.84 0.792 6.24 3.85 15.2 4.87 1.12 0.83 0.44 1.59 5.85 231.47 CWD16-2.2 15.9 2.26 13.4 2.88 7.95 1.14 6.84 1.08 6.45 3.91 19.5 5.53 1.19 0.81 0.3 1.32 4.47 311.47 CWD16-2.4 8.22 1.21 7.07 1.49 4.11 0.599 3.72 0.592 6.47 4.07 14.7 5.2 0.67 0.95 0.68 1.23 4.26 207.08 CWD16-2.5 7.38 1.12 6.54 1.39 3.87 0.576 3.63 0.58 6.12 3.7 7.7 4.67 0.57 0.95 0.76 1.17 3.79 182.93 CWD16-2.6 10.9 1.59 9.58 2.1 5.93 0.87 5.35 0.849 6.83 4.37 13.7 5.56 1.35 0.87 0.53 1.38 4.75 258.55 紫
檀
海
山CWD10-2② 2.85 0.48 2.96 0.631 1.77 0.261 1.61 0.246 1.9 0.475 1.03 0.358 0.16 1.02 0.69 1.05 1.74 39.44 CWD10-3 3.1 0.514 3.2 0.699 1.94 0.285 1.78 0.274 1.83 0.452 0.943 0.374 0.18 0.98 0.56 1.16 2.35 44.69 CWD12-1① 7.02 0.982 5.94 1.33 3.68 0.517 3.04 0.479 2.01 0.752 9.07 0.67 0.42 0.79 0.18 1.66 5.09 121.4 CWD12-2 2.32 0.391 2.4 0.526 1.49 0.223 1.4 0.216 2.39 0.815 1.61 0.59 0.39 1.15 0.81 1.11 2.39 40.04 CWD12-3② 2.79 0.469 2.89 0.61 1.7 0.25 1.54 0.237 2.36 0.776 1.38 0.618 0.3 1.06 0.77 1.06 2.21 45.65 注:微量元素单位为10-6;δEu= EuN/(SmN × GdN)0.5,δCe= CeN/(LaN × PrN)0.5,δY=YN/(DyN × HoN)0.5。 -
[1] White W M. Isotopes, DUPAL, LLSVPs, and Anekantavada [J]. Chemical Geology, 2015, 419: 10-28. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.09.026
[2] White W M, Hofmann A W. Sr and Nd isotope geochemistry of oceanic basalts and mantle evolution [J]. Nature, 1982, 296(5860): 821-825. doi: 10.1038/296821a0
[3] Zindler A, Hart S. Chemical geodynamics [J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1986, 14: 493-571. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.14.050186.002425
[4] 卜文瑞, 石学法, 彭建堂, 等. 大洋岛屿玄武岩低温蚀变作用及其对大洋过渡金属循环的贡献[J]. 海洋学报, 2007, 29(5):55-68
BU Wenrui, SHI Xuefa, PENG Jiantang, et al. Low-temperature alteration of oceanic island basalts and their contribution to transition metal cycle of the ocean [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2007, 29(5): 55-68.
[5] 卜文瑞, 李力, 朱爱美, 等. 海底蚀变玄武岩中次生组分去除实验研究[J]. 地球科学进展, 2012, 27(10):1167-1172
BU Wenrui, LI Li, ZHU Aimei, et al. Leaching experiments of secondary components in altered submarine basalts [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2012, 27(10): 1167-1172.
[6] Guy C, Daux V, Schott J. Behaviour of rare earth elements during seawater/basalt interactions in the Mururoa Massif [J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 158(1-2): 21-35. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00019-4
[7] Alt J C, Teagle D A H. Hydrothermal alteration of upper oceanic crust formed at a fast-spreading ridge: mineral, chemical, and isotopic evidence from ODP Site 801 [J]. Chemical Geology, 2003, 201(3-4): 191-211. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(03)00201-8
[8] 陈建林, 马维林, 高水土, 等. 中太平洋结壳区海山燧石岩成因研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2003, 25(3):53-58
CHEN Jianlin, MA Weilin, GAO Shuitu, et al. Genetic study on flint from the crust area of the central Pacific Ocean mountains [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2003, 25(3): 53-58.
[9] 陈建林, 马维林, 武光海, 等. 中太平洋海山富钴结壳与基岩关系的研究[J]. 海洋学报(中文版), 2004, 26(4):71-79
CHEN Jianlin, MA Weilin, WU Guanghai, et al. Research on the relationships between cobalt-rich crusts and substrate rocks in the Mid-Pacific Mountains [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2004, 26(4): 71-79.
[10] 初凤友, 陈建林, 马维林, 等. 中太平洋海山玄武岩的岩石学特征与年代[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2005, 25(4):55-59 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2005.04.010
CHU Fengyou, CHEN Jianlin, MA Weilin, et al. Petrologic characteristics and ages of basalt in Middle Pacific Mountains [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2005, 25(4): 55-59. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2005.04.010
[11] Melson W G, Thompson G. Glassy abyssal basalts, Atlantic sea floor near St. Paul's Rocks: petrography and composition of secondary clay minerals [J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1973, 84(2): 703-716. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1973)84<703:GABASF>2.0.CO;2
[12] Thompson G. A geochemical study of the low-temperature interaction of seawater and oceanic igneous rocks [J]. Transactions-American Geophysical Union, 1973, 54: 1015-1019.
[13] 鄢全树, 张平阳, 石学法, 等. 海底熔岩风化作用及其地质意义[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2017, 35(3):369-381
YAN Quanshu, ZHANG Pingyang, SHI Xuefa, et al. Weathering of seafloor lavas and its geological significance [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2017, 35(3): 369-381.
[14] Koppers A A P, Staudigel H, Pringle M S, et al. Short‐lived and discontinuous intraplate volcanism in the South Pacific: Hot spots or extensional volcanism? [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2003, 4(10): 1089.
[15] Corliss J B. The origin of metal‐bearing submarine hydrothermal solutions [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1971, 76(33): 8128-8138. doi: 10.1029/JC076i033p08128
[16] Hart S R. K, Rb, Cs contents and K/Rb, K/Cs ratios of fresh and altered submarine basalts [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1969, 6(4): 295-303. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(69)90171-X
[17] Thompson G. Metamorphic and hydrothermal processes: basalt-seawater interactions[M]//Floyd P A. Oceanic Basalts. Dordrecht: Springer, 1991: 148-173.
[18] 刘晖, 卢正权, 梅燕雄, 等. 海洋磷块岩形成环境与资源分布[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(3):49-56
LIU Hui, LU Zhengquan, MEI Yanxiong, et al. Depositional environment and world distribution of marine phosphorites [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(3): 49-56.
[19] 王吉中. 磷酸盐化对中太平洋海山富钴结壳物质组分的影响[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2005
WANG Jizhong. Effects of phosphatization on composition of Co-rich crusts on central pacific seamounts[D]. Doctor Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2005.
[20] 李江山, 石学法, 刘季花, 等. 西太平洋富钴结壳中磷酸盐化的制约因素探讨[J]. 矿物学报, 2011, 31(S1):693-694 doi: 10.16461/j.cnki.1000-4734.2011.s1.465
LI Jiangshan, SHI Xuefa, LIU Jihua, et al. Restriction factors of phosphorylation in cobalt-rich crusts in the Western Pacific Ocean [J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2011, 31(S1): 693-694. doi: 10.16461/j.cnki.1000-4734.2011.s1.465
[21] 崔迎春, 石学法, 刘季花, 等. 磷酸盐化作用对富钴结壳元素相关性的影响[J]. 地质科技情报, 2008, 27(3):61-67
CUI Yingchun, SHI Xuefa, LIU Jihua, et al. Effects of phosphatization on the elemental association of cobalt-rich crusts [J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2008, 27(3): 61-67.
[22] 刘家岐, 兰晓东. 中太平洋莱恩海山富钴结壳元素地球化学特征及成因[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(2):81-91
LIU Jiaqi, LAN Xiaodong. Element geochemistry and genesis of cobalt-rich crust on the Line Seamount of the Central Pacific [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(2): 81-91.
[23] 任向文, 刘季花, 石学法, 等. 西太平洋Lamont海山中新世以来富钴结壳成矿环境的演化[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2006, 24(1):17-29
REN Xiangwen, LIU Jihua, SHI Xuefa, et al. Evolution of ore-forming condition of Co-rich crusts from Lamont Guyot in the western Pacific since the Miocene [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2006, 24(1): 17-29.
[24] Hein J R, Koschinsk A, Bau M, et al. Cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts in the Pacific[M]//Cronan D S. Handbook of Marine Mineral Deposits. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2017: 239-279.
[25] Ji L H, Liu G S, Huang Y P, et al. The distribution of iodine and effects of phosphatization on it in the ferromanganese crusts from the Mid-Pacific Ocean [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2015, 34(8): 13-19. doi: 10.1007/s13131-015-0704-x
[26] Nishi K, Usui A, Nakasato Y, et al. Formation age of the dual structure and environmental change recorded in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts from Northwest and Central Pacific seamounts [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 87: 62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.004
[27] Jeong K S, Jung H S, Kang J K, et al. Formation of ferromanganese crusts on northwest intertropical Pacific seamounts: electron photomicrography and microprobe chemistry [J]. Marine Geology, 2000, 162(2-4): 541-559. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(99)00091-2
[28] 潘家华, 刘淑琴, Decarlo E. 大洋磷酸盐化作用对富钴结壳元素富集的影响[J]. 地球学报, 2002, 23(5):403-407
PAN Jiahua, LIU Shuqin, Decarlo E. The effects of marine phospharization on element concentration of Cobalt-rich crusts [J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2002, 23(5): 403-407.
[29] 武光海, 周怀阳, 凌洪飞, 等. 富钴结壳中的磷酸盐岩及其古环境指示意义[J]. 矿物学报, 2005, 25(1):39-44 doi: 10.16461/j.cnki.1000-4734.2005.01.007
WU Guanghai, ZHOU Huaiyang, LING Hongfei, et al. Phosphorites in Co-rich crusts and their palaeooceanographic singificance [J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2005, 25(1): 39-44. doi: 10.16461/j.cnki.1000-4734.2005.01.007
[30] 王洋, 方念乔. 多金属结壳生长间断期与磷酸盐化事件的关系[J]. 海洋学报, 2021, 43(1):102-109 doi: 10.12284/hyxb2021017
WANG Yang, FANG Nianqiao. The relationship between the growth discontinuity of polymetallic crusts and phosphatization events [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2021, 43(1): 102-109. doi: 10.12284/hyxb2021017
[31] 朱佛宏. 太平洋海山玄武岩的磷酸盐化[J]. 海洋地质动态, 1988(7):9-10
ZHU Fohong. Phosphatization of Pacific seamount basalts [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 1988(7): 9-10.
[32] 朱克超. 麦哲伦海山区MA、MC、MD、ME、MF海山结壳基岩的岩石学[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2002, 22(1):49-56 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2002.01.008
ZHU Kechao. Petrology of the substrate in seamounts MA, MC, MD, ME and MF from Magellan seamounts [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2002, 22(1): 49-56. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2002.01.008
[33] 潘家华, 刘淑琴, 杨忆, 等. 太平洋水下海山磷酸盐的成因及形成环境[J]. 地球学报, 2004, 25(4):453-458
PAN Jiahua, LIU Shuqin, YANG Yi, et al. The origin and formation environment of phosphates on submarine guyots of the Pacific ocean [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2004, 25(4): 453-458.
[34] 汪在聪, 李胜荣, 刘鑫, 等. 中太平洋WX海山富钴结壳磷酸盐矿物学研究及成因类型分析[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2007, 26(5):441-448
WANG Zaicong, LI Shengrong, LIU Xin, et al. A mineralogical study and genetic analysis of phosphate in Co-rich crusts from the Central Pacific WX seamount [J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2007, 26(5): 441-448.
[35] Kellogg J N, Ogujiofor I J. Gravity field analysis of Sio Guyot: An isostatically compensated seamount in the Mid-Pacific Mountains [J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 1985, 5(2): 91-97. doi: 10.1007/BF02233933
[36] Nemoto K, Kroenke L W. Sio Guyot: a complex volcanic edifice in the western Mid-Pacific Mountains [J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 1985, 5(2): 83-89. doi: 10.1007/BF02233932
[37] Kroenke L W, Kellogg J N, Nemoto K. Mid-Pacific Mountains revisited [J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 1985, 5(2): 77-81. doi: 10.1007/BF02233931
[38] Wilson P A, Jenkyns H C, Elderfield H, et al. The paradox of drowned carbonate platforms and the origin of Cretaceous Pacific guyots [J]. Nature, 1998, 392(6679): 889-894. doi: 10.1038/31865
[39] Thiede J, Dean W E, Rea D K, et al. The geologic history of the Mid-Pacific Mountains in the central North Pacific Ocean; a synthesis of deep-sea drilling studies [J]. Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project, 1981, 62: 1073-1120.
[40] Hamilton E L. Sunken Islands of the Mid-Pacific Mountains[M]. New York: Geological Society of America, 1956.
[41] Winterer E L, Metzler C V. Origin and subsidence of Guyots in Mid‐Pacific Mountains [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 1984, 89(B12): 9969-9979. doi: 10.1029/JB089iB12p09969
[42] Larson R L, Chase C G. Late Mesozoic evolution of the western Pacific Ocean [J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1972, 83(12): 3627-3644. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1972)83[3627:LMEOTW]2.0.CO;2
[43] Ozima M, Honda M, Saito K. 40Ar-39Ar ages of guyots in the western Pacific and discussion of their evolution [J]. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 1977, 51(2): 475-485. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1977.tb06930.x
[44] Pringle M S, Duncan R A. Radiometric ages of basaltic lavas recovered at Sites 865, 866, and 869: Northwest Pacific atolls and guyots[C]//Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program. Scientific results. 1995, 142: 277-283.
[45] Winterer E L, Natland J H, Van Waasbergen R J, et al. Cretaceous guyots in the northwest Pacific: An overview of their geology and geophysics[M]//Pringle M S, Sager W W, Sliter W V, et al. The Mesozoic Pacific: Geology, Tectonics, and Volcanism. Washington: American Geophysical Union, 1993, 77: 307-334.
[46] Larson R L, Moberly R, Lancelot Y. Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project 32[M]. Washington: U. S. Government Printing Office, 1975.
[47] Larson R L, Lancelot Y, Gardner J V. Magnetic, bathymetric, seismic reflection, and positioning data collected underway on Glomar Challenger, Leg 32[M]//Larson R L, Moberly R. Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project 32. Washington: U. S. Government Printing Office, 1975: 393-427.
[48] Baker P E, Castillo P R, Condliffe E. Petrology and geochemistry of igneous rocks from Allison and Resolution guyots, Sites 865 and 866: Northwest Pacific atolls and guyots[C]//Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program. Scientific Results. 1995, 142: 245-261.
[49] 何欣, 孙国胜, 初凤友, 等. 中太平洋CA海山玄武岩中斜长石化学成分特征及地质意义[J]. 海洋学研究, 2017, 35(2):23-32
HE Xin, SUN Guosheng, CHU Fengyou, et al. Chemical characteristics and geological implication of plagioclase in CA Seamount basalts from the Middle Pacific [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2017, 35(2): 23-32.
[50] Chen S S, Liu J Q. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of Cretaceous phonotephrite from the Mid-Pacific Mountains [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(6): 745-764. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9172-4
[51] 中国大洋矿产资源研究开发协会办公室. 中国大洋海底地理实体名录-2016[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2016
China Ocean Mineral Resources Research and Development Association Office. Chinese Gazetteer of Undersea Features on the International Seabed, 2016[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2016.
[52] Li X H, Sun M, Wei G J, et al. Geochemical and Sm-Nd isotopic study of amphibolites in the Cathaysia Block, southeastern China: evidence for an extremely depleted mantle in the Paleoproterozoic [J]. Precambrian Research, 2000, 102(3-4): 251-262. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(00)00067-X
[53] Qi L, Hu J, Gregoire D C. Determination of trace elements in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry [J]. Talanta, 2000, 51(3): 507-513. doi: 10.1016/S0039-9140(99)00318-5
[54] Gurenko A A, Hoernle K A, Hauff F, et al. Major, trace element and Nd–Sr–Pb–O–He–Ar isotope signatures of shield stage lavas from the central and western Canary Islands: insights into mantle and crustal processes [J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 233(1-2): 75-112. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.02.016
[55] 苏蓉. 中太平洋CNW海山玄武岩岩石地球化学特征及对富钴结壳生长的影响[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2015
SU Rong. Geochemical characteristics of basalt and effect of cobalt-rich crusts growth in the Mid-Pacific CNW Seamount[D]. Master Dissertation of Jilin University, 2015.
[56] 李超. 中太平洋CH海山玄武岩地球化学特征及富钴结壳成因[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2013
LI Chao. Geochemical characteristics of basalt and research on Co-rich crust formation in the Mid-Pacific CH Seamount[D]. Master Dissertation of Jilin University, 2013.
[57] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes [J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[58] Boynton W V. Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies [J]. Developments in Geochemistry, 1984, 2: 63-114.
[59] Wei X, Zhang Y, Shi X F, et al. Co-occurrence of HIMU and EM1 components in a single Magellan seamount: implications for the formation of west pacific seamount province [J]. Journal of Petrology, 2022, 63(4): egac022. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egac022
[60] 任向文. 西太平洋富钴结壳成矿系统[D]. 中国科学院研究生院博士学位论文, 2005
REN Xiangwen. The metallogenic system of Co-rich manganese crusts in Western Pacific[D]. Doctor Dissertation of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2005.
[61] Bau M, Koschinsky A, Dulski P, et al. Comparison of the partitioning behaviours of yttrium, rare earth elements, and titanium between hydrogenetic marine ferromanganese crusts and seawater [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(10): 1709-1725. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(96)00063-4
[62] 刘佳辉, 曲扬, 李伟强, 等. 西太平洋铁锰结壳中两类不同成因磷酸盐的元素特征、形成机制及指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(2):36-45 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2021052701
LIU Jiahui, QU Yang, LI Weiqiang, et al. Elemental distribution pattern and forming mechanism of the two types of phosphates in ferromanganese crust in Western Pacific Ocean and their implications [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(2): 36-45. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2021052701
[63] Koschinsky A, Hein J R. Marine ferromanganese encrustations: archives of changing oceans [J]. Elements, 2017, 13(3): 177-182. doi: 10.2113/gselements.13.3.177
-



 下载:
下载: