Rethinking on sedimentary sequence and geochronological framework of Core NTCJ1 in the Sheyang estuary of Northern Jiangsu, East China
-
摘要:
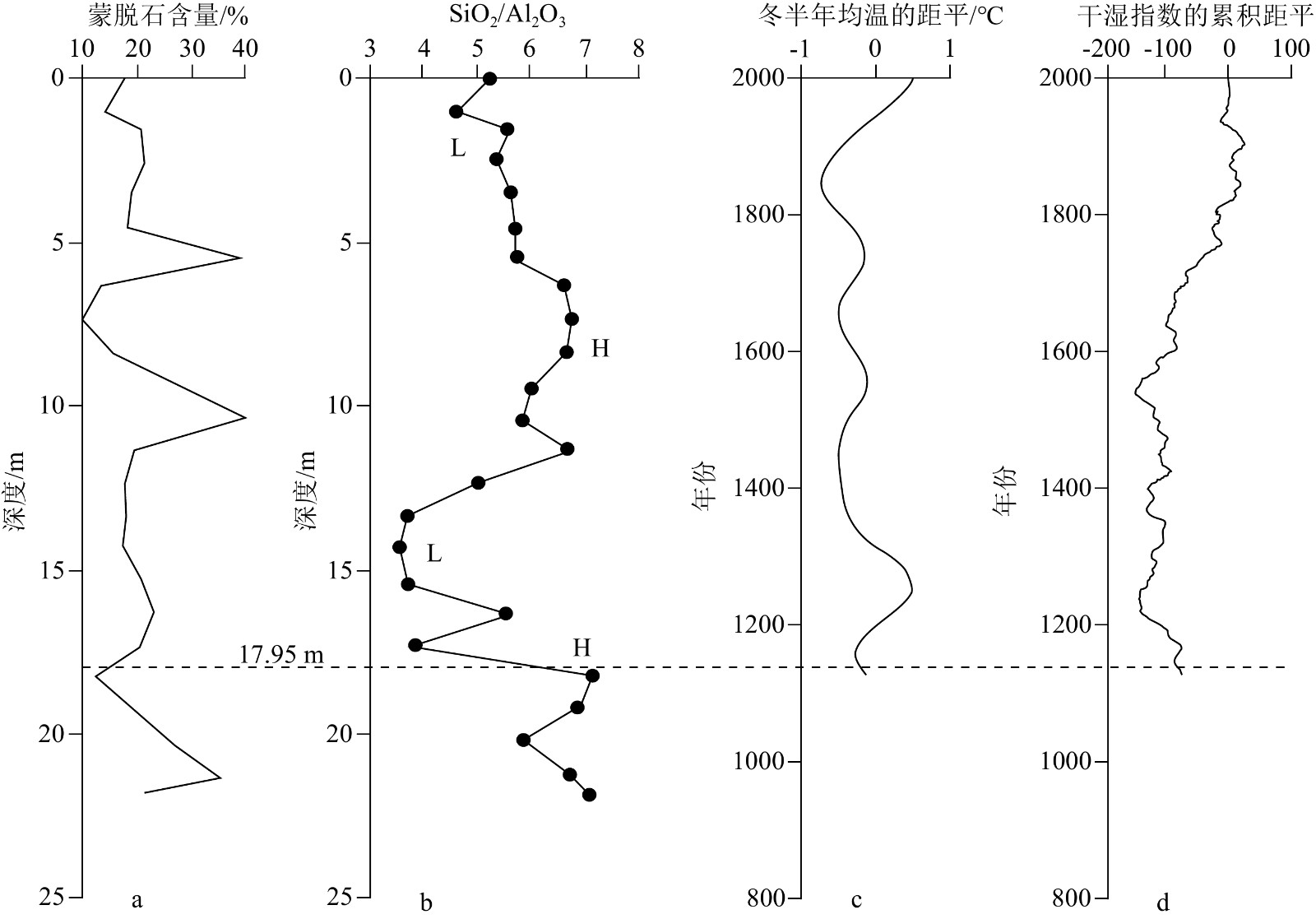
射阳河口位于苏北粉砂淤泥质海岸上,处在苏北废黄河三角洲侵蚀岸段与江苏中部淤积岸段之间的过渡区域,是淤蚀交替地带,系现代海岸地貌演变的节点处,同时也是晚第四纪古黄河古长江交互作用的关键区域之一。为了深入研究不同大河交互作用下的海岸、陆架晚第四纪沉积层序模式,最近就苏北射阳河口NTCJ1孔沉积序列和年代,根据该孔的岩性、粒度、介形虫、有孔虫、黏土矿物、地球化学元素和ESR测年等结果,并结合邻近其他钻孔和浅层地震剖面资料进行再研究和再认识,主要得到以下两点新认识:① NTCJ1孔22.00 m岩芯记录了MIS 5以来的沉积环境演化过程,可能缺失形成于MIS 4—2的第一陆相沉积层,MIS 1海相沉积层直接上覆于MIS 5海相沉积层,且尚未钻及形成于MIS 6的第二陆相沉积层;② NTCJ1孔中上部0~17.95 m颗粒较细,以粉砂质为主和暗黄色为基调,明显上粗下细,基本为AD 1128—1855年间形成的废黄河三角洲沉积,为一进积序列,底部可能含有少量全新世滨浅海沉积,但目前尚难以甄别;下部17.95~22.00 m颗粒较粗,以细砂质为主和深灰色为基调,尚未钻穿,是受到古黄河明显影响的MIS 5潮汐河口的水道充填沉积。
Abstract:The Sheyang estuary is located in the muddy coast of Northern Jiangsu, East China, in the transition zone between the eroded coast of the abandoned Yellow River delta in Northern Jiangsu and the silted coast in central Jiangsu, which is characterized by the alternation of erosion and siltation as a node of modern coastal geomorphic evolution, as well as one of the key areas of geo-interactions between the old Yellow River and old Changjiang River during the Late Quaternary. To investigate deeply the Late Quaternary sedimentary sequence models of the coasts and continental shelves under the interactions among different large rivers, the sedimentary sequence and geochronology of 22.00 m-long Core NTCJ1 drilled at the Sheyang estuary were recently re-studied in lithology, grain size, ostracods, foraminifera, clay minerals, elemental geochemistry, and ESR dating, and the results were compared with those of other adjacent cores and shallow seismic profiles. The new results show that: (1) Core NTCJ1 recorded the sedimentary environment evolution since Marine Isotope Stage 5 (MIS 5), the first continental facies layer formed from MIS 4 to MIS 2 may be missing, the MIS 1 marine facies layer overlain directly the MIS 5 marine facies layer, and the second continental facies layer formed in MIS 6 has not been drilled yet; (2) The middle-upper part of Core NTCJ1 sediments (0~17.95 m) are characterized by fine grain size, mainly silty, and dark yellow in color, and obvious reversal graded bedding, which could be interpreted as the abandoned Yellow River deltaic deposits formed between AD 1128 and 1855 with a progradational sequence, and may contain a small amount of the Holocene coastal-shallow marine deposits at the bottom, but it is difficult to identify them yet. The lower part sediments (17.95~22.00 m) are characterized by coarse grain size, mainly fine sandy, and dark grey in color; they had not been drilled through and could be explained as a channel-fill deposit in the MIS 5 tidal estuary and were obviously influenced by the old Yellow River.
-
Key words:
- sedimentary sequence /
- geochronology /
- Late Quaternary /
- South Yellow Sea /
- middle Jiangsu coast /
- Sheyang estuary
-

-
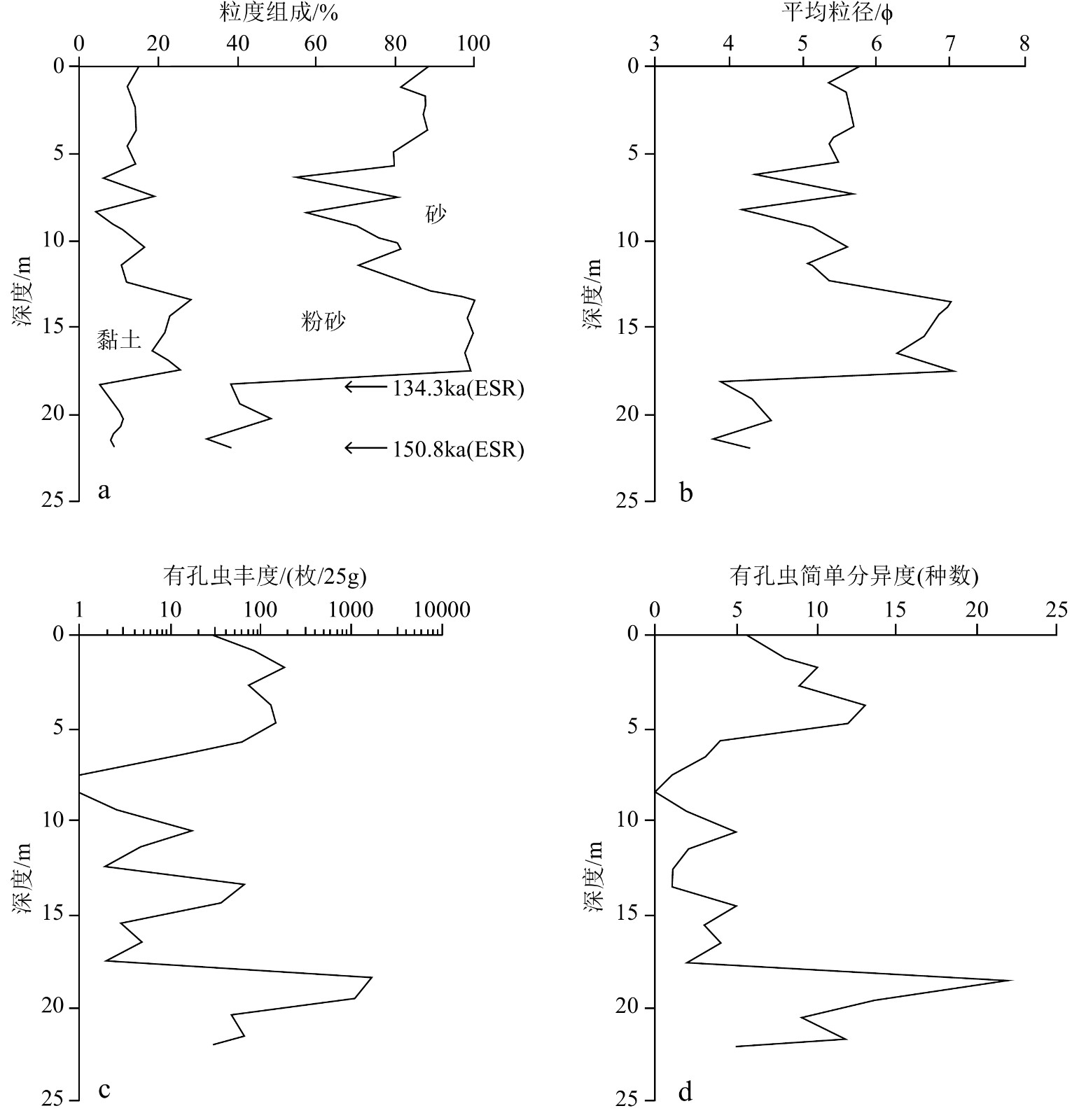
图 2 NTCJ1钻孔沉积物粒度和有孔虫若干参数的垂向分布[7]
Figure 2.
表 1 NTCJ1和NTCJ2钻孔沉积物石英砂ESR测年结果[7]
Table 1. ESR dating results of quartz sands from the sediments of Cores NTCJ1 and NTCJ2 [7]
样品编号 取样深度/m U/10−6 Th/10−6 K2O/% AD/Gy 年代/ka 备注 1E-2 18.38~18.41 1.44 9.09 1.92 316.9 134.3 可参考 1E-3 21.98~22.00 1.41 7.75 1.94 343.9 150.8 可参考 2E-4 20.57~20.60 1.74 10.9 2.14 240.3 87.4 可参考 注:“1E”和“2E”分别表示NTCJ1和NTCJ2钻孔样品;测试方法:Ge心法,测试条件:室温、X波段、中心磁场为348 mT、扫宽为5 mT、调制幅度为0.1 mT、微波功率为2 mW、转换时间为5.12 ms、时间常数为40.96 ms;测年误差约为10%~15%;备注内容由本文添加。 -
[1] 高抒. 海岸与陆架沉积: 动力过程、全球变化影响和地层记录[J]. 第四纪研究, 2010, 30(5):856-863
GAO Shu. Coastal and shelf sedimentation in association with dynamic processes, global change impacts, and stratigraphic records: an overview of the scientific problems [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2010, 30(5): 856-863.
[2] Gao S, Collins M B. Holocene sedimentary systems on continental shelves [J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 352: 268-294. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.03.021
[3] Li G X, Li P, Liu Y, et al. Sedimentary system response to the global sea level change in the East China Seas since the last glacial maximum [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 139: 390-405. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.09.007
[4] 夏非, 张永战, 刘德政. 南黄海辐射沙脊群西洋潮流通道的浅部沉积层序及其形成演化再认识[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(4):13-26
XIA Fei, ZHANG Yongzhan, LIU Dezheng. Rethinking on shallow sedimentary sequence and its evolution of the Xiyang tidal channel in the Radial Sand Ridge Field, South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(4): 13-26.
[5] 任美锷. 江苏省海岸带和海涂资源综合调查报告[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1986: 1-134
REN Mei’e. Report for Comprehensive Investigation on Recourses of Coastal Zones and Tidal Flats in Jiangsu Province[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1986: 1-134.
[6] 叶汇. 江苏沿海地区综合开发战略研究(港口交通卷): 江苏沿海地区港口布局与交通网建设研究[M]. 南京: 江苏人民出版社, 2008: 137-145
YE Hui. Research on the Comprehensive Development Strategy of Jiangsu Coastal Areas (Vol. Port Traffic): Research on the Port Layout and Traffic Network Construction in Jiangsu Coastal Areas[M]. Nanjing: Jiangsu People's Publishing House, 2008: 137-145.
[7] 张训华, 张志珣, 蓝先洪, 等. 南黄海区域地质[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2013: 153-221
ZHANG Xunhua, ZHANG Zhixun, LAN Xianhong, et al. Regional Geology of the South Yellow Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2013: 153-221.
[8] 薛春汀, 周永青, 朱雄华. 晚更新世末至公元前7世纪的黄河流向和黄河三角洲[J]. 海洋学报, 2004, 26(1):48-61
XUE Chunting, ZHOU Yongqing, ZHU Xionghua. The Huanghe River course and delta from end of Late Pleistocene to the 7th century BC [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2004, 26(1): 48-61.
[9] 汪品先, 卞云华. 介形虫/有孔虫比值作为沉积环境的标志[J]. 微体古生物学报, 1986, 3(1):37-50
WANG Pingxian, BIAN Yunhua. Ostracod/Foraminifer ratios as indicators of sedimentary environments [J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 1986, 3(1): 37-50.
[10] 范德江, 杨作升, 毛登, 等. 长江与黄河沉积物中粘土矿物及地化成分的组成[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(4):7-12
FAN Dejiang, YANG Zuosheng, MAO Deng, et al. Clay minerals and geochemistry of the sediments from the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2001, 21(4): 7-12.
[11] 胡邦琦, 李军, 李国刚, 等. 长江和黄河入海沉积物的物源识别研究进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(6):147-156
HU Bangqi, LI Jun, LI Guogang, et al. Distinguishing the Changjiang and Huanghe sediments: a review [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(6): 147-156.
[12] 钟巍, 王立国, 熊黑钢, 等. 塔里木盆地南缘和田绿洲中全新世以来气候环境变化与人类活动[J]. 中国沙漠, 2007, 27(2):171-176
ZHONG Wei, WANG Liguo, XIONG Heigang, et al. Climate-Environment changes and possible human activity effect since Mid-Holocene in Hetian Oasis, southern margin of Tarim Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2007, 27(2): 171-176.
[13] 胡梦珺, 杨爱丽, 张文丽. 常量元素氧化物含量及其比值揭示的中晚全新世以来玛曲高原的环境演变[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(2):313-321
HU Mengjun, YANG Aili, ZHANG Wenli. Environmental evolution since the Middle-Late Holocene in the Maqu Plateau reflected by constant element oxides content and ratios [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2015, 35(2): 313-321.
[14] 葛全胜. 中国历朝气候变化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011: 61-103
GE Quansheng. Climate Change in the Past Dynasties of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2011: 61-103.
[15] 张欣. 中国东部海岸带-陆架区近20万年来沉积物年代学与沉积环境演化[D]. 中国地质大学(武汉)博士学位论文, 2021: 1-122
ZHANG Xin. Chronology and sedimentary environment change in the coastal-shelf areas of eastern China since 200 ka[D]. Doctor Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2021: 1-122.
[16] 夏非. 辐射沙脊群西洋潮流通道的浅部层序地层与沉积环境演化[D]. 南京大学博士学位论文, 2016: 1-187
XIA Fei. Shallow sequence stratigraphy and sedimentary evolution of the Xiyang tidal channel in the Radial Sand Ridge Field[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Nanjing University, 2016: 1-187.
[17] 刘德政, 夏非. 江苏中部海岸晚第四纪沉积物的粒度与磁化率特征及其古环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(5):210-220
XIA Fei, LIU Dezheng. Characteristics of grain size and magnetic susceptibility of the Late Quaternary sediments from core 07SR01 in the middle Jiangsu coast and their paleoenvironmental significances [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(5): 210-220.
[18] Veeken P C H, Moerkerken B van. Seismic Stratigraphy and Depositional Facies Models[M]. Houten: EAGE Publications bv, 2013: 107-214.
[19] Gao L, Long H, Tamura T, et al. A ~130 ka terrestrial-marine interaction sedimentary history of the northern Jiangsu coastal plain in China [J]. Marine Geology, 2021, 435: 106455. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2021.106455
-




 下载:
下载: