Geochemical characteristics of polymetallic nodules and adjacent sediments in the western Pacific Ocean: effects of sedimentary environments on nodules
-
摘要:
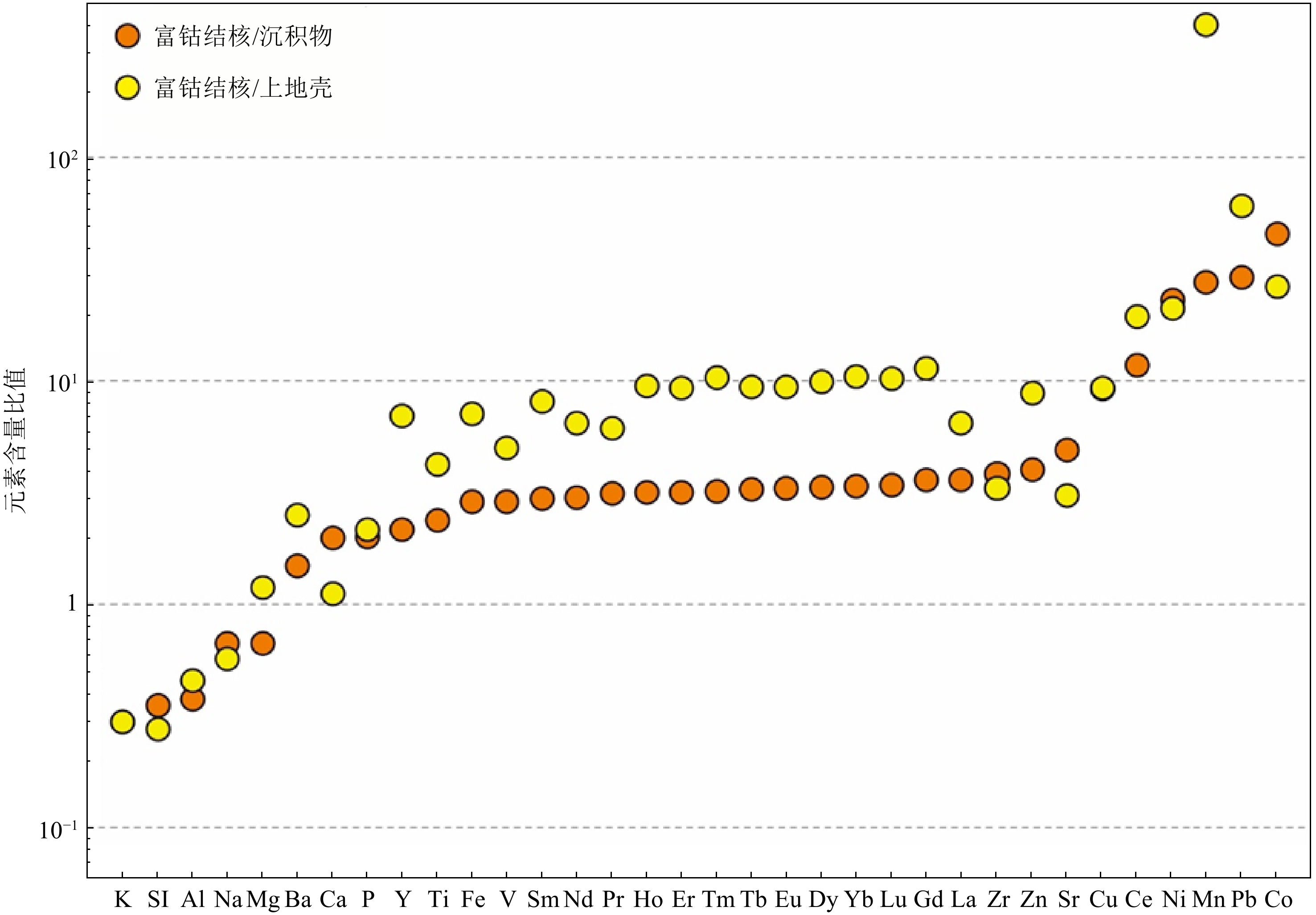
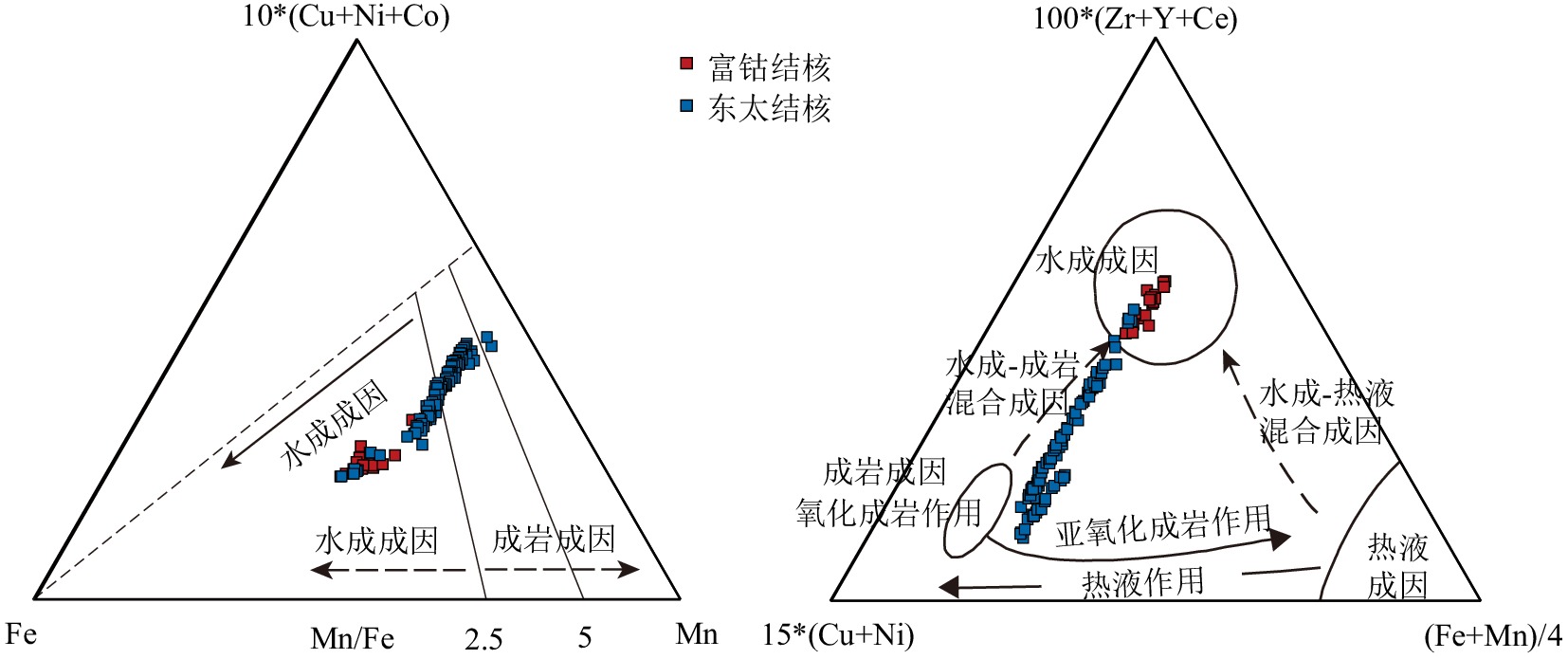
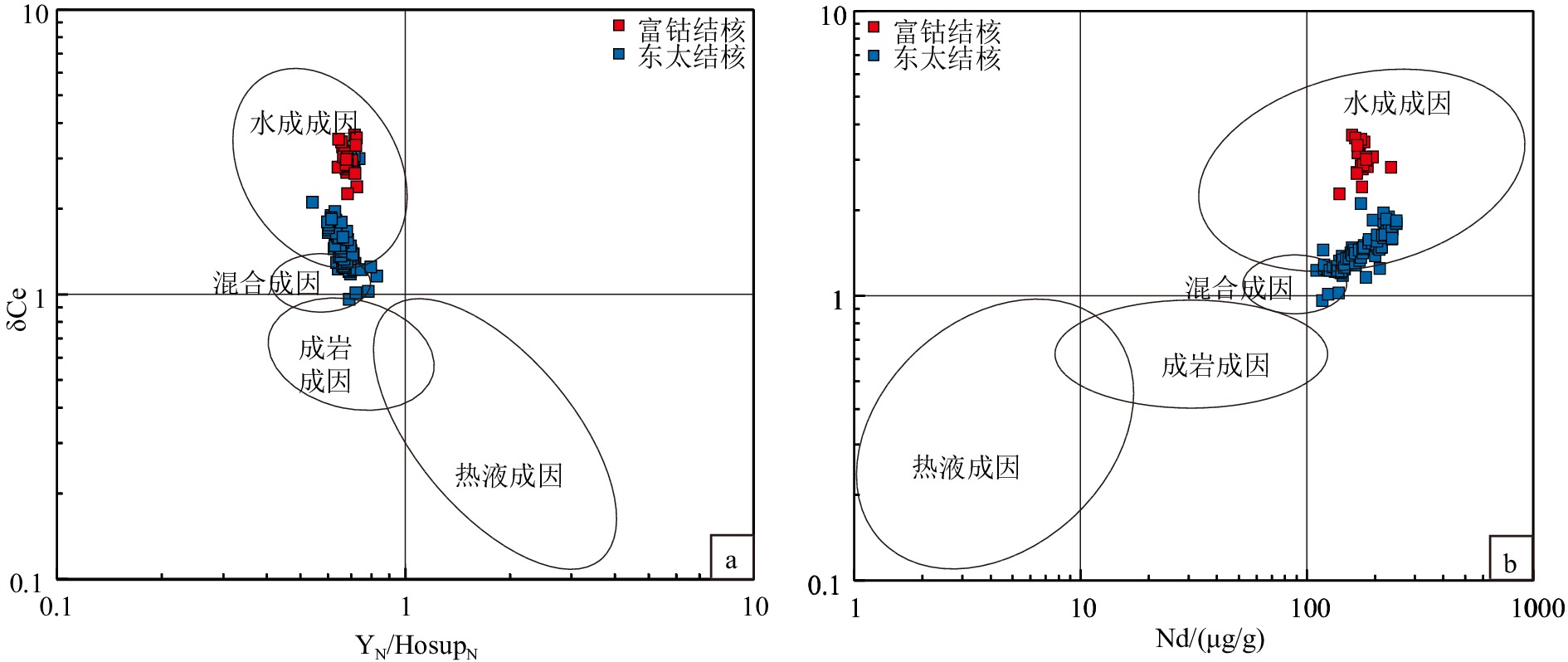
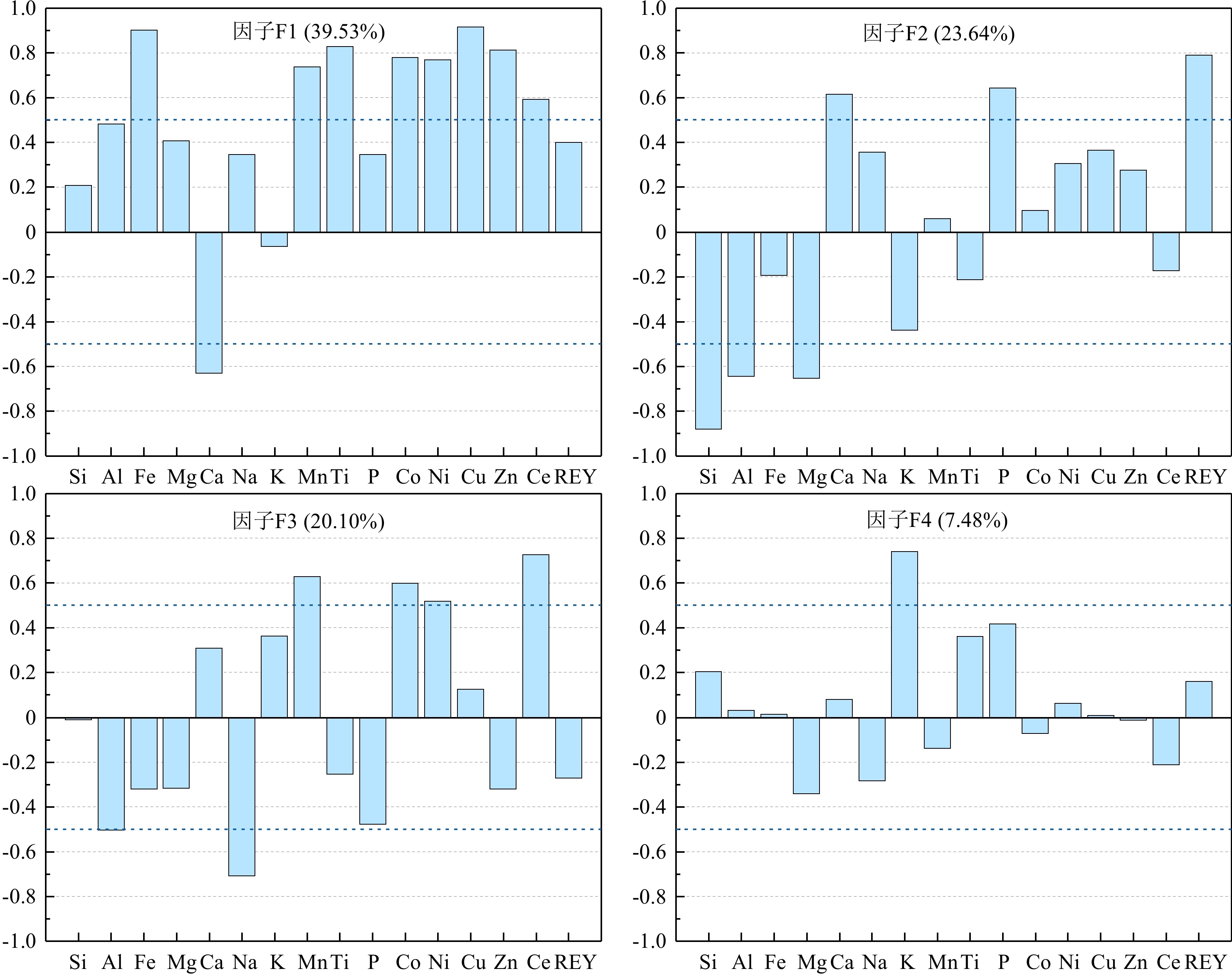
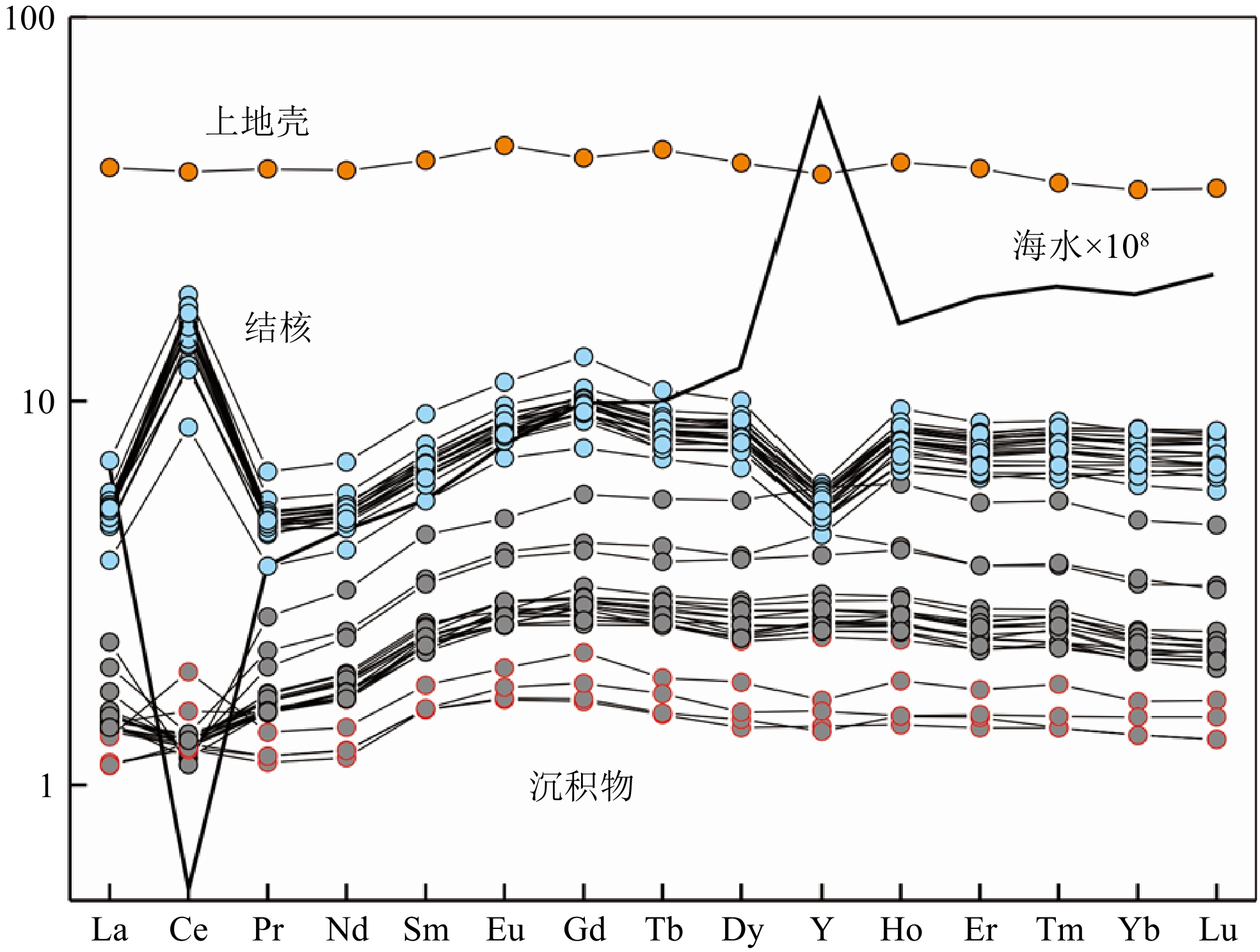
西太平洋深海盆地同时发育多金属结核和富稀土沉积物,但针对多金属结核及其表层沉积物之间关系的研究较少。通过多金属结核-表层沉积物地球化学分析,揭示关键金属元素在结核、沉积物中的富集和分馏过程,探讨沉积过程与环境对多金属结核生长的影响。研究区多金属结核具有相对高的Co、REY含量,低的Mn/Fe比值,显示为典型的水成成因。主成分分析及相关性分析结果指示结核的成矿过程是在水成作用、成岩作用以及陆地碎屑、生物碎屑输入的作用下,Fe-Mn氧化物对海水及孔隙水中各类金属元素的选择性富集。研究区表层沉积物主要为深海黏土,相较于多金属结核富集大部分金属元素,深海黏土更为富集Si、Al、Na、K等元素。沉积物中Co、Ni、Cu等金属元素的富集与Fe-Mn微结核的含量相关,而REY与磷酸盐组分更为密切。Fe-Mn氧化物组分对海水中金属元素选择性吸附形成多元素的富集及显著的Ce正异常、Y负异常,而磷酸盐组分主要继承海水的稀土特征,它们的含量决定了沉积物中金属元素及稀土元素的含量和模式。结核及沉积物在关键元素富集的过程中有相似的过程,Fe-Mn氧化物组分是二者元素富集过程的载体。研究区的低生物生产力和低沉积速率,导致海水中相关元素的沉降通量减少、沉积速率减慢,为水成型结核生长提供有利条件。受到南极底流的影响,研究区底层海水具有富氧特征,且在其强底流冲刷作用下造成了频繁的沉积间断,促进了铁锰氧化物的形成和关键金属元素的富集。
Abstract:Polymetallic nodules and rare earth-rich sediments are developing simultaneously in the western Pacific Deep Sea Basin, but there are few studies on the relationship between polymetallic nodules and their surface sediments. In this study, the geochemical analysis of polymetallic nodules and surface sediments was used to reveal the enrichment and fractionation processes of critical metal elements in nodules-sediments and to explore the influence of deposition processes and environment on the growth of polymetallic nodules. The polymetallic nodules in the study area have relatively high Co and REY contents and low Mn/Fe ratios, indicating a typical hydrogenetic precipitation. The results of principal component analysis and correlation analysis indicate the nodule formation process is a selective enrichment of Fe-Mn oxides for various metal elements in seawater and pore water under the influence of hydrogenesis, diagenesis and input from terrestrial debris and bioclastic. The surface sediments in the study area are mainly deep-sea clays, which are more enriched in Si, Al, Na, K, and other elements than the polymetallic nodules, which are enriched in most metal elements. The enrichment of metallic elements such as Co, Ni, and Cu in the sediments is related to the content of Fe-Mn micronodules, while REY is more closely related to the phosphate fraction. the Fe-Mn oxide fraction selectively adsorbs metallic elements in seawater to form multi-element enrichment and significant positive Ce anomalies and negative Y anomalies, while the phosphate fraction mainly inherits the rare earth characteristics of seawater, and their content determines the content and pattern of metallic elements and rare earth elements in the sediments. The nodule and sediments have similar processes in the enrichment of critical elements, and Fe-Mn oxide components are the carriers of elemental enrichment processes in both. The low biological productivity and low sedimentation rate in the study area result in reduced sedimentation fluxes and slower sedimentation rates of the relevant elements in seawater, providing favorable conditions for hydroformed nodule growth. Affected by the Antarctic Bottom Water, the bottom seawater in the study area is characterized by oxygen enrichment, and under the effect of its strong bottom current scouring causes frequent deposition interruptions, which promotes the formation of Fe-Mn oxides and the enrichment of critical metal.
-

-
表 1 沉积物涂片鉴定结果
Table 1. Sediment smear identification results
样品号 层位/cm 视域总量/% 黏土 钙质 硅质 生物碎屑 长英矿物 微结核 沸石 辉石 角闪石 WMA1302 0~10 48 − + 30 22 − + − − WMA1306 0~5 70 − + 10 20 − + − − WMA1309 0~10 71 − 1 10 18 − + − − WMA1317 0~5 65 − + 15 20 − + − − WMA1318 0~5 67 − + 10 15 − 8 − − WNB1201 0~10 77 12 + + 10 − 1 − − WPN1402 0~15 88 − + 10 − + − 1 1 WPN1403 0~15 93 − + 5 − − − 1 1 WPN1404 0~20 92 − + 5 − − − 1 2 WPN1405 0~15 94 − + 3 − − − + 3 WPN1406 0~15 96 − + 2 − − − + 2 WPN1407 0~20 95 − − 3 − − − + 2 WPN1408 0~15 95 − − 1 − − − 1 3 W1M1502 0~16 84 5 + − 4 + 7 − − WMC1505 0~15 79 10 2 − 3 + 6 − − W1M1504 0~15 94 + + − 4 + 2 − − W3C1704 0~12 88 + + − 12 + + − − W3C1705 0~12 85 − + − 15 + + − − W3C1707 0~10 92 + + + 8 + − − − W3C1708 0~15 83 − + + 17 + + − − W3M1701 0~15 92 − − − 7 + 1 − − 注:+表示视域范围中可见但含量未达到1%,−表示视域范围中不可见。 -
[1] Hein J R, Koschinsky A, Kuhn T. Deep-ocean polymetallic nodules as a resource for critical materials [J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2020, 1(3): 158-169.
[2] Toro N, Robles P, Jeldres R I. Seabed mineral resources, an alternative for the future of renewable energy: A critical review [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 126: 103699. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103699
[3] Machida S, Fujinaga K, Ishii T, et al. Geology and geochemistry of ferromanganese nodules in the Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone around Minamitorishima Island [J]. Geochemical Journal, 2016, 50(6): 539-555. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.2.0419
[4] Ohta J, Yasukawa K, Nakamura K, et al. Geological features and resource potential of deep-sea mud highly enriched in rare-earth elements in the Central Pacific Basin and the Penrhyn Basin [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 139: 104440. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104440
[5] 任江波, 邓义楠, 赖佩欣, 等. 太平洋调查区多金属结核的地球化学特征和成因[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(2):412-425
REN Jiangbo, DENG Yi’nan, LAI Peixin, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of the polymetallic nodules in the Pacific survey area [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(2): 412-425.
[6] Hein J R, Koschinsky A. Deep-ocean ferromanganese crusts and nodules[M]//Holland H D, Turekian K K. Treatise on Geochemistry. 2nd ed. Oxford: Elsevier, 2014, 13: 273-291.
[7] Wang F L, He G W, Deng X G, et al. Fish teeth Sr isotope stratigraphy and Nd isotope variations: New insights on REY enrichments in deep-sea sediments in the Pacific [J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2021, 9(12): 1379. doi: 10.3390/jmse9121379
[8] Dutkiewicz A, Judge A, Müller R D. Environmental predictors of deep-sea polymetallic nodule occurrence in the global ocean [J]. Geology, 2020, 48(3): 293-297. doi: 10.1130/G46836.1
[9] 刘永刚, 杜德文, 李钟山, 等. 太平洋CC区及周边多金属结核分布及资源量预测[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2009, 27(3):342-350 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2009.03.007
LIU Yonggang, DU Dewen, LI Zhongshan, et al. Estimation of polymetallic nodule distribution and resource quantity in the CC zone and its adjacent areas of the Pacific Ocean [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2009, 27(3): 342-350. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2009.03.007
[10] Alevizos E, Huvenne V A I, Schoening T, et al. Linkages between sediment thickness, geomorphology and Mn nodule occurrence: New evidence from AUV geophysical mapping in the Clarion-Clipperton Zone [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers, 2022, 179: 103645. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2021.103645
[11] Kim J, Hyeong K, Lee H B, et al. Relationship between polymetallic nodule genesis and sediment distribution in the KODOS (Korea Deep Ocean Study) Area, Northeastern Pacific [J]. Ocean Science Journal, 2012, 47(3): 197-207. doi: 10.1007/s12601-012-0020-8
[12] Amparo C R M, Arturo C E, Marlene O C. Morphology and texture of polymetallic nodules and their association with sediments of the Mexican Pacific [J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2013, 31(2): 154-175.
[13] Calvert S E, Price N B. Geochemical variation in ferromanganese nodules and associated sediments from the Pacific Ocean [J]. Marine Chemistry, 1977, 5(1): 43-74. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(77)90014-7
[14] Pattan J N, Parthiban G. Geochemistry of ferromanganese nodule-sediment pairs from Central Indian Ocean Basin [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 40(2): 569-580. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.10.010
[15] Pattan J N, Rao C M, Migdisov A A, et al. Ferromanganese nodules and their associated sediments from the Central Indian Ocean Basin: Rare earth element geochemistry [J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2001, 19(3): 155-165.
[16] Elderfield H, Hawkesworth C J, Greaves M J, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry of oceanic ferromanganese nodules and associated sediments [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1981, 45(4): 513-528. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(81)90184-8
[17] Ren J B, He G W, Deng X G, et al. Metallogenesis of Co-rich ferromanganese nodules in the northwestern Pacific: Selective enrichment of metallic elements from seawater [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2022, 143: 104778. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.104778
[18] Deng X Z, He G W, Xu Y, et al. Oxic bottom water dominates polymetallic nodule formation around the Caiwei Guyot, northwestern Pacific Ocean [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2022, 143: 104776. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.104776
[19] Li D F, Fu Y, Sun X M, et al. Critical metal enrichment mechanism of deep-sea hydrogenetic nodules: Insights from mineralogy and element mobility [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 118: 103371. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103371
[20] Reykhard L Y, Shulga N A. Fe-Mn nodule morphotypes from the NE Clarion-Clipperton Fracture Zone, Pacific Ocean: Comparison of mineralogy, geochemistry and genesis [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 110: 102933. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.102933
[21] Ren J B, Liu Y, Wang F L, et al. Mechanism and influencing factors of REY enrichment in deep-sea sediments [J]. Minerals, 2021, 11(2): 196. doi: 10.3390/min11020196
[22] Yu M, Shi X F, Huang M, et al. The transfer of rare earth elements during early diagenesis in REY-rich sediments: An example from the Central Indian Ocean Basin [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 136: 104269. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104269
[23] Zhou T C, Shi X F, Huang M, et al. Genesis of REY-rich deep-sea sediments in the Tiki Basin, eastern South Pacific Ocean: Evidence from geochemistry, mineralogy and isotope systematics [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 138: 104330. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104330
[24] Konter J G, Hanan B B, Blichert-Toft J, et al. One hundred million years of mantle geochemical history suggest the retiring of mantle plumes is premature [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 275(3-4): 285-295. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2008.08.023
[25] Karl S M, Wandless G A, Karpoff A M. Sedimentological and geochemical characteristics of Leg 129 siliceous deposits[C]//Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results. College Station, Texas: Ocean Drilling Program, 1992, 129: 31-79.
[26] Müller R D, Sdrolias M, Gaina C, et al. Age, spreading rates, and spreading asymmetry of the world's ocean crust [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2008, 9(4): Q04006.
[27] Deng X G, Yi L, Paterson G A, et al. Magnetostratigraphic evidence for deep-sea erosion on the Pacific Plate, south of Mariana Trench, since the Middle Pleistocene: potential constraints for Antarctic bottom water circulation [J]. International Geology Review, 2016, 58(1): 49-57. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2015.1055597
[28] Jiang X D, Gong J L, Ren J B, et al. An interdependent relationship between microbial ecosystems and ferromanganese nodules from the Western Pacific Ocean [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2020, 398: 105588. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2019.105588
[29] 何高文, 杨永, 韦振权, 等. 西太平洋中国富钴结壳勘探合同区矿床地质[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2021, 31(10):2649-2664
HE Gaowen, YANG Yong, WEI Zhenquan, et al. Mineral deposit characteristics of cobalt-rich Fe-Mn crusts in COMRA contract area, Western Pacific Ocean [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2021, 31(10): 2649-2664.
[30] Yi L, Wang H F, Deng X G, et al. Geochronology and geochemical properties of Mid-Pleistocene sediments on the Caiwei Guyot in the Northwest Pacific imply a surface-to-deep linkage [J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2021, 9(3): 253. doi: 10.3390/jmse9030253
[31] Anderson D L. Chemical composition of the mantle [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 1983, 88(S01): B41-B52. doi: 10.1029/JB088iS01p00B41
[32] Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1985.
[33] Josso P, Pelleter E, Pourret O, et al. A new discrimination scheme for oceanic ferromanganese deposits using high field strength and rare earth elements [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 87: 3-15. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.003
[34] Schmidt K, Bau M, Hein J R, et al. Fractionation of the geochemical twins Zr-Hf and Nb-Ta during scavenging from seawater by hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 140: 468-487. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.05.036
[35] Bau M, Schmidt K, Koschinsky A, et al. Discriminating between different genetic types of marine ferro-manganese crusts and nodules based on rare earth elements and yttrium [J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 381: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.05.004
[36] Menendez A, James R H, Lichtschlag A, et al. Controls on the chemical composition of ferromanganese nodules in the Clarion-Clipperton Fracture Zone, eastern equatorial Pacific [J]. Marine Geology, 2019, 409: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2018.12.004
[37] 邓贤泽, 任江波, 邓希光, 等. 富钴结壳关键元素赋存状态与富集机理[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(2-3):376-384
DENG Xianze, REN Jiangbo, DENG Xiguang, et al. Cobalt-rich crust obtains high contents of key elements from seawater: element absorption and distribution [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(2-3): 376-384.
[38] Hein J R, Mizell K, Koschinsky A, et al. Deep-ocean mineral deposits as a source of critical metals for high- and green-technology applications: Comparison with land-based resources [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2013, 51: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.12.001
[39] 任江波, 何高文, 朱克超, 等. 富稀土磷酸盐及其在深海成矿作用中的贡献[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(6):1312-1325
REN Jiangbo, HE Gaowen, ZHU Kechao, et al. REY-rich Phosphate and Its Effects on the Deep-Sea Mud Mineralization [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(6): 1312-1325.
[40] Halbach P, Scherhag C, Hebisch U, et al. Geochemical and mineralogical control of different genetic types of deep-sea nodules from the Pacific Ocean [J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1981, 16(1): 59-84.
[41] Kuhn T, Wegorzewski A, Rühlemann C, et al. Composition, formation, and occurrence of polymetallic nodules[M]//Kuhn T, Wegorzewski A, Rühlemann C, et al. Deep-Sea Mining: Resource Potential, Technical and Environmental Considerations. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2017: 23-63.
[42] 何高文, 孙晓明, 薛婷. 太平洋多金属结核和富钴结壳地质地球化学特征与成矿机制对比[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011
HE Gaowen, SUN Xiaoming, XUE Ting. Geological and Geochemical Characteristics and Metallogenic Mechanism of Polymetallic Nodules and Cobalt Rich Crusts in the Pacific Ocean[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 2011.
[43] 石学法, 符亚洲, 李兵, 等. 我国深海矿产研究: 进展与发现(2011-2020)[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2021, 40(2):305-318
SHI Xuefa, FU Yazhou, LI Bing, et al. Research on deep-sea minerals in China: Progress and discovery (2011-2020) [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2021, 40(2): 305-318.
[44] 任江波, 姚会强, 朱克超, 等. 稀土元素及钇在东太平洋CC区深海泥中的富集特征与机制[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(4):200-211
REN Jiangbo, YAO Huiqiang, ZHU Kechao, et al. Enrichment mechanism of rare earth elements and yttrium in deep-sea mud of Clarion-Clipperton Region [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(4): 200-211.
[45] 王汾连, 何高文, 王海峰, 等. 中太平洋深海沉积物中元素组合特征及地质意义[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(7):11-18
WANG Fenlian, HE Gaowen, WANG Haifeng, et al. The element association characteristics and geological significance of deep-sea sediments in the Central Pacific Ocean [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(7): 11-18.
[46] Vallee B L, Auld D S. Zinc: biological functions and coordination motifs [J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 1993, 26(10): 543-551. doi: 10.1021/ar00034a005
[47] Smrzka D, Zwicker J, Bach W, et al. The behavior of trace elements in seawater, sedimentary pore water, and their incorporation into carbonate minerals: a review [J]. Facies, 2019, 65(4): 41. doi: 10.1007/s10347-019-0581-4
[48] Heller C, Kuhn T, Versteegh G J M, et al. The geochemical behavior of metals during early diagenetic alteration of buried manganese nodules [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers, 2018, 142: 16-33. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2018.09.008
[49] Jiang X J, Lin X H, Yao D, et al. Enrichment mechanisms of rare earth elements in marine hydrogenic ferromanganese crusts [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2011, 54(2): 197-203. doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-4070-4
[50] Bau M, Koschinsky A. Oxidative scavenging of cerium on hydrous Fe oxide: Evidence from the distribution of rare earth elements and yttrium between Fe oxides and Mn oxides in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts [J]. Geochemical Journal, 2009, 43(1): 37-47. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.1.0005
[51] Takebe M. Carriers of rare earth elements in pacific deep-sea sediments [J]. The Journal of Geology, 2005, 113(2): 201-215. doi: 10.1086/427669
[52] Loges A, Wagner T, Barth M, et al. Negative Ce anomalies in Mn oxides: The role of Ce4+ mobility during water–mineral interaction [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2012, 86: 296-317. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.03.017
[53] German C R, Elderfield H. Application of the Ce anomaly as a paleoredox indicator: The ground rules [J]. Paleoceanography, 1990, 5(5): 823-833. doi: 10.1029/PA005i005p00823
[54] Schijf J, Christenson E A, Byrne R H. YREE scavenging in seawater: A new look at an old model [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2015, 177: 460-471. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2015.06.010
[55] 任江波, 邓希光, 邓义楠, 等. 中国富钴结壳合同区海水的稀土元素特征及其意义[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(10):3529-3540
REN Jiangbo, DENG Xiguang, DENG Yi’nan, et al. Rare earth element characteristics and its geological implications for seawater from cobalt-rich ferromanganese crust exploration contract area of China [J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(10): 3529-3540.
[56] 任江波, 何高文, 姚会强, 等. 西太平洋海山富钴结壳的稀土和铂族元素特征及其意义[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(10):1745-1757
REN Jiangbo, HE Gaowen, YAO Huiqiang, et al. Geochemistry and significance of REE and PGE of the cobalt-rich crusts from West Pacific ocean seamounts [J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(10): 1745-1757.
[57] Hein J R, Koschinsky A, Mikesell M, et al. Marine phosphorites as potential resources for heavy rare earth elements and yttrium [J]. Minerals, 2016, 6(3): 88. doi: 10.3390/min6030088
[58] Li D F, Fu Y, Liu Q F, et al. High-resolution LA-ICP-MS mapping of deep-sea polymetallic micronodules and its implications on element mobility [J]. Gondwana Research, 2020, 81: 461-474. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2019.12.009
[59] Zhou T C, Shi X F, Huang M, et al. The influence of hydrothermal fluids on the REY-rich deep-sea sediments in the Yupanqui Basin, Eastern South Pacific Ocean: Constraints from bulk sediment geochemistry and mineralogical characteristics [J]. Minerals, 2020, 10(12): 1141. doi: 10.3390/min10121141
[60] Liao J L, Sun X M, Wu Z W, et al. Fe-Mn (oxyhydr)oxides as an indicator of REY enrichment in deep-sea sediments from the central North Pacific [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 112: 103044. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103044
[61] Bi D J, Shi X F, Huang M, et al. Geochemical and mineralogical characteristics of deep-sea sediments from the western North Pacific Ocean: Constraints on the enrichment processes of rare earth elements [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 138: 104318. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104318
[62] 石学法, 毕东杰, 黄牧, 等. 深海稀土分布规律与成矿作用[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(2-3):195-208
SHI Xuefa, BI Dongjie, HUANG Mu, et al. Distribution and metallogenesis of deep-sea rare earth elements [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(2-3): 195-208.
[63] Deng Y N, Ren J B, Guo Q J, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry characteristics of seawater and porewater from deep sea in western Pacific [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 16539. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16379-1
[64] Verlaan P A, Cronan D S. Origin and variability of resource-grade marine ferromanganese nodules and crusts in the Pacific Ocean: A review of biogeochemical and physical controls [J]. Geochemistry, 2022, 82(1): 125741. doi: 10.1016/j.chemer.2021.125741
[65] Haley B A, Klinkhammer G P, Mcmanus J. Rare earth elements in pore waters of marine sediments [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(6): 1265-1279. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2003.09.012
[66] 王海峰, 王汾连, 朱克超, 等. 东太平洋CC区WPC1101柱样沉积环境及埋藏多金属结核成因[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(11):1-11
WANG Haifeng, WANG Fenlian, ZHU Kechao, et al. Depositional environment and origin of buried pollymetallic nodules: an interpretation of piston core WPC1101 from CC zone of Eastern Pacific [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(11): 1-11.
[67] 陈宗团, 许东禹, 刘季花, 等. 东北太平洋中新世古海洋环境与事件[J]. 海洋学报, 1994, 16(6):80-91
CHEN Zongtuan, XU Dongyu, LIU Jihua, et al. Miocene paleomarine environment and events in the Northeast Pacific [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1994, 16(6): 80-91.
-




 下载:
下载: