Research status and prospect of surface sediment types in the China-ASEAN seas and adjacent areas
-
摘要:
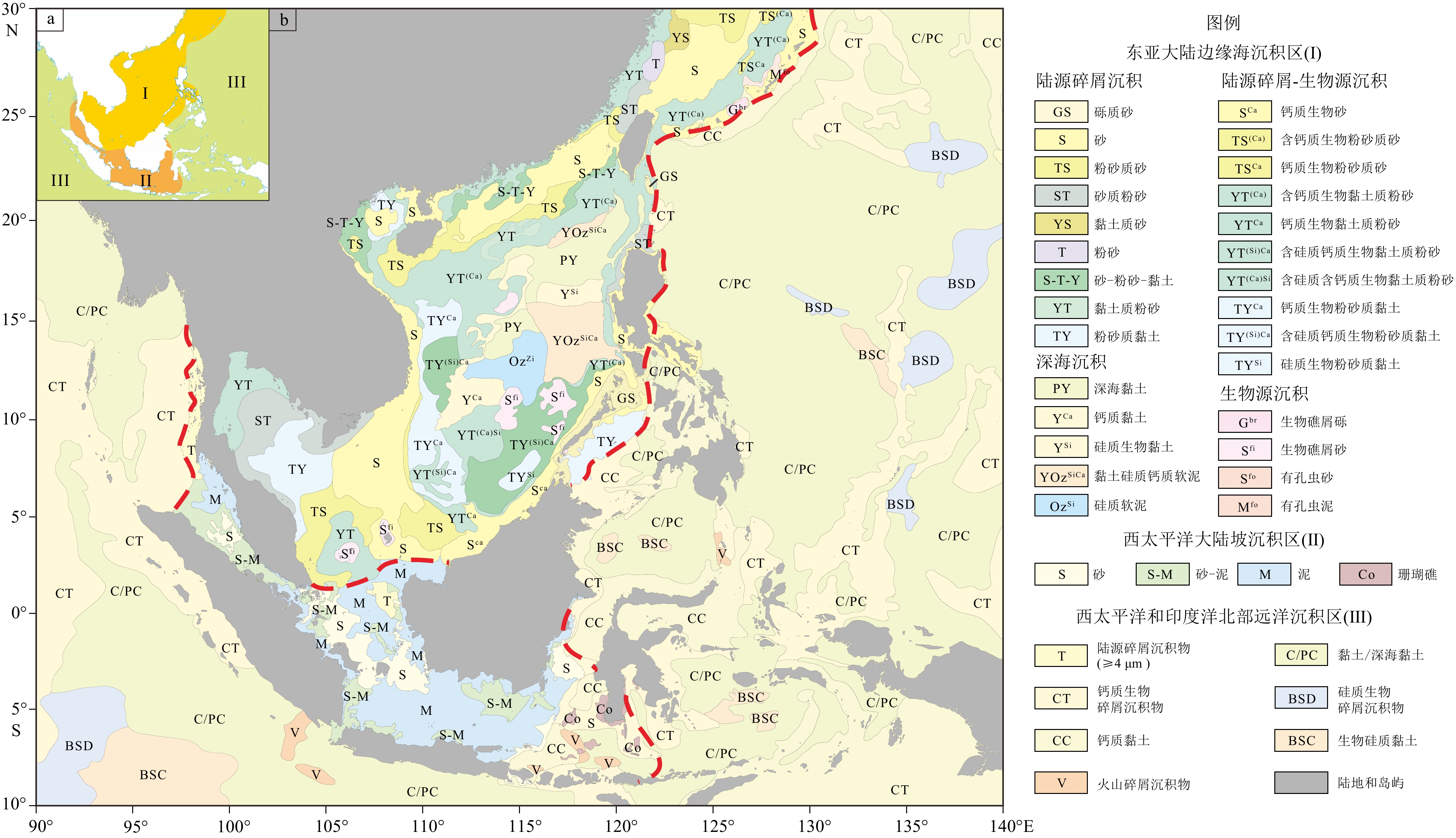
表层沉积物类型图是海洋地质系列图的主要图件之一,可直观反映出海底沉积物的分布特征和变化规律。中国-东盟海区及邻域海底沉积物类型调查和研究程度差异明显,中国海域调查程度较高,底质数据详细可靠,马六甲海峡和印度尼西亚西部海区相对较好,而西太平洋和印度洋北部大部分地区资料较为缺乏。该海域表层沉积物主要是陆源碎屑沉积物、生物源-陆源碎屑沉积物、深海沉积物、生物源沉积物和火山源沉积物,综合已有资料划分为三个沉积区。东亚大陆边缘海沉积区以陆源碎屑沉积物为主,西太平洋大陆坡沉积区以陆源碎屑沉积物和生物源-陆源碎屑沉积物为主,西太平洋和印度洋北部远洋沉积区以内源成因沉积为主。影响该区海底沉积物分布的主要因素是沉积物物源、地形、水动力环境以及构造活动等。中国-东盟海区及邻域表层沉积物类型图的编制可为深入理解不同地质和气候背景下太平洋和印度洋的沉积物分布及规律提供依据。
Abstract:The map of surface sediment types is one of the main components of marine geological series maps, which is used to describe the distribution characteristics and variation patterns of seafloor sediments. There are significant differences in the investigation and research levels of seafloor sediment types in the China-ASEAN seas and its adjacent regions. The investigation level in Chinese seas is relatively high, and the bottom data is detailed and reliable. The Malacca Strait and the western Indonesian sea areas are relatively well-investigated, while most of the data in the western Pacific and northern Indian Ocean are lacking. The surface sediments in those areas are mainly composed of terrigenous clastic sediments, biogenic-terrigenous clastic sediments, deep-sea sediments, biogenic sediments, and volcanogenic sediments, which are divided into three sedimentary areas based on the present data. The sedimentary area of the East Asian continental margin sea is dominated by terrigenous clastic sediments, while the sedimentary area of the western Pacific continental slope is dominated by terrigenous clastic sediments and biogenic-terrigenous clastic sediments. The pelagic sedimentary area of the western Pacific and northern Indian Ocean is significantly dominated by endogenic sediments. The main factors affecting the distribution of seafloor sediments in the areas are sediment sources, topography, hydrodynamic environment, and tectonic activity. The compilation of the map of surface sediment types in the China-ASEAN seas and adjacent areas helps us to understand the distribution and patterns of sediment in the Pacific and Indian Oceans under different geological and climatic backgrounds.
-
Key words:
- China-ASEAN seas /
- surface sediments /
- sediment type /
- current research /
- prospect
-

-
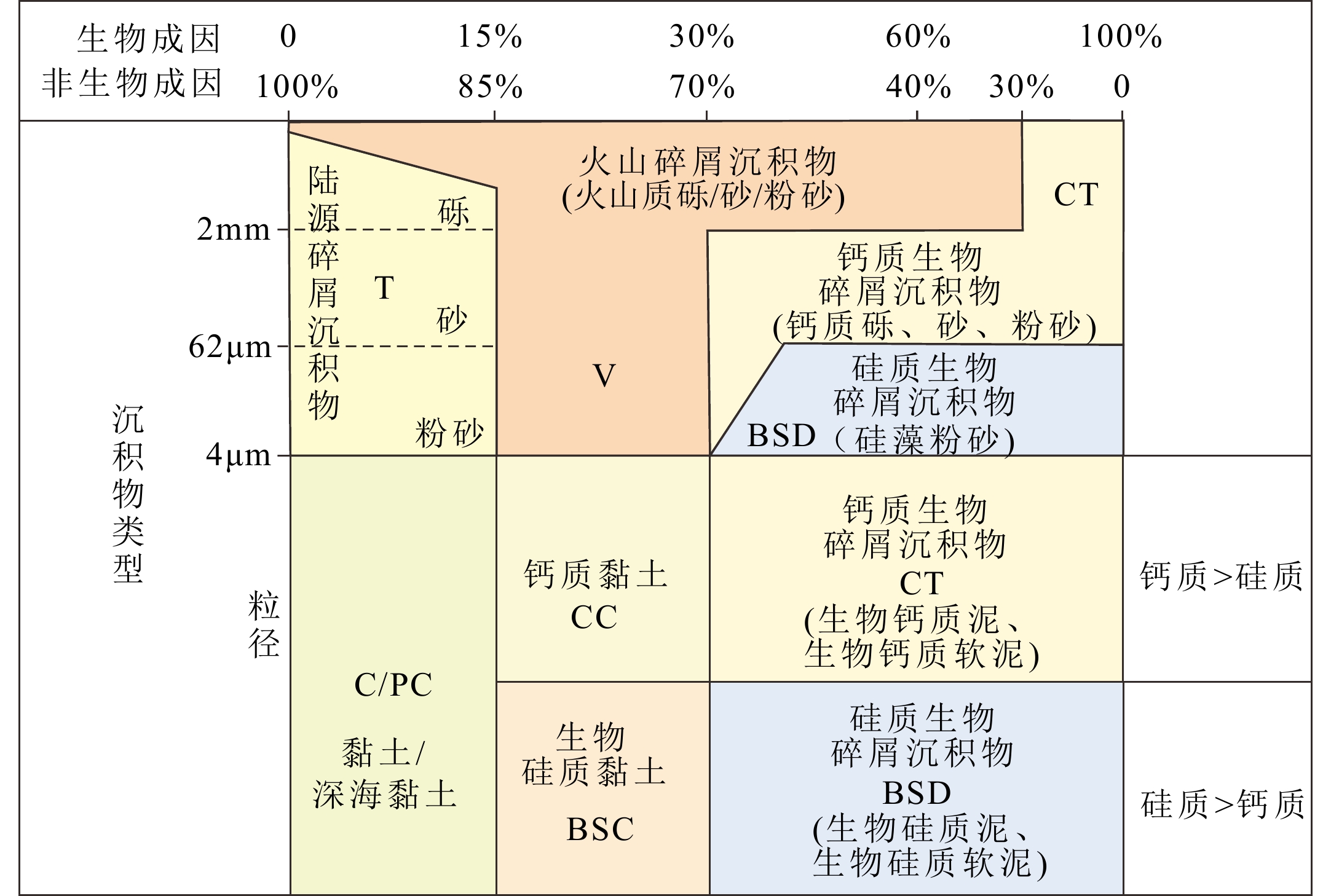
图 2 环太平洋海域表层沉积物分类图解[47]
Figure 2.
-
[1] 程鹏, 高抒. 北黄海西部海底沉积物的粒度特征和净输运趋势[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2000, 31(6):604-615
CHENG Peng, GAO Shu. Net sediment transport patterns over the northwestern Yellow Sea, based upon grain size trend analysis [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2000, 31(6): 604-615.
[2] 乔淑卿, 石学法, 王国庆, 等. 渤海底质沉积物粒度特征及输运趋势探讨[J]. 海洋学报, 2010, 32(4):139-147
QIAO Shuqing, SHI Xuefa, WANG Guoqing, et al. Discussion on grain-size characteristics of seafloor sediment and transport pattern in the Bohai Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2010, 32(4): 139-147.
[3] 王中波, 杨守业, 张志珣, 等. 东海外陆架晚第四纪若干沉积学问题的研究现状与展望[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(3):1-10
WANG Zhongbo, YANG Shouye, ZHANG Zhixun, et al. A review of the Late Quaternary sedimentological studies on the outer shelf of the East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(3): 1-10.
[4] 王中波, 杨守业, 张志珣, 等. 东海陆架中北部沉积物粒度特征及其沉积环境[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(6):1039-1049
WANG Zhongbo, YANG Shouye, ZHANG Zhixun, et al. The grain size compositions of the surface sediments in the East China Sea: indication for sedimentary environments [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2012, 43(6): 1039-1049.
[5] 王中波, 陆凯, 温珍河, 等. 中国东部海域表层沉积物粒度组成及影响因素[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(7):2709-2721
WANG Zhongbo, LU Kai, WEN Zhenhe, et al. Grain size compositions and their influencing factors of the surface sediments in Eastern China Seas [J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(7): 2709-2721.
[6] 石学法, 刘焱光, 乔淑卿, 等. 渤海、黄海和东海沉积物类型图[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021
SHI Xuefa, LIU Yanguang, QIAO Shuqing, et al. Sediment Type Map of the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021.
[7] Chen Z Y, Stanley D J. Quaternary subsidence and river channel migration in the Yangtze delta plain, Eastern China [J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 1995, 11(3): 927-945.
[8] 李乃胜. 冲绳海槽的地质构造属性[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1990, 21(6):536-543
LI Naisheng. On the geologic nature of Okinawa Trough [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1990, 21(6): 536-543.
[9] Li N S. On tectonic problems of the Okinawa Trough [J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2001, 19(3): 255-264. doi: 10.1007/BF02850663
[10] 孙卫东, 林秋婷, 张丽鹏, 等. 跳出南海看南海—新特提斯洋闭合与南海的形成演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(12):3467-3478
SUN Weidong, LIN Qiuting, ZHANG Lipeng, et al. The Formation of the South China Sea resulted from the closure of the Neo-Tethys: a perspective from regional geology [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2018, 34(12): 3467-3478.
[11] 张国良, 王帅, 张吉, 等. 西太平洋若干沟-弧-盆体系及板内岩浆成因研究进展[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(6):1220-1234
ZHANG Guoliang, WANG Shuai, ZHANG Ji, et al. Proceedings of subduction system and intra-oceanic volcanism of the Western Pacific [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(6): 1220-1234.
[12] 李常珍, 李乃胜, 林美华. 菲律宾海的地势特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2000, 24(6):47-51
LI Changzhen, LI Naisheng, LIN Meihua. Terrain features of the Philippine Sea [J]. Marine Sciences, 2000, 24(6): 47-51.
[13] Okino K, Fujioka K. The central Basin spreading center in the Philippine Sea: structure of an extinct spreading center and implications for marginal Basin Formation [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2003, 108(B1): 2040. doi: 10.1029/2001JB001095
[14] 吴时国, 范建柯, 董冬冬. 论菲律宾海板块大地构造分区[J]. 地质科学, 2013, 48(3):677-692
WU Shiguo, FAN Jianke, DONG Dongdong. Discussion on the tectonic division of the Philippine Sea plate [J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2013, 48(3): 677-692.
[15] Mrozowski C L, Lewis S D, Hayes D E. Complexities in the tectonic evolution of the west Philippine Basin [J]. Tectonophysics, 1982, 82(1-2): 1-24. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(82)90085-3
[16] Curray J R. The Bengal depositional system: from rift to orogeny [J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 352: 59-69. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.02.001
[17] Curray J R. Sediment volume and mass beneath the Bay of Bengal [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1994, 125(1-4): 371-383. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(94)90227-5
[18] Varkey M J, Murty V S N, Suryanarayana A. Physical oceanography of the Bay of Bengal and Andaman Sea [J]. Oceanography and Marine Biology:An Annual Review, 1996, 34: 1-70.
[19] Suwannathatsa S, Wongwises P, Vongvisessomjai S, et al. Phytoplankton tracking by oceanic model and satellite data in the Bay of Bengal and Andaman Sea [J]. APCBEE Procedia, 2012, 2: 183-189. doi: 10.1016/j.apcbee.2012.06.033
[20] Robinson R A J, Bird M I, Oo N W, et al. The Irrawaddy River sediment flux to the Indian Ocean: the original nineteenth-century data revisited [J]. The Journal of Geology, 2007, 115(6): 629-640. doi: 10.1086/521607
[21] Tessler Z D, Gordon A L, Pratt L J, et al. Transport and dynamics of the Panay sill overflow in the Philippine seas [J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2010, 40(12): 2679-2695. doi: 10.1175/2010JPO4395.1
[22] Ferrera C M, Jacinto G S, Chen C T A, et al. Carbonate parameters in high and low productivity areas of the Sulu Sea, Philippines [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2017, 195: 2-14. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2017.08.005
[23] Masumoto Y, Kagimoto T, Yoshida M, et al. Intraseasonal eddies in the Sulawesi Sea simulated in an ocean general circulation model [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2001, 28(8): 1631-1634. doi: 10.1029/2000GL011835
[24] Nagara G A, Adi Sasongko N, Olakunle O J. Introduction to Java Sea[M]. Stavanger: University of Stavanger, 2007.
[25] Poliakova A, Zonneveld K A F, Kwiatkowski C, et al. Marine environment, vegetation and land use changes during the Late Holocene in South Kalimantan and East Java reconstructed based on pollen and organic-walled dinoflagellate cysts analysis [J]. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 2017, 238: 105-121. doi: 10.1016/j.revpalbo.2016.11.012
[26] Wyrtki K. Physical oceanography of the southeast Asian water[R]. La Jolla: Scripps Institution of Oceanography, 1961.
[27] Handley H K, Blichert-Toft J, Gertisser R, et al. Insights from Pb and O isotopes into along-arc variations in subduction inputs and crustal assimilation for volcanic rocks in Java, Sunda arc, Indonesia [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 139: 205-226. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.04.025
[28] Sprintall J, Wijffels S, Molcard R, et al. Direct evidence of the south Java current system in Ombai Strait [J]. Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans, 2010, 50(2): 140-156. doi: 10.1016/j.dynatmoce.2010.02.006
[29] Alongi D M, da Silva M, Wasson R J, et al. Sediment discharge and export of fluvial carbon and nutrients into the Arafura and Timor Seas: a regional synthesis [J]. Marine Geology, 2013, 343: 146-158. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2013.07.004
[30] Shi X F, Liu S F, Fang X S, et al. Distribution of clay minerals in surface sediments of the western Gulf of Thailand: sources and transport patterns [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 105: 390-398. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.02.005
[31] Milliman J D, Syvitski J P M. Geomorphic/tectonic control of sediment discharge to the ocean: the importance of small mountainous rivers [J]. The Journal of Geology, 1992, 100(5): 525-544. doi: 10.1086/629606
[32] Milliman J D, Farnsworth K L, Albertin C S. Flux and fate of fluvial sediments leaving large islands in the East Indies [J]. Journal of Sea Research, 1999, 41(1-2): 97-107. doi: 10.1016/S1385-1101(98)00040-9
[33] Summerfield M A, Hulton N J. Natural controls of fluvial denudation rates in major world drainage basins [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 1994, 99(B7): 13871-13883. doi: 10.1029/94JB00715
[34] Liu Z F, Zhao Y L, Colin C, et al. Chemical weathering in Luzon, Philippines from clay mineralogy and major-element geochemistry of river sediments [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2009, 24(11): 2195-2205. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.09.025
[35] Liu Z F, Stattegger K. South China Sea fluvial sediments: an introduction [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 79: 507-508. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.11.003
[36] Liu J G, Xiang R, Chen M H, et al. Influence of the Kuroshio current intrusion on depositional environment in the Northern South China Sea: evidence from surface sediment records [J]. Marine Geology, 2011, 285(1-4): 59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2011.05.010
[37] Milliman J D, Farnsworth K L. River Discharge to the Coastal Ocean: A Global Synthesis[M]. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2011.
[38] Unverricht D, Nguyen T C, Heinrich C, et al. Suspended sediment dynamics during the inter-monsoon season in the subaqueous Mekong Delta and adjacent shelf, southern Vietnam [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 79: 509-519. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.10.008
[39] Xue Z, Liu J P, DeMaster D, et al. Sedimentary processes on the Mekong subaqueous delta: clay mineral and geochemical analysis [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 79: 520-528. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.07.012
[40] Tan M T, Dung L V, Bach L D, et al. Pliocene-Quaternary evolution of the continental shelf of central Vietnam based on high resolution seismic data [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 79: 529-539. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.08.001
[41] Hein H, Hein B, Pohlmann T. Recent sediment dynamics in the region of Mekong water influence [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2013, 110: 183-194. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2013.09.008
[42] Liu J P, DeMaster D J, Nittrouer C A, et al. A seismic study of the Mekong subaqueous delta: proximal versus distal sediment accumulation [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2017, 147: 197-212. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2017.07.009
[43] Kuang Z G, Zhong G F, Wang L L, et al. Channel-related sediment waves on the eastern slope offshore Dongsha Islands, northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 79: 540-551. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.09.025
[44] Shepard F P. Nomenclature based on sand-silt-clay ratios [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1954, 24(3): 151-158.
[45] 王中波, 密蓓蓓. 中国南部海域海底沉积物类型图[M]//吴自银, 温珍河. 中国海海洋地质系列图. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019
WANG Zhongbo, MI Beibei. Submarine sediment type map of Southern China Seas[M]//WU Ziyin, WEN Zhenhe. Map Series of Marine Geology of China Seas. Beijing: Science Press, 2019.
[46] 刘锡清. 中国边缘海的沉积物分区[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1996, 16(3):1-11
LIU Xiqing. Sedimentary division in marginal seas of China [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1996, 16(3): 1-11.
[47] Kenneth J D, José C, Johson R W, et al. Geological Map of the Circum-Pacific Region (1: 17 000 000, Pacific Basin Sheet)[Z]. U. S. Geological Survey, 2000.
[48] Emery. Bottom sediment map of Malacca Strait. In: Economic Commission for Asia and the Far East Committee for Co-ordination of Joint Prospecting for Mineral Resources in Asian Offshore Areas. Technical Bulletin[Z]. 1971, 4: 149-152.
[49] Emery. Distribution pattern of sediments on the continental shelves of western Indonesia. In: Economic Commission for Asia and the Far East Committee for Co-ordination of Joint Prospecting for Mineral Resources in Asian Offshore Areas. Technical Bulletin[Z]. 1969, 2: 79-82.
[50] Roonwal G S, Glasby G P, Chugh R. Mineralogy and geochemistry of surface sediments from the Bengal Fan, Indian Ocean [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 1997, 15(1): 33-41. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(97)90104-8
[51] 李景瑞, 刘升发, 冯秀丽, 等. 孟加拉湾中部表层沉积物稀土元素特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(4):41-50
LI Jingrui, LIU Shengfa, FENG Xiuli, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry of surface sediments in mid-Bengal Bay and implications for provenance [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(4): 41-50.
[52] Li J R, Liu S F, Shi X F, et al. Distributions of clay minerals in surface sediments of the Middle Bay of Bengal: source and transport pattern [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2017, 145: 59-67. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2017.06.017
[53] 孙兴全, 刘升发, 李景瑞, 等. 孟加拉湾南部表层沉积物稀土元素组成及其物源指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(2):80-89
SUN Xingquan, LIU Shengfa, LI Jingrui, et al. Rare earth element composition of the surface sediments from the South Bay of Bengal and its implications for provenance [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(2): 80-89.
[54] 曹鹏, 石学法, 李巍然, 等. 安达曼海东南部海域表层沉积物稀土元素特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(5):57-67
CAO Peng, SHI Xuefa, LI Weiran, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry of surface sediments in southeastern Andaman Sea and implications for provenance [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(5): 57-67.
[55] Exon N F, Haake F W, Hartmann M, et al. Morphology, water characteristics and sedimentation in the silled Sulu Sea, southeast Asia [J]. Marine Geology, 1981, 39(3-4): 165-195. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(81)90071-2
[56] Calvert S E, Pedersen T F, Thunell R C. Geochemistry of the surface sediments of the Sulu and South China Seas [J]. Marine Geology, 1993, 114(3-4): 207-231. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(93)90029-U
[57] Wan S M, Yu Z J, Clift P D, et al. History of Asian eolian input to the West Philippine Sea over the last one million years [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 326-328: 152-159. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2012.02.015
[58] Xu Z K, Li T G, Clift P D, et al. Quantitative estimates of Asian dust input to the western Philippine Sea in the mid-Late Quaternary and its potential significance for paleoenvironment [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2015, 16(9): 3182-3196. doi: 10.1002/2015GC005929
[59] 朱潇, 蒋富清, 冯旭光, 等. 菲律宾海沉积物中石英的来源及其搬运方式[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2018, 49(6):1190-1202
ZHU Xiao, JIANG Fuqing, FENG Xuguang, et al. The provenance and transportation of quartz in the Philippines Sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2018, 49(6): 1190-1202.
[60] Asahara Y, Tanaka T, Kamioka H, et al. Provenance of the north Pacific sediments and process of source material transport as derived from Rb-Sr isotopic systematics [J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 158(3-4): 271-291. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00056-X
[61] Xu Z K, Li A C, Jiang F Q, et al. Geochemical character and material source of sediments in the eastern Philippine Sea [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(6): 923-931.
[62] Savov I P, Hickey-Vargas R, D’antonio M, et al. Petrology and geochemistry of West Philippine Basin basalts and early Palau-Kyushu Arc volcanic clasts from ODP Leg 195, Site 1201D: implications for the early history of the Izu-Bonin-Mariana arc [J]. Journal of Petrology, 2006, 47(2): 277-299. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egi075
[63] 鄢全树, 石学法, 王昆山, 等. 西菲律宾海盆表层沉积物中的轻碎屑分区及物质来源[J]. 地质论评, 2007, 53(6):765-773
YAN Quanshu, SHI Xuefa, WANG Kunshan, et al. Provinces and material provenance of light detritus in the surficial sediments from the Western Philippine Sea [J]. Geological Review, 2007, 53(6): 765-773.
[64] Smith R B, Betzler C, Brass G W, et al. Depositional history of the Celebes Sea from ODP Sites 767 and 770 [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1990, 17(11): 2061-2064. doi: 10.1029/GL017i011p02061
[65] Nichols G, Hall R. History of the Celebes Sea Basin based on its stratigraphic and sedimentological record [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 1999, 17(1-2): 47-59. doi: 10.1016/S0743-9547(98)00034-8
[66] Dekov V M, Van Put A, Eisma D, et al. Single particle analysis of suspended matter in the Makasar Strait and Flores Sea with particular reference to tin-bearing particles [J]. Journal of Sea Research, 1999, 41(1-2): 35-53. doi: 10.1016/S1385-1101(98)00035-5
[67] Friedman G M. Case histories of coexisting reefs and terrigenous sediments: the Gulf of Elat (Red Sea), Java Sea, and Neogene Basin of the Negev, Israel [J]. Developments in Sedimentology, 1988, 42: 77-97.
[68] Mount J F. Mixing of siliciclastic and carbonate sediments in shallow shelf environments [J]. Geology, 1984, 12(7): 432-435. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1984)12<432:MOSACS>2.0.CO;2
[69] Xu Y H, Wang L, Yin X J, et al. The influence of the Sunda Strait opening on paleoenvironmental changes in the eastern Indian Ocean [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 146: 402-411. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.06.014
[70] 张杨硕, 乔淑卿, 石学法, 等. 泰国湾底质沉积物输运趋势[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(1):86-92
ZHANG Yangshuo, QIAO Shuqing, SHI Xuefa, et al. Moving trend of bottom sediments in Gulf of Thailand [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(1): 86-92.
[71] Emery K O, Niino H. Sediments of the Gulf of Thailand and adjacent continental shelf [J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1963, 74(5): 541-554. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1963)74[541:SOTGOT]2.0.CO;2
[72] Meksumpun S, Meksumpun C, Hoshika A, et al. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios of sediment in the gulf of Thailand: evidence for understanding of marine environment [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2005, 25(15): 1905-1915. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2005.04.009
[73] Srisuksawad K, Porntepkasemsan B, Nouchpramool S, et al. Radionuclide activities, geochemistry, and accumulation rates of sediments in the Gulf of Thailand [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1997, 17(8): 925-965. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(96)00065-9
[74] Liu S F, Zhang H, Zhu A M, et al. Distribution of rare earth elements in surface sediments of the western Gulf of Thailand: constraints from sedimentology and mineralogy [J]. Quaternary International, 2019, 527: 52-63. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2018.08.010
[75] Troelstra S R, Klaver G J, Kleijne A, et al. Actuomicropalaeontology and sediment distribution of three transects across the Banda Arc, Indonesia (Snellius-II expedition, Cruise G5) [J]. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 1989, 24(4): 477-489. doi: 10.1016/0077-7579(89)90125-7
[76] van de Paverd P J, Bjørklund K R. Frequency distribution of polycystine radiolarians in surface sediments of the Banda Sea, eastern Indonesia [J]. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 1989, 24(4): 511-521. doi: 10.1016/0077-7579(89)90129-4
[77] van Waveren I M. Palynofacies analysis of surface sediments from the northeastern Banda Sea (Indonesia) [J]. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 1989, 24(4): 501-509. doi: 10.1016/0077-7579(89)90128-2
[78] Kroon D, Ganssen G. Northern Indian Ocean upwelling cells and the stable isotope composition of living planktonic foraminifers [J]. Deep Sea Research Part A. Oceanographic Research Papers, 1989, 36(8): 1219-1236. doi: 10.1016/0198-0149(89)90102-7
-



 下载:
下载: