Depositional mode for the seamount-terrace-canyon sedimentary combination under the impacts of intermediate and deep circulation dynamics in the northern margin of the South China Sea
-
摘要:
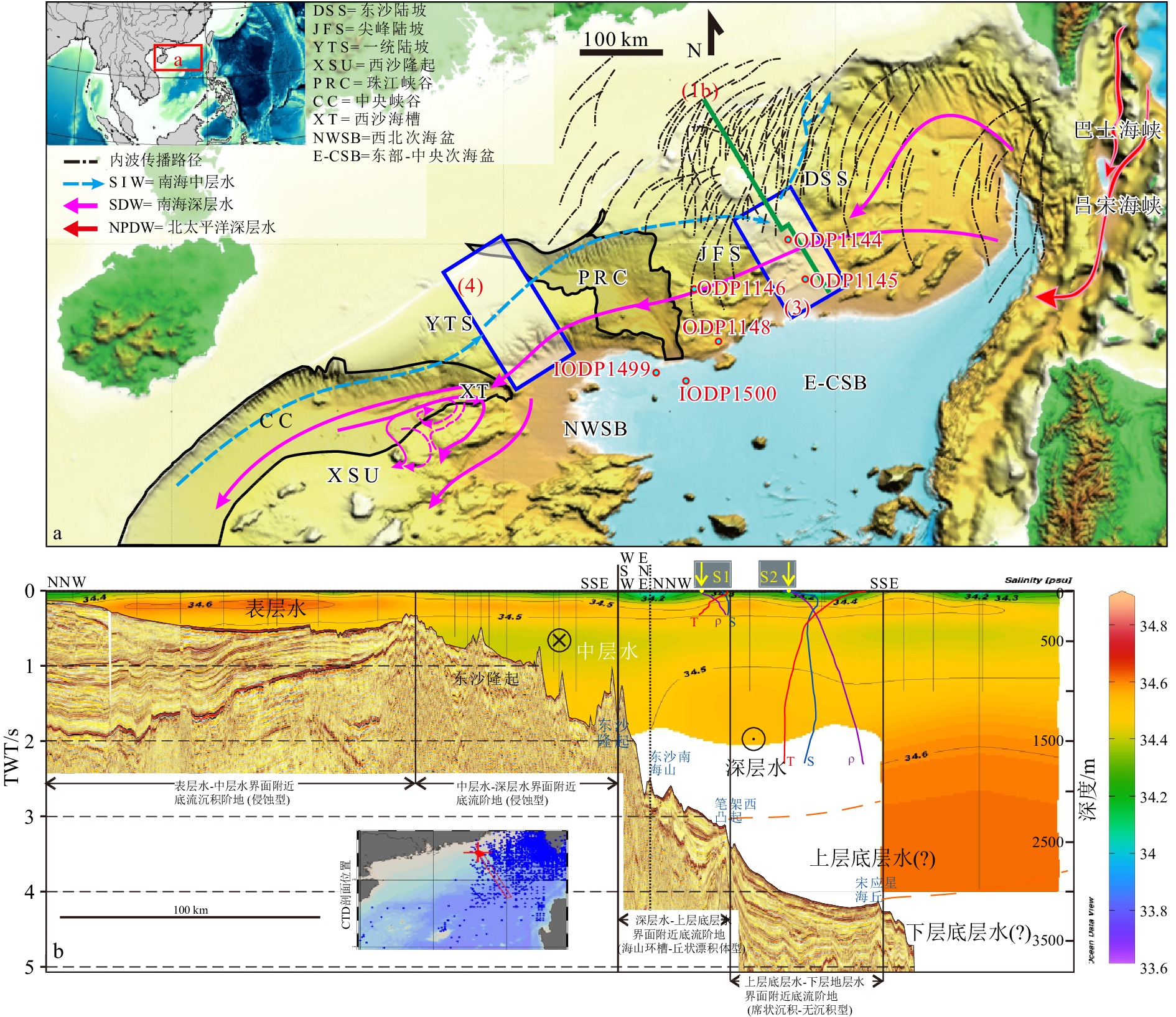
作为研究水-岩界面物质能量交换的天然实验室,南海北缘陆坡区具有复杂的地形地貌(如凸起海山、平坦阶地、下凹峡谷等),并发育不同类型的深水沉积体系(包括重力流滑移滑塌、浊流和底流沉积等)。基于高分辨率海底地形、地震反射资料,海水温盐深(CTD)观测资料,以及已发表的海洋沉积学及物理海洋数值模拟结果,本文针对南海北缘代表型陆坡区开展中—深层环流格局下海山-阶地-峡谷沉积效应分析。发现了尖峰陆坡区侵蚀型-海山型(环槽-丘状漂积体)和席状/无沉积型底流阶地的沉积组合,以及一统陆坡区海山相关底流沉积(环槽-丘状漂积体)-席状/无沉积型底流阶地-黏附型漂积体-陡坡滑塌/峡谷体系的沉积组合;揭示了这些典型深水沉积组合与南海中—深层环流动力格局的耦合关系。该成果对于深入了解深水沉积过程对中-深层动力格局的响应及其对于大陆边缘形态的塑造具有较好的启示意义。
Abstract:As a natural laboratory for studying energy and material exchange at water-rock interfaces, the northern slope area of the South China Sea possesses complex geomorphology, such as uplifted seamounts, flat terraces, and depressed canyons. It also develops various types of deep-water depositional systems, including gravity flow slides/slumps, turbidity currents, and contouritic deposits. Based on high-resolution bathymetry and seismic reflection data, CTD data, as well as published results from marine sedimentology and physical oceanic numerical simulations, this study focuses on analyzing the seamount-terrace-canyon sedimentary combination under intermediate and deep circulation bottom currents on the South China Sea northern margins. This study identifies the seamount-related moat-drift systems, the erosional/sheeted-nondepositional/seamount related contourite terraces, the plastered drifts, as well as the steep slopes with slides/slumps and canyons. This research reveals the coupling relationship between these deep-water sedimentary combinations and the hydrodynamic patterns among the intermediate and deep circulations. The findings obtained have significant implications for further understanding of the response of deep-water depositional processes to intermediate and deep circulation hydrodynamics and their impact on shaping continental margin morphology.
-

-
表 1 物理海洋CTD观测站位信息
Table 1. Information of CTD stations
站位号 位置 CTD最大采水深度/m S1 20.059°N 、117.424°E 208 S2 20.006°N 、117.573°E 1 791 T1 19.619°N 、114.150°E 544 T2 19.024°N 、114.424°E 1 604 -
[1] 汪品先. 深海沉积与地球系统[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(4):1-11
WANG Pinxian. Deep sea sediments and Earth system [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(4): 1-11.
[2] 田纪伟, 曲堂栋. 南海深海环流研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57(24):3115-3120 doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5269-x
TIAN Jiwei, QU Tangdong. Advances in research on the deep South China Sea circulation [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(24): 3115-3120. doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5269-x
[3] Mulder T, Hüneke H, Van Loon A J. Progress in deep-sea sedimentology[M]//Hüneke H, Mulder T. Deep-Sea Sediments: Developments in Sedimentology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2011: 1-24.
[4] Micallef A, Krastel S, Savini A. Submarine Geomorphology[M]. Cham: Springer, 2018.
[5] Stow D A V, Faugères J C, Howe J A, et al. Bottom currents, contourites and deep-sea sediment drifts: current state-of-the-art[C]//Stow D A V, Pudsey C J, Howe J A, et al. Deep-Water Contourite Systems: Modern Drifts and Ancient Series, Seismic and Sedimentary Characteristics. London: Geological Society of London, 2002: 7-20.
[6] Rebesco M, Camerlenghi A, Van Loon A J. Contourite research: a field in full development[C]//Rebesco M, Camerlenghi A. Contourites: Developments in Sedimentology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2008: 1-10.
[7] 高抒. 海洋沉积地质过程模拟: 性质与问题及前景[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(5):1-7
GAO Shu. Numerical modeling of marine sedimentary processes: the nature, scientific problems, and prospect [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(5): 1-7.
[8] Hernández-Molina F J, Serra N, Stow D A V, et al. Along-slope oceanographic processes and sedimentary products around the Iberian margin [J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2011, 31(5): 315-341.
[9] Rebesco M, Hernández-Molina F J, Van Rooij D, et al. Contourites and associated sediments controlled by deep-water circulation processes: State-of-the-art and future considerations [J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 352: 111-154. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.03.011
[10] 赵玉龙, 刘志飞. 等积体在全球大洋中的空间分布及其古环境意义: 国际大洋钻探计划对全球等深流沉积研究的贡献[J]. 地球科学进展, 2017, 32(12):1287-1296
ZHAO Yulong, LIU Zhifei. Spatial distribution of contourites in global ocean and its paleoclimatic significance: the contribution of international ocean drilling to the studies of contourites [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2017, 32(12): 1287-1296.
[11] 吴立新. 气候变暖背景下全球平均海洋环流在加速[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2020, 63(7):1039-1040 doi: 10.1007/s11430-020-9610-9
WU Lixin. Acceleration of global mean ocean circulation under the climate warming [J]. Science in China:Earth Sciences, 2020, 63(7): 1039-1040. doi: 10.1007/s11430-020-9610-9
[12] Chen H, Xie X N, Van Rooij D, et al. Depositional characteristics and processes of alongslope currents related to a seamount on the northwestern margin of the Northwest Sub-Basin, South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 355: 36-53. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.05.008
[13] Chen H, Xie X N, Zhang W Y, et al. Deep-water sedimentary systems and their relationship with bottom currents at the intersection of Xisha Trough and Northwest Sub-Basin, South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2016, 378: 101-113. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.11.002
[14] Chen H, Zhang W Y, Xie X N, et al. Sediment dynamics driven by contour currents and mesoscale eddies along continental slope: A case study of the northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2019, 409: 48-66. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2018.12.012
[15] Delivet S, Van Eetvelt B, Monteys X, et al. Seismic geomorphological reconstructions of Plio-Pleistocene bottom current variability at Goban Spur [J]. Marine Geology, 2016, 378: 261-275. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2016.01.001
[16] Ribó M, Puig P, Muñoz A, et al. Morphobathymetric analysis of the large fine-grained sediment waves over the Gulf of Valencia continental slope (NW Mediterranean) [J]. Geomorphology, 2016, 253: 22-37. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.09.027
[17] Shu Y Q, Xue H J, Wang D X, et al. Persistent and energetic bottom-trapped topographic Rossby waves observed in the southern South China Sea [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 24338. doi: 10.1038/srep24338
[18] Thran A C, Dutkiewicz A, Spence P, et al. Controls on the global distribution of contourite drifts: Insights from an eddy-resolving ocean model [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2018, 489: 228-240. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2018.02.044
[19] Tang Q S, Gulick S P S, Sun J, et al. Submesoscale features and turbulent mixing of an oblique anticyclonic eddy in the gulf of Alaska investigated by marine seismic survey data [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2020, 39: e2019JC015393.
[20] Turnewitsch R, Falahat S, Nycander J, et al. Deep-sea fluid and sediment dynamics-influence of hill- to seamount-scale seafloor topography [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2013, 127: 203-241. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.10.005
[21] Llave E, Hernández-Molina F J, Stow D A V, et al. Reconstructions of the Mediterranean Outflow Water during the Quaternary based on the study of changes in buried mounded drift stacking pattern in the Gulf of Cadiz [J]. Marine Geophysical Researches, 2007, 28(4): 379-394. doi: 10.1007/s11001-007-9040-7
[22] Hernández-Molina F J, Larter R D, Rebesco M, et al. Miocene reversal of bottom water flow along the Pacific Margin of the Antarctic Peninsula: stratigraphic evidence from a contourite sedimentary tail [J]. Marine Geology, 2006, 228(1-4): 93-116. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2005.12.010
[23] Preu B, Hernández-Molina F J, Violante R, et al. Morphosedimentary and hydrographic features of the northern Argentine margin: the interplay between erosive, depositional and gravitational processes and its conceptual implications [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers, 2013, 75: 157-174. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2012.12.013
[24] Thiéblemont A, Hernández-Molina F J, Miramontes E, et al. Contourite depositional systems along the Mozambique channel: the interplay between bottom currents and sedimentary processes [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers, 2019, 147: 79-99. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2019.03.012
[25] Rodrigues S, Roque C, Hernández-Molina F J, et al. The Sines contourite depositional system along the SW Portuguese margin: Onset, evolution and conceptual implications [J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 430: 106357. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106357
[26] Yenes M, Casas D, Nespereira J, et al. The Guadiaro-Baños contourite drifts (SW Mediterranean). A geotechnical approach to stability analysis [J]. Marine Geology, 2021, 437: 106505. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2021.106505
[27] Miramontes E, Thiéblemont A, Babonneau N, et al. Contourite and mixed turbidite-contourite systems in the Mozambique Channel (SW Indian Ocean): link between geometry, sediment characteristics and modelled bottom currents [J]. Marine Geology, 2021, 437: 106502. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2021.106502
[28] Hernández-Molina F J, Wåhlin A, Bruno M, et al. Oceanographic processes and morphosedimentary products along the Iberian margins: A new multidisciplinary approach [J]. Marine Geology, 2016, 378: 127-156. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.12.008
[29] Hernández-Molina F J, Campbell S, Badalini G, et al. Large bedforms on contourite terraces: Sedimentary and conceptual implications [J]. Geology, 2018, 46(1): 27-30. doi: 10.1130/G39655.1
[30] Steinmann L, Baques M, Wenau S, et al. Discovery of a giant cold-water coral mound province along the northern Argentine margin and its link to the regional Contourite Depositional System and oceanographic setting [J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 427: 106223. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106223
[31] Shanmugam G. A preliminary experimental study of turbidite fan deposits: discussion [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2003, 73(5): 838-839. doi: 10.1306/101002730838
[32] Moscardelli L, Wood L. New classification system for mass transport complexes in offshore Trinidad [J]. Basin Research, 2008, 20(1): 73-98. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2007.00340.x
[33] Twichell D C, Roberts D G. Morphology, distribution, and development of submarine canyons on the United States Atlantic continental slope between Hudson arid Baltimore Canyons [J]. Geology, 1982, 10(8): 408-412. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1982)10<408:MDADOS>2.0.CO;2
[34] Farre J A, McGregor B A, Ryan W B F, et al. Breaching the shelfbreak: passage from youthful to mature phase in submarine canyon evolution[M]//Stanley D J, Moore G T. The Shelfbreak: Critical Interface on Continental Margins. Tulsa: SEPM, 1983, 33: 25-39.
[35] Harris P T, Whiteway T. Global distribution of large submarine canyons: Geomorphic differences between active and passive continental margins [J]. Marine Geology, 2011, 285(1-4): 69-86. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2011.05.008
[36] 徐景平. 科学与技术并进: 近20年来海底峡谷浊流观测的成就和挑战[J]. 地球科学进展, 2013, 28(5):552-558
XU Jingping. Accomplishments and challenges in measuring turbidity currents in submarine canyons [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2013, 28(5): 552-558.
[37] 徐景平. 海底浊流研究百年回顾[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2014, 44(10):98-105
XU Jingping. Review on the research of submarine turbidity current in one hundred years [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2014, 44(10): 98-105.
[38] 钟广法. 海底峡谷科学深潜考察研究现状[J]. 地球科学进展, 2019, 34(11):1111-1119
ZHONG Guangfa. Current status of scientific deep-diving investigations in submarine canyons [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2019, 34(11): 1111-1119.
[39] Laursen J, Scholl D W, von Huene R. Neotectonic deformation of the central Chile margin: Deepwater forearc basin formation in response to hot spot ridge and seamount subduction[T]. Tectonics, 2002, 21(5): 2-1-2-27.
[40] Antobreh A A, Krastel S. Morphology, seismic characteristics and development of Cap Timiris Canyon, offshore Mauritania: A newly discovered canyon preserved-off a major arid climatic region [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2006, 23(1): 37-59. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2005.06.003
[41] Xu J P, Noble M A, Rosenfeld L K. In-situ measurements of velocity structure within turbidity currents [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 31(9): L09311.
[42] Xu J P, Swarzenski P W, Noble M, et al. Event-driven sediment flux in Hueneme and Mugu submarine canyons, southern California [J]. Marine Geology, 2010, 269(1-2): 74-88. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2009.12.007
[43] Gavey R, Carter L, Liu J T, et al. Frequent sediment density flows during 2006 to 2015, triggered by competing seismic and weather events: Observations from subsea cable breaks off southern Taiwan [J]. Marine Geology, 2017, 384: 147-158. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2016.06.001
[44] Zhang Y W, Liu Z F, Zhao Y L, et al. Long-term in situ observations on typhoon-triggered turbidity currents in the deep sea [J]. Geology, 2018, 46(8): 675-678. doi: 10.1130/G45178.1
[45] Gong C L, Wang Y M, Rebesco M, et al. How do turbidity flows interact with contour currents in unidirectionally migrating deep-water channels? [J]. Geology, 2018, 46(6): 551-554. doi: 10.1130/G40204.1
[46] Miramontes E, Jouet G, Thereau E, et al. The impact of internal waves on upper continental slopes: insights from the Mozambican margin (Southwest Indian Ocean) [J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2020, 45(6): 1469-1482. doi: 10.1002/esp.4818
[47] Gong C L, Wang Y M, Peng X C, et al. Sediment waves on the South China Sea Slope off southwestern Taiwan: Implications for the intrusion of the Northern Pacific Deep Water into the South China Sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 32(1): 95-109. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.12.005
[48] Gong C L, Wang Y M, Zhu W L, et al. Upper Miocene to Quaternary unidirectionally migrating deep-water channels in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(2): 285-308. doi: 10.1306/07121211159
[49] Sun Q L, Xie X N, Piper D J W, et al. Three dimensional seismic anatomy of multi-stage mass transport deposits in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea: their ages and kinematics [J]. Marine Geology, 2017, 393: 93-108. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2017.05.005
[50] Yin S R, Hernández-Molina F J, Zhang W Y, et al. The influence of oceanographic processes on contourite features: A multidisciplinary study of the northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2019, 415: 105967. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2019.105967
[51] Alford M H, Peacock T, MacKinnon J A, et al. The formation and fate of internal waves in the South China Sea [J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7550): 65-69. doi: 10.1038/nature14399
[52] Zhang Y W, Liu Z F, Zhao Y L, et al. Mesoscale eddies transport deep-sea sediments [J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 5937. doi: 10.1038/srep05937
[53] Xie X H, Liu Q, Zhao Z X, et al. Deep sea currents driven by breaking internal tides on the continental slope [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(12): 6160-6166.
[54] Lüdmann T, Wong H K, Berglar K. Upward flow of North Pacific Deep Water in the northern South China Sea as deduced from the occurrence of drift sediments [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2005, 32(5): L05614.
[55] Shao L, Li X J, Geng J H, et al. Deep water bottom current deposition in the northern South China Sea [J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2007, 50(7): 1060-1066. doi: 10.1007/s11430-007-0015-y
[56] Zhao Y L, Liu Z F, Zhang Y W, et al. In situ observation of contour currents in the northern South China Sea: applications for Deepwater sediment transport [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 430: 477-485. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2015.09.008
[57] 魏泽勋, 郑全安, 杨永增, 等. 中国物理海洋学研究70年: 发展历程、学术成就概览[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(10):23-64
WEI Zexun, ZHENG Quanan, YANG Yongzeng, et al. Physical oceanography research in China over past 70 years: Overview of development history and academic achievements [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2019, 41(10): 23-64.
[58] Wang P X, Li Q Y. The South China Sea: Paleoceanography and Sedimentology[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 2009: 25-73.
[59] 谢强, 肖劲根, 王东晓, 等. 基于8个准全球模式模拟的南海深层与底层环流特征分析[J]. 科学通报, 2013, 58(32):4000-4011 doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5791-5
XIE Qiang, XIAO Jingen, WANG Dongxiao, et al. Analysis of deep-layer and bottom circulations in the South China Sea based on eight quasi-global ocean model outputs [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(32): 4000-4011. doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5791-5
[60] Shu Y Q, Xue H J, Wang D X, et al. Meridional overturning circulation in the South China Sea envisioned from the high-resolution global reanalysis data GLBa0.08 [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2014, 119(5): 3012-3028. doi: 10.1002/2013JC009583
[61] Gan J P, Li H, Curchitser E N, et al. Modeling South China Sea circulation: Response to seasonal forcing regimes [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2006, 111(C6): C06034.
[62] Wynn R B, Stow D A V. Classification and characterisation of deep-water sediment waves [J]. Marine Geology, 2002, 192(1-3): 7-22. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(02)00547-9
[63] Wang D X, Xiao J G, Shu Y Q, et al. Progress on deep circulation and meridional overturning circulation in the South China Sea [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2016, 59(9): 1827-1833. doi: 10.1007/s11430-016-5324-6
[64] Cai Z Y, Gan J P, Liu Z Q, et al. Progress on the formation dynamics of the layered circulation in the South China Sea [J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2020, 181: 102246. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2019.102246
[65] 朱伟林, 钟锴, 李友川, 等. 南海北部深水区油气成藏与勘探[J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57(24):3121-3129 doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4940-y
ZHU Weiling, ZHONG Kai, LI Youchuan, et al. Characteristics of hydrocarbon accumulation and exploration potential of the northern South China Sea deepwater basins [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(24): 3121-3129. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4940-y
[66] 袁圣强. 南海北部陆坡区深水水道沉积体系研究[D]. 中国科学院海洋研究所博士学位论文, 2009: 121
YUAN Shengqiang. Sedimentary system of deepwater channel, the slope area of Northern South China Sea[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2009: 121.
[67] 苏明. 南海北部琼东南盆地中新世以来中央峡谷体系内部构成及沉积模式[D]. 中国地质大学(武汉), 2011: 138
SU Ming. Internal composition and depositional model of Central canyon system since Miocene in Qiongdongnan Basin northern South China Sea[D]. China University of Geosciences, 2011: 138. ] (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献信息, 请确认
[68] Ding W W, Li J B, Li J, et al. Morphotectonics and evolutionary controls on the Pearl River Canyon system, South China Sea [J]. Marine Geophysical Research, 2013, 34(3): 221-238.
[69] Gong C L, Wang Y M, Zhu W L, et al. The Central Submarine Canyon in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northwestern South China Sea: Architecture, sequence stratigraphy, and depositional processes [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(9): 1690-1702. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.06.005
[70] Li C, Lv C F, Chen G J, et al. Source and sink characteristics of the continental slope-parallel Central Canyon in the Qiongdongnan Basin on the northern margin of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 134: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.10.014
[71] Su M, Hsiung K H, Zhang C M, et al. The linkage between longitudinal sediment routing systems and basin types in the northern South China Sea in perspective of source-to-sink [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 111: 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.05.011
[72] Su M, Lin Z X, Wang C, et al. Geomorphologic and infilling characteristics of the slope-confined submarine canyons in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 424: 106166. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106166
[73] Zhong G F, Cartigny M J B, Kuang Z G, et al. Cyclic steps along the South Taiwan Shoal and West Penghu submarine canyons on the northeastern continental slope of the South China Sea [J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2015, 127(5-6): 804-824. doi: 10.1130/B31003.1
[74] 吴时国, 秦蕴珊. 南海北部陆坡深水沉积体系研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(5):922-930
WU Shiguo, QIN Yunshan. The research of deepwater depositional system in the northern South China Sea [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(5): 922-930.
[75] 何云龙. 琼东南盆地陆坡区重力流沉积特征及其成因机制[D]. 中国地质大学(武汉)博士学位论文, 2012: 131
HE Yunlong. The characteristics and mechanism of sediment gravity flow in slope Area in Qiongdongnan Basin[D]. Doctor Dissertation of China University of Geosciences, 2012: 131.
[76] 秦志亮. 南海北部陆坡块体搬运沉积体系的沉积过程、分布及成因研究[D]. 中国科学院海洋研究所博士学位论文, 2012: 121
QIN Zhiliang. Sedimentary process, distribution and mechanism of mass transport deposits, the slope area of Northern South China Sea[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2012: 121.
[77] Li W, Alves T M, Wu S G, et al. A giant, submarine creep zone as a precursor of large-scale slope instability offshore the Dongsha Islands (South China Sea) [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 451: 272-284. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.07.007
[78] Sun Q L, Alves T M, Lu X Y, et al. True volumes of slope failure estimated from a Quaternary mass-transport deposit in the northern South China Sea [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(6): 2642-2651. doi: 10.1002/2017GL076484
[79] 庞雄, 申俊, 袁立忠, 等. 南海珠江深水扇系统及其油气勘探前景[J]. 石油学报, 2006, 27(3):11-15,21
PANG Xiong, SHEN Jun, YUAN Lizhong, et al. Petroleum prospect in deep-water fan system of the Pearl River in the South China Sea [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2006, 27(3): 11-15,21.
[80] 庞雄, 彭大钧, 陈长民, 等. 三级“源-渠-汇”耦合研究珠江深水扇系统[J]. 地质学报, 2007, 81(6):857-864
PANG Xiong, PENG Dajun, CHEN Changmin, et al. Three hierarchies "Source-Conduit-Sink" coupling analysis of the Pearl River deep-water fan system [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2007, 81(6): 857-864.
[81] Zhu M Z, Graham S, Pang X, et al. Characteristics of migrating submarine canyons from the Middle Miocene to present: Implications for paleoceanographic circulation, northern South China Sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2010, 27(1): 307-319. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.05.005
[82] Wang X X, Zhuo H T, Wang Y M, et al. Controls of contour currents on intra-canyon mixed sedimentary processes: insights from the Pearl River Canyon, northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2018, 406: 193-213. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2018.09.016
[83] Chen H, Xie X N, Van Rooij D, et al. Depositional characteristics and spatial distribution of deep-water sedimentary systems on the northwestern middle-lower slope of the Northwest Sub-Basin, South China Sea [J]. Marine Geophysical Research, 2013, 34(3): 239-257.
[84] Li H, Wang Y M, Zhu W L, et al. Seismic characteristics and processes of the Plio-Quaternary unidirectionally migrating channels and contourites in the northern slope of the South China Sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 43: 370-380. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2012.12.010
[85] Chen H, Zhang W Y, Xie X N, et al. Linking oceanographic processes to contourite features: Numerical modelling of currents influencing a contourite depositional system on the northern South China Sea margin [J]. Marine Geology, 2022, 444: 106714. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2021.106714
[86] Wang X X, Kneller B, Wang Y M, et al. Along-strike Quaternary morphological variation of the Baiyun Sag, South China Sea: the interplay between deltas, pre-existing morphology, and oceanographic processes [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 122: 104640. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104640
[87] McCave I N, Hall I R. Size sorting in marine muds: processes, pitfalls, and prospects for paleoflow-speed proxies [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2006, 7(10): Q10N05.
[88] Zhong Y, Chen Z, Li L, et al. Bottom water hydrodynamic provinces and transport patterns of the northern South China Sea: evidence from grain size of the terrigenous sediments [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2017, 140: 11-26. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2017.01.023
[89] Adams G R, Jager A J, Roering C. Investigations of rock fractures around deep level gold mine stopes[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd US Symposium on Rock Mechanics. Cambridge: American Rock Mechanics Association, 1981: 213-218.
[90] Yin S R, Hernández-Molina F J, Lin L, et al. Plate convergence controls long-term full-depth circulation of the South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2023, 459: 107050. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2023.107050
[91] Hernández-Molina F, Llave E, Stow D A V. Continental slope contourites[M]//Rebesco M, Camerlenghi A. Contourites: Developments in Sedimentology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2008, 60: 379-408.
[92] Viana A R, Almeida Jr W, Machado L C. Different styles of canyon infill related to gravity and bottom current processes: Examples from the upper slope of the Se Brazilian margin[C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Congress of the Brazilian Geophysical Society. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers, 1999.
[93] He Y L, Xie X N, Kneller B C, et al. Architecture and controlling factors of canyon fills on the shelf margin in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 41: 264-276. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2012.03.002
[94] Chen Y H, Yao G S, Wang X F, et al. Flow processes of the interaction between turbidity flows and bottom currents in sinuous unidirectionally migrating channels: An example from the Oligocene channels in the Rovuma Basin, offshore Mozambique [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2020, 404: 105680. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2020.105680
[95] de Castro S, Hernández-Molina F J, de Weger W, et al. Contourite characterization and its discrimination from other deep-water deposits in the Gulf of Cadiz contourite depositional system [J]. Sedimentology, 2021, 68(3): 987-1027. doi: 10.1111/sed.12813
[96] Fonnesu M, Palermo D, Galbiati M, et al. A new world-class deep-water play-type, deposited by the syndepositional interaction of turbidity flows and bottom currents: The giant Eocene Coral Field in northern Mozambique [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 111: 179-201. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.07.047
[97] Fuhrmann A, Kane I A, Clare M A, et al. Hybrid turbidite-drift channel complexes: An integrated multiscale model [J]. Geology, 2020, 48(6): 562-568. doi: 10.1130/G47179.1
[98] Puzrin A M, Gray T E, Hill A J. Significance of the actual nonlinear slope geometry for catastrophic failure in submarine landslides [J]. Proceedings of The Royal Society A:Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2015, 471(2175): 20140772. doi: 10.1098/rspa.2014.0772
[99] Laberg J S, Vorren T O. The Trænadjupet Slide, offshore Norway-morphology, evacuation and triggering mechanisms [J]. Marine Geology, 2000, 171(1-4): 95-114. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(00)00112-2
[100] Lastras G, Canals M, Amblas D, et al. Eivissa slides, western Mediterranean Sea: morphology and processes [J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2006, 26(4): 225-233. doi: 10.1007/s00367-006-0032-4
[101] Santek D A, Winguth A. A satellite view of internal waves induced by the Indian Ocean tsunami [J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2007, 28(13-14): 2927-2936. doi: 10.1080/01431160601094534
[102] Pomar L, Morsilli M, Hallock P, et al. Internal waves, an under-explored source of turbulence events in the sedimentary record [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2012, 111(1-2): 56-81. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2011.12.005
-




 下载:
下载: