Study on the enrichment and mineralization of rare earth element cerium by marine bacteria
-
摘要:
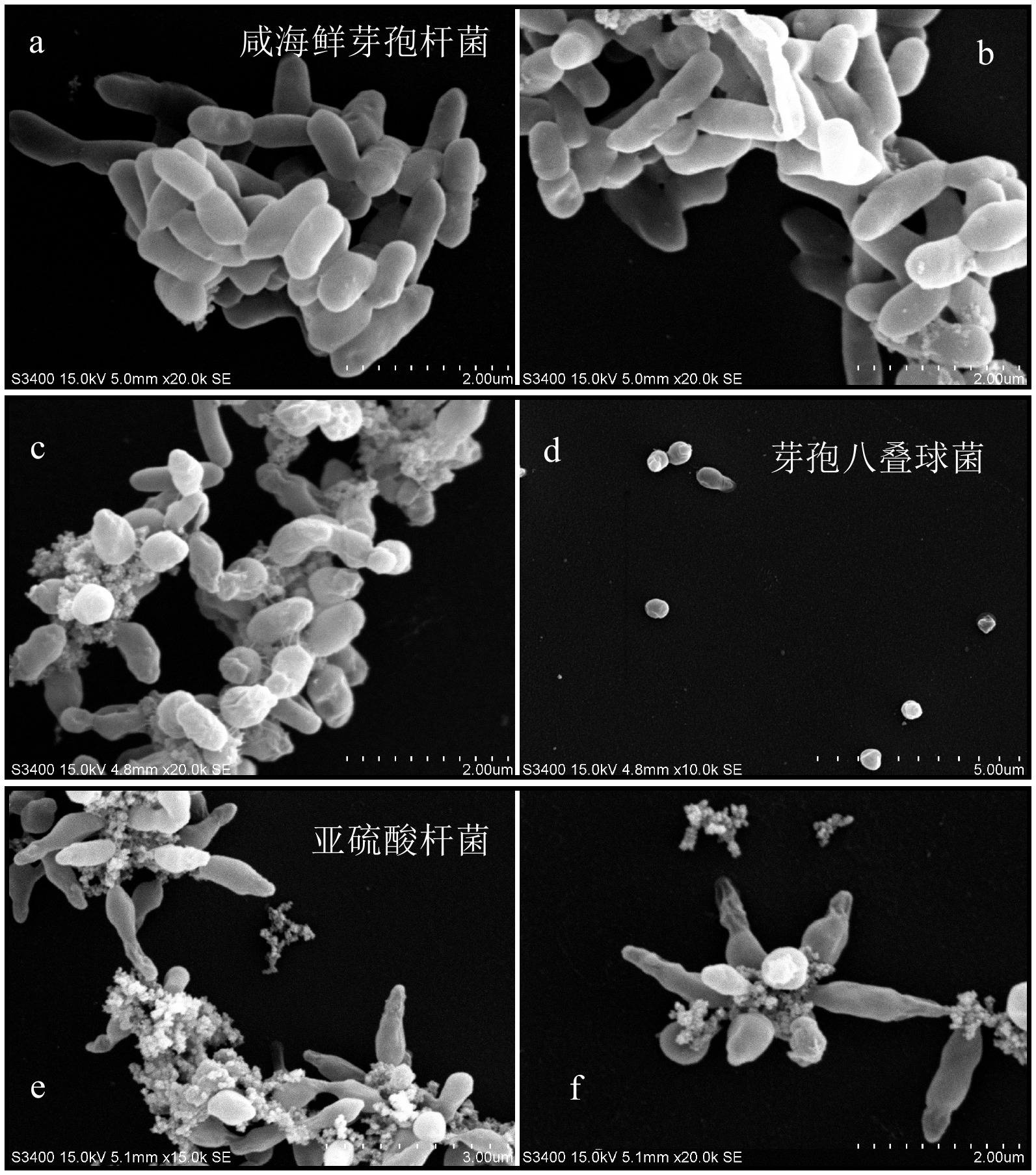
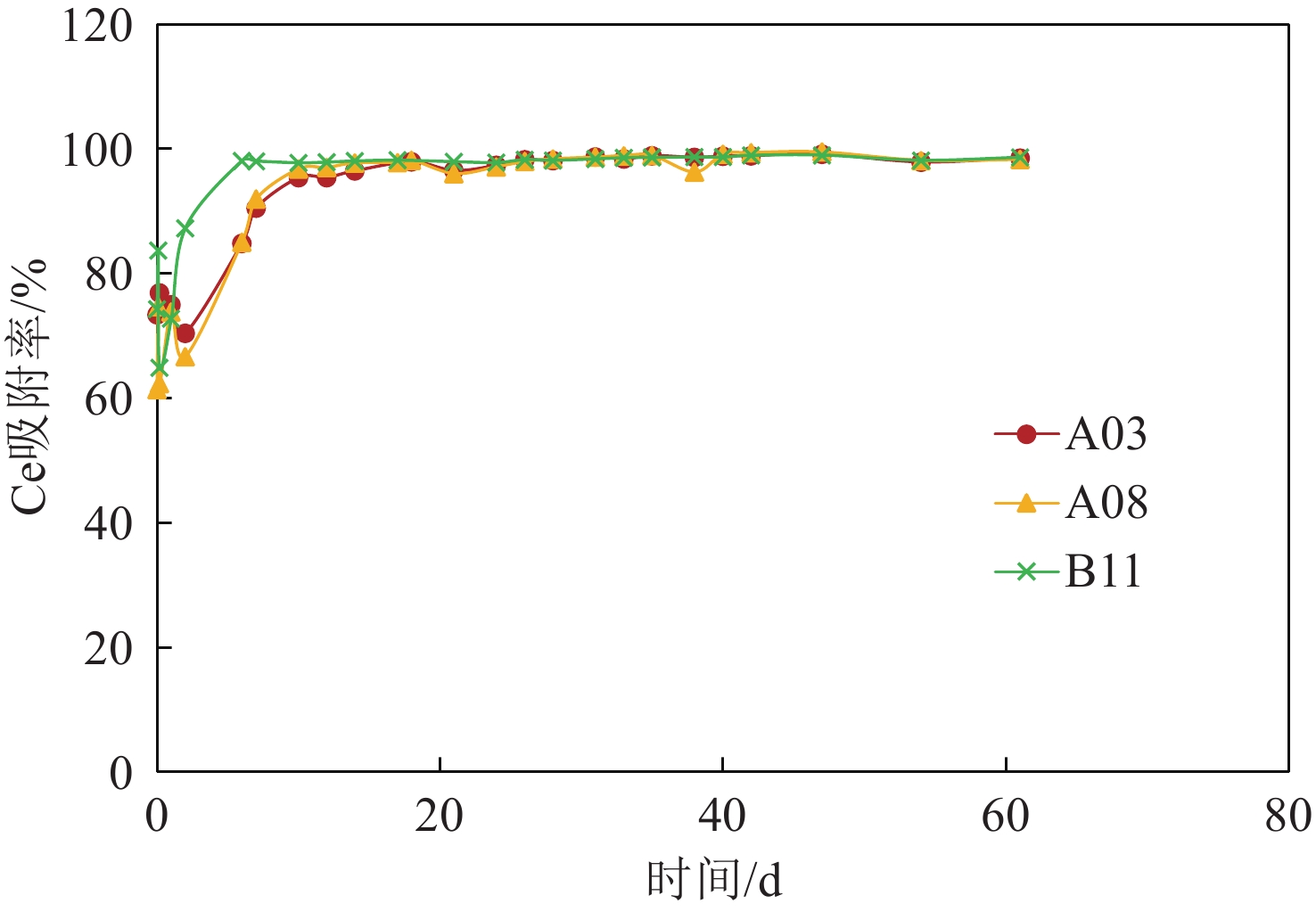
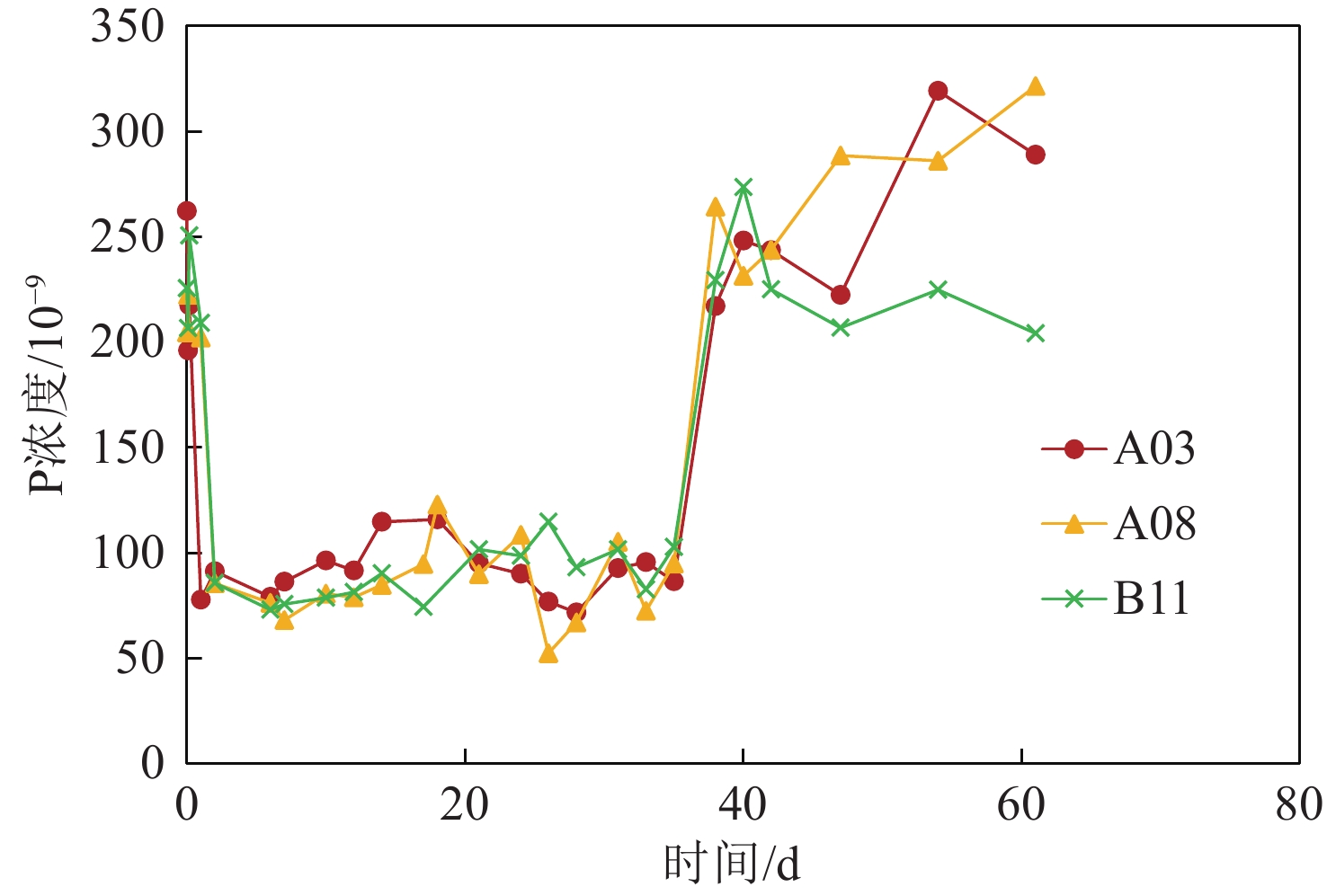
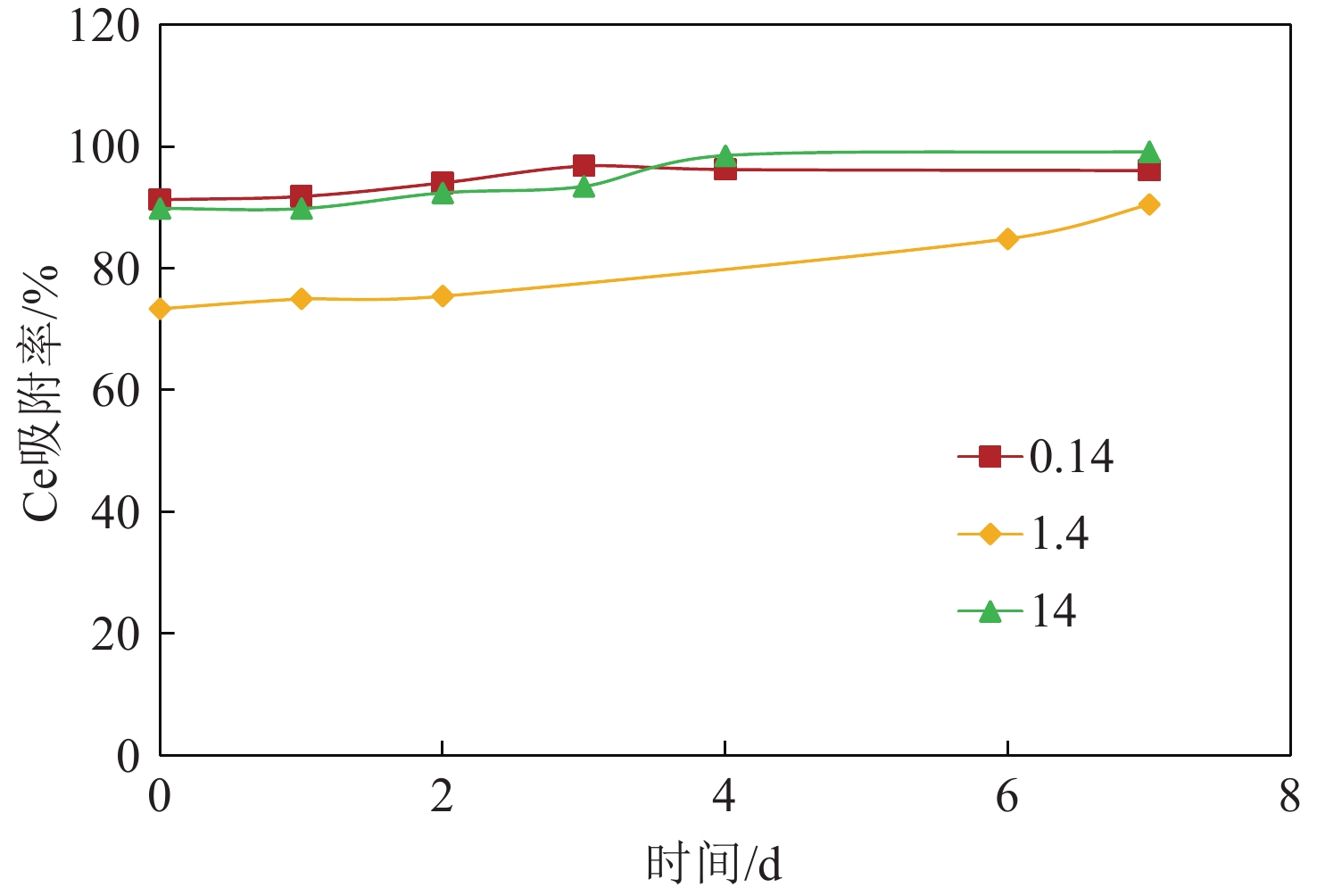
采用从深海沉积物样品中分离培养的海洋微生物,分别进行几种海洋细菌(Jeotgalibacillus sp., Paenisporosarcina sp., Sulfitobacter sp.)对稀土元素Ce的富集成矿过程的模拟实验。实验过程中利用ICP-MS、SEM、TEM等分析测试手段考察了微生物与稀土元素的相互作用过程。结果表明,三种海洋细菌对稀土Ce都有吸附富集作用,海洋细菌吸附富集稀土元素Ce的效率主要与细菌密度和稀土元素浓度有关,不同的海洋细菌对稀土元素的富集能力也有所不同。海洋细菌吸附富集稀土Ce并矿化的过程中,稀土元素Ce首先被吸附在细胞表面形成成核点,随后在细胞表面被矿化形成含稀土Ce的非晶相结构的矿物颗粒。通过考察海洋细菌对稀土Ce的生物成矿过程,进一步探讨了海洋微生物富集稀土成矿的过程和作用机制。
Abstract:Using Marine microorganisms isolated and cultured from deep-sea sediment samples, the accumulation and mineralization of rare earth element Ce by several marine bacteria (Jeotgalibacillus sp., Paenisporosarcina sp., Sulfitobacter sp.) were simulated. The interaction between marine bacteria and Ce was analyzed by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and other analytical methods. It was found that the three bacteria species could adsorb and enrich Ce, and the efficiencies of the adsorption and enrichment by the marine bacteria were mainly related to the bacteria density and the Ce concentration. In addition, the adsorption capacity of different marine bacterium to Ce was different. In the process of adsorption, enrichment, and mineralization of rare earth Ce by marine bacteria, rare earth Ce was first adsorbed at the cell surface to form nucleation cores, and then mineralized to form amorphous-structured mineral particles containing Ce on the cell surface. At last, the process and mechanism of rare earth mineralization enriched by marine microorganisms were further discussed.
-

-
[1] Liu S L, Fan H R, Liu X, et al. Global rare earth elements projects: New developments and supply chains[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2023, 157:105428. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2023.105428
[2] 黄牧, 石学法, 毕东杰, 等. 深海稀土资源勘查开发研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2021, 31(10):2665-2681 doi: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-37993
HUANG Mu, SHI Xuefa, BI Dongjie, et al. Advances on study of exploration and development of deep-sea rare earth resources[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2021, 31(10):2665-2681. doi: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-37993
[3] Kato Y, Fujinaga K, Nakamura K, et al. Deep-sea mud in the Pacific Ocean as a potential resource for rare-earth elements[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2011, 4(8):535-539. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1185
[4] Yuan X Y, Zhong R C, Xiong X, et al. Transition from carbonatitic magmas to hydrothermal brines: Continuous dilution or fluid exsolution?[J]. Science Advances, 2023, 9(29):eadh0458. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adh0458
[5] He Y L, Ma L Y, Li X R, et al. Mobilization and fractionation of rare earth elements during experimental bio-weathering of granites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2023, 343:384-395. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2022.12.027
[6] Ren J B, Jiang X X, He G W, et al. Enrichment and sources of REY in phosphate fractions: Constraints from the leaching of REY-rich deep-sea sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2022, 335:155-168. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2022.08.035
[7] Fan C X, Xu C, Shi A G, et al. Origin of heavy rare earth elements in highly fractionated peraluminous granites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2023, 343:371-383. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2022.12.019
[8] 伍普球, 周靖雯, 黄健, 等. 离子吸附型稀土矿床中稀土的富集—分异特征: 铁氧化物—黏土矿物复合体的约束[J]. 地球化学, 2022, 51(3):271-282
WU Puqiu, ZHOU Jingwen, HUANG Jian, et al. Enrichment and fractionation of rare earth elements in ion-adsorption rare earth elements deposits: Constraints of iron oxide-clay mineral composites[J]. Geochimica, 2022, 51(3):271-282.
[9] Dubinin A V, Sval’nov V N. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in ferromanganese micro- and macronodules from the Pacific nonproductive zone[J]. Lithology and Mineral Resources, 2000, 35(6):520-537. doi: 10.1023/A:1026693314236
[10] Takahashi Y, Hayasaka Y, Morita K, et al. Transfer of rare earth elements (REE) from manganese oxides to phosphates during early diagenesis in pelagic sediments inferred from REE patterns, X-ray absorption spectroscopy, and chemical leaching method[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2015, 49(6):653-674. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.2.0393
[11] 杨娅敏, 曾志刚, 殷学博, 等. 深海富REY泥中稀土元素赋存载体及其富集机制研究进展[J]. 海洋科学, 2019, 43(8):93-107 doi: 10.11759/hykx20181129002
YANG Yamin, ZENG Zhigang, YIN Xuebo, et al. Advances in research on the host and the enrichment mechanism of REY-rich mud in deep-sea Sediments[J]. Marine Sciences, 2019, 43(8):93-107. doi: 10.11759/hykx20181129002
[12] Yasukawa K, Liu H J, Fujinaga K, et al. Geochemistry and mineralogy of REY-rich mud in the eastern Indian Ocean[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 93:25-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.07.005
[13] 刘明, 孙晓霞, 石学法, 等. 印度洋钙质软泥和硅质软泥稀土元素组成和富集机制[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(1):58-71
LIU Ming, SUN Xiaoxia, SHI Xuefa, et al. Composition and enrichment of rare earth elements in calcareous and siliceous ooze in the Indian Ocean[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2019, 41(1):58-71.
[14] 任江波, 何高文, 朱克超, 等. 富稀土磷酸盐及其在深海成矿作用中的贡献[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(6):1312-1325 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.06.011
REN Jiangbo, HE Gaowen, ZHU Kechao, et al. REY-rich phosphate and its effects on the deep-sea mud mineralization[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(6):1312-1325. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.06.011
[15] 徐力, 曾令熙, 熊文良, 等. 西太平洋深海底泥中稀土元素赋存状态[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2022(1):195-199 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2022.01.028
XU Li, ZENG Lingxi, XIONG Wenliang, et al. Occurrence of rare earth elements in deep-sea mud from the Western Pacific Ocean[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2022(1):195-199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2022.01.028
[16] Dong H L, Huang L Q, Zhao L D, et al. A critical review of mineral–microbe interaction and co-evolution: mechanisms and applications[J]. National Science Review, 2022, 9(10):nwac128. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwac128
[17] Røy H, Kallmeyer J, Adhikari R R, et al. Aerobic microbial respiration in 86-million-year-old deep-sea red clay[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6083):922-925. doi: 10.1126/science.1219424
[18] Knoll A H. Biomineralization and evolutionary history[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2003, 54(1):329-356. doi: 10.2113/0540329
[19] 蒋宏忱, 黄柳琴, 冯灿, 等. 地质微生物: 地球环境中的"协调员"[J]. 自然杂志, 2016, 38(3):209-214
JIANG Hongchen, HUANG Liuqin, FENG Can, et al. Microbes: coordinators of the earth environments[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2016, 38(3):209-214.
[20] 姜明玉, 胡艺豪, 于心科, 等. 大洋铁锰结核的微生物成矿过程及其研究进展[J]. 海洋科学, 2020, 44(7):156-164 doi: 10.11759/hykx20200121002
JIANG Mingyu, HU Yihao, YU Xinke, et al. Advances in research on biological mineralization process of marine ferromanganese nodules[J]. Marine Sciences, 2020, 44(7):156-164. doi: 10.11759/hykx20200121002
[21] Wang X H, Muller W E G. Marine biominerals: perspectives and challenges for polymetallic nodules and crusts[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2009, 27(6):375-383. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2009.03.004
[22] Sulu-Gambari F, Seitaj D, Behrends T, et al. Impact of cable bacteria on sedimentary iron and manganese dynamics in a seasonally-hypoxic marine basin[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2016, 192:49-69. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2016.07.028
[23] 王风平, 彭方, 黄英, 等. 现代海洋极端环境微生物的地质作用及其分子和同位素响应年度报告[J]. 科技资讯, 2016, 14(21):177-178 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3791.2016.21.108
WANG Fengping, PENG Fang, HUANG Ying, et al. The geological roles and isotopic responses of the extremophiles in the modern ocean[J]. Science & Technology Information, 2016, 14(21):177-178. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3791.2016.21.108
[24] 王苑如, 崔鸿鹏, 李继东, 等. 西太平洋多金属结核区表层沉积物细菌群落结构及其对沉积扰动的响应[J]. 海洋学研究, 2021, 39(2):21-32 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2021.02.003
WANG Yuanru, CUI Hongpeng, LI Jidong, et al. The structure of bacterial communities and its response to the sedimentary disturbance in the surface sediment of western Pacific polymetallic nodule area[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2021, 39(2):21-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2021.02.003
[25] 李友训, 李富超, 秦松, 等. 东太平洋深海沉积物中DNA的提取及细菌多样性初步分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2008, 32(12):69-74
LI Youxun, LI Fuchao, QIN Song, et al. DNA extraction and DGGE analysis of the bacterial community of a deep-sea sediment sample collected at the East Pacific Ocean[J]. Marine Sciences, 2008, 32(12):69-74.
[26] Cupit C, Lomstein B A, Kjeldsen K U. Contrasting community composition of endospores and vegetative Firmicutes in a marine sediment suggests both endogenous and exogenous sources of endospore accumulation[J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 2019, 11(3):352-360. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12679
[27] Jiang M Y, Ohnuki T, Tanaka K, et al. Post-adsorption process of Yb phosphate nano-particle formation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2012, 93:30-46. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.06.016
[28] Jiang M Y, Ohnuki T, Utsunomiya S. Biomineralization of middle rare earth element samarium in yeast and bacteria systems[J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2018, 35(5):375-384. doi: 10.1080/01490451.2017.1377320
[29] Seweryn P, Van L B, Kjeldgaard M, et al. Structural insights into the bacterial carbon-phosphorus lyase machinery[J]. Nature, 2015, 525(7567):68-72. doi: 10.1038/nature14683
[30] Borrok D, Turner B F, Fein J B. A universal surface complexation framework for modeling proton binding onto bacterial surfaces in geologic settings[J]. American Journal of Science, 2005, 305(6-8):826-853. doi: 10.2475/ajs.305.6-8.826
[31] Borrok D M, Fein J B. The impact of ionic strength on the adsorption of protons, Pb, Cd, and Sr onto the surfaces of Gram negative bacteria: testing non-electrostatic, diffuse, and triple-layer models[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2005, 286(1):110-126. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2005.01.015
[32] Liu Y X, Alessi D S, Owttrim G W, et al. Cell surface acid-base properties of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus: influences of nitrogen source, growth phase and N: P ratios[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2016, 187:179-194. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2016.05.023
[33] Ngwenya B T, Mosselmans J F W, Magennis M, et al. Macroscopic and spectroscopic analysis of lanthanide adsorption to bacterial cells[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009, 73(11):3134-3147. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.03.018
-



 下载:
下载: