Subduction plate boundary thrust system and dynamic characteristics in the Western Pacific
-
摘要:
俯冲带是地球上最大地震的发源地。俯冲板块正断层为海水进入上地幔,引起蛇纹石化提供通道,其地震可能引发大海啸。研究其动力学机制,对推动俯冲带动力学过程研究及保护人类生命安全都具有重要意义。本文综述了西太平洋汤加海沟、马里亚纳海沟、伊豆-小笠原海沟和日本海沟俯冲板块外缘隆起带到海沟附近的正断层分布与变形特征,定量化阐明了地球动力学模拟方法揭示的西太平洋俯冲板块正断层形成过程。研究发现汤加海沟和马里亚纳海沟的正断层平均断距最大;俯冲板片有效弹性厚度变化直接影响正断层形成区域,而有效弹性厚度与板块年龄相关性较大。本文系统性回顾了西太平洋俯冲动力学研究并且提出了对未来相关研究的启示。
Abstract:The majority of the world's greatest earthquakes are generated in subduction zones. Normal faults in subducting plates provide pathways for seawater intrusion, which facilitates mantle serpentinization and consequently triggers seismic activities or large tsunamis. The formation mechanisms of these normal faults need to be better understood to advance the understanding of subduction zone dynamics and ensuring human life safety. This paper reviews the characteristics of normal faults and deformation of subducting plates in the Tonga Trench, Mariana Trench, Izu-Bonin Trench, and Japan Trench in the western Pacific Ocean, describe in quantitative detail the formation of bending-related normal faults through geodynamic modeling. The study finds that the Tonga Trench and Mariana Trench exhibit the largest average fault throws among these subduction systems. The variations in effective elastic thickness of the subducting plate directly influence the distribution of normal faulting region. There is a significant correlation between plate effective elastic thickness and plate age. This paper provides a systematic review of research on the dynamics of the Western Pacific subduction zone and offers insights for future studies in this field.
-
Key words:
- subduction zone /
- normal fault /
- geodynamics /
- Western Pacific
-

-
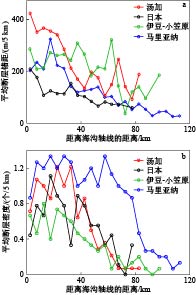
图 3 汤加海沟、日本海沟、伊豆-小笠原海沟和马里亚纳海沟跨海沟剖面上每 5 km的平均断层错距(a)和断层密度(b)[16]
Figure 3.
-
[1] de Bremaecker J C. Is the oceanic lithosphere elastic or viscous?[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1977, 82(14):2001-2004. doi: 10.1029/JB082i014p02001
[2] Hilde T W C. Sediment subduction versus accretion around the pacific[J]. Tectonophysics, 1983, 99(2-4):381-397. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(83)90114-2
[3] Melosh H J. Dynamic support of the outer rise[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1978, 5(5):321-324. doi: 10.1029/GL005i005p00321
[4] Parsons B, Molnar P. The origin of outer topographic rises associated with trenches[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 1976, 45(3):707-712. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1976.tb06919.x
[5] Watts A B, Taiwani M. Gravity anomalies seaward of deep‐sea trenches and their tectonic implications[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 1974, 36(1):57-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1974.tb03626.x
[6] Beavan J, Wang X, Holden C, et al. Near-simultaneous great earthquakes at Tongan megathrust and outer rise in September 2009[J]. Nature, 2010, 466(7309):959-963. doi: 10.1038/nature09292
[7] Christensen D H, Ruff L J. Outer-rise earthquakes and seismic coupling[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1983, 10(8):697-700. doi: 10.1029/GL010i008p00697
[8] Kanamori H. Seismological evidence for a lithospheric normal faulting—the Sanriku earthquake of 1933[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 1971, 4(4):289-300. doi: 10.1016/0031-9201(71)90013-6
[9] Lay T, Ammon C J, Kanamori H, et al. The 2009 Samoa-Tonga great earthquake triggered doublet[J]. Nature, 2010, 466(7309):964-968. doi: 10.1038/nature09214
[10] Kao H, Chen W P. Seismicity in the outer rise-forearc region and configuration of the subducting lithosphere with special reference to the Japan Trench[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 1996, 101(B12):27811-27831. doi: 10.1029/96JB01760
[11] Lefeldt M, Ranero C R, Grevemeyer I. Seismic evidence of tectonic control on the depth of water influx into incoming oceanic plates at subduction trenches[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2012, 13(5):Q05013.
[12] Kobayashi K, Nakanishi M, Tamaki K, et al. Outer slope faulting associated with the western Kuril and Japan trenches[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 1998, 134(2):356-372. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246x.1998.00569.x
[13] Turcotte D L, McAdoo D C, Caldwell J G. An elastic-perfectly plastic analysis of the bending of the lithosphere at a trench[J]. Tectonophysics, 1978, 47(3-4):193-205. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(78)90030-6
[14] Ivandic M, Grevemeyer I, Berhorst A, et al. Impact of bending related faulting on the seismic properties of the incoming oceanic plate offshore of Nicaragua[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2008, 113(B5):B05410.
[15] Zhou Z Y, Lin J, Zhang F. Modeling of normal faulting in the subducting plates of the Tonga, Japan, Izu-Bonin and Mariana Trenches: implications for near-trench plate weakening[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2018, 37(11):53-60. doi: 10.1007/s13131-018-1146-z
[16] Zhou Z Y, Lin J, Behn M D, et al. Mechanism for normal faulting in the subducting plate at the Mariana Trench[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(11):4309-4317. doi: 10.1002/2015GL063917
[17] Ranero C R, Morgan J P, McIntosh K, et al. Bending-related faulting and mantle serpentinization at the Middle America trench[J]. Nature, 2003, 425(6956):367-373. doi: 10.1038/nature01961
[18] Ranero C R, Sallarès V. Geophysical evidence for hydration of the crust and mantle of the Nazca plate during bending at the North Chile Trench[J]. Geology, 2004, 32(7):549-552. doi: 10.1130/G20379.1
[19] Zhang F, Lin J, Zhou Z Y, et al. Intra- and intertrench variations in flexural bending of the Manila, Mariana and global trenches: implications on plate weakening in controlling trench dynamics[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2018, 212(2):1429-1449. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggx488
[20] Tilmann F J, Grevemeyer I, Flueh E R, et al. Seismicity in the outer rise offshore southern Chile: indication of fluid effects in crust and mantle[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 269(1-2):41-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2008.01.044
[21] Wessel P, Smith W H F. New, improved version of generic mapping tools released[J]. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 1998, 79(47):579-579. doi: 10.1029/98EO00426
[22] Zhang F, Lin J, Zhan W H. Variations in oceanic plate bending along the Mariana Trench[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2014, 401:206-214. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2014.05.032
[23] Masson D G. Fault patterns at outer trench walls[J]. Marine Geophysical Researches, 1991, 13(3):209-225. doi: 10.1007/BF00369150
[24] Ranero C R, Villaseñor A, Morgan J P, et al. Relationship between bend-faulting at trenches and intermediate-depth seismicity[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2005, 6(12):Q12002.
[25] Zhou Z Y, Lin J. Elasto-plastic deformation and plate weakening due to normal faulting in the subducting plate along the Mariana Trench[J]. Tectonophysics, 2018, 734-735:59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2018.04.008
[26] 林间, 孙珍, 李家彪, 等. 南海成因: 岩石圈破裂与俯冲带相互作用新认识[J]. 科技导报, 2020, 38(18):35-39
LIN Jian, SUN Zhen, LI Jiabiao, et al. South China Seabasin opening: Lithospheric rifting and interactionwith surroundingsubduction zones[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2020, 38(18):35-39.
[27] 林间, 李家彪, 徐义刚, 等. 南海大洋钻探及海洋地质与地球物理前沿研究新突破[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(10):125-140
LIN Jian, LI Jiabiao, XU Yigang, et al. Ocean drilling and major advances in marine geological and geophysical research of the South China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(10):125-140.
[28] Lin J, Xu Y G, Sun Z, et al. Mantle upwelling beneath the South China Sea and links to surrounding subduction systems[J]. National Science Review, 2019, 6(5):877-881. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwz123
[29] Sun Z, Lin J, Qiu N, et al. The role of magmatism in the thinning and breakup of the South China Sea continental margin: special topic: the South China Sea Ocean Drilling[J]. National Science Review, 2019, 6(5):871-876. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwz116
[30] 汪品先, 翦知湣. 探索南海深部的回顾与展望[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2019, 49(10): 1590-1606
WANG Pinxian, JIAN Zhimin. Exploring the deep South China Sea: retrospects and prospects[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2019, 62(10): 1473-1488.
[31] 徐敏, 狄会哲, 周志远, 等. 俯冲带水圈-岩石圈相互作用研究进展与启示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(5):58-70
XU Min, DI Huizhe, ZHOU Zhiyuan, et al. Interaction between hydrosphere and lithosphere in subduction zones[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(5):58-70.
[32] Han S S, Carbotte S M, Canales J P, et al. Seismic reflection imaging of the Juan de Fuca plate from ridge to trench: new constraints on the distribution of faulting and evolution of the crust prior to subduction[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2016, 121(3):1849-1872. doi: 10.1002/2015JB012416
[33] Zhu G H, Wiens D A, Yang H F, et al. Upper mantle hydration indicated by decreased shear velocity near the southern Mariana Trench from Rayleigh wave tomography[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(15):e2021GL093309. doi: 10.1029/2021GL093309
[34] Zhang J Y, Zhang F, Lin J, et al. Yield failure of the subducting plate at the Mariana Trench[J]. Tectonophysics, 2021, 814:228944. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2021.228944
[35] 张江阳, 林间, 张帆, 等. 西太平洋俯冲带岩石圈变形研究[J]. 科技导报, 2023, 41(2):29-34
ZHANG Jiangyang, LIN Jian, ZHANG Fan, et al. Lithospheric deformation in western Pacific subduction zones[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2023, 41(2):29-34.
-




 下载:
下载: