Characteristics of rare earth elements in boron-rich thermal waters of the Xianshuihe Fault Belt Zone and its indication to the sources of boron
-
摘要:
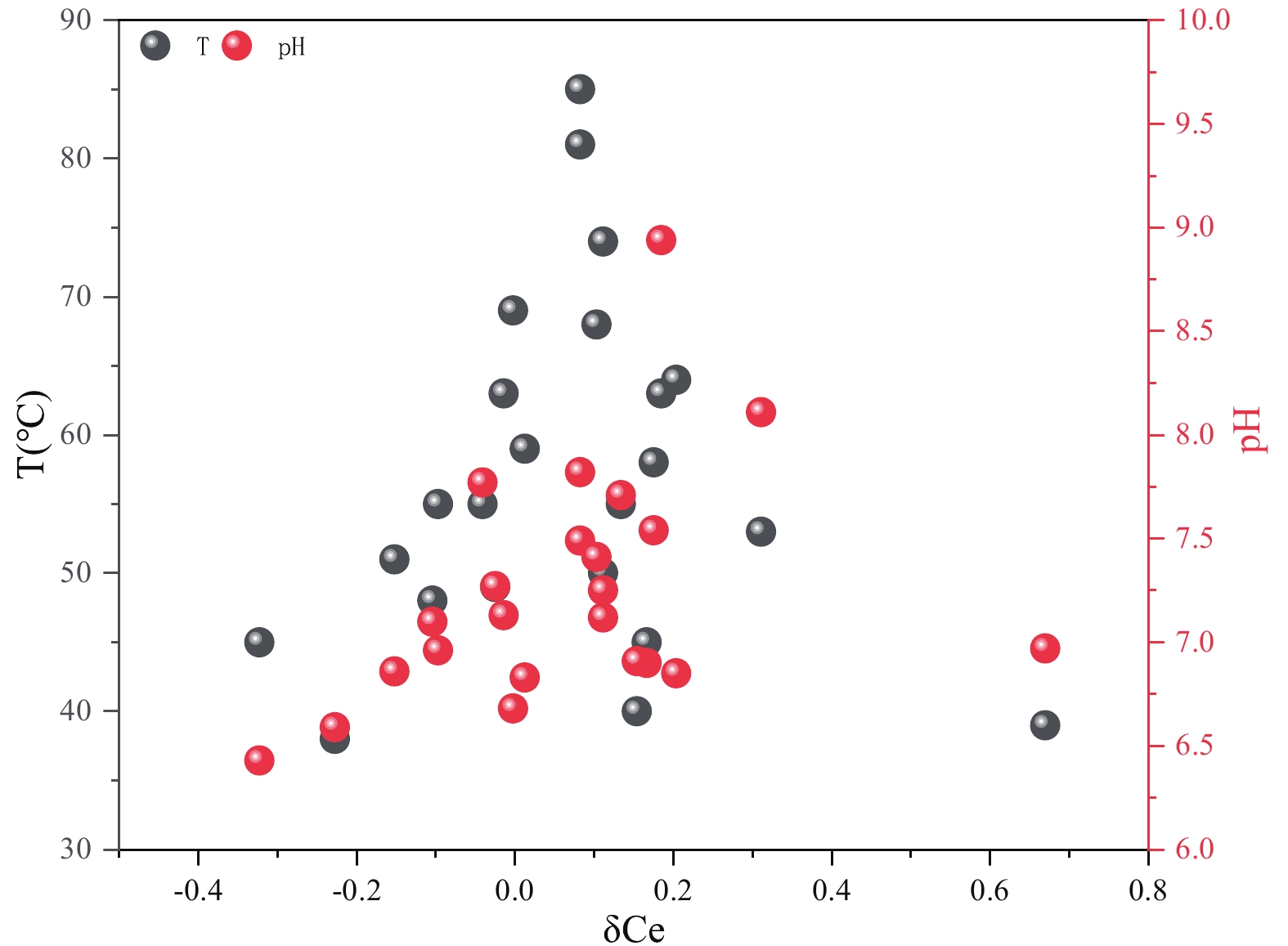
高温地热系统地热水中普遍富含高浓度的硼,其来源的研究一直是地热地质学者关注的热点问题。尽管众多的学者对地热水中硼形成机理开展了广泛的研究,但富硼地热水中稀土元素的分布特征及其迁移规律能否指示热水中硼的来源尚不清楚。本研究以鲜水河断裂带富硼地热水为研究对象,通过野外调查取样、室内测试分析、水文地球化学模拟和综合研究等技术手段和方法,探究断裂带地热水中硼和稀土元素的分布特征和迁移规律。研究结果显示:鲜水河断裂带地热水中硼含量90%超过我国饮用水标准规定值0.5 mg/L(地热水中硼含量最大值为10.50 mg/L);地热水中稀土元素含量为0.08~3.49 μg/L,且主要以LnCO3+和Ln(CO3)2−的络合物形态存在。地热水稀土元素PAAS归一化模式表现为重稀土元素相对于轻稀土元素富集((Nd/Yb)SN均值为0.41),且具有较显著的Eu(均值为0.34)和Ce(均值为0.07)正异常特征。地热水中硼和稀土元素的迁移均受到赋热含水层长英质和碳酸盐岩类矿物溶解过程的影响,且地热水中稀土元素的地球化学特征一定程度上可以指示地热水中硼的富集过程。研究成果拓展了稀土元素在富硼地热水研究中的应用,能为揭示富硼地热水成因研究提供依据。
Abstract:Geothermal water of high-temperature geothermal system is generally rich in high concentration of boron (B), and the research on B sources has been a hot topic for geothermal geologists. Although many researchers have conducted extensive research on the formation mechanism of high B geothermal water, it is unclear whether characteristics and migration laws of rare earth elements (REEs) in B-rich geothermal water can illustrate B sources in geothermal water. Our study focused on the B-rich geothermal water in the Xianshuihe Fault Belt Zone (XSHFZ) to explore the distribution and migration rules of B and REEs by combining with field survey and sampling, laboratory testing, hydrogeochemical modeling, and comprehensive analysis. The results showed that the maximum value of B in geothermal water was 10.50 mg/L, and the content of B in 90% of geothermal water samples was higher than 0.5 mg/L (China standard values for drinking water). The ∑REE value was 0.08-3.49 μg/L, mainly existed in the complex form of LnCO3+ and Ln(CO3)2−. PAAS-normalized model and (Nd/Yb)SN value of geothermal water in the XSHFZ showed that HREEs is enriched relative to LREEs, with significant positive Eu (an average value of δEu was 0.34) and Ce (an average value of δCe was 0.07) anomaly. Dissolving felsic mineral and carbonate rock controlled the migration of B and REEs in geothermal water. The geochemical characteristics of REEs in geothermal water can expound B's enrichment process in geothermal water to a certain extent. Our research results can expand the application of REEs in the study of B-rich geothermal water and provide a basis for illustrating the genesis study of B-rich geothermal water in similar areas.
-
Key words:
- Boron-rich geothermal water /
- REEs /
- Eu and Ce anomaly /
- B sources /
- The Xianshuihe Fault Belt Zone
-

-
图 1 研究区采样点分布图(a)和地质简图(b,引自唐渊等,2022,略有修改)
Figure 1.
-
[1] 陈维, 葛璐, 谭红兵, 2022. 西藏谷露—亚东裂谷南部温泉稀土元素特征及其控制因素[J]. 地质论评, 68(04): 1464-1479 doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2022.04.035
Chen W, Ge L, Tan H B, 2022. Rare earth element characteristics and controlling factors of hot springs in the Gulu-Yadong rift, Xizang (Xizang) [J]. Geologgical Review, 68(04): 1464-1479. doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2022.04.035
[2] 樊连杰, 裴建国, 卢丽, 等, 2018. 桂林寨底地下河系统中地下水稀土元素含量及分异特征[J]. 中国稀土学报, 36(02): 247-256
Fan L J, Pei J G, Lu L, et al. , 2018. Concentrations and Patterns of Rare Earth Elements in Groundwater from Zhaidi Underground River in Guilin [J]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 36(02): 247-256.
[3] 樊连杰, 邹胜章, 解庆林, 等, 2021. 云南鹤庆盆地岩溶地下水稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 中国稀土学报, 39(05): 805-815
Fan L J, Zou S Z, Xie Q L, et al. , 2021. Rare Earth Element Geochemical Characteristics of Karst Groundwater in Heqing Basin, Yunnan Province [J]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 39(05): 805-815.
[4] Gill L W, Babechuk M G, Kamber B S, et al. , 2018. Use of trace and rare earth elements to quantify autogenic and allogenic inputs within a lowland karst network[J]. Applied Geochemistry, Vol. 90: 101-114. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.01.001
[5] 桂和荣, 孙林华, 2011. 皖北任楼煤矿深层地下水稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 煤炭学报, 36(02): 210-216 doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2011.02.001
Gui H R, and Sun L H, 2011. Rare earth element geochemical characteristics of the deep underground water from Renlou Coal Mine, Northern Anhui Province [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 36(02): 210-216. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2011.02.001
[6] Guilin Han K Y, Jie Zeng, 2022. Spatio-Temporal Distribution and Environmental Behavior of Dissolved Rare Earth Elements (REE) in the Zhujiang River, Southwest China[J]. Bulletin of environmental contamination and toxicology, Vol. 108(No. 3): 555-562. doi: 10.1007/s00128-022-03459-w
[7] Guo Q, 2012. Hydrogeochemistry of high-temperature geothermal systems in China: A review[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 27(10): 1887-1898. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.07.006
[8] Guo Q, Liu M, Li J, et al. , 2017a. Fluid geochemical constraints on the heat source and reservoir temperature of the Banglazhang hydrothermal system, Yunnan-Xizang Geothermal Province, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 172: 109-119. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.10.012
[9] Guo Q, Pang Z, Wang Y, et al. , 2017b. Fluid geochemistry and geothermometry applications of the Kangding high-temperature geothermal system in eastern Himalayas[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 81: 63-75. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.03.007
[10] 郭清海, 张晓博, 2022. 高温热泉中稀土元素的地球化学行为及其指示意义: 以西藏搭格架热水区为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 41(5): 172-180
Guo Q, Zhang X, 2022. Geochemiccal behavior of rare earth elements in high-temperature hot springs and its implication: A case study in the Daggyai hydrothermal area, Xizang [J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 41(5): 172-180.
[11] Han G, Yang K, Zeng J, 2021. Distribution and fractionation of rare earth elements in suspended sediment of the Zhujiang River, Southwest China[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, Vol. 21(No. 8): 2981-2993. doi: 10.1007/s11368-021-03008-8
[12] Katsanou K, Siavalas G, Panagopoulos G, et al. , 2022. Rare earth element patterns in a rapidly changing karst environment[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 146: 105462. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2022.105462
[13] Li B, Kong Q, Wang G, et al. , 2022. Controls on the behaviors of rare earth elements in acidic and alkaline thermal springs[J]. Applied Geochemistry, Vol. 143: 105379. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2022.105379
[14] Li J, Yang G, Sagoe G, et al. , 2018. Major hydrogeochemical processes controlling the composition of geothermal waters in the Kangding geothermal field, western Sichuan Province[J]. Geothermics, 75: 154-163. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2018.04.008
[15] 李午阳, 张健, 唐显春, 等, 2018. 川西高温水热活动区深部热结构的地球物理分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 61(07): 2926-2936
Li W Y, Zhang J, Tang X C, et al. , 2018. The deep geothermal structure of high-temperature hydrothermal activity region in western Sichuan Plateuu: a geophysical study [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 61(07): 2926-2936.
[16] 李晓, 王金金, 黄珣, 等, 2018. 鲜水河断裂带康定至道孚段热水化学与同位素特征[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 45(06): 733-745 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2018.06.09
Li X, Wang J J, Huang X, et al. , 2018. Chemical and isotopic characteristics of hot water in the Kangding-Daofu section of Xianshuihe fault zone, Sichuan, China [J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science and Technology Edition), 45(06): 733-745. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2018.06.09
[17] 林秋婷, 陈晨, 刘海洋, 2020. 硼的地球化学性质及其在俯冲带的循环与成矿初探[J]. 岩石学报, 36(01): 5-12 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.01.02
Lin Q T, Chen C, and Liu H Y, 2020. Boron prospecting based on boron cycling in subduction zone [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(01): 5-12. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.01.02
[18] 刘海燕, 刘茂涵, 张卫民, 等, 2022. 华北平原高氟地下水中稀土元素分布和分异特征[J]. 地学前缘, 29(03): 129-144 doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2021.7.24
Liu H Y, Liu M H, Zhang W M, et al. , 2022. Distribution and fractionation of rare earth elements in high fluoride groundwater from the North China Plain [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 29(03): 129-144. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2021.7.24
[19] Liu M, Guo Q, Luo L, et al. , 2020. Environmental impacts of geothermal waters with extremely high boron concentrations: Insight from a case study in Xizang, China[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 397: 106887. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2020.106887
[20] Liu M, Guo Q, Wu G, et al. , 2019. Boron geochemistry of the geothermal waters from two typical hydrothermal systems in Southern Xizang (China): Daggyai and Quzhuomu[J]. Geothermics, 82: 190-202. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2019.06.009
[21] 刘明亮, 正安婷, 尚建波, 等, 2022. 高温地热流体中硼的地球化学研究进展[J]. 地球科学: 1 − 25. 网络首发: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20220711.0927.002.html.
Liu M L, Zheng A T, Shang J B, et al, 2022. Progress in study of boron geochemistry in high temperature geothermal fluids [J]. Earth Science, 1 − 25. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20220711.0927.002.html
[22] Liu W, Guan L, Liu Y, et al. , 2022. Fluid geochemistry and geothermal anomaly along the Yushu-Ganzi-Xianshuihe fault system, eastern Xizang Plateau: Implications for regional seismic activity[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 607: 127554. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127554
[23] Liu X, Gao W, Wei T, et al. , 2023. Distribution and sources of REEs in suspended particulate matter of cryospheric water in northeast Xizang plateau[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 148: 105536. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2022.105536
[24] 马莉, 刘茜, 何会军, 等, 2021. 大沽河流域地下水中稀土元素的地球化学特征[J]. 海洋学研究, 39(02): 33-42 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2021.02.004
Ma L, Liu Q, He H J, et al. , 2021. Geochimistry of rare earth elements in the groundwater of Dagu River Basin [J]. Journal of Marine Science, 39(02): 33-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2021.02.004
[25] Ogawa Y, Ishiyama D, Shikazono N, et al. , 2019. Fractionation of rare earth elements (REEs) and actinides (U and Th) originating from acid thermal water during artificial and natural neutralization processes of surface waters[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 249: 247-262. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2019.01.030
[26] 潘家伟, 李海兵, CHEVALIER M-L, et al. , 2020. 鲜水河断裂带色拉哈—康定段新发现的活动断层: 木格措南断裂[J]. 地质学报, 94(11): 3178-3188 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.11.002
Pan J W, Li H B, CHEVALIER M-L, et al. , 2020. A newly discovered active fault on the Selaha-Kangding segement along the SE Xianshuihe fault: South Mugecuo fault [J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 94(11): 3178-3188. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.11.002
[27] Pitikakis E, Katsanou K, Panagopoulos G, et al. , 2022. Distribution of rare earth elements in groundwater resources from sedimentary rocks of Eastern Crete, Greece[J]. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry: 1 − 18.
[28] Shakeri A, Ghoreyshinia S, Mehrabi B, et al. , 2015. Rare earth elements geochemistry in springs from Taftan geothermal area SE Iran[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 304: 49-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2015.07.023
[29] 唐渊, 王鹏, 邓红, 等, 2022. 青藏高原东缘鲜水河断裂带南东段渐新世以来主要构造岩浆事件的岩石记录[J]. 地质通报, 41(7): 1121-1143
Tang Y, Wang P, Deng H, et al. , 2022. Petrological records of major tectono-magmatic events since Oligeocene in the southeastern segment of Xianshuihe fault zone in the eastern margine of Xizang Plateau [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 41(7): 1121-1143.
[30] 王振, 郭华明, 刘海燕, 等, 2022. 贵德盆地高氟地下水稀土元素特征及其 指示意义[J]. 地学前缘: 1 − 13. https://doi.org/10.13745/j.esf.sf.2022.9.3
Wang Z, Guo H M, Liu H Y, et al, 2022. Characteristics and implications of rare earth elements in high fluoride groundwater in Guide basin [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 1 − 13. https://doi.org/10.13745/j.esf.sf.2022.9.3
[31] Wei S, Liu F, Zhang W, et al. , 2022a. Typical geothermal waters in the Ganzi–Litang fault, western Sichuan, China: hydrochemical processes and the geochemical characteristics of rare-earth elements[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 81(23): 538. doi: 10.1007/s12665-022-10652-x
[32] Wei S, Wei S, Liu F, et al. , 2022b. Geochemical Characteristics of Rare Earth Elements in the Chaluo Hot Springs in Western Sichuan Province, China[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, Vol. 10.
[33] 谢先军, 王焰新, 李俊霞, 等, 2012. 大同盆地高砷地下水稀土元素特征及其指示意义[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 37(02): 381-390
Xie X J, Wang Y X, Li J X, et al. , 2012. Chracteristics and implications of rare earth elements in high arsenic groundwater from Datong Basin [J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geoscience, 37(02): 381-390.
[34] 袁建飞, 2010. 西藏羊八井高温地热田水环境中硼的迁移和转化研究[D]: 中国地质大学.
Yuan J F, 2010. Transport of boron in the aquatic environment of the Yangbajing geothermal field, Xizang [D]. Wuhan: China University of Geoscience.
[35] 袁建飞, 毛绪美, 王焰新, 2013. 珠江口东北部地下水稀土元素的无机形态[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 40(06): 14-21+36 doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2013.06.016
Yuan J F, Mao X M, and Wang Y X, 2013. Inorganic speciation of rare earth elements for groundwater in northeastern of the Pearl River dealt mouth, south China [J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 40(06): 14-21+36. doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2013.06.016
[36] Yuan J, Guo Q, Wang Y, 2014a. Geochemical behaviors of boron and its isotopes in aqueous environment of the Yangbajing and Yangyi geothermal fields, Xizang, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 140: 11-22. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.01.006
[37] Yuan J, Mao X, Wang Y, et al. , 2014b. Geochemistry of rare-earth elements in shallow groundwater, northeastern Guangdong Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, Vol. 33(No. 1): 53-64. doi: 10.1007/s11631-014-0659-1
[38] 袁建飞, 邓国仕, 郑万模, 2017. 硼及硼同位素地球化学在地热研究中的应用[J]. 四川地质学报, 37(4): 686-691
Yuan J F, Deng G S, and Zheng W M, 2017. The application of boron and its isotopic geochemistry to the study of geothermal process [J]. ACTA GEOLOGICA SICHUAN, 37(4): 686-691.
[39] Yuan J, Xu F, Liu H, 2019. Chemical and isotopic compositions of boron in the geothermal waters in the Xianshuihe Fault Zone, Western Sichuan Province, China(Conference Paper)[C]. E3S Web of Conferences, Vol. 98.
[40] Yuan J, Xu F, Zheng T, 2022. The genesis of saline geothermal groundwater in the coastal area of Guangdong Province: Insight from hydrochemical and isotopic analysis[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 605: 127345. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.127345
[41] 张健, 李午阳, 唐显春, 等, 2017. 川西高温水热活动区的地热学分析[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 47(08): 899 − 915.
Zhang J, Li W Y, Tang X C, et al. , 2017. Geothermal data analysis at the high-temperature hydrothermal area in Western Sichuan [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 60: 1507 − 1521
[42] 张晓博, 郭清海, 张梦昭, 等, 2022. 碳酸盐岩热储中稀土元素的地球化学行为及其指示意义: 以施甸地热系统为例[J]. 地球科学: 1 − 23. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.p.20220831.1608.002.html
Zhang X B, Guo Q H, Zhang M Z, et al, 2022. Geochemical Behavior and Indicative Effect of REEs in Carbonate Geothermal Reservoir: A Case of Shidian Geothermal System [J]. Earth Science, 1 − 23. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.p.20220831.1608.002.html
[43] 张云辉, 2018. 鲜水河断裂康定−磨西段地热系统成因及开发利用研究[D]: 成都理工大学.
Zhang Y H, 2018. Research on genesis and development of the geothermal system in the Kangding−Moxi segment of the Xianshuihe fault [D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Science and Technology.
[44] Zhang Y, Zhou X, Liu H, et al. , 2020. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in the hot springs in the Simao Basin in southwestern China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, Vol. 79(No. 6): 1-10.
[45] 赵庆生, 1984. 鲜水河断裂带热水水文地球化学特征及形成模式[J]. 成都科技大学学报, (02): 77-88
Zhao Q S, 1984. The hydrogeochemical characteristics and forming model of hot water in the Xianshuihe fault zone [J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Science and Technology, (02): 77-88.
[46] 郑天亮, 邓娅敏, 鲁宗杰, 等, 2017. 江汉平原浅层含砷地下水稀土元素特征及其指示意义[J]. 地球科学, 42(05): 693-706
Zheng T L, Deng Y M, Lu Z J, et al. , 2017. Geochemistry and implications of rare earth elements in arsenic-affected shallow aquifer from Jianghan Plain, central China [J]. Earth Science, 42(05): 693-706.
[47] Zheng T, Lin H, Deng Y, et al. , 2023. Hydrogeochemical processes regulating the enrichment and migration of As and B from the river sediments in the Singe Tsangpo River Bain, Western Xizang plateau[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 148: 105549. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2022.105549
[48] 周海玲, 苏春利, 李俊霞, 等, 2017. 大同盆地沉积物REE分布特征及其对碘富集的指示[J]. 地球科学, 42(02): 298-306
Zhou H L, Sun C L, Li J X, et al. , 2017. Characteristics of rare earth elements in the sediments of the Datong Basin and its incication to the iodine enrichment [J]. Earth Science, 42(02): 298-306.
-




 下载:
下载: