Speciation of arsenic and antimony in geothermal water affected by their competitive hiolation: A case study in several typical Ali hydrothermal areas, Xizang
-
摘要:
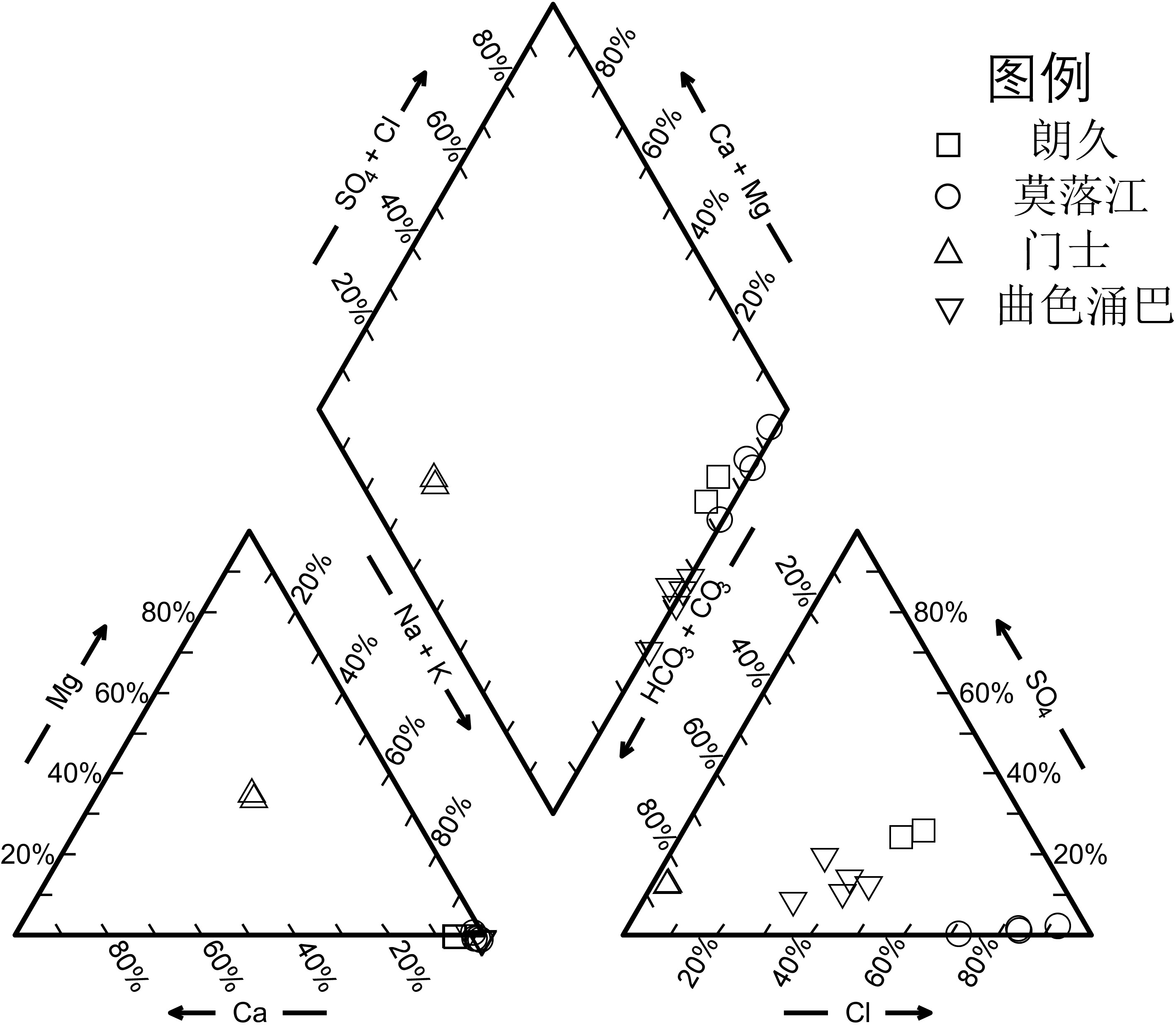
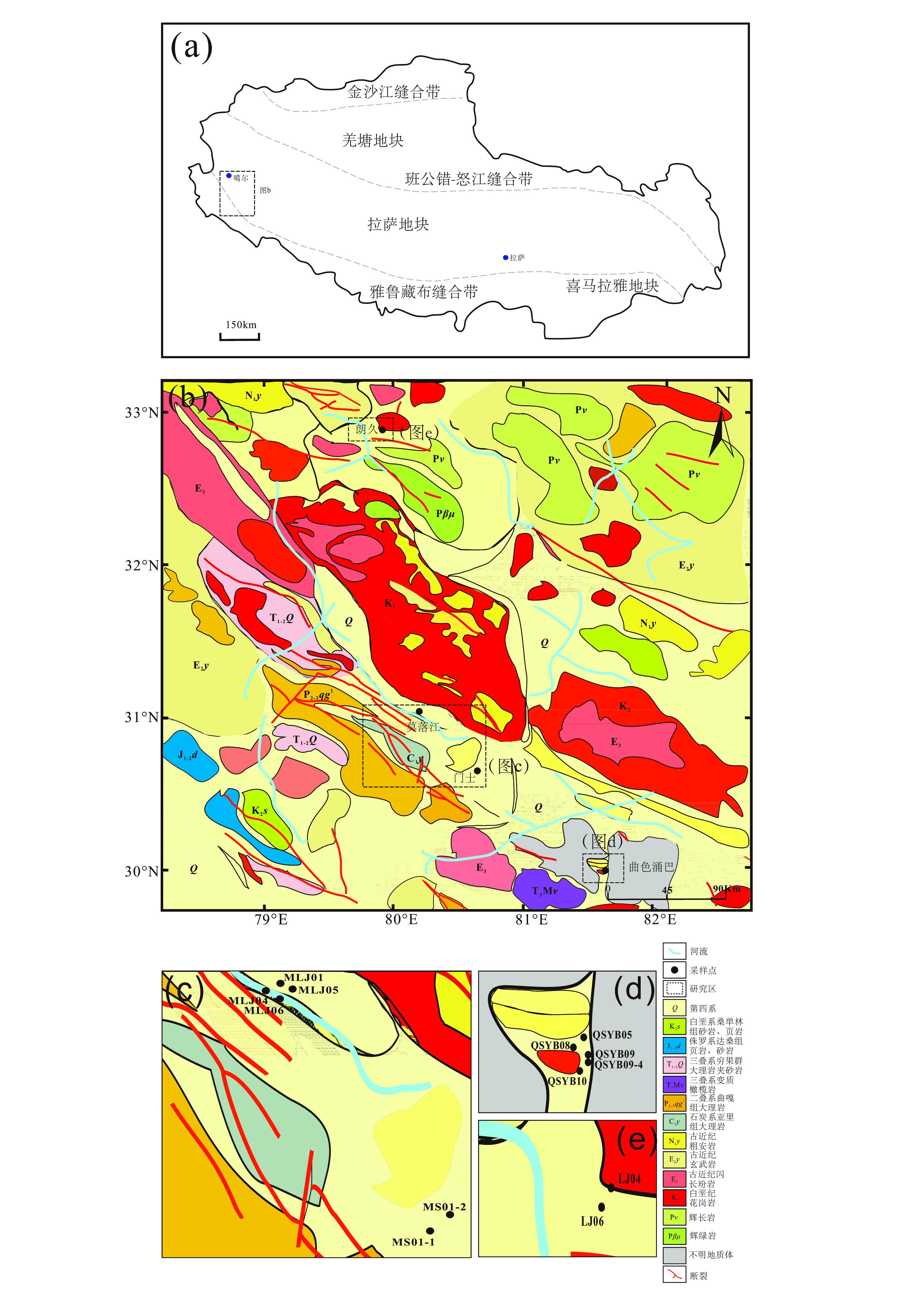
砷、锑是地热水中的典型有害组分,受地热水独特水化学条件影响,常呈现与其他类型天然水体相异的形态分布特征。本文以西藏阿里的朗久、曲色涌巴、门士、莫落江等地热区为研究区,分析了含硫化物地热水中砷、锑在竞争巯基化过程影响下的形态分布特征。受富砷、锑岩浆流体输入或高温条件下热储围岩加强淋滤的影响,上述地热区排泄的地热水中砷、锑浓度范围分别可达
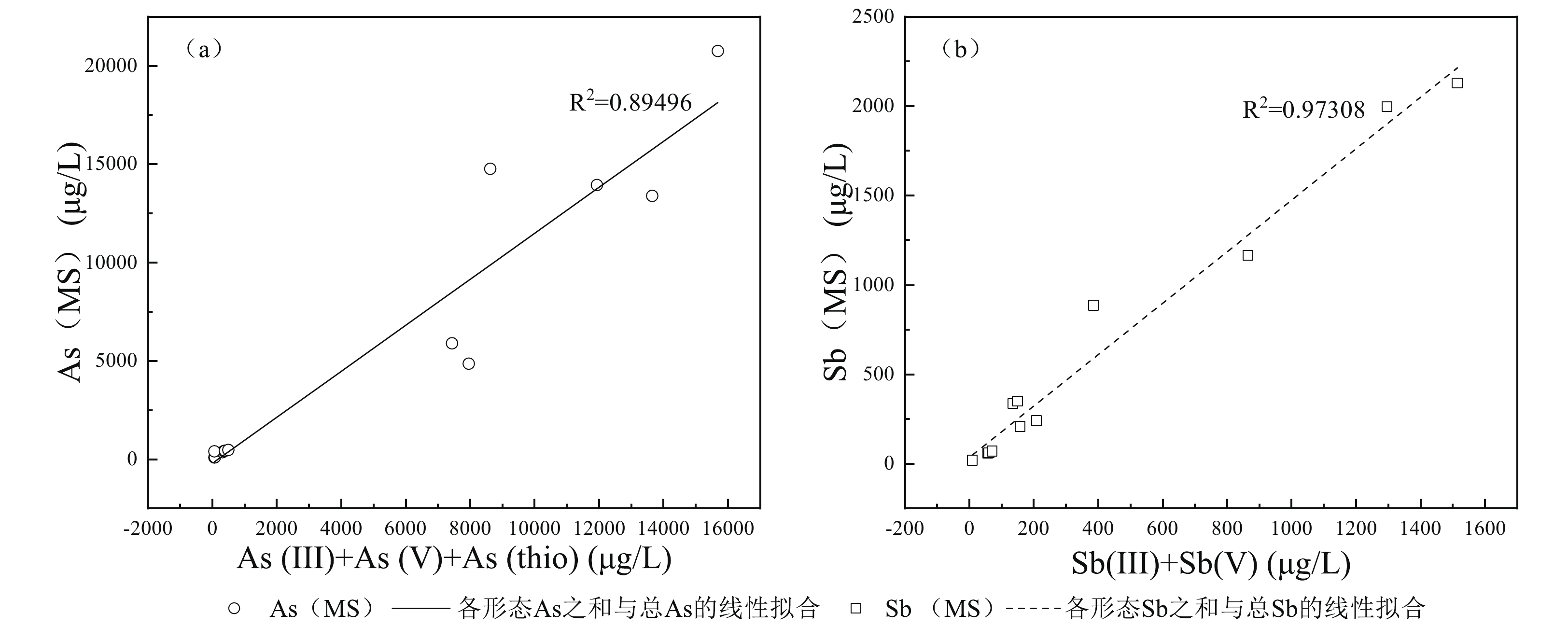
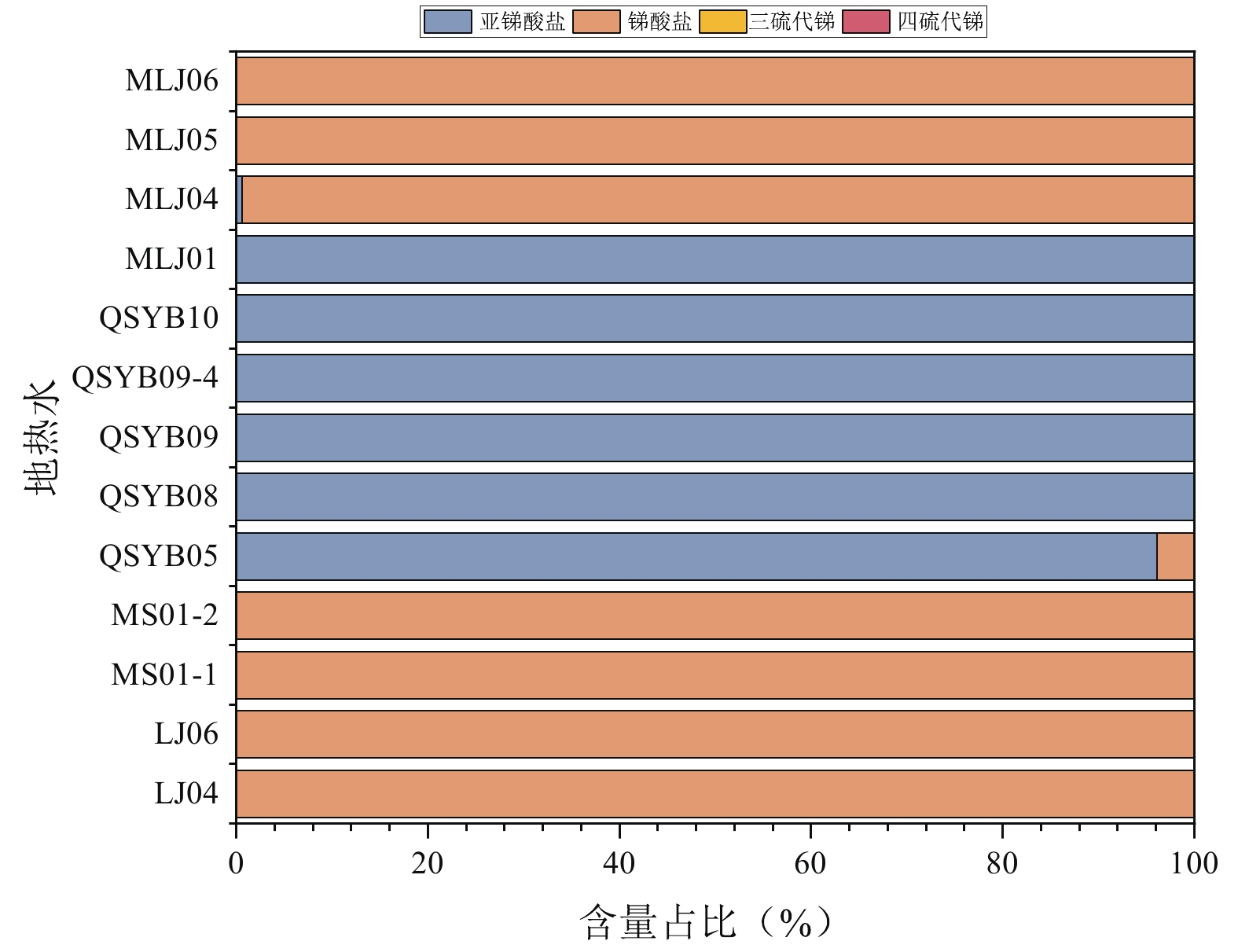
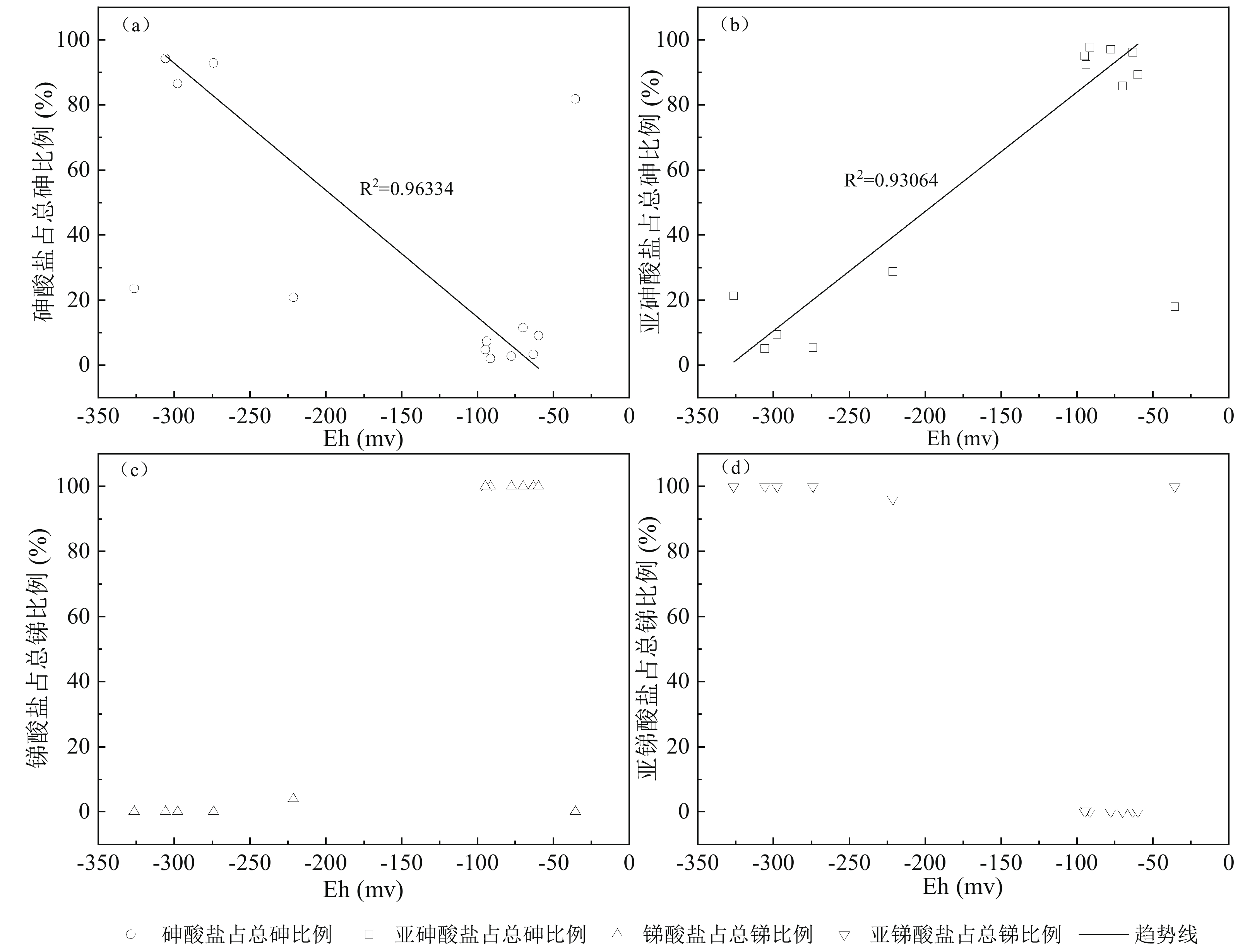
5833 ~20750 μg/L和579~2129 μg/L。地热水中砷以亚砷酸盐和砷酸盐为主要存在形态,但同时存在占总砷百分比在0.1%~55.1%之间的硫代砷酸盐;与砷的情况不同,地热水中锑检测出的形态均为亚锑酸盐和/或锑酸盐,所有样品中均未检出硫代锑酸盐。考虑到相当一部分地热水样品的S/Sb摩尔比在理论上满足硫代锑酸盐的形成条件,且所有样品中砷的富集程度均不同程度高于锑,我们认为地热水中锑的含氧络阴离子的巯基化过程受到了共存砷的强烈抑制。在硫化物相对于砷、锑总量并不充分盈余的情况下,砷的竞争巯基化是控制地热水中硫代锑酸盐形成的最重要因素。本工作及其研究结果有助于深入理解西藏地热水环境中砷、锑的环境地球化学行为。Abstract:Arsenic and antimony are typical harmful constituents in geothermal water, in which they usually show different speciationfrom other types of natural waters, as a result of the unique hydrochemical conditions there. With the Langjiu, Quseyongba, Menshi and Moluojiang geothermal areas in Ali, Xizang asthe study areas,, the arsenic and antimony speciation in the sulfide-bearing geothermal waters under the influence of competitive thiolation between their oxyanions was investigated. Owing toinput of arsenic- and antimony-rich magmatic fluids and/or enhanced leaching of reservoir hostrocks at elevated temperature, the arsenic and antimony concentrations in the geothermal waters discharged from the sehydrothermal areas range from
5833 to20750 μg/L and from 579 to2129 μg/L, respectively. Arsenite and arsenate are the main species of arsenic in the geothermal waters, but thioarsenates exist as well with their proportions in total arsenic ranging from 0.1 to 55.1%. Different from arsenic, the species of antimony in all the geothermal water samples are antimonite and/or antimonatewith thioantimonates being undetected. Considering that the S/Sb molar ratios of a large part of the geothermal waters are high enough for formation of thioantimonates and that arsenic in all the samples is more enriched than antimony to varying degrees, we concluded that thiolation of antimony oxyanions in the geothermal waters was strongly inhibited by coexisting arsenic oxyanions. Provided that there were no a large excess of sulfide over the sum of arsenic and antimony in geothermal water, competitive thiolation of arsenic oxyanions would be the most critical factor impeding formation of thioantimonates. The present work and the results obtained in this study would be helpful for an in-depth understanding of the environmental geochemical behaviour of arsenic and antimony in geothermal water environments in Xizang.-
Key words:
- Geothermal water /
- Speciation /
- Thioarsenates /
- Thioantimonates /
- Competitive thiolation /
- Xizang
-

-
[1] Boreiko C J, Rossman T G, 2020. Antimony and its Compounds: Health Impacts Related to Pulmonary Toxicity, Cancer, and Genotoxicity [J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 403: 115156
[2] Couture R M , Rose J , Kumar N, et al., 2013. Sorption of Arsenite, Arsenate, and Thioarsenates to Iron Oxides and Iron Sulfides: A Kinetic and Spectroscopic Investigation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(11): 5652 − 5659.
[3] 丁爱中, 杨双喜, 张宏达, 2007. 地下水砷污染分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 37(2): 319-325
Ding A Z, Yang S X, Zhang H D, 2007. Arsenic contamination analysis of groundwater[J]. Journal of Jilin University Sciences (Earth Sciences), 37(2): 319-325.
[4] Ellis A J, Mahon W A J, 1964. Natural Hydrothermal System s and Experimental Hot Water/rock Interactions (Part II)[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 31(4): 519−538.
[5] Guo Q, Planer-Friedrich B, Luo L, et al. , 2020. Speciation of antimony in representative sulfidic hot springs in the YST Geothermal Province (China) and its immobilization by spring sediments[J]. Environmental Pollution, 266: 115221. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115221
[6] Guo Q, Planer-Friedrich B, Liu M, et al. , 2017. Arsenic and thioarsenic species in the hot springs of the Rehai magmatic geothermal system, Tengchong volcanic region, China[J]. Chemical Geology, 453: 12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.02.010
[7] Guo Q, Planer−Friedrich B, Liu M, et al. 2017b. Arsenic and Thioarsenic Species in the Hot Springs of the Rehai Magmatic Geothermal System, Tengchong Volcanic Region, China[J]. Chemical Geology, 453: 12 − 20.
[8] Guo Q, Planer−Friedrich B, Liu M, et al. 2019. Magmatic Fluid Input Explaining the Geochemical Anomaly of very High Arsenic in some Southern Xizang Geothermal Waters[J]. Chemical Geology , 513: 32 − 43.
[9] 郭清海, 2020. 岩浆热源型地热系统及其水文地球化学判据[J]. 地质学报, 94(12): 3544 − 3554.
Guo Q H, 2020. Magmatic heat source type geothermal system and its hydrogeochemical criteria[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(12): 3544 − 3554 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] 郭清海, 杨晨 2021. 西藏搭格架高温热泉中钨的水文地球化学异常[J]. 地球科学, 46(7): 2544 − 2554
Guo Q H, Yang C, 2021. Hydrogeochemical anomalies of tungsten in high−temperature hot springs in Xizang[J]. Earth Science, 46(7): 2544 − 2554(in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] 郭清海, 孟越, 严克涛, 2023. 地热水中多种甲基硫代砷酸盐的同时定量测定[J]. 地球科学, 48(3): 1138
Guo Q H, Meng Y, Yan K T, 2023. Simultaneous quantitative determination of multiple methyl thioarsenates in geothermal water [J] Earth Science, 48(3): 1138(in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Hinrichsen S, Geist F, Planer-Friedrich B, 2015. Inorganic and methylated thioarsenates pass the gastrointestinal barrier[J]. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 28(9): 1678-1680. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00268
[13] 廖忠礼, 廖光宇, 潘桂棠, 等, 2005. 西藏阿里地热资源的分布特点及开发利用[J]. 中国矿业, 14(8): 43 − 46
Liao Z L, Liao G Y, Pan G T, et al., 2005. Distribution characteristics, development and utilization of geothermal resources in Ali, Xizang [J] China Mining, 14(8): 43 − 46.
[14] 刘洪, 黄瀚霄, 张林奎, 李光明, 欧阳渊, 黄勇, 吕梦鸿, 兰双双, 2021. 西藏冈底斯成矿带西段鲁尔玛晚三叠世斑岩型铜(金)矿点的发现及意义[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 41(4): 599-611
Liu H, Huang H X, Zhang L K, Li G M, Ouyang Y, Huang Y, Lu M H, Lan S S, 2021. Discovery and significance of the Late Triassic porphyry copper (gold) occurrences at Lurma in the western section of the Xizang Gangdis mineralization belt[J]. Sedimentary and Tethys Geology, 41(4): 599-611.
[15] Naranmandura H, Carew M W, Xu S, et al. , 2011. Comparative toxicity of arsenic metabolites in human bladder cancer EJ-1 cells[J]. Chemical research in toxicology, 24(9): 1586-1596. doi: 10.1021/tx200291p
[16] 潘敖然, 2019. 高砷地下水中硫代砷形态分布及其吸附行为特征[D]. 桂林理工大学.
Pan A R, 2019. The speciation distribution and adsorption behavior characteristics of thioarsenic in high−arsenic groundwater [D] Guilin University of Technology, 2019(in Chinese).
[17] 潘桂棠, 王立全, 尹福光, 等, 2022. 青藏高原形成演化研究回顾, 进展与展望[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 42(2): 151-175
Pan G T, Wang L Q, Yin F G, et al. , 2022. Researches on geological-tectonic evolution of Xizang Plateau: A review, recent advances, and directions in the future[J]. Sedimentary and Tethys Geology, 42(2): 151-175.
[18] Planer-Friedrich B, Scheinost A C, 2011. Formation and structural characterization of thioantimony species and their natural occurrence in geothermal waters[J]. Environmental science & technology, 45(16): 6855-6863.
[19] Planer-Friedrich B, Forberg J, Lohmayer R, et al. , 2020. Relative abundance of thiolated species of As, Mo, W, and Sb in hot springs of Yellowstone National Park and Iceland[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(7): 4295-4304.
[20] Planer-Friedrich B, London J, McCleskey R B, et al. , 2007. Thioarsenates in geothermal waters of Yellowstone National Park: determination, preservation, and geochemical importance[J]. Environmental science & technology, 41(15): 5245-5251.
[21] Planer-Friedrich B, Wilson N, 2012. The stability of tetrathioantimonate in the presence of oxygen, light, high temperature and arsenic[J]. Chemical Geology, 322: 1-10.
[22] Smedley P L, Kinniburgh D G, 2002. A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters[J]. Applied geochemistry, 17(5): 517-568. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00018-5
[23] 宋泓禹, 郭清海, 2023. 典型高温热泉中锑的形态分布及其地球化学成因[J]. 地球科学, 48(3), 946 − 957
Song H Y, Guo Q H, 2023. Morphological distribution of antimony in typical high−temperature hot springs and its geochemical genesis [J]. Earth Science, 48(3), 946 − 957.
[24] Sun S, Xie X, Li J, et al. , 2020. Distribution and formation of thioarsenate in high arsenic groundwater from the Datong Basin, northern China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 590: 125268. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125268
[25] 佟伟, 廖志杰, 刘时彬, 等, 2000. 西藏温泉志. 北京: 科学出版社.
Tong W, Liao Z J, Liu S B, et al., 2000. Records of Xizang Hot Springs Beijing: Science Press(in Chinese)
[26] Ullrich M K, Pope J G, Seward T M, et al. , 2013 Sulfur redox chemistry governs diurnal antimony and arsenic cycles at Champagne Pool, Waiotapu, New Zealand[J]. Journal of volcanology and geothermal research, 262: 164-177. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2013.07.007
[27] 王立全, 王保弟, 李光明, 等, 2021. 东特提斯地质调查研究进展综述[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 41(2): 283-296
Wang L Q, Wang B D, Li G M, et al. , 2021. A review of the progress of geological investigations in the Eastern Tethys[J]. Sedimentary and Tethys Geology, 41(2): 283-296.
[28] 王冠, 陶晓风, 2009. 西藏阿里地区多桑地堑的构造特征及成因机制[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 29(1): 46-52
Wang G, Tao X F, 2009. Structural features and genetic mechanism of the Duosang graben in the Ali area, Xizang[J]. Sedimentary and Tethys Geology, 29(1): 46-52.
[29] Webster J G, Nordstrom D K. , 2003 Geothermal arsenic: The source, transport and fate of arsenic in geothermal systems[J]. Arsenic in ground water: geochemistry and occurrence, 31: 101-125.
[30] 解超明, 李才, 李光明, 等, 2020. 西藏松多古特提斯洋研究进展与存在问题[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 40(2): 1-13
Xie C M, Li C, Li G M, et al. , 2020. The research progress and problem of the Sumdo Paleo-Tethys Ocean, Xizang[J]. Sedimentary and Tethys Geology, 40(2): 1-13.
[31] 严克涛, 郭清海, 刘明亮, 2019. 西藏搭格架高温热泉中砷的地球化学异常及其存在形态[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 49(2): 548-558
Yan K T, Guo Q H, Liu M L, 2019 Geochemical anomaly and existing form of arsenic in Tagejia hot spring, Xizang[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 49(2): 548-558
[32] 张梦昭, 郭清海, 刘明亮, 等, 2023. 山西忻州盆地地热水地球化学特征及其成因机制[J]. 地球科学, 48(3), 973 − 987
Zhang M Z, Guo Q H, Liu M L, et al., 2023. Geochemical characteristics and genetic mechanism of geothermal water in Xinzhou Basin, Shanxi Province[J]. Earth Science, 48(3), 973 − 987.
-



 下载:
下载: