Hydrogeochemical and seismic activity characteristics of hot springs in Daocheng area, Sichuan Province
-
摘要:
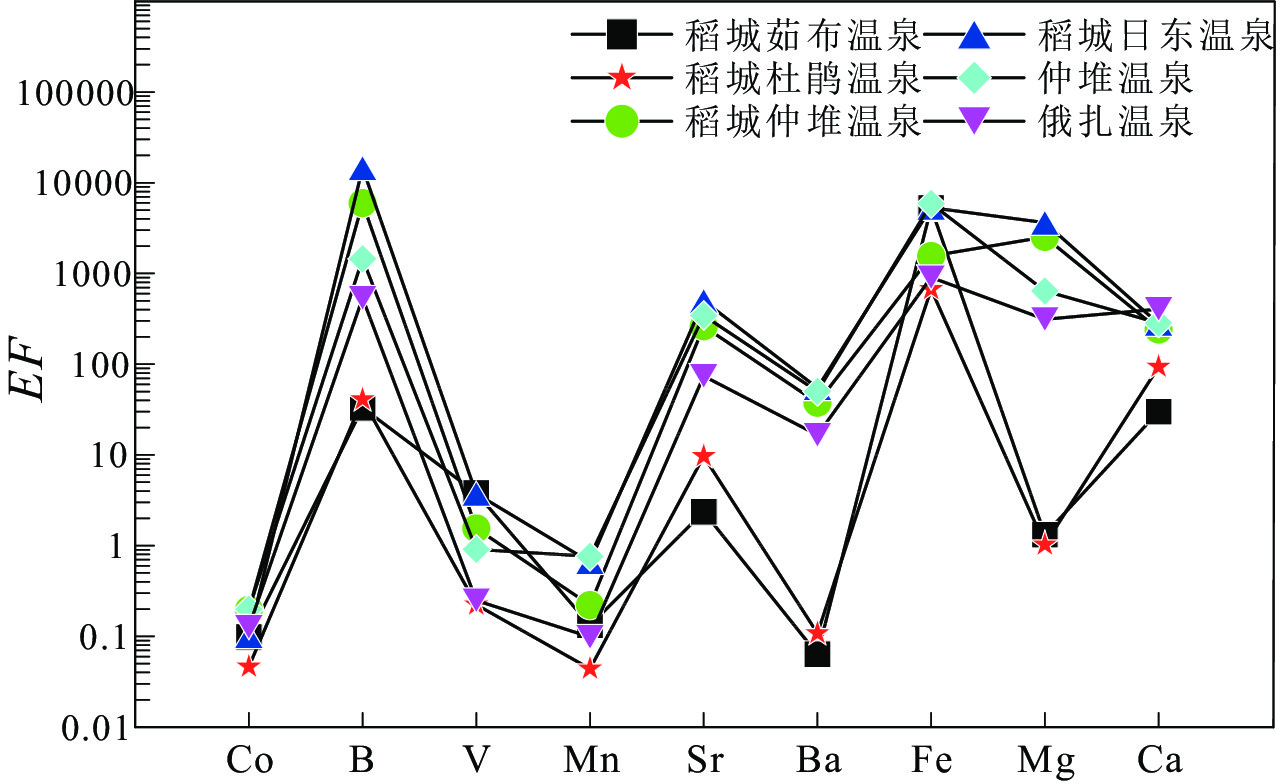
稻城地区位于青藏高原东南缘的川滇地块北部,为揭示该区域温泉流体地球化学特征以及其和地震活动性之间的关系,本次研究采集了稻城地区6个温泉的水样以及逸出气体样品。对温泉水中离子组分和浓度,温泉逸出气体组分及气体同位素进行了测试,得到以下认识。研究区温泉水化学类型主要为HCO3-Na和HCO3-Na·Ca型,通过阳离子温标估算热储温度在74℃~159℃之间,循环深度在2.2 km~5.0 km之间。温泉气体中CO2主要是由储层中的碳酸盐岩受热分解或溶解产生的,氦来自幔源组分的比例较低,在0.4%~2.4%之间,研究区的温泉是由沿断裂带渗入的大气降水经地壳深部的热源加热形成的。在稻城地区,循环深度以及幔源气体贡献率等不同的温泉流体地球化学特征与地震活动性之间有很好的对应关系,并且研究区地震活动性要弱于周缘鲜水河断裂地区等深部流体上涌地区。同时在区域尺度上,未来位于断裂交汇部位的稻城仲堆温泉一带的地震活动性最值得关注。
Abstract:Daocheng area is located in the northern part of Sichuan-Yunnan block on the southeastern margin of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. In order to reveal the geochemical characteristics of hot spring fluid and the relationship between the fluid and seismic activity in this area, hot spring water samples and gas samples from six hot springs in Daocheng area were collected, and the ion components and concentrations in hot spring water, gas components and gas isotopes of hot spring were tested. The following conclusions are obtained: the chemical types of hot spring water in the study area are mainly HCO3-Na and HCO3-Na·Ca types. The Reservoir temperature is estimated to be between 74℃ and 159℃ by cationic temperature scale, and the circulation depth is between 2.2 km and 5.0 km. The CO2 in the hot spring gas is mainly generated by the decomposition or dissolution of the carbonate rocks in the reservoir, and the proportion of helium from the mantle component is relatively low, ranging from 0.4% to 2.4%. The hot spring in the study area is formed by the heating of the deep crustal heat source caused by the atmospheric precipitation penetrating along the fault zone. In Daocheng area, the geochemical characteristics of hot spring fluid such as circulation depth and contribution rate of mantle-derived gas have a good correlation with seismic activity, and the seismic activity of the study area is weaker than that of deep fluid upwelling areas such as the surrounding Xianshuihe fault area. At the same time, in the regional scale, the future seismic activity in the Zhongdui hot spring area of Daocheng, located at the intersection of faults, is the most noteworthy.
-
Key words:
- Hot spring /
- Hydrogeochemistry /
- Isotope /
- Seismicity /
- Daocheng
-

-
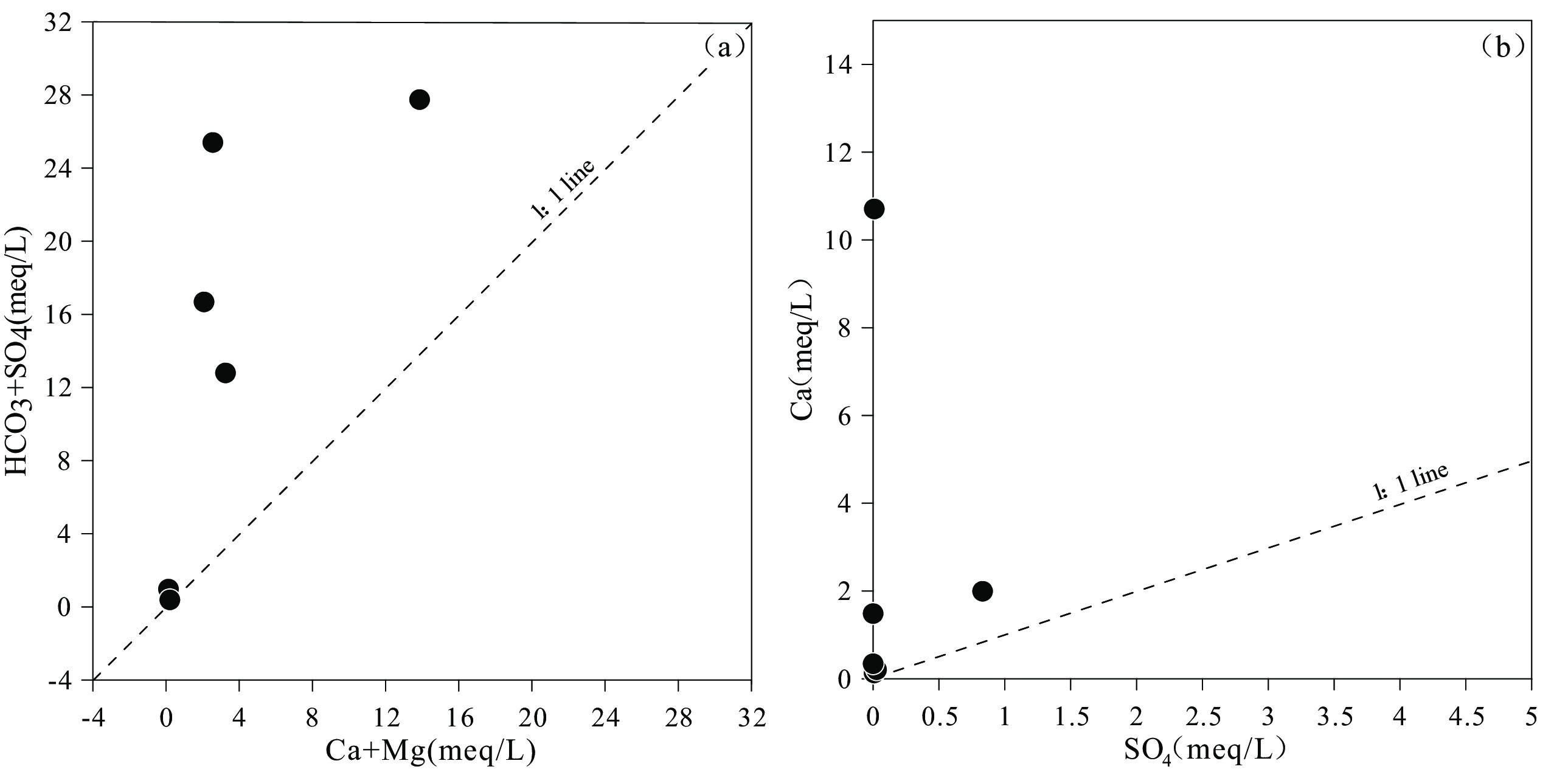
图 7 稻城地区温泉水样的Na-K-Mg三角图(底图据Giggenbach(1988))
Figure 7.
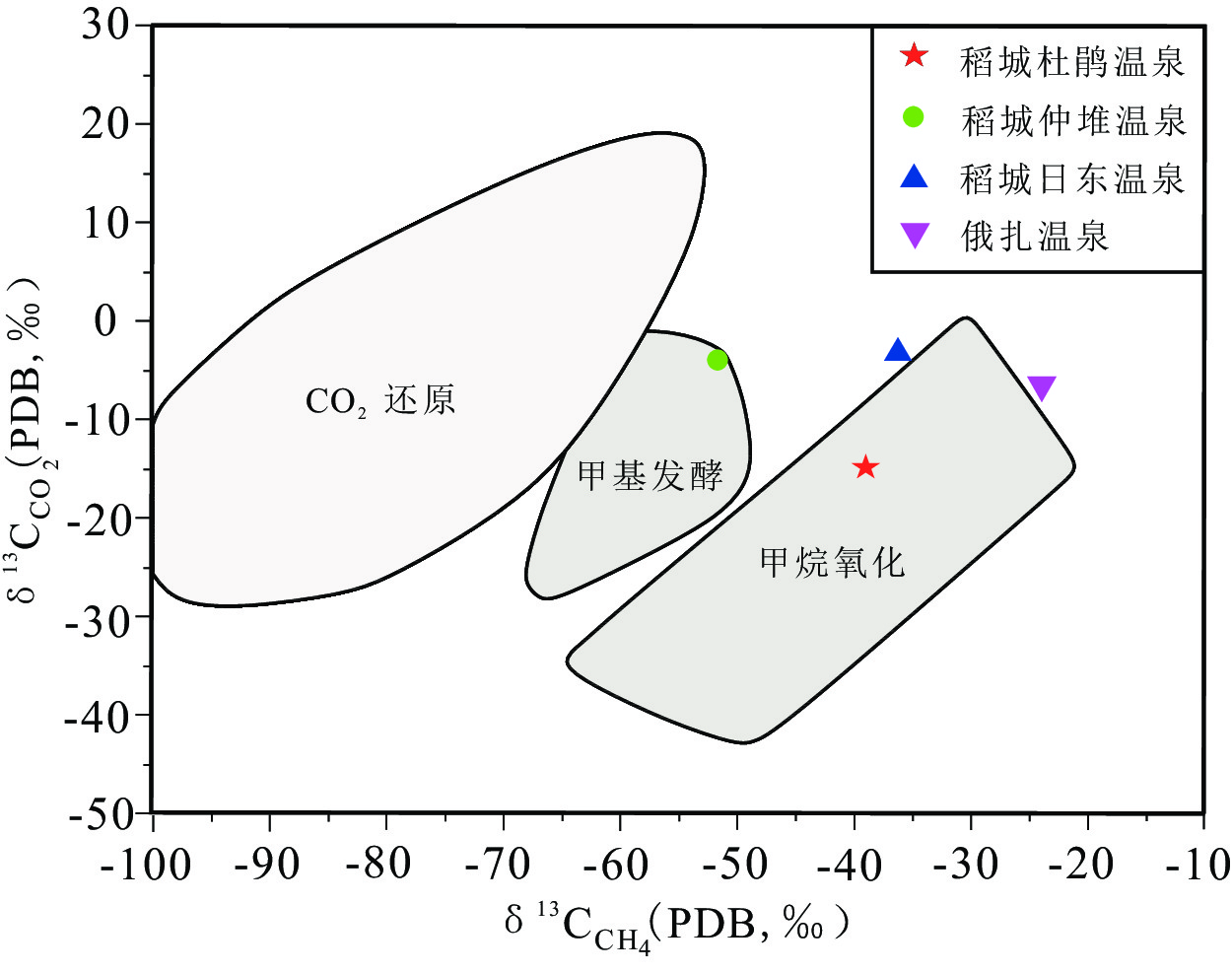
图 10 稻城地区温泉气体δ13CCO2-δ13CCH4关系图(底图据Woltemate et al.(1984))
Figure 10.
-
[1] Ballentine C J, Burnard P G, 2002. Production release and transport of noble gases in the continental crust[J]. Reviews In Mineralogy & Geochemistry, 47: 481-538.
[2] Ballentine C J, Marty B, Sherwood L B, et al. , 2005. Neon isotopes constrain convection and volatile origin in the Earth's mantle[J]. Nature, 433(7021): 33-38. doi: 10.1038/nature03182
[3] Bai D H, Unsworth M J, Meju M A, et al. , 2010. Crustal deformation of the eastern Xizang Plateau revealed by magnetotelluric imaging[J]. Nature Geoscience, 3: 358-362. doi: 10.1038/ngeo830
[4] Cao C H, Zhang M J, Tang Q Y, et al. , 2018. Noble gas isotopic variations and geological implication of Longmaxi shale gas in Sichuan Basin[J]. Marine And Petroleum Geology, 89: 38-46. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.01.022
[5] 曹文正, 刘哲, 2015. 稻城茹布查卡温泉地质构造环境及形成机理分析[J]. 人民珠江, 36(1): 61-65 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9235.2015.01.015
Cao W Z, Liu Z, 2015. Analysis on the Geotectonic Environment and the Forming Mechanism of the Rubuchaka Hot Spring in Daocheng[J]. Pearl River, 36(1): 61-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9235.2015.01.015
[6] Chen Z, Zhou X C, Du J G, et al. , 2015. Hydrochemical characteristics of hot spring waters in the Kangding district related to the Lushan Ms=7.0 earthquake in Sichuan[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 15: 1149-1156. doi: 10.5194/nhess-15-1149-2015
[7] 迟恩先, 兰波, 肖延卿, 2014. 溶液温度及CO2含量对长石溶解度的影响[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 25(2): 230-232
Chi E X, Lan B, Xiao Y Q, 2014. Impact of temperature and CO2 in solution on feldspar solubility[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 25(2): 230-232.
[8] Chiodini G, Cardellini C, Di L, et al. , 2020. Correlation between tectonic CO2 Earth degassing and seismicity is revealed by a 10-year record in the Apennines[J]. Science Advances, 6(35): eabc2938. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abc2938
[9] Chiodini G, Caliro S, Cardellini C, et al. , 2011. Geochemical evidence for and characterization of CO2 rich gas sources in the epicentral area of the Abruzzo 2009 earthquakes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 304(3–4): 389 − 398.
[10] Deutsch, W J, 1997. Groundwater Geochemistry: Fundamentals and Applications to Contamination[M]. New York: Lewis Publisher.
[11] Diamond L W, Wanner C, Waber H N, 2018. Penetration depth of meteoric water in orogenic geothermal systems[J]. Geology, 46: 1063-1066.
[12] Du J G, Cheng W Z, Zhang Y L, et al. , 2006. Helium and carbon isotopic compositions of thermal springs in the earthquake zone of Sichuan, Southwestern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 26(5): 533-539. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.11.006
[13] 杜建国, 仵柯田, 孙凤霞. 2018. 地震成因综述[J]. 地学前缘, 25(4): 255 − 267
Du J G, Wu K T, Sun F X, 2018. Earthquake generation: a review[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 25(4): 255 − 267.
[14] 段庆宝, 杨晓松, 陈建业, 等, 2015. 地震断层带流体作用的岩石物理和地球化学响应研究综述[J]. 地球物理学进展, 30(6): 2448-2462
Duan Q B, Yang X S, Cheng J Y, et al. , 2015. Review of geochemical and petrophysical responses to fluid processes within seismogenic fault zones[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 30(6): 2448-2462.
[15] Feng M, An M J, et al. , 2010. Lithospheric structure of the Chinese mainland determined from joint inversion of regional and teleseismic Rayleigh-wave group velocities[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 115: B06317.
[16] Fisher R S, Mullican F W, 1997. Hydrochemical evolution of sodium-sulfate and sodium-chloride groundwater beneath the Northern Chihuahuan Desert, Trans-Pecos, Texas[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 10(1997): 455-474.
[17] Fournier R O, Truesdell A H, 1973. An empirical Na-K-Ca geothermometer for natural waters[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 37(5): 1255-1275. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(73)90060-4
[18] 傅广海, 2009. 四川省甘孜州温泉类型、成因及旅游开发模式研究[D]: 成都理工大学.
Fu G H, 2009. A Study on The Types, Causes and Tourism development pattern about hot Springs of Ganzi prefecture in Sichuan Province[D]: Chengdu University of Technology.
[19] 高志友, 尹观, 范晓, 等, 2004. 四川稻城地热资源的分布特点及温泉水的同位素地球化学特征[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2: 134-139
Gao Z Y, Yin G, Fan X, et al. , 2004. Distribution characteristics of geothermal resources and Isotopic geochemistry of Hot-Water in the Daocheng County, Sichuan Province[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy Petrology and Geochemistry, 2: 134-139.
[20] Gaillardet J, Viers J, Dupré B, et al. , 2014. Trace elements in river waters[M]//Heinrich D, Holland, Karl K. et al. , Treatise on Geochemistry (Second Edition). Elsevier, 195 − 235.
[21] Giggenbach W F, 1988. Geothermal solute equilibria: derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 52(12): 2749-2765. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(88)90143-3
[22] Hilton D R, 1996. The helium and carbon isotope systematics of a continental geothermal system: Results from monitoring studies at Long Valley Caldera[J]. Chemical Geology, 127(4): 269-295. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(95)00134-4
[23] Hou Y, Shi Z, Mu W, 2018. Fluid geochemistry of fault zone hydrothermal system in the Yidun−Litang area, eastern Xizang Plateau geothermal belt[J]. Geofluids. 2018: 1 − 13.
[24] Huang X, Sillanpää M, Duo B, et al. , 2008. Water quality in the Xizang Plateau: Metal contents of four selected rivers[J]. Environmental Pollution, 156(2): 270-277. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2008.02.014
[25] Huang X, Sillanpää M, Gjessing E T, et al. , 2009. Water quality in the Xizang Plateau: Major ions and trace elements in the headwaters of four major Asian rivers[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 407(24): 6242-6254. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.09.001
[26] 姜光政, 高堋, 饶松, 等, 2016. 中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编(第四版)[J]. 地球物理学报, 59(8): 2892-2910
Jiang G Z, Gao P, Rao Song, et al. , 2016. Compilation of heat flow data in the continental area of China(4th edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 59(8): 2892-2910.
[27] Kharaka M, 1982. Chemical Geothermometers Applied to formation waters, Gulf of Mexico and California Basins: Abstract[J]. Aapg Bulletin, 66.
[28] Kharaka Y K, Mariner R H, 1989. Chemical geothermometers and their application to formation waters from sedimentary basins. 99~117. //Thermal History of Sedimentary Basins[M]. New York: Springer−Verlag.
[29] 李其林, 王云, 周艺颖, 等, 2019. 川滇菱块西北缘温泉地球化学特征与地震活动性关系研究[J]. 国际地震动态, 8: 121-122
Li Q L, Wang Y, Zhou Y Y, et al. , 2019. Study on the relationship between geochemical characteristics and seismicity of hot springs in the northwest margin of Sichuan-Yunnan Ling Block[J]. Progress in Earthquake Sciences, 8: 121-122.
[30] 李中平, 陶明信, 李立武, 等, 2007. 气相色谱-稳定同位素质谱法测定溶解无机碳碳同位素[J]. 分析化学, 35(10): 1455-1458 doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(07)60089-9
Li Z P, Tao M X, Li L W, et al. , 2007. Determination of isotope Composition of Dissolved inorganic Carbon by Gas-Chromatography-Conventional isotope-ratio Mass Spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 35(10): 1455-1458. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(07)60089-9
[31] Liu W, Guan L F, Liu Y, et al. , 2022. Fluid geochemistry and geothermal anomaly along the Yushu-Ganzi-Xianshuihe fault system, eastern Xizang Plateau: Implications for regional seismic activity[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 607: 127554. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127554
[32] 刘金华, 张世奇, 张鹏飞, 等, 2005. 川西地区上三叠统层序地层岩石地球化学特征[J]. 四川地质学报, 25(4): 198-201
Liu J H, Zhang S Q, Zhang P F, et al. , 2005. On the lithogeochemical features of the upper Triassic sequence strata in West Sichuan[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 25(4): 198-201.
[33] 刘明亮, 2018. 西藏典型高温水热系统中硼的地球化学研究[D]: 中国地质大学.
Liu M L, 2018. Boron geochemistry of the geothermal waters from typical hydrothermal systems in Xizang[D]: China University of Geosciences(Beijing).
[34] Luca U, Antonio P, Jonny R, et al. , 2016. Dynamic simulation of CO2-injection-induced fault rupture with slip-rate dependent friction coefficient[J]. Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 7: 47-65. doi: 10.1016/j.gete.2016.04.003
[35] Lyon G L, Hulston J R, 1984. Carbon and hydrogen isotopic compositions of geothermal gases[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 48: 169 − 173.
[36] Marty B, Jambon A, 1987. C/3He in volatile fluxes from the solid Earth: Implication for carbon geodynamics[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 83(1-4): 16-26. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(87)90047-1
[37] Miller S A, Ben-Zion Y, Burg J P, 1999, A three-dimensional fluid-controlled earthquake model: behavior and implications[J]. Journal of Geophysics Research, 104(B5): 10621-10638. doi: 10.1029/1998JB900084
[38] O'Nions R K, Oxburgh E R, 1988. Helium volatile fluxes and the development of continental crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 90(3): 331-347. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(88)90134-3
[39] 庞健峰, 丁孝忠, 韩坤英, 等, 2017.1: 100万中华人民共和国数字地质图空间数据库[J]. 中国地质, 44(S1): 8-18
Pang J F, Ding X Z, Han K Y, et al. , 2017. The National 1: 1000000 Geological Map Spatial Database[J]. Geology in China, 44(S1): 8-18.
[40] 庞忠和, 杨峰田, 罗璐, 等, 2013. 地热田储层温度的研究方法[M]//丁仲礼, 固体地球科学研究方法. 科学出版社, 219 − 242
Pang Z H, Yang F T, Luo L, et al. , 2013. Methods for studying reservoir temperature in geothermal fields[M]//Din Z L, Solid Earth Science Research Methods. Science Press, 219 − 242.
[41] Pérez N M, Hernández P A, Igarashi G, et al. , 2008. Searching and detecting earthquake geochemical precursors in CO2-rich groundwaters from Galicia, Spain[J]. Geochemical Journal, 42(1): 75-83. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.42.75
[42] Pili É, Poitrasson F, Gratier J P, 2002. Carbon-oxygen isotope and trace element constraints on how fluids percolate faulted limestones from the San Andreas Fault system; partitioning of fluid sources and pathways[J]. Chemical Geology, 190(1-4): 231-250. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00118-3
[43] Ray M C, Hilton D R, Mu J, et al. , 2009. The effects of volatile recycling, degassing and crustal contamination on the helium and carbon geochemistry of hydrothermal fluids from the Southern Volcanic Zone of Chile[J]. Chemical Geology, 266(1-2): 38-49. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.12.026
[44] Rouabhia A, Djabri L, Hadji R, et al. , 2012. Geochemical characterization of groundwater from shallow aquifer surrounding Fetzara Lake NE Algeria[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. 5: 1 − 13.
[45] Sano Y, Marty B, 1995. Origin of carbon in fumarolic gas from island arcs[J]. Chemical Geology, 119(1-4): 265-274. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)00097-R
[46] Sano Y, Takahata N, Igarashi G, et al. , 1998. Helium degassing related to the Kobe earthquake[J]. Chemical Geology, 150(1-2): 171-179. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00055-2
[47] 邵维晔, 王云, 李其林, 等. 2022. 红河断裂带温泉水文地球化学及构造活动特征研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 41(3): 612 − 624.
Shao W Y, Wang Y, Li Q L, et al., 2022. A study on hydrogeochemistry and tectonic activity features of hot springs in the Red River fault zone[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 41(3): 612 − 624.
[48] Skelton A, Andrén M, Kristmannsdóttir H, et al. , 2014. Changes in groundwater chemistry before two consecutive earthquakes in Iceland[J]. Nature Geoscience, 7(2014): 10.1038.
[49] Smeraglia L, Berra F, Billi A, et al. , 2016. Origin and role of fluids involved in the seismic cycle of extensional faults in carbonate rocks[J]. Earth And Planetary Science Letters, 450: 292-305. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.06.042
[50] Soto-Jimenez M F, Páez-Osuna F, 2001. Distribution and normalization of heavy metal concentrations in Mangrove and Lagoonal Sedi-ments from Mazatl6n Harbor (SE Gulf of California)[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 53(3): 259-274. doi: 10.1006/ecss.2000.0814
[51] Tamburello G, Pondrelli S, Chiodini G, et al. , 2018. Global-scale control of extensional tectonics on CO2 earth degassing[J]. Nature Communications, 9: 4608. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07087-z
[52] 孙红丽, 马峰, 蔺文静, 等, 2015. 西藏高温地热田地球化学特征及地热温标应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 34(3): 171-177
Sun H L, Ma F, Liu W J, et al. , 2015. Geochemical Characteristics and Geothermometer Application in High Temperature Geothermal Field in Xizang[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 34(3): 171-177.
[53] 唐晗晗, 郭良辉, 方圆, 2020. 青藏高原东南缘热流估算及与地震活动相关性分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 63(3): 1056-1069 doi: 10.6038/cjg2019N0045
Tang H H, Guo L H, Fang Y, 2020. Estimation of heat flow in southeastern margin of Xizang Plateau and its analysis of the correlation with earthquake activity[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 63(3): 1056-1069. doi: 10.6038/cjg2019N0045
[54] Tian J, Pang Z H, Liao D W, et al. , 2021. Fluid geochemistry and its implications on the role of deep faults in the genesis of high temperature systems in the eastern edge of the Qinghai Xizang Plateau[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 131: 105036. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2021.105036
[55] Tian J, Pang Z H, Guo Q, et al. , 2018. Geochemistry of geothermal fluids with implications on the sources of water and heat recharge to the Rekeng high-temperature geothermal system in the Eastern Himalayan Syntax[J]. Geothermics, 74: 92-105. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2018.02.006
[56] Walraevens K, Bakundukize C, Mtoni Y E, et al. , 2018. Understanding the hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in Precambrian basement aquifers: A case study of Bugesera region in Burundi[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 188(3): 24-42.
[57] Wang Q L, Cui D X, Wang W P, et al. , 2008. Research on current vertical crustal movement in Western Sichuan (in Chinese)[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 38: 598–610.
[58] 王茜, 2002. 四川稻城温泉同位素、元素水文地球化学特征研究[D]: 成都理工大学.
Wang Q, 2002. Study on the Thermal Spring Character of Isotope and Element Hydrogeochemistry in Daocheng, Sichuan[D]: Chengdu University of Technology.
[59] Wang W, Qiao X, Ding K, 2021. Present−day kinematics in southeastern Xizang inferred from GPS measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 126, e2020JB021305.
[60] Wang Y C, Zhou X C, Tian J et al. , 2023. Volatile characteristics and fluxes of He-CO2 systematics in the southeastern Xizang Plateau: Constraints on regional seismic activities[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 617(C): 129042.
[61] 汪洋, 2000. 利用地下流体氦同位素比值估算大陆壳幔热流比例[J]. 地球物理学报, 6: 762 − 770.
Wang Y, 2000. Estimations of the ratio of crust/mantle heat flow using helium isotope ratio of underground fluid[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 6: 762 − 770.
[62] 王莹, 周训, 于湲, 等, 2007. 应用地热温标估算地下热储温度[J]. 现代地质, 4: 605-612 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.04.003
Wang Y, Zhou X, Yu Y, et al. , 2007. Application of geothermometers to calculation of temperature of geothermal reservoirs[J]. Geoscience, 4: 605-612. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.04.003
[63] Wintsch R P, Christoffersen R, Kronenberg A K, 1995. Fluid-rock reaction weakening of fault zones[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 100: 13021-13032. doi: 10.1029/94JB02622
[64] Woltemate I, Whiticar M J, Schoell M, 1984. Carbon and hydrogen isotopic composition of bacterial methane in a shallow freshwater lake[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 29(5): 985-992. doi: 10.4319/lo.1984.29.5.0985
[65] 许鹏, 谭红兵, 张燕飞, 等. 2018. 特提斯喜马拉雅带地热水化学特征与物源机制[J]. 中国地质, 45(6): 1142 − 1154
Xu P, Tan H B, Zhang Y F, et al. , 2018. Geochemical characteristics and source mechanism of geothermal water in Tethys Himalaya belt[J]. Geology in China, 45(6): 1142 − 1154.
[66] 徐胜, 管芦峰, 张茂亮, 等, 2022. 青藏高原东缘鲜水河-安宁河断裂带深源气体释放[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 52(2): 291 − 308.
Xu S, Guan L F, Zhang M L, et al. , 2022. Degassing of deep-sourced CO2 from Xianshuihe-Anninghe fault zones in the eastern Xizang Plateau[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 65(1): 139 − 155.
[67] Xu X W, Wen X Z, Zheng R Z, et al. , 2003. Pattern of latest tectonic motion and its dynamics for active blocks in Sichuan-Yunnan region. China: Science in China Series D[J]. Earth Sciences, 46(2): 210-226.
[68] Yan Y C, Zhou X C, Liao L X, et al. , 2022. Hydrogeochemical Characteristic of geothermal water and precursory anomalies along the Xianshuihe Fault Zone, Southwestern China[J]. Water, 14: 550. doi: 10.3390/w14040550
[69] Zhang C, Zhang Y, Wu M, 2003. Study on relationship between earthquake and Hydro-Geochemistry of groundwater in southern part of North-South earthquake belt in China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 9: 21-30.
[70] Zhang J, Li W Y, Tang X C, et al. , 2017. Geothermal data analysis at the high-temperature hydrothermal area in Western Sichuan[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 60: 1507-1521. doi: 10.1007/s11430-016-9053-2
[71] Zhang Y, Replumaz A, Wang G, et al. , 2015. Timing and rate of exhumation along the Litang fault system, implication for fault reorganisation in South East Xizang[J]. Tectonics, 34(6): 1219-1243. doi: 10.1002/2014TC003671
[72] 张彦辉, 张良圣, 常阳, 等, 2018. 增压-微波消解电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定含难溶矿物岩石样品中的微量元素[J]. 铀矿地质, 34(2): 105-111
Zhang Y H, Zhang L S, Chang Y, et al. , 2018. Determining trace elements in rock samples containing Refractory minerals by pressurize-microwave inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Uranium Geology, 34(2): 105-111.
[73] Zhou R, Zhou X C, Li Y, et al. , 2022. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of the hot springs in the Litang fault zone, Southeast Qinghai−Xizang Plateau[J]. Water. 14, 1496.
[74] Zhou X C, Liu L, Chen Z, et al. , 2017. Gas geochemistry of the hot spring in the Litang fault zone, Southeast Xizang Plateau[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 79: 17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.01.022
[75] Zhou X C, Cheng J W, Yang L M, et al. , 2015. Hot Spring gas geochemistry in Western Sichuan Province, China After the Wenchuan Ms8.0 earthquake[J]. Terrestrial Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, 26(4): 361-373. doi: 10.3319/TAO.2015.01.05.01(TT)
[76] Zhou X C, Wang W L, Li L W, et al. , 2020. Geochemical features of hot spring gases in the Jinshajiang-Red River fault zone, Southeast Xizang Plateau[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(7): 2197-2214. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.07.18
-




 下载:
下载: