Experimental Study on Removing Cyanide and Fixing Arsenic from Cyanide Residue of a Gold Mine
-
摘要:
某金矿氰渣中总氰化物和总砷元素超标,研究了采用过氧化氢氧化分解氰化物、硫酸亚铁络合固砷工艺对氰渣进行无害化处理。结果表明:除氰段,过氧化氢加入量2 mL/L,反应时间2 h;固砷段,硫酸亚铁加入量0.5 g/L,过氧化氢加入量1 mL/L,硫酸加入量6.5 mL/L,反应时间1 h;经过除氰和固砷处理,所得氰渣的毒性浸出液中总氰化物质量浓度为0.25 mg/L,砷质量浓度为0.55 mg/L,满足标准要求,可进入尾矿库堆存。
Abstract:The total cyanide and arsenic in a cyanide residue of a gold mine exceed the standard requirements. The process of hydrogen peroxide oxidation decomposition cyanide and ferrous sulfate complexation fixation arsenic is studied. The results showed that in the cyanogen removal section, the amount of hydrogen peroxide added was 2 ml/L, the reaction time was 2 h, in the arsenic fixation section, the amount of ferrous sulfate added was 0.5 g/L, the amount of hydrogen peroxide added was 1 ml/L, the amount of sulfuric acid added was 6.5 ml/L, and the reaction time was 1 h. After the treatment of cyanide removal and arsenic fixation, the total cyanide concentration and arsenic concentration in the toxic leaching solution of the cyanogen residue are 0.25 mg/L and 0.55 mg/L, which meets the standard requirements and can be stored in the tailings pond.
-
Key words:
- Cyanide residue /
- Cyanide removal /
- Arsenic fixation /
- Harmless treatment
-

-
表 1 氰渣滤液主要成分分析结果/ (mgˑL-1)
Table 1. Analysis results of main components of cyanide residue filtration solution
总氰化物 易释放氰化物 Cu Zn Fe As Pb Hg Cd Cr Cr6+ 498.5 488.5 298.8 9.55 6.38 2.98 0.35 0.02 <0.05 <0.05 <0.04 表 2 氰渣毒性浸出液成分分析结果/(mgˑL-1)
Table 2. Analysis results of toxic leaching solution of cyanide residue
项目 总氰化物 Cu As Zn Pb Hg Cd Cr Cr6+ 毒性浸出液 31.2 18.5 3.28 <0.05 <0.02 <0.08 <0.04 <0.03 <0.004 标准① 5 75 2.5 75 5 0.25 0.5 12 2.5 标准② 6 120 1.2 120 1.2 0.12 0.6 15 6 注:① HJ 943—2018《黄金行业氰渣污染控制技术规范》(以下简称《氰渣规范》);
② GB 18598—2019《危险废物填埋污染控制标准》(以下简称《危废填埋标准》)。表 3 过氧化氢用量对除氰的影响
Table 3. Effect of hydrogen peroxide dosage on cyanide removal
H2O2加入量
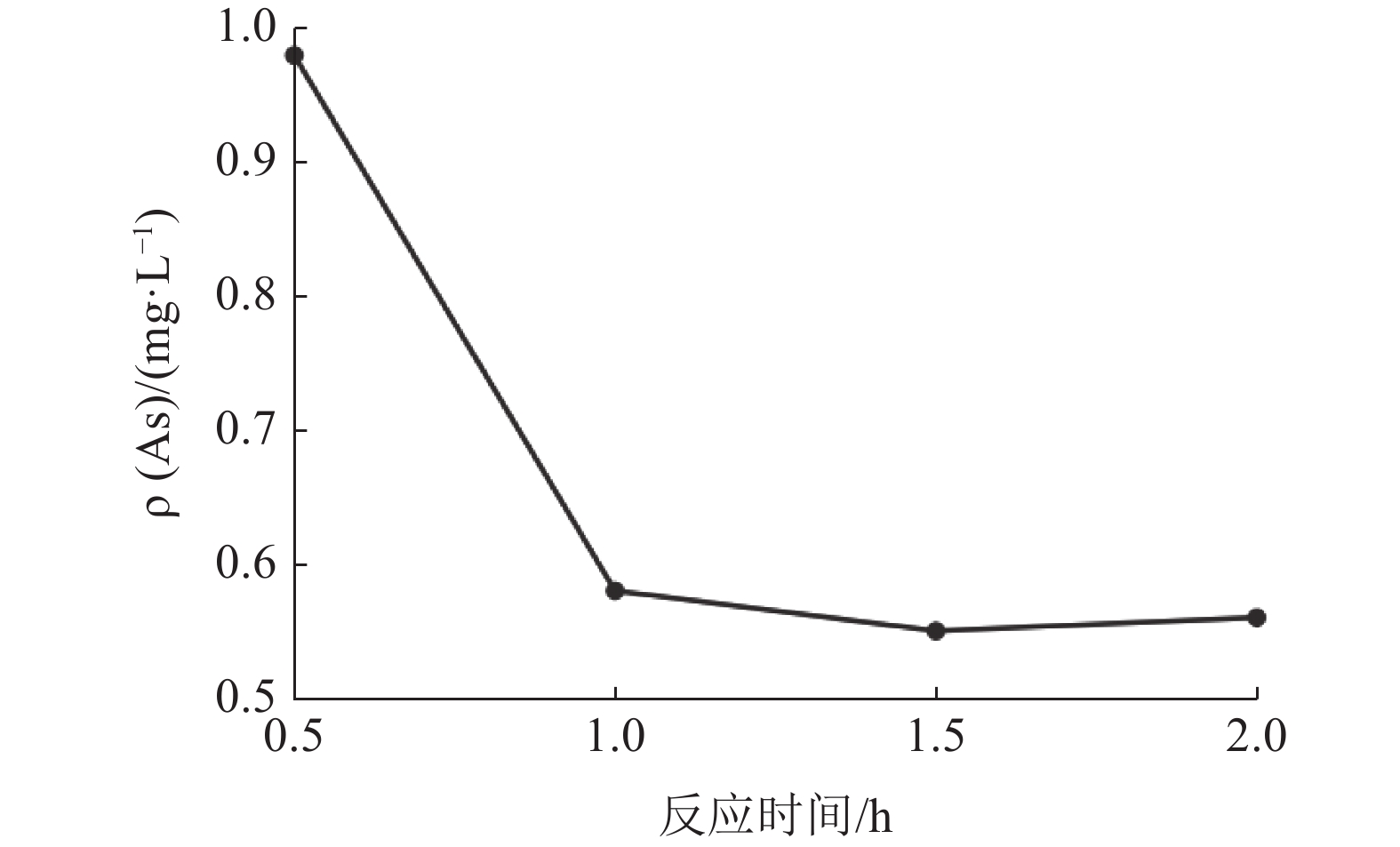
/(mLˑL-1)氰渣毒性浸出液ρ/(mgˑL-1) 总氰化物 As pH值 0 9.20 3.28 10.55 0.5 8.85 4.29 8.32 1.0 7.77 4.12 8.29 1.5 5.78 4.02 8.08 2.0 3.23 3.88 7.99 2.5 3.15 3.08 8.03 表 4 反应pH值对固砷的影响
Table 4. Effect of pH value on arsenic fixation
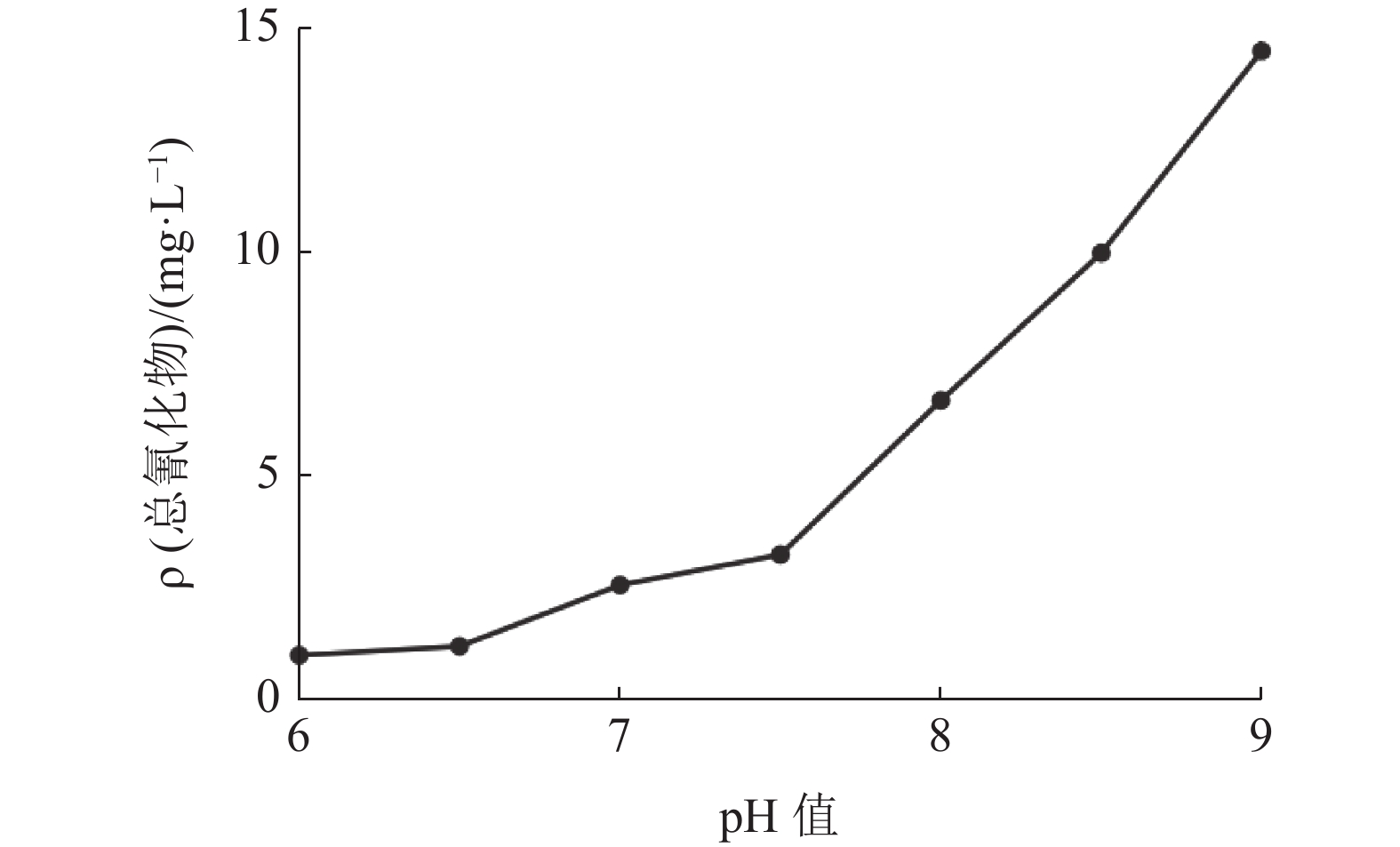
反应pH值 氰渣毒性浸出液ρ/(mgˑL-1) 总氰化物 As pH值 8.0 4.22 2.36 8.41 7.5 3.15 2.22 8.22 7.0 1.22 1.98 8.16 6.5 0.22 0.55 7.94 6.0 0.20 0.51 7.88 表 5 综合验证实验结果/(mgˑL-1)
Table 5. Comprehensive verification test results
总氰化物 Cu Zn Pb As Hg Cd Cr Cr6+ 0.25 1.25 0.06 0.05 0.55 <0.01 <0.05 <0.05 <0.05 -
[1] 杨静, 张亚莉, 于先进, 等. 氰化贫液处理方法研究现状[J]. 湿法冶金, 2012, 31(5):278-280. doi: 10.13355/j.cnki.sfyj.2012.05.017
YANG J, ZHANG Y L, YU X J, et al. Research status of treatment methods for cyanidation lean liquid[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2012, 31(5):278-280. doi: 10.13355/j.cnki.sfyj.2012.05.017
[2] 胡杨甲, 贺政, 赵志强, 等. 氰化浸出废水处理方法研究进展[J]. 中国矿业, 2015, 24(Z1):219-223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2015.z1.059
HU Y J, HE Z, ZHAO Z Q, et al. Progress in research on treatment methods of cyanide leaching wastewater[J]. China Mining, 2015, 24(Z1):219-223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2015.z1.059
[3] 吴铃, 楚金澄, 李延吉. 臭氧氧化法处理含氰废水工艺的系统优化[J]. 黄金, 2016, 37(7):69-72.
WU L, CHU J C, LI Y J. Systematic optimization of ozonation process for treatment of cyanide-containing wastewater[J]. Gold, 2016, 37(7):69-72.
[4] 周珉, 黄仕源, 瞿贤. 过氧化氢催化氧化法处理高浓度含氰废水研究[J]. 工业用水与废水, 2013, 44(5):31-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2455.2013.05.009
ZHOU M, HUANG S Y, QU X. Treatment of high concentration cyanide wastewater by catalytic oxidation of hydrogen peroxide[J]. Industrial Water and Wastewater, 2013, 44(5):31-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2455.2013.05.009
[5] 于艳杰, 方登志, 肖淑君, 等. 氰化渣的无害化处置实验研究[J]. 湿法冶金, 2019, 38(4):330-333.
YU Y J, FANG D Z, XIAO S J, et al. Experimental study on harmless treatment of cyanide residue[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2019, 38(4):330-333.
[6] 朱洪, 威石旭, 崔韬, 等. “铁络合-生物法”组合工艺降解有机、无机氰[J]. 环境与发展, 2019, 33(2):59-61.
ZHU H, WEI S X, CUI T, et al. Degradation of organic and inorganic cyanide by iron complexation-biological process[J]. Environment and Development, 2019, 33(2):59-61.
[7] 丛忠奎, 迟崇哲, 邱陆明, 等. 某黄金冶炼公司氰化尾矿无害化处理技术研究[J]. 黄金, 2017, 38(7):59-62. doi: 10.11792/hj20170716
CONG Z K, CHI C Z, QIU L M, et al. Research on harmless treatment technology of cyanidation tailings in a gold smelting company[J]. Gold, 2017, 38(7):59-62. doi: 10.11792/hj20170716
[8] 高腾跃. 氰化氰渣固液分离洗涤废水净化工艺研究[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2019, 37(12):5-7,12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2019.12.002
GAO T Y. Research on the purification process of washing wastewater from solid-liquid separation with cyanide residue[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2019, 37(12):5-7,12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2019.12.002
[9] 曾新民. 提高酸化法从废水回收氰化物的途径[J]. 工程设计与研究, 1994, 84(6):46-48.
ZENG X M. Methods to recover cyanide from wastewater by increasing acidification[J]. Engineering Design and Research, 1994, 84(6):46-48.
[10] 李亚峰, 顾涛. 金矿含氰废水处理技术[J]. 当代化工, 2003, 32(1):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2003.01.001
LI Y F, GU T. Treatment technology of cyanide wastewater from gold mines[J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2003, 32(1):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2003.01.001
[11] 王海娟, 宁平, 唐兴进, 等. 含砷金矿蜈蚣草除砷应用前景探讨[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2010(2):94-98. doi: 10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2010.02.006
WANG H J, NING P, TANG X J, et al. Discussion on the prospect of application of scolopendrium in arsenic removal in gold deposits[J]. Research and Development of Mining Industry, 2010(2):94-98. doi: 10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2010.02.006
[12] 陈京玉, 陈志国, 康卫刚. 新疆某伴生铜钴矿降砷回收工艺研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(1):51-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.01.011
CHEN J Y, CHEN Z G, KANG W G. Research on reducing arsenic and recovering mineral processing technology of certain arsenic-bearing copper ore in Xinjiang[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(1):51-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.01.011
[13] 任春玉. 过氧化氢法净化含氰废水工艺初步探讨[J]. 黄金, 1992, 13(10):37-40.
REN C Y. Preliminary study on purification process of cyanide containing wastewater by hydrogen peroxide method[J]. Gold, 1992, 13(10):37-40.
-



 下载:
下载: