Recent Progress on Reaction Mechanism, Properties, and Application of Alkali-Activated Geopolymer
-
摘要:
这是一篇陶瓷及复合材料领域的论文。碱激发地质聚合物(简称“地聚物”)是一种新型的无机胶凝材料,由硅-氧四面体和铝-氧四面体通过共用氧原子相互交联而形成,铝-氧四面体所带的负电荷通过碱金属阳离子平衡。由于具有高度聚合的氧化物网络结构,且结构稳定性高,地聚物具有优异的性能:高强度、耐久性、耐高温性等,使其在高性能建材的制备、废水的处理、固废资源化等领域得到广泛的应用与研究。为综合了解碱激发地聚物的研究现状,本文总结了国内外关于碱激发地聚物反应机理的研究现状,综述了地聚物微观结构与力学性能的最新进展,并介绍了其在建材、环境污染治理和固废资源化利用等领域的研究进展。
Abstract:This is an essay in the field of ceramics and composites. Alkali-activated geopolymer is a new kind of inorganic cementitious material, which is formed by cross-linking of silicon-oxygen tetrahedrons and aluminum-oxygen tetrahedrons through the bridging oxygen atoms. The negative charges of aluminum-oxygen tetrahedrons are balanced by alkali metal cations. Due to its three-dimensional network structure, geopolymers have excellent properties such as high mechanical properties, good durability, and excellent heat resistance. They have been widely used in the high-performance construction materials preparation, wastewater treatment, and solid waste recycling. This article reviews the research progress of the reaction mechanism, microstructure, and mechanical properties of alkali-activated geopolymers. In addition, the development of its application research in the fields of building materials, environmental pollution control, and solid waste resource utilization is also introduced in this article in order to comprehensively understand the research status of alkali-activated geopolymers.
-

-
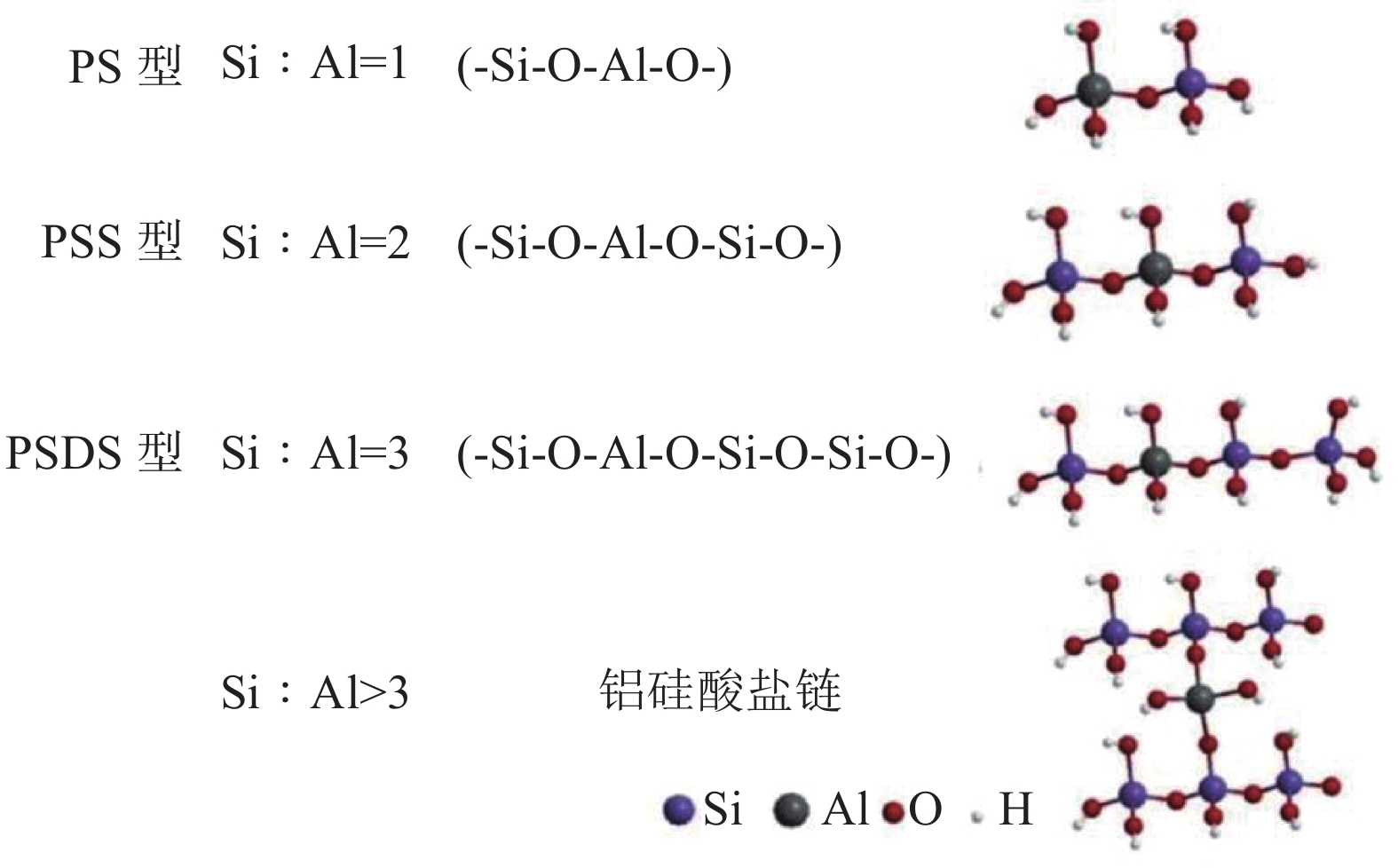
图 1 地聚物结构单元[20]
Figure 1.
-
[1] 李涛, 罗仙平, 钱有军. 加水一体化合成钨尾矿基地聚合物[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(1):83-87. LI T, LUO X P, QIAN Y J. Investigation on synthesis of tungsten tailings base geopolymer by water integration[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(1):83-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.01.018
LI T, LUO X P, QIAN Y J. Investigation on synthesis of tungsten tailings base geopolymer by water integration[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(1): 83-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.01.018
[2] 汪应玲, 罗绍华, 姜茂发, 等. 铁尾矿制备地质聚合物工艺条件研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(5):121-126. WANG Y L, LUO S H, JIANG M F, et al. Study on process conditions for geopolymer from iron tailings[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(5):121-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.05.026
WANG Y L, LUO S H, JIANG M F, et al. Study on process conditions for geopolymer from iron tailings[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(5): 121-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.05.026
[3] M Chougan, S Hamidreza Ghaffar, M Jahanzat, et al. The influence of nano-additives in strengthening mechanical performance of 3D printed multi-binder geopolymer composites[J]. Constrcution and Building Materials, 2020, 250:118928. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118928
[4] C Kuenzel, J F Cisneros, T P Neville, et al. Encapsulation of Cs/Sr contaminated clinoptilolite in geopolymers produced from metakaolin[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2015, 466:94-99. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2015.07.034
[5] T Lan, P Li, F U Rehman, et al. Efficient adsorption of Cd2+ from aqueous solution using metakaolin geopolymers[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 2019, 26:33555-33567. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06362-w
[6] R Bendoni, F Miccio, V Medri, et al. Geopolymer composites for the catalytic cleaning of tar in biomass-derived gas[J]. Renewable Energy, 2019, 131:1107-1116. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2018.08.067
[7] 邵宁宁. 碱激发粉煤灰过程机理及其发泡胶凝材料的高性能化[D] . 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2017.
SHAO N N. Mechanism of alkali-excited fly ash process and its high performance of foamed cementitious materials [D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing), 2017.
[8] M Sandanayake, C Gunasekara, D Law, et al. Greenhouse gas emissions of different fly ash based geopolymer concretes in building construction[J]. J Clean Prod, 2018, 204:399-408. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.311
[9] P Kinnunen, A Ismailov, S Solismaa, et al. Recycling mine tailings in chemically bonded ceramics - A review[J]. J Clean Prod, 2018, 174:634-649. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.280
[10] B Zhang, P Yuan, H Guo, et al. Effect of curing conditions on the microstructure and mechanical performance of geopolymers derived from nanosized tubular halloysite[J]. Constrcution and Building Materials, 2202, 1,68:121186.
[11] J Davidovits. Geopolymers and geopolymeric materials[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis, 1989, 35:429-441. doi: 10.1007/BF01904446
[12] D Khale, R Chaudhary. Mechanism of geopolymerization and factors influencing its development: a review[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42:729-746. doi: 10.1007/s10853-006-0401-4
[13] X Yao, Z Zhang, H Zhu, et al. Geopolymerization process of alkali–metakaolinite characterized by isothermal calorimetry[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2009, 493:49-54. doi: 10.1016/j.tca.2009.04.002
[14] 吴静. 新型地聚合物基建筑材料的研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2007.
WU J. Research on new geopolymer-based building materials [D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2007.
[15] M Bing-hui, Z He, C Xue-min, et al. Effect of curing temperature on geopolymerization of metakaolin-based geopolymers[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2014, 99:144-148. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2014.06.024
[16] 张云升, 孙伟, 林玮, 等. 用环境扫描电镜原位定量研究K-PS型地聚合物水泥的水化过程[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 33(3):351-354. ZHANG Y S, SUN W, LIN W, et al. In situ quantitative study of the hydration process of K-PS geopolymer cement by environmental scanning electron microscopy[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2003, 33(3):351-354. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0505.2003.03.026
ZHANG Y S, SUN W, LIN W, et al. In situ quantitative study of the hydration process of K-PS geopolymer cement by environmental scanning electron microscopy[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2003, 33(3): 351-354. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0505.2003.03.026
[17] A Fernández-Jiménez, A Palomo, M Criado. Microstructure development of alkali-activated fly ash cement: a descriptive model[J]. Cement & Concrete Research, 35(2005) 1204-1209.
[18] 闫姝. 氧化石墨烯增强铝硅酸盐聚合物的聚合与陶瓷化机制[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2016.
YAN S. Polymerisation and ceramisation mechanism of graphene oxide reinforced aluminosilicate polymers [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2016.
[19] 贾德昌, 何培刚, 苑景坤, 等. 铝硅酸盐聚合物及其复合材料研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2017, 45(12):17-37. JIA D C, HE P G, YUAN J K, et al. Research progress on aluminosilicate polymers and their composites[J]. Journal of Silicates, 2017, 45(12):17-37. doi: 10.14062/j.issn.0454-5648.2017.12.02
JIA D C, HE P G, YUAN J K, et al. Research progress on aluminosilicate polymers and their composites[J]. Journal of Silicates, 2017, 45(12): 17-37. doi: 10.14062/j.issn.0454-5648.2017.12.02
[20] 刘意. 开孔地质聚合物与多级孔分子筛的制备及吸附Pb2+、Cu2+的研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2018.
LIU Y. Preparation of open-pore geopolymer with multistage porous molecular sieves and adsorption of Pb2+ and Cu2+ [D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2018.
[21] V Barbosa, K Mackenzie, C Thaumaturgo. Synthesis and characterisation of materials based on inorganic polymers of alumina and silica[J]. Sodium Polysialate Polymers, 2(2000) 0-317.
[22] P Duxson, S W Mallicoat, G C Lukey, et al. The effect of alkali and Si/Al ratio on the development of mechanical properties of metakaolin-based geopolymers[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 292(2007) 8-20.
[23] S Das, P Yang, S. S Singh, et al. Effective properties of a fly ash geopolymer: Synergistic application of X-ray synchrotron tomography, nanoindentation, and homogenization models[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 78(2015) 252-262.
[24] Jaroslav, Melar, Guillaume, et al. The porous network and its interface inside geopolymers as a function of alkali cation and aging[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 119(2015) 17619-17632.
[25] Lolli, Francesca, Manzano, et al. Atomistic simulations of geopolymer models: the impact of disorder on structure and mechanics[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, (2018).
[26] R Wang, J Wang, T Dong, et al. Structural and mechanical properties of geopolymers made of aluminosilicate powder with different SiO2/Al2O3 ratio: Molecular dynamics simulation and microstructural experimental study[J]. Constrcution and Building Materials, 240(2020) 117935.
[27] Z Ji, Y Pei. Bibliographic and visualized analysis of geopolymer research and its application in heavy metal immobilization: a review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 231(2019) 256-267.
[28] 简家成, 刘峥, 杨宏斌, 等, 地聚物胶凝材料制备及应用研究现状[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2014: 18-22.
JIAN J C, LIU Z, YANG H B, et al. Research on preparation and application status of geopolymers[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2014: 18-22.
[29] P Krivenko, R Drochytka, A Gelevera, et al. Mechanism of preventing the alkali–aggregate reaction in alkali activated cement concretes[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 45(2014) 157-165.
[30] K Chen, D Wu, L Xia, et al. Geopolymer concrete durability subjected to aggressive environments – a review of influence factors and comparison with ordinary Portland cement[J]. Constrcution and Building Materials, 279(2021) 122496.
[31] 陶文宏, 付兴华, 孙凤金, 等. 地聚物胶凝材料性能与聚合机理的研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2008: 730-735+739.
TAO W H, FU X H, SUN F J, et al. Studies on properties and mechanisms of geopolymer cementitious material[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2008: 730-735+739.
[32] G. F Huseien, J Mirza, M Ismail, et al. Geopolymer mortars as sustainable repair material: A comprehensive review[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 80(2017) 54-74.
[33] 张晓飞. 地质聚合物聚合机理的第一性原理研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2010.
ZHANG X F. First-principles study on the polymerisation mechanism of geopolymers[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010.
[34] C Shi, B Qu, J L Provis. Recent progress in low-carbon binders[J]. Cement & Concrete Research, 122(2019) 227-250.
[35] B Zhang, H Guo, P Yuan, et al. Geopolymerization of halloysite via alkali-activation: Dependence of microstructures on precalcination[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2020, 185:105375. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2019.105375
[36] B Walkley, R San Nicolas, M A Sani, et al. Phase evolution of C-(N)-A-S-H/N-A-S-H gel blends investigated via alkali-activation of synthetic calcium aluminosilicate precursors[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2016, 89:120-135. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2016.08.010
[37] J Davidovits, 30 years of successes and failures in geopolymer applications[J]. Market Trends and Potential Breakthroughs, 2002.
[38] Z Zhang, J L Provis, A Reid, et al. Mechanical, thermal insulation, thermal resistance and acoustic absorption properties of geopolymer foam concrete[J]. Cement & Concrete Composites, 2015, 62:97-105.
[39] P Duan, C Yan, W Luo, et al. A novel surface waterproof geopolymer derived from metakaolin by hydrophobic modification[J]. Materials Letters, 164(2016): 172-175.
[40] A R G Azevedo, C M F Vieira, W M Ferreira, et al. Potential use of ceramic waste as precursor in the geopolymerization reaction for the production of ceramic roof tiles[J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 29(2020) 101156.
[41] Z Zhang, X Yao, H Wang. Potential application of geopolymers as protection coatings for marine concrete III Field experiment[J]. Applied Clay Science, 67-68(2012) 57-60.
[42] 王开拓. 碱基地质聚合物在低温及真空条件下的反应机理与应用探索[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2016.
WANG K T. Exploration of reaction mechanism and application of alkali geopolymers under low temperature and vacuum conditions [D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2016.
[43] M. Z Naser, Extraterrestrial construction materials[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2019, 105:100577. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2019.100577
[44] E Hermann, C Kunze, R Gatzweiler, et al. Solidification of various radioactive residues by géopolymère®with special emphasis on long-term-stability[J]. Geopolymere ’99 Proceedings, [2023-09-15]
[45] X Guo, L Zhang, J Huang, et al. Detoxification and solidification of heavy metal of chromium using fly ash-based geopolymer with chemical agents[J]. Constrcution and Building Materials, 2017, 151:394-404. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.05.199
[46] M. R El-Naggar, E. H El-Masry, A. A El-Sadek. Assessment of individual and mixed alkali activated binders for solidification of a nuclear grade organic resin loaded with 134Cs, 60Co and 152+154Eu radionuclides[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 375:149-160. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.04.063
[47] Immobilization behavior of Sr in geopolymer and itsceramic product[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019.
[48] A Al-Mashqbeh, S Abuali, B El-Eswed, et al. Immobilization of toxic inorganic anions(Cr2O72-, MnO4- and Fe(CN)63-) in metakaolin based geopolymers: A preliminary study[J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44:5613-5620. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.12.208
[49] T Luukkonen, A Heponiemi, H Runtti, et al. Application of alkali-activated materials for water and wastewater treatment: a review[J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio-Technology, 2019, 18:271-297. doi: 10.1007/s11157-019-09494-0
[50] S Andrejkovičová, A Sudagar, J Rocha, et al. The effect of natural zeolite on microstructure, mechanical and heavy metals adsorption properties of metakaolin based geopolymers[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2016, 126:141-152. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2016.03.009
[51] İ Kara, D Yilmazer, S T Akar, Metakaolin based geopolymer as an effective adsorbent for adsorption of zinc(II) and nickel(II) ions from aqueous solutions[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2017, 139: 54-63.
[52] T Hertel, R M Novais, R M Alarcon, et al. Use of modified bauxite residue-based porous inorganic polymer monoliths as adsorbents of methylene blue[J]. J Clean Prod, 2019, 227:877-889. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.084
[53] S Zhao, F Muhammad, L Yu, et al. Solidification/stabilization of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash using uncalcined coal gangue–based alkali-activated cementitious materials[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 2019.
[54] M C M Nasvi, P G Ranjith, J Sanjayan. The permeability of geopolymer at down-hole stress conditions: Application for carbon dioxide sequestration wells[J]. Applied Energy, 2013, 102: 1391-1398.
[55] B Panda, S. C Paul, N. A. N Mohamed, et al. Measurement of tensile bond strength of 3D printed geopolymer mortar[J]. Measurement, 2018, 113:108-116. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2017.08.051
[56] B Cai, H Engqvist, S Bredenberg. Evaluation of the resistance of a geopolymer-based drug delivery system to tampering[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2014, 465:169-174. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.02.029
[57] G Ascensão, M. P Seabra, J. B Aguiar, et al. Red mud-based geopolymers with tailored alkali diffusion properties and pH buffering ability[J]. J Clean Prod, 2017, 148:23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.150
[58] Y. J Zhang, P. Y He, Y. X Zhang, et al. A novel electroconductive graphene/fly ash-based geopolymer composite and its photocatalytic performance[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 334:2459-2466. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.171
[59] J Davidovits, L Huaman, R Davidovits. Ancient geopolymer in south-American monument SEM and petrographic evidence[J]. Materials Letters, 2019, 235: 120-124.
-



 下载:
下载: