Geological Characteristics, Genetic Analysis and Extraction Technology of Potassium Salt Deposits along Hormuz Strait, Iran
-
摘要:
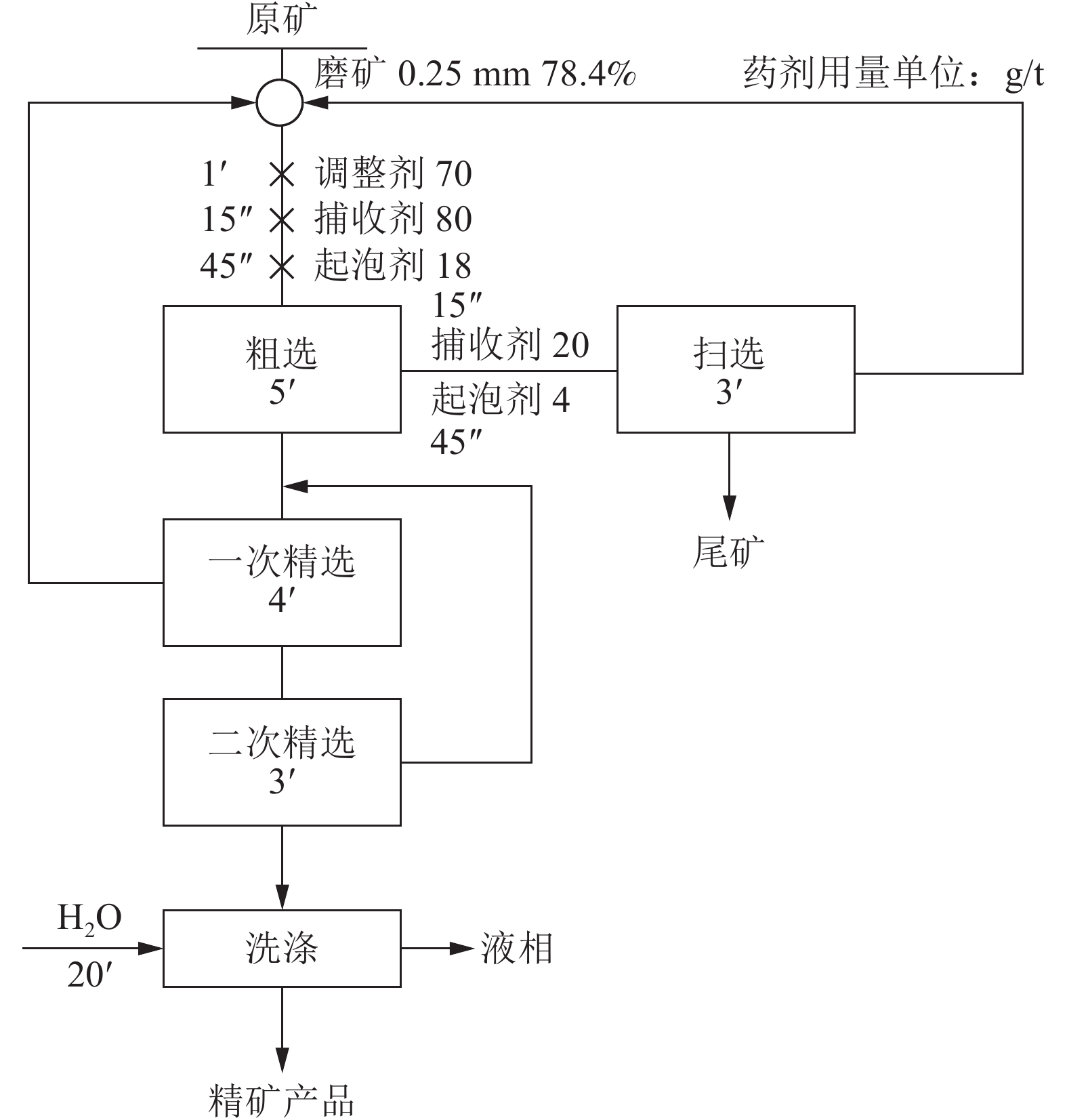
这是一篇地球科学及矿物加工工程领域的论文。伊朗霍尔木兹海峡沿岸钾盐矿赋存于寒武系Hormuz组盐层内,矿体受褶皱构造控制,形态复杂,形成的“S”形、顶厚、平卧等褶皱形态,矿石类型为氯化物型钾石盐矿石,主要矿石矿物为钾石盐,KCl含量2.5%~35.20%。研究区寒武系为泻湖相沉积,波斯湾含钾卤水持续蒸发形成一套含钾石盐海相蒸发岩序列,受阿尔卑斯早期构造活动影响,含钾盐层受挤压作用,形成盐底辟构造。采用一次粗选一次扫选二次精选及浮选精矿加洗涤的实验流程,可以获得了含KCl(湿基87.44%,干基91.14%)或KCl(湿基88.97%,干基93.69%)两种的氯化钾产品,KCl回收率分别为85.93%、81.70%,钾盐选矿指标良好。
Abstract:This is an article in the field of earth sciences and mining processing engineering. Potash ore occurs in the salt layer of Cambrian Hormuz Formation, The ore body is in dancing band with great thickness variation. The ore type is chloride-type sylvite ore, the main ore mineral is sylvite, with KCl content of 2.5%~35.20%. The Cambrian is a lagoon facies deposit. The continuous evaporation of potassium-bearing brine in the Persian Gulf formed a series of marine evaporite sequence containing potassium salt.Affected by the early Alpine structureactivity, the salt layer was compressed to form a salt diapir structure.Using the test flow of one roughing, one scavenger, two concentrating and Coarse ore washing, good test indexes have been achieved, and potassium chloride products containing 87.44% KCl (wet basis) (91.14% dry basis) or 88.97% KCl (wet basis) (93.69% dry basis) can be obtained, with KCl recovery rates of 85.93% and 81.70% , respectively.
-

-
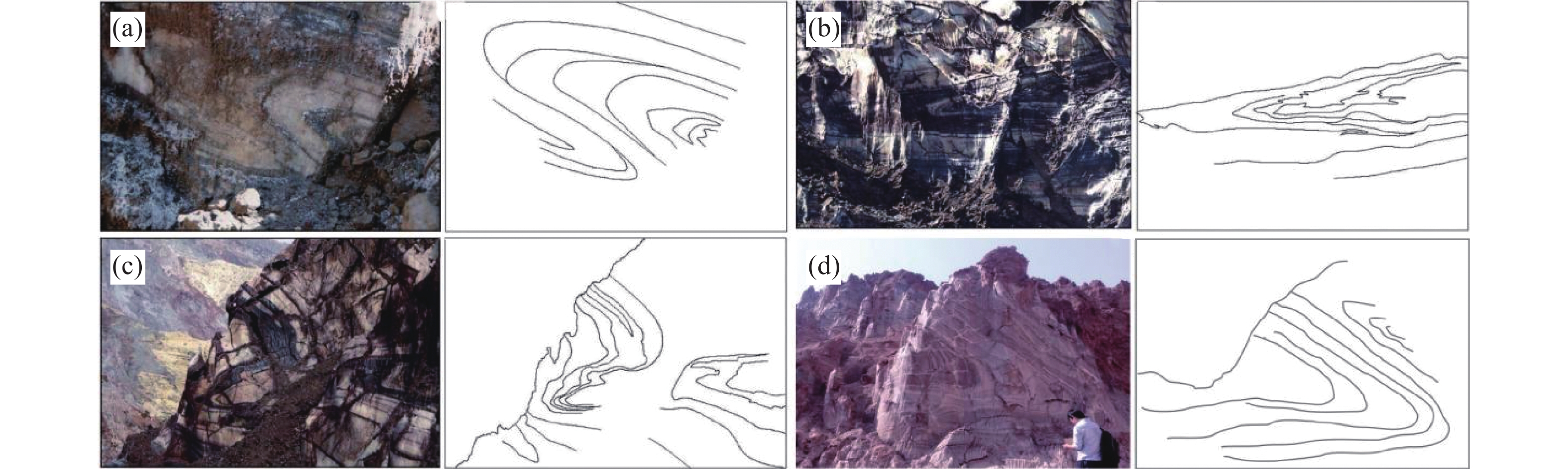
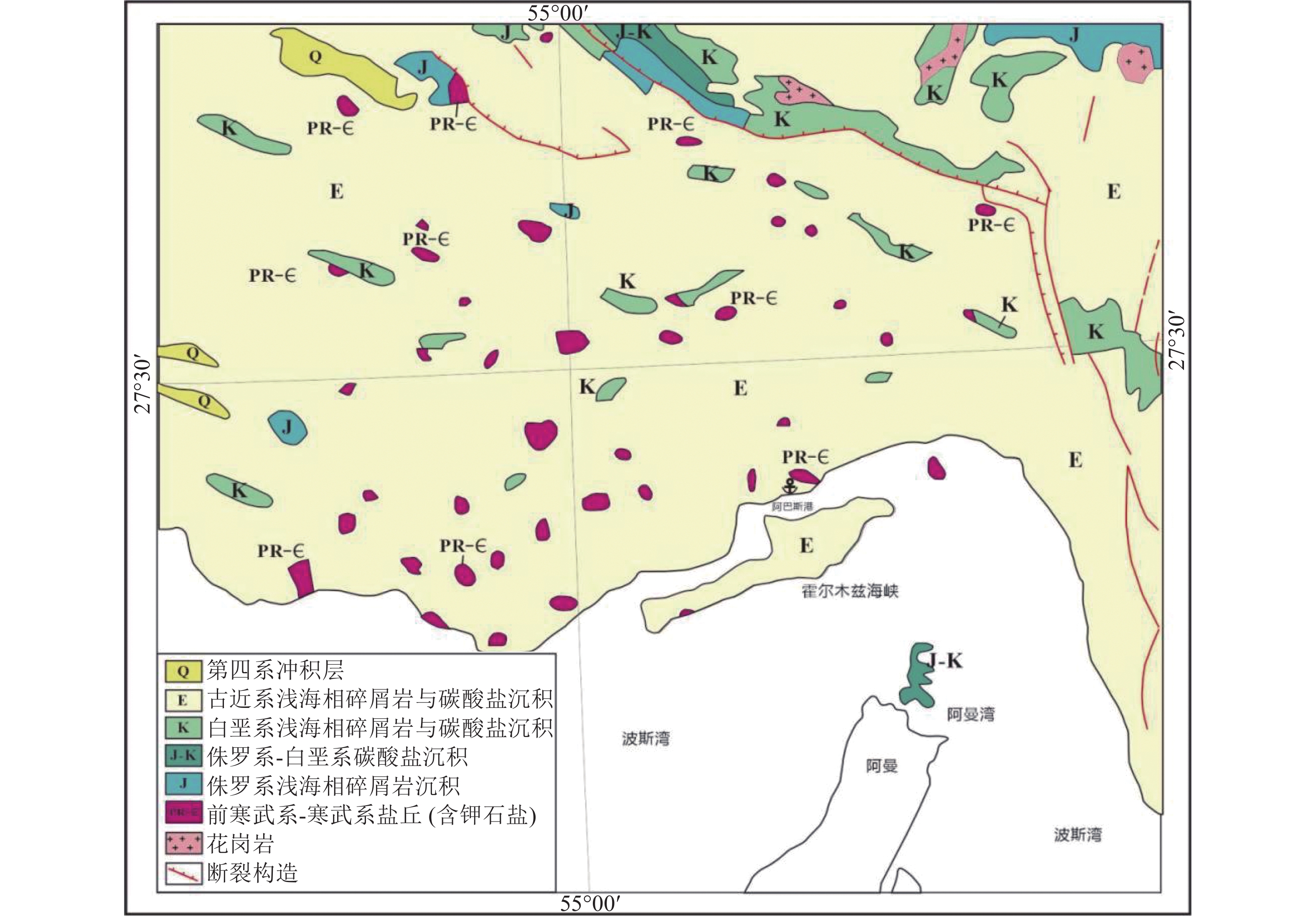
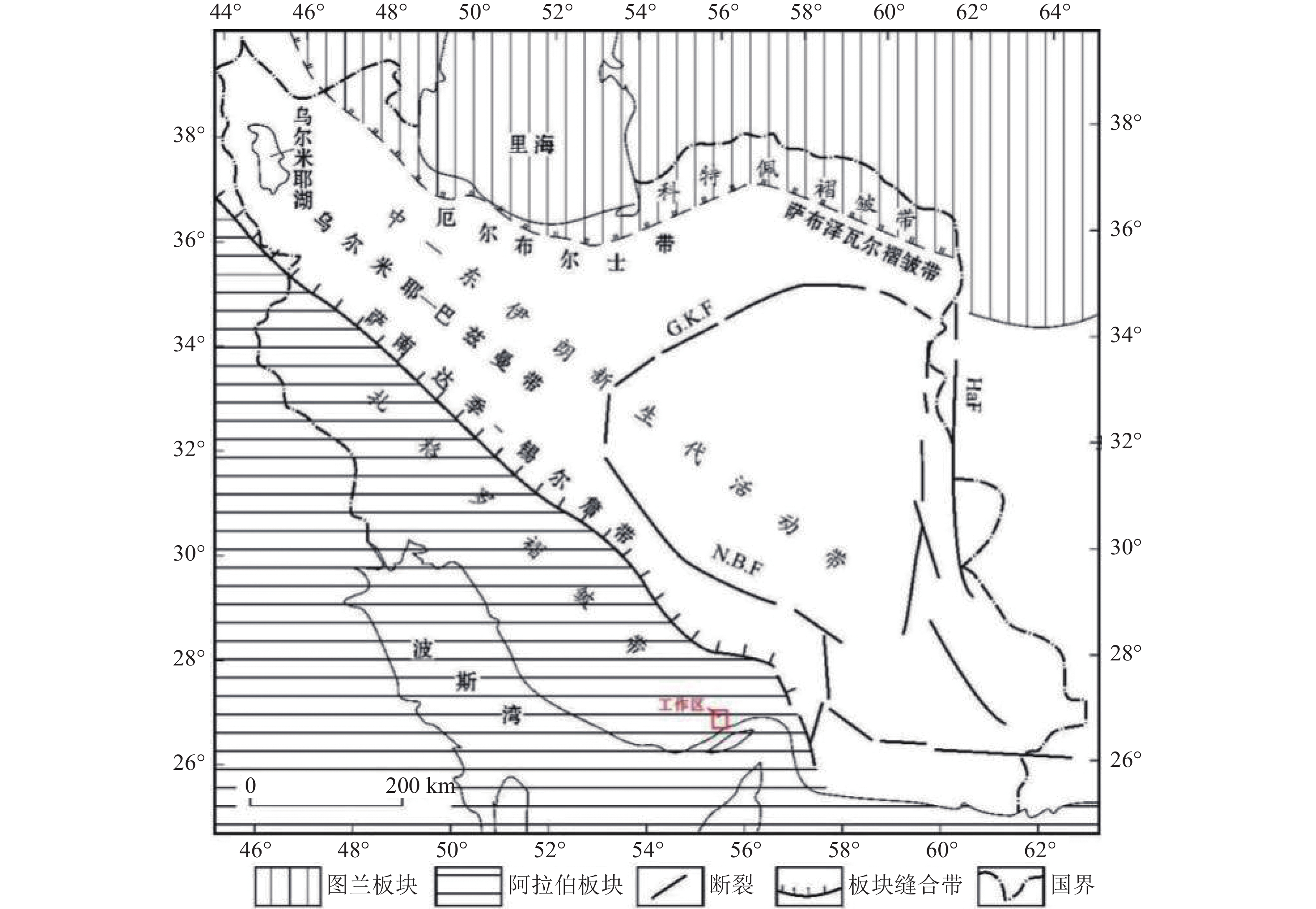
图 1 研究区大地构造[13]
Figure 1.
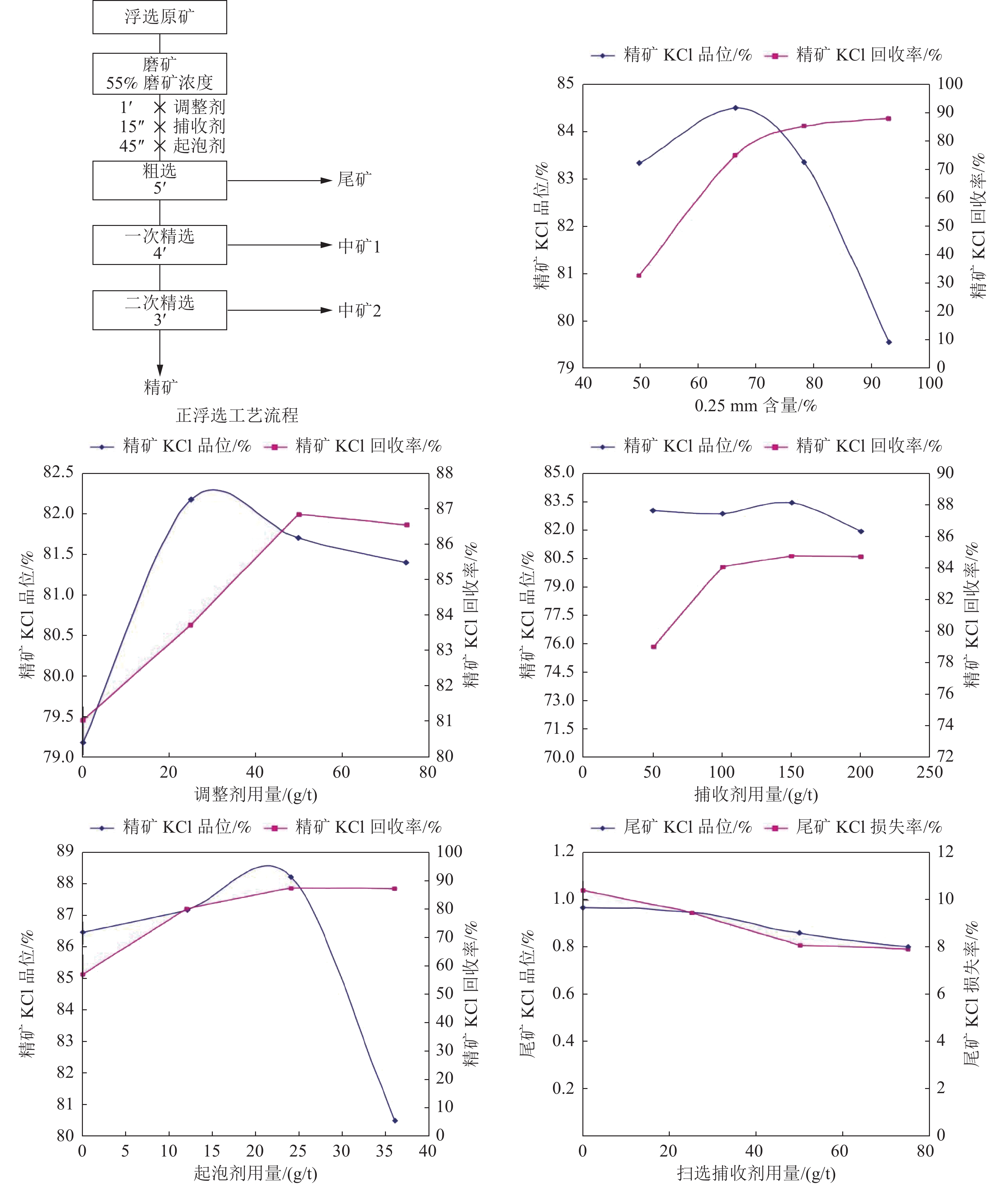
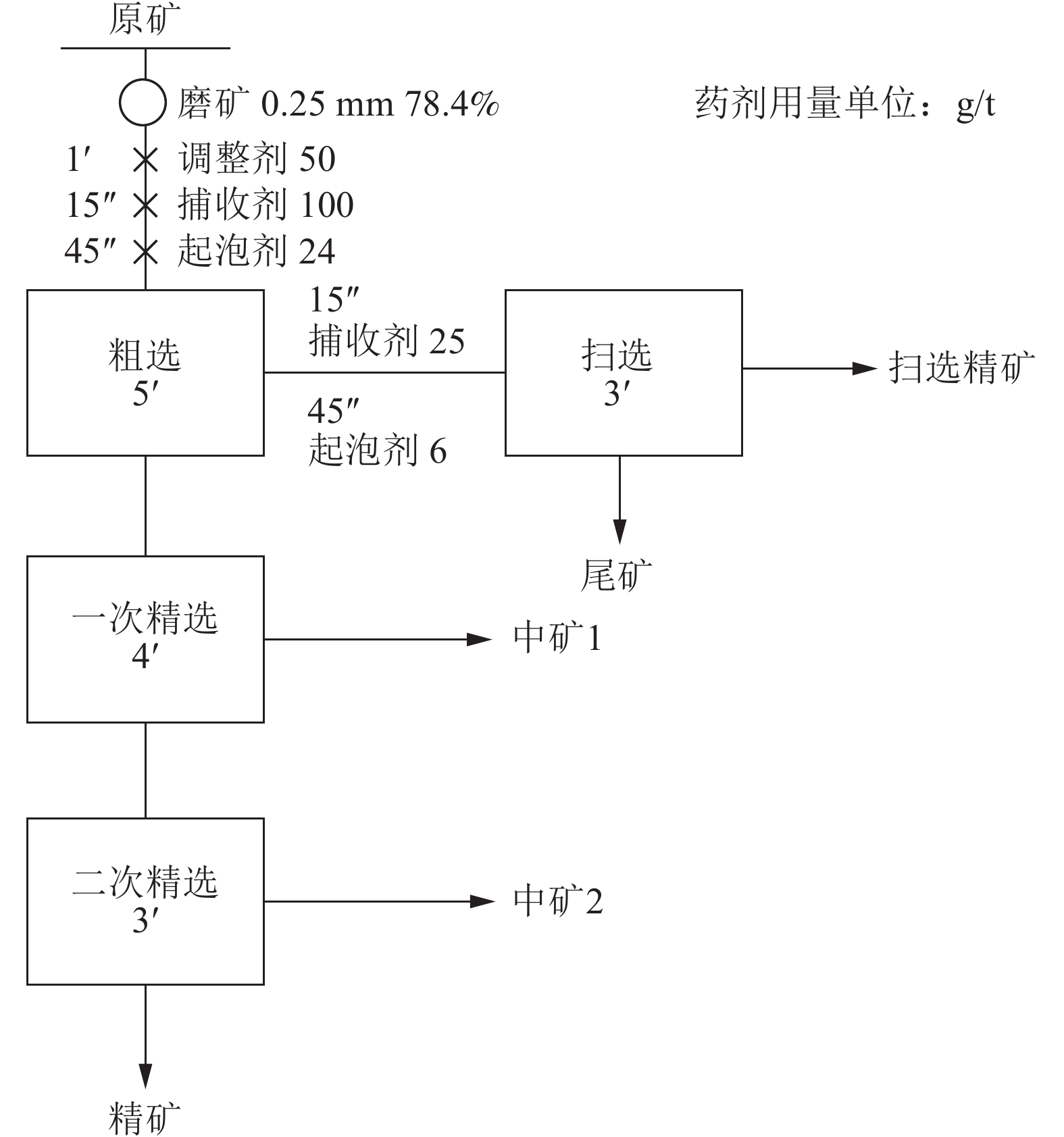
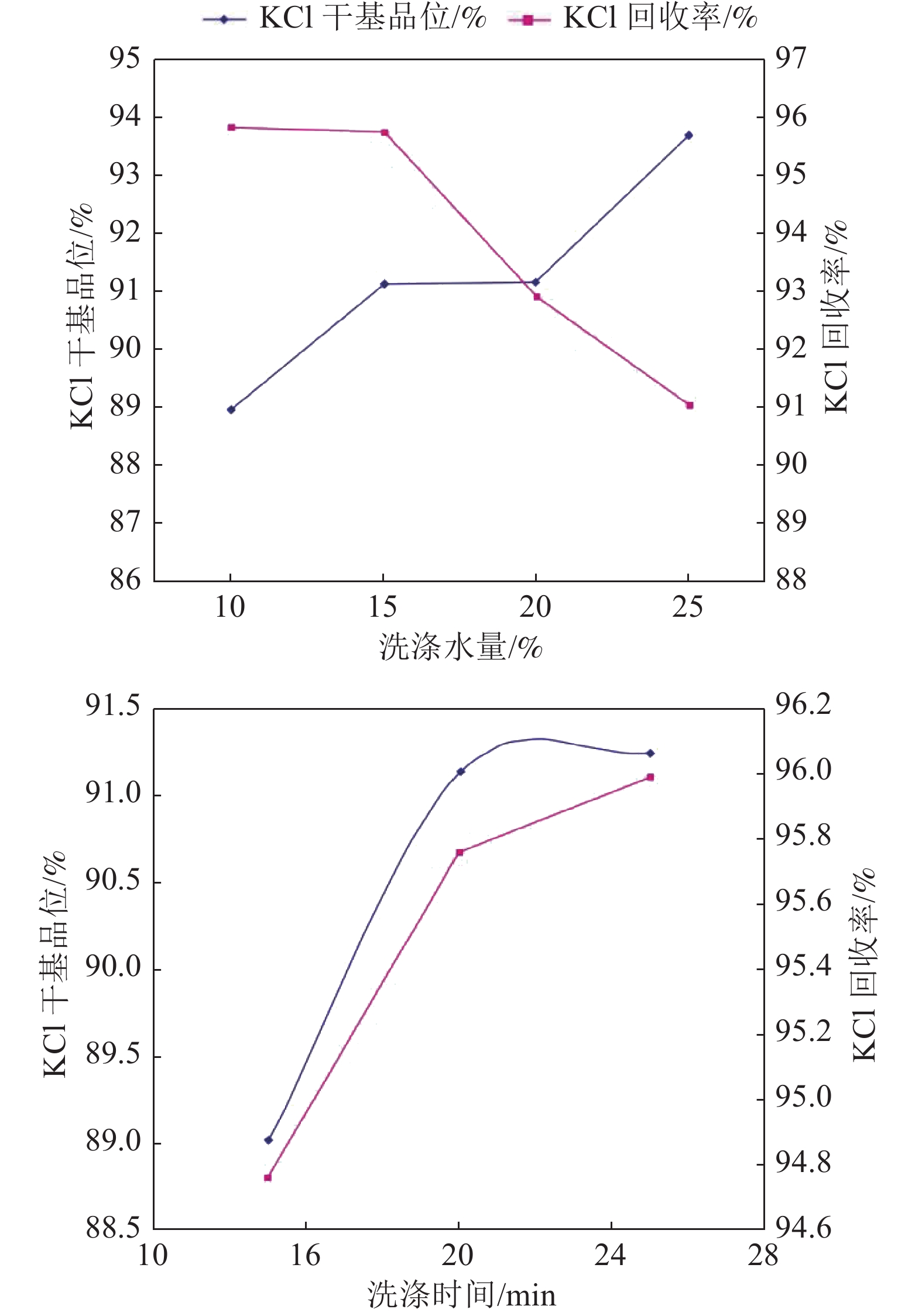
表 1 全开路流程实验结果
Table 1. Open-circuit process test results
产品名称 产率/% KCl品位/% KCl回收率/% 精矿 9.19 84.71 87.36 中矿2 1.33 14.57 2.17 中矿1 6.92 2.71 2.11 扫选精矿 1.36 3.98 0.61 尾矿 81.2 0.85 7.76 表 2 闭路流程实验结果
Table 2. Close-circuit process test results
产品名称 产率/% KCl品位/% KCl回收率/% 原矿 100.00 8.75 100.00 精矿 9.39 83.55 89.37 尾矿 90.61 0.99 10.27 表 3 一次粗选一次扫选二次精选及浮选精矿加洗涤流程实验结果
Table 3. One roughing, one scavenger, two concentrating and coarse ore washing test results
产品 KCl品位/% KCl总回收率/% 湿基 干基 90% KCl 87.44 91.14 85.93 93% KCl 88.97 93.69 81.70 -
[1] 王松, 赵元芝, 汪傲, 等. “一带一路”国家钾盐及硼资源分布规律与开采技术[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(1):35-49.WANG S, ZHAO Y Z, WANG A, et al. A study of distribution regularity and exploitation techniques of potash and boronresources in countries of "One Belt, One Road"a[J]. Geological Bulletin of Chin, 2017, 36(1):35-49.
WANG S, ZHAO Y Z, WANG A, et al . A study of distribution regularity and exploitation techniques of potash and boronresources in countries of "One Belt, One Road"a[J]. Geological Bulletin of Chin,2017 ,36 (1 ):35 -49 .[2] 马鸿文, 苏双青, 刘浩, 等. 中国钾资源与钾盐工业可持续发展[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(1):294-310.MA H W, SU S Q, LIU H, et al. Potassium resource and sustainable development of potash salt industry in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(1):294-310.
MA H W, SU S Q, LIU H, et al . Potassium resource and sustainable development of potash salt industry in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2010 ,17 (1 ):294 -310 .[3] 李萌, 刘正阳, 王建平, 等. 我国钾盐资源现状分析及可持续发展建议[J]. 中国矿业, 2016, 25(9):1-7.LI M, LIU Z Y, WANG J P, et al. Current status and sustainable development of potash resources in China[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2016, 25(9):1-7.
LI M, LIU Z Y, WANG J P, et al . Current status and sustainable development of potash resources in China[J]. China Mining Magazine,2016 ,25 (9 ):1 -7 .[4] 刘佳. 我国钾盐资源供需态势与国内外供矿前景分析[J]. 中国矿业, 2011, 20(SI):24-27.LIU J. Analysis on China’s demand-supply status and world potentials of potash resource[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2011, 20(SI):24-27.
LIU J . Analysis on China’s demand-supply status and world potentials of potash resource[J]. China Mining Magazine,2011 ,20 (SI ):24 -27 .[5] 郑厚义, 陆渝霞, 焦森, 等. “一带一路”沿线地区钾盐资源分布与战略选区分析[J]. 中国矿业, 2017, 26(11):42-46,52.ZHENG H Y, LU Y X, JIAO S, et al. Discussion on investment strategy layout of potash resources along“Belt and Road”[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2017, 26(11):42-46,52.
ZHENG H Y, LU Y X, JIAO S, et al . Discussion on investment strategy layout of potash resources along“Belt and Road”[J]. China Mining Magazine,2017 ,26 (11 ):42 -46,52 .[6] 邢万里, 陈其慎. 中国钾盐资源安全简析[J]. 中国矿业, 2013, 22(12):11-14.XING W L, CHEN Q S. Analysis of potash resource security in China[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2013, 22(12):11-14.
XING W L, CHEN Q S . Analysis of potash resource security in China[J]. China Mining Magazine,2013 ,22 (12 ):11 -14 .[7] 罗婷, 张永庆, 郑明贵, 等. 中国钾盐资源安全评估与预警研究[J]. 地球科学进展, 2022, 37(6):575-587.LUO T, ZHANG Y Q, ZHENG M G, et al. Security assessment and early warning of potash resources in China[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2022, 37(6):575-587.
LUO T, ZHANG Y Q, ZHENG M G, et al . Security assessment and early warning of potash resources in China[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2022 ,37 (6 ):575 -587 .[8] 曹文虎, 吴蝉, 等. 卤水资源及其综合利用技术[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004.CAO W H, WU C, et al. Brine resources and its comprehensive utilization technology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2004.
CAO W H, WU C, et al. Brine resources and its comprehensive utilization technology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2004. [9] 乜贞, 卜令忠, 刘建华, 等. 我国盐湖钾盐资源现状及提钾工艺技术进展[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(6):869-874.NIE Z, BU L Z, LIU J H, et al. Status of potash resources in salt lakes and progress in potash technologies in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, 31(6):869-874.
NIE Z, BU L Z, LIU J H, et al . Status of potash resources in salt lakes and progress in potash technologies in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2010 ,31 (6 ):869 -874 .[10] 商朋强, 祁才吉, 焦森, 等. 中国钾盐矿产预测评价模型和资源潜力分析[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(10):1758-1767.SHANG P Q, QI C J, JIAO S, et al. Potash assessment models and resource potential analysis in China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2019, 38(10):1758-1767.
SHANG P Q, QI C J, JIAO S, et al . Potash assessment models and resource potential analysis in China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2019 ,38 (10 ):1758 -1767 .[11] 贺令邦, 杨绍祥. 湘西地区钾、镁、钒矿资源特点及开发利用现状[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(2):125-131.HE L B, YANG S X. Characteristics and status of developing and utilizing potassium, magnesium, and vanadium resources in Western Hunan[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(2):125-131.
HE L B, YANG S X . Characteristics and status of developing and utilizing potassium, magnesium, and vanadium resources in Western Hunan[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources,2021 (2 ):125 -131 .[12] 孙小虹, 王春连, 马黎春. 伊朗蒸发岩、钾盐矿床及开发利用现状[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(4):725-726.SUN X H, WANG C L, MAO L C. Evaporite and potash deposits in Iran and their development and utilization status[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2010, 29(4):725-726.
SUN X H, WANG C L, MAO L C . Evaporite and potash deposits in Iran and their development and utilization status[J]. Mineral Deposits,2010 ,29 (4 ):725 -726 .[13] 李锦平, 吴良士. 伊朗地质构造及其区域成矿[J]. 矿床地质, 2008, 27(1):120-121.LI J P, WU L S. Geological structure and regional mineralization in Iran[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2008, 27(1):120-121.
LI J P, WU L S . Geological structure and regional mineralization in Iran[J]. Mineral Deposits,2008 ,27 (1 ):120 -121 .[14] 魏东岩. 试论钾盐矿床成矿条件[J]. 化工矿产地质, 1999, 21(1):1-6,14.WEI D Y. Deal with metallogenic conditions of potash deposits[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 1999, 21(1):1-6,14.
WEI D Y . Deal with metallogenic conditions of potash deposits[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals,1999 ,21 (1 ):1 -6,14 .[15] 唐敏, 刘成林, 焦鹏程, 等. 世界海相钾盐矿床特征定量化分析及其意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(2):326-333.TANG M, LIU C L, JIAO P C, et al. Quantitative analysis and significance of the marine potash deposits in the world[J]. Acta Sedmentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(2):326-333.
TANG M, LIU C L, JIAO P C, et al . Quantitative analysis and significance of the marine potash deposits in the world[J]. Acta Sedmentologica Sinica,2009 ,27 (2 ):326 -333 . -



 下载:
下载: