Effect of Limestone Powder Content and Particle Size on Mechanical Properties of Cement-based Materials
-
摘要:
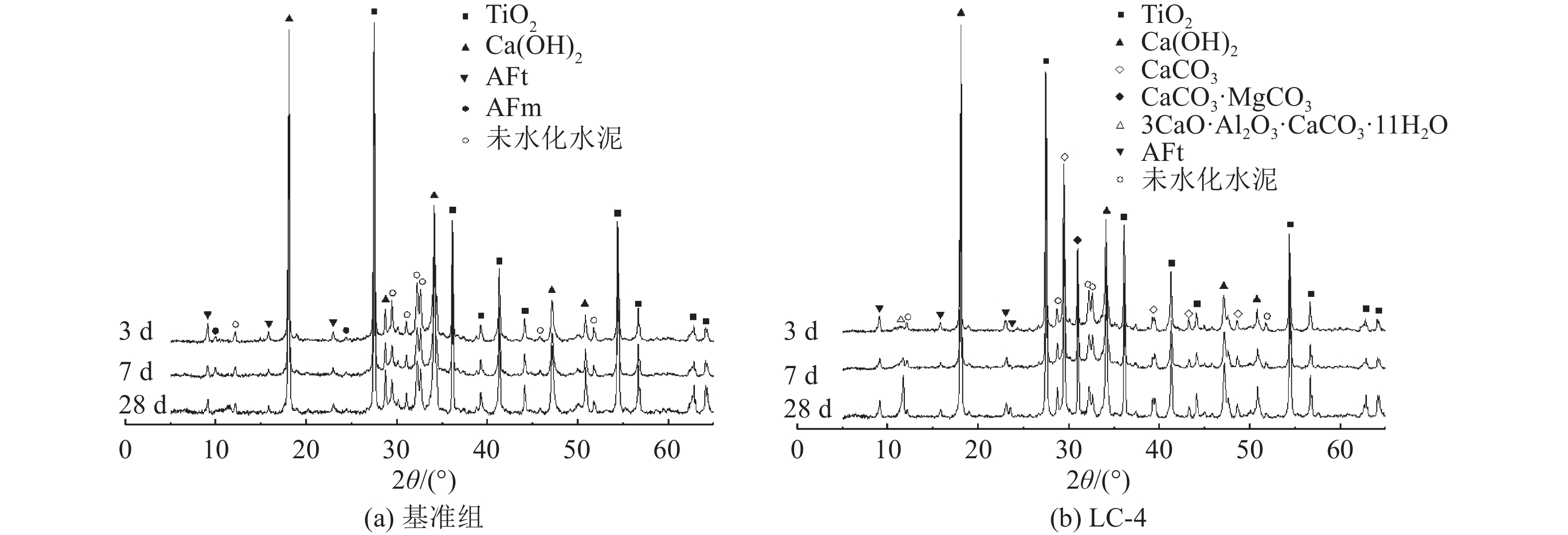
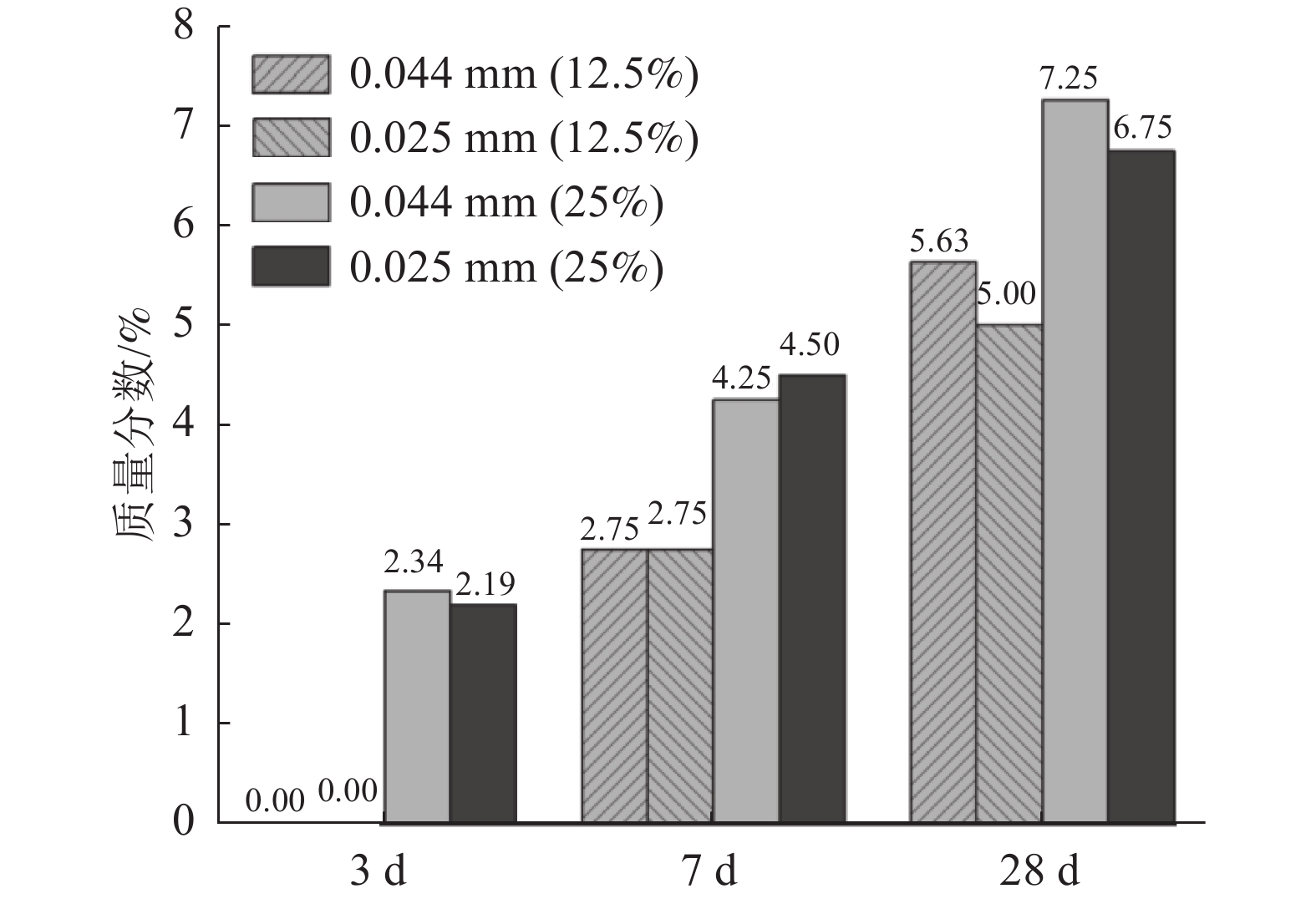
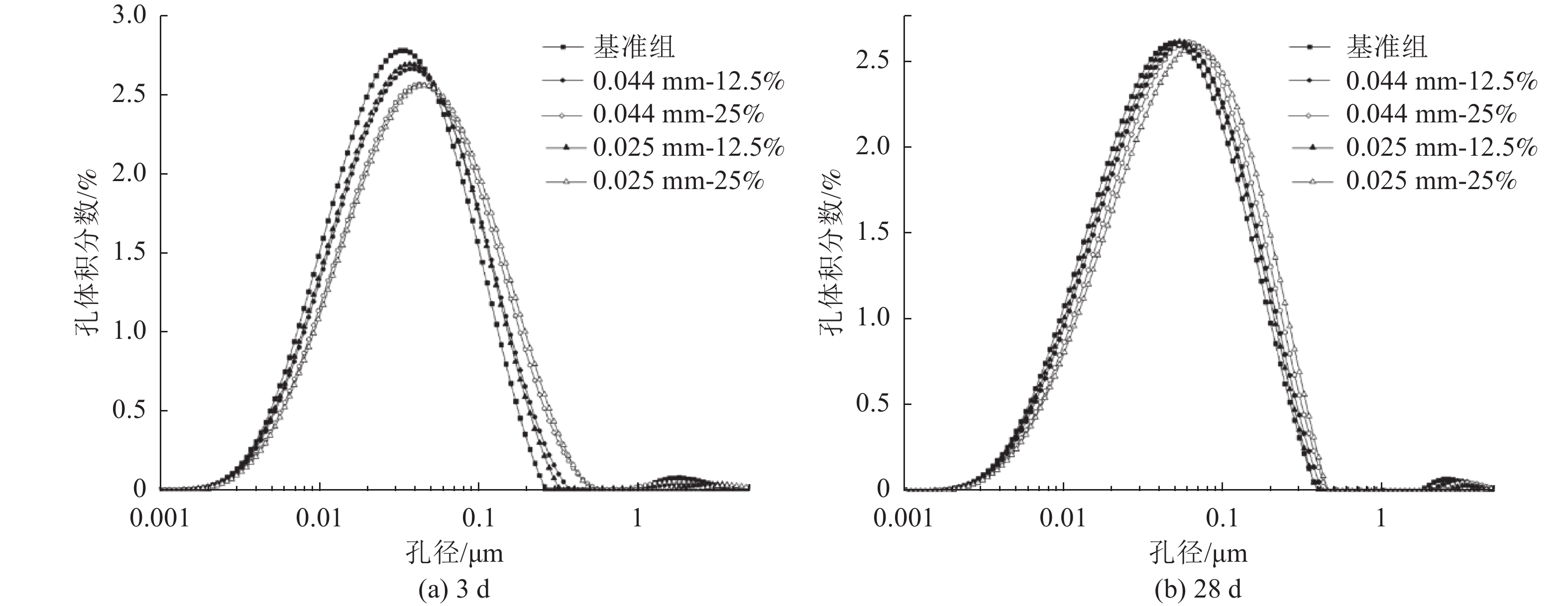
这是一篇陶瓷及复合材料领域的论文。通过混料设计原理设计石灰石粉水泥配合比,对石灰石粉掺量及粒径对石灰石粉-硅酸盐水泥体系力学性能的影响展开了研究;并通过X射线衍射(XRD)、低场核磁共振技术(NMR)等技术对掺入0.44 mm和0.025 mm石灰石粉的硅酸盐水泥净浆水化物相及微孔结构展开了分析。结果表明,两种石灰石粉对早期抗压强度起负面作用;但随着水化的进行,在一定掺量范围内的石灰石粉对水泥后期强度有一定的增强作用,当掺量超过该范围后抗压强度随着掺量的增加而逐渐减小。石灰石粉的掺入虽使得水化产物中生成了有利于水泥石力学性能的水化碳铝酸钙,但其对微孔结构的粗化,使得石灰石粉掺量超过一定值后石灰石粉水泥试件抗压强度大幅降低。
Abstract:This is an article in the field of ceramics and composites. The mix proportion of limestone powder cement is designed based on the mixture design principle, and the effects of limestone powder content and particle size on the mechanical properties of limestone powder Portland cement system are studied. The hydrate phase and microporous structure of portland cement paste mixed with 0.44 mm and 0.025 mm limestone powder were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and low field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The results show that the two limestone powders have a negative effect on the early compressive strength. However, with the progress of hydration, limestone powder within a certain dosage range can enhance the later strength of cement. When the dosage exceeds this range, the compressive strength decreases gradually with the increase of dosage. Although the addition of limestone powder produces hydrated calcium carboaluminate in the hydration products which is conducive to the mechanical properties of cement stone, its coarsening of microporous structure greatly reduces the compressive strength of limestone powder cement specimens when the content of limestone powder exceeds a certain value.
-
Key words:
- Ceramics and composites /
- Limestone powder /
- Strength /
- Pore structure /
- Hydration products
-

-
表 1 水泥和石灰石粉主要化学成分/%
Table 1. Main chemical composition of cement and limestone powders
材料 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO TiO2 SO3 K2O MnO P2O5 水泥 19.56 4.35 3.36 61.14 1.71 0.33 3.28 0.63 0.27 0.28 石灰石粉 1.15 0.25 0.21 67.09 6.43 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.01 0.01 表 2 石灰石粉水泥配合比及其抗压强度
Table 2. Limestone powder cement ratios and their compressive strengths
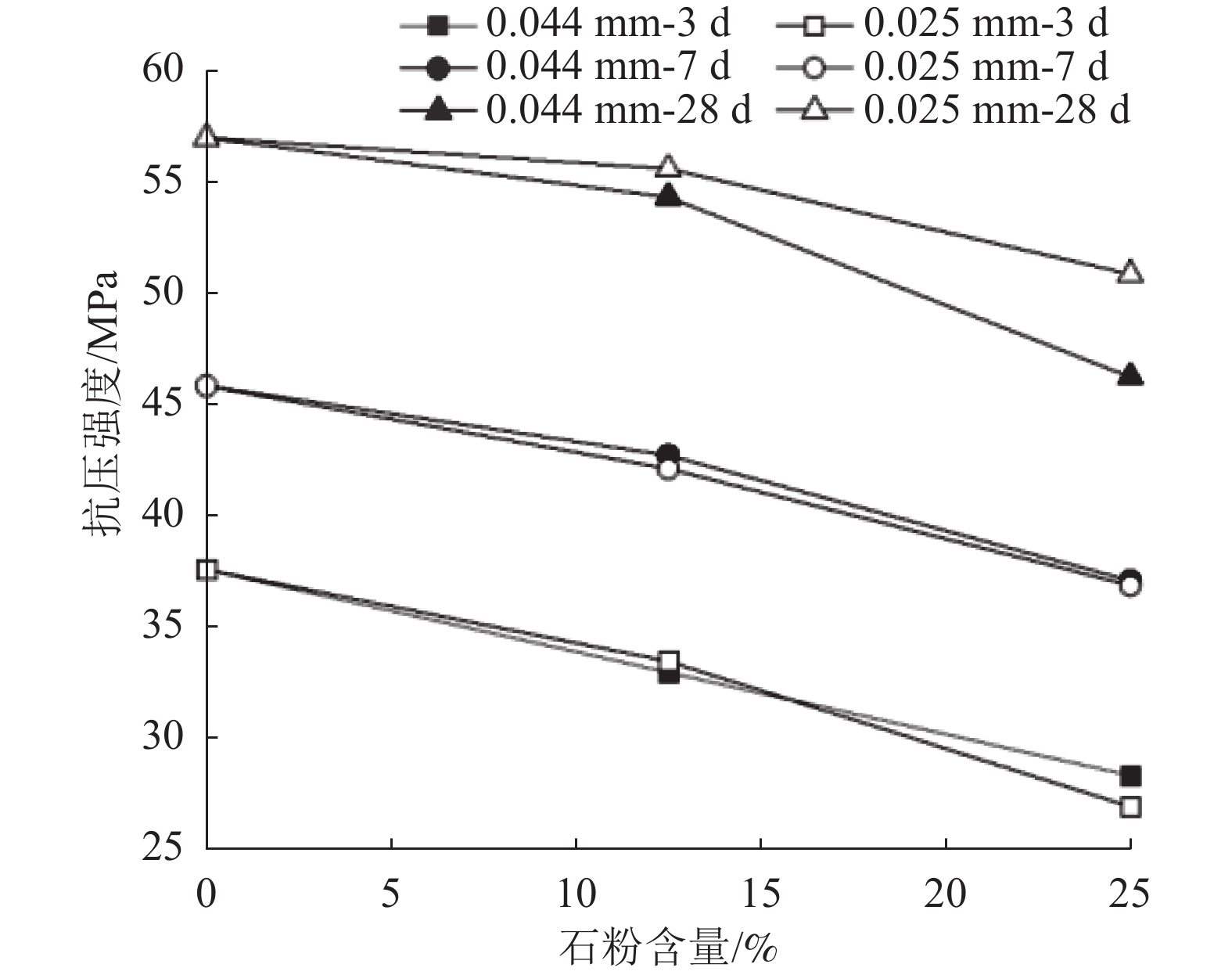
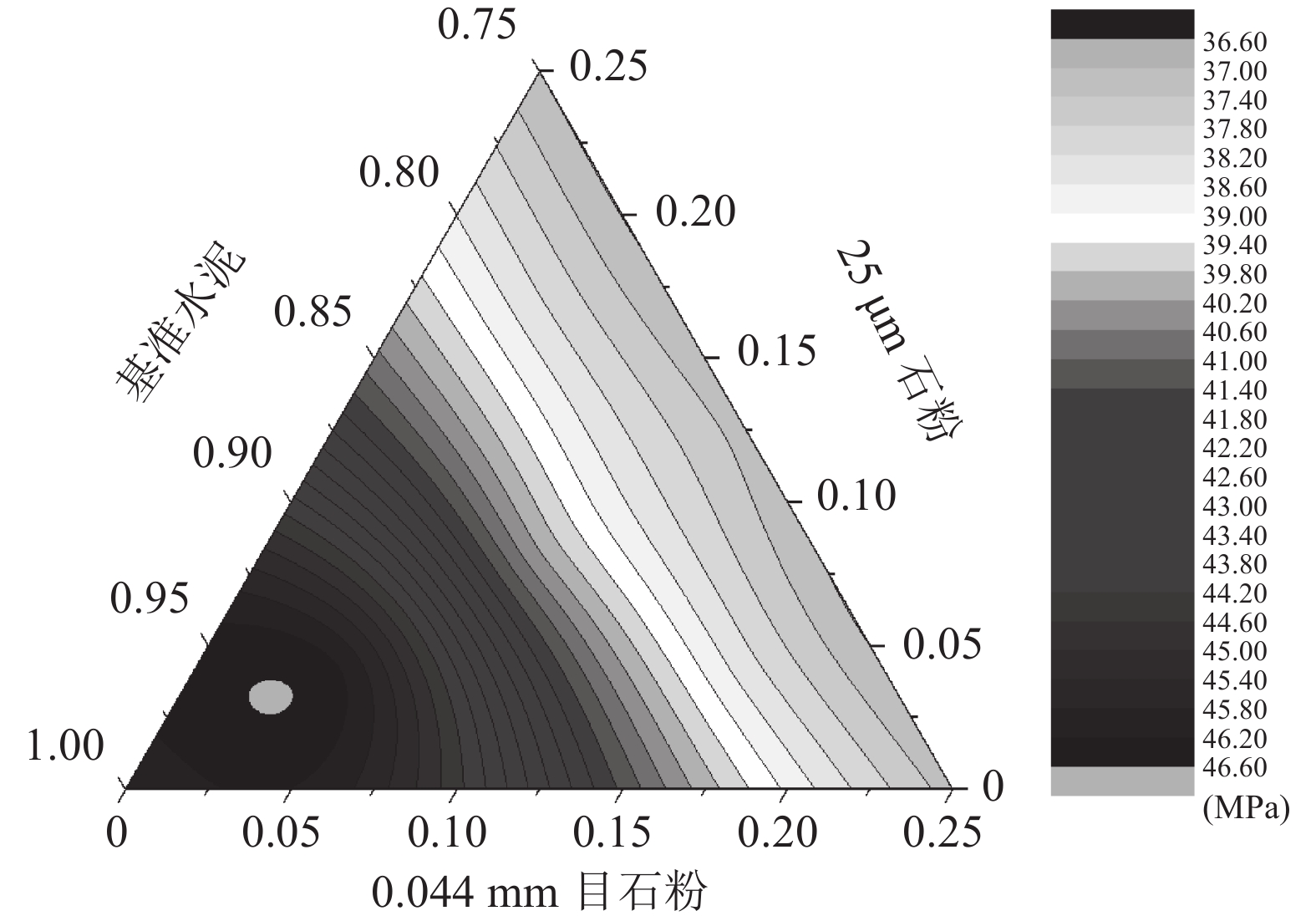
组 配合比/ % 抗压强度/MPa 0.044 mm 0.025 mm 水泥 3 d 7 d 28 d LC-1 0.0 0.0 100.0 37.7 45.9 57.0 LC-2 12.5 0.0 87.5 33.1 42.8 54.3 LC-3 25.0 0.0 75.0 28.5 37.2 46.3 LC-4 0.0 12.5 87.5 33.6 42.2 55.6 LC-5 0.0 25.0 75.0 27.1 37.0 50.9 LC-6 4.2 4.2 91.6 34.4 46.3 60.4 LC-7 8.3 8.3 83.4 30.4 40.2 57.3 LC-8 12.5 12.5 75.0 28.8 37.2 45.6 LC-9 4.2 16.7 79.1 29.0 38.3 53.0 LC-10 16.7 4.2 79.1 31.1 38.4 47.2 -
[1] 寿立永, 严鹏程, 韩鹏飞, 等. 陕西某水泥用灰岩矿废石综合利用实验[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(5):142-147.SHOU L Y, YAN P C, HAN P F, et al. Experimental study on comprehensive utilization of waste rock in a cement limestone mine in Shaanxi Province[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(5):142-147.
SHOU L Y, YAN P C, HAN P F, et al. Experimental study on comprehensive utilization of waste rock in a cement limestone mine in Shaanxi Province[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(5):142-147.
[2] G. MENENDEZ, V. BONAVETTI, E. F. IRASSAR. Strength development of ternary blended cement with limestone filler and blast-furnace slag[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2003, 25(1):61-67 doi: 10.1016/S0958-9465(01)00056-7
[3] M. F. CARRASCO, G. MENENDEZ, V. BONAVETT. Strength optimization of "tailor-made cement" with limestone filler and blast furnace slag[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2005, 35(7): 1324-1331.
[4] 霍冀川, 卢忠远, 张红英, 等. 石灰石硅酸盐水泥的研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2000(6):41-44.HUO J C, LU Z Y, ZHANG H Y, et al. Study on limestone portland cement[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2000(6):41-44
HUO J C, LU Z Y, ZHANG H Y, et al. Study on limestone portland cement[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2000(6):41-44
[5] 殷素红, 文梓芸. 低品位石灰岩用作胶凝—灌浆材料的研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2002(4):35-40.YIN S H, WEN Z Y. Research on the low-purity limestone used as cementitious-grout materials[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2002(4):35-40.
YIN S H, WEN Z Y. Research on the low-purity limestone used as cementitious-grout materials[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2002(4):35-40.
[6] 张洪萍, 白培康, 王建弘, 等. 多种掺合料颗粒群分布与水泥基复合体系强度关系研究[J]. 混凝土与水泥制品, 2019(1):23-25.ZHANG H P, BAI P K, WANG J H, et al. Study on the relationship between particle swarm distribution of various admixtures and strength of cement-based composite system[J]. China Concrete and Cement Products, 2019(1):23-25.
ZHANG H P, BAI P K, WANG J H, et al. Study on the relationship between particle swarm distribution of various admixtures and strength of cement-based composite system[J]. China Concrete and Cement Products, 2019(1):23-25.
[7] 肖佳. 水泥-石灰石粉胶凝体系特性研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2008.XIAO J. Study on characteristics of cement - limestone powder cementitious system[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2008.
XIAO J. Study on characteristics of cement - limestone powder cementitious system[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2008.
[8] D P BENTZ. Modeling the influence of limestone filler on cement hydration using CEMHYD3D[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2006, 28(2):124-129. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2005.10.006
[9] 陈剑雄, 李鸿芳, 陈鹏, 等. 石灰石粉锂渣超早强超高强混凝土研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2007(1): 190-193.CHEN J X, LI H F, CHEN P, et al. Study on super early-strength , high-strength and high-performance concrete containing limestonepowder composite admixture[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2007(1): 190-193.
CHEN J X, LI H F, CHEN P, et al. Study on super early-strength , high-strength and high-performance concrete containing limestonepowder composite admixture[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2007(1): 190-193.
[10] 邱鸿鑫, 陈浙锐, 陈颂, 等. 基于XRD与XRF分析矿物质对浮选尾煤图像灰度特征影响[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(2):114-117.QIU H X, CHEN Z R, CHEN S, et al. Study on the influence of minerals on the gray characteristics of flotation coal image based on XRD and XRF[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(2):114-117.
QIU H X, CHEN Z R, CHEN S, et al. Study on the influence of minerals on the gray characteristics of flotation coal image based on XRD and XRF[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(2):114-117.
[11] M CYR, P LAWRENCE, E RINGOT. Mineral admixtures in mortars: Quantification of the physical effects of inert materials on short-term hydration[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2005, 35(4): 719-730.
[12] 吴中伟, 廉慧珍. 高性能混凝土[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 1999.WU Z W, LIAO H Z. High performance concrete[M]. Beijing: China Railway Publishing House, 1999
WU Z W, LIAO H Z. High performance concrete[M]. Beijing: China Railway Publishing House, 1999
[13] 徐江涛, 卢都友, 张少华, 等. 不同养护温度下含白云石和石灰石微粉砂浆的孔结构[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2017, 45(2):268-273.XU J T, LU D Y, ZHANG S H, et al. Pore structures of mortars with dolomite and limestone powders cured at various temperatures[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2017, 45(2):268-273.
XU J T, LU D Y, ZHANG S H, et al. Pore structures of mortars with dolomite and limestone powders cured at various temperatures[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2017, 45(2):268-273.
-




 下载:
下载: