RARE EARTH ELEMENTAL GEOCHEMISTRY OF THE SEDIMENTS IN COLD-SEEP AREA IN DONGSHA AREA OF SOUTH CHINA SEA
-
摘要:
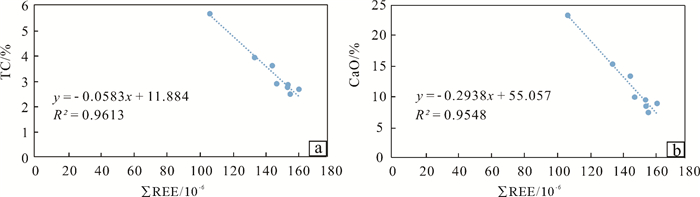
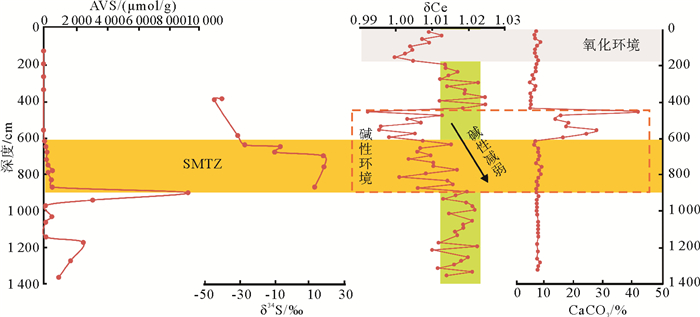
东沙海域是我国典型的冷泉活动区,该区域表层沉积物的稀土元素地球化学特征不仅受其源区控制,同时也可能会受到冷泉渗漏活动的影响。本文选取位于南海北部陆坡973-4站位的柱状样为研究对象,该站位位于21°54.3247’N、118°49.0818’E,水深为1666m,柱状样总长1375cm,采用电感耦合等离子质谱(ICP-MS)、X射线荧光光谱(XRF)等分析测试方法,测得样品的稀土元素以及部分微量和主量元素数据,并结合总碳(TC)、总有机碳(TOC)以及有孔虫质量分数等数据,探讨了冷泉泄漏对周围成岩环境及沉积物稀土元素地球化学特征的影响。结果发现,973-4站位柱状样在海底以下459~619cm深度范围内稀土元素含量整体异常减少,但所有样品稀土元素分布模式及相关稀土元素参数均十分一致。结合冷泉活动研究,表明该区域沉积物元素地球化学特征的异常与物源无关,是受自生碳酸盐岩的增加所影响。此外,通过分析δCe值随深度的变化以及自生碳酸盐岩和硫酸盐-甲烷转换带(SMTZ)的分布情况发现三者相关度很高,表明自生碳酸盐岩的增加很可能是该区域发生的冷泉渗漏导致的甲烷厌氧氧化作用(AOM)所产生的。
Abstract:The Dongsha Area is one of the most important natural gas hydrate zones on the northern slope of the South China Sea. The rare earth elemental geochemical characteristics of surface sediments in this area are controlled not only by their sources but also by the activities of cold seeps. In this paper, a 1 375 cm-long gravity core of 973-4 (21°54.3247′N、118°49.0818′E), which is located on the northern slope of South China Sea at water depth of 1 666 m, is selected as the study subject. The contents of rare earth elements (REE) and some trace and major elements are measured by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF). Combined with the value of total carbon (TC), total organic carbon (TOC) and foraminiferal mass fractions, these data are used to study the influence of cold seeps on the geochemical characteristics of REE and the surrounding diagenetic environment.
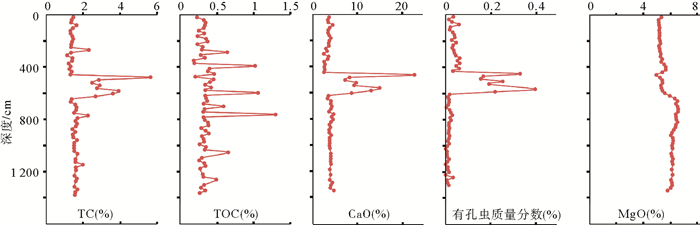
The results show that the content of rare earth elements in the Core 973-4 sediments reduces significantly in the depth range of 459-619 cm below the seafloor, but the distribution pattern of REE and the REE-related data are consistent to each other. Combined with the study of cold seeps activities, it is found out that the anomalies of the geochemical characteristics of sediments in this area are independent from provenance, but affected by the increase in authigenic carbonate rocks. In addition, by analyzing the variation in δCe value with depth and the distribution pattern of authigenic carbonate and sulfate-methane conversion zone (SMTZ), it is found that the correlation between the three is very high, indicating that the increase of authigenic carbonate came from the anaerobic oxidation of methane(AOM) caused by cold seeps.
-
Key words:
- rare earth elements /
- cold seeps /
- dongsha area /
- authigenic carbonate
-

-
图 2 973-4柱状样岩性分析[14]
Figure 2.
表 1 973-4柱状样稀土元素含量(×10-6)及主要参数
Table 1. Abundance and characteristic parameters of REE in the sediments of Core 973-4
异常区 非异常区 最大值 最小值 平均值 标准偏差 最大值 最小值 平均值 标准偏差 La 38.31 22.57 32.48 4.50 39.81 35.07 37.50 1.04 Ce 76.65 44.72 64.06 9.04 79.19 69.88 74.56 2.18 Pr 8.57 5.21 7.26 0.97 8.77 7.90 8.36 0.22 Nd 31.92 19.48 27.23 3.54 33.09 29.31 31.22 0.80 Sm 6.14 3.86 5.28 0.67 6.58 5.45 6.08 0.22 Eu 1.28 0.81 1.10 0.14 1.30 1.17 1.24 0.03 Gd 5.17 3.36 4.61 0.52 5.62 4.87 5.28 0.16 Tb 0.80 0.53 0.71 0.08 0.89 0.75 0.82 0.03 Dy 4.94 3.10 4.20 0.53 5.35 4.51 4.84 0.17 Ho 0.97 0.62 0.83 0.10 1.03 0.88 0.95 0.03 Er 2.66 1.74 2.35 0.27 2.95 2.42 2.72 0.11 Tm 0.41 0.27 0.36 0.04 0.43 0.37 0.40 0.01 Yb 2.78 1.71 2.28 0.28 2.78 2.46 2.64 0.08 Lu 0.40 0.25 0.34 0.04 0.43 0.36 0.39 0.01 Y 27.40 17.76 23.87 2.83 28.80 25.25 27.27 0.91 ∑REE 180.96 108.25 153.07 20.66 188.03 166.34 177.00 4.84 LREE 162.87 96.66 137.40 18.84 168.64 149.33 158.96 4.39 HREE 18.09 11.59 15.67 1.85 19.39 16.73 18.04 0.55 LREE/HREE 9.08 8.34 8.75 0.25 9.35 8.52 8.81 0.16 (La/Yb)N 10.48 8.90 9.58 0.46 10.27 9.24 9.59 0.22 (La/Sm)N 4.00 3.67 3.87 0.09 4.10 3.68 3.88 0.09 (Gd/Yb)N 1.71 1.50 1.63 0.06 1.71 1.54 1.62 0.04 δCe 1.02 0.99 1.00 0.01 1.02 1.00 1.01 0.01 δEu 0.70 0.64 0.68 0.02 0.70 0.64 0.67 0.01 -
[1] Campbell K A. Hydrocarbon seep and hydrothermal vent paleoenvironments and paleontology: past developments and future research directions[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2006, 232(2-4): 362-407. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.06.018
[2] Lim Y C, Lin S, Yang T F, et al. Variations of methane induced pyrite formation in the accretionary wedge sediments offshore southwestern Taiwan[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(10): 1829-1837. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.04.004
[3] Li N, Feng D, Chen L Y, et al. Using sediment geochemistry to infer temporal variation of methane flux at a cold seep in the South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 77: 835-845. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.07.026
[4] Roberts H H, Feng D, Joye S B. Cold-seep carbonates of the middle and lower continental slope, northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2010, 57(21-23): 2040-2054. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2010.09.003
[5] Mansour A S. Hydrocarbon-derived carbonates along the upper-lower continental slope, Gulf of Mexico: a mineralogical and stable isotopic study[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites, 2014, 29(1): 89-105. doi: 10.1007/s13146-013-0185-y
[6] Chen D F, Cathles Ⅲ L M, Roberts H H. The geochemical signatures of variable gas venting at gas hydrate sites[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2004, 21(3): 317-326. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2003.12.003
[7] Wu N Y, Zhang G X, Liang J Q, et al. Progress of gas hydrate research in northern south China Sea[J]. Advances in New and Renewable Energy, 2013, 1(1): 80-94. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzxb-e201903015
[8] Wang T K, Chen T R, Deng J M, et al. Velocity structures imaged from long-offset reflection data and four-component OBS data at Jiulong Methane Reef in the northern South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 68: 206-218. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.08.024
[9] Feng D, Chen D F. Authigenic carbonates from an active cold seep of the northern South China Sea: new insights into fluid sources and past seepage activity[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2015, 122: 74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2015.02.003
[10] Chen F, Hu Y, Feng D, et al. Evidence of intense methane seepages from molybdenum enrichments in gas hydrate-bearing sediments of the northern South China Sea[J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 443: 173-181. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.09.029
[11] Lin Q, Wang J S, Algeo T J, et al. Enhanced framboidal pyrite formation related to anaerobic oxidation of methane in the sulfate-methane transition zone of the northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2016, 379: 100-108. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2016.05.016
[12] 张劼, 雷怀彦, 欧文佳, 等.南海北部陆坡973-4柱沉积物中硫酸盐—甲烷转换带(SMTZ)研究及其对水合物的指示意义[J].天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(11): 1811-1820. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2014.11.1811
ZHANG Jie, LEI Huaiyan, OU Wenjia, et al. Research of the sulfate-methane transition zone (SMTZ) in sediments of 973-4 column in continental slope of northern south China Sea[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25(11): 1811-1820. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2014.11.1811
[13] 庄畅, 陈芳, 程思海, 等.南海东北部陆坡天然气水合物分解释放成因的有孔虫碳同位素轻值事件[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2016, 46(10): 1334-1348. doi: 10.1360/N072015-00392
ZHUANG Chang, CHEN Fang, CHENG Sihai, et al. Light carbon isotope events of foraminifera attributed to methane release from gas hydrates on the continental slope, northeastern South China Sea[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2016, 59(10): 1981-1995. doi: 10.1360/N072015-00392
[14] 曲莹.南海北部陆坡冷泉区晚更新世以来底栖有孔虫与甲烷喷溢[D].中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2013.
QU Ying. Response of cold seep benthic forminifera and methane eruption in northern slope of the South China Sea[D]. Master's Thesis of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2013.
[15] 刘宝林, 王亚平, 王吉中, 等.南海北部陆坡海洋沉积物稀土元素及物源和成岩环境[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(4): 17-23. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200404003
LIU Baolin, WANG Yaping, WANG Jizhong, et al. Geochemical characters of REE in the seafloor sediment in northern continental slope of the South China Sea and analysis of source of material and diagenesis environment[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2004, 24(4): 17-23. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200404003
[16] Budakoglu M, Abdelnasser A, Karaman M, et al. The rare earth element geochemistry on surface sediments, shallow cores and lithological units of Lake Acigol basin, Denizli, Turkey[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 111: 632-662. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.05.016
[17] 韩吟文, 马振东.地球化学[M].北京:地质出版社, 2003.
HAN Yinwen, MA Zhendong. Geochemistey[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2003.
[18] 陆红锋, 刘坚, 陈芳, 等.南海台西南区碳酸盐岩矿物学和稳定同位素组成特征-天然气水合物存在的主要证据之一[J].地学前缘, 2005, 12(3): 268-276. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.03.030
LU Hongfeng, LIU Jian, CHEN Fang, et al. Mineralogy and stable isotopic composition of authigenic carbonates in bottom sediments in the offshore area of southwest Taiwan, South China Sea: evidence for gas hydrates occurrence[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2005, 12(3): 268-276. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.03.030
[19] 邬黛黛, 吴能友, 付少英, 等.南海北部东沙海域水合物区浅表层沉积物的地球化学特征[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(5): 41-51.
WU Daidai, WU Nengyou, FU Shaoying, et al. Geochemical characteristics of shallow sediments in the gas hydrate distribution area of Dongsha, the Northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(5): 41-51.
[20] 邬黛黛, 吴能友, 叶瑛, 等.南海北部陆坡九龙甲烷礁冷泉碳酸盐岩沉积岩石学特征[J].热带海洋学报, 2009, 28(3): 74-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2009.03.012
WU Daidai, WU Nengyou, YE Ying, et al. Petrographic characteristics of authigenic carbonates from Jiulong methane reef of northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2009, 28(3): 74-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2009.03.012
[21] 栾锡武, 彭学超, 邱燕.南海北部陆坡高速堆积体的构造成因[J].现代地质, 2009, 23(2): 183-199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2009.02.001
LUAN Xiwu, PENG Xuechao, QIU Yan. Tectonic control on the formation of high-deposition-rate sediment drift in the northern slope of the South China Sea[J]. Geoscience, 2009, 23(2): 183-199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2009.02.001
[22] 朱赖民, 高志友, 尹观, 等.南海表层沉积物的稀土和微量元素的丰度及其空间变化[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(11): 2963-2980. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.11.027
ZHU Laimin, GAO Zhiyou, YIN Guan, et al. Content and spatial change of rare earth element and trace element of surficial sediment in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(11): 2963-2980. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.11.027
[23] Liu F W, Miao L, Cai G Q, et al. The rare earth element geochemistry of surface sediments in four transects in the South China Sea and its geological significance[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 74(3): 2511-2522. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4265-2
[24] 王汾连, 何高文, 王海峰, 等.马里亚纳海沟柱状沉积物稀土地球化学特征及其指示意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(4): 67-75. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201604008
WANG Fenlian, HE Gaowen, WANG Haifeng, et al. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in a core from mariana trench and its significance[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(4): 67-75. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201604008
[25] 彭娜娜, 曾志刚.冲绳海槽中部17000 a以来沉积物中微量元素的组成特征及其对古环境的指示[J].海洋科学, 2016, 40(4): 126-139. doi: 10.11759/hykx20160129003
PENG Nana, ZENG Zhigang. Trace elements geochemistry composition and paleoenvironmental reflections of central Okinawa Trough over last 17 000 years[J]. Marine Sciences, 2016, 40(4): 126-139. doi: 10.11759/hykx20160129003
[26] 苗卫良, 邵磊, 庞雄, 等.南海北部渐新世以来的稀土元素地球化学特征及其意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28(2): 71-78. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200802011
MIAO Weiliang, SHAO Lei, PANG Xiong, et al. REE geochemical characteristics in the northern South China Sea since the Oligocene[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2008, 28(2): 71-78. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200802011
[27] 李双林, 李绍全.黄海YA01孔沉积物稀土元素组成与源区示踪[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(3): 51-56. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200103008
LI Shuanglin, LI Shaoquan. REE composition and source tracing of sediments from core YA01 in Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2001, 21(3): 51-56. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200103008
[28] 赵一阳, 鄢明才.中国浅海沉积物地球化学[M].北京:科学出版社, 1994: 46-89.
ZHAO Yiyang, YAN Mingcai. Geochemistry of Sediments of the China Shelf Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1994: 46-89.
[29] 蓝先洪, 张宪军, 赵广涛, 等.南黄海NT1孔沉积物稀土元素组成与物源判别[J].地球化学, 2009, 38(2): 123-132. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2009.02.003
LAN Xianhong, ZHANG Xianjun, ZHAO Guangtao, et al. Distributions of rare earth elements in sediments from Core NT1 of the south Yellow Sea and their provenance discrimination[J]. Geochimica, 2009, 38(2): 123-132. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2009.02.003
[30] 杨守业, 李从先. REE示踪沉积物物源研究进展[J].地球科学进展, 1999, 14(2): 164-167. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1999.02.010
YANG Shouye, LI Congxian. Research progress in REE tracer for sediment source[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 1999, 14(2): 164-167. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1999.02.010
[31] 张必东, 邬黛黛, 吴能友.南海北部东沙海域沉积物地球化学特征及其反映的冷泉活动[J].海洋地质前沿, 2015, 31(9): 14-27. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2015.09003
ZHANG Bidong, WU Daidai, WU Nengyou. Characteristics of sedimentary geochemistry and their responses to Cold-seep activities in Dongsha, the Northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2015, 31(9): 14-27. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2015.09003
[32] 冯东, 陈多福, 苏正, 等.海底甲烷缺氧氧化与冷泉碳酸盐岩沉淀动力学研究进展[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(3): 125-131. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200603018
FENG Dong, CHEN Duofu, SU Zheng, et al. Anaerobic oxidation of methane and seep carbonate precipitation kinetics at seafloor[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(3): 125-131. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200603018
[33] 卞友艳, 林治家, 冯东, 等.冷泉碳酸盐岩的稀土元素地球化学特征及氧化还原条件示踪[J].热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(5): 37-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2012.05.006
BIAN Youyan, LIN Zhijia, FENG Dong, et al. Rare earth elements of seep carbonates and using them to trace redox variation at seep sites[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(5): 37-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2012.05.006
[34] 曹鹏, 石学法, 李巍然, 等.安达曼海东南部海域表层沉积物稀土元素特征及其物源指示意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(5): 57-67. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201505009
CAO Peng, SHI Xuefa, LI Weiran, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry of surface sediments in Southeastern Andaman Sea and implications for provenance[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(5): 57-67. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201505009
[35] 李双林.东海陆架HY126EA1孔沉积物稀土元素地球化学[J].海洋学报, 2001, 23(3): 127-132. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2001.03.016
LI Shuanglin. Geochemistry of rare earth element in sediments at HY126EA1 hole in the continental shelf of the East China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2001, 23(3): 127-132. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2001.03.016
[36] Toyoda K, Nakamura Y, Masuda A. Rare earth elements of Pacific pelagic sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1990, 54(4): 1093-1103. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(90)90441-M
[37] 赵一阳, 鄢明才.中国浅海沉积物化学元素丰度[J].中国科学(B辑), 1993, 23(10): 1084-1090.
ZHAO Yiyang, YAN Mingcai. Mineral element abundance of sediments of the China Shelf Sea[J]. Science in China (Series B), 1993, 23(10): 1084-1090.
[38] Hoehler T M, Alperin M J, Albert D B, et al. Field and laboratory studies of methane oxidation in an anoxic marine sediment: evidence for a methanogen sulfate reducer consortium[J]. Blobal Biogeochemical Cycles, 1994, 8(4): 451-463. doi: 10.1029/94GB01800
[39] Hallam S J, Putnam N, Preston C M, et al. Reverse methanogenesis: testing the hypothesis with environmental genomics[J]. Science, 2004, 305(5689): 1457-1462. doi: 10.1126/science.1100025
-




 下载:
下载: