-
摘要: 粉煤灰制备成地质聚合物,不仅能够使固体废弃物得到资源化利用,而且还能够发挥地质聚合物在重金属离子吸附、防火保温、耐腐蚀以及低碳排放等领域的作用,从而实现资源的高效利用。主要总结了近年来粉煤灰基地质聚合物的研究及应用,并对当前存在的问题以及今后的发展趋势进行了总结和展望。Abstract: As the synthetic raw material of geopolymers, fly ash can not only make the solid waste be used as resources, but also give full play to the advantages of geopolymers in heavy metal ion adsorption, fire protection and heat preservation, corrosion resistance, low carbon emission and other fields, so as to realize the efficient utilization of resources. The research of fly ash based geopolymers and its application in recent years were summarized in this paper, and the current problems and future development trend were pointed out and prospected.
-
Key words:
- fly ash /
- geopolymers /
- application
-

-
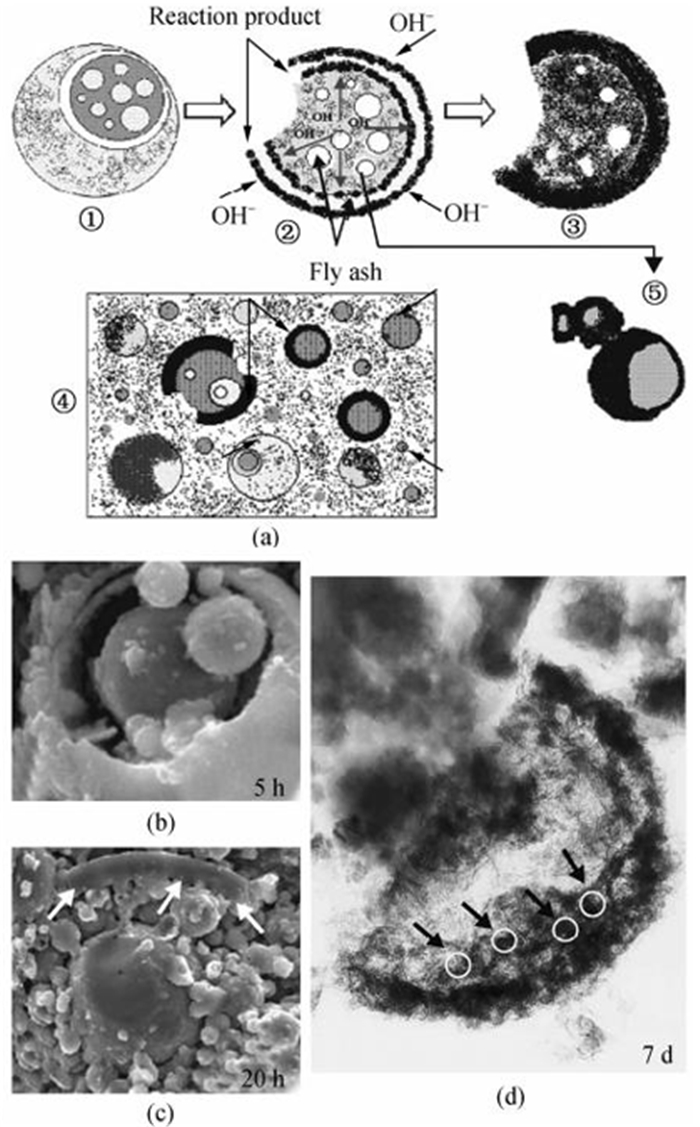
图 1 粉煤灰在碱激发作用下的描述性机理模型[19]
Figure 1.
图 2 粉煤灰基地聚合物纳米结构模型[21]
Figure 2.
-
[1] DAVIDOVITS J. The ancient egyptian pyramids-concrete or rock[J]. Concrete International, 1987, 9(12):28-32. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/296447482_Ancient_Egyptian_pyramids_-_concrete_or_rock
[2] DAVIDOVITS J. Geopolymers and geopolymeric new materials[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis, 1989, 35(2):429-441. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF01904446
[3] DAVIDOVITS J. Geopolymers:Inorganic polymer new materials[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis, 1991, 37:1633-1656. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/244026389_Geopolymers_Inorganic_Polymeric_New_Materials
[4] LOUISE K. T, FRANK G. C. Carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2-e) emissions:A comparison between geopolymer and OPC cement concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 43:125-130. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0950061813000871
[5] MCLELLAN B C, WILLIAMS R P, LAY J. et al. Costs and carbon emissions for geopolymer pastes in comparison to ordinary portland cement[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2011, 19(9):1080-1090. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652611000680
[6] 王磊.我国工业固废综合利用的现状及进展[J].资源节约与环保, 2017(2):16-17. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zyjyyhb201702015
[7] 张灿强.不同种类粉煤灰特性的试验研究[D].南京: 东南大学, 2017.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10286-1018040753.htm [8] Cao D Z, Selic E, Herbell. Utilization of fly ash from coal-fired power plants in China[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University Science A, 2008(9):681-687. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/88140X/200805/27139777.html
[9] HUA XU, VAN DEVENTER J S J. The geopolymerisation of alumino-Silicate minerals, mineral process, International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2000(59):247-226. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000034188691010_3fd2.html
[10] HUA XU, VAN DEVENTER J S J. Effect of alkali metals on the perferential geopolymerization of stilbite/kaolinite mixtures[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2001(40):3749-3756. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ie010042b
[11] 马鸿文, 杨静, 任玉峰, 等.矿物聚合物材料:研究现状与发展前景[J].地学前沿, 2002, 9(4):398-407. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xngxyxb200203018
[12] 张书政, 龚克成.地聚物[J].材料科学与工程学报, 2003, 21(3):430-435. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=clkxygc200303030
[13] KHATE D, CHAUDHARY R. Mechanism of geopolymerization and factors influencing its development:a review[J]. Journal of Materials Science 2007, 42:729-746. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10853-006-0401-4
[14] HUA X, DEVENTER J S, J VAN. The geopolymerisation-silica minerals[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2000, 114:497-500. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301751699000745
[15] Davidovits J. Geopolymer chemistry and properties[C]//Proceedings of the First European Conference on Soft Mineralogy. Paris, 1988: 25-48.
[16] 王丽萍, 李超.粉煤灰资源化技术开发与利用研究进展[J].矿产保护与利用, 2019(4):38-44. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=5900e8bd-58c1-4356-9856-35a01ec40e39
[17] 孙道胜, 王爱国, 胡普华.地质聚合物的研究与应用发展前景[J].材料导报, 2009, 23(4):61-65. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cldb200907016
[18] 倪文, 王恩, 周佳.地质聚合物-21世纪的绿色胶凝材料[J].新材料产业, 2003(6):24-28. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200301818860
[19] FERNáNDEZ-JIMéNEZ A, PALOMO A, CRIADO M. Microstructure development of alkali-activated fly ash cement:A descriptive model[J]. Cem Concr Res, 2005, 35(6):1204-1209. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0008884604004053
[20] CRIADO M, PALOMO A, FERNANDEZJIMENEZ A. Alkali activa tion of fly ashes. Part Ⅰ:Effect of curing conditions on the carbonation of the reaction products[J]. Fuel, 2005, 84(16):2048-2054. http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s11884-013-0176-9
[21] CRIADO M, FERNáNDEZ-JIMéNEZ A, PALOMO A. Alkali activa tion of fly ash. Part Ⅲ:Effect of curing conditions on reaction and its graphical description[J]. Fuel, 2010, 89(11):3185-3192. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236110001572
[22] QIAN G, CAO Y, CHUI P, et al. Utilization of MSWI fly ash for stabilization/solidification of industrial waste sludge[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 129:274-281. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=43f1777361859779a0868dd758eb8e82
[23] DAVIDOVITS J. Properties of geopolymer cement[C]//Proceedings First International Conference on Alkaline Cements and Concretes, Scientific Research. Kiev, 1994: 131-149.
[24] WILLIAM A M. Fixation of haxardous wastes and related products: US, 5976244[P]. 1999-11-01.
[25] TEMUUJIN J, MINJIGMA A A, DAVAABAL B, et al. Utilization of radioactive high-calcium Mongolian fly ash for the preparation of alkali-activated geopolymers for safe use as construction materials[J]. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(10):16475-16483. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d1394812db3a49949d401671f63b1f8e
[26] ZHANG J, PROVIS J L, FENG D, et al. Geopolymers for immobilization of Cr6+、Cd2+and Pb2+[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 157(2-3):587-598. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/18313213
[27] 刘泽, 李丽, 张媛, 王栋民.粉煤灰基地质聚合物固化重金属Pb2+的研究[J].硅酸盐通报, 2018, 37(4):1382-1386. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gsytb201804043
[28] ONUTAI S, KOBAYASHI T, THAVORNITI P, et al. The adsorption of cadmium ions on fly ash based geopolymer particles[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2018, 766:65-70. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.766.65
[29] MOHAMMAD S Al H, KAMEL Al Z, LEEMA Al M, et al. Fly ash based geopolymer for heavy metal removal:A case study on copper removal[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2015, 3(3):1669-1677. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213343715001451
[30] WANG S B, LI L, ZHU Z H. Solid-state conversion of flyash to effective adsorbents for Cu removal from wastewater[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 139(2):254-259. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304389406006510
[31] 王英明, 姜亮, 董彦博, 等.粉煤灰基地质聚合物制备及其对Cu2+的吸附性能[J].洁净煤技术, 2018, 24(5):120-125. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jjmjs201805018
[32] 毛林清, 武双磊, 李鹏飞, 等.粉煤灰基地质聚合物固化含铬电镀污泥研究[J].新型建筑材料, 2018(10):29-34. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xxjzcl201810009
[33] MALEKI A, HAJIZADEH Z, SHARIFI V, et al. A green, porous and eco-friendly magnetic geopolymer adsorbent for heavy metals removal from aqueous solutions[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 215:1233-1245. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cda92e190361dd627f9cae6e73dccd2a
[34] SUN T, CHEN J Y, LEI X R, et al. Detoxification and immobilization of chromite ore p rocessing residue with metakaolin-based geopolymer[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2014, 2(1):304-309. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213343713002698
[35] 王霞, 卓锦德, 季宏伟, 等.分级粉煤灰对地质聚合物发泡材料性能的影响[J].洁净煤技术, 2018, 24(4):136-140. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jjmjs201804024
[36] 亢一星, 王启宝, 秦子敬, 等.锂渣掺量对粉煤灰基发泡地质聚合物性能的影响[J].新型建筑材料, 2019(8):115-118. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xxjzcl201908030
[37] 景宏君, 景宏彬, 艾涛, 等.地质聚合物隧道防火涂料配方设计及应用[J].筑路机械与施工机械化, 2017, 34:72-76. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zljxysgjxh201711010
[38] 雷耀武, 王晋峰, 齐彦, 等.模拟酸雨环境下地质聚合物耐久性研究[J].建筑材料·节能, 2019, 16:29-30. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=csjz201924010
[39] 倪成林.微硅粉和粉煤灰高强混凝土的制备及其酸侵蚀性能研究[D].昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2014: 1-95.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10674-1015539744.htm [40] HUNTZINGER D N, EATMON T D. A life-cycle assessment of Portland cement manufacturing:comparing the traditional process with alternative technologies[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2009, 17(7):668-675. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652608000826
[41] MCLELLAN B C, WILLIAMS R P, LAY J, et al. Costs and carbon emissions for geopolymer pastes in comparison to ordinary portland cement[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2011, 19(9):1080-1090. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652611000680
[42] STENGEL T, REGER J, HEINZ D. LCA of geopolymer concrete-what is the environmental benefit[C]//In Proceedings Concrete 09, 24th Biennial Conf Australian Concrete Institute, Concrete Institute of Australia. Sydney, 2009: 54-62.
[43] 蒲云辉, 王清远, 李文渊, 等.粉煤灰基地质聚合物混凝土和普通混凝土温室气体排放量的对比研究[J].混凝土, 2019(4):10-13. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hnt201904004
[44] 柴淑媛, 李艳, 张雪芳, 等.高钙粉煤灰地质聚合物制备及强度特性研究[J].墙材革新与建筑节能, 2019(11):70-72. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qcgxyjjjn201911014
[45] 冯泽平.高钙粉煤灰地质聚合物的制备及耐久性研究[J].矿产保护与利用, 2018(2):107-110. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=ea9bd840-fbc4-4d92-813d-3b28fe8fad63
-

| 引用本文: | 王丽萍, 徐靓, 王永旺, 李超. 粉煤灰基地质聚合物研究进展[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2020, 40(3): 90-94. doi: 10.13779/j.cnki.issn1001-0076.2020.03.015 |
| Citation: | Liping WANG, Liang XU, Yongwang WANG, Chao LI. Research Progress of Fly Ash Based Geopolymers[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020, 40(3): 90-94. doi: 10.13779/j.cnki.issn1001-0076.2020.03.015 |


 下载:
下载:
